heater BMW M3 1992 E36 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: BMW, Model Year: 1992, Model line: M3, Model: BMW M3 1992 E36Pages: 759
Page 176 of 759
130-
3
0
FUEL
INJECTION
Pin
Signal
Component/function
Signal
ECM
PIN
ASSIGNMENTS
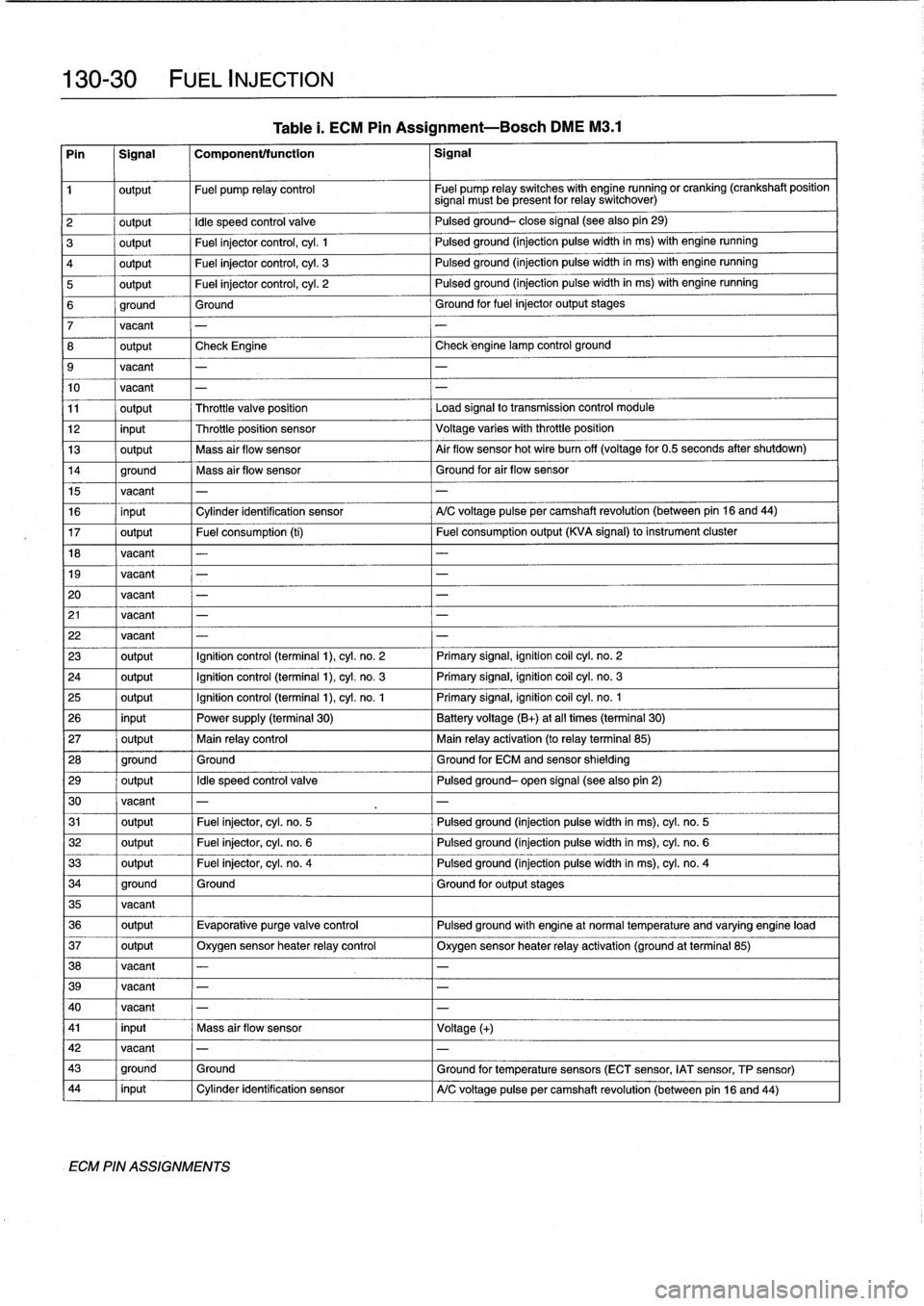
Table
1.
ECM
Pin
Assignment-Bosch
DME
M3
.1
1
output
Fuel
pump
relay
control
Fuel
pump
relay
switches
with
engine
runningor
cranking
(crankshaft
position
Signal
mustbe
present
for
relay
switchover)
2
1
output
1
Idle
speed
control
valve
1
Pulsad
ground-
close
signal
(seealsopin29)
3
output
Fuel
injectorcontrol,
cyl
.
1
Pulsedground
(injection
pulsewidth
in
ms)
with
engine
running
4
output
Fuel
injectorcontrol,
cyl
.
3
Pulsedground
(injection
pulsewidth
in
ms)
with
engine
running
5
output
Fuel
injector
control,
cyl
.
2
Pulsedground
(injection
pulse
width
in
ms)
with
enginerunning
6
ground
Ground
Ground
for
fuel
injector
output
stages
7
vacant
-
-
8
output
Check
Engine
Check
éngine
lamp
control
ground
9
vacant
-
-
10
vacant
-
-
11
output
Throttle
valve
position
Load
signal
to
transmission
control
module
12
input
Throttle
position
sensor
Voltage
varies
with
throttle
position
13
output
Mass
air
flow
sensor
Air
flow
sensor
hotwire
burn
off
(voltage
for
0
.5
seconds
after
shutdown)
14
ground
Mass
air
flow
sensor
Ground
for
air
flow
sensor
15
vacant
-
-
16
input
Cylinder
identification
sensor
A/C
voltage
pulse
per
camshaft
revolution
(between
pin
16
and
44)
17
output
Fuel
consumption
(ti)
Fuel
consumption
output
(KVA
Signal)
to
instrument
cluster
18
vacant
-
-
19
vacant
-
-
20
vacant
-
-
21vacant
-
-
22
vacant
-
-
23
output
Ignition
control
(terminal
1),
cyl
.
no
.
2
Primary
Signal,
ignition
coil
cyl
.
no
.
2
24
output
Ignition
control
(terminal
1),
cyl
.
n
o
.
3
Primary
signal,
ignition
coil
cyl
.
no
.
3
25
output
Ignition
control
(terminal
1),
cyl
.
n
o
.
1
Primary
signal,
ignitioh
coil
cyl
.
no
.
1
26
input
Power
supply
(terminal
30)
Battery
voltage
(B+)
at
al¡
times
(terminal
30)
27
output
Main
relay
control
Main
relay
activation
(to
relay
terminal
85)
28
ground
Ground
Ground
for
ECM
and
sensor
shielding
29
output
Idle
speed
control
valve
Pulsed
ground-
open
signal
(see
also
pin
2)
30
vacant
-
-
31
output
Fuel
injector,cyl
.
no
.
5
Pulsedground
(injection
pulsewidth
in
ms),
cyl
.
no
.
5
32
output
Fuel
injector,cyl
.
no
.
6
Pulsedground
(injection
pulse
width
in
ms),
cyl
.
no
.
6
33
output
Fuel
injector,cyl
.
no
.
4
Pulsedground
(injection
pulsewidth
in
ms),
cyl
.
no
.
