brake fluid CHEVROLET DYNASTY 1993 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHEVROLET, Model Year: 1993, Model line: DYNASTY, Model: CHEVROLET DYNASTY 1993Pages: 2438, PDF Size: 74.98 MB
Page 196 of 2438

removal will be necessary. Remove the shoe and lin-
ing assemblies (see Brake Shoe Removal).Combined shoe and lining thickness should be
measured at the thinnest part of the assembly. When a shoe and lining assembly is worn to a
thickness of approximately 7.0 mm (9/32 inch) it
should be replaced. Replace both shoe assemblies (inboard and out-
board) on both wheels whenever shoe assemblies on
either side are replaced. If a shoe assembly does not require replacement.
Reinstall it, making sure each shoe assembly is re-
turned to its original position on the wheel of the ve-
hicle from which it was removed. (See Brake Shoe
Installation).
SERVICE PRECAUTIONS
WARNING: DUST AND DIRT ON BRAKE PARTS
GENERATED DURING THE NORMAL USE AND
WEAR OF MOTOR VEHICLE BRAKE SYSTEMS CAN
CONTAIN ASBESTOS FIBERS. BREATHING EXCES-
SIVE CONCENTRATIONS OF ASBESTOS FIBERS
CAN CAUSE SERIOUS BODILY HARM, SUCH AS
ASBESTOSIS AND CANCER. EXTREME CARE
SHOULD BE EXERCISED WHILE SERVICING
BRAKE ASSEMBLIES OR COMPONENTS. DO NOT CLEAN BRAKE ASSEMBLIES OR COM-
PONENTS WITH COMPRESSED AIR OR BY DRY
BRUSHING; USE A VACUUM CLEANER SPECIFI-
CALLY RECOMMENDED FOR USE WITH ASBES-
TOS FIBERS. IF A SUITABLE VACUUM CLEANER IS
NOT AVAILABLE, CLEANING SHOULD BE DONE
WET USING A WATER DAMPENED CLOTH. DO NOT CREATE DUST BY SANDING, GRINDIN-
G,AND/OR SHAVING BRAKE LININGS OR PADS
UNLESS SUCH OPERATION IS DONE WHILE USING
PROPERLY EXHAUST VENTILATED EQUIPMENT. DISPOSE OF ALL DUST AND DIRT SUSPECTED
TO CONTAIN ANY ASBESTOS FIBERS IN SEALED
BAGS OR CONTAINERS TO MINIMIZE DUST EXPO-
SURE TO YOURSELF AND OTHERS. FOLLOW ALL RECOMMENDED PRACTICES PRE-
SCRIBED BY THE OCCUPATIONAL SAFETY AND
HEALTH ADMINISTRATION AND THE ENVIRON-
MENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY. FOR THE HAN-
DLING, PROCESSING, AND DISPOSITION OF DUST
OR DIRT WHICH MAY CONTAIN ASBESTOS FI-
BERS. IT IS RECOMMENDED NOT TO BREATH ANY
TYPE OF BRAKE LINING MATERIAL DUST EVEN
ASBESTOS FREE, DUE TO THE FIBROUS NATURE
OF THE MATERIALS BEING USED.
Grease or any other foreign material must be kept
off the caliper assembly, surfaces of the braking disc
and external surfaces of the hub, during service pro-
cedures. Handling the braking disc and caliper should be done
in such a way as to avoid deformation of the disc and
scratching or nicking the brake linings (pads). During removal and installation of a wheel and tire
assembly, use care not to strike the caliper. Before vehicle is moved after any brake service
work, be sure to obtain a firm brake pedal.
BRAKE SHOE REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle on jackstands or centered on a
hoist. (2) Remove rear wheel and tire assemblies.
(3) Remove caliper attaching bolts (Fig. 2).
(4) Lift caliper away from adapter rails (Fig. 3).
(5) Remove outboard shoe. By prying the shoe re-
taining clip over the raised area on the caliper. Then
slide the shoe down and off the caliper (Fig. 4). (6) Pull inboard shoe away from piston, until the
retaining clip is free from the cavity in the piston. (Fig.
5).
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
Check for piston seal leaks (brake fluid in and
around boot area and inboard lining) and for any
ruptures of piston dust boot. If the boot is damaged, or
fluid leak is visible, disassemble caliper assembly and
install a new seal and boot (and piston if scored). Refer
to procedure titled Disc Brake Caliper Disassembly.
