traction control CHEVROLET S10 1993 2.G Owners Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHEVROLET, Model Year: 1993, Model line: S10, Model: CHEVROLET S10 1993 2.GPages: 356, PDF Size: 20.85 MB
Page 73 of 356

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine CAUTION I
If you skip more than one gear when you downshift, you could lose
control of your vehicle. And you could injure yourself or others.
NOTICE
Locking Rear Axle
If you have this feature, your rear axle can give you additio\
nal traction on
snow, mud, ice, sand or gravel. It works like a standard axle\
most of the
time, but one of the rear wheels has no traction and the other does, the
locking feature will allow the wheel with traction to move the vehicle.
Parking Brake
KO424
To set the parking brake:
Hold the regular brake pedal down with your right foot. Push \
down the
parking brake pedal with your left foot.
If the ignition is on, the brake system
warning light will come on.
2-21
Page 80 of 356
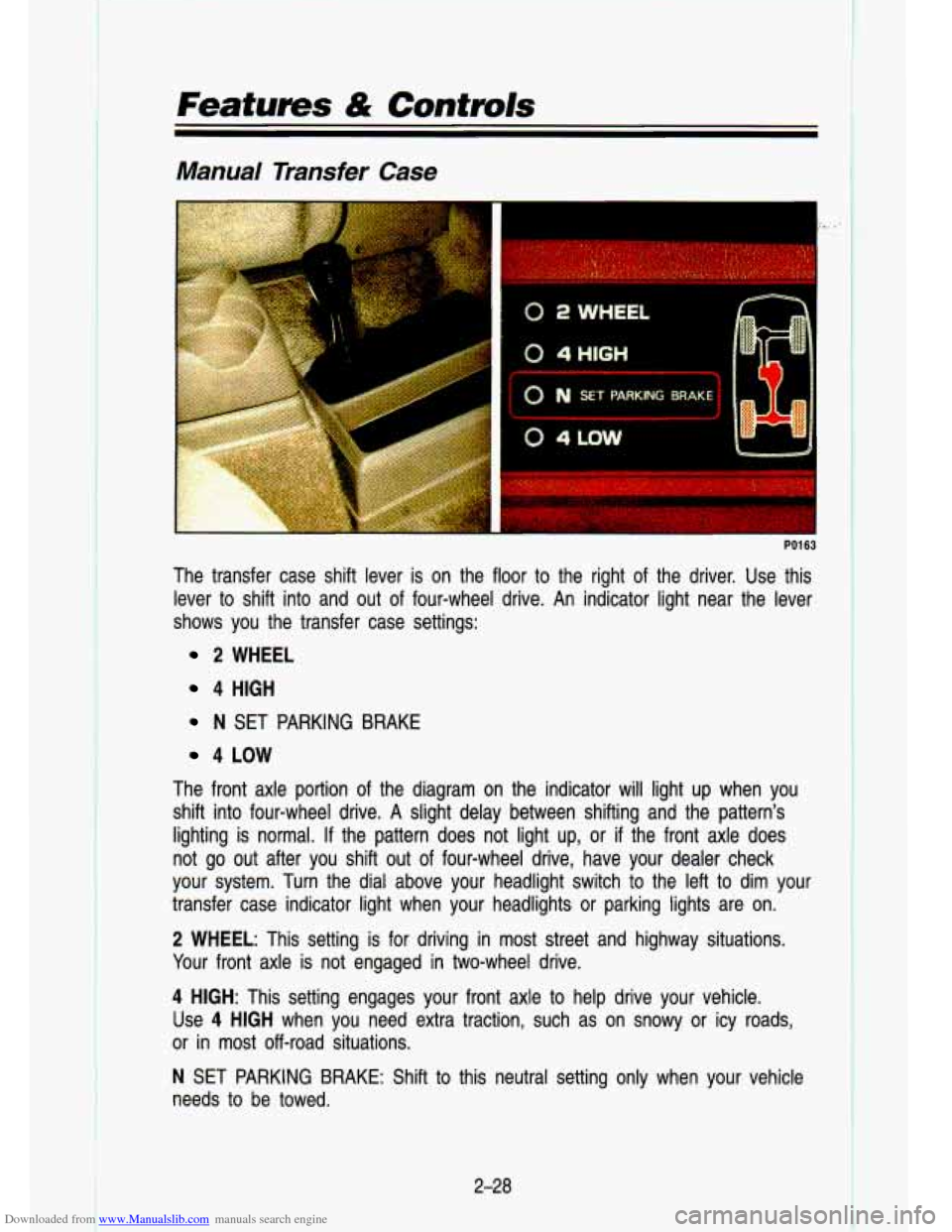
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Features & Controls
Manual Transfer Case
I
PO1 63
The transfer case shift lever is on the floor to the right of the driver. Use this
lever
to shift into and out of four-wheel drive. An indicator light near the lever
shows you the transfer case settings:
2 WHEEL
4 HIGH
N SET PARKING BRAKE
4 LOW
The front axle portion
of the diagram on the indicator will light up when you
shift into four-wheel drive. A slight delay between shifting and the patte\
rn's
lighting is normal.
If the pattern does not light up, or if the front axle does
not go out after you shift out
of four-wheel drive, have your dealer check
your system. Turn the dial above your headlight switch
to the left to dim your
transfer case indicator light when your headlights or parking l\
ights are on.
2 WHEEL: This setting is for driving in most street and highway situations.
Your front axle is not engaged in two-wheel drive.
4 HIGH: This setting engages your front axle to help drive your vehicle.
Use
4 HIGH when you need extra traction, such as on snowy or icy roads, \
or in most off-road situations.
N SET PARKING BRAKE: Shift to this neutral setting only when your vehicle
needs
to be towed.
2-28
I
Page 94 of 356

