transfer CHRYSLER CARAVAN 2002 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2002, Model line: CARAVAN, Model: CHRYSLER CARAVAN 2002Pages: 2399, PDF Size: 57.96 MB
Page 14 of 2399

LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE
SPECIFICATIONS - FLUID CAPACITIES.......1
INTERNATIONAL SYMBOLS
DESCRIPTION..........................2
FLUID TYPES
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - ENGINE OIL AND
LUBRICANTS.........................2
DESCRIPTION - ENGINE COOLANT........3
DESCRIPTION - FLEXIBLE FUEL ENGINE
OIL .................................3
DESCRIPTION - AUTOMATIC
TRANSMISSION FLUID..................4
DESCRIPTION - FUEL REQUIREMENTS.....4
DESCRIPTION - FUEL REQUIREMENTS -
DIESEL ENGINE.......................6DESCRIPTION - ENGINE OIL - DIESEL
ENGINES............................6
FLUID FILL/CHECK LOCATIONS
DESCRIPTION..........................6
LUBRICATION POINTS
DESCRIPTION..........................6
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES
DESCRIPTION..........................6
HOISTING
STANDARD PROCEDURE - HOISTING........6
JUMP STARTING
STANDARD PROCEDURE - JUMP STARTING . . 7
TOWING
STANDARD PROCEDURE - TOWING.........8
LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE
SPECIFICATIONS - FLUID CAPACITIES
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Fuel Tank (Gas) 75 L (20 gal.)
Fuel Tank (Diesel) 75 L (20 gal.)
Engine Oil* - 2.4 L 4.7 L (5.0 qts.)
Engine Oil* - 3.3/3.8 L 4.0 L (4.5 qts.)
Engine Oil* - 2.5 L
(Diesel)6.0 L (6.3 qts.)
Cooling System** - 2.4 L 10.7 L (11.4 qts.)
Cooling System** - 2.5 L
Turbo Diesel with
Auxiliary Heater13.8 L (14.6 qts.)
Cooling System** -
3.3/3.8 L without Auxiliary
Heater12.6 L (13.4 qts.)
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Cooling System** -
3.3/3.8 L with Auxiliary
Heater15.4 L (16.3 qts.)
Automatic Transaxle -
Service Fill3.8 L (4.0 qts.)
Automatic Transaxle -
31TH Overhaul Fill8.6 L (9.1 qts.)
Automatic Transaxle -
41TE Overhaul Fill9.2 L (9.7 qts.)
Manual Transaxle (T850
5-Speed)2.4-2.7 L (2.5-2.9 qts.)
AWD Power Transfer Unit 1.15 L (2.4 pts.)
Power Steering 1.2 L (2.5 pts.)
AWD Bi-directional
Overrunning Clutch0.575 L (1.22 pts.)
AWD Rear Carrier 0.7 L (1.48 pts.)
* (includes oil filter)
** (includes heater and recovery/reserve bottle)
RSLUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE0-1
ProCarManuals.com
Page 16 of 2399

GEAR LUBRICANTS
SAE ratings also apply to multigrade gear lubri-
cants. In addition, API classification defines the
lubricants usage. Such as API GL-5 and SAE 75W-
90.
LUBRICANTS AND GREASES
Lubricating grease is rated for quality and usage
by the NLGI. All approved products have the NLGI
symbol (Fig. 4) on the label. At the bottom of the
NLGI symbol is the usage and quality identification
letters. Wheel bearing lubricant is identified by the
letter ªGº. Chassis lubricant is identified by the letter
ªLº. The letter following the usage letter indicates
the quality of the lubricant. The following symbols
indicate the highest quality.
SPECIALIZED LUBRICANTS AND OILS
Some maintenance or repair procedures may
require the use of specialized lubricants or oils. Con-
sult the appropriate sections in this manual for the
correct application of these lubricants.
DESCRIPTION - ENGINE COOLANT
WARNING: ANTIFREEZE IS AN ETHYLENE GLYCOL
BASE COOLANT AND IS HARMFUL IF SWAL-
LOWED OR INHALED. IF SWALLOWED, DRINK
TWO GLASSES OF WATER AND INDUCE VOMIT-
ING. IF INHALED, MOVE TO FRESH AIR AREA.
