change wheel BUICK CENTURY 1996 Owners Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: BUICK, Model Year: 1996, Model line: CENTURY, Model: BUICK CENTURY 1996Pages: 340, PDF Size: 17.61 MB
Page 89 of 340

I
Cruise control can be dangerous where you
can't drive safely at
a steady speed. So,
don't use your cruise control on winding
roads or in heavy traffic.
slippery roads.
On such roads, fast changes
in tire traction can cause needless wheel
spinning, and you could
lose control. Don't
use cruise control on slippery roads.
Cruise control can be dangerous on
If you leave your cruise control switch on when
you're not using cruise, you might hit
a button
and go into cruise when you don't want to.
You
could be startled and even lose control. Keep the
cruise control switch
OFF until you want to use it.
1. Move the cruise control switch to ON.
2. Get up to the speed you want.
3. Push in the SET button
at
the end of the lever
and release it.
4. Take your foot off the accelerator pedal.
2-31
ProCarManuals.com
Page 137 of 340

Here’s how anti-lock works. Let’s say the road is wet.
You’re driving safely. Suddenly an animal jumps out
in
front of you.
You slam on the brakes. Here’s what happens with
ABS.
A computer senses that wheels are slowing down. If one
of the wheels is about to stop rolling, the computer will
separately work the brakes at each front wheel and at the
rear wheels. The anti-lock system can change the
brake pressure
faster than any driver could. The computer
is
programmed to make the most of available tire and
road conditions.
You can steer around the obstacle while braking hard.
As you brake, your computer keeps receiving updates on
wheel speed and controls braking pressure accordingly.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 139 of 340

Steering Tips
Driving on Curves
It’s important to take curves at a reasonable speed.
H lot of the “driver lost control” accidents mentioned on
the news happen
on curves. Here’s why:
Experienced driver or beginner, each of
us is subject to
the same laws of physics when driving on curves. The
traction
of the tires against the road surface makes it
possible for the vehicle to change its path when you turn
the front wheels. If there’s no traction, inertia will keep
the vehicle going
in the same direction. If you’ve ever
tried to steer a vehicle on wet ice,
YOU'^^ understand this.
The traction
you can get in a curve depends on the
condition of your tires and the road surface, the angle at
which the curve is banked, and your speed. While you’re
in a curve, speed is the one factor you can control. Suppose you’re steering
through
a sharp curve. Then you
suddenly accelerate. Both control systems
-- steering and
acceleration
-- have to do their work where the tires meet
the road. Adding the sudden acceleration can demand too
much
of those places. You can lose control.
What should
you do if this ever happens? Ease up on the
accelerator pedal, steer the vehicle the way you want it
to go, and slow down.
Speed limit signs near curves warn that you should
adjust your speed. Of course, the posted speeds
are
based on good weather and road conditions. Under less
favorable conditions you’ll want to go slower.
If you need to reduce your speed as you approach a
curve, do it before you enter the curve, while
your front
wheels are straight ahead.
Try to adjust your speed
so you can “drive” through the
curve. Maintain a reasonable, steady speed. Wait to
accelerate
until you are out of the curve, and then
accelerate gently into
the straightaway.
4-9
ProCarManuals.com
Page 143 of 340

Let’s review what driving experts say about what
happens when the three control systems (brakes, steering
and acceleration) don’t have enough friction where the
tires meet the road to do what the driver has asked.
In any emergency, don’t give up. Keep trying to steer and
constantly seek an escape route or area of less danger.
In a skid, a driver can lose control of the vehicle.
Defensive drivers avoid most skids by taking reasonable
care suited to existing conditions, and by not
“overdriving” those conditions. But skids are always
possible.
The three types of skids correspond to your Buick’s
three control systems. In the braking skid, your wheels
aren’t rolling.
In the steering or cornering skid, too
much speed or steering in a curve causes tires to slip and
lose cornering force. And in the acceleration skid, too
much throttle causes the driving wheels
to spin.
A cornering skid and an acceleration skid are best
handled by easing your foot
off the accelerator pedal. If
your vehicle starts to slide, ease your foot
off the
accelerator pedal and quickly steer the way you want the
vehicle to go. If you start steering quickly enough, your
vehicle may straighten out. Always be ready for a
second skid if it occurs.
Of course, traction is reduced when water, snow, ice,
gravel or other material is on the road. For safety, you’ll
want to slow down and adjust your driving to these
conditions. It is important to slow down on slippery
surfaces because stopping distance will be longer and
vehicle control more limited.
While driving
on a surface with reduced traction, try
your best to avoid sudden steering, acceleration or
braking (including engine braking by shifting to a lower
gear). Any sudden changes could cause the tires to
slide.
You may not realize the surface is slippery until
your vehicle is skidding. Learn to recognize warning
clues
-- such as enough water, ice or packed snow
on the road to make a “mirrored surface”
-- and
slow down when you have any doubt.
Remember: Any anti-lock brake system (ABS) helps
avoid only the braking skid.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 160 of 340

