trim BMW 540i 1999 E39 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: BMW, Model Year: 1999, Model line: 540i, Model: BMW 540i 1999 E39Pages: 1002
Page 936 of 1002
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
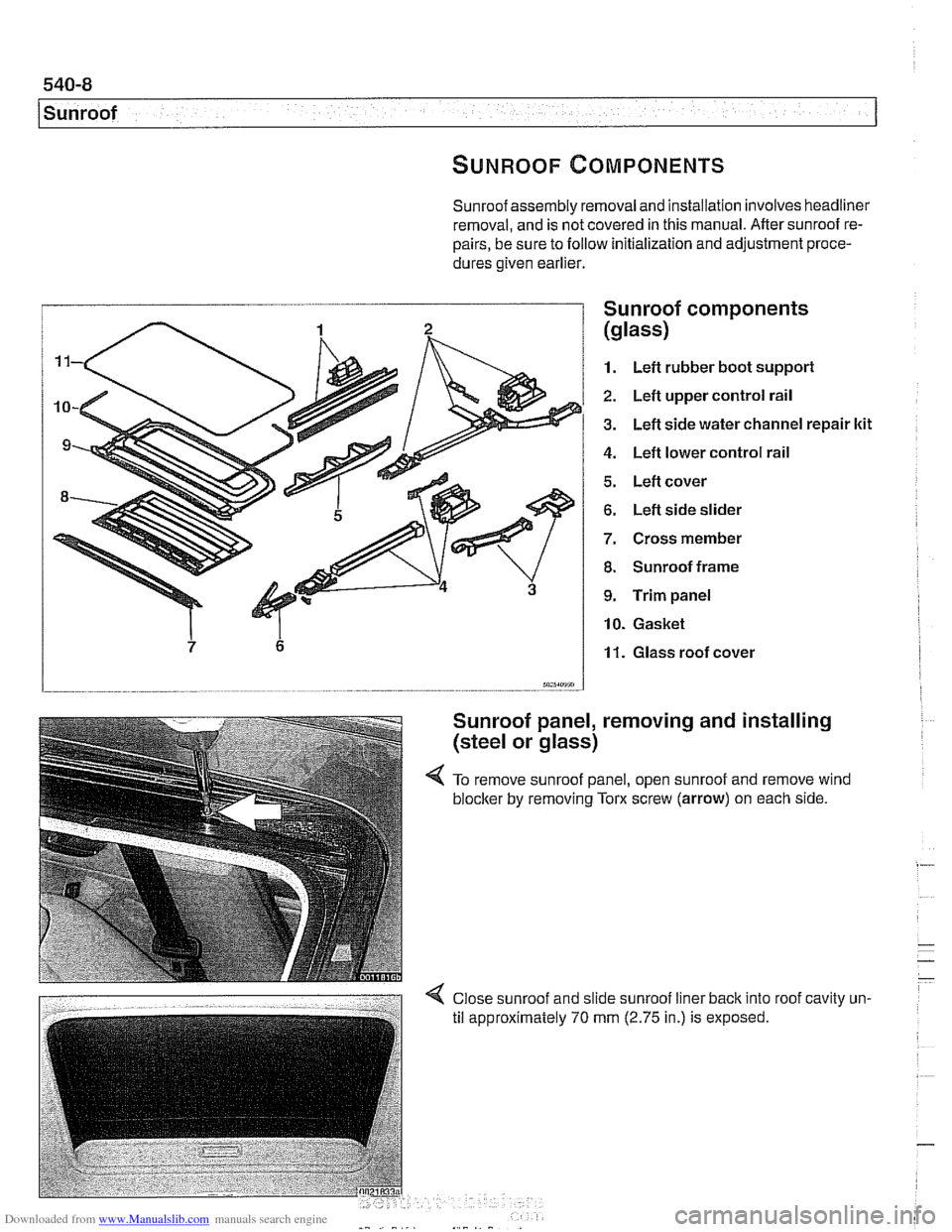
1 Sunroof
Sunroof assembly removal and installation involves headliner
removal, and is not covered in this manual. After sunroof re-
pairs, be sure to follow initialization and adjustment proce-
dures given earlier.
