four wheel drive CHEVROLET DYNASTY 1993 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHEVROLET, Model Year: 1993, Model line: DYNASTY, Model: CHEVROLET DYNASTY 1993Pages: 2438, PDF Size: 74.98 MB
Page 31 of 2438

COMPONENT AND SYSTEM INDEX
Name Group-page Name Group-page
BODY ................................... 23-1
AA-VEHICLE BODY COMPONENT SERVICE .......23-11
AC-VEHICLE BODY COMPONENT SERVICE .......23-37
AG-VEHICLE BODY COMPONENT SERVICE .......23-52
AJ/27-VEHICLE CONVERTIBLE BODY COMPONENT SERVICE ............................ 23-86
AJ-VEHICLE BODY COMPONENT SERVICE .......23-71
AP-VEHICLE BODY COMPONENT SERVICE .......23-97
AY-VEHICLE BODY COMPONENT SERVICE .......23-133
BODY DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURES .............23-2
GENERAL SERVICE INFORMATION .............23-1
PAINT ................................. 23-4
POWER SUNROOF ........................ 23-6
WINDSHIELD ............................ 23-9
BRAKES ..................................5-1
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEMÐBENDIX ANTI-LOCK 10 AC/Y BODY ......................... 5-72
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEMÐBENDIX ANTI-LOCK 6 AA,AG,AJ,AP BODY .................... 5-113
BRAKE DISC (ROTOR) ...................... 5-53
BRAKE SUPPORT ASSEMBLY .................5-25
FRONT DISC BRAKES ...................... 5-31
GENERAL INFORMATION .....................5-1
HYDRAULIC SYSTEM CONTROL VALVES .........5-26
KELSEY HAYES DOUBLE PIN FAMILY CALIPER .....5-35
KELSEY HAYES DOUBLE PIN NON-FAMILY CALIPER ............................. 5-38
MASTER CYLINDER ....................... 5-66
PARKING BRAKES ........................ 5-57
POWER BRAKES ......................... 5-68
REAR DISC BRAKES ....................... 5-45
REAR WHEEL DRUM BRAKES ................5-18
SERVICE ADJUSTMENTS .....................5-4
WHEEL BEARINGS ........................ 5-70
WHEEL CYLINDERS ....................... 5-23
COOLING SYSTEM ...........................7-1
ACCESSORY DRIVE BELTS ................... 7-24
ENGINE BLOCK HEATER .................... 7-28
GENERAL INFORMATION .....................7-1
SERVICE PROCEDURES ..................... 7-10
SPECIFICATIONS ......................... 7-29
ENGINE ..................................9-1
2.2/2.5L ENGINES .........................9-8
3.0L ENGINE ............................ 9-66
3.3/3.8L ENGINE ......................... 9-98
STANDARD SERVICE PROCEDURES .............9-1
EXHAUST SYSTEM AND INTAKE MANIFOLD .........11-1
GENERAL INFORMATION .................... 11-1
SERVICE PROCEDURES ..................... 11-4
TORQUE SPECIFICATION ................... 11-25
FRAME AND BUMPERS ....................... 13-1
BUMPER AND FASCIA ...................... 13-1
FRAME ................................ 13-9
HEATING AND AIR CONDITIONING ...............24-1
AUTOMATIC TEMPERATURE CONTROL (ATC) .....24-66 COMPONENT SERVICE PROCEDURES
..........24-47
FIXED DISPLACEMENT COMPRESSORÐMODEL 10PA17............................. 24-24
FIXED DISPLACEMENT COMPRESSORÐMODEL SD709P ............................. 24-38
FIXED DISPLACEMENT COMPRESSORÐMODEL TR105 .............................. 24-32
GENERAL INFORMATION .................... 24-1
HEATER AND A/C PERFORMANCE TESTS .........24-6
REFRIGERANT SERVICE PROCEDURES ..........24-8
VACUUM CONTROL SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS .........24-4
VARIABLE DISPLACEMENT COMPRESSORÐMODEL 6C17 ............................... 24-13
INTRODUCTION .......................... Intro.-1
LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE ................0-1
CHASSIS AND BODY ....................... 0-19
DRIVETRAIN ............................ 0-16
ENGINE ................................0-8
GENERAL INFORMATION .....................0-1
