ABS CHEVROLET DYNASTY 1993 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHEVROLET, Model Year: 1993, Model line: DYNASTY, Model: CHEVROLET DYNASTY 1993Pages: 2438, PDF Size: 74.98 MB
Page 1883 of 2438

(7) Check injector O-ring for damage. If O-ring is
damaged, it must be replaced. If injector is to be re-
used, a protective cap must be installed on the injec-
tor tip to prevent damage. (8) Repeat procedure for remaining injectors.
INSTALLATION
(1) Before installing an injector, the rubber O-ring
must be lubricated with a drop of clean engine oil to
aid in installation. (2) Being careful not to damage O-ring, install in-
jector nozzle end into fuel rail receiver cap (Fig. 15). (3) Install injector clip by sliding open end into top
slot of the injector. The edge of the receiver cup will
slide into the side slots of clip (Fig. 14). (4) Repeat steps for remaining injectors.
(5) Install fuel rail assembly. Refer to Fuel Rail
Assembly Installation in this section. (6) Connect electrical connectors to injectors in cor-
rect order. (7) Connect negative battery cable.
CAUTION: When using the ASD Fuel System Test,
the Auto Shutdown (ASD) Relay remains energized
for either 7 minutes, until the test is stopped, or un-
til the ignition switch is turned to the Off position.
(8) With the ignition key in ON position, access
the DRBII scan tool ASD Fuel System Test to pres-
surize the fuel system. Check for leaks.
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE (MAP) SENSOR
(1) Remove vacuum hose and mounting screws
from manifold absolute pressure (MAP) sensor (Fig.
16).
(2) Disconnect electrical connector from sensor. Re-
move sensor. (3) Reverse the above procedure for installation.
CANISTER PURGE SOLENOID SERVICE
(1) Remove vacuum hose and electrical connector
from solenoid (Fig. 17).
(2) Slide solenoid and silencer assembly off of
bracket. (3) Reverse above procedure to install.
PCM
(1) Remove air cleaner duct from PCM.
(2) Disconnect negative cable from battery. Discon-
nect positive cable from battery. (3) Remove battery holddown. Remove battery.
(4) Remove PCM mounting screws (Fig. 18, Fig. 19
or Fig. 20). (5) Remove the electrical connector from PCM. Re-
move PCM. (6) Reverse the above procedure for installation.
Fig. 16 Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor
Fig. 17 Canister Purge Solenoid
Fig. 18 PCMÐAA Body
Ä FUEL SYSTEMS 14 - 143
Page 1885 of 2438
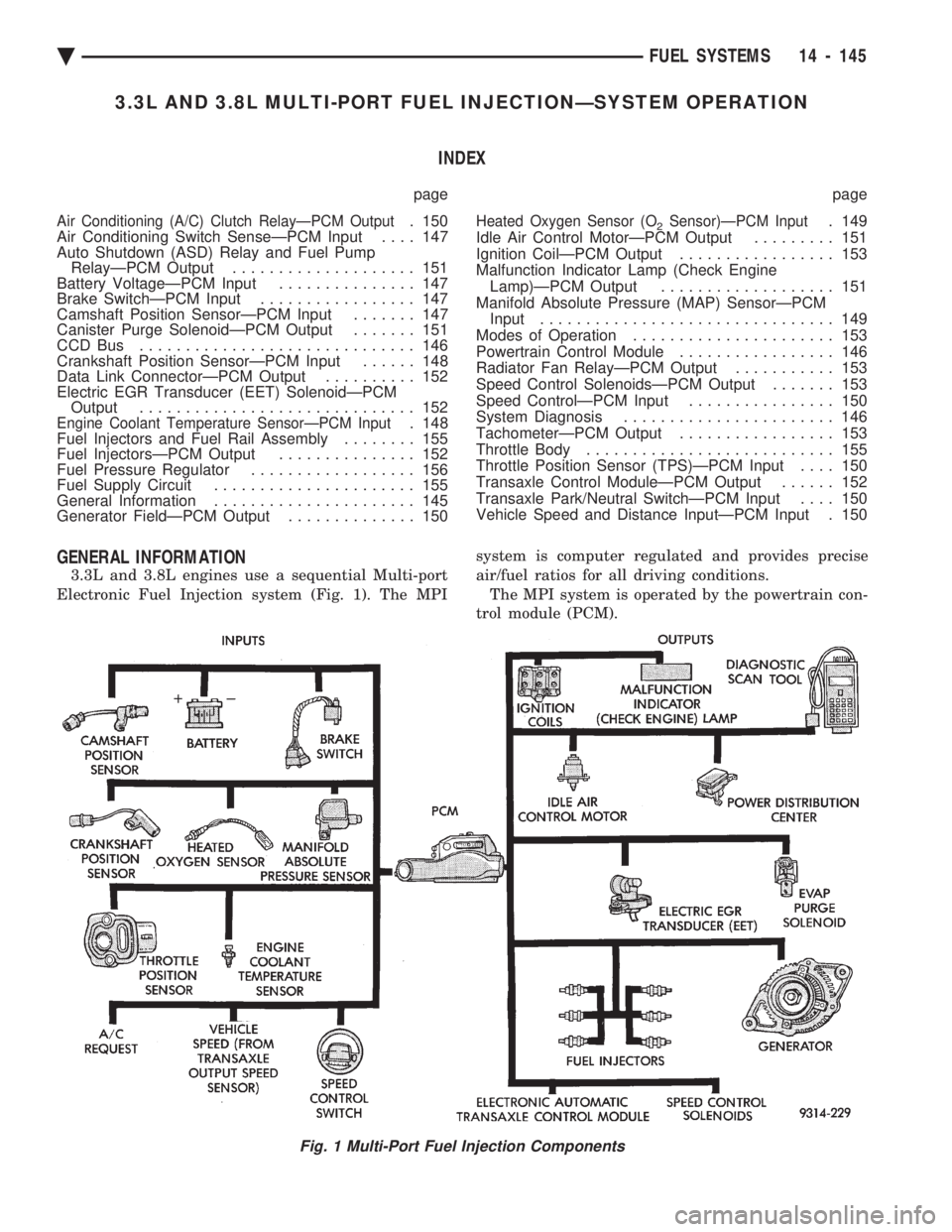
3.3L AND 3.8L MULTI-PORT FUEL INJECTIONÐSYSTEM OPERATION INDEX
page page