BRAKE SHOE INSTALLATION
(1) Retract piston.
If the originally removed brake shoe assem-
blies are to be replaced back on vehicle. Be sure
Fig. 2 Removing Caliper Attaching Bolts
5 - 46 BRAKES Ä
Page 198 of 2438

DISASSEMBLING REAR CALIPER ASSEMBLY
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
Check for piston fluid seal leaks (brake fluid in and
around boot area and inboard lining) and for any
ruptures of piston dust boot. If boot is damaged, or
fluid leak is visible, disassemble caliper assembly
and install a new seal and boot,(and piston if scored).
Refer to procedures titled Disc Brake Caliper Disas-
sembly. Check the caliper dust boot and caliper pin bush-
ings to determine if they are in good condition. Re- place if they are damaged, dry, or found to be brittle.
Refer to Cleaning And Inspection Of Brake Caliper. (1) Remove caliper from braking disc (See Brake
Shoe Removal). Hang assembly on a wire hook away
from braking disc, so hydraulic fluid cannot get on
braking disc (See Fig. 4 in Brake Shoe Removal). Place
a small piece of wood between the piston and caliper
fingers. (2) Carefully depress brake pedal to hydraulically
push piston out of bore. (Brake pedal will fall away
when piston has passed bore opening.) Then prop up
the brake pedal to any position below the first inch of
pedal travel, this will prevent loss of brake fluid from
the master cylinder. (3) If both front caliper pistons are to be removed,
disconnect flexible brake line at frame bracket after
removing piston. Plug brake tube and remove piston
from opposite caliper. Using the same process as above
for the first piston removal.
WARNING: UNDER NO CONDITION SHOULD AIR
PRESSURE BE USED TO REMOVE PISTON FROM
CALIPER BORE. PERSONAL INJURY COULD RE-
SULT FROM SUCH A PRACTICE.
(4) Disconnect brake flexible hose from the caliper.
To disassemble, mount caliper assembly in a vise
equipped with protective jaws.
CAUTION: Excessive vise pressure will cause bore
distortion and binding of piston.
Support rear caliper assembly in a vise. Then remove
caliper to piston dust boot and discard (Fig. 1).
Using a plastic trim stick, work piston seal out of its
groove in caliper piston bore (Fig. 2). Discard old seal.
Do not use a screwdriver or other metal
Fig. 7 Installing Caliper
Fig. 8 Installing Attaching Bolts
Fig. 1 Removing Piston Dust Boot
5 - 48 BRAKES Ä
Page 199 of 2438

tool for this operation, because of the possibility
of scratching piston bore or burring edges of seal
groove. The double pin caliper uses a sealed for life bushing
and sleeve assembly. If required this assembly can be
serviced using the following procedure. (1) Using your fingers push on one end the inner
sleeve until it pops out of the bushing. Then grasp the
inner sleeve with your fingers and pull the inner sleeve
out from the inside of the bushing (Fig. 3). (2) Using your fingers collapse one side of the bush-
ing. Then pull on the opposite side to remove the
bushing from the caliper assembly (Fig. 4).
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
Clean all parts using alcohol or a suitable solvent
and wipe dry. Clean out all drilled passages and bores
on the caliper assembly body. (Whenever a caliper
has been disassembled, a new boot and seal must
be installed at assembly). Inspect the caliper assembly piston bore for scoring
or pitting. Bores that show light scratches or corrosion,
can usually have the scratches or corrosion removed
using crocus cloth. Bores that have deep scratches or scoring should be
honed. Use Caliper Hone, Special Tool C-4095, or
equivalent providing the diameter of the bore is not
increased more than 0.0254 mm (0.001 inch) (Fig. 5). If the bore does not clean up within this specification,
a new caliper housing should be installed. Install a new
piston if the old one is pitted or scored. When using Caliper Honing Tool, Special Tool
C-4095, coat the stones and bore with brake fluid.
After honing the bore, carefully clean the seal
and boot grooves with a stiff non-metallic rotary
brush. Use extreme care in cleaning the caliper after
honing. Remove all dirt and grit by flushing the
caliper with brake fluid; wipe dry with a clean,
lint free cloth and then clean a second time.
ASSEMBLING REAR DISC BRAKE CALIPER
Clamp caliper in vise (with protective caps on vise
jaws).