MANUAL TRANSAXLE CLUTCH ...................6-1
STEERING ................................ 19-1
ACUSTAR STANDARD AND TILT STEERING COLUMN ............................ 19-28
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION SHIFTER/IGNITION INTERLOCK .......................... 19-36
GENERAL INFORMATION .................... 19-1
POWER STEERING GEAR ................... 19-25
POWER STEERING PUMPS ..................19-1
SPECIFICATIONS AND TIGHTENING REFERENCE . . . 19-42
SUSPENSION AND DRIVESHAFTS .................2-1
AUTOMATIC AIR LOAD LEVELING SYSTEM ........2-59
AUTOMATIC AIR SUSPENSION ................2-73
DRIVESHAFTS ........................... 2-25
FRONT SUSPENSION .......................2-2
FRONT SUSPENSION SERVICE PROCEDURES .......2-5
GENERAL INFORMATION .....................2-1
REAR (STUB) AXLE ALIGNMENT ALL MODELS .....2-89
REAR SUSPENSION ....................... 2-50
SPECIFICATIONS ......................... 2-91
TRANSAXLE .............................. 21-85
41TE FOUR SPEED AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE ......21-85
41TE FOUR SPEED TRANSAXLE HYDRAULIC SCHEMATICS ........................ 21-170
41TE ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS .............21-145
A-523, A-543, and A-568 MANUAL TRANSAXLE ....21-1
SPECIFICATIONS ........................ 21-183
THREE SPEED TORQUEFLITE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE .......................... 21-35
THREE SPEED TRANSAXLE HYDRAULIC SCHEMATICS ........................ 21-162
WHEELSÐTIRES ........................... 22-1
SPECIFICATIONS ......................... 22-8
TIRE SERVICE PROCEDURES .................22-1
WHEELS SERVICE PROCEDURES ..............22-6
Page 78 of 2438

(14) Lower vehicle.
(15) Align the front wheels of the vehicle. Use the
procedure listed under Wheel Alignment, in the
Front Suspension Service Procedures section of this
service manual.
HUB AND BEARING ASSEMBLY
The Unit III Front Hub and Bearing (Fig. 1) is used
on all Front Wheel Drive Applications. All hub and bearing assemblies mount to the steer-
ing knuckle the same way, but very by the wheel size
on the vehicle. Vehicles equipped with 14 inch wheels
have a 4 inch wheel mounting stud pattern. Vehicles
equipped with 15 inch wheels hav e a 4 1/2 inch wheel
mounting stud pattern. If a hub and bearing assembly
needs to be replaced, be sure that the replacement
assembly has the same size wheel mounting stud
pattern as the original part.
This unit is serviced only as a complete assembly
(Fig. 1). It is mounted to the steering knuckle by four
mounting bolts that are removed from the rear of the
steering knuckle (Fig. 2).
REMOVAL
Replacement of the front (drive) hub and bearing
assembly can be done without having to remove the
steering knuckle from the vehicle. (1) Remove cotter pin, hub nut lock, and spring
washer (Fig. 3). (2) Loosen hub nut while the vehicle is on the floor
with the brakes applied (Fig. 4). The hub and drive-
shaft are splined together through the knuckle
(bearing assembly) and retained by the hub nut. (3) Raise vehicle, see Hoisting Recommendations in
Group 0 of this service manual. (4) Remove the hub nut and the washer from the
stub axle (Fig. 3). (5) Remove the wheel lug nuts, and tire and wheel
assembly from the vehicle.
Fig. 16 Install Washer and Hub Nut
Fig. 17 Tighten Hub Nut
Fig. 18 Install Spring Washer, Nut Lock, & Cotter Pin
Fig. 1 Unit III Front Hub And Bearing Assembly
2 - 20 SUSPENSION AND DRIVESHAFTS Ä
Page 107 of 2438

mount have been loosened for any reason, or if vehicle
has experienced front structural damage, driveshaft
lengths must be checked and corrected, if required. A
shorter than required driveshaft length can result in ob-
jectionable noise. A longer than required driveshaft
length may result in potential damage.