4
34
ground
Ground
Ground
for
output
stages
35
vacant
36
output
Evaporative
purgevalve
control
Pulsed
ground
with
engine
at
normal
temperature
and
varying
engine
load
37
output
Oxygen
sensor
heater
relay
control
Oxygen
sensor
heater
relayactivation
(ground
at
terminal
85)
38
vacant
-
-
39
vacant
-
-
40
vacant
-
41
input
Mass
air
flow
sensor
Voltage
(+)
42
vacant
-
-
43
ground
Ground
Ground
for
temperatura
sensors
(ECT
sensor,
IAT
sensor,
TP
sensor)
44
input
Cylinder
identification
sensor
A/C
voltagepulseper
camshaft
revolution
(between
pin
16
and
44)
Page 178 of 759
130-
3
2
FUEL
INJECTION
Pin
1
Signal
1
Component/function
1
Signal
1
output
Fuel
pump
relay
control
Fuel
pump
relay
switches
with
engine
running
or
cranking
(crankshaft
position
signal
must
be
present
for
relay
switchover)
2
output
Idle
speed
control
valve
Pulsed
ground-close
signal
(seealso
pin
29)
3
output
Fuel
ínjectorcontrol,
cyl
.
5
Pulsed
ground
(injection
pulsewidth
in
ms)
cyl
.
5
4
output
Fuel
injectorcontrol,
cyl
.
6
Pulsed
ground
(injection
pulsewidth
in
ms)
cyl
.
6
5
output
Fuel
injectorcontrol,
cyl
.
4
Pulsed
ground
(injection
pulsewidth
in
ms)
cyl
.
4
6
ground
Ground
Ground
for
fuel
injector
output
stage
7
output
Camshaft
actuator
(VANOS
solenoid)
control
Camshaft
actuator
(VANOS
solenoid)
8
output
Check
Engine
Instrument
cluster,
Check
Engine
lamp
9
vacant
-
-
10
vacant
-
-
11
output
Throttle
position
Throttle
angle
signal
to
A/T
control
module
12
vacant
-
-
13
input
Oxygen
sensor
Oxygen
sensor
signal
(0-1
VDC
fluctuating
with
engine
running)
14
input
Mass
air
flow
sensor
Mass
air
flow
sensor
15
ground
Ground
Ground
16
input
Crankshaft
position/rpm
sensor
Voltage
pulse
(VAC)
between
pin
16
and
43
(crank
position/rpm
sensor)
17
input
Camshaft
position
sensor
Halleffect
camshaft
sensor
18
vacant
-
-
19
vacant
-
-
20
vacant
-
-
21
vacant
-
-
22
vacant
-
-
23
output
Ignition
coil
control,
cyl
.
4
Ignition
coil
4
24
output
Ignition
coil
control,
cyl
.
6
Ignition
coil
6
25
output
Ignition
coil
control,
cyl
.
5
Ignition
coil
5
26
input
Power
supply
(terminal
30)
Battery
voltage(B+)
at
all
times
27
input
Main
relay
control
Main
relayactivation
(terminal
85)
28
ground
Ground
Ground
for
ECM
and
sensor
shielding
29
output
Idle
speed
control
valve
Pulsed
ground-open
signal
(seealsopin
2)
30
vacant
-
-
31
output
Fuel
injectorcontrol,
cyl
.
3
Injection
pulse
wicith
in
ms-cyl
.
3
32
output
Fuel
injectorcontrol,
cyl
.
2
Injection
pulse
wicith
in
ms-cyl
.
2
33
output
Fuel
injectorcontrol,
cyl
.
1
Injection
pulsewidth
in
ms-cyl
.
1
34
ground
Ground
Ground
for
remaining
output
stages
35
vacant
-
-
36
output
Evaporative
purge
valve
control
37
vacant
-
-
38
output
Oxygen
sensor
heater
relay
control
Oxygen
sensor
heater
relay
switchover
(terminal
85)
39
vacant
-
-
40
ground
Oxygen
sensor
Oxygen
sensor
signal
ground
41
input
Mass
air
flow
sensor
Mass
air
flow
voltage
signal
42
input
Vehicle
speed
Vehicle
speed
signal
from
instrument
cluster
43
input
Crankshaft
position/rpm
sensor
Voltage
pulse
(VAC)
between
pin16
and
43
44
ground
Ground
Ground
for
intake
air
temp
.
sensor,
engine
coolant
temp
.
sensor,
throttle
position
sensor
ECM
PIN
ASSIGNMENTS
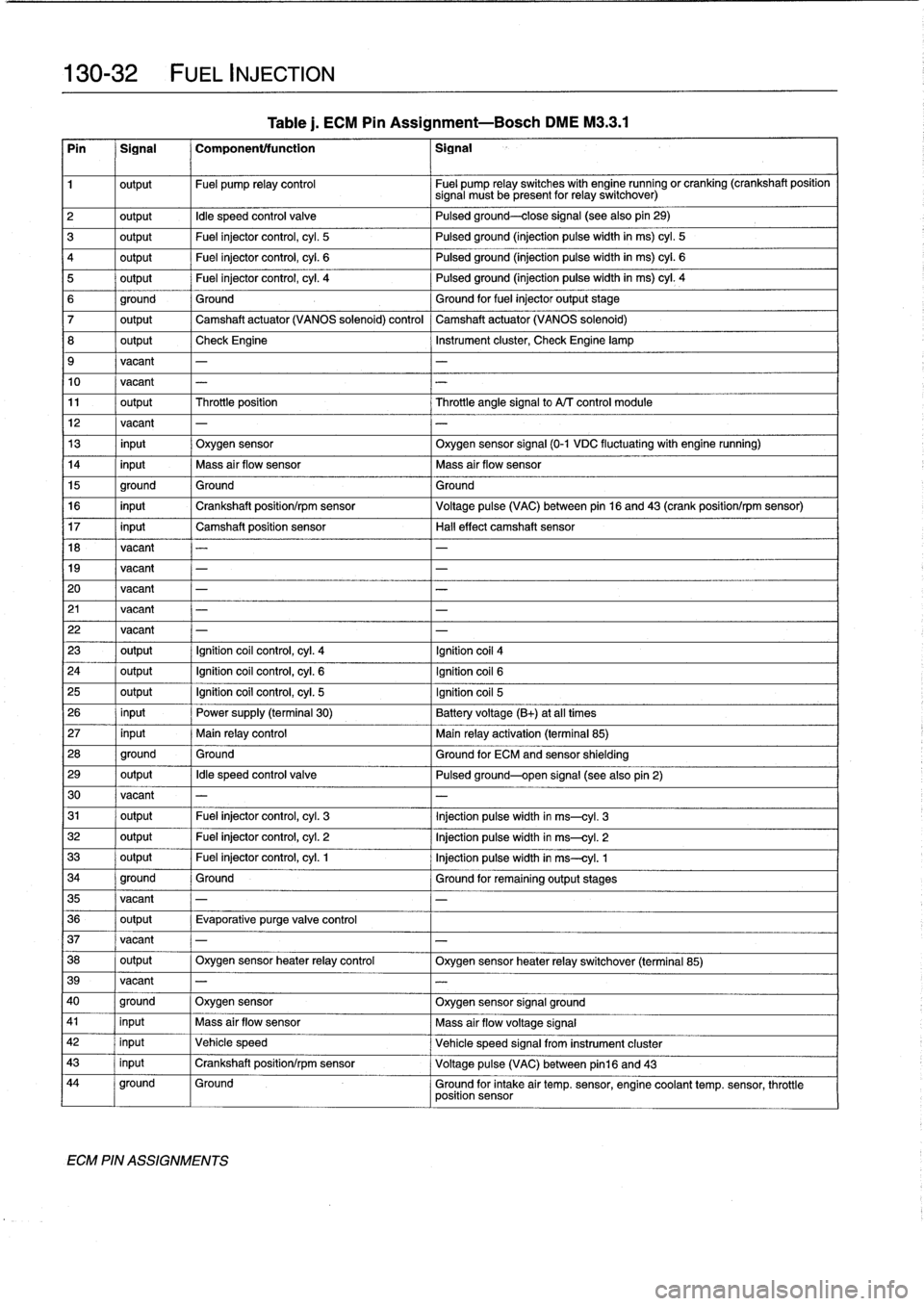
Table
j
.
