oil change CHRYSLER CARAVAN 2005 Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2005, Model line: CARAVAN, Model: CHRYSLER CARAVAN 2005Pages: 2339, PDF Size: 59.69 MB
Page 1183 of 2339
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE DIAGNOSIS - MECHANICAL
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
NOISY VALVES 1. High or low oil level in
crankcase.1. Check and correct engine oil
level.
2. Thin or diluted oil. 2. Change oil to correct viscosity.
3. Thick oil 3. (a) Change engine oil and filter.
(b) Run engine to operating
temperature.
(c) Change engine oil and filter
again.
4. Low oil pressure. 4. Check and correct engine oil
pressure problem.
5. Dirt in hydraulic lifters/lash
adjusters.5. Replace hydraulic lifters/lash
adjusters.
6. Worn rocker arms. 6. Inspect oil supply to rocker arms.
7. Worn hydraulic lifters/lash
adjusters.7. Replace hydraulic lifters/lash
adjusters.
8. Worn valve guides. 8. Replace cylinder head assembly.
9. Excessive runout of valve seats
on valve faces.9. Grind valve seats and valves.
CONNECTING ROD NOISE 1. Insufficient oil supply. 1. Check engine oil level.
2. Low oil pressure. 2. Check engine oil level. Inspect oil
pump relief valve and spring.
3. Thin or diluted oil. 3. Change oil to correct viscosity.
4. Thick oil 4. (a) Change engine oil and filter.
(b) Run engine to operating
temperature.
(c) Change engine oil and filter
again.
5. Excessive bearing clearance. 5. Measure bearings for correct
clearance. Repair as necessary.
6. Connecting rod journal
out-of-round.6. Replace crankshaft or grind
surface.
7. Misaligned connecting rods. 7. Replace bent connecting rods.
9 - 6 ENGINE 2.4LRS
ENGINE 2.4L (Continued)
Page 1184 of 2339
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
MAIN BEARING NOISE 1. Insufficient oil supply. 1. Check engine oil level.
2. Low oil pressure. 2. Check engine oil level. Inspect oil
pump relief valve and spring.
3. Thin or diluted oil. 3. Change oil to correct viscosity.
4. Thick oil 4. (a) Change engine oil and filter.
(b) Run engine to operating
temperature.
(c) Change engine oil and filter
again.
5. Excessive bearing clearance. 5. Measure bearings for correct
clearance. Repair as necessary.
6. Excessive end play. 6. Check thrust bearing for wear on
flanges.
7. Crankshaft journal out-of-round
or worn.7. Replace crankshaft or grind
journals.
8. Loose flywheel or torque
converter.8. Tighten to correct torque.
OIL PRESSURE DROP 1. Low oil level. 1. Check engine oil level.
2. Faulty oil pressure sensor/switch. 2. Replace oil pressure sensor/
switch.
3. Low oil pressure. 3. Check oil pressure sensor/switch
and main bearing oil clearance.
4. Clogged oil filter. 4. Install new oil filter.
5. Worn parts in oil pump. 5. Replace worn parts or pump.
6. Thin or diluted oil. 6. Change oil to correct viscosity.
7. Oil pump relief valve stuck. 7. Remove valve and inspect, clean,
or replace.
8. Oil pump suction tube loose. 8. Remove oil pan and install new
tube or clean, if necessary.
9. Oil pump cover warped or
cracked.9. Install new oil pump.
10. Excessive bearing clearance. 10. Measure bearings for correct
clearance.
OIL LEAKS 1. Misaligned or deteriorated
gaskets.1. Replace gasket(s).
2. Loose fastener, broken or porous
metal part.2. Tighten, repair or replace the
part.
3. Misaligned or deteriorated cup or
threaded plug.3. Replace as necessary.
