check engine CHEVROLET CAMARO 1982 Repair Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHEVROLET, Model Year: 1982, Model line: CAMARO, Model: CHEVROLET CAMARO 1982Pages: 875, PDF Size: 88.64 MB
Page 749 of 875
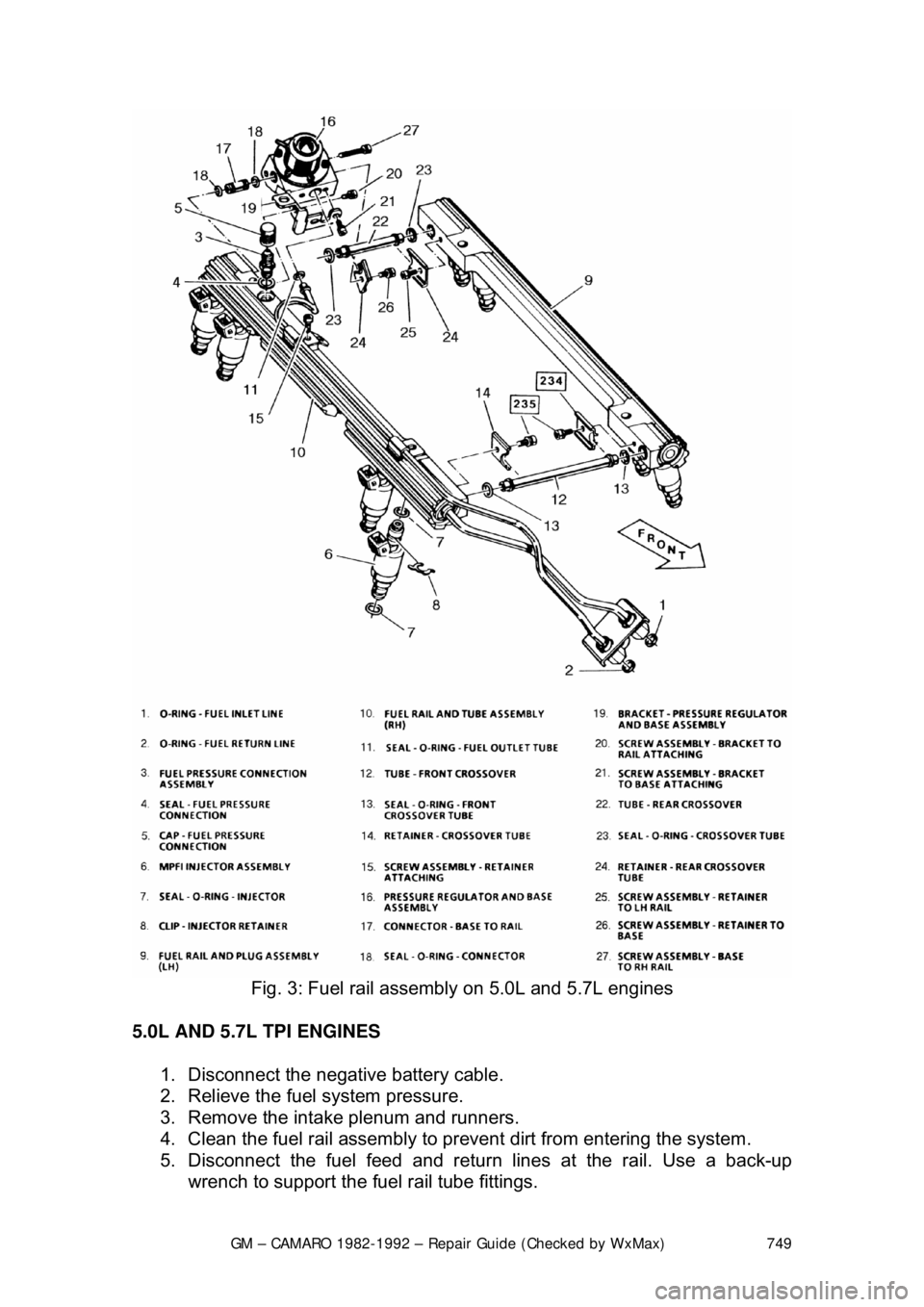
GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 749
Fig. 3: Fuel rail assembly on 5.0L and 5.7L engines
5.0L AND 5.7L TPI ENGINES 1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Relieve the fuel system pressure.
