light CHEVROLET TRACKER 1998 1.G Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHEVROLET, Model Year: 1998, Model line: TRACKER, Model: CHEVROLET TRACKER 1998 1.GPages: 386, PDF Size: 21.17 MB
Page 154 of 386

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Remember: Anti-lock doesn’t change the time you need
to get your foot up to the brake pedal or always decrease
stopping distance. If you get too close
to the vehicle in
front of you, you won’t have time to apply your brakes
if that vehicle suddenly
slows or stops. Always leave
enough room up ahead to stop, even though you have anti-lock brakes.
Using Anti-Lock
Don’t pump the brakes. Just hold the brake pedal down
firmly and let anti-lock work for you. You may feel a
slight brake pedal pulsation or notice some noise, but
this is normal.
ABS
ACTIVE
When your anti-lock system
is adjusting brake pressure
to help avoid a braking skid,
this light will come on. See
“Anti-Lock Brake System
Active Light” in the Index.
Braking in Emergencies
At some time, nearly every driver gets into a situation
that requires hard braking.
If you have anti-lock, you can steer and brake at the
same time. However, if you don’t have anti-lock, your
first reaction
-- to hit the brake pedal hard and hold it
down
-- may be the wrong thing to do. Your wheels can
stop rolling. Once they do, the vehicle can’t respond to
your steering. Momentum will carry it in whatever direction it was headed when the wheels stopped rolling.
That could be
off the road, into the very thing you were
trying to avoid, or into traffic.
If you don’t have anti-lock, use a “squeeze” braking
technique. This
will give you maximum braking while
maintaining steering control.
You do this by pushing on
the brake pedal with steadily increasing pressure.
In an emergency, you will probably want to squeeze the
brakes hard without locking the wheels. If you hear or
feel the wheels sliding, ease
off the brake pedal. This
will help
you retain steering control. (If you do have
anti-lock, it’s different: see “Anti-Lock Brakes” in
the Index
.)
In many emergencies, steering can help you more than
even
the very best braking.
4-9
Page 157 of 386
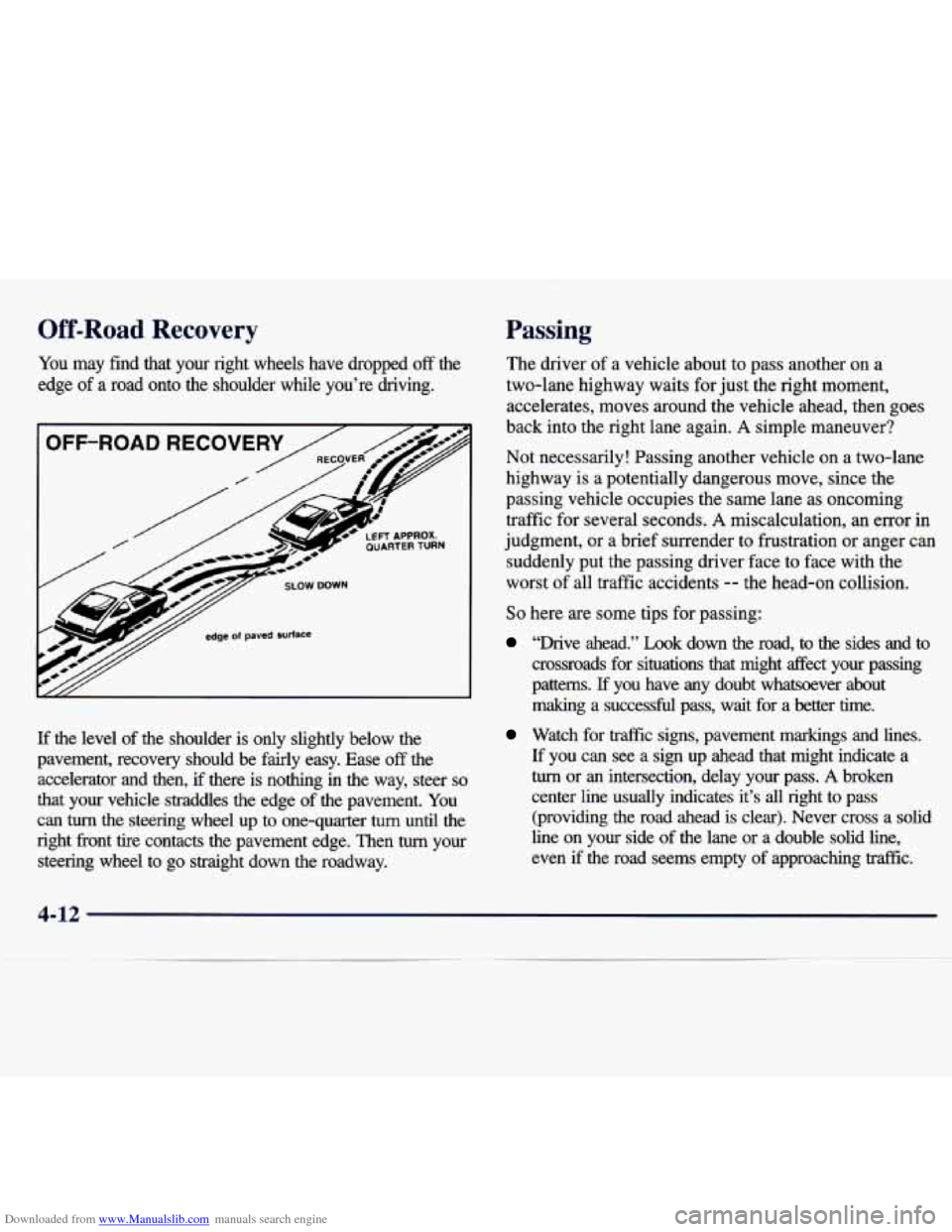
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Off-Road Recovery
You may find that your right wheels have dropped off the
edge
of a road onto the shoulder while you’re driving.
T/ edge of paved surface
If the level of the shoulder is only slightly below the
pavement, recovery should be fairly easy. Ease
off the
accelerator and then, if there is nothing in the way, steer
so
that your vehicle straddles the edge of the pavement. You
can
turn the steering wheel up to one-quarter turn until the
right front tire contacts the pavement edge. Then
turn your
steering wheel to
go straight down the roadway.
Passing
The driver of a vehicle about to pass another on a
two-lane highway waits for just the right moment,
accelerates, moves around the vehicle ahead, then goes
back into the right lane again.
A simple maneuver?
Not necessarily! Passing another vehicle on a two-lane
highway is a potentially dangerous move, since the
passing vehicle occupies the same lane as oncoming traffic for several seconds.
A miscalculation, an error in
judgment, or a brief surrender to frustration or anger can
suddenly put the passing driver face to face with the
worst of all traffic accidents
-- the head-on collision.
So here are some tips for passing:
“Drive ahead.” Look down the road, to the sides and to
crossroads for situations that might
&kt your passing
patterns.
If you have any doubt whatsoever about
making a successful pass, wait for a better time.
Watch for traffic signs, pavement markings and lines.
If you can see a sign up ahead that might indicate a
turn or an intersection, delay your pass. A broken
center line usually indicates it’s
all right to pass
(providing the road ahead is clear). Never cross a solid
line on your side
of the lane or a double solid line,
even if the road seems empty of approaching traffic.
4-12
Page 164 of 386