Fig. 2 Removing Piston Seal
Fig. 3 Removing Inner Sleeve From Bushing
Fig. 4 Removing Bushings From Caliper
Ä BRAKES 5 - 49
Page 200 of 2438

CAUTION: Excessive vise pressure will cause bore
distortion and binding of piston. Dip new piston seal in clean brake fluid and install
in the groove of the caliper bore. Seal should be po-
sitioned at one area in groove and gently worked
around the groove (Fig. 6), using only your fingers
until properly seated. NEVER USE AN OLD PISTON SEAL. (Be sure
that fingers are clean and seal is not twisted or
rolled) (Fig. 6).
Coat new piston boot with clean brake fluid leav-
ing a generous amount inside boot. Position dust boot over piston after coating with
brake fluid. Install piston into caliper bore pushing it past the
piston seal until it bottoms in the caliper bore (Fig.
7).
CAUTION: Force must be applied to the piston uni-
formly to avoid cocking and binding of the piston in
the bore of the caliper.
Position dust boot in counterbore of the caliper pis-
ton bore. Using a hammer and Installer Piston Caliper Boot,
Special Tool C-4383-7 and Handle, Special Tool
C-4171, drive boot into counterbore of the caliper
(Fig. 8).
Fig. 5 Honing Piston Bore
Fig. 6 Installing New Piston Seal
Fig. 7 Pushing Piston into Bore
Fig. 8 Installing Boot in Caliper
5 - 50 BRAKES Ä
Page 216 of 2438

MASTER CYLINDER INDEX
page page
Brake Fluid Level Sensor .................. 66
General Information ....................... 66 Master Cylinder Service Procedures
.......... 67
Testing the Master Cylinder ................. 66
GENERAL INFORMATION
The tandem master cylinder (Fig. 1) has a glass re-
inforced nylon reservoir and an anodized aluminum
body. Do not hone the bore of the cylinder, as this will
remove the anodized surface. The reservoir is indexed to prevent installation in
the wrong direction (Fig. 2). The cap diaphragms are
slit to allow atmospheric pressure to equalize on both
sides of the diaphragm. The primary and secondary outlet tubes from the
master cylinder are connected to the valve mounted
under the master cylinder. The front part of this
block connects to the secondary outlet tube and sup-
plies the right rear and left front brakes. The rear
portion of the block connects to the primary outlet
tube and supplies the right front and left rear
brakes.
BRAKE FLUID LEVEL SENSOR
The Brake Fluid Level sensor is found only in the
AJ body vehicles with the visual electronic message
center. The purpose of the sensor is to provide the
driver with an early warning message that brake
fluid in master cylinder reservoir has dropped to a
below normal. As the fluid drops below the design level the sensor
closes the warning message circuit. Approximately
15 seconds later the message BRAKE FLUID LOW
appears on the instrument panel. At this time the master cylinder reservoir should be checked and filled
to the bottom of the rings with DOT 3 brake fluid. To check the operation of the Brake Fluid Level
sensor, with ignition on and wiring still attache-
d,remove sensor from master cylinder and hold in
upright position. Within 30 seconds the instrument
panel message BRAKE FLUID LOW should appear.
Next invert the sensor. The instrument panel message
should turn off immediately. If the above sequence
occurs the sensor is operating properly. If the message
does not appear remove the wiring from the sensor and
using a jumper wire connect both sides of the plug. The
instrumental panel message BRAKE FLUID LOW
should appear within 30 seconds. If the message does
not appear a problem exists in the wiring or instru-
mentation. If the message does appear the sensor is
faulty and must be replaced. The Brake Fluid Level
sensor is not a repairable item (Fig. 2).
TESTING THE MASTER CYLINDER
Be sure master cylinder vents at both ports.
Apply pedal lightly with engine running and look for
fluid squirting or swirling into reservoirs. In this master cylinder, a special baffle reduces the
amount of fluid entering the secondary reservoir only a
small disturbance may be seen.