lg a Trailer Do not tow a trailer if your vehicle is equipped with a
2.2L (VIN Code 4) engine.
A CAUTION:
If you don’t use the correct equipment and drive
properly, you can lose control when you pull a
trailer.
For example, if the trailer is too heavy, the
brakes may not work
well -- or even at all. You
and your passengers could be seriously injured.
Pull
a trailer only if you have followed all the
steps in this section. Ask your Buick dealer for
advice and information about towing
a trailer
with your vehicle.
NOTICE:
Pulling a trailer improperly can damage your
vehicle and result in costly repairs not covered by
your warranty.
To pull a trailer correctly, follow
the advice in this part, and see your Buick dealer
for important information about towing a trailer
with your vehicle. Your
vehicle can tow
a trailer if it is equipped with the
3.1L V6 (VTN Code M) engine and proper trailer towing
equipment.
To identify what the vehicle trailering
capacity
is for your vehicle, you should read the
information
in “Weight of the Trailer” that appears later
in this section. But trailering is different than just
driving your vehicle by itself. Trailering means changes
in handling, durability and fuel economy. Successful,
safe trailering takes correct equipment, and it has to be
used properly.
That’s the reason for this part. In
it are many
time-tested, important trailering tips
and safety rules.
Many of these are important for your safety and that
of
your passengers. So please read this section carefully
before you pull
a trailer.
Load-pulling components such
as the engine, transaxle,
wheel assemblies and tires are forced to work harder
against the drag of the added weight. The engine is
required to operate
at relatively higher speeds and under
greater loads, generating extra heat. What’s more, the
trailer adds considerably to wind resistance, increasing
the pulling requirements.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 173 of 340
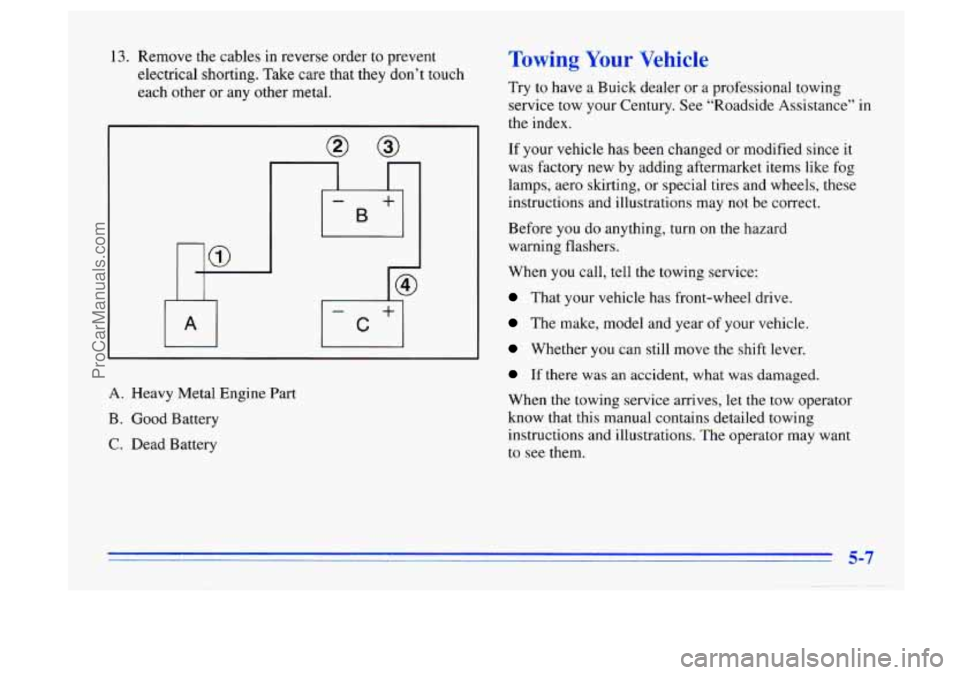
13. Remove the cables in reverse order to prevent
electrical shorting. Take care that they don’t touch
each other
or any other metal.
A. Heavy Metal Engine Part
B. Good Battery
C. Dead Battery
Towing Your Vehicle
Try to have a Buick dealer or a professional towing
service tow your Century. See “Roadside Assistance” in
the index.
If your vehicle has been changed or modified since it
was factory new by adding aftermarket items like fog
lamps, aero skirting, or special tires and wheels, these
instructions and illustrations may
not be correct.
Before you do anything, turn on the hazard
warning flashers.
When you call, tell the towing service:
That your vehicle has front-wheel drive.
The make, model and year of your vehicle.
Whether you can still move the shift lever.
If there was an accident, what was damaged.
When
the towing service arrives, let the tow operator
know that this manual contains detailed towing
instructions and illustrations. The operator may want
to see them.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 190 of 340

