ors CHRYSLER CARAVAN 2005 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2005, Model line: CARAVAN, Model: CHRYSLER CARAVAN 2005Pages: 2339, PDF Size: 59.69 MB
Page 1780 of 2339

BODY
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
BODY
DESCRIPTION - VEHICLE IDENTIFICATION....1
WARNING
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS AND WARNINGS . . . 1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
WATER LEAKS........................1
WIND NOISE..........................2
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - PLASTIC BODY
PANEL REPAIR........................3
STANDARD PROCEDURE - HEAT STAKING . . 9
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE............................10
BODY LUBRICATION...................12
SPECIAL TOOLS
BODY..............................13DOOR - FRONT.........................14
DOORS - SLIDING.......................24
DECKLID/HATCH/LIFTGATE/TAILGATE.......40
EXTERIOR.............................45
HOOD.................................62
INSTRUMENT PANEL.....................65
INTERIOR..............................78
PAINT................................100
SEATS...............................102
STATIONARY GLASS....................161
WEATHERSTRIP/SEALS..................166
SUNROOF.............................169
BODY STRUCTURE.....................177
BODY
DESCRIPTION - VEHICLE IDENTIFICATION
Throughout this group, references to the
DaimlerChrysler Corporation vehicle family identifi-
cation code are used when describing a procedure
that is unique to that vehicle. Refer to Introduction
Group of this manual for detailed information on
vehicle identification. If a procedure is common to all
vehicles covered in this manual, no reference will be
made to a vehicle family code.
WARNING
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS AND WARNINGS
WARNING: USE A OSHA APPROVED BREATHING
FILTER WHEN SPRAYING PAINT OR SOLVENTS IN
A CONFINED AREA. PERSONAL INJURY CAN
RESULT.
AVOID PROLONGED SKIN CONTACT WITH PETRO-
LEUM OR ALCOHOL ± BASED CLEANING SOL-
VENTS. PERSONAL INJURY CAN RESULT.
DO NOT STAND UNDER A HOISTED VEHICLE THAT
IS NOT PROPERLY SUPPORTED ON SAFETY
STANDS. PERSONAL INJURY CAN RESULT.
CAUTION: When holes must be drilled or punched
in an inner body panel, verify depth of space to the
outer body panel, electrical wiring, or other compo-nents. Damage to vehicle can result.
Do not weld exterior panels unless combustible
material on the interior of vehicle is removed from
the repair area. Fire or hazardous conditions, can
result.
Always have a fire extinguisher ready for use when
welding.
Disconnect the negative (-) cable clamp from the
battery when servicing electrical components that
are live when the ignition is OFF. Damage to electri-
cal system can result.
Do not use abrasive chemicals or compounds on
painted surfaces. Damage to finish can result.
Do not use harsh alkaline based cleaning solvents
on painted or upholstered surfaces. Damage to fin-
ish or color can result.
Do not hammer or pound on plastic trim panel
when servicing interior trim. Plastic panels can
break.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
WATER LEAKS
Water leaks can be caused by poor sealing,
improper body component alignment, body seam
porosity, missing plugs, or blocked drain holes. Cen-
trifugal and gravitational force can cause water to
drip from a location away from the actual leak point,
making leak detection difficult. All body sealing
points should be water tight in normal wet-driving
conditions. Water flowing downward from the front of
RSBODY23-1
Page 1781 of 2339

the vehicle should not enter the passenger or luggage
compartment. Moving sealing surfaces will not
always seal water tight under all conditions. At
times, side glass or door seals will allow water to
enter the passenger compartment during high pres-
sure washing or hard driving rain (severe) condi-
tions. Overcompensating on door or glass
adjustments to stop a water leak that occurs under
severe conditions can cause premature seal wear and
excessive closing or latching effort. After completing
a repair, water test vehicle to verify leak has stopped
before returning vehicle to use.
VISUAL INSPECTION BEFORE WATER LEAK TESTS
Verify that floor and body plugs are in place, body
drains are clear, and body components are properly
aligned and sealed. If component alignment or seal-
ing is necessary, refer to the appropriate section of
this group for proper procedures.
WATER LEAK TESTS
WARNING: DO NOT USE ELECTRIC SHOP LIGHTS
OR TOOLS IN WATER TEST AREA. PERSONAL
INJURY CAN RESULT.
When the conditions causing a water leak have
been determined, simulate the conditions as closely
as possible.
²If a leak occurs with the vehicle parked in a
steady light rain, flood the leak area with an open-
ended garden hose.
²If a leak occurs while driving at highway speeds
in a steady rain, test the leak area with a reasonable
velocity stream or fan spray of water. Direct the
spray in a direction comparable to actual conditions.
²If a leak occurs when the vehicle is parked on an
incline, hoist the end or side of the vehicle to simu-
late this condition. This method can be used when
the leak occurs when the vehicle accelerates, stops or
turns. If the leak occurs on acceleration, hoist the
front of the vehicle. If the leak occurs when braking,
hoist the back of the vehicle. If the leak occurs on left
turns, hoist the left side of the vehicle. If the leak
occurs on right turns, hoist the right side of the vehi-
cle. For hoisting recommendations (Refer to LUBRI-
CATION & MAINTENANCE/HOISTING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE).