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Features & Contmls
t
1 CALITION I. - .. ;Fg ,. L A Cruise Control can be dangerous where you can't drive safely a\
t
a steady speed.
So, don't use your Cruise Control on winding
roads
or in heavy traffic.
Cruise Control can be dangerous on slippery roads. On such
roads, fast changes in tire traction can cause needless wheel
spinning, and you could lose control. Don't use Cruise Control \
on slippery roads.
To Set Cruise Control
Move the Cruise Control switch to ON.
1 CAUTION
A If you leave your Cruise Control switch on when you're not using \
k Cruise, you might hit a button and go into Cruise when you don't
want to. You could be startled and even lose control. Keep the
Cruise Control switch
OFF until you want to use it.
Get up to the speed you want.
Push in the set button at the end of the lever and release it.
Take your foot off the accelerator pedal.
2-42
Page 172 of 356

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Your Driving and the Road
Steering Tips
Driving on Curves
It’s important to take curves at a reasonable speed.
A lot of the “driver lost control” accidents mentioned on the news \
happen on
curves. Here’s why:
Experienced driver or beginner, each of us is subject to the same laws of
physics when driving on curves. The traction of the tires against the road
surface makes it possible for the vehicle to change its path when you turn
the front wheels.
If there’s no traction, inertia will keep the vehicle going in
the same direction.
If you’ve ever tried to steer a vehicle on wet ice, you’ll \
understand this.
The traction you can get in a curve depends on the condition of your tires
and the road surface, the angle at which the curve is banked, and your
speed. While you’re in a curve, speed is the one factor you can control.
Suppose you’re steering through a sharp curve. Then you sudd\
enly apply the
brakes. Both control systems-steering and braking-have to do their work
where the tires meet the road. Adding the hard braking can de\
mand too
much at those places. You can lose control. The same thing can happen
if
you’re steering through a sharp curve and you suddenly accel\
erate. Those
two control systems-steering and acceleration-can overwhelm those places
where the tires meet the road and make you lose control.
What should you
do if this ever happens? Let up on the brake or accelerator
pedal, steer the vehicle the way you want it to go, and slow down.
Speed limit signs near curves warn that you should adjust your\
speed. Of
course, the posted speeds are based on good weather and road \
conditions. Under less favorable conditions you’ll want to go slower.
If you need to reduce your speed as you approach a curve, do it before you
enter the curve, while your front wheels are straight ahead. Try to adjust your
speed
so you can “drive” through the curve. Maintain a reasonable, \
steady
speed. Wait to accelerate until you are out of the curve, and then accelerate
gently into the straightaway.
When you drive into a curve at night, it’s harder to see the road ahead of
you because it bends away from the straight beams of your lights. This is
one
good reason to drive slower.
Steering in Emergencies
There are times when steering can be more effective than braki\
ng. For
example, you come over a hill and find a truck stopped in your lane, or a
4-1 %
Page 176 of 356