Fig. 1 Aluminum Master Cylinder (Cutaway View)
Fig. 2 Brake Fluid Level Sensor
5 - 66 BRAKES Ä
Page 217 of 2438
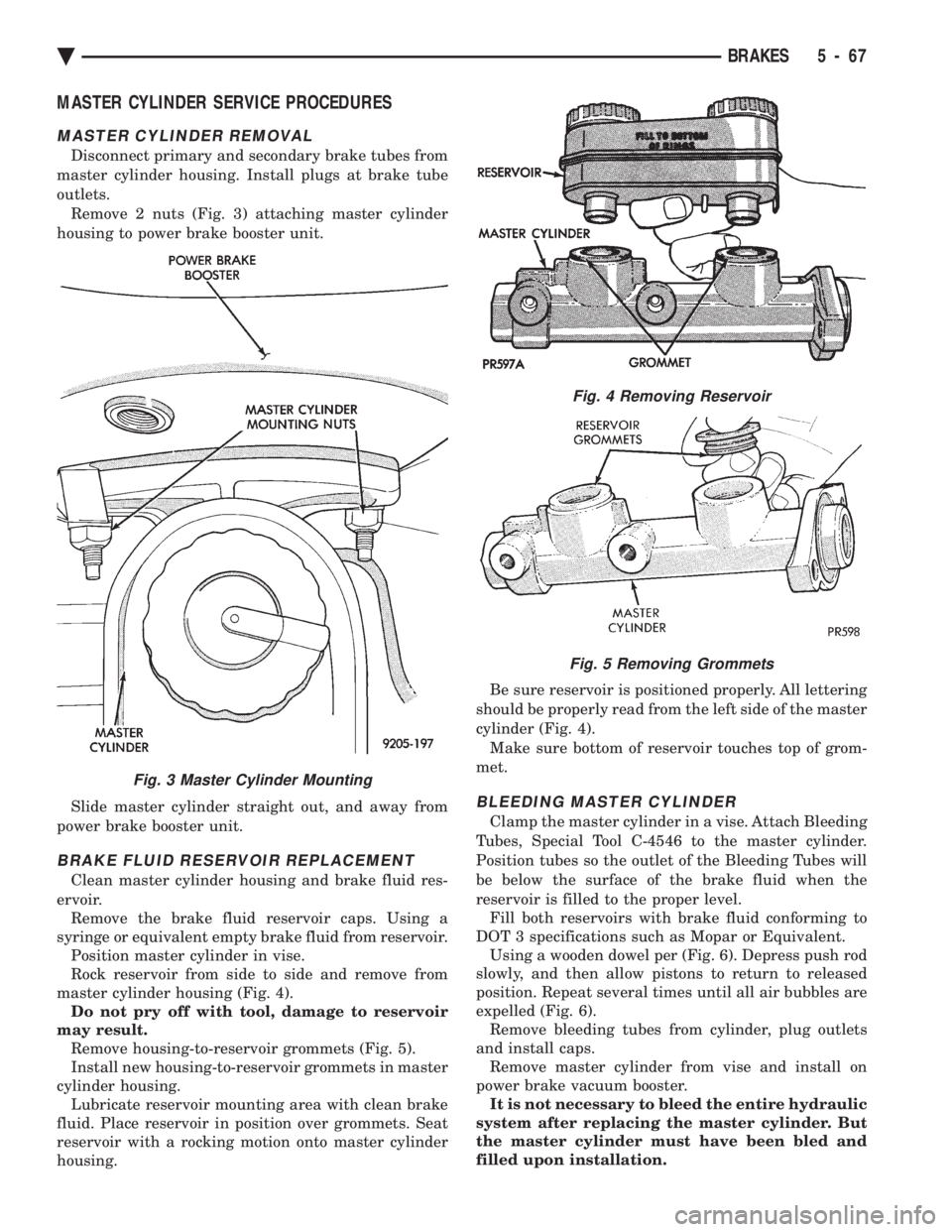
MASTER CYLINDER SERVICE PROCEDURES
MASTER CYLINDER REMOVAL
Disconnect primary and secondary brake tubes from
master cylinder housing. Install plugs at brake tube
outlets. Remove 2 nuts (Fig. 3) attaching master cylinder
housing to power brake booster unit.
Slide master cylinder straight out, and away from
power brake booster unit.
BRAKE FLUID RESERVOIR REPLACEMENT
Clean master cylinder housing and brake fluid res-
ervoir. Remove the brake fluid reservoir caps. Using a
syringe or equivalent empty brake fluid from reservoir. Position master cylinder in vise.
Rock reservoir from side to side and remove from
master cylinder housing (Fig. 4). Do not pry off with tool, damage to reservoir
may result. Remove housing-to-reservoir grommets (Fig. 5).