Air Conditioning (A/C) Clutch RelayÐPCM Output. 150
Air Conditioning Switch SenseÐPCM Input .... 147
Auto Shutdown (ASD) Relay and Fuel Pump RelayÐPCM Output .................... 151
Battery VoltageÐPCM Input ............... 147
Brake SwitchÐPCM Input ................. 147
Camshaft Position SensorÐPCM Input ....... 147
Canister Purge SolenoidÐPCM Output ....... 151
CCD Bus .............................. 146
Crankshaft Position SensorÐPCM Input ...... 148
Data Link ConnectorÐPCM Output .......... 152
Electric EGR Transducer (EET) SolenoidÐPCM Output .............................. 152
Engine Coolant Temperature SensorÐPCM Input. 148
Fuel Injectors and Fuel Rail Assembly ........ 155
Fuel InjectorsÐPCM Output ............... 152
Fuel Pressure Regulator .................. 156
Fuel Supply Circuit ...................... 155
General Information ...................... 145
Generator FieldÐPCM Output .............. 150
Heated Oxygen Sensor (O2Sensor)ÐPCM Input. 149
Idle Air Control MotorÐPCM Output ......... 151
Ignition CoilÐPCM Output ................. 153
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (Check Engine Lamp)ÐPCM Output ................... 151
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) SensorÐPCM Input ................................ 149
Modes of Operation ...................... 153
Powertrain Control Module ................. 146
Radiator Fan RelayÐPCM Output ........... 153
Speed Control SolenoidsÐPCM Output ....... 153
Speed ControlÐPCM Input ................ 150
System Diagnosis ....................... 146
TachometerÐPCM Output ................. 153
Throttle Body ........................... 155
Throttle Position Sensor (TPS)ÐPCM Input .... 150
Transaxle Control ModuleÐPCM Output ...... 152
Transaxle Park/Neutral SwitchÐPCM Input .... 150
Vehicle Speed and Distance InputÐPCM Input . 150
GENERAL INFORMATION
3.3L and 3.8L engines use a sequential Multi-port
Electronic Fuel Injection system (Fig. 1). The MPI system is computer regulated and provides precise
air/fuel ratios for all driving conditions.
The MPI system is operated by the powertrain con-
trol module (PCM).
Fig. 1 Multi-Port Fuel Injection Components
Ä FUEL SYSTEMS 14 - 145
Page 1886 of 2438

The PCM regulates ignition timing, air-fuel ratio,
emission control devices, cooling fan, charging sys-
tem, idle speed and speed control. Various sensors
provide the inputs necessary for the PCM to correctly
operate these systems. In addition to the sensors,
various switches also provide inputs to the PCM. All inputs to the PCM are converted into signals.