SEEK MEDICAL ATTENTION IMMEDIATELY. DO NOT
STORE IN OPEN OR UNMARKED CONTAINERS.
WASH SKIN AND CLOTHING THOROUGHLY AFTER
COMING IN CONTACT WITH ETHYLENE GLYCOL.
KEEP OUT OF REACH OF CHILDREN. DISPOSE OF
GLYCOL BASE COOLANT PROPERLY, CONTACT
YOUR DEALER OR GOVERNMENT AGENCY FOR
LOCATION OF COLLECTION CENTER IN YOUR
AREA. DO NOT OPEN A COOLING SYSTEM WHEN
THE ENGINE IS AT OPERATING TEMPERATURE OR
HOT UNDER PRESSURE, PERSONAL INJURY CAN
RESULT. AVOID RADIATOR COOLING FAN WHENENGINE COMPARTMENT RELATED SERVICE IS
PERFORMED, PERSONAL INJURY CAN RESULT.
CAUTION: Use of Propylene Glycol based coolants
is not recommended, as they provide less freeze
protection and less boiling protection.
The cooling system is designed around the coolant.
The coolant must accept heat from engine metal, in
the cylinder head area near the exhaust valves and
engine block. Then coolant carries the heat to the
radiator where the tube/fin radiator can transfer the
heat to the air.
The use of aluminum cylinder blocks, cylinder
heads, and water pumps requires special corrosion
protection. MopartAntifreeze/Coolant, 5
Year/100,000 Mile Formula (MS-9769), or the equiva-
lent ethylene glycol base coolant with hybrid organic
corrosion inhibitors (called HOAT, for Hybrid Organic
Additive Technology) is recommended. This coolant
offers the best engine cooling without corrosion when
mixed with 50% Ethylene Glycol and 50% distilled
water to obtain a freeze point of -37ÉC (-35ÉF). If it
loses color or becomes contaminated, drain, flush,
and replace with fresh properly mixed coolant solu-
tion.
The green coolantMUST NOT BE MIXEDwith
the orange or magenta coolants. When replacing cool-
ant the complete system flush must be performed
before using the replacement coolant.
CAUTION: MoparTAntifreeze/Coolant, 5
Year/100,000 Mile Formula (MS-9769) may not be
mixed with any other type of antifreeze. Doing so
will reduce the corrosion protection and may result
in premature water pump seal failure. If non-HOAT
coolant is introduced into the cooling system in an
emergency, it should be replaced with the specified
coolant as soon as possible.DESCRIPTION - FLEXIBLE FUEL ENGINE OIL
The information in this section is for Flexible Fuel
Vehicles (FFV) only. These vehicles can be identified
by the unique Fuel Filler Door Label that states
Ethanol (E-85) or Unleaded Gasoline Only. This sec-
tion only covers those subjects that are unique to
these vehicles. Please refer to the other sections of
this manual for information on features that are
common between Flexible Fuel and gasoline only
powered vehicles.
ETHANOL FUEL (E-85)
E-85 is a mixture of approximately 85% fuel etha-
nol and 15% unleaded gasoline.
Fig. 4 NLGI SYMBOL
1 - WHEEL BEARINGS
2 - CHASSIS LUBRICATION
3 - CHASSIS AND WHEEL BEARINGS
RSLUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE0-3
FLUID TYPES (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 101 of 2399

PROPELLER SHAFT
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
PROPELLER SHAFT
DESCRIPTION.........................22
OPERATION...........................22REMOVAL.............................23
INSTALLATION.........................23
SPECIFICATIONS - PROPELLER SHAFT.....23
PROPELLER SHAFT
DESCRIPTION
WARNING: Due to propeller shaft imbalance con-
cerns, the propeller shaft can only be serviced as
an assembly.
AWD models utilize a ªtwo-pieceº propeller shaft
(Fig. 1) to transmit power to the rear driveline mod-
ule assembly. This two-piece design consists of:
²Front and rear shaft segments.
²Plunging center CV joint²Center support bearing
²Rubber coupler at driveline module flange
The front shaft segment utilizes a CV joint at the
power transfer unit connection, and a plunging CV
joint at the center bearing location.
The rear shaft segment utilizes a center support
bearing at the forward position, and a rubber coupler
at the driveline module flange.