Use of the following procedure will ensure satisfac-
tory driveshaft engagement under all normal vehicle
operating conditions. (1) The vehicle must be completely assembled.
Front wheels must be properly aligned and in the
straight ahead position. The vehicle must be in a po-
sition so that the full weight of the body is distrib-
uted to all four tires. A platform hoist, or front end
alignment rack, is recommended.
(2) Using a tape measure or other suitable measuring
device. Measure the direct distance from the inner edge of the outboard boot to the inner edge of the inboard
boot on both driveshafts. This measurement must be
taken at the bottom (six o'clock position) of the drive-
shafts (Fig. 1).
Note that the required dimension varies with car-line,
engine, transaxle, and driveshaft manufacturer (Fig. 2).
(3) If the lengths of both shafts are within the
range specified, no further action is required. If either left or right driveshaft length is not
within the specified range. Refer to Group 09, Engine
Removal and Installation to properly position engine
according to specified driveshaft lengths.
(4) If proper driveshaft lengths cannot be achieved
within the travel limits available in the slotted engine
mounts. Check for any condition that could effect the
side to side position of the measurement locations (e.g.,
engine support brackets, siderail alignment, etc.).
(5) After ensuring proper driveshaft lengths the
transmission shift linkage must be adjusted to en-
sure proper operation. Refer to Transaxle, Group 21.
Fig. 2 Driveshaft Identification and Dimensions
Fig. 19 Left Driveshaft with Damper Weight
Fig. 1 Driveshaft Positioning
Ä SUSPENSION AND DRIVESHAFTS 2 - 49
Page 147 of 2438

REAR (STUB) AXLE ALIGNMENT ALL MODELS INDEX
page page
General Information ....................... 89 Rear Wheel Alignment..................... 89
GENERAL INFORMATION
Because front wheel drive vehicles are equipped with
rear suspension incorporating stub axles (or wheel
spindles). It is possible to align both the camber and toe
of the rear wheels.
REAR WHEEL ALIGNMENT
Alignment adjustment if required. Is made by adding
0.010 inch shims (from the service package kit) be-
tween the spindle mounting surface and axle mounting
plate. Each shim equals wheel change by .3É as shown
(for all car lines) in (Figs. 3 to 6). If rear wheel alignment is required, place vehicle on
alignment rack and check alignment specifications.
When recording rear toe-in (vehicle backed onto
alignment rack) REMEMBER to reverse sign
convention; a total toe-in on direct reading
charts is actually toe-out while driving. Maintain
rear alignment within Chrysler Motors recommenda-
tions, found in Specifications.
INSTALLATION OF REAR ALIGNMENT SHIMS
(1) Block front tires so vehicle will not move.
(2) Release parking brake.
(3) Hoist vehicle so that rear suspension is in full
rebound and tires are off the ground. See Hoisting in
Lubrication and Maintenance, Group 0. (4) Remove wheel and tire assembly.
(5) Pry off grease cap.
(6) Remove cotter pin and castle lock.
(7) Remove adjusting nut.
(8) Remove brake drum (Fig. 1). (9) Loosen four (4) brake assembly and spindle
mounting bolts enough to allow clearance for shim
installation (Fig. 2). Do not remove mounting
bolts.
(10) Install shims as shown in Figs. 3, 4, 5 and 6
for desired wheel change. No more than two shims
on each spindle should be used to bring alignment
within acceptable range. Wheel change by .3É per shim.
(11) Tighten down the 4 brake support plate and
spindle to axle mounting bolts until they are snug.
Then tighten the 4 bolts to the torque values listed
for the vehicle line which is being serviced.
² AA, AG, AJ, AP Bodies 75 N Im (55 ft. lbs.)
