mileage CHEVROLET DYNASTY 1993 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHEVROLET, Model Year: 1993, Model line: DYNASTY, Model: CHEVROLET DYNASTY 1993Pages: 2438, PDF Size: 74.98 MB
Page 2057 of 2438

first separator plate and watch carefully for the pis-
ton to move forward. The piston should return to its
original position after the air pressure is removed.
UNDERDRIVE CLUTCH
Because this clutch piston cannot be seen, its oper-
ation is checked by function. Air pressure is applied
to the low/reverse and the 2/4 clutches. This locks
the output shaft. Use a piece of rubber hose wrapped
around the input shaft and a pair of clamp-on pliers
to turn the input shaft. Next apply air pressure to
the underdrive clutch. The input shaft should not ro-
tate with hand torque. Release the air pressure and
confirm that the input shaft will rotate.
FLUID LEAKAGE-TORQUE CONVERTER HOUSING
AREA
(1) Check for source of leakage.
Since fluid leakage at or around the torque con-
verter area may originate from an engine oil leak,
the area should be examined closely. Factory fill
fluid is dyed red and, therefore, can be distinguished
from engine oil. (2) Prior to removing the transaxle, perform the
following checks: When leakage is determined to originate from the
transaxle, check fluid level prior to removal of the
transaxle and torque converter. High oil level can result in oil leakage out the vent
in the manual shaft. If the fluid level is high, adjust
to proper level. After performing this operation, inspect for leak-
age. If a leak persists, perform the following opera-
tion on the vehicle to determine if it is the torque
converter or transaxle that is leaking.
LEAKAGE TEST PROBE
(1) Remove torque converter housing dust shield.
(2) Clean the inside of torque converter housing
(lower area) as dry as possible. A solvent spray fol-
lowed by compressed air drying is preferable. (3) Fabricate and fasten test probe (Fig. 4) securely
to convenient dust shield bolt hole. Make certain
torque converter is cleared by test probe. Tool must be
clean and dry. (4) Run engine at approximately 2,500 rpm with
transaxle in neutral, for about 2 minutes. Transaxle
must be at operating temperature. (5) Stop engine and carefully remove tool.
(6) If upper surface of test probe is dry, there is no
torque converter leak. A path of fluid across probe
indicates a torque converter leak. Oil leaking under the
probe is coming from the transaxle torque converter
area. (7) Remove transaxle and torque converter assembly
from vehicle for further investigation. The fluid should
be drained from the transaxle. Re install oil pan (with
MOPAR tAdhesive Sealant) at specified torque.
Possible sources of transaxle torque converter area
fluid leakage are: (1) Torque converter hub seal.
² Seal lip cut, check torque converter hub finish.
² Bushing moved and/or worn.
² Oil return hole in pump housing plugged or omitted.
² Seal worn out (high-mileage vehicles).
(2) Fluid leakage at the outside diameter from pump
housing O-ring. (3) Fluid leakage at the front pump to case bolts.
Check condition of washers on bolts and use new bolts,
if necessary. (4) Fluid leakage due to case or front pump housing
porosity.
TORQUE CONVERTER LEAKAGE
Possible sources of torque converter leakage are:
² Torque converter weld leaks at the out side (periph-
eral) weld.
² Torque converter hub weld.
Hub weld is inside and not visible. Do not
attempt to repair. Replace torque converter. If the torque converter must be replaced, refer
to Torque Converter Clutch Break-in Procedure
in this section. This procedure will reset the
transmission control module break-in status.
Failure to perform this procedure may cause
transaxle shutter.
AIR PRESSURE TEST OF TRANSAXLE
Fabricate equipment needed for test as shown in
Figures 5 and 6. The transaxle should be prepared for pressure test as
follows after removal of the torque converter: (1) Plug dipstick tube and plug oil cooler line fitting.
Remove vent from manual shaft and in stall a 1/8 inch
pipe plug.Fig. 4 Leak Locating Test Probe Tool
Ä TRANSAXLE 21 - 97
Page 2064 of 2438

(7) Press the number 5 on the DRB II scan tool
key pad (Adjustments). (8) Press the number 3 on the DRB II scan tool
key pad (Quick Learn). Then follow the instructions
on the DRB II scan tool screen.