3. Remove the intake plenum and runners.
4. Clean the fuel rail assembly to pr event dirt from entering the system.
5. Disconnect the fuel feed and return lines at the rail. Use a back-up
wrench to support the fuel rail tube fittings.
Page 750 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 750
6. Disconnect the vacuum hose
at the pressure regulator.
7. Unplug the electrical connectors.
8. Loosen and remove the fuel rail attaching bolts.
9. Remove the fuel rail assembly from the intake manifold.
10. Discard all of the O-ring seals t hat are exposed during this procedure.
To install: 11. Lubricate with clean engine oil, then install the injector nozzle O-rings.
12. Install the fuel rail assembly in the intake manifold.
13. Tighten the fuel rail attachi ng bolts to specification.
14. Engage the injector electrical connectors. Rotate each injector as
required to avoid stretching the harness.
15. Connect the vacuum hose to the pressure regulator.
16. Connect the fuel feed and return lines. New O-rings must be used.
17. Temporarily connect the negative battery terminal. a. With the engine OF F and the ignition ON, check for fuel leaks.
Repair as necessary.
b. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
18. Install the intake plenum and runners. Use new gaskets.
19. Connect the negative battery cable.
FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION
2.8L AND 3.1L ENGINES
The pressure regulator and the fuel rail are serviced as a complete assembly
only. DO NOT attempt to remove the regulator cove r from the fuel rail.
5.0L AND 5.7L TPI ENGINES 1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Relieve the fuel system pressure.
3. Remove the intake plenum and runners.
4. Remove the fuel rail assembly.
5. Remove the rear crossover re tainer and base attaching screw.
6. Remove the rear crossover tube and O-ring from the regulator base.
Discard the O-ring.
7. Remove the pressure regulator bracket.
8. Remove the pressure r egulator base-to-rail screw.
9. Separate the regulator base from the fuel rail, then disconnect from the
fuel outlet tube.
10. Remove the fuel outle t tube O-ring and discard.
11. Remove the regulator bas e-to-fuel rail connector.
To install: 12. Lubricate and install new regul ator base-to-fuel rail O-rings.
Page 751 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 751
13. Lubricate a new outlet tube 0-ring and in
stall it on the end of the tube.
14. Connect the regulator base to the fuel outlet tube, then to the fuel rail.
15. Finger-tighten the base-to-rail screw.
16. Install the pressure regulator br acket. Finger-tighten the screws only.
17. Lubricate a new rear crossover tube O-ring and install it on the end of the
tube.
18. Install the rear crossover tube to the regulator base.
19. Install the crossover tube reta iner and finger-tighten the screw.
20. Tighten all attaching screws to 44 inch lbs. (5 Nm).
21. Install the fuel rail assembly.
22. Temporarily connect the negative battery cable. a. With the engine OFF and the igniti on ON, check for fuel leaks.
b. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
23. Install the intake plenum and runners.
24. Connect the negative battery cable.
IDLE AIR CONTROL VALVE
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION 1. Unplug the electrical connector from idle air control valve.
2. Remove the idle air control valve.
To install: 3. Before installing the idle air contro l valve, measure the distance that the
valve is extended. Measurement s hould be made from the motor housing
to the end of the cone. It should not exceed 28.5mm (1
1/8 in.), or damage
to the valve may occur when installed.
4. On 1985-1992 models, identify the replacement IAC valve as being
either Type 1 (with collar at electric terminal end) or Type 2 (without
collar). If measuring distance is great er than specified above, proceed as
follows:
• Type 1: Use finger pressure to slowly retract the pintle.