WATER LEAK DETECTION
To detect a water leak point-of-entry, do a water
test and watch for water tracks or droplets forming
on the inside of the vehicle. If necessary, remove inte-
rior trim covers or panels to gain visual access to the
leak area. If the hose cannot be positioned without
being held, have someone help do the water test.Some water leaks must be tested for a considerable
length of time to become apparent. When a leak
appears, find the highest point of the water track or
drop. The highest point usually will show the point of
entry. After leak point has been found, repair the
leak and water test to verify that the leak has
stopped.
Locating the entry point of water that is leaking
into a cavity between panels can be difficult. The
trapped water may splash or run from the cavity,
often at a distance from the entry point. Most water
leaks of this type become apparent after accelerating,
stopping, turning, or when on an incline.
MIRROR INSPECTION METHOD
When a leak point area is visually obstructed, use
a suitable mirror to gain visual access. A mirror can
also be used to deflect light to a limited-access area
to assist in locating a leak point.
BRIGHT LIGHT LEAK TEST METHOD
Some water leaks in the luggage compartment can
be detected without water testing. Position the vehi-
cle in a brightly lit area. From inside the darkened
luggage compartment inspect around seals and body
seams. If necessary, have a helper direct a drop light
over the suspected leak areas around the luggage
compartment. If light is visible through a normally
sealed location, water could enter through the open-
ing.
PRESSURIZED LEAK TEST METHOD
When a water leak into the passenger compart-
ment cannot be detected by water testing, pressurize
the passenger compartment and soap test exterior of
the vehicle. To pressurize the passenger compart-
ment, close all doors and windows, start engine, and
set heater control to high blower in HEAT position. If
engine can not be started, connect a charger to the
battery to ensure adequate voltage to the blower.
With interior pressurized, apply dish detergent solu-
tion to suspected leak area on the exterior of the
vehicle. Apply detergent solution with spray device or
soft bristle brush. If soap bubbles occur at a body
seam, joint, seal or gasket, the leak entry point could
be at that location.
WIND NOISE
Wind noise is the result of most air leaks. Air leaks
can be caused by poor sealing, improper body compo-
nent alignment, body seam porosity, or missing plugs
in the engine compartment or door hinge pillar areas.
All body sealing points should be airtight in normal
driving conditions. Moving sealing surfaces will not
always seal airtight under all conditions. At times,
side glass or door seals will allow wind noise to be
23 - 2 BODYRS
BODY (Continued)
Page 1782 of 2339

noticed in the passenger compartment during high
cross winds. Over compensating on door or glass
adjustments to stop wind noise that occurs under
severe conditions can cause premature seal wear and
excessive closing or latching effort. After a repair pro-
cedure has been performed, test vehicle to verify
noise has stopped before returning vehicle to use.
VISUAL INSPECTION BEFORE TESTS
Verify that floor and body plugs are in place and
body components are aligned and sealed. If compo-
nent alignment or sealing is necessary, refer to the
appropriate section of this group for proper proce-
dures.
ROAD TESTING WIND NOISE
(1) Drive the vehicle to verify the general location
of the wind noise.
(2) Apply 50 mm (2 in.) masking tape in 150 mm
(6 in.) lengths along weatherstrips, weld seams or
moldings. After each length is applied, drive the vehi-
cle. If noise goes away after a piece of tape is applied,
remove tape, locate, and repair defect.
POSSIBLE CAUSE OF WIND NOISE
²Moldings standing away from body surface can
catch wind and whistle.
²Gaps in sealed areas behind overhanging body
flanges can cause wind-rushing sounds.
²Misaligned movable components.
²Missing or improperly installed plugs in pillars.
²Weld burn through holes.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - PLASTIC BODY
PANEL REPAIR
There are many different types of plastics used in
today's automotive environment. We group plastics in
three different categories: Rigid, Semi-Rigid, and
Flexible. Any of these plastics may require the use of
an adhesion promoter for repair. These types of plas-
tic are used extensively on DaimlerChrysler Motors
vehicles. Always follow repair material manufactur-
er's plastic identification and repair procedures.
Rigid Plastics:
Examples of rigid plastic use: Fascias, Hoods,
Doors, and other Body Panels, which include SMC,
ABS, and Polycarbonates.
Semi-Rigid Plastics:
Examples of semi-rigid plastic use: Interior Panels,
Under Hood Panels, and other Body Trim Panels.
Flexible Plastics:
Examples of flexible plastic use: Fascias, Body
Moldings, and upper and lower Fascia Covers.
Repair Procedure:
The repair procedure for all three categories of
plastics is basically the same. The one difference is
the material used for the repair. The materials must
be specific for each substrate, rigid repair material
for rigid plastic repair, semi-rigid repair material for
semi-rigid plastic repair and flexible repair material
for flexible plastic repair.
Adhesion Promoter/Surface Modifier:
Adhesion Promoters/Surface Modifiers are required
for certain plastics. All three categories may have
plastics that require the use of adhesion promoter/
surface modifiers. Always follow repair material man-
ufacturer's plastic identification and repair
procedures.
SAFETY PRECAUTION AND WARNINGS
WARNING:
²EYE PROTECTION SHOULD BE USED WHEN
SERVICING COMPONENTS. PERSONAL INJURY
CAN RESULT.
²USE AN OSHA APPROVED BREATHING MASK
WHEN MIXING EPOXY, GRINDING, AND SPRAYING
PAINT OR SOLVENTS IN A CONFINED AREA. PER-
SONAL INJURY CAN RESULT.
²AVOID PROLONGED SKIN CONTACT WITH
RESIN, PETROLEUM, OR ALCOHOL BASED SOL-
VENTS. PERSONAL INJURY CAN RESULT.