The PCM can adapt its programming to meet chang-
ing operating conditions. Fuel is injected into the intake port above the in-
take valve in precise metered amounts through elec-
trically operated injectors. The PCM fires the
injectors in a specific sequence. The PCM maintains
an air fuel ratio of 14.7 parts air to 1 part fuel by
constantly adjusting injector pulse width. Injector
pulse width is the length of time the injector is ener-
gized. The PCM adjusts injector pulse width by opening
and closing the ground path to the injector. Engine
RPM (speed) and manifold absolute pressure (air
density) are the primary inputs that determine injec-
tor pulse width.
SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
The PCM tests many of its own input and output
circuits. If a fault is found in a major system, the in-
formation is stored in memory. Technicians can dis-
play fault information through the malfunction
indicator lamp (instrument panel Check Engine
lamp) or by connecting the DRBII scan tool. For di-
agnostic trouble code information, refer to the 3.3L/
3.8L Multi-Point Fuel InjectionÐOn-Board
Diagnostics section of this group.
CCD BUS
Various modules exchange information through a
communications port called the CCD Bus. The pow-
ertrain control module (PCM) transmits engine RPM
and vehicle load information on the CCD Bus.
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE
The powertrain control module (PCM) is a digital
computer containing a microprocessor (Fig. 2). The
PCM receives input signals from various switches
and sensors that are referred to as PCM Inputs.
Based on these inputs, the PCM adjusts various en-
gine and vehicle operations through devices that are
referred to as PCM Outputs. PCM Inputs:
² Air Conditioning Controls
² Battery Voltage
² Brake Switch
² Camshaft Position Sensor
² Crankshaft Position Sensor
² Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
² Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
² Oxygen Sensor
² SCI Receive ²
Speed Control System Controls
² Throttle Position Sensor
² Transaxle Park/Neutral Switch (automatic tran-
saxle)
² Vehicle Speed Sensor
PCM Outputs:
² Air Conditioning Clutch Relay
² Generator Field
² Idle Air Control Motor
² Auto Shutdown (ASD) and Fuel Pump Relays
² Canister Purge Solenoid
² Malfunction Indicator Lamp (Check Engine Lamp)
² Data Link Connector
² Electronic EGR Transducer
² Fuel Injectors
² Ignition Coil
² Radiator Fan Relay
² Speed Control Solenoids
² Tachometer Output
Based on inputs it receives, the PCM adjusts the
EGR system, fuel injector pulse width, idle speed, ig-
nition spark advance, ignition coil dwell and canister
purge operation. The PCM regulates the cooling fan,
air conditioning and speed control systems. The PCM
changes generator charge rate by adjusting the gen-
erator field. The PCM adjusts injector pulse width (air-fuel ra-
tio) based on the following inputs.
² battery voltage
² engine coolant temperature
² exhaust gas oxygen content (oxygen sensor)
² engine speed (crankshaft position sensor)
² manifold absolute pressure
² throttle position
The PCM adjusts ignition timing based on the fol-
lowing inputs.
² engine coolant temperature
² engine speed (crankshaft position sensor)
² manifold absolute pressure
² throttle position
Fig. 2 PCM
14 - 146 FUEL SYSTEMS Ä
Page 1887 of 2438

² transaxle gear selection (park/neutral switch)
The PCM also adjusts engine idle speed through
the idle air control motor based on the following in-
puts.
² brake switch
² engine coolant temperature
² engine speed (crankshaft position sensor)
² throttle position
² transaxle gear selection (park/neutral switch)
² vehicle speed
The auto shutdown (ASD) and fuel pump relays are
mounted externally, but turned on and off by the
PCM through the same circuit. The camshaft position sensor and crankshaft posi-
tion sensor signals are sent to the PCM. If the PCM
does not receive both signals within approximately
one second of engine cranking, it deactivates the
ASD and fuel pump relays. When these relays are
deactivated, power is shut off to the fuel injector, ig-
nition coil, oxygen sensor heating element and fuel
pump. The PCM contains a voltage converter that
changes battery voltage to a regulated 8.0 volts. The
8.0 volts power the camshaft position sensor, crank-
shaft position sensor and vehicle speed sensor. The
PCM also provides a 5.0 volts supply for the coolant
temperature sensor, manifold absolute pressure sen-
sor and throttle position sensor.