OPERATION
The propeller shaft (Fig. 1) is used to transmit
torque from the transaxle power transfer unit (PTU)
Fig. 1 Propeller Shaft Removal/Installation
1 - PTU FLANGE 3 - REAR DRIVELINE MODULE 5 - BOLT-CENTER SUPPORT BEARING-TO-
CROSSMEMBER
2 - CROSSMEMBER 4 - BOLT-PROPELLER SHAFT COUPLER-
T0-DRIVELINE MODULE6 - PROPELLER SHAFT ASSEMBLY
3 - 22 PROPELLER SHAFTRS
ProCarManuals.com
Page 102 of 2399

to the rear driveline module of AWD equipped mod-
els.
The propeller shaft front half utilizes a CV joint at
the PTU flange, and a plunging CV joint at the cen-
ter bearing location. These joints are flexible, allow-
ing for torsional movement of the powertrain.
The propeller shaft rear half utilizes a center sup-
port bearing, which supports this two-piece assembly.
The bearing also stabilizes the rear shaft segment to
minimize axle wind-up. The rubber coupler at the
driveline module flange dampens out propeller shaft
torsional vibrations, as the driveline module it con-
nects to is fastened to the vehicle body.
REMOVAL
CAUTION: Propeller shaft removal is a two-man
operation. Never allow propeller shaft to hang while
connected to power transfer unit (PTU) or rear driv-
eline module flanges. A helper is required.
(1) Make sure transaxle is in neutral (N). Using
chalk, mark propeller shaft flanges at PTU and rear
driveline module for installation reference.
(2) Remove six propeller shaft-to-power transfer
unit bolts.
(3) Have helper remove three propeller shaft rub-
ber coupler-to-driveline module bolts while he/she
supports rear shaft by hand.
(4) Remove center bearing support-to-crossmember
bolts, while supporting front shaft with two hands.(5) Lower propeller shaft assembly to ground,
using care not to damage fore and aft flanges (Fig.
1).
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Propeller shaft installation is a two-man
operation. Never allow propeller shaft to hang while
connected to power transfer unit (PTU) or rear driv-
eline module flanges. A helper is required.
(1) Make sure transaxle is in Neutral (N) position.
(2) Obtain a helper and lift propeller shaft assem-
bly into position (Fig. 1).
(3) While helper supports front half of shaft level
to underbody, align paint marks at driveline module
flange and install three propeller shaft rubber cou-
pler-to-rear driveline module bolts by hand. Do not
torque at this time.
(4) While helper supports front half of shaft level
to underbody, align chalk marks at PTU flange.
Install six propeller shaft-to-PTU flange bolts and
torque to 30 N´m (22 ft. lbs.). Torque bolts alternately
to ensure proper flange mating.
(5) Place center bearing into position. Install and
torque center bearing-to-crossmember bolts to 54
N´m (40 ft. lbs.).
(6) Torque propeller shaft rubber coupler-to-rear
driveline module assembly to 54 N´m (40 ft. lbs.).