²DO NOT VENTURE UNDER A HOISTED VEHI-
CLE THAT IS NOT PROPERLY SUPPORTED ON
SAFETY STANDS. PERSONAL INJURY CAN
RESULT.
NOTE:
²When holes must be drilled or cut in body pan-
els, verify locations of internal body components
and electrical wiring. Damage to vehicle can result.
²Do not use abrasive chemicals or compounds
on undamaged painted surfaces around repair
areas. Damage to finish can result.
RSBODY23-3
BODY (Continued)
Page 1783 of 2339

RIGID, SEMI-RIGID, AND FLEXIBLE PLASTIC PARTS TYPES
CODE FAMILY NAME COMMON TRADE NAME TYPICAL APPLICATION
ASA ACRYLONITRILE STYRENE
ACRYLITELURAN S CONSOLES, GRILLES
ABS ACRYLONITRILE
BUTADIENE STYRENETERLURAN9A9PILLARS, CONSOLES,
GRILLES
ABS/PC ABS/PC ALLOY PULSE, PROLOY, BAYBLEND DOORS, INSTRUMENT
PANELS
ABS/PVC ABS/PV ALLOY PROLOY, PULSE, LUSTRAN,
CYCLOVINDOOR PANELS, GRILLES,
TRIM
BMC BULK MOLDING
COMPOUNDBMC FENDER EXTENSIONS
EMA EHTYLENE METHYL
ACRYLATE/IONOMERSURLYN, EMA, IONOMER BUMPER GUARDS, PADS
METTON METTON METTON GRILLES, KICK PANELS,
RUNNING BOARDS
MPPO MODIFIED
POLYPHENYLENE OXIDEMPPO SPOILER ASSEMBLY
PA POLYAMID ZYTEL, VYDYNE, PA,
MINLONFENDERS, QUARTER
PANELS
PET THERMOPLASTIC
POLYESTERRYNITE TRIM
PBT/PPO PBT/PPO ALLOY GERMAX CLADDINGS
PBTP POLYBUTYLENE
THEREPTHALATEPBT, PBTP, POCAN, VALOX WHEEL COVERS, FENDERS,
GRILLES
PBTP/EEBC POLYBUTYLENE
THEREPTHALATE/EEBC
ALLOYBEXLOY,9M9, PBTP/EEBC FASCIAS, ROCKER PANEL,
MOLDINGS
PC POLYCARBONATE LEXAN, MERLON, CALIBRE,
MAKROLON PCTAIL LIGHT LENSES, IP TRIM,
VALANCE PANELS
PC/ABS PC/ABS ALLOY GERMAX, BAY BLENDS,
PULSEDOORS, INSTRUMENT
PANELS
PPO POLYPHENYLENE OXIDE AZDEL, HOSTALEN,
MARLEX, PRFAX, NORYL,
GTX, PPOINTERIOR TRIM, DOOR
PANELS, SPLASH SHIELDS,
STEERING COLUMN
SHROUD
PPO/PA POLYPHENYLENE/
POLYAMIDPPO/PA, GTX 910 FENDERS, QUARTER
PANELS
PR/FV FIBERGLASS REINFORCED
PLASTICFIBERGLASS, FV, PR/FV BODY PANELS
PS POLYSTYRENE LUSTREX, STYRON, PS DOOR PANELS, DASH
PANELS
RTM RESIN TRANSFER
MOLDING COMPOUNDRTM BODY PANELS
SMC SHEET MOLDED
COMPOUNDSMC BODY PANELS
TMC TRANSFER MOLDING
COMPOUNDTMC GRILLES
23 - 4 BODYRS
BODY (Continued)
Page 1786 of 2339
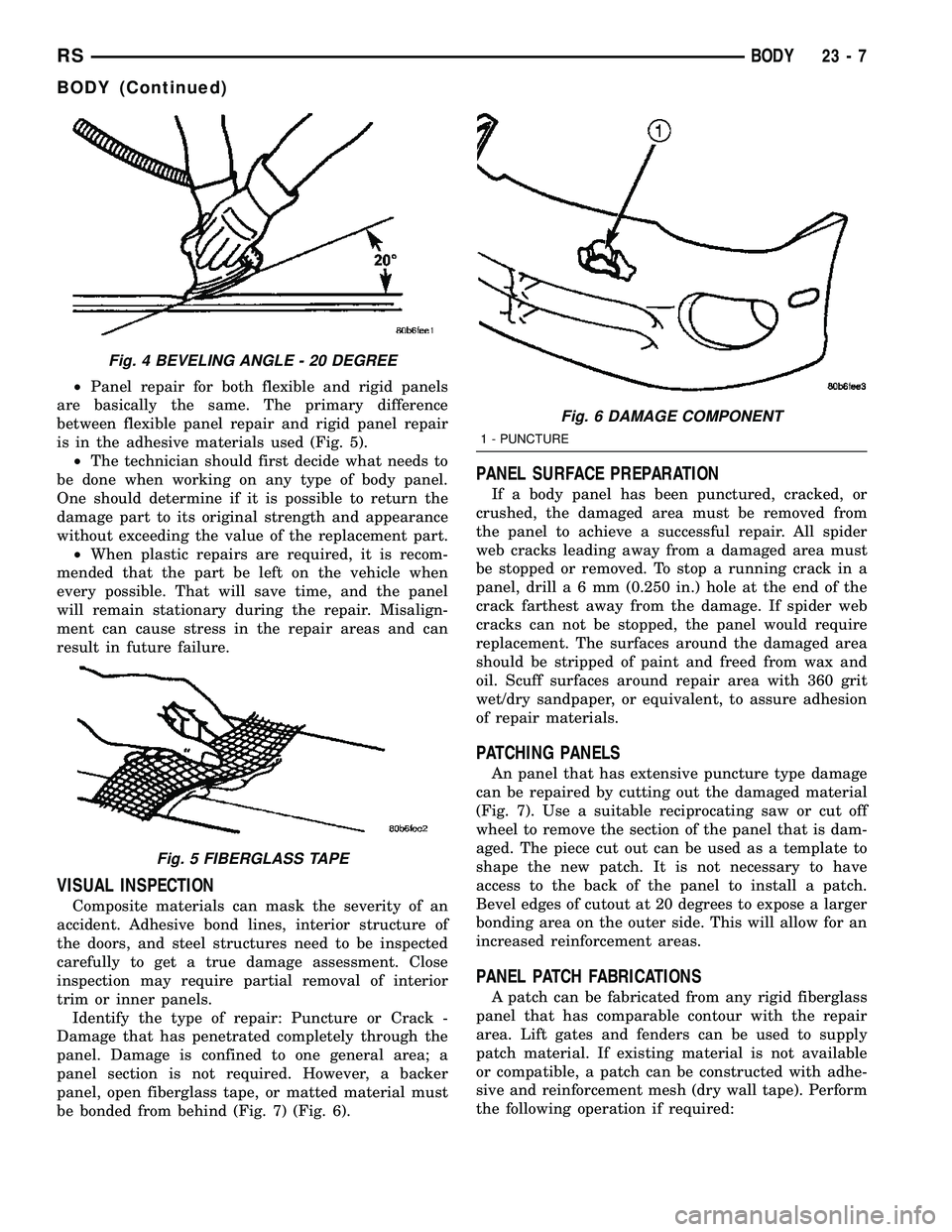
²Panel repair for both flexible and rigid panels
are basically the same. The primary difference
between flexible panel repair and rigid panel repair
is in the adhesive materials used (Fig. 5).