Install new housing-to-reservoir grommets in master
cylinder housing. Lubricate reservoir mounting area with clean brake
fluid. Place reservoir in position over grommets. Seat
reservoir with a rocking motion onto master cylinder
housing. Be sure reservoir is positioned properly. All lettering
should be properly read from the left side of the master
cylinder (Fig. 4). Make sure bottom of reservoir touches top of grom-
met.
BLEEDING MASTER CYLINDER
Clamp the master cylinder in a vise. Attach Bleeding
Tubes, Special Tool C-4546 to the master cylinder.
Position tubes so the outlet of the Bleeding Tubes will
be below the surface of the brake fluid when the
reservoir is filled to the proper level. Fill both reservoirs with brake fluid conforming to
DOT 3 specifications such as Mopar or Equivalent. Using a wooden dowel per (Fig. 6). Depress push rod
slowly, and then allow pistons to return to released
position. Repeat several times until all air bubbles are
expelled (Fig. 6). Remove bleeding tubes from cylinder, plug outlets
and install caps. Remove master cylinder from vise and install on
power brake vacuum booster. It is not necessary to bleed the entire hydraulic
system after replacing the master cylinder. But
the master cylinder must have been bled and
filled upon installation.
Fig. 4 Removing Reservoir
Fig. 5 Removing Grommets
Fig. 3 Master Cylinder Mounting
Ä BRAKES 5 - 67
Page 223 of 2438
speed sensors (WSS) at each wheel and received at
the Controller-Anti-Lock Brake (CAB).
MAJOR ABS COMPONENTS
The following is a list of major system components.
Details of all components can be found later in this
section.
HYDRAULIC ASSEMBLY
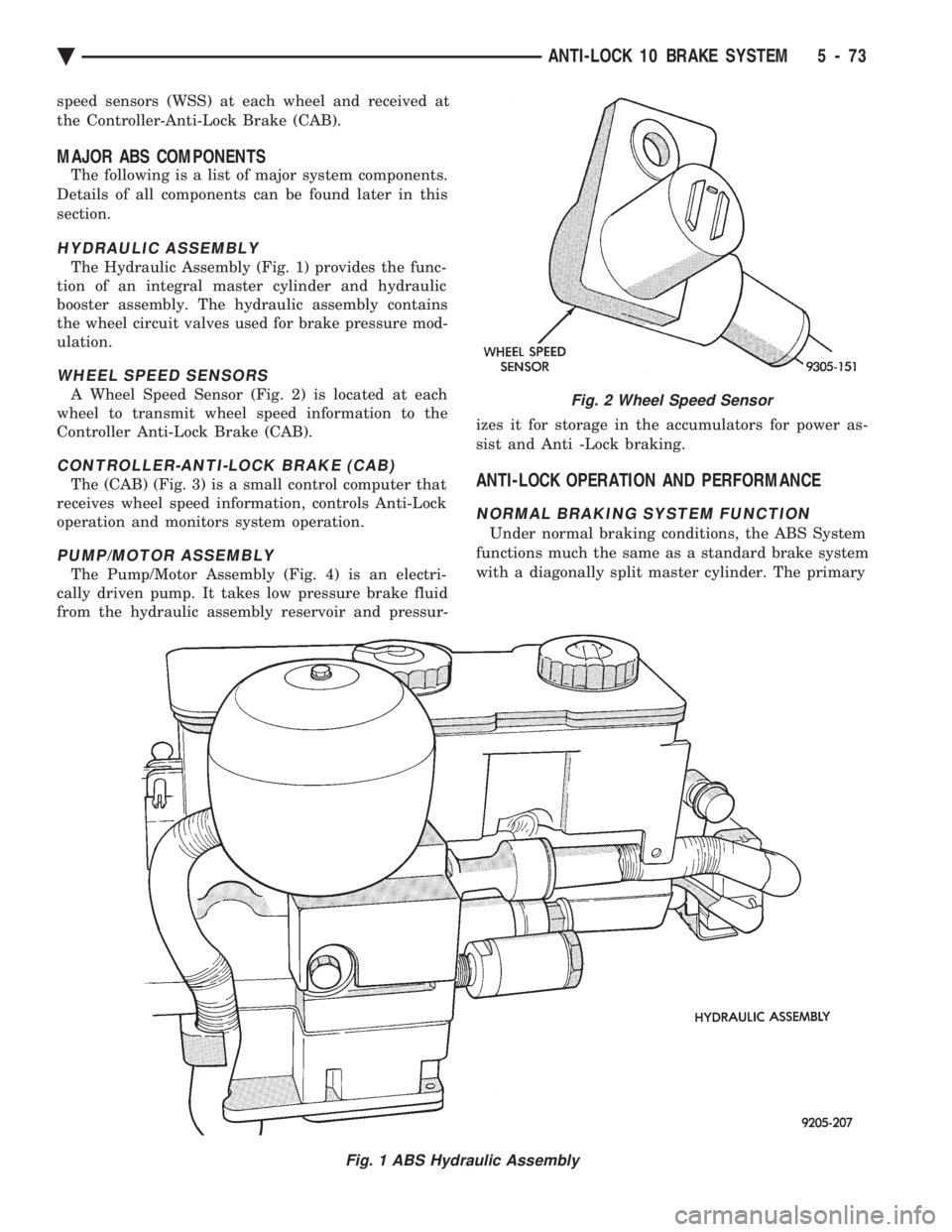
The Hydraulic Assembly (Fig. 1) provides the func-
tion of an integral master cylinder and hydraulic
booster assembly. The hydraulic assembly contains
the wheel circuit valves used for brake pressure mod-
ulation.
