seat memory BMW 740IL 1995 E38 Central Body Electronics ZKE Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: BMW, Model Year: 1995, Model line: 740il, Model: BMW 740il 1995 E38Pages: 80, PDF Size: 4.14 MB
Page 62 of 80
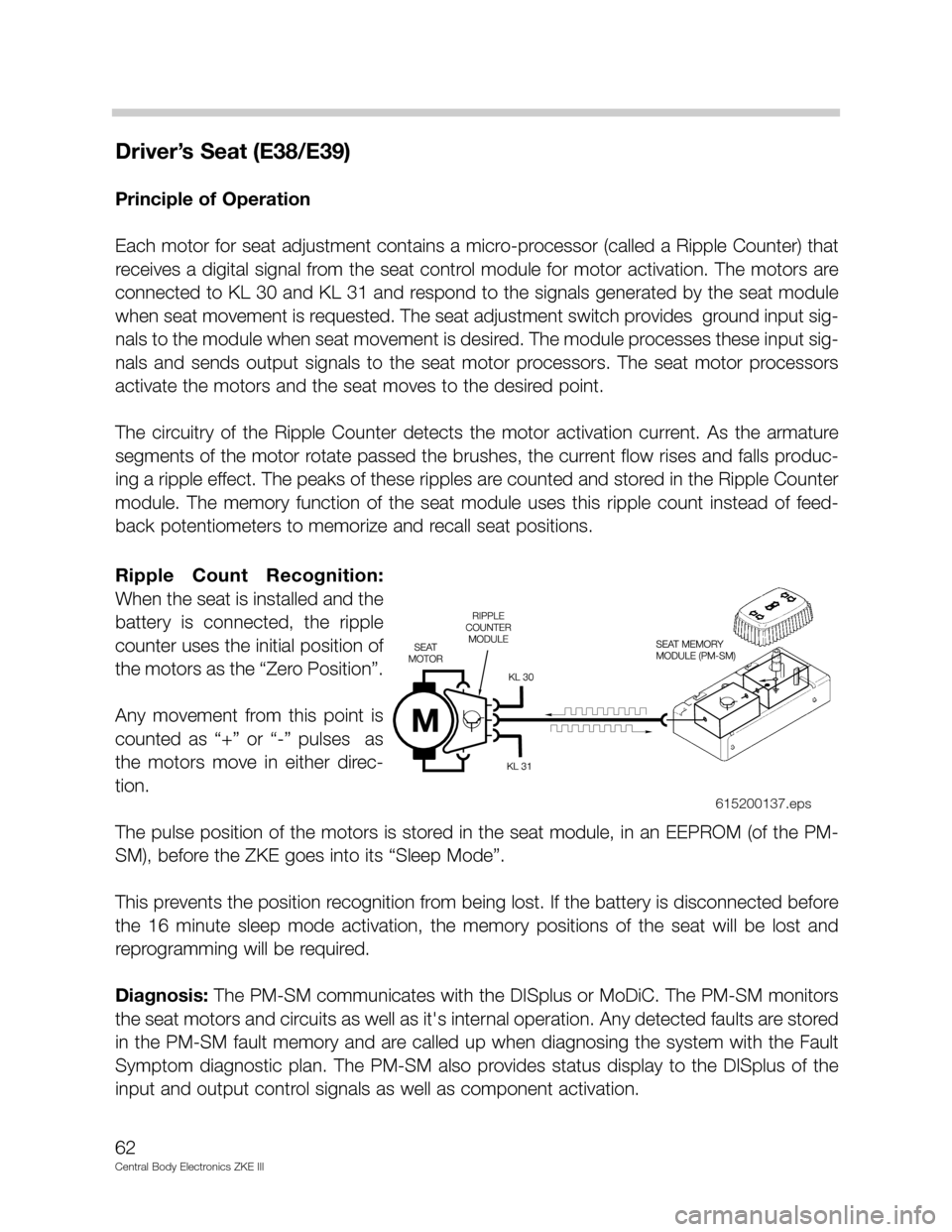
Driver’s Seat (E38/E39)
Principle of Operation
Each motor for seat adjustment contains a micro-processor (called a Ripple Counter) that
receives a digital signal from the seat control module for motor activation. The motors are
connected to KL 30 and KL 31 and respond to the signals generated by the seat module
when seat movement is requested. The seat adjustment switch provides ground input sig-
nals to the module when seat movement is desired. The module processes these input sig-
nals and sends output signals to the seat motor processors. The seat motor processors
activate the motors and the seat moves to the desired point.