²The technician should first decide what needs to
be done when working on any type of body panel.
One should determine if it is possible to return the
damage part to its original strength and appearance
without exceeding the value of the replacement part.
²When plastic repairs are required, it is recom-
mended that the part be left on the vehicle when
every possible. That will save time, and the panel
will remain stationary during the repair. Misalign-
ment can cause stress in the repair areas and can
result in future failure.
VISUAL INSPECTION
Composite materials can mask the severity of an
accident. Adhesive bond lines, interior structure of
the doors, and steel structures need to be inspected
carefully to get a true damage assessment. Close
inspection may require partial removal of interior
trim or inner panels.
Identify the type of repair: Puncture or Crack -
Damage that has penetrated completely through the
panel. Damage is confined to one general area; a
panel section is not required. However, a backer
panel, open fiberglass tape, or matted material must
be bonded from behind (Fig. 7) (Fig. 6).
PANEL SURFACE PREPARATION
If a body panel has been punctured, cracked, or
crushed, the damaged area must be removed from
the panel to achieve a successful repair. All spider
web cracks leading away from a damaged area must
be stopped or removed. To stop a running crack in a
panel, drilla6mm(0.250 in.) hole at the end of the
crack farthest away from the damage. If spider web
cracks can not be stopped, the panel would require
replacement. The surfaces around the damaged area
should be stripped of paint and freed from wax and
oil. Scuff surfaces around repair area with 360 grit
wet/dry sandpaper, or equivalent, to assure adhesion
of repair materials.
PATCHING PANELS
An panel that has extensive puncture type damage
can be repaired by cutting out the damaged material
(Fig. 7). Use a suitable reciprocating saw or cut off
wheel to remove the section of the panel that is dam-
aged. The piece cut out can be used as a template to
shape the new patch. It is not necessary to have
access to the back of the panel to install a patch.
Bevel edges of cutout at 20 degrees to expose a larger
bonding area on the outer side. This will allow for an
increased reinforcement areas.