WHEEL SPEED SENSORS
A Wheel Speed Sensor (Fig. 2) is located at each
wheel to transmit wheel speed information to the
Controller Anti-Lock Brake (CAB).
CONTROLLER-ANTI-LOCK BRAKE (CAB)
The (CAB) (Fig. 3) is a small control computer that
receives wheel speed information, controls Anti-Lock
operation and monitors system operation.
PUMP/MOTOR ASSEMBLY
The Pump/Motor Assembly (Fig. 4) is an electri-
cally driven pump. It takes low pressure brake fluid
from the hydraulic assembly reservoir and pressur- izes it for storage in the accumulators for power as-
sist and Anti -Lock braking.
ANTI-LOCK OPERATION AND PERFORMANCE
NORMAL BRAKING SYSTEM FUNCTION
Under normal braking conditions, the ABS System
functions much the same as a standard brake system
with a diagonally split master cylinder. The primary
Fig. 1 ABS Hydraulic Assembly
Fig. 2 Wheel Speed Sensor
Ä ANTI-LOCK 10 BRAKE SYSTEM 5 - 73
Page 224 of 2438

difference is that power assist is provided by hydrau-
lic power assist instead of the conventional vacuum
assist. If a wheel locking tendency is noticed during a
brake application, the system will enter Anti-Lock
mode. During Anti-Lock braking, hydraulic pressure
in the four wheel circuits is modulated to prevent
any wheel from locking. Each wheel has a set of elec-
trical solenoid valves and a hydraulic line to provide
hydraulic modulation. For vehicle stability, though
both rear wheel valves receive the same electrical
signal. The system can build, hold or reduce pressure
at each wheel. Depending on the signals generated
by the wheel speed sensors (WSS) at each wheel and
received at the Controller-Anti-Lock Brake (CAB). The ABS system represents current state-of-the-art
in vehicle braking systems. The ABS system offers the driver increased safety and vehicle control during
hard braking. This is accomplished by a sophisticated
system of electrical and hydraulic components. That
differ from conventional vacuum boosted hydraulic
actuation systems. Because, there are several perfor-
mance characteristics that may at first seem differ-
ent but should be considered normal. These
characteristics are discussed below. More technical
details are discussed further in this section.
PEDAL FEEL
The ABS System uses hydraulic power assist for
both normal power assisted braking and to provide a
source of high pressure hydraulic fluid during Anti-
Lock Braking. In general, pedal feel will be similar
to that of a conventional vacuum boosted brake sys-
tem. If during an Anti-Lock stop additional force is
applied to the brake pedal, or the brake pedal is re-
leased and reapplied rapidly. The driver may notice a
very hard pedal feel. This is due to normal isolation
of the master cylinder during A.B.S. operation as
wheel brake pressure is fed from the hydraulic
booster.