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine When you drive over obstacles or rough terrain, keep a
firm grip on the steering wheel. Ruts, troughs or other
surface features can jerk the wheel out of your hands if
you’re not prepared.
When you drive over bumps, rocks, or other obstacles,
your wheels can leave the ground.
If this happens, even
with one or two wheels, you can’t control the vehicle as
well or at all.
Because you will be on an unpaved surface, it’s
especially important to avoid sudden acceleration, sudden turns or sudden braking.
Driving on Off-Road Hills
Off-road driving often takes you up, down or across a
hill. Driving safely on hills requires good judgment and
an understanding of what your vehicle can and can’t do.
There
are some hills that simply can’t be driven, no
matter how well built the vehicle.
In a way, off-road driving requires a different kind
of
alertness from driving on paved roads and highways.
There are no road signs, posted speed
limits or signal
lights.
You have to use your own good judgment about
what is safe and what isn’t.
Drinking and driving can be very dangerous on any
road. And this is certainly true for off-road driving.
At
the very time you need special alertness and driving
skills, your reflexes, perceptions and judgment can be
affected by even a small amount
of alcohol. You could
have
a serious -- or even fatal -- accident if you drink
and drive or ride with a driver who has been drinking.
See “Drunken Driving” in the Index.
Many hills are simply too steep for any vehicle. If
you drive up them, you will stall. If you drive
down them, you can’t control your speed. If you
drive across them, you will roll over.
You could be
seriously injured or killed. If you have any doubt
about the steepness, don’t drive the hill.
4-19
Page 168 of 386