• Type 2: Compress retaining spring from valve while turning valve
in with a clockwise motion. Return spring to original position with
straight portion of spring end aligned with flat surface of valve.
On IAC valves that have already been in service, do not push or pull on the
valve pintle. The force required to move the pintle may damage the threads on
the worm drive.
5. Use a new gasket or O-ring and install the IAC valve into the throttle body.
6. Allow the ECM to reset the idle air control valve using the procedure
described earlier in this section.
Page 753 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 753
THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR (TPS)
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Detach the electrical connector from the sensor.
3. Remove the attaching screws, lockw ashers and retainers. Some models
use a seal between the throttle body and the sensor, do not lose this! \
4. Remove the throttle position sensor.
To install: 5. Install the throttle position sensor seal, if applicable.
6. With the throttle valve in the norma l closed idle position, install the
sensor on the throttle body assembly. Make sure the sensor pickup lever
is properly located on the th rottle actuator lever.
7. Install the retainers, screws and lockwashers using a thread locking
compound. On models up to 1989, DO NOT tighten the screws until the
sensor is adjusted. Follow the procedures outlined earli er in this section.
COLD START VALVE
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION 1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Relieve the fuel system pressure.
3. Remove the intake manifold plenum.
4. Unplug the electrical connection.
5. Clean the fuel rail around the cold start valve tube fitting.
6. Remove the tube fitting from t he fuel rail. Use a backup wrench to
prevent it from turning.
7. Remove the cold start valve retain ing bolt and remove the valve from the
intake manifold.
To install: 8. Use new O-rings and install the valve and bolt.
9. Connect the wiring harness.
10. Connect the cold start tube at the f uel rail. Use a wrench to prevent it
from turning.
11. Install the intake manifold plenum.
12. Connect the negative battery cable. With the engine OFF and the ignition
ON, check for fuel leaks.
Page 755 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 755
16. With the aid of an assistant, posit
ion and support the fuel tank with the
straps. Loosely install the front fuel tank attaching bolts.
17. Engage the electrical connection.
18. Connect the fuel hoses and li nes separated during removal.
19. Install the muffler heat sh ield and the exhaust system.
20. Install the rear axle and the fuel filler neck shield.
21. Lower the vehicle.
22. Add fuel and install the filler cap.
23. Connect the negative battery cable.
24. With the engine OFF, turn the igni tion switch to the ON position for 2
seconds, then turn it to the OFF positi on for 10 seconds. Again turn it to
the ON position and check for fuel leaks.
SENDING UNIT REPLACEMENT 1. Remove the fuel tank.
2. Clean the area surrounding t he sender assembly to prevent
contamination of the fuel system.
3. Using tool J-24187 or equivalent, re move the sending unit retaining cam.
Remove the fuel sender and O-rings fr om the tank. Discard the O-rings.
4. If necessary, separate the fuel pum p from the sending unit assembly.
To install: 5. If removed, install the fuel pump to the sending unit. If the strainer was
removed, it must be re placed with a new one.
6. Inspect and clean the O-ring mating surfaces.
7. Install a new O-ring in the groove around the tank opening. If applicable,
install a new O-ring on t he fuel sender feed tube.
8. Install the fuel sender assembly as follows: a. The fuel pump strainer must be in a horizontal position, and when
installed, must not block the travel of the float arm. Gently fold the
strainer over itself an d slowly position the sending assembly in the
tank so the strainer is not dam aged or trapped by the sump walls.
9. Install the retaining cam us ing tool J-24187 or equivalent.
10. Install the fuel tank assembly.
Page 760 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 760
GENERAL INFORMATION & MAINTENANCE
HOW TO USE THIS INFORMATION
The introductory part of this repair gui de is intended to help you learn more
about the inner workings of your Camaro while saving you money on its upkeep
and operation.