SPECIFICATIONS - PROPELLER SHAFT
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Bolt, Propeller Shaft Front
Flange-to-PTU Flange30 22 Ð
Bolt, Propeller Shaft Rear
Flange-to-Driveline Module Flange54 40 Ð
Bolt, Center Support Bearing-to-
Body54 40 Ð
RSPROPELLER SHAFT3-23
PROPELLER SHAFT (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 106 of 2399
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REAR DRIVELINE
MODULE OPERATION
Driveline module operation requires relatively
straight-forward diagnosis. Refer to the following
chart:
DRIVELINE MODULE DIAGNOSIS CHART
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
Rear wheels not
overrunning1) Bi-directional overrunning clutch
failure1) Replace overrunning clutch
components as required
No AWD in forward or
reverse directions, propeller
shaft turning1) Bi-directional overrunning clutch
failure1) Replace overrunning clutch
components as required
2) Viscous coupling failure 2) Replace viscous coupling
3) Rear differential failure 3) Replace the rear differential
assembly
No AWD in forward or
reverse directions, propeller
shaft not turning1) Power transfer unit failure. 1) Replace power transfer unit
components as necessary
Vibration at all speeds,
continuous torque transfer1) Mis-matched tires, worn tires on
front axle.1) Replace worn or incorrect
(mis-matched) tires with same
make and size
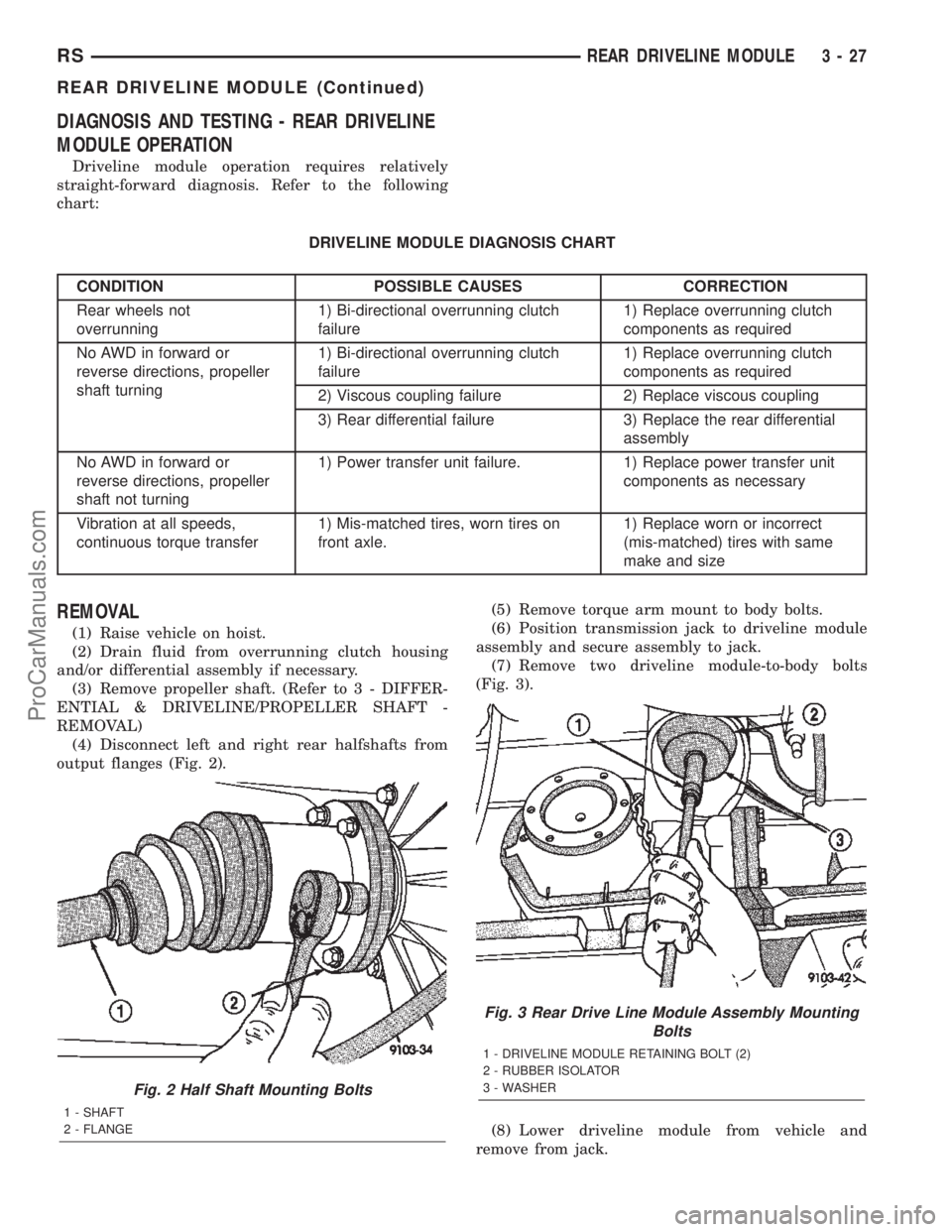
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(2) Drain fluid from overrunning clutch housing
and/or differential assembly if necessary.
(3) Remove propeller shaft. (Refer to 3 - DIFFER-
ENTIAL & DRIVELINE/PROPELLER SHAFT -
REMOVAL)
(4) Disconnect left and right rear halfshafts from
output flanges (Fig. 2).(5) Remove torque arm mount to body bolts.