I Sunroof comDonents
1. Left rubber boot suppori
2. Left upper control rail
3. Left side water channel repair ltit
4. Left lower control rail
5. Left cover
6. Left side slider
7. Cross member
8. Sunroof frame
9. Trim panel
10. Gasket
11. Glass roof cover
m5sm.7 - -.
Sunroof panel, removing and installing
(steel or glass)
4 To remove sunroof panel, open sunroof and remove wind
blocker
by removing Tom screw (arrow) on each side.
Page 945 of 1002

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
Seat Belts
Remove lower B-pillar (door pillar) plastic trim
Pry carefully along bottom of trim to disengage
pillar.
Slide trim down (arrow) and out to remove. clips
from
4 Carefully pry bottom of upper door post trim away from post
to release clips.
Slide upper trim panel down (arrow) to remove.
Remove automatic reel from B-pillar:
- Remove upper seat belt anchor bolt (A).
Remove cross-brace mounting bolts (B).
Remove sound insulation at base of 8-pillar.
Then remove automatic seat belt reel mounting bolt
(C).
Lift out reel.
If it is necessary to remove sliding seat belt height adjuster,
unscrew mounting bolts from B-pillar.
Page 947 of 1002
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
-- -
Seat Belts
Rear seat belts (sedan)
- Remove rear parcel shelf to access shoulder belt assembly
mounting bolts. See 513 Interior Trim.
- Remove rear seat cushion to access rear seat belt lock
mounting bolts. See 520 Seats.
- When installing seat belt lock straps:
Install right lock strap (which is shorter) underneath middle
lock strap.
Install left lock strap underneath middle lap belt strap.
Metal strap ends must rest against stop on floor under-
neath seat.
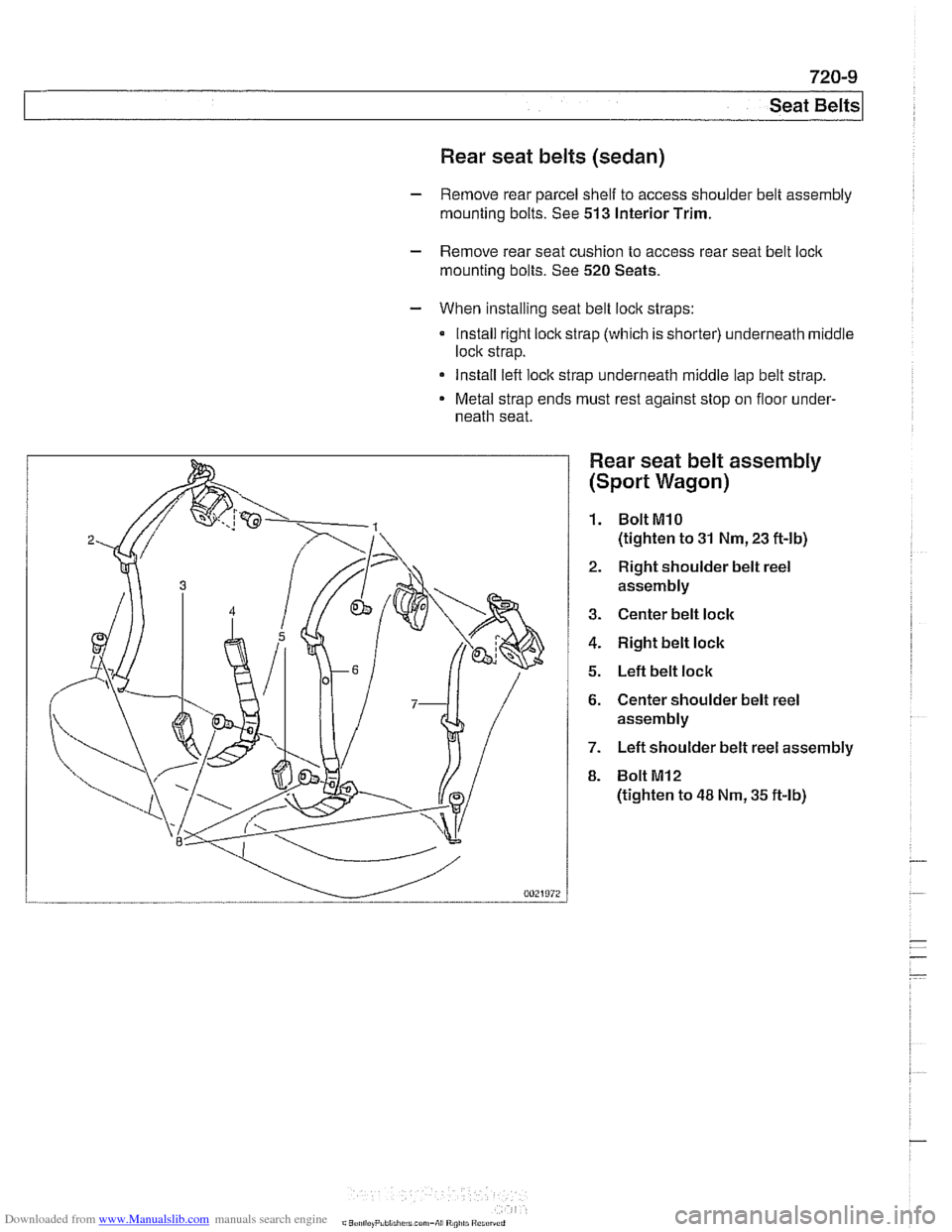
Rear seat belt assembly
(Sport Wagon)
1. BoltMlO
(tighten to 31 Nm, 23 ft-lb)
2. Right shoulder belt reel
assembly
3. Center belt lock
4. Right belt lock
5. Left belt lock
6. Center shoulder belt reel
assembly
7. Left shoulder belt reel assembly
8. Bolt
MI2
(tighten to 48 Nm, 35 ft-lb)
Page 948 of 1002

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
720-1 0
Seat Belts
Rear seat belts (Sport Wagon)