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Your Driving and the Road
Don’t overtake a slowly moving vehicle too rapidly. Even tho\
ugh the
brake lights are not flashing, it may be slowing down or starting to turn.
If you’re being passed, make it easy for the following driv\
er to get ahead
of you. Perhaps you can ease a little to the right.
Loss of Control
Let’s review what driving experts say about what happens whe\
n the three
control systems (brakes, steering and acceleration) don’t ha\
ve enough friction
where the tires meet the road to
do what the driver has asked.
In any emergency, don’t give up. Keep trying to steer, and constantly seek an
escape route or area of less danger.
Skidding
In a skid, a driver can lose control of the vehicle. Defensive drivers avoid
most skids by taking reasonable care suited to existing conditi\
ons, and by not
“overdriving” those conditions. But skids are always possib\
le.
The three types
of skids correspond to your vehicle’s three control systems.
In the braking skid, your wheels aren’t rolling. In the steering or cornering
skid, too much speed or steering in a curve causes tires to \
slip and lose
cornering force. And in the acceleration skid, too much throttle causes the
driving wheels to spin.
A cornering skid and an acceleration skid are best handled by easing your
foot off the accelerator pedal. If your vehicle starts to slide (as when you turn
a corner on a wet, snow- or ice-covered road), ease your foo\
t
off the
accelerator pedal as soon as you feel the tires start to slide. Quickly steer
the way you want the vehicle to go. If you start steering quickly enough, your
vehicle will straighten out.
As it does, straighten the front wheels.
Of course, traction is reduced when water, snow, ice, gravel, or other material
is on the road. For safety, you’ll want to slow down and adjust your driving to
these conditions.
It is important to slow down on slippery surfaces because
stopping distance will be longer and vehicle control more limit\
ed.
While driving on a surface with reduced traction, try your bes\
t to avoid
sudden steering, acceleration, or braking (including engine brak\
ing by shifting
to a lower gear). Any sudden move could cause the tires to slide. You may
not realize the surface is slippery until your vehicle is skidding. Learn to
recognize warning clues-such as enough water, ice or packed snow on the
road to make
a “mirrored surface”-and slow down when you have any
doubt.
4-22
Page 179 of 356

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Controlling your vehicle is the key to successful off-road driving. One of the
best ways to control your vehicle is to control your speed. Here are some
things to keep in mind. At higher speeds:
you approach things faster and you have less time to scan the terrain
for obstacles.
you have less time to react.
you have more vehicle bounce when you drive over obstacles.
you’ll need more distance for braking, especially since you’\
re on an
unpaved surface.
I CAUTION
A When you’re driving off road, bouncing and quick changes in direc-
1 tion can easily throw you out of position. This could cause you to
lose control and crash. So, whether you’re driving on or off the road,
you and your passengers should wear safety belts.
Scanning the Terrain
Off-road driving can take you over many different kinds of terrain. You need
to be familiar with the terrain and its many different features. \
Here are some
things
to consider.
Surface Conditions
Off-roading can take you over hard-packed dirt, gravel, rocks, grass, sand,
mud, snow or ice. Each of these surfaces affects the steering, acceleration,
and braking of your truck in different ways. Depending upon the kind of
surface you are on, you may experience slipping, sliding, wheel spinning,
delayed acceleration, poor traction, and longer braking distances\
.
Surface Obstacles
Unseen or hidden obstacles can be hazardous. A rock, log, hole, rut, or
bump can startle you
if you’re not prepared for them. Often these obstacles
are hidden by grass, bushes, snow or even the rise and fall of the terrain
itself. Here are some things to consider:
Is the path ahead clear?
Will the surface texture change abruptly up ahead?
Does the travel take you uphill or downhill? (There’s more discussion of
Will you have to stop suddenly or change direction quickly?
these subjects
later.)
4-25
Page 187 of 356