(6) Position transmission jack to driveline module
assembly and secure assembly to jack.
(7) Remove two driveline module-to-body bolts
(Fig. 3).
(8) Lower driveline module from vehicle and
remove from jack.
Fig. 2 Half Shaft Mounting Bolts
1 - SHAFT
2 - FLANGE
Fig. 3 Rear Drive Line Module Assembly Mounting
Bolts
1 - DRIVELINE MODULE RETAINING BOLT (2)
2 - RUBBER ISOLATOR
3 - WASHER
RSREAR DRIVELINE MODULE3-27
REAR DRIVELINE MODULE (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 115 of 2399

BI-DIRECTIONAL
OVERRUNNING CLUTCH
DESCRIPTION
The bi-directional overrunning clutch (BOC) (Fig.
28) works as a mechanical disconnect between the
front and rear axles, preventing torque from being
transferred from the rear axle to the front. The BOC
is a simply an overrunning clutch which works in
both clockwise and counter-clockwise rotations. This
means that when the output (the rear axle) is rotat-
ing faster in one direction than the input (front axle),
there is no torque transmission. But when the input
speed is equal to the output speed, the unit becomes
locked. The BOC provides significant benefits regard-
ing braking stability, handling, and driveline durabil-
ity. Disconnecting the front and the rear driveline
during braking helps to maintain the braking stabil-
ity of an AWD vehicle. In an ABS/braking event, the
locking of the rear wheels must be avoided for stabil-
ity reasons. Therefore brake systems are designed to
lock the front wheels first. Any torque transfer from
the rear axle to the front axle disturbs the ABS/brak-
ing system and causes potential instabilities on aslippery surface. The BOC de-couples the rear driv-
eline as soon the rear wheels begin to spin faster
than the front wheels (front wheels locked) in order
to provide increased braking stability. Furthermore
the BOC also reduces the likelihood of throttle off
over-steer during cornering. In a throttle off maneu-
ver, the BOC once again de-couples the rear driveline
forcing all the engine brake torque to the front
wheels. This eliminates the chance of lateral slip on
the rear axle and increases it on the front. The vehi-
cle will therefore tend to understeer, a situation
which is considered easier to manage in most circum-
stances. During this maneuver, and during the ABS
braking event, the BOC does not transmit torque
through to the rear wheels. The rear driveline mod-
ule, with the BOC, will perform the same as a front
wheel drive vehicle during these events. The gear
ratio offset between the front and rear differentials
force the BOC into the overrunning mode most of the
time. This allows BOC to significantly reduce the
rolling resistance of the vehicle, which improves fuel
consumption, allows the downsizing of the driveline
components, and prevents the PTU and propshaft
joints from overheating.
3 - 36 REAR DRIVELINE MODULERS
ProCarManuals.com
Page 117 of 2399

OPERATION
In order to achieve all-wheel drive operation in
reverse, the overrunning clutch locking functional direc-
tion must be reversible. The bi-directional overrunning
clutch (BOC) changes the operational mode direction
depending on the propeller shaft direction. The propel-
ler shaft rotates in the clockwise (when viewed from the
front) direction when the vehicle is moving forward,
which indexes the BOC to the forward overrunning
position. When the vehicle is in reverse, the propeller
shaft will rotate counter-clockwise and index the BOC
to the reverse overrunning position.
The BOC acts as a mechanical stator. It is active
(transmitting torque), or it is not active and in over-
running mode (not transmitting torque). This ªall or
nothingº approach to torque transfer would cause a
sudden application of all available power to the rear
wheels, which is not desirable. Therefore it is run in
series with a viscous coupler to smooth, dampen, and
limit the transmission of torque to the rear axle and
to prevent a step style torque input to the rear axle.
STEADY STATE, LOW TO MODERATE SPEED, NO
FRONT WHEEL SLIP, FORWARD DIRECTION
During normal driving conditions, (no wheel slip), the
inner shaft (front axle) and outer race (viscous coupler)
are running at different speeds due to the different gear
ratios between the front and rear differentials. In this
condition, the outer race is always spinning faster (over-
driving between 5-32 rpm) than the inner shaft. When
the BOC (Fig. 29) is running under these conditions, at
low vehicle speeds the drag shoes and the cage keep the
rollers up on the left side (forward side) of the inner
shaft flats. This is what is known as ªoverrunning
mode.º Notice that when the clutch is in overrunning
mode, the rollers are spinning clockwise and with the
outer race, thus no torque is being transferred.