PANEL PATCH FABRICATIONS
A patch can be fabricated from any rigid fiberglass
panel that has comparable contour with the repair
area. Lift gates and fenders can be used to supply
patch material. If existing material is not available
or compatible, a patch can be constructed with adhe-
sive and reinforcement mesh (dry wall tape). Perform
the following operation if required:
Fig. 4 BEVELING ANGLE - 20 DEGREE
Fig. 5 FIBERGLASS TAPE
Fig. 6 DAMAGE COMPONENT
1 - PUNCTURE
RSBODY23-7
BODY (Continued)
Page 1794 of 2339
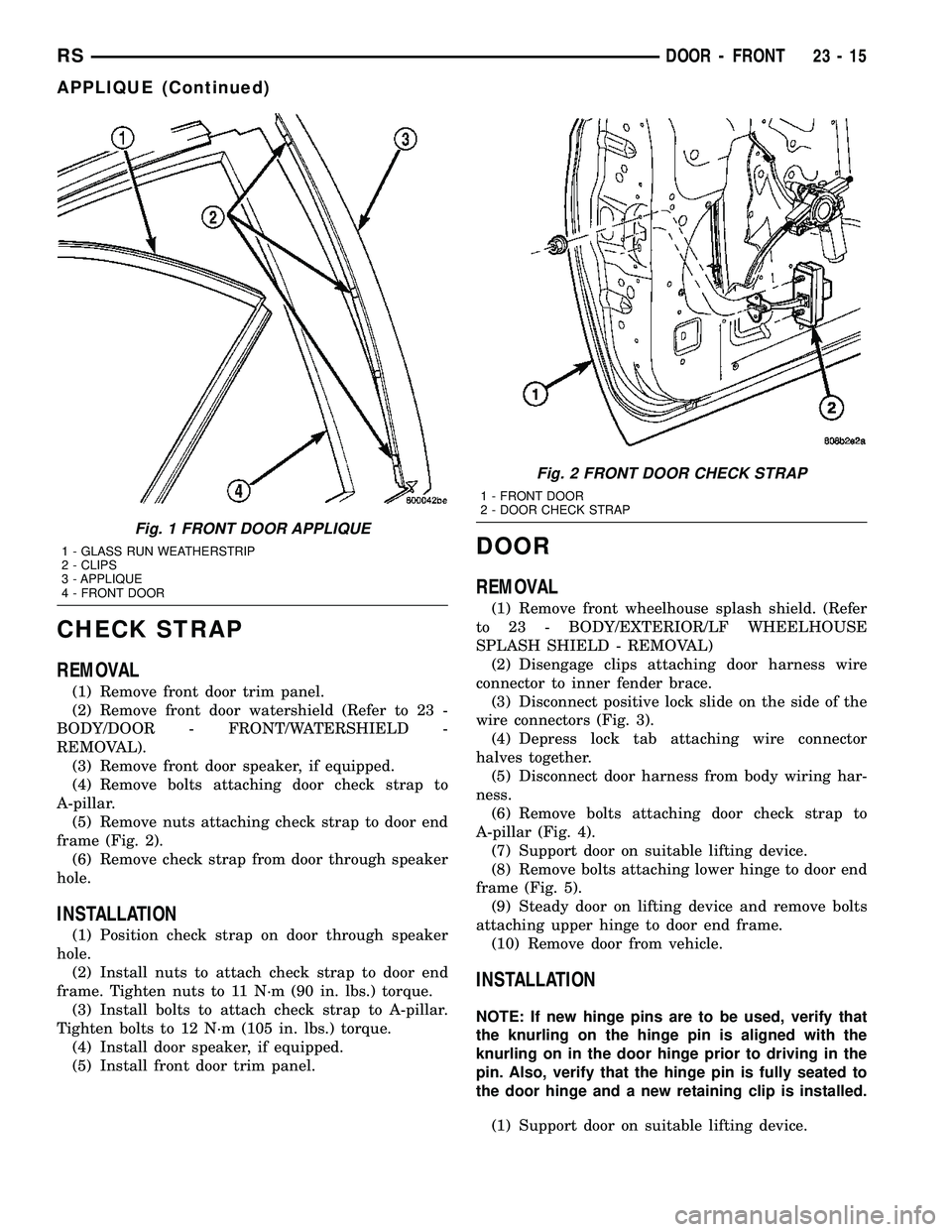
CHECK STRAP
REMOVAL
(1) Remove front door trim panel.
(2) Remove front door watershield (Refer to 23 -
BODY/DOOR - FRONT/WATERSHIELD -
REMOVAL).
(3) Remove front door speaker, if equipped.
(4) Remove bolts attaching door check strap to
A-pillar.
(5) Remove nuts attaching check strap to door end
frame (Fig. 2).
(6) Remove check strap from door through speaker
hole.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position check strap on door through speaker
hole.
(2) Install nuts to attach check strap to door end
frame. Tighten nuts to 11 N´m (90 in. lbs.) torque.
(3) Install bolts to attach check strap to A-pillar.
Tighten bolts to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs.) torque.
(4) Install door speaker, if equipped.
(5) Install front door trim panel.
DOOR
REMOVAL
(1) Remove front wheelhouse splash shield. (Refer
to 23 - BODY/EXTERIOR/LF WHEELHOUSE
SPLASH SHIELD - REMOVAL)
(2) Disengage clips attaching door harness wire
connector to inner fender brace.
(3) Disconnect positive lock slide on the side of the
wire connectors (Fig. 3).
(4) Depress lock tab attaching wire connector
halves together.
(5) Disconnect door harness from body wiring har-
ness.