ANTI-LOCK OPERATION
During Anti-Lock Braking, brake pressures are
modulated by cycling electric valves. The cycling of
these valves can be heard as a series of popping or
ticking noises. In addition, the cycling may be felt as
a pulsation in the brake pedal, although no pedal
movement will be noticed. If Anti-Lock operation oc-
curs during hard braking. Some pulsation may be
felt in the vehicle body due to fore and aft movement
of the vehicles suspension as brake pressures are
modulated. Although ABS operation is available at virtually
all vehicle speeds. It will automatically turn off at
speeds below 3 to 5 mph. Therefore wheel lock-up
may be perceived at the very end of an Anti-Lock
stop and should be considered normal.
TIRE NOISE & MARKS
Although the ABS system prevents complete wheel
lock-up, some wheel slip is desired to achieve opti-
mum braking performance. During brake pressure
modulation, as brake pressure is increased, wheel
slip is allowed to reach up to 30%. This means that
the wheel rolling velocity is 30% less than that of a
free rolling wheel at a given vehicle speed. This slip
may result in some tire chirping, depending on the
road surface. This sound should not be interpreted as
total wheel lock-up. Complete wheel lock-up normally leaves black tire
marks on dry payment. However, Anti-Lock Braking
will not leave dark black tire marks since the wheel
never reaches a locked condition. Tire marks may
however be noticeable as light patched marks.
Fig. 3 (CAB) Controller Anti-Lock Brake Module
Fig. 4 ABS Pump/Motor Assembly
5 - 74 ANTI-LOCK 10 BRAKE SYSTEM Ä
Page 225 of 2438

ABS EQUIPPED VEHICLE PERFORMANCE
Anti-Lock Brakes provide the driver with some
steering control during hard braking. However there
are conditions where the system does not provide any
benefit. In particular, hydroplaning is still possible
when the tires ride on a film of water. Hydroplaning
results in the vehicle tires leaving the road surface
rendering the vehicle almost uncontrollable. In addi-
tion, extreme steering maneuvers at high speed or
high speed cornering beyond limits of tire adhesion
to the road surface may cause vehicle skidding. So,
the ABS system is termed Anti-Lock instead of Anti-
Skid. One of the significant benefits of the ABS system is
that of maintaining steering control during hard
braking or during braking on slippery surfaces. It is
therefore possible to steer the vehicle while braking
on almost any road surface.
ABS SYSTEM SELF-DIAGNOSTICS
The ABS system has been designed with Self Diag-
nostic Capability. There are two self checks the sys-
tems performs every time the vehicle is started.
First, when the key is turned on the system performs
an electrical check called Start-Up Cycle. During this
check, the Red Brake Warning Lamp and the Amber
Anti-Lock Warning Lamp are illuminated. Then
turned off at the end of the test, after about 1 to 2
seconds. When the vehicle reaches a speed of about 3
to 4 miles per hour. The system performs a func-
tional check called Drive-Off. During Drive-Off. hy-
draulic valves are activated briefly to test their
function. Drive-Off can be detected as a series of
rapid clicks upon driving off the first time the car is
started. If the brake pedal is applied during Drive-
Off, the test is by-passed. Both of these conditions
are a normal part of the system self test. Most fault
conditions will set a ABS Fault Code in the (CAB),
which can be retrieved to aid in fault diagnosis. De-
tails can be found in Diagnosis Section.
ABS WARNING SYSTEMS OPERATION
The ABS system uses two methods for notifying
the driver of a system malfunction. These include the
standard Red Brake Warning Lamp and an Amber
Anti-Lock Warning Lamp, both located in the instru-
ment cluster. The purpose of these two lamps are dis-
cussed in detail below.
RED BRAKE WARNING LAMP
The Red Brake Warning Lamp, located in the in-
strument cluster, will Turn On to warn the driver of
brake system conditions that may result in reduced
braking ability. The lamp is also turned on when the
parking brake is not fully released. Conditions which
may cause the Red Brake Warning Lamp to Turn On
include: ²
Parking brake not fully released. If the parking
brake is applied or not fully released. The switch on the
parking brake pedal assembly will ground the Red
Brake Warning Lamp circuit and cause the lamp to
turn on. On vehicles equipped with mechanical instru-
ment clusters, the Amber Anti-Lock Lamp will turn on
if the vehicle is driven above 3 miles per hour with the
Parking Brake applied.
² Low brake fluid. The fluid level sensor in the hy-
draulic assembly reservoir will ground the Red Brake
Warning Lamp circuit if low brake fluid level is de-
tected. In addition, ABS will be deactivated above 3
miles per hour and the Amber Anti-Lock Warning
Lamp will be illuminated. If the vehicle is equipped
with EVIC, a low fluid condition will also cause the
Low Brake Fluid message to appear.