RSENGINE 2.4L9-7
ENGINE 2.4L (Continued)
Page 1207 of 2339
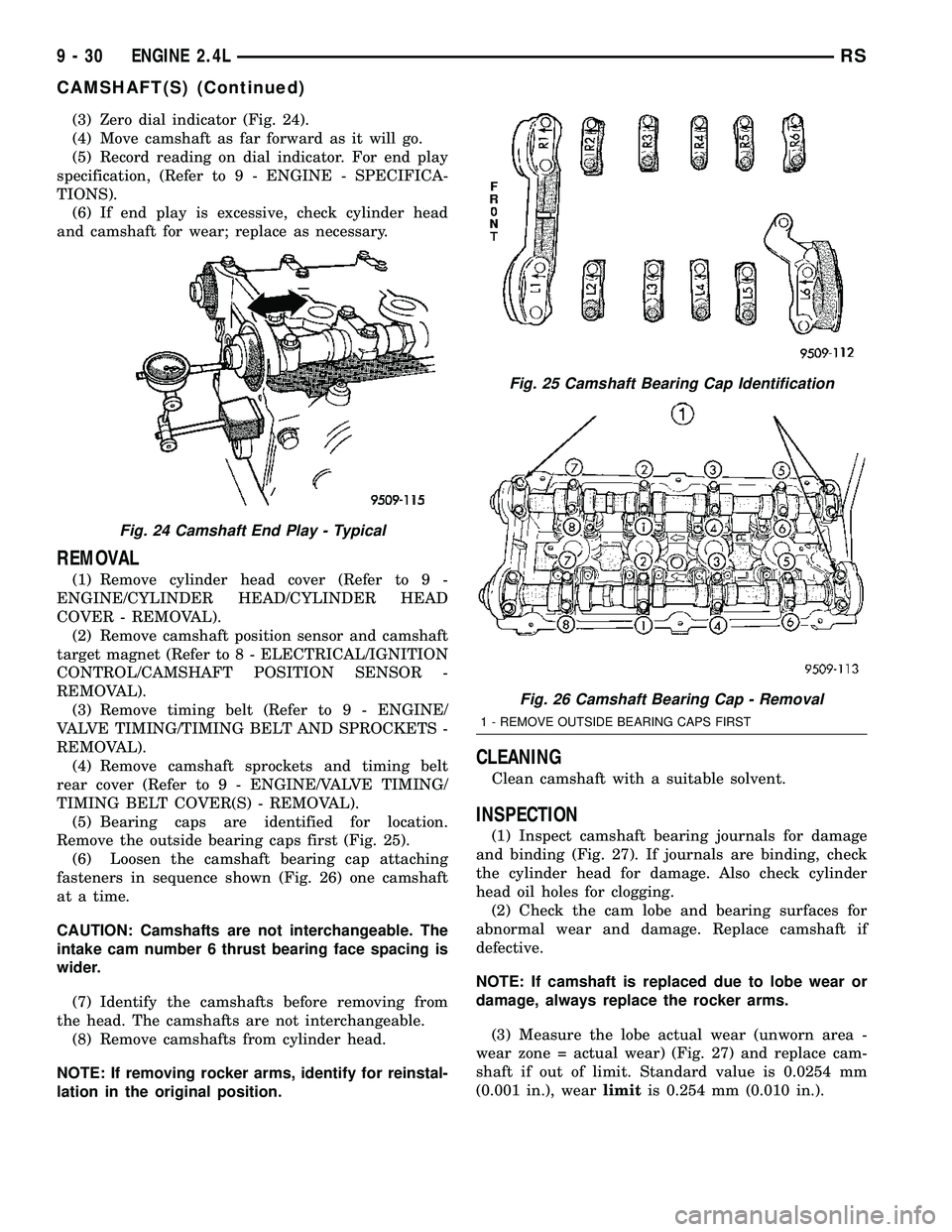
(3) Zero dial indicator (Fig. 24).
(4) Move camshaft as far forward as it will go.
(5) Record reading on dial indicator. For end play
specification, (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIFICA-
TIONS).
(6) If end play is excessive, check cylinder head
and camshaft for wear; replace as necessary.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove cylinder head cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER - REMOVAL).
(2) Remove camshaft position sensor and camshaft
target magnet (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/IGNITION
CONTROL/CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR -
REMOVAL).
(3) Remove timing belt (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT AND SPROCKETS -
REMOVAL).
(4) Remove camshaft sprockets and timing belt
rear cover (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/
TIMING BELT COVER(S) - REMOVAL).
(5) Bearing caps are identified for location.
Remove the outside bearing caps first (Fig. 25).
(6) Loosen the camshaft bearing cap attaching
fasteners in sequence shown (Fig. 26) one camshaft
at a time.
CAUTION: Camshafts are not interchangeable. The
intake cam number 6 thrust bearing face spacing is
wider.
(7) Identify the camshafts before removing from
the head. The camshafts are not interchangeable.
(8) Remove camshafts from cylinder head.