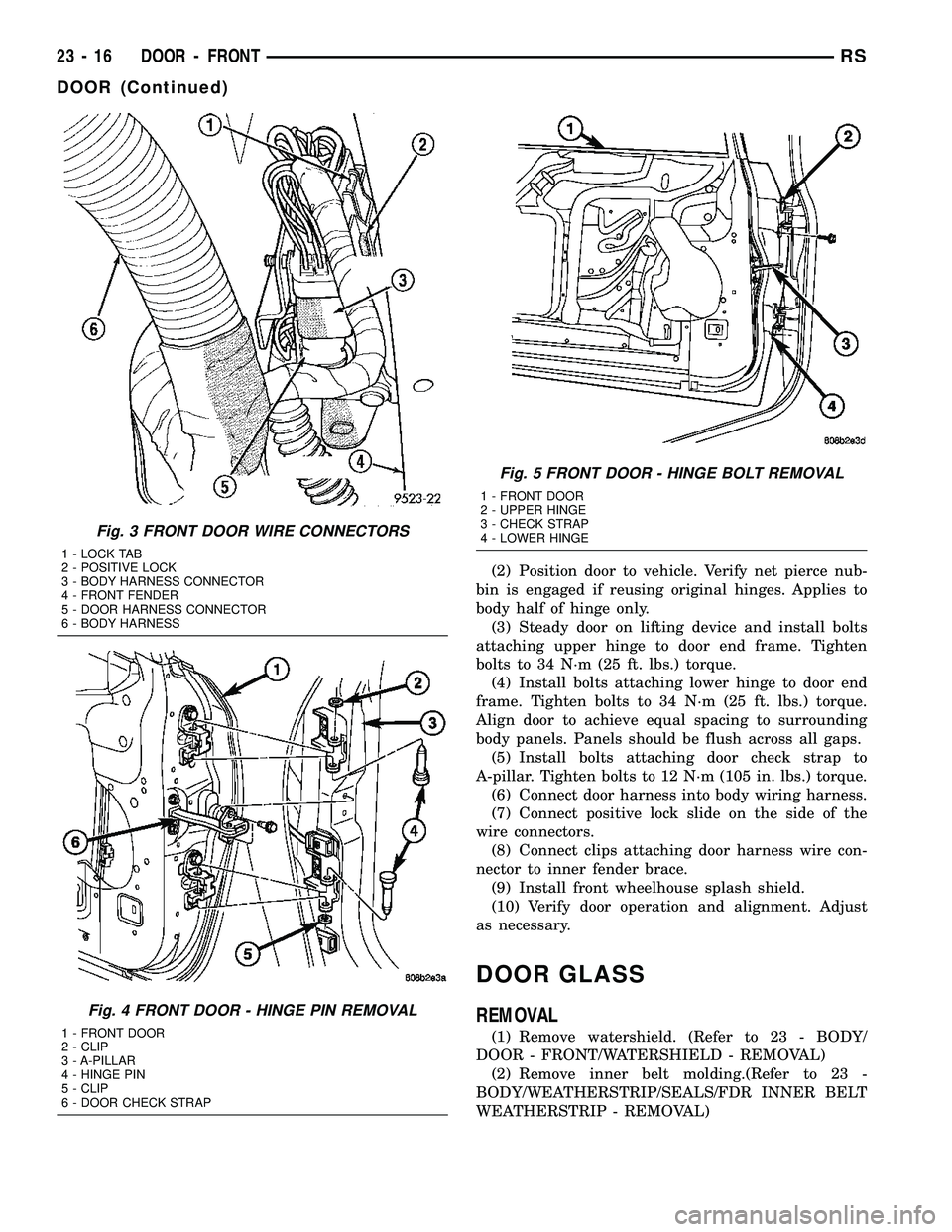
(6) Remove bolts attaching door check strap to
A-pillar (Fig. 4).
(7) Support door on suitable lifting device.
(8) Remove bolts attaching lower hinge to door end
frame (Fig. 5).
(9) Steady door on lifting device and remove bolts
attaching upper hinge to door end frame.
(10) Remove door from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
NOTE: If new hinge pins are to be used, verify that
the knurling on the hinge pin is aligned with the
knurling on in the door hinge prior to driving in the
pin. Also, verify that the hinge pin is fully seated to
the door hinge and a new retaining clip is installed.
(1) Support door on suitable lifting device.
Fig. 1 FRONT DOOR APPLIQUE
1 - GLASS RUN WEATHERSTRIP
2 - CLIPS
3 - APPLIQUE
4 - FRONT DOOR
Fig. 2 FRONT DOOR CHECK STRAP
1 - FRONT DOOR
2 - DOOR CHECK STRAP
RSDOOR - FRONT23-15
APPLIQUE (Continued)
Page 1795 of 2339
(2) Position door to vehicle. Verify net pierce nub-
bin is engaged if reusing original hinges. Applies to
body half of hinge only.
(3) Steady door on lifting device and install bolts
attaching upper hinge to door end frame. Tighten
bolts to 34 N´m (25 ft. lbs.) torque.
(4) Install bolts attaching lower hinge to door end
frame. Tighten bolts to 34 N´m (25 ft. lbs.) torque.
Align door to achieve equal spacing to surrounding
body panels. Panels should be flush across all gaps.
(5) Install bolts attaching door check strap to
A-pillar. Tighten bolts to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs.) torque.
(6) Connect door harness into body wiring harness.
(7) Connect positive lock slide on the side of the
wire connectors.
(8) Connect clips attaching door harness wire con-
nector to inner fender brace.
(9) Install front wheelhouse splash shield.
(10) Verify door operation and alignment. Adjust
as necessary.
DOOR GLASS
REMOVAL
(1) Remove watershield. (Refer to 23 - BODY/
DOOR - FRONT/WATERSHIELD - REMOVAL)
(2) Remove inner belt molding.(Refer to 23 -
BODY/WEATHERSTRIP/SEALS/FDR INNER BELT
WEATHERSTRIP - REMOVAL)
Fig. 3 FRONT DOOR WIRE CONNECTORS
1 - LOCK TAB
2 - POSITIVE LOCK
3 - BODY HARNESS CONNECTOR
4 - FRONT FENDER
5 - DOOR HARNESS CONNECTOR
6 - BODY HARNESS
Fig. 4 FRONT DOOR - HINGE PIN REMOVAL
1 - FRONT DOOR
2 - CLIP
3 - A-PILLAR
4 - HINGE PIN
5 - CLIP
6 - DOOR CHECK STRAP
Fig. 5 FRONT DOOR - HINGE BOLT REMOVAL
1 - FRONT DOOR
2 - UPPER HINGE
3 - CHECK STRAP
4 - LOWER HINGE
23 - 16 DOOR - FRONTRS
DOOR (Continued)
Page 1799 of 2339

TRIM PANEL
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the plug and remove screw attaching
door pull cup to inner door panel.