The beginning of the repair guide will likely be referred to the most, since that is
where you will find information for maintenance and tune-up. The other
information deals with the more complex systems of your vehicle. Systems
(from engine through brakes) are covered to the extent that the average do-it-
yourselfer can attempt. This repair guide will not explain such things as
rebuilding a differential because the ex pertise required and the special tools
necessary make this uneconomical. It will, however, give you detailed
instructions to help you change your own brake pads and shoes, replace spark
plugs, and perform many more jobs that can save you money and help avoid
expensive problems.
A secondary purpose of this repair guide is a reference for owners who want to
understand their vehicle and/or their mechanics better.
WHERE TO BEGIN
Before removing any bolts, read through t he entire procedure. This will give you
the overall view of what tools and supplies will be required. So read ahead and
plan ahead. Each operation should be approached logically and all procedures
thoroughly understood before attempting any work.
If repair of a component is not considered practical, we tell you how to remove
the part and then how to insta ll the new or rebuilt replacement. In this way, you
at least save labor costs.
AVOIDING TROUBLE
Many procedures in this repair guide r equire you to "label and disconnect ..." a
group of lines, hoses or wires. Don't be think you can remember where
everything goes - you won't. If you hook up va cuum or fuel lines incorrectly, the
vehicle may run poorly, if at all. If you hook up electrical wiring incorrectly, you
may instantly learn a very expensive lesson.
You don't need to know the proper name for each hose or line. A piece of
masking tape on the hose and a piece on its fitting will allow you to assign your
own label. As long as you remember your own code, the lines can be
reconnected by matching your tags. Re member that tape will dissolve in
gasoline or solvents; if a part is to be washed or cleaned, use another method
of identification. A permanent felt-tipped marker or a metal scribe can be very
handy for marking metal parts. Remove any tape or paper labels after
assembly.
Page 761 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 761
MAINTENANCE OR REPAIR?
Maintenance includes routine inspecti
ons, adjustments, and replacement of
parts which show signs of normal wear . Maintenance compensates for wear or
deterioration. Repair implies that someth ing has broken or is not working. A
need for a repair is often caused by lack of maintenance. for example: draining
and refilling automatic transmission fl uid is maintenance recommended at
specific intervals. Failure to do this can shorten the life of the
transmission/transaxle, requiring very expen sive repairs. While no maintenance
program can prevent items from eventually breaking or wearing out, a general
rule is true: MAINTENANCE IS CHEAPER THAN REPAIR.
Two basic mechanic's rules should be mentioned here. First, whenever the left
side of the vehicle or engine is refe rred to, it means the driver's side.
Conversely, the right side of the vehi cle means the passenger's side. Second,
screws and bolts are removed by turn ing counterclockwise, and tightened by
turning clockwise unless specifically noted.
Safety is always the most important rule. Constantly be aware of the dangers
involved in working on an automobile and take the proper precautions. Please
refer to the information in this se ction regarding SERVICING YOUR VEHICLE
SAFELY and the SAFETY NOTICE on the acknowledgment page.
AVOIDING THE MOST COMMON MISTAKES
Pay attention to the instructions prov ided. There are 3 common mistakes in
mechanical work:
1. Incorrect order of assembly, di sassembly or adjustment. When taking
something apart or putting it toget her, performing steps in the wrong
order usually just costs you ex tra time; however, it CAN break
something. Read the entire proc edure before beginning. Perform
everything in the order in which the instructions say you should, even if
you can't see a reason for it. When you' re taking apart something that is
very intricate, you might want to draw a picture of how it looks when
assembled in order to make sure you get everything back in its proper
position. When making adjustments, per form them in the proper order.
One adjustment possibly will affect another.
2. Overtorquing (or undertorquing). While it is more common for overtorquing to cause damage, undertorquing may allow a fastener to
vibrate loose causing serious dam age. Especially when dealing with
aluminum parts, pay attention to tor que specifications and utilize a torque
wrench in assembly. If a torque figure is not available, remember that if
you are using the right tool to perfo rm the job, you will probably not have
to strain yourself to get a fast ener tight enough. The pitch of most
threads is so slight that the te nsion you put on the wrench will be
multiplied many times in actual fo rce on what you are tightening.