PINION FACTOR PROCEDURE
The vehicle speed readings for the speedometer are
taken from the output speed sensor. Because of dif-
ferent tire sizes and final drive ratios, the transmis-
sion control module must be calibrated to reflect the
different combinations of equipment. A procedure has
been developed called Pinion Factor. It allows the
technician to set the transmission control module ini-
tial setting so that the speedometer readings will be
correct. Failure to perform this procedure will cause a ``No
Speedometer Operation'' condition. This procedure must be performed if the transmis-
sion control module has been replaced. To properly read or reset the Pinion Factor, it is
necessary to use a DRB II scan tool. Perform the fol-
lowing steps with the DRB II scan tool to read or re-
set the Pinion Factor: (1) Plug the DRB II scan tool into the blue CCD
Bus connector. The connector is located under the in-
strument panel on the drivers side of the vehicle. (2) Insert the 1993 DRB II scan tool cartridge into
the DRB II scan tool. (3) The red and green lights on the DRB II scan
tool will light up and then begin flashing. Wait until
the lights stop flashing before continuing with this
procedure. (4) Press the number 4 key (Select System) on the
DRB II scan tool key pad. Item number 4 will not ap-
pear on the DRB II scan tool screen unless you scroll
down. It is not necessary to scroll down to be able to
choose item 4. (5) Press the number 2 on the DRB II scan tool
key pad (Transmission). (6) Press the number 1 on the DRB II scan tool
key pad. Wait for the DRB II scan tool to perform the
following three tests before continuing (These tests
are done automatically by the DRB II scan tool).
² Bus Test
² Initialize
² Transmission Control Module Part Number
(7) Press the number 5 on the DRB II scan tool
key pad (Adjustments). (8) Press the number 2 on the DRB II scan tool
key pad (Pinion Factor). Then follow the instructions
on the DRB II scan tool screen.
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH BREAK-IN
PROCEDURE
A torque converter clutch break-in program is be-
ing used on all models with a 41TE. This program
will properly condition the torque converter clutch. This will eliminate shudder during partial torque
converter clutch operation on a new torque converter.
If the torque converter is replaced, the new clutch
within the torque converter will require break-in.
The current break-in status stored in the transmis-
sion control module will have to be reset to the start
of break-in with the DRB II scan tool. If a new transmission control module is put on the
vehicle, the status will be at the start of break-in.
This status is acceptable regardless of the mileage on
the torque converter. No modification of the break-in
status is required. To properly service these vehicles, it is necessary to
use a DRB II scan tool to read or reset the break-in
status. Perform the following steps with the DRB II
scan tool to reset the break-in status: (1) Plug the DRB II scan tool into the blue CCD
Bus connector. The connector is located under the in-
strument panel on the drivers side of the vehicle. (2) Insert the 1993 DRB II scan tool cartridge into
the DRB II scan tool. (3) The red and green lights on the DRB II scan
tool will light up and then begin flashing. Wait until
the lights stop flashing before continuing with this
procedure. (4) Press the number 4 key (Select System) on the
DRB II scan tool key pad. Item number 4 will not ap-
pear on the DRB II scan tool screen unless you scroll
down. It is not necessary to scroll down to be able to
choose item 4. (5) Press the number 2 on the DRB II scan tool
key pad (Transmission). (6) Press the number 1 on the DRB II scan tool
key pad. Wait for the DRB II scan tool to perform the
following three tests before continuing (These tests
are done automatically by the DRB II scan tool).
² Bus Test
² Initialize
² Transmission Control Module Part Number
(7) Press the number 5 on the DRB II scan tool
key pad (Adjustments). (8) Press the number 1 on the DRB II scan tool
key pad (Reset LU Clutch). The DRB II scan tool will
display one of three screens. (a) LU Clutch Break-in Status: Start
(b) LU Clutch Break-in Status: In-progress
Press ENTER to Reset Break-in status (c) LU Clutch Break-in Status: CompletePress
ENTER to Reset Break-in status
If screen (a) appears, the transmission control mod-
ule is at the beginning of its break-in program. No
further action is required. If screen (b) appears, the transmission control mod-
ule is in the middle of a its break-in program. Press
the enter key on the DRB II scan tool key pad to re-
turn the status to the start of break-in.