ECM
Pin
Assignment-Bosch
DME
M3
.3
.1
Page 180 of 759
130-
34
FUEL
INJECTION
Pin
i
Signal
1
Component/function
1
Signal
1
output
Oxygen
sensor
(monitoring
sensor)heater
Oxygen
sensor
heater
control
(switched
ground)
2
output
Idle
speed
control
valve
Pulsed
ground-close
signal
(see
also
pin
29)
3
output
Fuel
injector
control,
cyl
.
1
Pulsed
ground
(injection
pulsewidth
in
ms)
cyl
.
1
4
output
Fuel
injector
control,
cyl
.
4
Pulsed
ground
(injection
pulse
width
in
ms)
cyl
.
4
5
not
used
-
-
6
ground
Ground
Ground
for
fuel
injector
output
stage
7
not
used
-
8
1
output
1
Check
Engine
1
Instrument
cluster,
Check
Engine
lamp
9
not
used
-
-
10
input
Electronic
immobilizer
control
(EWS
II)
Electronic
immobilizer
control
(EWS
II)
module
11
output
Automatic
climate
control
Automatic
climate
control,
to
evaporator
controlier
12
not
used
-
-
13
not
used
-
-
14
not
used
-
-
15
not
used
-
-
16
input
Intake
air
temperature
Intake
air
temperature
Signal
17
input
Mass
air
flow
meter
Intake
air
signal
18
not
used
-
-
19
input
Oxygen
sensor
(monitoring
sensor)
Oxygen
sensor
control
20
output
Crankshaft/rpm
sensor
Crankshaft/rpm
sensor
control
21
input
Camshaft
position
sensor
Camshaft
position
signal
22
output
Ignition
coil
control,
cyl
.
3
Primary
signal,
ignitioncoil
3
23
output
Ignition
coil
control,
cyl
.
4
Primary
signal,
ignitioncoil
4
24
not
used
-
-
25
not
used
-
-
26
input
Power
supply
(terminal
30)
Battery
voltage
(B+)
at
al¡
times
27
input
Main
relay
control
Main
relay
activation
(terminal
85)
28
ground
Ground
Ground
for
ECM
and
sensor
shielding
29
output
Idle
speed
control
valve
Pulsed
ground-open
signal
(seealsopin
2)
30
output
Oxygen
sensor
(monitoring
sensor)
heater
Oxygen
sensor
heater
control
(switched
ground)
31
output
Fuel
injectorcontrol,
cyl
.
3
Pulsed
ground
(injection
pulsewidth
in
ms)
cyl
.
3
32
output
Fuel
injector
control,
cyl
.
2
Pulsed
ground
(injection
pulsewidth
in
ms)
cyl
.
2
33
I
not
used
40
input
Knock
sensor
#2
(cyl
.
3,4)
Knock
sensor
#2
signal
41
not
used
-
-
42
input
Vehicle
speed
Vehicle
speed
signal
from
instrument
cluster
43
not
used
-
-
44
output
Throttleposition
sensor
(TPS)
Throttleposition
reference
signal
ECM
PIN
ASSIGNMENTS
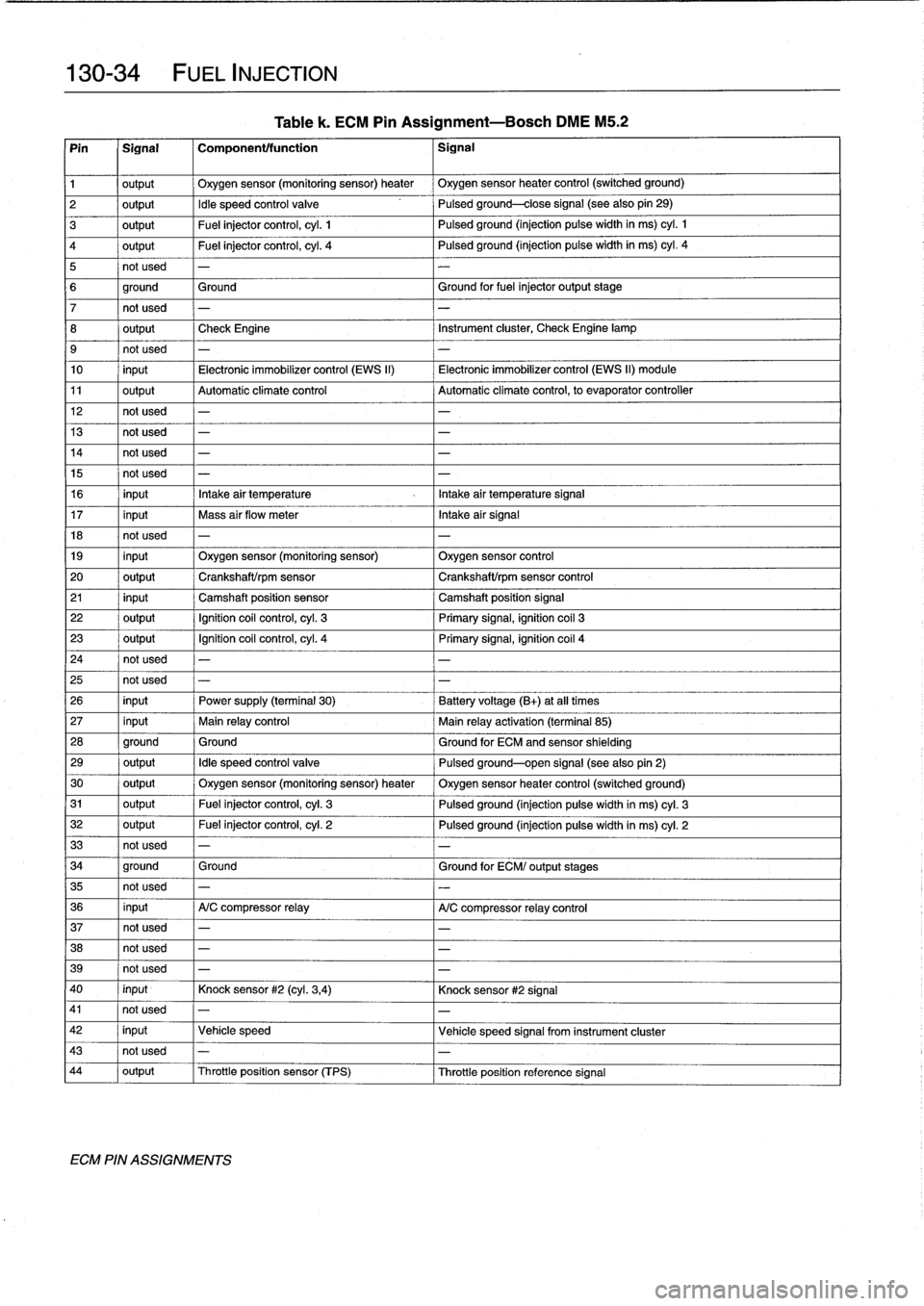
Table
k
.