NOTE: If removing rocker arms, identify for reinstal-
lation in the original position.
CLEANING
Clean camshaft with a suitable solvent.
INSPECTION
(1) Inspect camshaft bearing journals for damage
and binding (Fig. 27). If journals are binding, check
the cylinder head for damage. Also check cylinder
head oil holes for clogging.
(2) Check the cam lobe and bearing surfaces for
abnormal wear and damage. Replace camshaft if
defective.
NOTE: If camshaft is replaced due to lobe wear or
damage, always replace the rocker arms.
(3) Measure the lobe actual wear (unworn area -
wear zone = actual wear) (Fig. 27) and replace cam-
shaft if out of limit. Standard value is 0.0254 mm
(0.001 in.), wearlimitis 0.254 mm (0.010 in.).
Fig. 24 Camshaft End Play - Typical
Fig. 25 Camshaft Bearing Cap Identification
Fig. 26 Camshaft Bearing Cap - Removal
1 - REMOVE OUTSIDE BEARING CAPS FIRST
9 - 30 ENGINE 2.4LRS
CAMSHAFT(S) (Continued)
Page 1222 of 2339

(4) Remove top ridge of cylinder bores with a reli-
able ridge reamer before removing pistons from cyl-
inder block.Be sure to keep tops of pistons
covered during this operation.
(5) Pistons have a directional stamping in the
front half of the piston facing towards thefrontof
engine (Fig. 62).
(6) Pistons and connecting rods must be removed
from top of cylinder block. Rotate crankshaft so that
each connecting rod is centered in cylinder bore.
(7) Using a permanent ink or paint marker, iden-
tify cylinder number on each connecting rod cap (Fig.
63).
CAUTION: DO NOT use a number stamp or a punch
to mark connecting rods. Damage to connecting
rod could occur.
(8) Remove connecting rod bolts and cap. Care
should be taken not to damage the fracture rod and
cap surfaces.
NOTE: Do not reuse connecting rod bolts.
CAUTION: Care must be taken not to damage the
fractured rod and cap joint surfaces, as engine
damage many occur.
(9) To protect crankshaft journal and fractured rod
surfaces, install Special Tool 8189, connecting rod
guides onto connecting rod (Fig. 64). Carefully push
each piston and rod assembly out of cylinder bore.
(10) Remove Special Tool 8189, connecting rod
guides and re-install bearing cap on the mating rod.
NOTE: Piston and rods are serviced as an assem-
bly.(11) Repeat procedure for each piston and connect-
ing rod assembly.
(12) Remove piston rings (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
ENGINE BLOCK/PISTON RINGS - REMOVAL).
INSTALLATION
(1) Install piston rings on piston (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/PISTON RINGS -
INSTALLATION)
(2) Before installing pistons and connecting rod
assemblies into the bore, be sure that compression
ring gaps are staggered so that neither is in line with
oil ring rail gap (Fig. 65).
(3) Before installing the ring compressor, make
sure the oil ring expander ends are butted and the
rail gaps located as shown in (Fig. 65). As viewed
from top.
(4) Immerse the piston head and rings in clean
engine oil, slide the ring compressor, over the piston
(Fig. 66).Be sure position of rings does not
change during this operation.
(5) The directional stamp on the piston should face
toward the front of the engine (Fig. 62).
Fig. 62 Piston Markings
1 - DIRECTIONAL ARROW WILL BE IMPRINTED IN THIS AREA
Fig. 63 Identify Connectng Rod to Cylinder - Typical
Fig. 64 Connecting Rod Guides - Typical
1 - SPECIAL TOOL 8189 CONNECTING ROD GUIDES
RSENGINE 2.4L9-45
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD (Continued)
Page 1231 of 2339

(6) Install oil pressure switch and connector. (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRICATION/OIL PRESSURE
SENSOR/SWITCH - INSTALLATION)
OIL
STANDARD PROCEDURE
ENGINE OIL LEVEL CHECK
The best time to check engine oil level is after it
has sat overnight, or if the engine has been running,
allow the engine to be shut off for at least 5 minutes
before checking oil level.
Checking the oil while the vehicle is on level
ground will improve the accuracy of the oil level
reading. Remove dipstick and observe oil level. Add
oil only when the level is at or below the ADD mark
(Fig. 87).