- Center shoulder belt:
Remove shoulder belt guide trim at top of seat backrest.
Feed belt out through slot in trim. Working in cargo com-
partment, partially remove backrest cover to access shoul-
der belt reel.
Remove shoulder belt reel mounting bolt inside backrest.
- Outboard shoulder belt:
Remove roof-pillar (C-pillar) trim.
Remove center shoulder belt.
- Lift up rear seat cushion(s) to access rear seat belt loclc
mounting
bolt(s).
- When installing seat belt loclc straps:
Install right belt loclc strap (which is shorter) underneath
center belt lock strap.
Install left belt loclc strap underneath center lap belt strap.
- Metal strap ends must rest against stop on floor underneath
seat.
Page 955 of 1002

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
Airbag System (SRS)~
MRS control module, replacing
- Disconnect negative (-) cable from battery and cover nega-
tive terminal with insulating material.
CAUTIOI\C
Prior to disconnecting the battery, read the battery discon-
nection cautionsgiven in001 General Warnings and
Cau-
tions.
- Remove center console between front seats. See 513 lnteri-
or Trim.
Remove module mounting nuts (arrows) and lift up control
module. Disconnect electrical harness connector.
Installation is reverse of removal.
Be sure that MRS control module ground cable is attached
to the module mounting stud.
Side-impact crash sensor, removing and
installing
- Make sure ignition key is OFF.
- Remove front seat. See 520 Seats.
Remove plastic door sill trim by lifting to release clips at one
end, then sliding off. Fold up carpet towards rear seat floor. If
necessary, remove floor level heater duct.
Page 960 of 1002

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
721-12
Airbag System (SRS)
Head protection airbag (HPS)
4 Replacement of a head protection airbag (HPS) is an exten-
sive operation, including removal of the following:
Complete dashboard
Complete headliner
Windshield pillar (A-pillar) trim
Door pillar (B-pillar) trim
- Before starting work on the HPS airbag, disconnect negative
(-) cable from battery and cover negative terminal with insu-
lating material.