ECM
Pin
Assignment-Bosch
DME
M5
.2
34
ground
Ground
Ground
for
ECM/
output
stages
35
not
used
-
-
36
input
A/C
compressor
relay
A/C
compressor
relay
control
37
not
used
-
-
38
not
used
-
-
39
not
used
-
-
Page 182 of 759
130-
3
6
FUEL
INJECTION
Pin
1
Signal
1
Componentffunction
1
Signal
1
output
Ignition
coil
control,
cyl
.
2
Primary
signal,
ignition
coil
2
2
output
Ignition
coil
control,
cyl
.
4
Primary
signal,
ignitioncoil
4
3
output
Ignition
coil
control,
cyl
.
6
Primary
signal,
ignition
coil
6
4
ground
Ground
Ground
5
output
Fuel
injectorcontrol,
cyl
.
2
Pulsed
ground
(injection
pulse
width
in
ms)
cyl
.
2
6
output
Fuel
injectorcontrol,
cyl
.
1
Pulsed
ground
(injection
pulse
width
in
ms)
cyl
.
1
7
output
Mass
air
flow
meter
Mass
air
meter
signal
8
input
Mass
air
flow
meter
Mass
air
meter
signal
9
output
Instrument
cluster
Fuel
consumption
signal
10
output
Engine
coolant
temperature
(ECT)
sensor
ECT
signal
11
output
Fueltankpressure
sensor
Fueltankpressure
sensor
control
12
input
Throttleposition
sensor
(TPS)
Throttleposition
signal
13
-
14
input
Intake
air
temperature
(IAT)
sensor
Intake
air
temperature
signal
15
Traction
control
AST
module
16
input
Automatic
climate
control
Automatic
climate
control
17
18
input
Electronic
immobilizer
control
(EWS
II)
Electronic
immobilizer
control
(EWS
II)
module
19
Automatic
climate
control
Automatic
climate
control
20
-
Instrument
cluster
Instrument
cluster
21
output
Camshaft
actuator
(VANOS
solenoid)
control
Camshaft
actuator
(VANOS
solenoid),
switched
ground
22
output
Fuel
injectorcontrol,
cyl
.
3
Pulsed
ground
(injection
pulse
width
in
ms)
cyl
.
3
23
Fuel
injectorcontrol,
cyl
.
6
Pulsed
ground
(injection
pulse
width
in
ms)
cyl
.
6
24
Fuel
injectorcontrol,
cyl
.
4
Pulsed
ground
(injection
pulse
width
in
ms)
cyl
.
4
25
output
Oxygen
sensor
heater
control
Oxygen
sensor
heater
ground
26
input
Power
supply
(terminal
30)
Battery
voltage(B+)
at
all
times
27
output
Idle
speed
control
valve
Pulsed
ground-open
signal
(see
also
pin
53)
28
ground
Ground
Ground
29
output
Ignition
coil
control,
cyl
.
1
Primary
signal,
ignition
coíl
1
30
output
Ignition
coil
control,
cyl
.
3
Primary
signal,
ignition
coil
3
31
output
Ignition
coil
control,
cyl
.
5
Primary
signal,
ignition
coil
5
32
ground
Ground
Ground
33
output
Fuel
injector
control,
cyl
.
5
Pulsedground
(injection
pulsewidth
in
ms)
cyl
.
5
34
ground
Ground
Ground
35
output
Secondary
air
injection
Secondary
air
injection
pump
relay
control
36
output
Engine
speed
output
Engine
speed
signal
37
-
38
ground
Knock
sensor
Shielding
for
knock
sensors
39
output
Intake
air
temperature
sensor
(IAT
Sensor)
Voltagesupply
to
IAT
sensor
and
ECT
sensorEngine
coolant
temperature
(ECT)
sensor
40
output
Crankshaft
position
sensor
(Hall
effect)
Crankshaft
position
sensor
control
41
ground
Camshaft
position
(CMP)
sensor
Shielding
for
CMP
sensor
42
output
Throttle
position
sensor
(TPS)
TPS
ground
43
input
Camshaft
position/rpm
sensor
Camshaft
position/rpm
sensor
control
44
output
Throttle
position
sensor
(TPS)
Voltagesupply
to
TPS
(5
VDC)
45
Traction
control
AST
module
46
-
Instrument
cluster
Instrument
cluster
ECM
PIN
ASSIGNMENTS
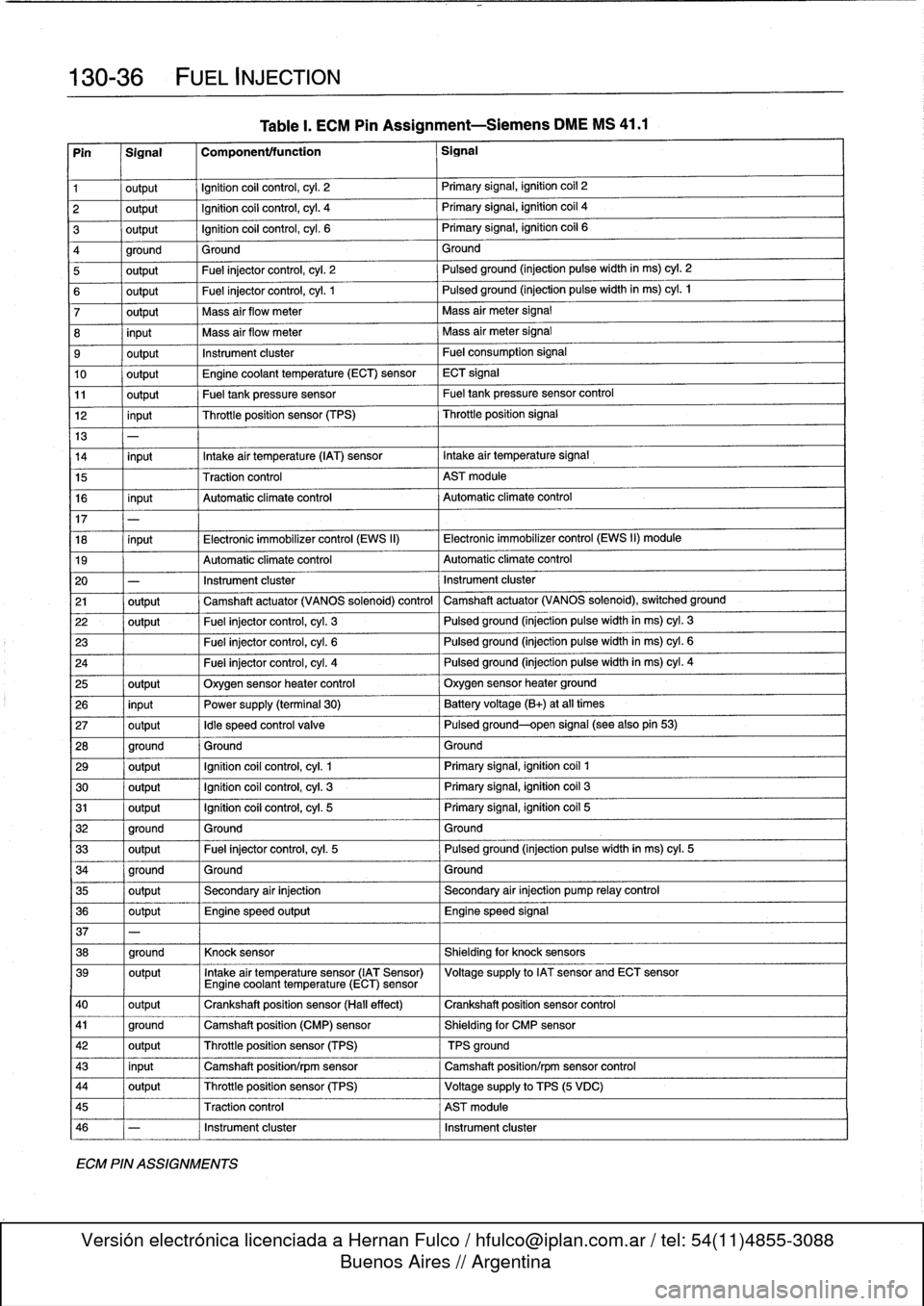
Table
I.