The circuitry of the Ripple Counter detects the motor activation current. As the armature
segments of the motor rotate passed the brushes, the current flow rises and falls produc-
ing a ripple effect. The peaks of these ripples are counted and stored in the Ripple Counter
module. The memory function of the seat module uses this ripple count instead of feed-
back potentiometers to memorize and recall seat positions.
Ripple Count Recognition:
When the seat is installed and the
battery is connected, the ripple
counter uses the initial position of
the motors as the “Zero Position”.
Any movement from this point is
counted as “+” or “-” pulses as
the motors move in either direc-
tion.
The pulse position of the motors is stored in the seat module, in an EEPROM (of the PM-
SM), before the ZKE goes into its “Sleep Mode”.
This prevents the position recognition from being lost. If the battery is disconnected before
the 16 minute sleep mode activation, the memory positions of the seat will be lost and
reprogramming will be required.
Diagnosis: The PM-SM communicates with the DISplus or MoDiC. The PM-SM monitors
the seat motors and circuits as well as it's internal operation. Any detected faults are stored
in the PM-SM fault memory and are called up when diagnosing the system with the Fault
Symptom diagnostic plan. The PM-SM also provides status display to the DISplus of the
input and output control signals as well as component activation.
62
Central Body Electronics ZKE III
615200137.eps
Page 63 of 80
Passenger’s Seat (without memory)
Principle of Operation
The passenger seat control switch is purely a mechanical switching module that activates
the passenger seat motors without position monitoring capabilities. Due to the limited op-
eration requirements, the passenger seat control switch is not equipped with on board
diagnostics.
The Passenger Seat control switch is equipped with an overload protection function. If
excessive amperage is drawn due to a defective motor or a switch is stuck driving a motor
to the end limit, the function activates opening the motor control circuit.
Passenger Seat Motors: Each motor is individually controlled by the Seat Control Switch.
Each position motor is connected to the seat position switch by a two wire circuit provid-
ing motor activation in both directions (no position recognition).
Passenger Seat Adjustment: Operation of the passenger seat is always possible regard-
less of the ignition key position. Moving a position switch operates a the motor control con-
tacts directly, the switch applies voltage and ground path directly to operate the motor.
Reversing the switch simply changes the motor polarity. More than one passenger seat
motor can be run simultaneously.
Optional Seat Back Lumbar Support