Fig. 2 Loosen Mounting Bolts
Fig. 3 Shim Installation for Toe-Out
Fig. 1 Remove Brake Drum
Ä SUSPENSION AND DRIVESHAFTS 2 - 89
Page 157 of 2438

expel all the trapped air. Be sure to monitor the fluid
level in the pressure bleeder. It must stay at the
proper level so air will not be allowed to reenter the
brake system through the master cylinder.
BLEEDING WITHOUT A PRESSURE BLEEDER
If a pressure bleeder is not available. A good brake
fluid flow can be obtained by manual bleeding of the
brake hydraulic system, following these steps. Manual bleeding of the brakes hydraulic sys-
tem will require the aid of a helper to correctly
perform manual brake bleeding procedure. The following wheel sequence for bleeding the
brake hydraulic system should be used to ensure ad-
equate removal of all trapped air from the hydraulic
system. ²
Right rear wheel
² Left front wheel
² Left rear wheel
² Right front wheel
(1) Pump the brake pedal three or four times and
hold it down before the bleeder screw is opened. (2) Then open the bleeder screw at least 1 full
turn. When the bleeder screw opens the brake pedal
will drop all the way to the floor. (3) Release the brake pedal only afterthe bleeder
screw is closed. (4) Repeat steps 1 through 3, four or five times, at
each bleeder screw. This should pass a sufficient
amount of fluid to expel all the trapped air from the
brake system. Be sure to monitor the fluid level in
the master cylinder, so it stays at a proper level so
air will not reenter the brake system through the
master cylinder. Test drive vehicle to be sure brakes are operating
correctly and that pedal is solid.
TEST FOR FLUID CONTAMINATION
Indications of fluid contamination are swollen or
deteriorated rubber parts. Swollen rubber parts indicate the presence of petro-
leum in the brake fluid. To test for contamination, put small amount of
drained brake fluid in clear glass jar. If fluid sepa-
rates into layers, there is mineral oil contamination. If contaminated, drain and thoroughly flush sys-
tem. Replace master cylinder, proportioning valve,
caliper seals, wheel cylinder seals and all hoses.
WHEEL STUD NUT TIGHTENING
When tightening wheel stud nuts, a criss-cross
tightening sequence should be followed (Fig. 9).
Tighten all stud nuts to one-half specified torque.
Repeat, fully tightening to 129 N Im (95 ft. lbs.).
Fig. 9 Wheel Stud Nut Tightening Sequence
Fig. 7 Proper Method for Purging Air From Brake
System (Typical)
Fig. 8 Open Bleeder Screw at Least One Full Turn (Typical)
Ä BRAKES 5 - 7
Page 222 of 2438

ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEMÐBENDIX ANTI-LOCK 10 AC/Y BODY INDEX
page page
ABS Brake System Diagnostic Features ....... 92
ABS Braking System Diagnosis .............. 87
ABS Controller Anti-Lock Brake (CAB) Service Precautions ........................... 88
ABS Equipped Vehicle Performance .......... 75
ABS Hydraulic Circuits and Valve Operation .... 85
ABS System Diagnostic Connector ........... 82
ABS System General Service Precautions ...... 88
ABS System Self-Diagnostics ............... 75
ABS Warning Systems Operation ............ 75
Anti-Lock Brake System Components ......... 76 Anti-Lock Brake System Definitions
........... 72
Anti-Lock Operation and Performance ......... 73
Anti-Lock System Relays and Warning Lamps . . . 82
Controller Anti-Lock Brake (CAB) ............. 80
Electronic Components ................... 103
General Information ....................... 72
General Service Precautions ................ 93
Major ABS Components ................... 73
Mechanical Diagnostics and Service Procedures . 89
Normal Braking System Function ............. 72
On Car Hydraulic ABS Component Service ..... 93
GENERAL INFORMATION
The purpose of the Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS)
is to prevent wheel lock-up under heavy braking con-
ditions on virtually any type of road surface. Anti-
Lock Braking is desirable because a vehicle which is
stopped without locking the wheels will retain direc-
tional stability and some steering capability. This al-
lows the driver to retain greater control of the
vehicle during heavy braking.