ECM
Pin
Assignment-Siemens
DME
MS
41
.1
Page 183 of 759
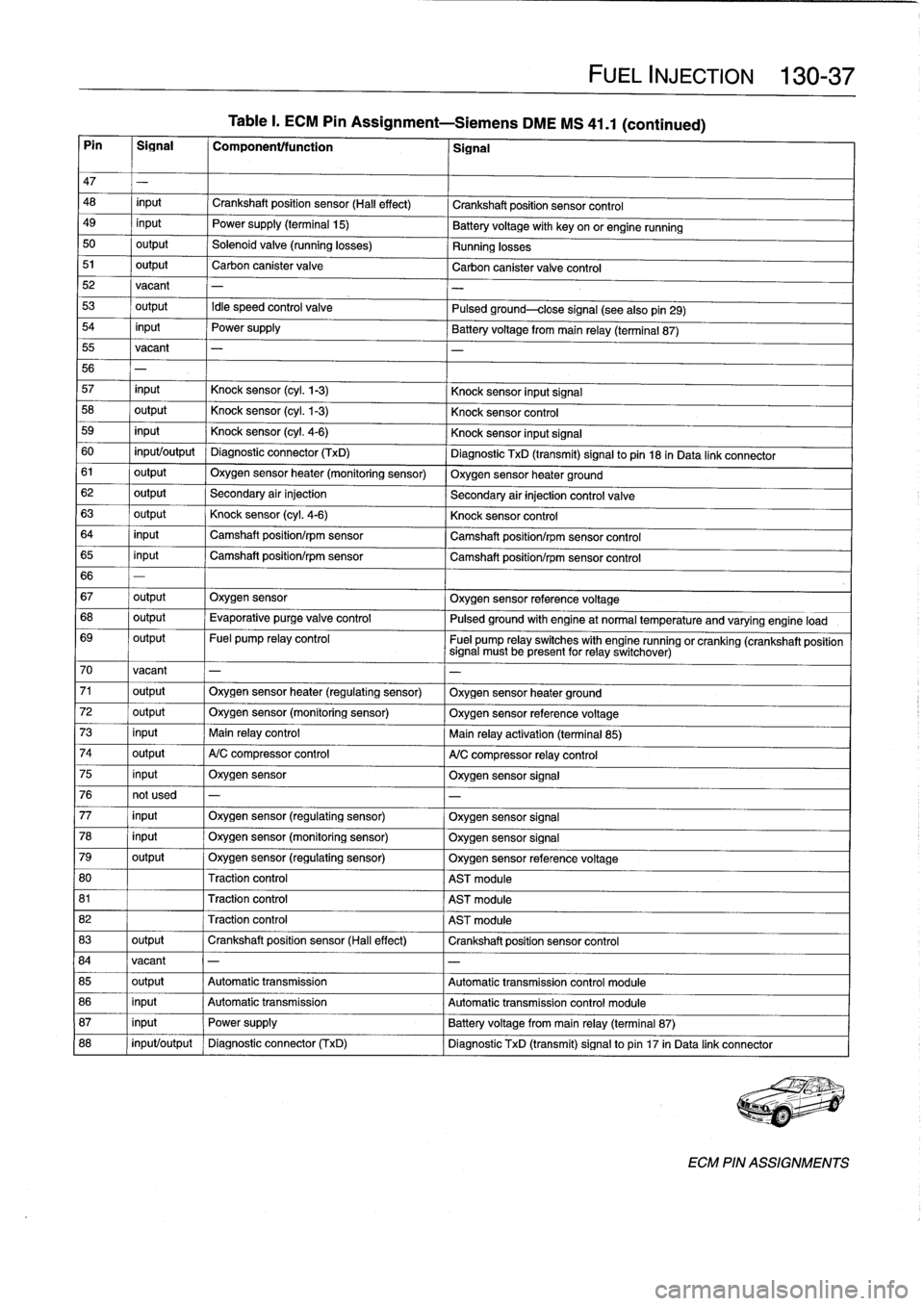
Table
I
.
ECM
Pin
Assignment-Siemens
DME
MS
41
.1
(continued)
Pin
I
Signal
I
Component/function
1
Signal
FUEL
INJECTION
130-
37
47
-
48
input
Crankshaft
position
sensor
(Hall
effect)
Crankshaft
position
sensor
control
49
input
Power
supply
(terminal
15)
Batteryvoltage
with
key
onor
engine
running
50
output
Solenoid
valve
(running
losses)
Running
losses
51
output
Carbon
canister
valve
Carbon
canister
valve
control
52vacant
-
53
output
Idle
speed
control
valve
Pulsed
ground-close
signal
(seealsopin29)
54
input
Power
supply
Battery
voltagefrom
main
relay
(terminal
87)
55
vacant
-
56
-
57
input
Knock
sensor
(cyl
.
1-3)
Knock
sensor
input
Signal
58
output
Knock
sensor
(cyl
.
1-3)
Knock
sensor
control
59
input
Knock
sensor
(cyl
.
4-6)
Knock
sensor
input
Signal
60
input/output
Diagnostic
connector
(TxD)
Diagnostic
TxD
(transmit)
signal
to
pin
18
in
Data
link
connector
61
output
Oxygen
sensor
heater
(monitoring
sensor)
Oxygen
sensor
heater
ground
62
output
Secondary
air
injection
Secondary
air
injection
control
valve
63
output
Knock
sensor
(cyl
.
4-6)
Knock
sensor
control
64
input
Camshaft
position/rpm
sensor
Camshaft
position/rpm
sensor
control
65
input
Camshaft
position/rpm
sensor
Camshaft
position/rpm
sensor
control
66
-
67
output
Oxygen
sensor
Oxygen
sensor
reference
voltage
68
output
Evaporative
purge
valve
control
Pulsed
ground
with
engine
at
normal
temperature
and
varyingengine
load
69
output
Fuel
pump
relay
control
Fuel
pump
relay
switches
with
engine
runningorcranking
(crankshaft
position
signal
must
be
present
for
relay
switchover)
70
vacant
-
-
71
output
Oxygen
sensor
heater
(regulating
sensor)
Oxygen
sensor
heater
ground
72
output
Oxygen
sensor
(monitoring
sensor)
Oxygen
sensor
referencevoltage
73
input
Main
relay
control
Main
relay
activation
(terminal
85)
74
output
A/C
compressor
control
A/C
compressor
relay
control
75
input
Oxygen
sensor
Oxygen
sensor
signal
76
not
used
-
-
77
input
Oxygen
sensor
(regulating
sensor)
Oxygen
sensor
signal
78
input
Oxygen
sensor
(monitoring
sensor)
Oxygen
sensor
signal
79
output
Oxygen
sensor
(regulating
sensor)
Oxygen
sensor
referencevoltage
80
Traction
control
AST
module
81
Traction
control
AST
module
82
Traction
control
AST
module
83
output
Crankshaft
position
sensor
(Hall
effect)
Crankshaft
position
sensor
control
84
vacant
-
-
85
output
Automatic
transmission
Automatic
transmission
control
module
86
input
Automatic
transmission
Automatic
transmissíon
control
module
87
input
Power
supply
Battery
voltage
from
main
relay
(terminal
87)
88
input/output
Diagnostic
connector
(TxD)
Diagnostic
TxD
(transmit)
signal
to
pin
17
in
Data
link
connector
ECM
PIN
ASSIGNMENTS
Page 185 of 759

160
Fuel
Tank
and
Fuel
Pump
GENERAL
.