(2) Remove switch bezel and disconnect power win-
dow/memory switch.
(3) Remove screws attaching trim panel to door
from below map pocket.
(4) If equipped, remove window crank. (Refer to 23
- BODY/DOOR - FRONT/WINDOW CRANK -
REMOVAL)
(5) Remove screw holding door trim to door panel
from behind inside latch release handle.
(6) Disengage clips attaching door trim to door
frame around perimeter of panel.
(7) Lift trim panel upward to disengage flange
from inner belt molding at top of door.
(8) Tilt top of trim panel away from door to gain
access to latch linkage.
(9) Disengage clip attaching linkage rod to inside
latch release handle (Fig. 12).
(10) Separate linkage rod from latch handle.
(11) Disconnect the power door switch, courtesy
lamp electrical connectors.
(12) Remove front door trim panel from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Hold top of trim panel away from door to gain
access to latch linkage.
(2) Place linkage rod in position on latch handle.
(3) Engage clip to hold linkage rod to inside latch
release handle.
Fig. 11 OUTSIDE DOOR HANDLE
1 - CLIP
2 - LOCK CYLINDER
3 - KEY CYLINDER TO LATCH LINK
4 - OUTSIDE HANDLE TO LATCH LINK5 - LOCK KNOB LINK
6 - FRONT DOOR
7 - KEY POSITION SWITCH
8 - OUTSIDE HANDLE
Fig. 12 INSIDE DOOR HANDLE LINKAGE
1 - DOOR LATCH HANDLE
2 - DOOR TRIM
3 - LATCH LINKAGE
4 - CLIP
5 - MEMORY SEAT SWITCH
23 - 20 DOOR - FRONTRS
LOCK CYLINDER (Continued)
Page 1803 of 2339

DOORS - SLIDING
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
CENTER HINGE
REMOVAL.............................24
INSTALLATION.........................24
SLIDING DOOR STOP BUMPER BEZEL
REMOVAL.............................25
INSTALLATION.........................25
STOP BUMPER
REMOVAL.............................25
INSTALLATION.........................25
HOLD OPEN LATCH
REMOVAL.............................25
INSTALLATION.........................25
HOLD OPEN LATCH STRIKER
REMOVAL.............................26
INSTALLATION.........................26
LATCH / LOCK ASSEMBLY
REMOVAL.............................26
INSTALLATION.........................27
INSIDE HANDLE ACTUATOR
REMOVAL.............................27
INSTALLATION.........................27
CENTER STRIKER
REMOVAL.............................28
INSTALLATION.........................28
LOWER HINGE
REMOVAL.............................28
INSTALLATION.........................28
REAR LATCH STRIKER
REMOVAL.............................29
INSTALLATION.........................29
SLIDING DOOR
REMOVAL.............................29
INSTALLATION.........................29ADJUSTMENTS
SLIDING DOOR ADJUSTMENTS..........30
STABILIZER
REMOVAL.............................33
INSTALLATION.........................33
STABILIZER SOCKET
REMOVAL.............................33
INSTALLATION.........................33
TRIM PANEL
REMOVAL.............................34
INSTALLATION.........................34
INSIDE LATCH HANDLE
REMOVAL.............................34
INSTALLATION.........................34
BELLCRANK
REMOVAL.............................35
INSTALLATION.........................35
OUTSIDE HANDLE
REMOVAL.............................35
INSTALLATION.........................36
UPPER HINGE
REMOVAL.............................36
INSTALLATION.........................36
OUTSIDE HANDLE CABLE
REMOVAL.............................37
INSTALLATION.........................37
INSIDE HANDLE CABLE
REMOVAL.............................37
INSTALLATION.........................38
HOLD OPEN LATCH CABLE
REMOVAL.............................38
INSTALLATION.........................38
CENTER HINGE
REMOVAL
NOTE: For power sliding door procedures refer to
POWER SLIDING DOOR SYSTEM in the ELECTRI-
CAL section.
(1) Open sliding door to the mid point of its travel.
(2) Support sliding door on a suitable lifting
device.
(3) Mark outline of center hinge of inner door
panel to aid installation.(4) Remove bolts attaching center hinge to sliding
door.
(5) Remove center hinge from sliding door.
(6) Roll center hinge to rear of roller channel.
(7) Remove center hinge from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
NOTE: For power sliding door procedures refer to
POWER SLIDING DOOR SYSTEM in the ELECTRI-
CAL section.