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE OIL AND
FILTER CHANGE
Change engine oil at mileage and time intervals
described in the Maintenance Schedule. (Refer to
LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE/MAINTE-
NANCE SCHEDULES - DESCRIPTION)
WARNING: NEW OR USED ENGINE OIL CAN BE
IRRITATING TO THE SKIN. AVOID PROLONGED OR
REPEATED SKIN CONTACT WITH ENGINE OIL.
CONTAMINANTS IN USED ENGINE OIL, CAUSED BY
INTERNAL COMBUSTION, CAN BE HAZARDOUS TO
YOUR HEALTH. THOROUGHLY WASH EXPOSED
SKIN WITH SOAP AND WATER. DO NOT WASH
SKIN WITH GASOLINE, DIESEL FUEL, THINNER, OR
SOLVENTS, HEALTH PROBLEMS CAN RESULT. DO
NOT POLLUTE, DISPOSE OF USED ENGINE OIL
PROPERLY. CONTACT YOUR DEALER OR GOVERN-
MENT AGENCY FOR LOCATION OF COLLECTION
CENTER IN YOUR AREA.
Run engine until achieving normal operating tem-
perature.
(1) Position the vehicle on a level surface and turn
engine off.
(2) Remove oil fill cap.(3) Hoist and support vehicle on safety stands.
Refer to Hoisting and Jacking Recommendations.
(Refer to LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE/HOIST-
ING - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(4) Place a suitable drain pan under crankcase
drain.
(5) Remove drain plug from crankcase and allow
oil to drain into pan. Inspect drain plug threads for
stretching or other damage. Replace drain plug and
gasket if damaged.
(6) Remove oil filter. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRI-
CATION/OIL FILTER - REMOVAL)
(7) Install and tighten drain plug in crankcase.
(8) Install new oil filter. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LU-
BRICATION/OIL FILTER - INSTALLATION)
(9) Lower vehicle and fill crankcase with specified
type and amount of engine oil. (Refer to LUBRICA-
TION & MAINTENANCE/FLUID TYPES -
DESCRIPTION)
(10) Install oil fill cap.
(11) Start engine and inspect for leaks.
(12) Stop engine and inspect oil level.
NOTE: Care should be exercised when disposing
used engine oil after it has been drained from a
vehicle engine. Refer to the WARNING listed above.
OIL FILTER
DESCRIPTION
The engine oil filter (Fig. 88) is a high quality full-
flow, disposable type. Replace the oil filter with a
Mopartor the equivalent.
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(2) Position an oil collecting container under oil fil-
ter location.
CAUTION: When servicing the oil filter avoid
deforming the filter can by installing the remove/in-
stall tool band strap against the can to base lock
seam. The lock seam joining the can to the base is
reinforced by the base plate.
(3) Using a suitable filter wrench, turn oil filter
(Fig. 88) counterclockwise to remove.
INSTALLATION
(1) Clean and check filter mounting surface. The
surface must be smooth, flat and free of debris or
pieces of gasket.
(2) Lubricate new oil filter gasket with clean
engine oil.
Fig. 87 Oil Level
1 - ENGINE OIL LEVEL DIPSTICK
9 - 54 ENGINE 2.4LRS
LUBRICATION (Continued)
Page 1254 of 2339

INSPECTION..........................115
HYDRAULIC LIFTERS (CAM IN BLOCK)
DESCRIPTION........................116
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HYDRAULIC
LIFTERS...........................116
REMOVAL............................117
INSTALLATION........................117
CAMSHAFT & BEARINGS (IN BLOCK)
DESCRIPTION........................118
OPERATION..........................118
REMOVAL............................118
INSPECTION..........................118
INSTALLATION........................118
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD
DESCRIPTION........................119
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FITTING
CONNECTING RODS..................119
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FITTING
PISTONS...........................120
REMOVAL............................120
INSTALLATION........................121
CONNECTING ROD BEARINGS
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MEASURING
CONNECTING ROD BEARING
CLEARANCE........................123
PISTON RINGS
STANDARD PROCEDURE - PISTON RING
FITTING............................124
REMOVAL............................124
INSTALLATION........................124
CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARINGS
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MAIN BEARING
FITTING............................125
REMOVAL - CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARINGS . 127
INSTALLATION - CRANKSHAFT MAIN
BEARINGS..........................127
CRANKSHAFT
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - 3.3L..................128
DESCRIPTION - 3.8L..................128
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MEASURING
CRANKSHAFT END PLAY..............128