.
.
.
.
.
...........
.
....
.
.
.
.
.
.
160-1
Operating
fuel
pump
for
tests
.
.
.
.
.
.
.......
.160-6
Fuel
Pump
Electrical
Tests
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
...
.
.
.
.
.
160-7
FUEL
TANK
AND
LINES
..
.
.
.
..........
160-2
Fuel
pump
electrical
circuit,
testing.
...
.
.
.
.
.
160-7
Fuel
tank,
draining
..
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
..........
160-2
Fuel
pump
power
consumption,
testing
.
.
.
.
.
.
160-7
Fuel
tank,
removing
and
installing
.........
160-3
Fuel
Delivery
Tests
....
.
.
.
...
.
.....
.
.
.
..
160-8
Fuel
Tank
Evaporative
Control
System
.....
160-4
Relieving
fuel
pressure
and
connecting
fuel
pressure
gauge
..
.
...........
.
.
.
..
160-8
FUEL
LEVEL
SENDERS
.
.
.
.
.
.......
.
.
.
160-4
System
pressure,
testing
.................
160-9
Fuel
level
senders,
testing
.
.
.
.
.
.......
.
.
.
160-5
Fuel
delivery
volume,
testing
.............
160-10
Fuel
leve¡
sender
and
fuel
pump
(right
side),
emoving
and
installing
.
.
.
.
.
.
160-5
TABLES
Fuel
leve¡
sender
(left
side),
a
.
FuelLeve¡
Sender
Resistances
...........
.
.
..
.160-5
removing
and
installing
.........
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
160-6
b
.
Fuel
Pump
Current
...
.................
..
...
160-8
c
.
Fuel
Pressure
Specifications
..............
.
..
160-10
FUEL
PUMP
.
.
.
................
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
160-6
d
.
Fuel
Pump
Delivery
Specifications
.........
.
..
160-10
Fuel
Pump
Fuse
and
Relay
.
.
.
....
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
160-6
GENERAL
This
repair
group
covers
service
information
specifically
for
The
cautions
and
warnings
on
this
page
should
beob
the
fuel
supply
system
.
Information
on
the
fue¡
injection
sys-
served
when
servicing
the
fuel
system
.
tem
is
covered
in
130
Fuel
Injection
.
NOTE-
Fue¡
filter
replacement
is
covered
in
020
Maintenance
Program
.
WARNING
-
"
The
fuel
system
is
designed
to
retain
pressure
even
when
the
ignition
isoff
.
When
working
with
the
fuel
system,
loosen
the
fuel
lines
slowly
toal-
low
residual
fuel
pressure
to
dissipate
gradually
.
Avoid
spraying
fuel
.
"
Before
beginning
any
work
on
the
fuel
system,
place
a
tire
extinguisher
in
the
vicinity
of
the
work
area
.
"
Fuel
is
highly
flammable
.
When
working
around
fuel,
do
not
disconnect
any
wires
that
could
cause
electrical
sparks
.
Do
not
smoke
or
work
near
heaters
or
other
tire
hazards
.
"
Always
unscrew
the
fuel
tank
cap
to
release
pres-
sure
in
the
tank
before
working
on
the
tank
or
fines
.
"
Do
not
use
a
work
light
near
any
fuel
.
Fuel
may
spray
onto
the
hot
bulb
causing
a
tire
.
"
Make
sure
the
work
area
is
properly
ventifated
.
FUEL
TANK
AND
FUEL
PUMP
160-1
CAUTION-
"
Prior
to
disconnecting
the
battery,
read
the
bat-tery
disconnection
cautions
given
at
the
front
of
this
manual
onpage
viü
.
"
Before
making
any
electrical
tests
with
the
ignition
tumed
on,
disable
the
ignition
system
as
de-
scribed
in
120
Ignition
System
.
Be
sure
the
bat-tery
is
disconnected
when
replacing
components
.
"
To
prevent
damage
to
the
ignition
system
or
the
electronic
fuel
system
components,
including
the
control
unit,
aiways
connect
and
disconnect
wires
and
test
equipment
with
the
ignition
off
.
"
Cleanliness
is
essential
when
working
with
the
fuel
system
.
Thoroughly
clean
the
fuel
fine
unionsbefore
disconnecting
any
of
the
fines
.
"
Use
only
clean
tools
.
Keep
removed
parts
clean
and
sealed
or
covered
with
a
clean,
lint-free
cloth,
especially
if
completion
of
the
repair
is
delayed
.
"
Do
not
move
the
car
while
the
fuel
system
is
open
.
"
Avoid
using
high
pressure
compressed
air
to
blow
out
fines
and
componente
.
High
pressure
can
rupture
infernal
seals
and
gaskets
.
"
Always
replace
seals
and
O-rings
.
GENERAL
Page 186 of 759
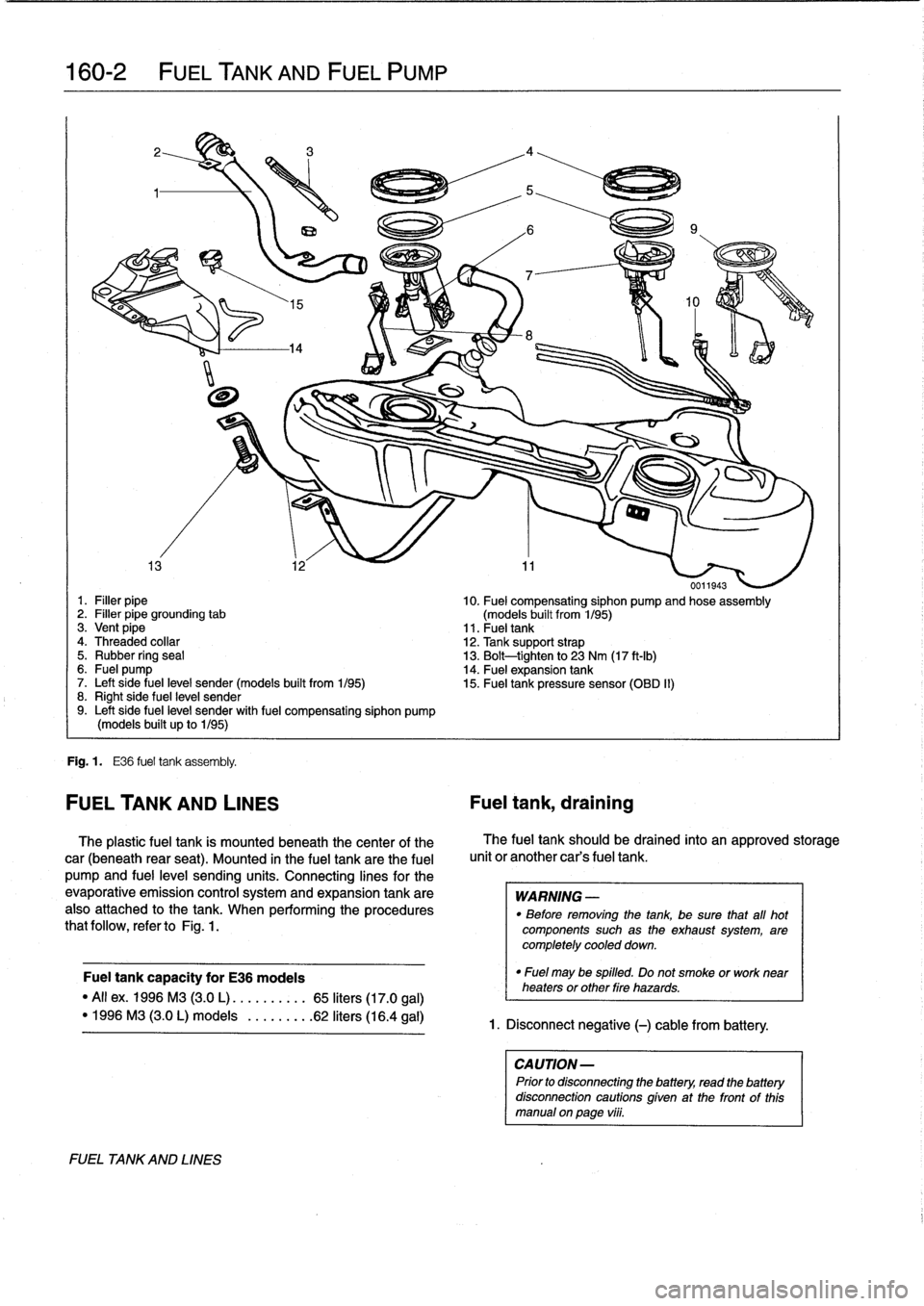
160-2
FUEL
TANK
AND
FUEL
PUMP
0011943
1
.