NOTE: Low speed, forward and reverse operation is
identical, just in opposite directions. (Fig. 29) shows
forward direction in reverse the rollers are on the other
side of the flats due to a reversal of the cage force.
TRANSIENT CONDITION (BOC LOCKED), FRONT
WHEEL SLIP, FORWARD DIRECTION
When the front wheels lose traction and begin to
slip, the propeller shaft and rear axle pinion speed
difference decreases to zero. At this point the input
shaft (cam) becomes the driving member of the BOC
(Fig. 30), compressing the rollers against the outer
race. This locks the input shaft with the outer race
and transmits torque to the housing of the viscous
coupler, that in turn transmits torque to the rear
axle pinion. It should also be noted that when the
device is locked, the inner shaft and the outer raceare rotating at the same speed. The rollers are
pinched at this point and will stay locked until a
torque reversal (no front wheel slip) occurs. When
locked, the viscous coupler slips during the torque
transfer and the amount of torque transferred is
dependent on the coupling characteristic and the
amount of front wheel slip.
Fig. 29 BOC Operation at Low Speeds With No
Front Wheel Slip
1 - CAGE
2 - ROLLER
3 - INPUT SHAFT
Fig. 30 BOC Operation with Front Wheel Slip
3 - 38 REAR DRIVELINE MODULERS
BI-DIRECTIONAL OVERRUNNING CLUTCH (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 119 of 2399
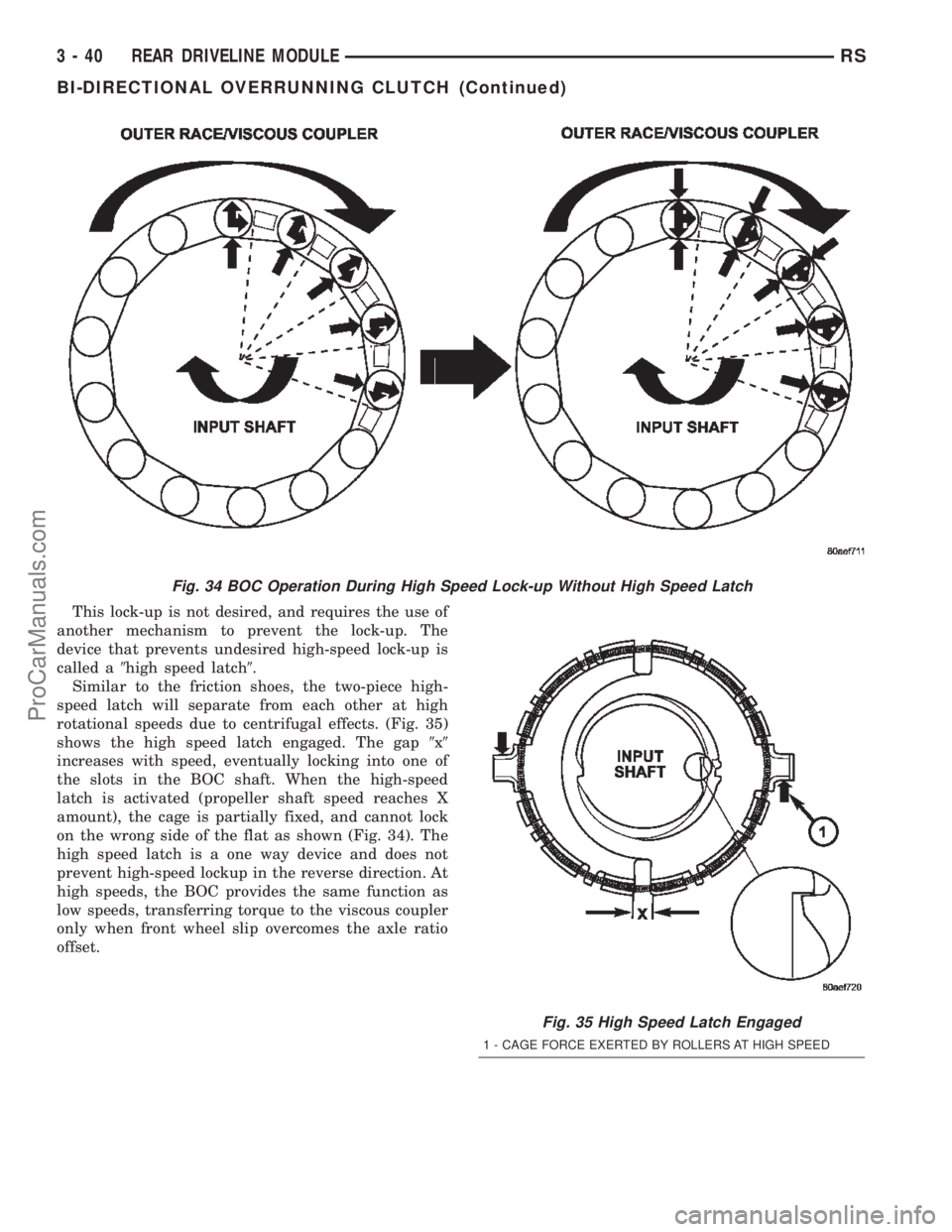
This lock-up is not desired, and requires the use of
another mechanism to prevent the lock-up. The
device that prevents undesired high-speed lock-up is
called a9high speed latch9.
Similar to the friction shoes, the two-piece high-
speed latch will separate from each other at high
rotational speeds due to centrifugal effects. (Fig. 35)
shows the high speed latch engaged. The gap9x9
increases with speed, eventually locking into one of
the slots in the BOC shaft. When the high-speed
latch is activated (propeller shaft speed reaches X
amount), the cage is partially fixed, and cannot lock
on the wrong side of the flat as shown (Fig. 34). The
high speed latch is a one way device and does not
prevent high-speed lockup in the reverse direction. At