Prior to disconnecting the battery, read the battery discon-
nection cautionsgiven in001 General Warnings and Cau-
tions.
Tightening torque HPS
airbag to body 11 Nm (8 ft-lb)
HPS airbag mounting bracket
to A or B-pillar
HPS gas generator to
dashboard reinforcement
(M6
self-tapping screw) 2.5
Nm (22 in-lb)
4 Nm (35 in-lb)
Page 966 of 1002

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
OBD-6
On-Board Diagnostics
Fuel system monitoring. This monitor looks at the fuel
delivery needed (long
/short term fuel trim) for proper engine
operation based on programmed data. If too much or not
enough fuel is delivered over a predetermined time, a DTC is
set and the MIL illuminates.
Fuel trim refers to adiustments to base fuel schedule.
Lono- ., term fuel trim refers to gradual adjustments to the fuel
calibration adjustment as compared to short term fuel trim.
Long term fuel trim adjustments compensate for gradual
changes that occur over time.
Fuel system monitoring monitors the calculated injection time
(ti) in relation to enginespeed, load and precatalyticconverter
oxygen
sensor(s) signals.
Using this data, the system optimizes fuel delivery for all
engine operating conditions.
Evaporative system monitoring. This monitor checks the
the fuel storage system and related fuel lines for leaks. It can
detect very small leaks anywhere in the system.
A leak detection unit (LDP or DMTL) is used to pressurize the
evaporative control system on a continuous basis (as the
drive cycle allows) and to
check system integrity.
Drive cycle
The OED II drive cycle is an important concept in
understanding OBD
II requirements. The purpose of the drive
cycle is to run ail of the emission-related on-board diagnostics
over a broad range of driving conditions.
A drive cycle is considered complete when all of the
diagnostic monitors have run their tests without interruption.
~ora drive cycle to be initiated, the vehicle must be started
cold and brought up to
1 60°F and at least 40°F above its
original starting temperature.
Readiness codes
Inspection/maintenance (I/M) readiness codes are mandated
as part of OBD
II. The readiness code is stored aftercomplete
diagnostic monitoring of specified components and systems
is carried out. The readiness code function was designed to
prevent manipulating an
I/M emission test procedure by
clearing faults codes or disconnecting the ECM or battery.
Page 968 of 1002

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
OBD-8
I On-Board Diagnostics
DTC digit interpretation
1st digit
P powertrain
B body
C chassis
2nd digit
0 SAE
1 BMW
3rd digit
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
4th - 5th digits total
system
airlfuei induction
fuel injection
ignition system or misfire
auxiliary emission control
vehicle speed
& idle control
ECM
inputs/outputs
transmission
individual circuits or
components
DTC example: P 0 3 0 6
P: A powertrain problem
0: SAE sanctioned or 'generic'
a 3: Related to an ignition system / misfire
06 Misfire detected at cylinder #6
DTCs provide a freeze frame or snap-shot of a vehicle
performance or emissions fault at the moment that the fault
first occurs. This information is accessible through generic
OED I1 scan tools.