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM DEFINITIONS
In this section of the manual several abbreviations
are used for the components that are in the Anti-
Lock Braking System They are listed below for your
reference.
² CABÐController Anti-Lock Brake
² ABSÐAnti-Lock Brake System
² PSIÐPounds per Square Inch (pressure)
² WSSÐWheel Speed Sensor
NORMAL BRAKING SYSTEM FUNCTION
Under normal braking conditions, the ABS System
functions much the same as a standard brake system
with a diagonally split master cylinder. The primary
difference is that power assist is provided by hydrau-
lic power assist instead of the conventional vacuum
assist. If a wheel locking tendency is noticed during a
brake application, the system will enter Anti-Lock
mode. During Anti-Lock braking, hydraulic pressure
in the four wheel circuits is modulated to prevent
any wheel from locking. Each wheel of the vehicle
has a set of electrical solenoid valves and hydraulic
line to provide hydraulic modulation. For vehicle sta-
bility, though both rear wheel valves receive the
same electrical signal. The system can build, hold or
reduce pressure at each wheel of the vehicle. This is
determined by the signals generated by the wheel
Four-Wheel Anti-Lock Brake System
5 - 72 ANTI-LOCK 10 BRAKE SYSTEM Ä
Page 224 of 2438

difference is that power assist is provided by hydrau-
lic power assist instead of the conventional vacuum
assist. If a wheel locking tendency is noticed during a
brake application, the system will enter Anti-Lock
mode. During Anti-Lock braking, hydraulic pressure
in the four wheel circuits is modulated to prevent
any wheel from locking. Each wheel has a set of elec-
trical solenoid valves and a hydraulic line to provide
hydraulic modulation. For vehicle stability, though
both rear wheel valves receive the same electrical
signal. The system can build, hold or reduce pressure
at each wheel. Depending on the signals generated
by the wheel speed sensors (WSS) at each wheel and
received at the Controller-Anti-Lock Brake (CAB). The ABS system represents current state-of-the-art
in vehicle braking systems. The ABS system offers the driver increased safety and vehicle control during
hard braking. This is accomplished by a sophisticated
system of electrical and hydraulic components. That
differ from conventional vacuum boosted hydraulic
actuation systems. Because, there are several perfor-
mance characteristics that may at first seem differ-
ent but should be considered normal. These
characteristics are discussed below. More technical
details are discussed further in this section.
PEDAL FEEL
The ABS System uses hydraulic power assist for
both normal power assisted braking and to provide a
source of high pressure hydraulic fluid during Anti-
Lock Braking. In general, pedal feel will be similar
to that of a conventional vacuum boosted brake sys-
tem. If during an Anti-Lock stop additional force is
applied to the brake pedal, or the brake pedal is re-
leased and reapplied rapidly. The driver may notice a
very hard pedal feel. This is due to normal isolation
of the master cylinder during A.B.S. operation as
wheel brake pressure is fed from the hydraulic
booster.
ANTI-LOCK OPERATION
During Anti-Lock Braking, brake pressures are
modulated by cycling electric valves. The cycling of
these valves can be heard as a series of popping or
ticking noises. In addition, the cycling may be felt as
a pulsation in the brake pedal, although no pedal
movement will be noticed. If Anti-Lock operation oc-
curs during hard braking. Some pulsation may be
felt in the vehicle body due to fore and aft movement
of the vehicles suspension as brake pressures are
modulated. Although ABS operation is available at virtually
all vehicle speeds. It will automatically turn off at
speeds below 3 to 5 mph. Therefore wheel lock-up
may be perceived at the very end of an Anti-Lock
stop and should be considered normal.
TIRE NOISE & MARKS
Although the ABS system prevents complete wheel
lock-up, some wheel slip is desired to achieve opti-
mum braking performance. During brake pressure
modulation, as brake pressure is increased, wheel
slip is allowed to reach up to 30%. This means that
the wheel rolling velocity is 30% less than that of a
free rolling wheel at a given vehicle speed. This slip
may result in some tire chirping, depending on the
road surface. This sound should not be interpreted as
total wheel lock-up. Complete wheel lock-up normally leaves black tire
marks on dry payment. However, Anti-Lock Braking
will not leave dark black tire marks since the wheel
never reaches a locked condition. Tire marks may
however be noticeable as light patched marks.