high speeds, the BOC provides the same function as
low speeds, transferring torque to the viscous coupler
only when front wheel slip overcomes the axle ratio
offset.
Fig. 34 BOC Operation During High Speed Lock-up Without High Speed Latch
Fig. 35 High Speed Latch Engaged
1 - CAGE FORCE EXERTED BY ROLLERS AT HIGH SPEED
3 - 40 REAR DRIVELINE MODULERS
BI-DIRECTIONAL OVERRUNNING CLUTCH (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 120 of 2399

At high speed, the rollers are forced outward to the
outer race because of centrifugal force. At high
speeds, the friction shoes can no longer prevent lock-
up. When the teeth on the high-speed latch engage
into the input shaft, it keeps the rollers centered
above the flats because the tabs on the latch are
locked into the cage. (Fig. 36) shows the roller config-
uration with the High-Speed Latch engaged.
On the BOC shaft, the high speed latch teeth lock
up in the grooved areas, shown in (Fig. 37), when the
turning speed reaches the critical value. (Fig. 37)
also shows the outer race/viscous coupler. Notice the
surface (outer race) the rollers mate against when
transferring torque.
DIFFERENTIAL ASSEMBLY
DESCRIPTION
The differential gear system divides the torque
between the axle shafts. It allows the axle shafts to
rotate at different speeds when turning corners.
Each differential side gear is splined to an axle
shaft. The pinion gears are mounted on a pinion
mate shaft and are free to rotate on the shaft. The
pinion gear is fitted in a bore in the differential case
and is positioned at a right angle to the axle shafts.
OPERATION
In operation, power flow occurs as follows:
²The pinion gear rotates the ring gear²The ring gear (bolted to the differential case)
rotates the case
²The differential pinion gears (mounted on the
pinion mate shaft in the case) rotate the side gears
²The side gears (splined to the axle shafts) rotate
the shafts
During straight-ahead driving, the differential pin-
ion gears do not rotate on the pinion mate shaft. This
occurs because input torque applied to the gears is
divided and distributed equally between the two side
gears. As a result, the pinion gears revolve with the
pinion mate shaft but do not rotate around it (Fig.
38).