Freeze frame data contains, but is not limited to, the following
information:
Engine load (calculated)
Engine rpm
Short and
long term fuel trim
Vehicle speed
Coolant temperature Intake manifold pressure
Open/closed loop operation
Fuel pressure (if available)
DTC
Page 974 of 1002
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
OBD-14
I On-Board Diagnostics
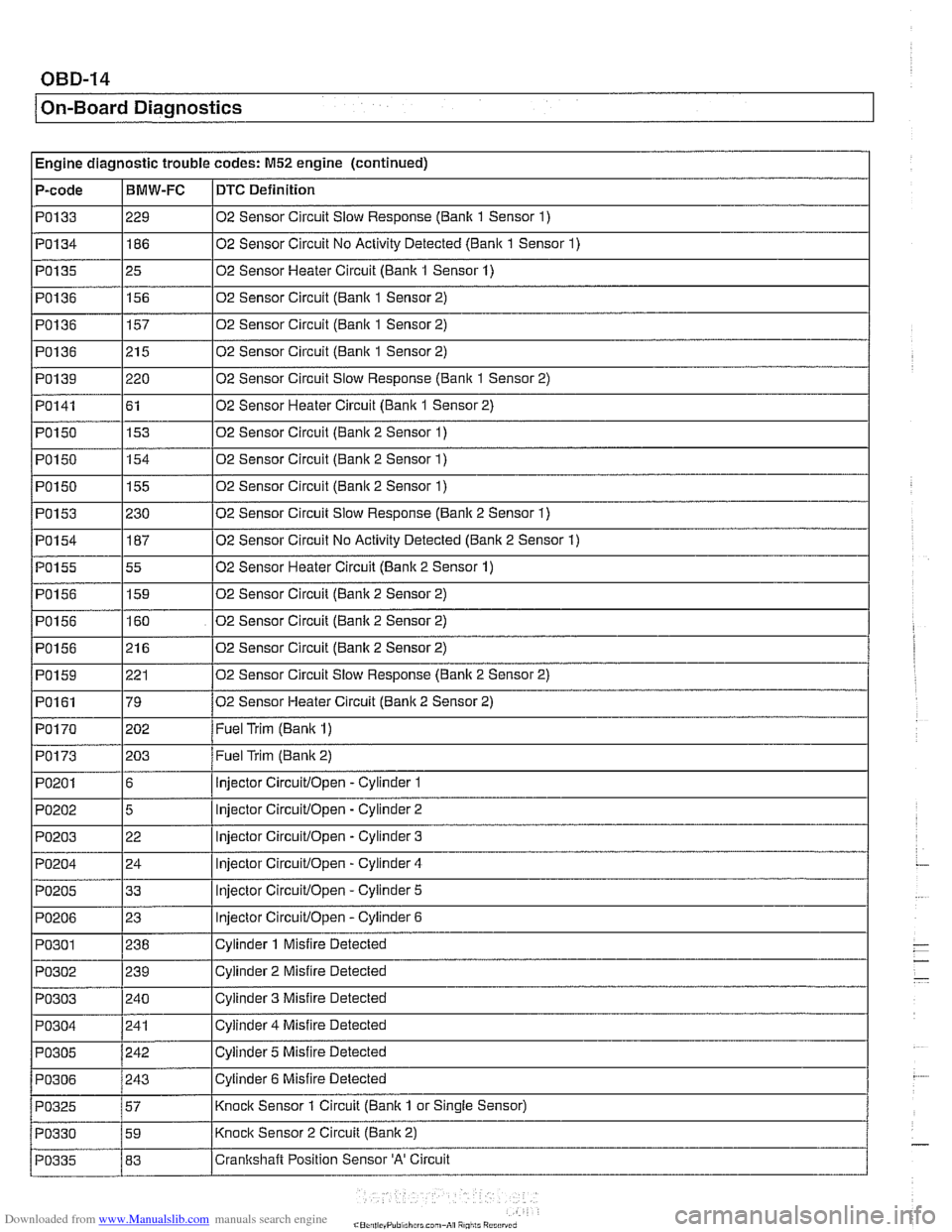
I Engine diagnostic trouble codes: M52 engine (continued) - - -
P-code IBMW-FC ~DTC Definition
PO133
PO134
PO135
PO136
PO136
PO136
PO139
PO141
I I
PO150 1155 102 Sensor Circuit (Bank 2 Sensor 1)
I
I
229
186
25
156
157
215
220 61
PO150 02
Sensor Circuit
Slow Response (Banlc 1 Sensor 1)
02 Sensor Circuit No Activity Detected
(Bank 1 Sensor 1)
02 Sensor Heater Circuit (Bank 1 Sensor 1)
02 Sensor Circuit
(Banlc 1 Sensor 2)
02 Sensor Circuit (Bank 1 Sensor 2)
02 Sensor Circuit (Bank 1 Sensor 2)
02 Sensor Circuit Slow Response
(Bank 1 Sensor 2)
02 Sensor Heater Circuit
(Bank 1 Sensor 2)
PO153
PO154
PO155
PO156
PO156
PO156
PO150 1154 102 Sensor Circuit (Bank 2 Sensor 1)
153
PO159
PO161
PO170
02
Sensor Circuit (Banic 2 Sensor 1)
230
187
55
159
160
21 6
p~-~~--~ PO173
PO201
PO202
PO203
PO204
PO205
PO206
02 Sensor Circuit Slow Response (Banlc 2 Sensor 1)
02 Sensor Circuit No Activity Detected (Bank 2 Sensor
1)
02 Sensor Heater Circuit (Bank 2 Sensor 1)
02 Sensor Circuit (Bank 2 Sensor 2)
02 Sensor Circuit (Banlc 2 Sensor 2)