21 - 104 TRANSAXLE Ä
Page 2101 of 2438
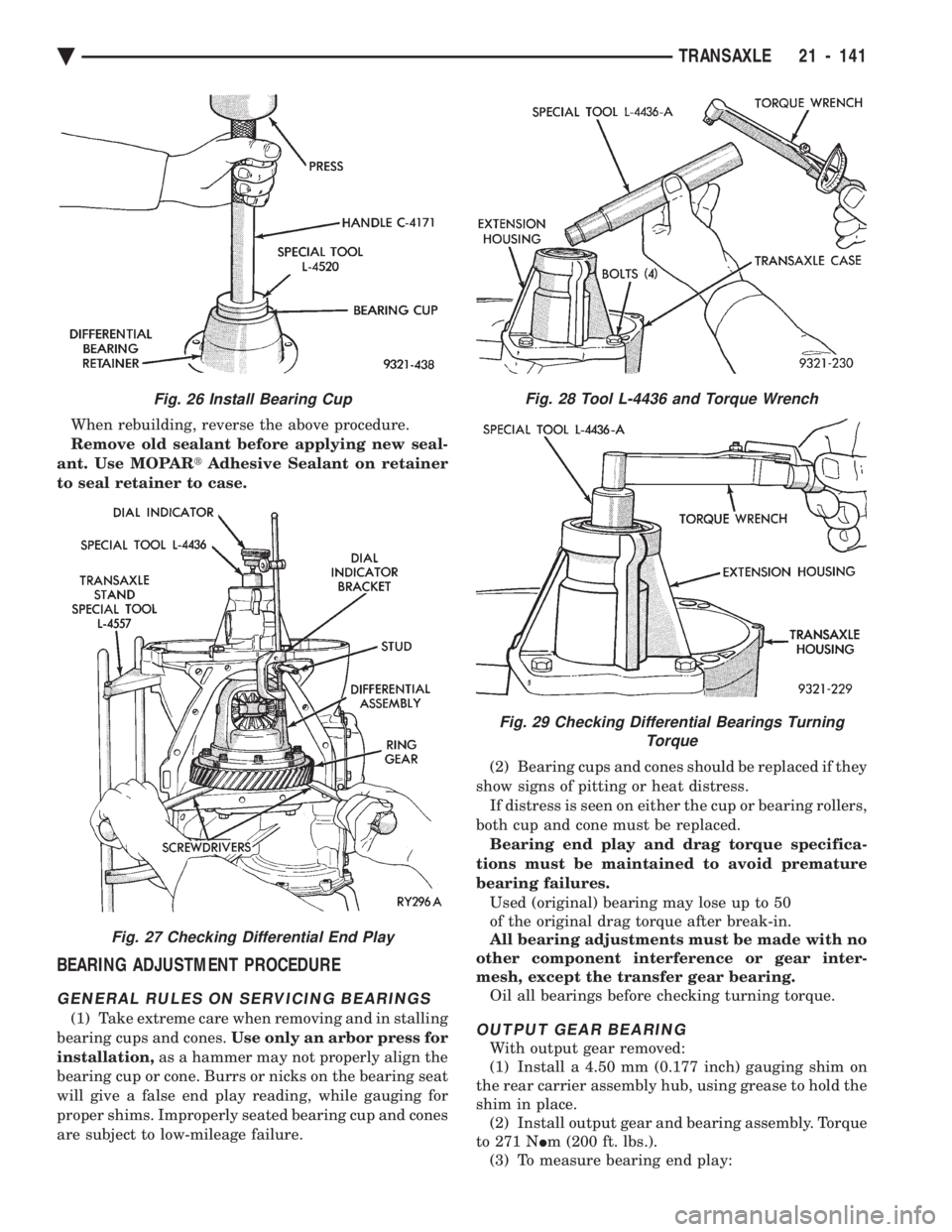
When rebuilding, reverse the above procedure.