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine on beaches or sand dunes) your tires will tend to sink into \
the sand. This has an effect on steering, accelerating, and braking. You may want to reduce
the air pressure in your tires slightly when driving on sand. \
This will improve
traction.
Hard packed snow and ice offer the worst tire traction. On these surfaces, it’s
very easy to lose control. On wet ice, for example, the tract\
ion
is so poor
that you will have difficulty accelerating. And
if you do get moving, poor
steering and difficult braking can cause you to slide out of control.
nds or rivers can be dangerous.
~;~:.cx :. 2’’
nderwater springs, currents under the ice, or sudden thaws can \
25
weaken the ice. Your vehicle could fall through the ice and you ad.
. your passengers could drown. Drive your vehicle on safe surface\
s
~~ : . I’ .: . :j/-
,. ,/ ., ‘!...,I:, I -
Driving In Water
Light rain causes no special off-road driving problems. But hea\
vy rain can
mean flash flooding, and flood waters demand extreme caution.
Find out how deep the water is before you drive through
it. If it’s deep
enough to cover your wheel hubs, axles, or exhaust pipe, don’t
try it-you
probably won’t get through. Also, water that deep can damage\
your axle and
other vehicle parts.
If the water isn’t too deep, then drive through it slowly. At fast speeds, water
splashes on your ignition system and your vehicle can stall. S\
talling can also
occur
if you get your tailpipe under water. And, as long as your tailp\
ipe is
under water, you’ll never be able to start your engine. Whe\
n you go through
water, remember that when your brakes get wet,
it may take you longer to
stop.
A
Driving through rushing water can be dangerous. Deep water can
sweep your vehilcle downstream and you and your passengers could
drown.
If it’s only inches deep, it can still wash away the ground
from under your tires, and you could lose traction and roll the vehicle
over.
Don’t drive through rushing water.
4-33
Page 295 of 356

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine If you ever replace your tires with those not having a TPC Spec number,
make sure they are the same size, load range, speed rating an\
d construction
type (bias, bias-belted or radial) as your original tires.
Mixing tires
could cause you to lose control while driving. If you mix
tires of different types (like radial and bias-belted tires) the vehicl\
e
may nlot handle properly, an'd you could have a cras'h. Be sure to
use the same size 'and type tires on all four wheels.
It's all right to drive with your compact spare (if you have one). It
I was developed for use on your vehicle.
Uniform Tire Quality Grading
The following information relates to the system developed by th\
e United
States National Highway Traffic Safety Administration which grade\
s tires by
treadwear, traction and temperature performance. (This applies o\
nly to
vehicles
sold in the United States.)
Treadwear
The treadwear grade is a comparative rating based on the wear rate of the
tire when tested under controlled conditions on a specified government test
course. For example, a tire graded
150 would wear one and a half (1 -1/2)
times as well on the government course as a tire graded 100. The relative
performance of tires depends upon the actual conditions of their use,
however, and may depart significantly from the norm due to var\
iations in
driving habits, service practices and differences in road charac\
teristics and
climate.
Traction-A, B, C
The traction grades, from highest to lowest are: A, B, and C. They represent
the tire's ability to stop on wet pavement as measured under controlled
conditions on specified government test surfaces of asphalt and concrete.
A
tire marked C may have poor traction performance.
Warning: The traction grade assigned to this tire is based on braking
(straight-ahead) traction tests and does not include cornering \
(turning) traction.
Temperature-A, B, C
The temperature grades are A (the highest), B, and C, representing the tire's
resistance
to the generation of heat and its ability to dissipate heat when
tested under controlled conditions on a specified indoor laboratory test wheel,
Sustained high temperature can cause the material of the tire
to degenerate
and reduce tire life, and excessive temperature can lead to sudden tire
6-47