REMOVAL............................128
INSTALLATION........................129
CRANKSHAFT OIL SEAL - FRONT
REMOVAL............................130
INSTALLATION........................130
CRANKSHAFT OIL SEAL - REAR
REMOVAL............................131
INSTALLATION........................131
CRANKSHAFT REAR OIL SEAL RETAINER
REMOVAL............................132
INSTALLATION........................132
VIBRATION DAMPER
REMOVAL............................132
INSTALLATION........................132FLEX PLATE
REMOVAL............................133
INSTALLATION........................133
ENGINE MOUNTING
DESCRIPTION........................134
FRONT MOUNT
REMOVAL............................134
INSTALLATION........................134
LEFT MOUNT
REMOVAL............................136
INSTALLATION........................136
REAR MOUNT
REMOVAL............................136
INSTALLATION........................137
RIGHT MOUNT
REMOVAL............................138
INSTALLATION........................138
LUBRICATION
DESCRIPTION........................138
OPERATION..........................138
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE OIL
PRESSURE.........................138
OIL
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE OIL
AND FILTER CHANGE.................139
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE OIL
LEVEL CHECK.......................140
OIL COOLER & LINES
DESCRIPTION........................141
OPERATION..........................141
REMOVAL............................141
INSTALLATION........................141
OIL FILTER
REMOVAL............................141
INSTALLATION........................141
OIL FILTER ADAPTER
REMOVAL............................142
INSTALLATION........................142
OIL PAN
REMOVAL............................142
CLEANING...........................142
INSPECTION.........................143
INSTALLATION........................143
OIL PRESSURE RELIEF VALVE
REMOVAL............................143
INSTALLATION........................144
OIL PRESSURE SWITCH
DESCRIPTION........................144
OPERATION..........................144
REMOVAL............................144
INSTALLATION........................144
OIL PUMP
DESCRIPTION........................144
REMOVAL............................144
DISASSEMBLY........................145
CLEANING...........................145
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9-77
Page 1259 of 2339

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE DIAGNOSIS - MECHANICAL
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
NOISY VALVES 1. High or low oil level in
crankcase.1. Check and correct engine oil
level.
2. Thin or diluted oil. 2. Change oil to correct viscosity.
3. Thick oil 3. (a) Change engine oil and filter.
(b) Run engine to operating
temperature.
(c) Change engine oil and filter
again.
4. Low oil pressure. 4. Check and correct engine oil
pressure problem.
5. Dirt in hydraulic lifters/lash
adjusters.5. Replace hydraulic lifters/lash
adjusters.
6. Worn rocker arms. 6. Inspect oil supply to rocker arms.
7. Worn hydraulic lifters/lash
adjusters.7. Replace hydraulic lifters/lash
adjusters.
8. Worn valve guides. 8. Replace cylinder head assembly.
9. Excessive runout of valve seats
on valve faces.9. Grind valve seats and valves.
CONNECTING ROD NOISE 1. Insufficient oil supply. 1. Check engine oil level.
2. Low oil pressure. 2. Check engine oil level. Inspect oil
pump relief valve and spring.
3. Thin or diluted oil. 3. Change oil to correct viscosity.
4. Thick oil 4. (a) Change engine oil and filter.
(b) Run engine to operating
temperature.
(c) Change engine oil and filter
again.
5. Excessive bearing clearance. 5. Measure bearings for correct
clearance. Repair as necessary.
6. Connecting rod journal
out-of-round.6. Replace crankshaft or grind
surface.
7. Misaligned connecting rods. 7. Replace bent connecting rods.
9 - 82 ENGINE 3.3/3.8LRS
ENGINE 3.3/3.8L (Continued)
Page 1260 of 2339

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
MAIN BEARING NOISE 1. Insufficient oil supply. 1. Check engine oil level.
2. Low oil pressure. 2. Check engine oil level. Inspect oil
pump relief valve and spring.
3. Thin or diluted oil. 3. Change oil to correct viscosity.
4. Thick oil 4. (a) Change engine oil and filter.
(b) Run engine to operating
temperature.
(c) Change engine oil and filter
again.
5. Excessive bearing clearance. 5. Measure bearings for correct
clearance. Repair as necessary.
6. Excessive end play. 6. Check thrust bearing for wear on
flanges.
7. Crankshaft journal out-of-round
or worn.7. Replace crankshaft or grind
journals.
8. Loose flywheel or torque
converter.8. Tighten to correct torque.