AIR CONDITIONING SWITCH SENSEÐPCM INPUT
When the air conditioning or defrost switch is put
in the ON position and the low pressure, high pres-
sure and ambient temperature switches are closed,
the PCM receives an input for air conditioning. After
receiving this input, the PCM activates the A/C com-
pressor clutch by grounding the A/C clutch relay.
BATTERY VOLTAGEÐPCM INPUT
The PCM monitors the battery voltage input to de-
termine fuel injector pulse width and generator field
control. If battery voltage is low the PCM will in-
crease injector pulse width.
BRAKE SWITCHÐPCM INPUT
When the brake switch is activated, the PCM re-
ceives an input indicating that the brakes are being
applied. the brake signal cancels speed control and
unlocks the torque convertor. The brake switch is
mounted on the brake pedal support bracket.
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSORÐPCM INPUT
The camshaft position sensor provides cylinder
identification to the powertrain control module
(PCM) (Fig. 3). The sensor generates pulses as
groups of notches on the camshaft sprocket pass un-
derneath it (Fig. 4). The PCM keeps track of crank-
shaft rotation and identifies each cylinder by the pulses generated by the notches on the camshaft
sprocket. Four crankshaft pulses follow each group of
camshaft pulses.
When the PCM receives two camshaft pulses fol-
lowed by the long flat spot on the camshaft sprocket,
it knows that the crankshaft timing marks for cylin-
der one are next (on driveplate). When the PCM re-
ceives one camshaft pulse after the long flat spot on
the sprocket, cylinder number two crankshaft timing
marks are next. After 3 camshaft pulses, the PCM
knows cylinder four crankshaft timing marks follow.
One camshaft pulse after the three pulses indicates
cylinder five. The two camshaft pulses after cylinder
5 signals cylinder six (Fig. 4). The PCM can synchro-
nize on cylinders 1 or 4.
When metal aligns with the sensor, voltage goes
low (less than 0.5 volts). When a notch aligns with
the sensor, voltage spikes high (5.0 volts). As a group
of notches pass under the sensor, the voltage
switches from low (metal) to high (notch) then back
Fig. 3 Camshaft Position Sensor
Fig. 4 Camshaft Sprocket
Ä FUEL SYSTEMS 14 - 147
Page 1889 of 2438

tion timing from the crankshaft position sensor. Once
crankshaft position has been determined, the PCM
begins energizing the injectors in sequence. The crankshaft position sensor is located in the
transaxle housing, above the vehicle speed sensor (Fig.
9). The bottom of the sensor is positioned next to the
drive plate. The distance between the bottom of
sensor and the drive plate is critical to the op-
eration of the system. When servicing the crank-
shaft position sensor, refer to the Multi-Port Fuel
Injection Service ProceduresÐ3.3L Engine sec-
tion in this Group.
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE (MAP)
SENSORÐPCM INPUT
The PCM supplies 5 volts to the MAP sensor. The
MAP sensor converts intake manifold pressure into
voltage. The PCM monitors the MAP sensor output
voltage. As vacuum increases, MAP sensor voltage
decreases proportionately. Also, as vacuum decreases,
MAP sensor voltage increases proportionately. During cranking, before the engine starts running,
the PCM determines atmospheric air pressure from
the MAP sensor voltage. While the engine operates, the
PCM determines intake manifold pressure from the
MAP sensor voltage. Based on MAP sensor voltage and
inputs from other sensors, the PCM adjusts spark
advance and the air/fuel mixture. The MAP sensor (Fig. 10) mounts to the side of the
intake manifold, below the positive crankcase ventila-
tion (PCV) valve. The sensor connects electrically to
the PCM.
HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR (O2SENSOR)ÐPCM
INPUT
The O2sensor is located in the exhaust manifold and
provides an input voltage to the PCM. The input tells
the PCM the oxygen content of the exhaust gas (Fig.
11). The PCM uses this information to fine tune the
air-fuel ratio by adjusting injector pulse width. The O
2sensor produces voltages from 0 to 1 volt, depending upon the oxygen content of the exhaust gas
in the exhaust manifold. When a large amount of
oxygen is present (caused by a lean air-fuel mixture),
the sensor produces a low voltage. When there is a
lesser amount present (rich air-fuel mixture) it pro-
duces a higher voltage. By monitoring the oxygen
content and converting it to electrical voltage, the
sensor acts as a rich-lean switch. The oxygen sensor is equipped with a heating ele-
ment that keeps the sensor at proper operating tem-
perature during all operating modes. Maintaining cor-
rect sensor temperature at all times allows the system
to enter into closed loop operation sooner. Also, it
allows the system to remain in closed loop operation
during periods of extended idle. In Closed Loop operation the PCM monitors the O
2
sensor input (along with other inputs) and adjusts the
injector pulse width accordingly. During Open Loop
operation the PCM ignores the O
2sensor input. The
PCM adjusts injector pulse width based on prepro-
grammed (fixed) values and inputs from other sensors.