Remove old sealant before applying new seal-
ant. Use MOPAR tAdhesive Sealant on retainer
to seal retainer to case.
BEARING ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURE
GENERAL RULES ON SERVICING BEARINGS
(1) Take extreme care when removing and in stalling
bearing cups and cones. Use only an arbor press for
installation, as a hammer may not properly align the
bearing cup or cone. Burrs or nicks on the bearing seat
will give a false end play reading, while gauging for
proper shims. Improperly seated bearing cup and cones
are subject to low-mileage failure. (2) Bearing cups and cones should be replaced if they
show signs of pitting or heat distress. If distress is seen on either the cup or bearing rollers,
both cup and cone must be replaced. Bearing end play and drag torque specifica-
tions must be maintained to avoid premature
bearing failures. Used (original) bearing may lose up to 50
of the original drag torque after break-in.
All bearing adjustments must be made with no
other component interference or gear inter-
mesh, except the transfer gear bearing. Oil all bearings before checking turning torque.OUTPUT GEAR BEARING
With output gear removed:
(1) Install a 4.50 mm (0.177 inch) gauging shim on
the rear carrier assembly hub, using grease to hold the
shim in place. (2) Install output gear and bearing assembly. Torque
to 271 N Im (200 ft. lbs.).
(3) To measure bearing end play:
Fig. 26 Install Bearing Cup
Fig. 27 Checking Differential End Play
Fig. 28 Tool L-4436 and Torque Wrench
Fig. 29 Checking Differential Bearings Turning Torque
Ä TRANSAXLE 21 - 141
Page 2149 of 2438

WHEELSÐTIRES
CONTENTS
page page
SPECIFICATIONS ........................ 8
TIRE SERVICE PROCEDURES .............. 1 WHEELS SERVICE PROCEDURES
........... 6
TIRE SERVICE PROCEDURES INDEX
page page
Cleaning of Tires .......................... 1
General Information ........................ 1
Pressure Gauges ......................... 2
Radial-Ply Tires ........................... 1
Repairing Leaks .......................... 3
Rotation ................................ 3 Spare TireÐCompact
...................... 1
Tire Inflation Pressures ..................... 2
Tire Noise or Vibration ..................... 3
Tire Wear Patterns ........................ 3
Tread Wear Indicators ...................... 3
GENERAL INFORMATION
Throughout this group, references may be made to a
particular vehicle by letter or number designation. A
chart showing the breakdown of these designations is
included in the Introduction Section. Tires are designed for the vehicle and provide the
best overall performance for normal operation. The
ride and handling characteristics match the vehicle's
requirements. With proper care they will give excellent
reliability traction, skid resistance and tread life. They
have load carrying capacity, when properly inflated, to
operate at loads up to the specified Maximum Vehicle
Capacity. Driving habits have more effect on tire life than any
other factor. Careful drivers will obtain, in most cases,
much greater mileage than severe or careless drivers. A
few of the driving habits which will shorten the life of
any tire are:
² Rapid acceleration and deceleration
² Severe application of brakes
² High-speed driving
² Taking turns at excessive speeds
² Striking curbs and other obstacles
Radial ply tires can be more susceptible to irregular
tread wear. It is very important to follow the tire
rotation interval shown in the section on Tire
Rotation to achieve a greater tread life potential.
RADIAL-PLY TIRES
Radial-ply tires improve handling, tread life, and
ride quality and decrease rolling resistance. Radial-ply tires must always be used in sets of four
and under no circumstances should they be used on
the front only. However, they may be mixed with temporary spare tires when necessary,
but reduced speeds are recommended. Radial-ply tires have the same load carrying capac-
ity as other types of tires of the same size. They also
use the same recommended inflation pressures.
SPARE TIREÐCOMPACT
The compact spare tire is designed for emergency
use only. The original tire should be repaired and re-
installed at the first opportunity. Refer to Owner's
Manual for complete details.
TIRE CHAINS
Tire snow chains may be used on certainmodels.