OIL PRESSURE DROP 1. Low oil level. 1. Check engine oil level.
2. Faulty oil pressure sensor/switch. 2. Replace oil pressure sensor/
switch.
3. Low oil pressure. 3. Check oil pressure sensor/switch
and main bearing oil clearance.
4. Clogged oil filter. 4. Install new oil filter.
5. Worn parts in oil pump. 5. Replace worn parts or pump.
6. Thin or diluted oil. 6. Change oil to correct viscosity.
7. Oil pump relief valve stuck. 7. Remove valve and inspect, clean,
or replace.
8. Oil pump suction tube loose. 8. Remove oil pan and install new
tube or clean, if necessary.
9. Oil pump cover warped or
cracked.9. Install new oil pump.
10. Excessive bearing clearance. 10. Measure bearings for correct
clearance.
OIL LEAKS 1. Misaligned or deteriorated
gaskets.1. Replace gasket(s).
2. Loose fastener, broken or porous
metal part.2. Tighten, repair or replace the
part.
3. Misaligned or deteriorated cup or
threaded plug.3. Replace as necessary.
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9-83
ENGINE 3.3/3.8L (Continued)
Page 1282 of 2339
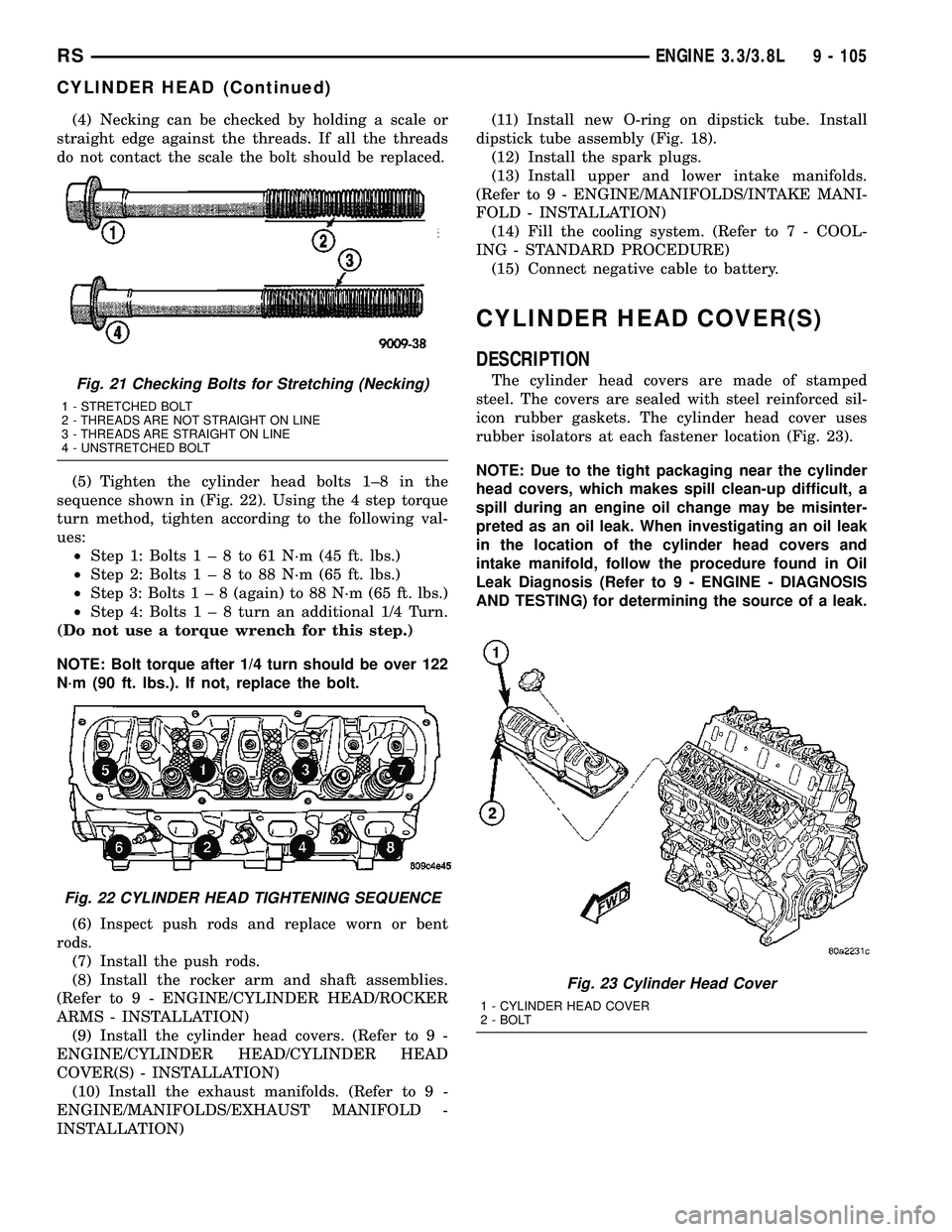
(4) Necking can be checked by holding a scale or
straight edge against the threads. If all the threads
do not contact the scale the bolt should be replaced.