Fig. 3 (CAB) Controller Anti-Lock Brake Module
Fig. 4 ABS Pump/Motor Assembly
5 - 74 ANTI-LOCK 10 BRAKE SYSTEM Ä
Page 263 of 2438
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEMÐBENDIX ANTI-LOCK 6 AA,AG,AJ,AP BODY INDEX
page page
ABS Brake System Diagnosis .............. 123
ABS Brake System Diagnostic Features ...... 125
ABS Computer System Service Precautions . . . 124
ABS General Service Precautions ........... 124
Anti-Lock Brake System Components ........ 116
Anti-Lock Brake System Definitions .......... 113
Anti-Lock Brakes Operation and Performance . . 115
Anti-Lock System Relays and Warning Lamps . . 120
Controller Anti-Lock Brake (CAB) ............ 119
Diagnostic Connector ..................... 120
Electronic Components ................... 130 General Information
...................... 113
Hydraulic Circuits and Valve Operation ....... 121
Major Components ...................... 114
Mechanical Diagnostics and Service Procedures . 125
Normal Braking System Function ............ 114
On-Car ABS Brake System Service .......... 126
Specifications .......................... 135
System Self-Diagnostics .................. 115
Vehicle Performance ..................... 115
Warning Systems Operation ............... 116
GENERAL INFORMATION
The purpose of the Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS)
is to prevent wheel lock-up under heavy braking con-
ditions on virtually any type of road surface. Anti-
Lock Braking is desirable because a vehicle which is
stopped without locking the wheels will retain direc-
tional stability and some steering capability. This al-
lows the driver to retain greater control of the
vehicle during heavy braking. This section of the service manual covers the de-
scription, diagnostics, and on car service for the Ben-
dix Anti-Lock 6 Brake System. If other service is required on the non ABS related components of the
brake system. Refer to the appropriate section in this
group of the manual for the specific service procedure
required.
ANTI-LOCK BRAKE SYSTEM DEFINITIONS
In this section of the manual several abbreviations
are used for the components that are in the Anti-
Lock Braking System They are listed below for your
reference.
² CABÐController Anti-Lock Brake