Fig. 9 Crankshaft Position Sensor Location
Fig. 10 Map Sensor
Fig. 11 Heated Oxygen SensorÐ3.3L Engine
Ä FUEL SYSTEMS 14 - 149
Page 1892 of 2438

operator that the PCM has entered a Limp-in mode.
During Limp-in Mode, the PCM attempts to keep the
system operational. The malfunction indicator signals
the need for immediate service. In limp-in mode, the
PCM compensates for the failure of certain components
that send incorrect signals. The PCM substitutes for
the incorrect signals with inputs from other sensors. Signals that can trigger the Malfunction Indi-
cator lamp (Check Engine Lamp).
² Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
² Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor
² Throttle Position Sensor
² Battery Voltage Input
² An Emission Related System (California vehicles)
² Charging system
The malfunction indicator (Check Engine Lamp) can
also display diagnostic trouble codes. Cycle the ignition
switch on, off, on, off, on, within five seconds and any
diagnostic trouble codes stored in the PCM will be
displayed. Refer to the 3.3L and 3.8L Multi-Port Fuel
InjectionÐOn-Board Diagnostics section of this Group
for Diagnostic Trouble Code Descriptions.
DATA LINK CONNECTORÐPCM OUTPUT
The data link connector provides the technician with
the means to connect the DRBII scan tool to diagnosis
the vehicle.
TRANSAXLE CONTROL MODULEÐPCM OUTPUT
The PCM supplies the following information to the
electronic automatic transaxle control module through
the CCD Bus:
² battery temperature
² brake switch input
² engine coolant temperature
² manifold absolute pressure (MAP)
² speed control information
ELECTRIC EGR TRANSDUCER (EET)
SOLENOIDÐPCM OUTPUT
The electronic EGR transducer (EET) contains an
electrically operated solenoid and a back-pressure
transducer (Fig. 16). The PCM operates the solenoid.
The PCM determines when to energize the solenoid.
Exhaust system back-pressure controls the transducer. When the PCM energizes the solenoid, vacuum does
not reach the EGR valve. Vacuum flows to the EGR
valve when the PCM de-energizes the solenoid. When exhaust system back-pressure becomes high
enough, it fully closes a bleed valve in the transducer.
When the PCM de-energizes the solenoid and back-
pressure closes the transducer bleed valve, vacuum
flows through the transducer to operate the EGR valve. De-energizing the solenoid, but not fully closing the
transducer bleed hole (because of by low back- pressure), varies the strength of vacuum applied to
the EGR valve. Varying the strength of the vacuum
changes the amount of EGR supplied to the engine.
This provides the correct amount of exhaust gas re-
circulation for different operating conditions.
FUEL INJECTORSÐPCM OUTPUT
The fuel injectors are electrical solenoids (Fig. 17).
The injector contains a pintle that closes off an ori-
fice at the nozzle end. When electric current is sup-
plied to the injector, the armature and needle move a
short distance against a spring, allowing fuel to flow
out the orifice. Because the fuel is under high pres-
sure, a fine spray is developed in the shape of a hol-
low cone. The spraying action atomizes the fuel,
adding it to the air entering the combustion cham-
ber. The injectors are positioned in the intake mani-
fold.
The fuel injectors are operated by the PCM. They
are energized in a sequential order during all engine
operating conditions except start up. The PCM ini-
tially energizes all injectors at the same time. Once
Fig. 16 Electric EGR Transducer (EET) Assembly
Fig. 17 Fuel InjectorÐ3.3L Engine
14 - 152 FUEL SYSTEMS Ä
Page 1894 of 2438

IGNITION SWITCH ON (ZERO RPM) MODE When the multi-port fuel injection system is acti-
vated by the ignition switch, the following actions oc-
cur:
² The PCM determines atmospheric air pressure
from the MAP sensor input to determine basic fuel
strategy.
² The PCM monitors the coolant temperature sensor
and throttle position sensor input. The PCM modifies
fuel strategy based on this input. When the key is in the ON position and the engine
is not running (zero rpm), the auto shutdown (ASD)
relay and fuel pump relay are not energized. There-
fore battery voltage is not supplied to the fuel pump,
ignition coil, fuel injectors or oxygen sensor heating
element.