02 Sensor Circuit (Banlc 2 Sensor 2)
221
79
202 02
Sensor Circuit Slow Response (Banic 2 Sensor 2)
02 Sensor Heater Circuit
(Banic 2 Sensor 2)
Fuel Trim
(Banic 1)
203
6
5
22
24
33
23
Fuel Trim (Banic 2)
injector
Circuitlopen -Cylinder 1
injector
Circuitlopen - Cylinder 2
injector
Circuitlopen -Cylinder 3
Injector
Circuitlopen - Cylinder 4
injector
Circuitlopen - Cylinder 5
lniector
CircuitlOpen - Cvlinder 6
Page 975 of 1002
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine
OBD-15
On-Board ~iagnosticsl
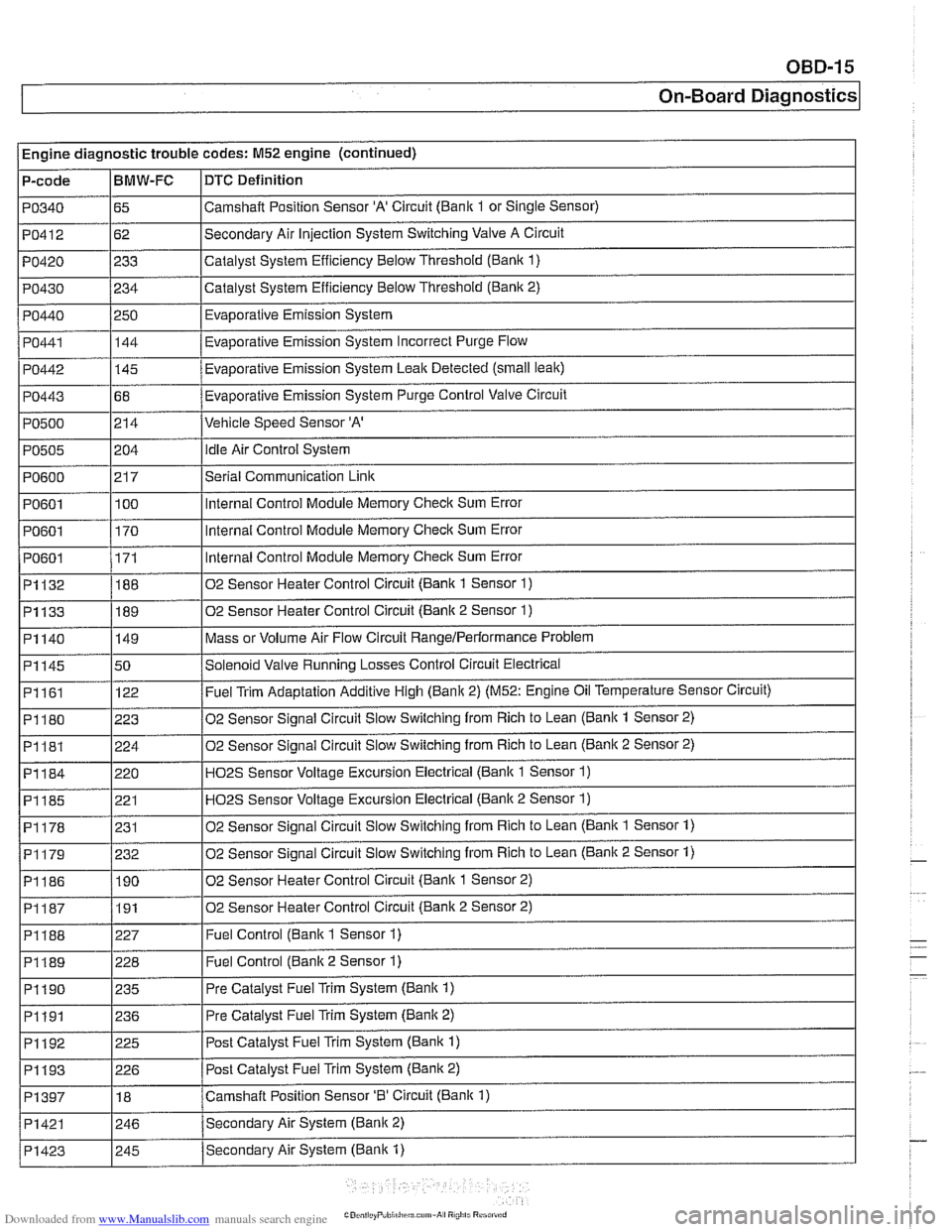
Engine diagnostic trouble codes: M52 engine (continued)
P-code
PO340
PO412
PO420
PO430
PO440
PO441
PO442
PO443
PO500
PO505
PO600
PO601
PO601
I PO601
~1132
~1133
BMW-FC
65
62
233
234
250 144
-
145
68
214
i I
DTC Definition
Camshalt Position Sensor 'A' Circuit (Bank 1 or Single Sensor)
Secondary Air Injection System Switching Valve A Circuit
Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold
(Bank 1)
Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 2)
Evaporative Emission System
Eva~orative Emission Svstem Incorrect Purge Flow .
Evaporative Emission System Leak Detected (small leak)
Evaporative Emission System Purge Control Valve Circuit
Vehicle Speed Sensor 'A'
204
21 7
100
170
171
188
189
PI161
PI180
PI181
PI184
PI185
PI178
02 Sensor Heater Control Circuit (Bank 2 Sensor 2) I
idle Air Control System
Serial Communication
Link
Internal Control Module Memory Check Sum Error