23 - 24 DOORS - SLIDINGRS
Page 1804 of 2339
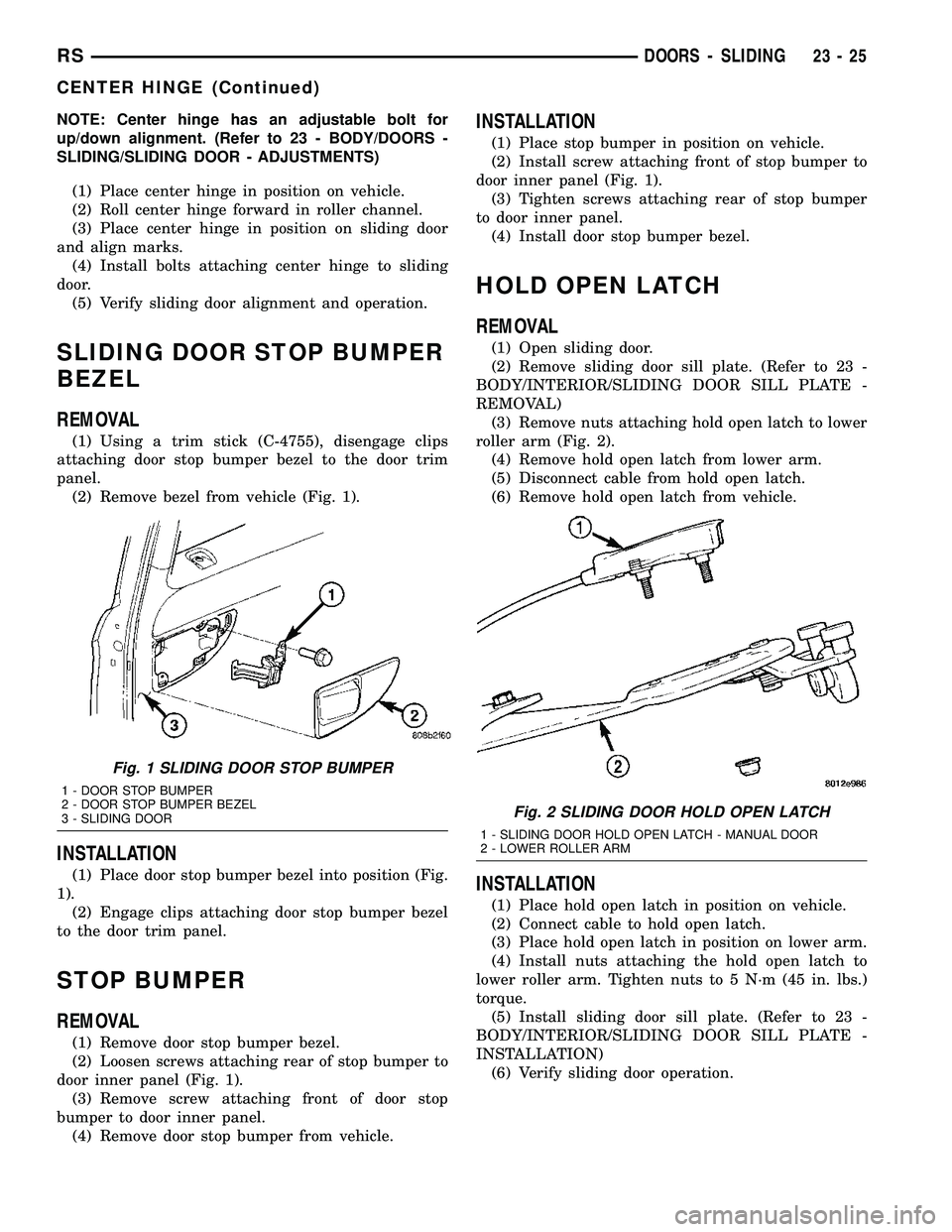
NOTE: Center hinge has an adjustable bolt for
up/down alignment. (Refer to 23 - BODY/DOORS -
SLIDING/SLIDING DOOR - ADJUSTMENTS)
(1) Place center hinge in position on vehicle.
(2) Roll center hinge forward in roller channel.
(3) Place center hinge in position on sliding door
and align marks.
(4) Install bolts attaching center hinge to sliding
door.
(5) Verify sliding door alignment and operation.
SLIDING DOOR STOP BUMPER
BEZEL
REMOVAL
(1) Using a trim stick (C-4755), disengage clips
attaching door stop bumper bezel to the door trim
panel.
(2) Remove bezel from vehicle (Fig. 1).
INSTALLATION
(1) Place door stop bumper bezel into position (Fig.
1).
(2) Engage clips attaching door stop bumper bezel
to the door trim panel.
STOP BUMPER
REMOVAL
(1) Remove door stop bumper bezel.
(2) Loosen screws attaching rear of stop bumper to
door inner panel (Fig. 1).
(3) Remove screw attaching front of door stop
bumper to door inner panel.
(4) Remove door stop bumper from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Place stop bumper in position on vehicle.
(2) Install screw attaching front of stop bumper to
door inner panel (Fig. 1).
(3) Tighten screws attaching rear of stop bumper
to door inner panel.
(4) Install door stop bumper bezel.
HOLD OPEN LATCH
REMOVAL
(1) Open sliding door.
(2) Remove sliding door sill plate. (Refer to 23 -
BODY/INTERIOR/SLIDING DOOR SILL PLATE -
REMOVAL)
(3) Remove nuts attaching hold open latch to lower
roller arm (Fig. 2).
(4) Remove hold open latch from lower arm.
(5) Disconnect cable from hold open latch.
(6) Remove hold open latch from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Place hold open latch in position on vehicle.
(2) Connect cable to hold open latch.
(3) Place hold open latch in position on lower arm.
(4) Install nuts attaching the hold open latch to
lower roller arm. Tighten nuts to 5 N´m (45 in. lbs.)
torque.
(5) Install sliding door sill plate. (Refer to 23 -
BODY/INTERIOR/SLIDING DOOR SILL PLATE -
INSTALLATION)
(6) Verify sliding door operation.
Fig. 1 SLIDING DOOR STOP BUMPER
1 - DOOR STOP BUMPER
2 - DOOR STOP BUMPER BEZEL
3 - SLIDING DOOR
Fig. 2 SLIDING DOOR HOLD OPEN LATCH
1 - SLIDING DOOR HOLD OPEN LATCH - MANUAL DOOR
2 - LOWER ROLLER ARM
RSDOORS - SLIDING23-25
CENTER HINGE (Continued)