ENGINE START-UP MODE
This is an OPEN LOOP mode. The following ac-
tions occur when the starter motor is engaged. If the PCM receives the camshaft position sensor
and crankshaft position sensor signals, it energizes
the auto shutdown (ASD) relay and fuel pump relay.
These relays supply battery voltage to the fuel pump,
fuel injectors, ignition coil, and oxygen sensor heat-
ing element. If the PCM does not receive the cam-
shaft position sensor and crankshaft position sensor
signals within approximately one second, it de-ener-
gizes the ASD relay and fuel pump relay. The PCM energizes all six injectors until it deter-
mines crankshaft position from the camshaft position
sensor and crankshaft position sensor signals. The
PCM determines crankshaft position within 1 engine
revolution. After determining crankshaft position, the PCM
begins energizing the injectors in sequence. The PCM
adjusts injector pulse width and controls injector syn-
chronization by turning the individual ground paths
to the injectors On and Off. When the engine idles within 664 RPM of its tar-
get RPM, the PCM compares current MAP sensor
value with the atmospheric pressure value received
during the Ignition Switch On (Zero RPM) mode. If
the PCM does not detect a minimum difference be-
tween the two values, it sets a MAP fault into mem-
ory. Once the ASD and fuel pump relays have been en-
ergized, the PCM:
² Determines injector pulse width based on battery
voltage, coolant temperature, engine rpm and the
number of engine revolutions since cranking was ini-
tiated.
ENGINE WARM-UP MODE This is a OPEN LOOP mode. The following inputs
are received by the PCM:
² engine coolant temperature ²
manifold absolute pressure (MAP)
² engine speed (crankshaft position sensor)
² throttle position
² A/C switch
² battery voltage
The PCM adjusts injector pulse width and controls
injector synchronization by turning the individual
ground paths to the injectors On and Off. The PCM adjusts ignition timing and engine idle
speed. Engine idle speed is adjusted through the idle
air control motor.
CRUISE OR IDLE MODE
When the engine is at operating temperature this
is a CLOSED LOOP mode. During cruising speed the
following inputs are received by the PCM:
² engine coolant temperature
² manifold absolute pressure
² engine speed (crankshaft position sensor)
² throttle position
² exhaust gas oxygen content
² A/C control positions
² battery voltage
The PCM adjusts injector pulse width and controls
injector synchronization by turning the individual
ground paths to the injectors On and Off. The PCM adjusts engine idle speed and ignition
timing. The PCM adjusts the air/fuel ratio according
to the oxygen content in the exhaust gas.
ACCELERATION MODE This is a CLOSED LOOP mode. The PCM recog-
nizes an abrupt increase in throttle position or MAP
pressure as a demand for increased engine output
and vehicle acceleration. The PCM increases injector
pulse width in response to increased fuel demand.
DECELERATION MODE This is a CLOSED LOOP mode. During decelera-
tion the following inputs are received by the PCM:
² engine coolant temperature
² manifold absolute pressure
² engine speed
² throttle position
² exhaust gas oxygen content
² A/C control positions
² battery voltage
The PCM may receive a closed throttle input from
the throttle position sensor (TPS) when it senses an
abrupt decrease in manifold pressure. This indicates
a hard deceleration. The PCM will reduce injector
pulse width. This helps maintain better control of the
air-fuel mixture (as sensed through the O
2sensor).
During a closed throttle deceleration condition, the
PCM grounds the exhaust gas recirculation (EGR)
solenoid. When the solenoid is grounded, EGR func-
tion stops.
14 - 154 FUEL SYSTEMS Ä
Page 1895 of 2438

WIDE OPEN THROTTLE MODE This is an OPEN LOOP mode. During wide-open-
throttle operation, the following inputs are received
by the PCM:
² battery voltage
² engine coolant temperature
² manifold absolute pressure
² engine speed
² throttle position
When the PCM senses wide open throttle condition
through the throttle position sensor (TPS) it will:
² De-energize the air conditioning relay. This dis-
ables the air conditioning system.
² Provide a ground for the electrical EGR transducer
(EET) solenoid. When the PCM grounds the solenoid,
the EGR system stops operating. The exhaust gas oxygen content input is not ac-
cepted by the PCM during wide open throttle opera-
tion. The PCM will adjust injector pulse width to
supply a predetermined amount of additional fuel.
IGNITION SWITCH OFF MODE When the ignition switch is turned to the OFF po-
sition, the following occurs:
² All outputs are turned off.
² No inputs are monitored.
² The PCM shuts down.