Internal Control Module Memory
Check Sum Error
Internal Control Module Memory
Check Sum Error
02 Sensor Heater Control Circuit (Bank 1 Sensor
1)
02 Sensor Heater Control Circuit (Bank 2 Sensor 1)
Mass or Volume Air Flow Circuit RangeIPerlormance Problem PI140
I
I I
P1188 1227 I Fuel Control (Bank 1 Sensor 1)
PI145 150 /Solenoid Valve Running Losses Control Circuit Electrical
149
122
223
224
220 221
231
I I
P1189 1228 I Fuel Control (Banlc 2 Sensor 1)
Fuel Trim Adaptation Additive High (Bank 2) (M52: Engine Oil Temperature Sensor Circuit)
02 Sensor Signal Circuit Slow Switching from Rich to Lean
(Bank 1 Sensor 2)
02 Sensor Signal Circuit Slow Switching from Rich to Lean
(Bank 2 Sensor 2)
H02S Sensor Voltage Excursion Electrical (Banlc 1 Sensor 1)
HO2S Sensor Voltage Excursion Electrical (Banlc 2 Sensor 1)
02 Sensor Sianai Circuit Slow Switchina from Rich to Lean (Bank 1 Sensor 1)
02 Sensor Signal Circuit Slow Switching from Rich to Lean (Bank 2 Sensor 1) PI179
I I
PI190 1235 I Pre Catalyst Fuel Trim System (Banlc 1)
PI186 1190 102 Sensor Heater Control Circuit (Banlc 1 Sensor 2)
232
I I
PI191 1236 I Pre
Catalyst Fuel Trim System (Banlc 2)
PI192
. . -- - i Pi193 1226 I Post Catalvst Fuel Trim Svstem (Bank 2)
225
PI397
I I
Post Catalyst Fuel Trim System (Bank 1)
PI421 1246 /Secondarv Air System (Bank 2)
18
Secondary Air System (Bank
1) PI423
Camshaft Position Sensor '0' Circuit (Bank 1)
I 245