Fig. 36 BOC Operation at High Speed with High
Speed Latch
Fig. 37 BOC Input Shaft
1 - GROOVED AREA (2 LOCATIONS)
2 - ROLLER MATING SURFACE
Fig. 38 Differential OperationÐStraight Ahead
Driving
1 - IN STRAIGHT AHEAD DRIVING EACH WHEEL ROTATES AT
100% OF CASE SPEED
2 - PINION GEAR
3 - SIDE GEAR
4 - PINION GEARS ROTATE WITH CASE
RSREAR DRIVELINE MODULE3-41
BI-DIRECTIONAL OVERRUNNING CLUTCH (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 132 of 2399

SUPPORT PLATE - DRUM BRAKE
REMOVAL.............................64
INSTALLATION.........................64
WHEEL CYLINDERS
REMOVAL.............................65
INSPECTION..........................65
INSTALLATION.........................65
PARKING BRAKE
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION........................65
DESCRIPTION - EXPORT...............66
OPERATION...........................66
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - PARKING
BRAKE AUTOMATIC ADJUSTER TENSION
RELEASE...........................66
STANDARD PROCEDURE - PARKING
BRAKE AUTOMATIC ADJUSTER TENSION
RESET.............................67
CABLES - PARKING BRAKE
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - PARKING BRAKE CABLE
(FRONT)............................67
REMOVAL - PARKING BRAKE CABLE
(INTERMEDIATE)......................68
REMOVAL - PARKING BRAKE CABLE
(RIGHT REAR)........................69
REMOVAL - PARKING BRAKE CABLE (LEFT
REAR)..............................70INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - PARKING BRAKE CABLE
(FRONT)............................71
INSTALLATION - PARKING BRAKE CABLE
(INTERMEDIATE)......................71
INSTALLATION - PARKING BRAKE CABLE
(RIGHT REAR)........................72
INSTALLATION - PARKING BRAKE CABLE
(LEFT REAR).........................72
ADJUSTMENTS
ADJUSTMENT - PARKING BRAKE CABLES . 72
CABLES - PARKING BRAKE (EXPORT)
REMOVAL - FRONT CABLE...............72
INSTALLATION - FRONT CABLE............72
LEVER - PARKING BRAKE
REMOVAL.............................72
INSTALLATION.........................73
LEVER - PARKING BRAKE (EXPORT)
REMOVAL - PARKING BRAKE LEVER AND
FRONT CABLE.......................74
INSTALLATION - PARKING BRAKE LEVER
AND FRONT CABLE...................75
SHOES - PARKING BRAKE
REMOVAL.............................75
INSTALLATION.........................81
ADJUSTMENTS
ADJUSTMENT - PARKING BRAKE SHOES . . 83
BRAKES - BASE
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - BASE BRAKES
The base brake system consists of the following
components:
²Brake pedal
²Power brake booster
²Master cylinder
²Brake tubes and hoses
²Proportioning valve (non-ABS vehicles only)
²Disc brakes
²Drum brakes
²Brake lamp switch
²Brake fluid level switch
²Parking brakes
Front disc brakes control the braking of the front
wheels; rear braking is controlled by rear drum
brakes or rear disc brakes depending on options.
The hydraulic brake system is diagonally split on
both the non-antilock braking systems and antilock
braking systems. That means the left front and right
rear brakes are on one hydraulic circuit and the right
front and left rear are on the other.For information on the brake lamp switch, (Refer
to 8 - ELECTRICAL/LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERI-
OR/BRAKE LAMP SWITCH - DESCRIPTION)
Vehicles equipped with the optional antilock brake
system (ABS) use a system designated Mark 20e. It
is available with or without traction control. This
system shares most base brake hardware used on
vehicles without ABS. ABS components are described
in detail in ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM.
DESCRIPTION - BASE BRAKES (EXPORT)
Four-Wheel Disc Antilock Brakes are standard on
all models.
OPERATION - BASE BRAKES
When a vehicle needs to be stopped, the driver
applies the brake pedal. The brake pedal pushes the
input rod of the power brake booster into the booster.
The booster uses vacuum to ease pedal effort as force
is transferred through the booster to the master cyl-
inder. The booster's output rod pushes in the master
cylinder's primary and secondary pistons applying
hydraulic pressure through the chassis brake tubes
to the brakes at each tire and wheel assembly.
The parking brakes are foot-operated. When
applied, the parking brake lever pulls on cables that
actuate brake shoes at each rear wheel. These shoes
RSBRAKES - BASE5-3
ProCarManuals.com