² Low Accumulator Pressure. In the event of low
accumulator pressure, the dual function pressure
switch in the hydraulic assembly will signal the (CAB)
to ground the Red Brake Warning Lamp circuit. This
will cause the Red Brake Warning Lamp to turn on.
Low accumulator pressure also results in the activa-
tion of the Yellow Anti-Lock Warning Lamp. Low accu-
mulator pressure may result in loss of power assist.
² Modulator Or (CAB) Faults. The modulator assem-
bly or (CAB) may turn on the Yellow Anti-Lock Warn-
ing Lamp, if certain faults are detected in either the
modulator assembly or the (CAB).
² Bulb check. As a bulb check, the Red Brake Warning
Lamp will illuminate whenever the ignition switch is
placed in the crank position. Illumination of the red Brake Warning Lamp
may indicate reduced braking ability. A vehicle
that has the Red Brake Warning Lamp ON should
not be driven except to do diagnostic procedures
described in Section 2 of this manual. Most con-
ditions that turn on the Red Brake Warning
Lamp will also turn on the Amber Anti-Lock
Warning Lamp, consequently disabling the Anti-
Lock function.
ANTI-LOCK WARNING LAMP
The Anti-Lock Warning Lamp is located in the in-
strument cluster and is Amber in color. The Amber
Anti-Lock Warning Lamp is illuminated when the
(CAB) detects a condition that results in a shutdown of
Anti-Lock function. The Amber Anti-Lock Warning
Lamp is normally on until the (CAB) completes its self
tests and turns the lamp off. For example, if the (CAB)
is disconnected, the lamp is on. Display of the Amber Anti-Lock Warning Lamp
without the Red Brake Warning Lamp indicates
only that Anti-Lock function has been disabled.
Power assisted normal braking is unaffected.
Ä ANTI-LOCK 10 BRAKE SYSTEM 5 - 75
Page 226 of 2438

NORMAL OPERATION OF WARNING LAMPS
With the ignition in the Crank position, the Red
Brake Warning Lamp will turn on as a bulb check.
The Amber Anti-Lock Warning Lamp will turn on
for as little as 1 second to as long as 30 seconds. If the car has not been started for several hours,
for example after sitting overnight. The Red Brake
Warning Lamp and the Amber Anti-Lock Warning
Lamp may both be turned on for as long as 60 sec-
onds after turning the ignition on. This condition is
caused by the loss of accumulator charge when the
vehicle is parked for extended periods, particularly in
cold weather. When the key is then turned on. The
Pump/Motor assembly must recharge the hydraulic
accumulator to its normal operating pressure. As re-
charging is completed, both warning lamps will turn
off when accumulator pressure reaches about (1,000
psi). Both lamps should remain off at all other times,
indicating normal operation.
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM COMPONENTS
The following is a detailed description of the Anti-
Lock Brake System components. For information on
servicing the other Non-ABS related components
that may be referred to in this section. See the Stan-
dard Brakes Section that refers to the specific com-
ponent.
HYDRAULIC ASSEMBLY
The ABS system uses an integral Hydraulic Assem-
bly (Fig. 1). The hydraulic assembly includes a
Booster/Master Cylinder, Modulator, Hydraulic Blad-
der Accumulator and Fluid Reservoir. The Hydraulic
Assembly is located on the dash panel cowl on the
drivers side of the vehicle. The following is a descrip-
tion of the components that make up the Hydraulic
Assembly.
HYDRAULIC ASSEMBLY BRAKE FLUID RES- ERVOIR
A one piece Fluid Reservoir is attached to the hy-
draulic assembly with rubber seals. The Fluid Reser-
voir (Fig. 1) is internally separated into three fluid
sections. Most of the brake fluid is contained in the
Fluid Reservoir and hydraulic bladder accumulator
(Fig. 1). Additional fluid is contained in the
pump/motor assembly accumulator.
BOOSTER/MASTER CYLINDER
The Booster/Master Cylinder portion of the
hydraulic assembly is an integral component and
should never be disassembled. The Booster/Master Cylinder uses a diagonally split
configuration during normal braking. The two
Fig. 1 Hydraulic Assembly
5 - 76 ANTI-LOCK 10 BRAKE SYSTEM Ä