The optional air bladder lumbar support system is similar in all
vehicles (if equipped). Each seat contains the following com-
ponents:
• Four position circular rocker switch in the seat base trim in
the area of the seat switches.
• Electrically controlled air compressor with over pressure cut
out under each seat.
• Two solenoid activated air controlling valve blocks (one per
air bladder). Each valve block includes an inlet and an outlet
valve. When energized they direct air into the bladder(s) to
inflate or relieve trapped air to deflate the bladders.
• Connecting hoses and air bladders in lower seat back.
63
Central Body Electronics ZKE III
Page 64 of 80
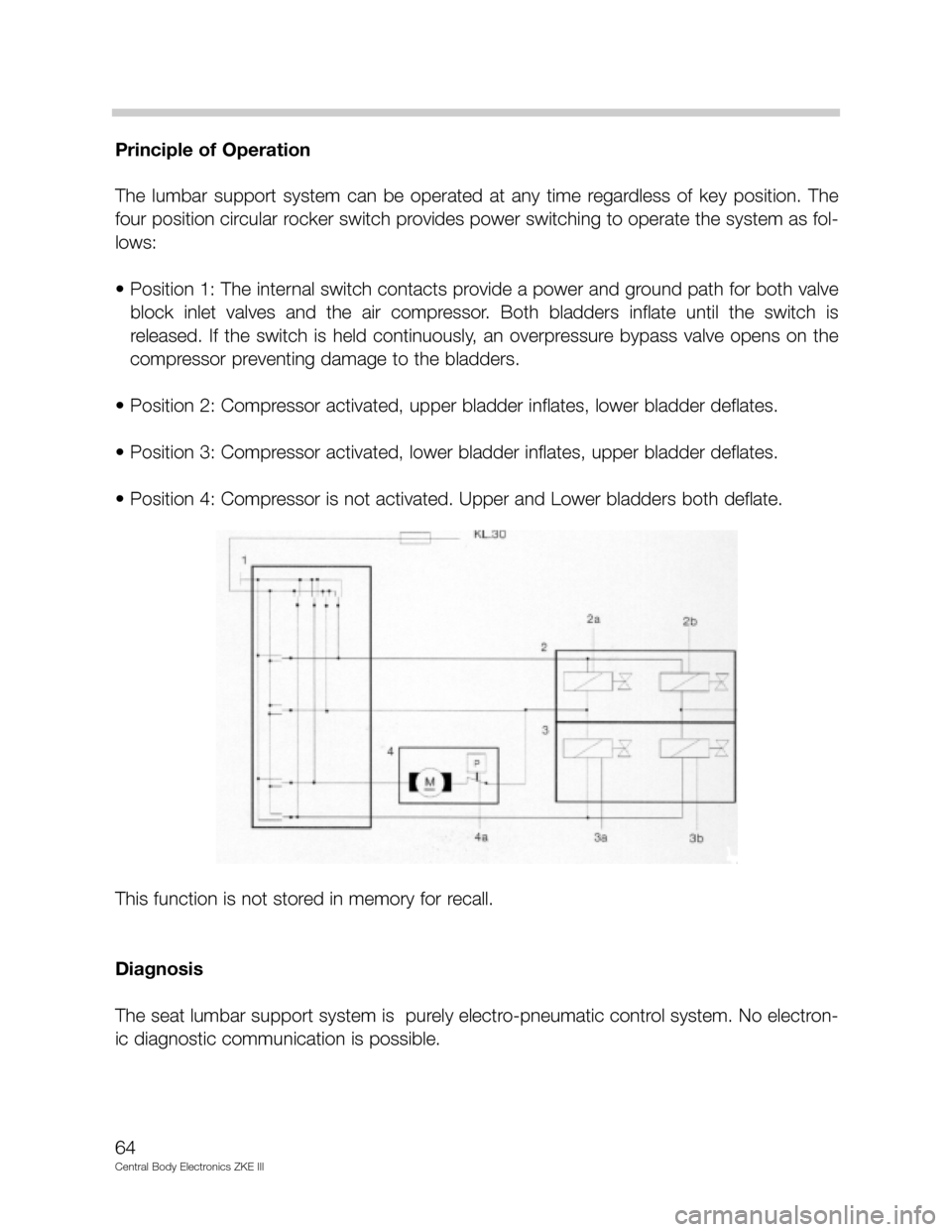
Principle of Operation
The lumbar support system can be operated at any time regardless of key position. The
four position circular rocker switch provides power switching to operate the system as fol-
lows:
• Position 1: The internal switch contacts provide a power and ground path for both valve
block inlet valves and the air compressor. Both bladders inflate until the switch is
released. If the switch is held continuously, an overpressure bypass valve opens on the
compressor preventing damage to the bladders.
• Position 2: Compressor activated, upper bladder inflates, lower bladder deflates.
• Position 3: Compressor activated, lower bladder inflates, upper bladder deflates.
• Position 4: Compressor is not activated. Upper and Lower bladders both deflate.
This function is not stored in memory for recall.
Diagnosis
The seat lumbar support system is purely electro-pneumatic control system. No electron-
ic diagnostic communication is possible.
64
Central Body Electronics ZKE III
Page 65 of 80
Comfort Seats (standard on E38 750iL, other models if equipped)
This option provides additional back support in the
shoulder area. An additional adjustment in the upper
backrest allows forward “contour” that is controlled by
a rocker switch in the side panel.
When the ignition is on or off, the two way rocker switch
can be pushed until the desired setting is achieved (for-
ward/backward tilt). The motor drive operates the same
as the seat motors.
The shoulder support adjustment is also stored in
memory for recall.
Active Seat (E38 - if equipped)
Purpose of the System
Actively changing the surface of the seat helps to prevent muscle tension and fatigue par-
ticularly on long trips or sitting in one position for a long period of time. The seat causes
weight transfers which are slight and imperceptible enhancing driving comfort. The basic
seating position is not changed by this.
In the seat’s upholstery beneath the surface of the seat is a cushion of fluid on the left and
right. The fluid is slowly circulated back and forth between the cushions by a pump.