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine A CAUTION:
I
Shifting the transfer case to NEUTRAL (N) can
cause your vehicle to roll even if the transmission
is in
PARK (P) (or, if you have the manual
transmission, even
if you’re in gear). This is
because the NEUTRAL
(N) position on the
transfer case overrides the transmission. You or
someone else could be injured. If you are going to
leave your vehicle, set the parking brake and
shift the transmission to PARK
(P) (or, put your
manual transmission in FIRST
(1)). But do not
shift the transfer case to the NEUTRAL
(N)
position. Leave the transfer case in the 2H, 4H or
4L position.
Driving Downhill
When off-roading takes you downhill, you’ll want to
consider a number of things:
0 How steep is the downhill? Will I be able to maintain
vehicle control?
0
0
0
What’s the surface like? Smooth? Rough? Slippery?
Hard-packed dirt? Gravel?
Are there hidden surface obstacles? Ruts?
Logs? Boulders?
What’s at the bottom of the hill?
Is there a hidden
creek bank
or even a river bottom with large rocks?
If you decide you can
go down a hill safely, then try to
keep your vehicle headed straight down, and use a low gear. This way, engine drag can help your brakes and
they won’t have to do all the work. Descend slowly,
keeping your vehicle under control at all times.
Heavy braking when going down
a hill can cause
your brakes to overheat and fade. This could
cause loss
of control and a serious accident.
Apply the brakes lightly when descending
a
hill and use a low gear to keep vehicle speed
under control.
4-23
Page 172 of 386

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Driving in Mud, Sand, Snow or Ice
When you drive in mud, snow or sand, your wheels
won’t get good traction. You can’t accelerate as
quickly, turning is more difficult, and you’ll need
longer braking distances.
It’s best to use a low gear when you’re in mud
-- the
deeper the mud, the lower the gear. In really deep mud,
the idea
is to keep your vehicle moving so you don’t
get stuck.
When you drive on sand, you’ll sense
a change in wheel
traction. But it will depend upon how loosely packed the
sand is. On loosely packed sand (as on beaches or sand
dunes) your tires will tend to sink into the sand. This has
an effect on steering, accelerating and braking.
You may
want to reduce the air pressure in your tires slightly
when driving on sand. This will improve traction. Hard packed snow and ice offer
the worst tire traction.
On these surfaces, it’s very easy to lose control. On wet
ice, for example, the traction is so poor that you will
have difficulty accelerating. And if you do get moving,
poor steering and difficult braking can cause
you to slide
out
of control.
Driving on frozen lakes, ponds or rivers can be
dangerous. Underwater springs, currents under
the ice, or sudden thaws can weaken the ice. Your
vehicle could fall through the ice and you and
your passengers could drown. Drive your vehicle
on safe surfaces only.
4-27
Page 173 of 386

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Driving in Water
Light rain causes no special off-road driving problems. But heavy rain can mean flash flooding, and flood
waters demand extreme caution.
Find out how deep the water is before you drive through
it.
If it’s deep enough to cover your wheel hubs, axles or
exhaust pipe, don’t try it
-- you probably won’t get
through. Also, water that deep can damage your axle
and other vehicle parts.
If the water isn’t too deep, then drive through it slowly.
At fast speeds, water splashes on your ignition system
and your vehicle can stall. Stalling can also occur if you
get your tailpipe under water. And, as long as your
tailpipe is under water, you’ll never be able
to start your
engine. When you
go through water, remember that
when your brakes get wet, it may take you longer
to stop.
A CAUTION:
Driving through rushing water can be dangerous.
Deep water can sweep your vehicle downstream
and you and your passengers could drown.
If it’s
only shallow water, it can still wash
away the
ground from under your tires, and you could lose
traction and roll the vehicle over. Don’t drive
through rushing water.
See “Driving Through Water” in the Index
for more
information on driving through water,
4-28
Page 175 of 386