If a Tire Goes Flat
It’s unusual for a tire to “blow out” while you’re driving,
especially
if you maintain your tires properly. If air goes
out of a tire, it’s much more likely to leak out slowly.
But
if you should ever have a “blowout,” here are a few
tips about what to expect and what to do:
If a front tire fails, the flat tire will create a drag that
pulls the vehicle toward that,side. Take your foot
off the
accelerator pedal and grip the steering wheel fely.
Steer to maintain lane position, and then gently brake to
a stop well out of the traffic lane.
A rear blowout, particularly on a curve; acts much like a
skid and may require
the same correction you’d use in a
skid. In any rear blowout, remove your foot from the
accelerator pedal. Get the vehicle under control by
steering the way you want the vehicle to
go. It may be
very bumpy and noisy, but you can still steer. Gently
brake to a
stop -- well off ‘the road if possible.
If a tire goes flat, the next part shows how to use your
jacking equipment to change a flat tire safely.
Changing a Flat Tire
If a tire goes flat, avoid further tire and wheel damage
by driving slowly to a level place. Turn on your hazard’
warning flashers.
I
Changing a tire can cause an injury. The vehicle
can slip
off the jack and roll over you or other
‘people. You and they could be badly injured.
Find a level place to change your tire. To help
prevent the vehicle from moving:
1. Set the parking brake firmly.
2. Put the shift lever in PARK (P).
3. ”urn off the engine.
To be even more certain the vehicle won’t ‘move,
you can put blocks at the front and rear of the
tire farthest away from the one being changed.
That would be the tire on the other side of the
vehicle,
at the opposite end.
ProCarManuals.com
Page 191 of 340