THROTTLE BODY
The throttle body assembly is located on the left
side of the intake manifold plenum (Fig. 19). The
throttle body houses the throttle position sensor and
the idle air control motor. Air flow through the throt- tle body is controlled by a cable operated throttle
blade located in the base of the throttle body.
FUEL SUPPLY CIRCUIT
Fuel is pumped to the fuel rail by an electrical
pump in the fuel tank. The pump inlet is fitted with
a strainer to prevent water and other contaminants
from entering the fuel supply circuit. Fuel pressure is controlled to a preset level above
intake manifold pressure by a pressure regulator.
The regulator is mounted on the fuel rail. The regu-
lator uses intake manifold pressure as a reference.
FUEL INJECTORS AND FUEL RAIL ASSEMBLY
Six fuel injectors are retained in the fuel rail by
lock rings (Fig. 20). The rail and injector assembly is
installed in position with the injectors inserted in re-
cessed holes in the intake manifold.
Fig. 19 Throttle Body
Fig. 20 Fuel Rail Assembly
Ä FUEL SYSTEMS 14 - 155
Page 1899 of 2438
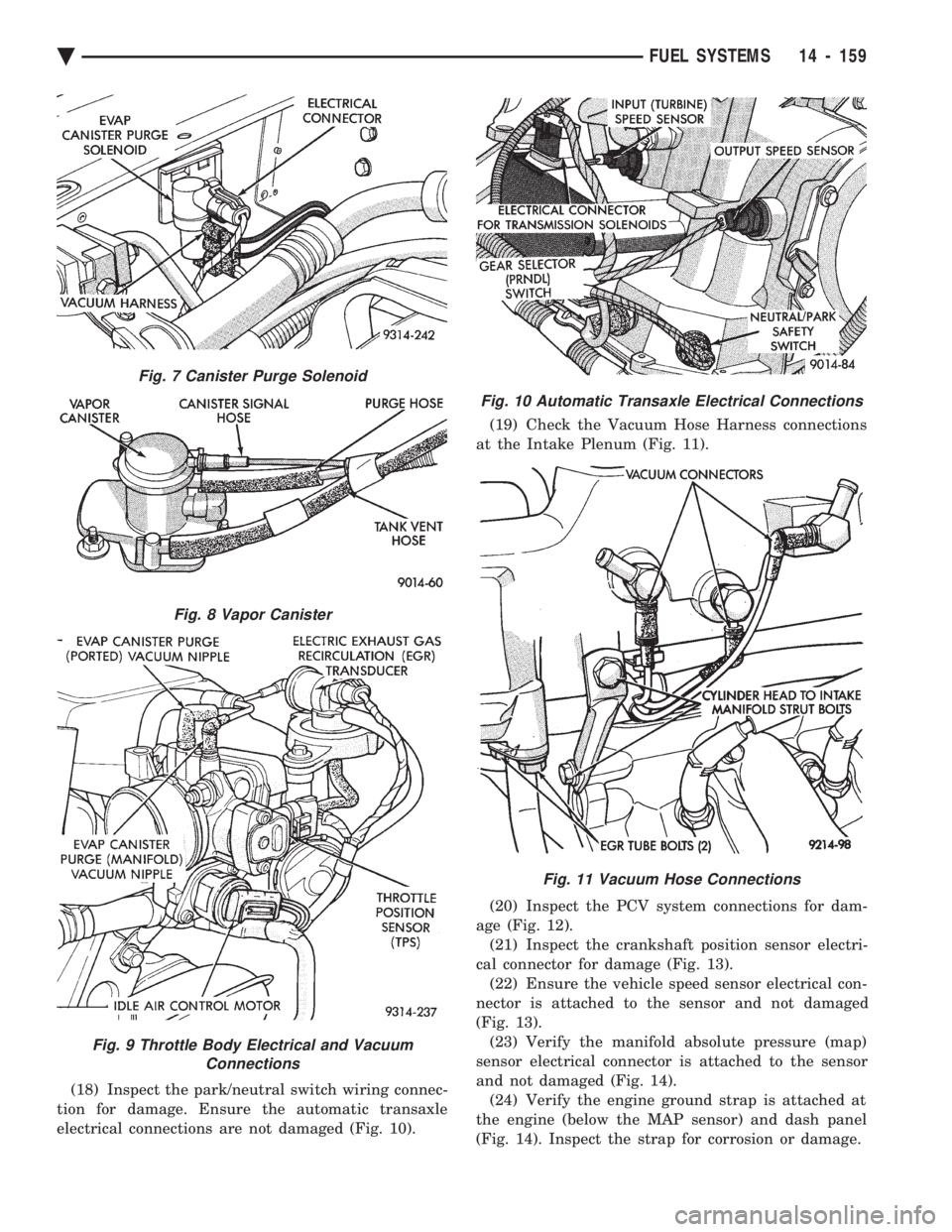
(18) Inspect the park/neutral switch wiring connec-
tion for damage. Ensure the automatic transaxle
electrical connections are not damaged (Fig. 10). (19) Check the Vacuum Hose Harness connections
at the Intake Plenum (Fig. 11).