Filler
pipe
10
.
Fuel
compensating
siphon
pump
and
hose
assembly
2
.
Filler
pipe
grounding
tab
(models
built
from
1/95)
3
.
Vent
pipe
11
.
Fueltank
4
.
Threaded
collar
12
.
Tank
support
strap
5
.
Rubber
ring
seal
13
.
Bolt-tighten
to
23
Nm
(17
ft-Ib)
6
.
Fuel
pump
14
.
Fuel
expansion
tank
7
.
Left
side
fuel
leve¡
sender(models
built
from
1/95)
15
.
Fuel
tank
pressure
sensor
(OBD
II)
8
.
Right
side
fuel
leve¡
sender9
.
Left
side
fuel
leve¡
sender
with
fuel
compensating
siphon
pump
(models
built
up
to
1/95)
Fig
.
1
.
E36
fuel
tank
assembly
.
FUEL
TANK
AND
LINES
Fuel
tank,
draining
The
plastic
fuel
tank
is
mounted
beneath
the
center
of
the
car
(beneath
rear
seat)
.
Mounted
in
the
fuel
tank
are
the
fuel
pump
and
fuel
leve¡
sending
units
.
Connecting
lines
for
the
evaporative
emission
control
systemand
expansion
tank
are
also
attached
to
the
tank
.
When
performing
the
procedures
that
follow,
refer
toFig
.
1
.
Fuel
tank
capacity
for
E36
modeis
"All
ex
.
1996
M3
(3
.0
L)
.....
.
..
..
65
liters
(17
.0
gal)
"
1996
M3
(3.0L)
modeis
.
...
.
..
.
.62
liters
(16
.4
gal)
FUEL
TA
NKAND
LINES
The
fuel
tank
should
be
drained
into
an
approved
storage
unit
or
another
car's
fuel
tank
.
WARNING
-
"
Before
removing
the
tank,
be
sure
that
afl
hot
components
such
as
the
exhaust
system,
are
completely
cooled
down
.
"
Fuel
may
be
spilled
.
Do
not
smoke
or
worknear
heaters
or
other
Pire
hazards
.
1
.
Disconnect
negative
(-)
cable
from
battery
.
CAUTION-
Prior
to
disconnectiog
the
battery,
read
the
battery
disconnection
cautions
given
at
the
front
of
this
manual
on
paga
vi¡¡
.
Page 187 of 759

2
.
Remove
fuel
tank
filler
cap
.
3
.
Remove
rearseat
cushion
and
pull
back
insulation
mats
to
expose
fuel
tank
access
covers
.
See
Fig
.
2
.
uui3140
Fig
.
2
.
Right
side
fuel
tank
access
cover
under
rear
seat
cushion
.
4
.
Remove
right
and
left
access
covers
to
expose
fuel
hoses
and
electrical
connections
at
tank
.
5
.
Label
fuel
hoses
.
Then
disconnect
hoses
and
harness
connectors
from
fuel
sending
units
and
fuel
pump
.
See
Fig
.
3
.
FUELTANK
AND
FUEL
PUMP
160-
3
NOTE-
"
If
necessary,
push
fuel
level
sender
arm
toward
fuel
pump
assembly
to
facilitate
removal
.
"
BMW
special
tool
no
.
16
1
020
should
beused
tore-
move
and
install
the
threaded
collar
.
Damage
to
thecollar
may
result
if
the
special
tool
is
not
used
.
"
Pump
out
contents
of
each
tanklobe
using
approved
pumpinglextraction
equipment
and
flexible
fuel-grade
hose
.
WARNING
-
Fuel
may
be
spilled
.
Do
not
smoke
or
work
near
heaters
or
other
fire
hazards
.
7
.
Installation
of
sending
units
is
reverse
of
removal,
not-
ing
the
following
:
"
Use
new
sealing
rings
when
installing
pump/sending
unit
assemblies
.
"
Be
sure
that
fuel
line
connections
point
in
same
direc-tion
as
they
carne
out
.
"
Fill
tank
and
check
for
leaks
by
running
engine
.
CA
UTION-
Before
starting
the
engine,
fill
the
fuel
tank
with
at
least
1.5
gallons
(5liters)
of
fuel
.
The
pump
will
be
damaged
if
you
run
it
without
fuel
.
Fuel
tank,
removing
and
installing
1.
Disconnect
negative
(-)cablefrom
battery
:
CAUTION-
Prior
to
disconnectiog
the
battery,
read
the
battery
disconnection
cautions
given
at
the
front
of
this
manual
onpage
viii
.
2
.
Remove
fuel
tank
filler
capand
drain
tank
as
described
earlier
.
3
.
Working
in
left
access
tank
access
hole
(under
rear
seat
cushion),
remove
vent
pipe
fromtank
.
4
.
Working
inside
car,
disconnectparking
brake
cable
ends
from
parking
brake
lever
.
See
340
Brakes
.
5
.
Working
underneath
car,
gently
pry
fuel
lines
away
from
retaining
bracket
in
front
of
tank
.
Remove
clamps
and
disconnect
fuel
hoses
as
shown
in
Fig
.
4
.
6
.
Remove
exhaust
system
and
heat
shield
as
described
ooisiai
in
180
Exhaust
System
.
See
Fig
.
5
.
Fig
.
3
.
Fuel
pump/fuel
level
sender
assembly
in
top
offuel
tank
(right
side
shown)
.
Disconnect
supply
hose
(A),
return
hose
(B)
and
7
.
Remove
driveshaft
.
See
260
Driveshaft
.
harness
connector
(C)
.