The following steps will tell you how to use the jack and
change a tire.
Removing the Spare Tire and Tools
Some steps apply to all models, others to just the
sedan or wagon models. Follow the steps listed for
your vehicle.
The tools
you’ll be using include the jack (A) and wheel
wrench
(B).
5-25
ProCarManuals.com
Page 195 of 340
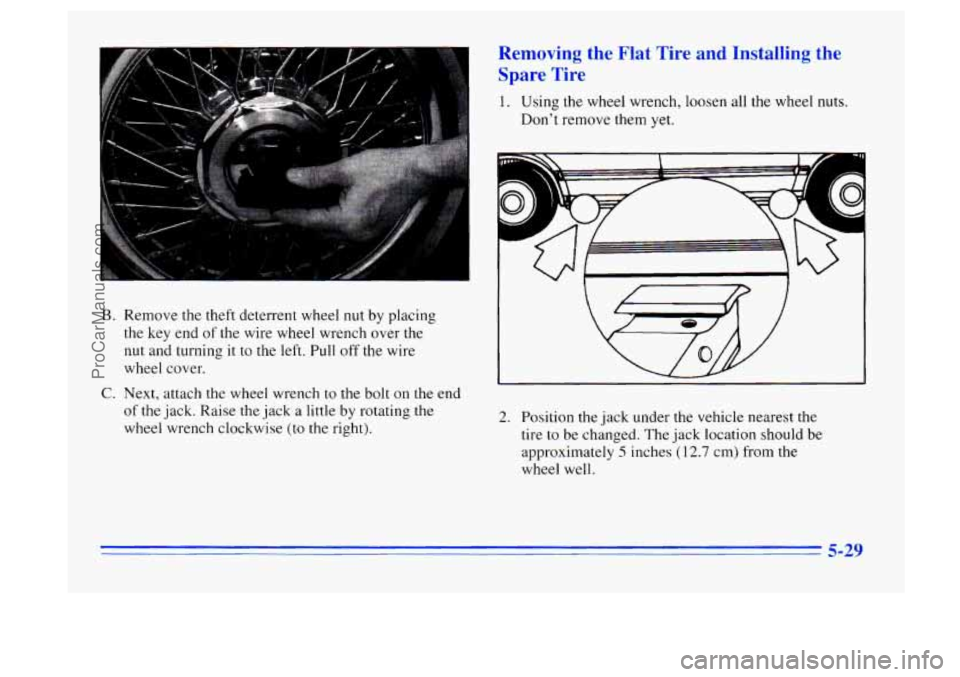
B. Remove the theft deterrent wheel nut by placing
the key end of the wire wheel wrench over the
nut and turning it to the left. Pull off the wire
wheel cover.
C. Next, attach the wheel wrench to the bolt on the end
of the jack. Raise the jack a little by rotating the
wheel wrench clockwise
(to the right).
Removing the Flat Tire and Installing the
Spare Tire
1. Using the wheel wrench, loosen all the wheel nuts.
Don't remove them yet.
2. Position the jack under the vehicle nearest the
tire to be changed. The jack location should be
approximately
5 inches (12.7 cm) from the
wheel well.
5-29
ProCarManuals.com
Page 197 of 340
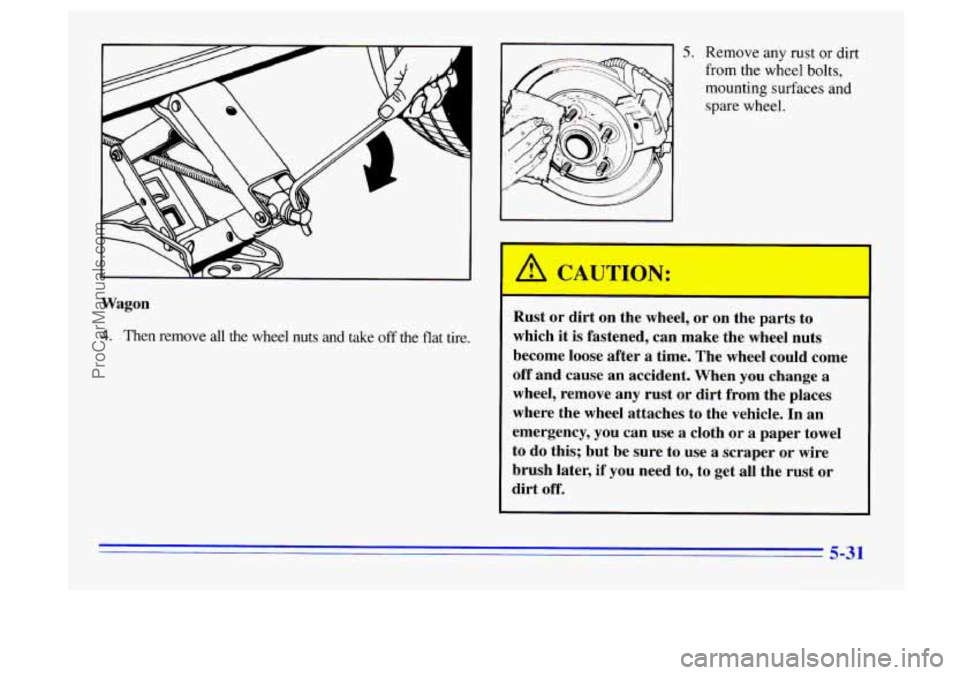
Wagon
4. Then remove all the wheel nuts and take off the flat tire.
5. Remove any rust or dirt
from the wheel bolts,
mounting surfaces and
spare wheel.
Rust or dirt on the wheel, or on the parts to
which it is fastened, can make the wheel nuts
become loose after
a time. The wheel could come
off and cause an accident. When
you change a
wheel, remove any rust or dirt from the places
where the wheel attaches to the vehicle. In an
emergency, you can use a cloth or
a paper towel
to do this; but be sure
to use a scraper or wire
brush later, if you need to, to get
all the rust or
dirt off.
5-31
ProCarManuals.com