Refer to Owner's Manual for more information.
CLEANING OF TIRES
Remove protective coating on tires before delivery
of vehicle, otherwise it could cause deterioration of
tires. Remove protective coating by applying warm wa-
ter, letting it soak one minute, and then scrubbing
the coating away with a soft bristle brush. Steam cleaning may also be used for cleaning.
DO NOT use gasoline or wire brush for cleaning.
DO NOT use mineral oil or an oil-based solvent.
Ä WHEELSÐTIRES 22 - 1
Page 2154 of 2438

WHEELS SERVICE PROCEDURES INDEX
page page
General Information ........................ 6
Tire and Wheel Balance .................... 6
Tire and Wheel Run Out .................... 7 Wheel Installation
......................... 6
Wheel Replacement ....................... 6
GENERAL INFORMATION
Original equipment wheels are designed for proper
operation at all loads up to the maximum vehicle ca-
pacity. All models use steel or cast aluminum drop center
wheels. The safety rim wheel (Fig. 1) has raised sec-
tions between the rim flanges and the rim well A.
Initial inflation of the tires forces the bead over
these raised sections. In case of tire failure the raised
sections help hold the tire in position on the wheel
until the vehicle can be brought to a safe stop. Cast aluminum wheels require special balance
weights and alignment equipment.
WHEEL INSTALLATION
The wheel studs and nuts are designed for specific
applications and must be replaced with equivalent
parts. Do not use replacement parts of lessor quality
or a substitute design. All aluminum and some steel
wheels have wheel stud nuts which feature an en-
larged nose. This enlarged nose is necessary to en-
sure proper retention of the aluminum wheels. Before installing the wheel, be sure to remove any
build up of corrosion on the wheel mounting surfaces
with scraping and wire brushing. Installing wheels
without good metal-to-metal contact could cause later
loosening of wheel nuts. This could adversely affect
the safety and handling of your vehicle. To install the wheel, position it properly on the
mounting surface using the hub pilot as a guide. All wheel nuts should be lightly tightened before progres-
sively tightening them in sequence (Fig. 2). Tighten
wheel nuts to 129 N Im (95 ft. lbs.). Never use oil or
grease on studs or nuts.
WHEEL REPLACEMENT
Wheels must be replaced if they:
² have excessive run out
² are bent or dented
² leak air through welds
² have damaged bolt holes
Wheel repairs employing hammering, heating, or
welding are not allowed. Original equipment replacement wheels are avail-
able through your dealer. When obtaining wheels from
any other source, the replacement wheels should be
equivalent in load carrying capacity. The wheel dimen-
sions (diameter, width, offset, and mounting configura-
tion) must match original equipment wheels. Failure to
use equivalent replacement wheels may adversely af-
fect the safety and handling of your vehicle. Replace-
ment with used wheels is not recommended as
their service history may have included severe
treatment or very high mileage and they could
fail without warning.
TIRE AND WHEEL BALANCE
Balancing need is indicated by vibration of seats,
floor pan, or steering wheel when driving over 90 km/h
(55 mph) on a smooth road.
Fig. 1 Safety Rim
Fig. 2 Tightening Wheel Nuts (5-Stud)
22 - 6 WHEELSÐTIRES Ä
Page 2404 of 2438

CRANKCASE VENT FILTER
All engines have a crankcase vent filter. The filter
cleans outside air before it enters the PCV system.
On 2.5L engines, the filter mounts to the upper shell
assembly of the air cleaner. On 2.5L MPI (Flexible
Fuel AA-body) and Turbo III engines, the filter at-
taches to the inside of the filter element box, next to
the filter element. On 3.0L engines, it attaches to the
inside of the filter element box under the filter ele- ment. On the 3.3L engines, the filter mounts to the
bottom of the filter element box. Refer to Group 0 for
mileage intervals and service procedures.
Fig. 14 PCV ValveÐ3.0L Engine
Fig. 15 PCV System Fresh Air HoseÐ3.0L Engine
Fig. 16 PCV SystemÐ3.3L/3.8L Engines
Fig. 17 Typical PCV Test
25 - 16 EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS Ä