There are many commercial products avai lable for ensuring that fasteners won't
come loose, even if they are not torqued just right (a very common brand is
Page 771 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 771
A more advanced set of tools, suit
able for tune-up work, can be drawn up
easily. While the tools are slightly more sophisticated, they need not be
outrageously expensive. There are severa l inexpensive tach/dwell meters on
the market that are every bit as good for the average mechanic as a
professional model. Just be sure that it goes to a least 1200-1500 rpm on the
tach scale and that it works on 4, 6 and 8-cylinder engines. The key to these
purchases is to make them with an eye towards adaptability and wide range. A
basic list of tune-up tools could include:
• Tach/dwell meter.
• Spark plug wrench and gapping tool.
• Feeler gauges for valve adjustment.
• Timing light.
The choice of a timing light should be made carefully. A light which works on the
DC current supplied by the vehicle's battery is the best choice; it should have a
xenon tube for brightness. On any vehi cle with an electronic ignition system, a
timing light with an inductive pickup that clamps around the No. 1 spark plug
cable is preferred.
In addition to these basic tools, ther e are several other tools and gauges you
may find useful. These include:
• Compression gauge. The screw-in type is slower to use, but eliminates
the possibility of a faulty r eading due to escaping pressure.
• Manifold vacuum gauge.
• 12V test light.
• A combination volt/ohmmeter
• Induction Ammeter. This is used for determining whether or not there is
current in a wire. These are handy fo r use if a wire is broken somewhere
in a wiring harness.
As a final note, you will probably find a torque wrench necessary for all but the
most basic work. The beam type models are perfectly adequate, although the
newer click types (breakaway) are eas ier to use. The click type torque
wrenches tend to be more expensive. Also keep in mind that all types of torque
wrenches should be periodically checked a nd/or recalibrated. You will have to
decide for yourself which better fits your pocketbook, and purpose.
SPECIAL TOOLS
Normally, the use of special factory tool s is avoided for repair procedures, since
these are not readily available for the do-it-yourself mechanic. When it is
possible to perform the job with more co mmonly available tools, it will be
pointed out, but occasionally, a special t ool was designed to perform a specific
function and should be used. Before s ubstituting another tool, you should be
convinced that neither your safety nor the performance of the vehicle will be
compromised.
Page 774 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 774
FLUIDS AND LUBRICANTS
FLUID DISPOSAL
Used fluids such as engine
oil, transmission fluid, antifreeze and brake fluid are
hazardous wastes and must be disposed of properly. Befo re draining any fluids,
consult with your local authorities; in many areas waste oil, etc. is being
accepted as a part of recycling programs. A number of service stations and auto
parts stores are also accepti ng waste fluids for recycling.
Be sure of the recycling cent er's policies before draining any fluids, as many will
not accept different fluids that have been mixed together.
FUEL RECOMMENDATIONS
The engine is designed to operate on unleaded gasoline ONLY and is essential
for the proper operation of the emissi on control system. The use of unleaded
fuel will reduce spark plug fouling, exhaust system corrosion and engine oil
deterioration.
In most parts of the United States, f uel with an octane rating of 87 should be
used; in high altitude areas, fuel wit h an octane rating as low as 85 may be
used.
In some areas, fuel consisting of a blen d of alcohol may be used; this blend of
gasoline and alcohol is known as gaso hol. When using gasohol, never use
blends exceeding 10% ethanol (e thyl or grain alcohol) or 5% methanol (methyl
or wood alcohol).
The use of fuel with excessive amounts of alcohol may jeopardize the new car
and emission control system warranties.