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Here are some tips on night driving.
Drive defensively.
Don’t drink and drive.
Adjust your inside rearview mirror to reduce the
Since you can’t see as well, you may need to
glare from headlamps behind you.
slow down and keep more space between you and
other vehicles.
Slow down, especially on higher speed roads. Your
headlamps can light up only
so much road ahead.
In remote areas, watch for animals.
If you’re tired, pull off the road in a safe place
and rest.
Night Vision
No one can see as well at night as in the daytime. But as
we get older these differences increase.
A 50-year-old
driver may require at least twice as much light
to see the
same thing at night as a 20-year-old.
What you do in the daytime can also affect your night
vision. For example, if you spend the day in bright
sunshine you are wise to wear sunglasses. Your eyes will
have less trouble adjusting to night. But
if you’re driving, don’t wear sunglasses
at night. They may cut
down on glare from headlamps, but they
also make a lot
of things invisible.
You can be temporarily blinded by approaching
headlamps. It can take a second or two, or even several
seconds, for your eyes to readjust to the dark. When you
are faced with severe glare (as from a driver who
doesn’t lower the high beams, or a vehicle with
misaimed headlamps), slow down a little. Avoid staring
directly into the approaching headlamps.
Keep your windshield and all the glass on your vehicle
clean
-- inside and out. Glare at night is made much
worse by dirt on the glass. Even the inside of the glass
can build up a film caused by dust. Dirty glass makes
lights dazzle and flash more
than clean glass would,
making the pupils of your eyes contract repeatedly.
Remember that your headlamps light up far less of a
roadway when you
are in a turn or curve. Keep your
eyes moving; that way, it’s easier to pick out dimly
lighted objects. Just as your headlamps should be
checked regularly for proper aim,
so should your eyes
be examined regularly. Some drivers suffer from night
blindness
-- the inability to see in dim light -- and
aren’t even aware of it.
4-30
Page 177 of 386

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine lb
CAC 'ION:
-
Wet brakes can cause accidents. They won't work
as well in a quick stop and may cause pulling to
one side. You could lose control of the vehicle.
After driving through a large puddle
of water or
a car wash, apply your brake pedal lightly until
your brakes work normally.
Driving too fast through large water puddles or even going through some car washes can cause problems,
too.
The water may affect your brakes. Try to avoid puddles.
But if you can't, try to slow down before you hit them.
4-32
Page 178 of 386

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Hydroplaning
Hydroplaning is dangerous. So much water can build up
under your tires that they can actually ride on the water.
This can happen if the road is
wet enough and you’re
going fast enough. When your vehicle is hydroplaning,
it has little
or no contact with the road.
Hydroplaning doesn’t happen often. But it can if your
tires do not have much tread or
if the pressure in one or
more
is low. It can happen if a lot of water is standing on
the road. If you can see reflections from trees, telephone
poles or other vehicles, and raindrops “dimple” the
water’s surface, there could be hydroplaning.
Hydroplaning usually happens at higher speeds. There
just isn’t a hard and fast rule about hydroplaning. The
best advice is to slow down when it is raining.
Driving Through Deep Standing Water
NOTICE:
If you drive too quickly through deep puddles or
standing water, water can come in through your engine’s air intake and badly damage your
engine. Never drive through water that
is slightly
lower than the underbody
of your vehicle. If you
can’t avoid deep puddles or standing water, drive
through them very slowly.
Some Other Rainy Weather Tips
Besides slowing down, allow some extra following
distance. And be especially careful when you pass
another vehicle. Allow yourself more clear room
ahead, and be prepared to have your view restricted
by road spray.
0 Have good tires with proper tread depth. (See “Tires” in the Index.)
4-33
Page 179 of 386

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 3ty Driving Here are ways to increase your safety in city driving:
Know the best way to get to where you are
going. Get
a city map and plan your trip into an
unknown part of the city just as you would for a
cross-country trip.
Try to use the freeways that rim and crisscross most
large cities. You’ll save time and energy. (See the
next part, “Freeway Driving.”)
light
is there because the corner is busy enough to
need it. When a light turns green, and just before you
start to move, check both ways for vehicles that have
not cleared the intersection or may be running the
red light.
Treat a green light as a warning signal. A traffic
One of the biggest problems with city streets is the
amount
of traffic on them. You’ll want to watch out for
what the other drivers are doing and pay attention to
traffic signals.
4-34