65
Central Body Electronics ZKE III
Page 70 of 80
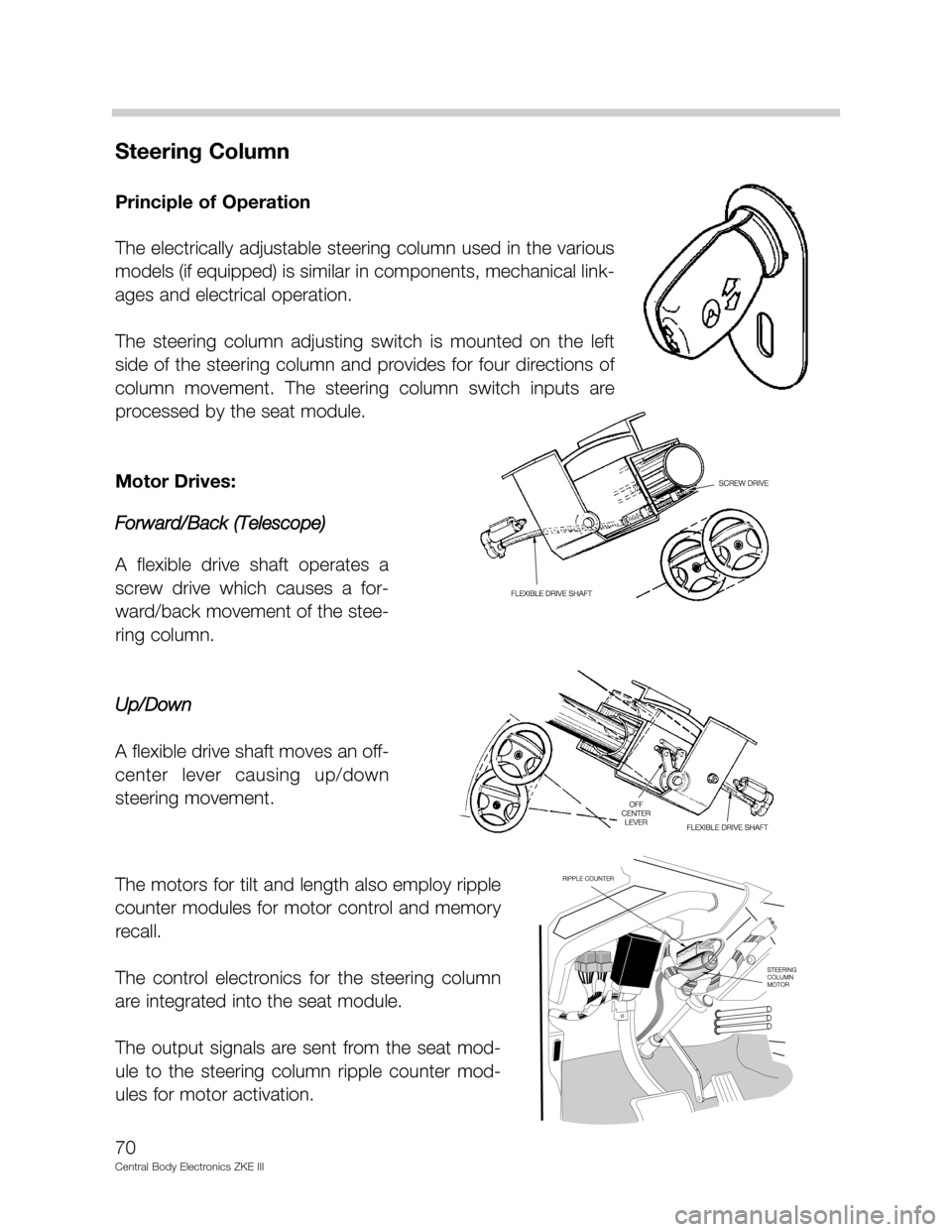
Steering Column
Principle of Operation
The electrically adjustable steering column used in the various
models (if equipped) is similar in components, mechanical link-
ages and electrical operation.
The steering column adjusting switch is mounted on the left
side of the steering column and provides for four directions of
column movement. The steering column switch inputs are
processed by the seat module.
Motor Drives:
Forward/Back (Telescope)
A flexible drive shaft operates a
screw drive which causes a for-
ward/back movement of the stee-
ring column.
Up/Down
A flexible drive shaft moves an off-
center lever causing up/down
steering movement.
The motors for tilt and length also employ ripple
counter modules for motor control and memory
recall.
The control electronics for the steering column
are integrated into the seat module.
The output signals are sent from the seat mod-
ule to the steering column ripple counter mod-
ules for motor activation.
70
Central Body Electronics ZKE III
Page 80 of 80

9. What type of sensor is used to detect the position of a seat with Memory? What type
of signal does it produce?__________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________
10. How does the Seat Module communicate a request for a stored memory position with
the mirror modules?_______________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
11. On an E38 with Servotronic, why is the speed signal provided to the GM from both
the IKE “A” signal and the K-Bus?___________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
12. An E38 customer complains that when exiting the vehicle the steering wheel moves
up. What is the cause of this?______________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
13. How does the SZM monitor the Seat Heating temperature?_____________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
14. What circuits are controlled by Consumer Cut Off? ____________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
15. If a technician double locked a 2000 MY E39 while still inside the vehicle, how could
he/she exit the vehicle?____________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
16. How is the MY 2000 key charged?__________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
17. How is the DWA Disarmed (emergency)?_____________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
18. What functions will deactivate the exterior door handle lighting? _________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________
80
Central Body Electronics ZKE III