Page 775 of 875
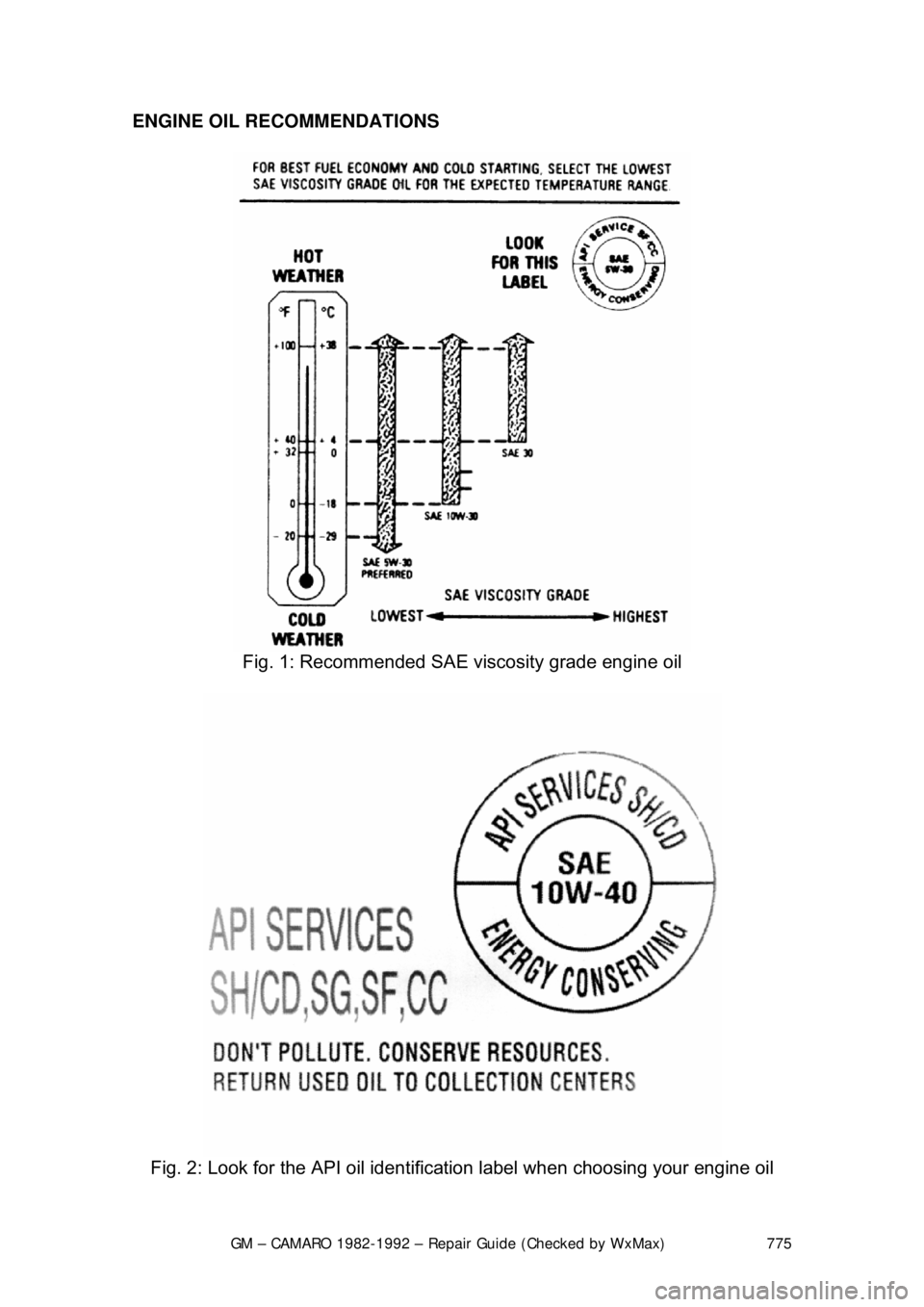
GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 775
ENGINE OIL RECOMMENDATIONS
Fig. 1: Recommended SAE viscosity grade engine oil
Fig. 2: Look for the API oil identific ation label when choosing your engine oil