8
.
Pull
parking
brake
cables
backward
away
from
bottom
of
6
.
Unscrew
threaded
collars
from
fuel
tank
.
Slowly
with-
fuel
tank,
disengaging
them
from
brackets
as
needed
.
draw
fuel
sender
assemblies
from
tank,allowing
fuel
to
drain
off
.
FUEL
TANKAND
LINES
Page 189 of 759

Fuel
leve¡
senders,
testing
Fuel
leve¡
sender
(right
side)
The
left
and
right
fuelleve¡
sending
units
are
wired
in
series
.
and
fuel
pump,
removing
and
installing
The
fuel
gauge
receives
a
signal
that
is
the
average
of
the
two
1
.
Disconnect
negative
(-)
cable
from
battery
.
input
values
.
1
.
Remove
rear
seat
cushion,
lift
up
insulation
mats,
andremove
both
fuel
tank
access
covers
.
2
.
Disconnect
white
plug
on
each
sending
unit
.
See
Fig
.
6
.
3
.
Check
resistance
value
of
eachsending
unit
.
Values
should
be
the
same
.
5
.
If
valuesare
different,
remove
sending
units
as
described
below,
and
check
resistance
valuésacross
terminals
.
Table
a
lists
resistance
values
for
senders
at
various
float
positions
.
Table
a
.
Fuel
Leve¡
Sender
Resistances
Float
position
Test
result
(ohms)
Right
side
empty
10
ohm
t2
Right
side
full
250
ohm
±
5
Left
side
empty
10
ohm
t
2
Left
side
fui¡
250
ohm
±
5
FUEL
TANK
AND
FUEL
PUMP
160-
5
CAUTION
-
Prior
to
disconnecting
the
battery,
read
the
battery
disconnection
cautionsglven
at
the
front
of
this
manual
onpage
viii
.
2
.
Drain
fuel
from
tank
as
described
earlier
.
WARNING
-
Always
unscrew
the
fuel
tank
cap
to
release
pres-
sure
in
the
tank
before
working
on
the
tank
or
fines
.
3
.
Remove
rear
seat
cushion
and
pull
back
insulation
pad
under
right
side
.
4
.
Remove
screws
holding
rightfuel
tank
accesscover
.
Remove
cover
.
5
.
Label
fuel
hoses
.
Disconnect
hoses
and
harness
con-
nectors
from
fuel
sending
unit
and
fuel
pump
.
6
.
Unscrew
threaded
collar
from
fuel
pumplfuel
leve¡
sender
.
Slowly
withdraw
assembly
from
tank,allowing
fuelto
drain
off
.
See
Fig
.
7
.
0013187
&
0013194
Fig
.
6
.
Fuel
pump/leve¡
sender
terminal
identification
.
Check
resis-
tance
at
terminals
of
white
connectors
(arrows)
.
"
If
necessary,
push
leve¡
sender
arm
toward
fuel
pump
assembly
to
facilitate
removal
.
NOTE
-
BMW
special
tool
no
.
16
1
020
should
beused
to
re-
move
and
install
the
threaded
collar
.
Damage
to
the
collar
may
result
if
the
special
tool
is
not
used
WARNING
-
NOTE-
Fuel
may
be
spilled
.
Do
not
smoke
or
work
near
The
compensating
siphon
pump
(Fig
.
1)
maintains
the
heaters
or
other
fire
hazards
.
fuel
leve¡
between
the
right
and
left
tank
lobes
.
If
the
re-
sistances
are
different
between
the
left
and
right
send-
ers,
remove
the
senders
and
visually
inspect
the
leve)
in
7
.
Using
a
new
sealing
ring,
install
pump
and
sending
each
lobe
.
If
the
leve¡
is
different,
check
the
siphon
com-
unit,
being
sure
that
fuel
line
connections
point
in
same
pensating
pump
.
direction
as
they
carne
out
.
8
.
Reconnect
harnessconnector
and
hoses
.
Fill
tank
and
check
for
leaks
by
running
engine
.
Insta¡¡
access
cover
and
its
mountingscrews
.
Reconnect
negative
(-)
cable
to
battery
.
CAUTION
-
Before
starting
the
engine,
fill
the
fuel
tank
with
at
least
1
.5
gallons
(5liters)
of
fuel
.
The
pump
will
be
damaged
if
you
run
it
without
fuel
.
FUEL
LEVEL
SENDERS
Page 192 of 759

160-
8
FUEL
TANK
AND
FUEL
PUMP
UU131
tst5
Fig
.
11
.
Voltage
supply
to
fuel
pump
harness
(black)
connector
being
checked
(arrow)
.
00131ts7
Fig
.
12
.
Test
fuel
pump
for
current
draw
by
attadhing
ammeter
andjumper
wire
as
shown
.
CAUTION-
Do
not
allow
the
test
leads
to
short
to
ground
.
NOTE-
See
600
Electrical
System-General
for
information
on
electricaltests
using
a
digital
multimeter
(DMM)
.
4
.
Run
pump
as
described
in
Operating
fuel
pump
for
tests
.
FUEL
PUMP
5
.
Compare
ammeter
reading
with
specification
listed
in
Table
b
.
Maximum
current
5
.0
amps
consumption
FuelDelivery
Tests
Table
b
.
Fuel
Pump
Current
Checking
fuel
delivery
is
a
fundamental
part
of
trouble-
shooting
and
diagnosing
the
DME
system
.
Fuelpressure
di-
rectly
influences
fuel
delivery
.
An
accurate
fuel
pressure
gauge
will
be
needed
to
make
the
tests
.
There
arethree
significant
fuel
delivery
values
to
bemea-
sured
:
"
System
pressure-created
by
the
fuel
pump
and
main-
tained
by
the
pressure
regulator
.
"
Fuel
delivery
volume-created
by
the
fuel
pump
and
af-
fected
by
restrictions,
suchas
clogged
fuel
filter
.
"
Residual
pressure-the
pressure
maintained
in
the
closed
system
after
the
engine
and
fuel
pump
areshut
off
.
Procedures
for
measuring
the
first
two
quantities
arede-
scribed
here
.
Residual
fuel
pressure
is
checked
using
the
procedurede-
tailed
in
130
Fuel
Injection
.
Relieving
fuel
pressure
and
connecting
fuel
pressure
gauge
WARNING
-
"
Gasoline
is
highly
flammable
and
its
vaporsare
explosive
.
Do
not
smoke
or
work
ona
car
near
heaters
or
other
fire
hazards
when
diagnosing
and
repairing
fuel
system
problems
.
Have
a
fire
extinguisher
available
in
case
of
an
emergency
.
"
When
working
onan
open
fuel
system,
wear
suit-
able
hand
protection
.
Prolonged
contact
with
fuel
can
cause
iflnesses
and
skin
disorders
.
CA
UTION-
Cleanliness
is
essential
when
working
withfuel
circuit
components
.
Thoroughly
clean
the
unionsbefore
disconnecting
fuel
fines
To
prevent
fuel
from
spraying
on
a
hotengine,
system
fuel
pressure
should
be
relieved
before
disconnecting
fuel
lines
.
One
method
is
to
tightly
wrap
a
shop
towel
around
a
fuel
line
fit-
ting
and
loosen
or
disconnect
the
fitting
.
Measuring
fuel
pressure
requires
special
tools
.
Earlier
cars
use
pressure
hose
with
clamps
for
fuel
delivery
.
These
can
be
attached
to
a
fuel
pressure
gauge
below
the
intake
manifold
.