(20) Inspect the PCV system connections for dam-
age (Fig. 12). (21) Inspect the crankshaft position sensor electri-
cal connector for damage (Fig. 13). (22) Ensure the vehicle speed sensor electrical con-
nector is attached to the sensor and not damaged
(Fig. 13). (23) Verify the manifold absolute pressure (map)
sensor electrical connector is attached to the sensor
and not damaged (Fig. 14). (24) Verify the engine ground strap is attached at
the engine (below the MAP sensor) and dash panel
(Fig. 14). Inspect the strap for corrosion or damage.
Fig. 10 Automatic Transaxle Electrical Connections
Fig. 11 Vacuum Hose Connections
Fig. 7 Canister Purge Solenoid
Fig. 8 Vapor Canister
Fig. 9 Throttle Body Electrical and Vacuum Connections
Ä FUEL SYSTEMS 14 - 159
Page 1909 of 2438

3.3L AND 3.8L MULTI-PORT FUEL INJECTIONÐSERVICE PROCEDURES INDEX
page page
Camshaft Position Sensor Service ........... 176
Crankshaft Position Sensor ................ 176
EVAP Canister Purge Solenoid Service ....... 175
Fuel Injector ........................... 174
Fuel Injector Rail Assembly ................ 170
Fuel Pressure Regulator .................. 173
Fuel System Pressure Release Procedure ..... 169 Heated Oxygen Sensor (O
2Sensor) Service . . . 177
Idle Air Control Motor .................... 170
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor ..... 175
PCM Service ........................... 175
Throttle Body ........................... 169
Throttle Body Removal ................... 169
Throttle Position Sensor .................. 169
THROTTLE BODY REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable.
(2) Remove the air cleaner to throttle body hose
clamp. Remove the nut holding the air cleaner as-
sembly to the air cleaner bracket. Remove the air
cleaner (Fig. 1). (3) Remove throttle and the speed control cables.
(4) Disconnect electrical connectors from the idle
air control motor and throttle position sensor (TPS). (5) Disconnect vacuum hoses from throttle body.
(6) Remove throttle body to intake manifold at-
taching nuts. (7) Remove throttle body and gasket.
(8) Reverse the above procedure for installation.
THROTTLE BODY
When servicing throttle body components, always
reassemble components with new O-rings and seals
where applicable (Fig. 2). Never use lubricants on
O-rings or seals, damage may result. If assembly of component is difficult, use water to aid assembly.
Use care when removing hoses to prevent damage to
hose or hose nipple.
FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE RELEASE PROCEDURE
WARNING: THE 3.3L AND 3.8L MPI FUEL SYSTEMS
ARE UNDER A CONSTANT PRESSURE OF AP-
PROXIMATELY 330 KPA (48 PSI). RELEASE FUEL
SYSTEM PRESSURE BEFORE SERVICING THE
FUEL PUMP, FUEL LINES, FUEL FILTER, THROT-
TLE BODY OR FUEL INJECTORS.
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove fuel filler cap.
(3) Remove the protective cap from the fuel pres-
sure test port on the fuel rail (Fig. 3). (4) Place the open end of fuel pressure release
hose, tool number C-4799-1, into an approved gaso-
line container. Connect the other end of hose
C-4799-1 to the fuel pressure test port. Fuel pressure
will bleed off through the hose into the gasoline con-
tainer. Fuel gauge C-4799-A contains hose C-4799-1. (5) Continue fuel system service.
THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove electrical connector from throttle posi-
tion sensor. (3) Remove throttle position sensor mounting
screws (Fig. 4). (4) Lift throttle position sensor off throttle shaft.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install throttle position sensor on throttle shaft.
Install mounting screws. Tighten screw to 2 N Im (17
in. lbs.) torque. (2) Connect electrical connector to throttle position
sensor. (3) Connect negative cable to battery.Fig. 1 Throttle Body Assembly
Ä FUEL SYSTEMS 14 - 169