² ABSÐAnti-Lock Brake System
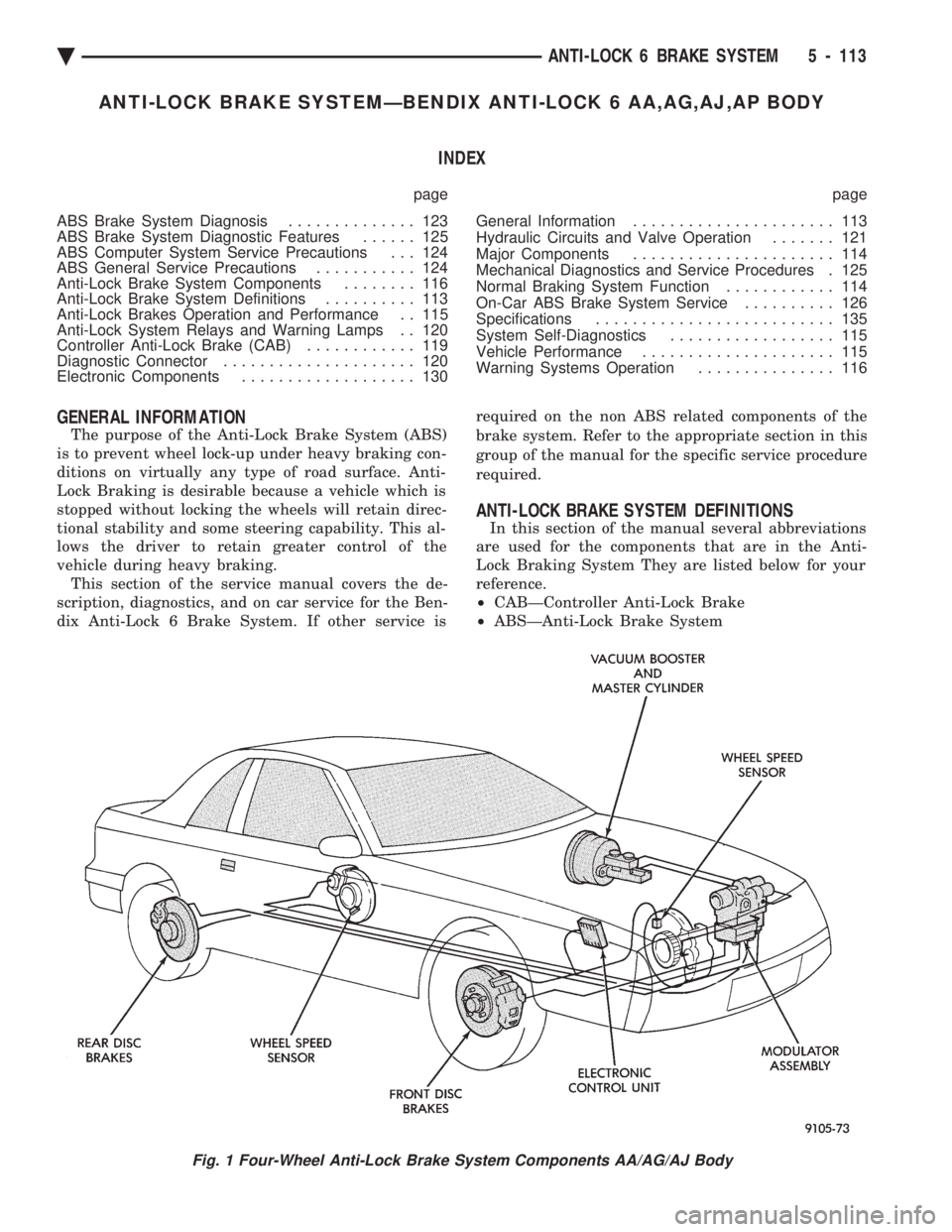
Fig. 1 Four-Wheel Anti-Lock Brake System Components AA/AG/AJ Body
Ä ANTI-LOCK 6 BRAKE SYSTEM 5 - 113
Page 290 of 2438

² Left rear wheel
² Right front wheel
(1) Pump brake pedal three or four times, then
hold a constant moderate to heavy foot pressure on
the brake pedal.
CAUTION: Just cracking the bleeder screw often re-
stricts fluid flow, and a slow, weak fluid discharge
will NOT get all the air out.
(2) Open bleeder screw (Fig. 7) at least 1 full turn.
When bleeder screw opens, brake pedal will drop to
the floor. (3) Close bleeder screw. Release brake pedal off
floor only afterbleeder screw is completely closed.
(4) Repeat steps 1 through 3, four or five times, at
each bleeder screw. This should pass a sufficient
amount of brake hydraulic fluid to expel all trapped
air. Be sure to monitor brake fluid level in master
cylinder fluid reservoir. It must stay at a level that
will not allow air to re-enter the hydraulic system
through the master cylinder. After 4 to 8 ounces of hydraulic fluid has been bled
from the bleeder screw at this wheel, and an air-free
flow has been maintained, a good bleed is indicated. Repeat above procedure at all other remaining
bleeder screws, while checking brake pedal for travel. If brake pedal travel is still excessive or has
not improved, enough brake fluid has not passed
through the hydraulic system to expel all trapped
air. Be sure to monitor brake fluid level in the mas-
ter cylinder brake fluid reservoir. It must stay at the
proper level so air will not be allowed to re-enter the
brake system through the master cylinder. Test drive vehicle to be sure brakes are operating
correctly and that pedal is not spongy.
TESTING FOR FLUID CONTAMINATION
Indications of fluid contamination are swollen or
deteriorated rubber parts. Swollen rubber parts indicate the presence of petro-
leum in the brake fluid. To test for contamination, put small amount of
drained brake fluid in clear glass jar. If fluid sepa-
rates into layers, there is mineral oil contamination. If contaminated, drain and thoroughly flush sys-
tem. Replace master cylinder, proportioning valve,
caliper seals, wheel cylinder seals and all hoses.
Fig. 6 Proper Method for Purging Air From Brake System
Fig. 7 Open Bleeder Screw at Least One Full Turn(Typical)
5 - 4 BRAKES Ä
Page 302 of 2438

(2) The voltage output from each of the wheel
speed sensors is verified to be within the correct op-
erating range. If a vehicle is not set in motion within 3 minutes
from the time the ignition switch is turned to the on
position. The solenoid valve test is bypassed but the
pump/motor is activated briefly to verify that it is op-
erating correctly.
WARNING SYSTEMS OPERATION
The ABS system uses an Amber Antilock Warning
Lamp, located in the instrument cluster. The purpose
of the warning lamp is discussed in detail below. The Amber Antilock Warning Light will turn on
whenever the CAB detects a condition which results
in a shutdown of the Antilock brake system. The
Amber Antilock Warning Lamp is normally on until
the CAB completes its self tests and turns the lamp
off (approximately 1-2 seconds). When the Amber
Antilock Warning Light is on, only the Antilock
brake function of the brake system if affected. The
standard brake system and the ability to stop the car
will not be affected when only the Amber Antilock
Warning Light is on.
NORMAL OPERATION OF WARNING LAMP
With ignition key turned to the Crank position, the
Red Brake Warning Lamp and Amber Antilock
Warning Lamp will turn on as a bulb check. The
Amber Antilock Warning Lamp will stay on for 1-2
seconds then turn off, once verification of Antilock
Brake System self diagnosis is completed.
ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM COMPONENTS
The following is a detailed description of the Ben-
dix Antilock 4 Brake System components. For infor-
mation on servicing the Four Wheel Disc Brake
System, see the standard Brake section in the Front
Wheel Drive Car, chassis service manual.
MODULATOR ASSEMBLY
WARNING: THE ONLY COMPONENTS OF THE
MODULATOR ASSSEMBLY THAT ARE SERVICE-
ABLE, ARE THE 2 PROPORTIONING VALVES,
BLEED SCREWS AND THREAD SAVERS. THE RE-
MAINING COMPONENTS OF THE MODULATOR AS-
SEMBLY ARE NOT INTENDED TO BE
SERVICEABLE ITEMS. NO ATTEMPT SHOULD BE
MADE TO REMOVE OR SERVICE ANY OTHER COM-
PONENTS OF THE MODEULATOR ASSEMBLY.
The Modulator Assembly (Fig. 1) is located under
the battery tray and is covered with an acid shield.
The Modulator Assembly contains the following com-
ponents for controlling the Antilock brake system. 4
Build/Decay Valves, 4 Shuttle Orifices, 2 Fluid
Sumps, 2 Accumulators, and a Pump/Motor assem- bly. Also attached to the Modulator Assembly are 6
brake tubes which are connected to a 12 way junc-
tion block. The junction block (Fig. 2) is mounted to
the left frame rail below the master cylinder in the
same location as the non ABS equipped combination
valve. The wheel brake lines are attached to the sys-
tem via the connector block.BUILD/DECAY VALVES
There are 4 Build/Decay valves, one for each
wheel. In the released position they provide a fluid
path direct to the wheel brakes. In the actuated (de-
cay) position, they provide a fluid path from the
wheel brakes to the sump. The Build/Decay valves
are spring loaded in the released (build) position.
SHUTTLE ORIFICE
There are 4 Shuttle Orifice Valves, one for each
wheel. The Shuttle Orifice Valve is a hydraulically
actuated valve which shuttles when the Build/Decay
valve is actuated. Actuating of the Build/Decay valve
causes a pressure differential to be created across the
Shuttle Orifice Valve. This acts like placing an ori-
Fig. 1 Modulator Assembly
Fig. 2 Antilock Brake Junction Block
5 - 16 ANTILOCK 4 BRAKE SYSTEM Ä