(5) Tighten the cylinder head bolts 1±8 in the
sequence shown in (Fig. 22). Using the 4 step torque
turn method, tighten according to the following val-
ues:
²Step 1: Bolts1±8to61N´m(45ft.lbs.)
²Step 2: Bolts1±8to88N´m(65ft.lbs.)
²Step 3: Bolts1±8(again) to 88 N´m (65 ft. lbs.)
²Step 4: Bolts1±8turn an additional 1/4 Turn.
(Do not use a torque wrench for this step.)
NOTE: Bolt torque after 1/4 turn should be over 122
N´m (90 ft. lbs.). If not, replace the bolt.
(6) Inspect push rods and replace worn or bent
rods.
(7) Install the push rods.
(8) Install the rocker arm and shaft assemblies.
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/ROCKER
ARMS - INSTALLATION)
(9) Install the cylinder head covers. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION)
(10) Install the exhaust manifolds. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/EXHAUST MANIFOLD -
INSTALLATION)(11) Install new O-ring on dipstick tube. Install
dipstick tube assembly (Fig. 18).
(12) Install the spark plugs.
(13) Install upper and lower intake manifolds.
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANI-
FOLD - INSTALLATION)
(14) Fill the cooling system. (Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(15) Connect negative cable to battery.
CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S)
DESCRIPTION
The cylinder head covers are made of stamped
steel. The covers are sealed with steel reinforced sil-
icon rubber gaskets. The cylinder head cover uses
rubber isolators at each fastener location (Fig. 23).
NOTE: Due to the tight packaging near the cylinder
head covers, which makes spill clean-up difficult, a
spill during an engine oil change may be misinter-
preted as an oil leak. When investigating an oil leak
in the location of the cylinder head covers and
intake manifold, follow the procedure found in Oil
Leak Diagnosis (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING) for determining the source of a leak.Fig. 21 Checking Bolts for Stretching (Necking)
1 - STRETCHED BOLT
2 - THREADS ARE NOT STRAIGHT ON LINE
3 - THREADS ARE STRAIGHT ON LINE
4 - UNSTRETCHED BOLT
Fig. 22 CYLINDER HEAD TIGHTENING SEQUENCE
Fig. 23 Cylinder Head Cover
1 - CYLINDER HEAD COVER
2 - BOLT
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9 - 105
CYLINDER HEAD (Continued)
Page 1286 of 2339

(2) Measure valve stems for wear (Fig. 32). For
valve specifications, (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECI-
FICATIONS).
NOTE: Valve stems are chrome plated and should
not be polished (Fig. 32).
VALVE GUIDES
(1) Remove carbon and varnish deposits from
inside of valve guides with a reliable guide cleaner.
(2) Measure valve stem-to-guide clearance as fol-
lows:
(3) Install valve into cylinder head so it is 15 mm
(0.590 inch.) off the valve seat. A small piece of hose
may be used to hold valve in place.
(4) Attach dial indicator Tool C-3339 to cylinder
head and set it at right angle of valve stem being
measured (Fig. 33).
(5) Move valve to and from the indicator. For cler-
ance specifications, (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIFI-
CATIONS).
NOTE: Replace cylinder head if stem-to-guide clear-
ance exceeds specifications, or if guide is loose in
cylinder head.
INSTALLATION
(1) Coat valve stems with clean engine oil and
insert them in cylinder head.
(2) Install valve spring seat on head (Fig. 35).
(3) Install new seals on all valve stems and over
valve guides (Fig. 35). Install valve springs and valve
retainers (Fig. 35).(4) Install the valve springs. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/VALVE SPRINGS -
INSTALLATION)
VALVE SPRINGS
DESCRIPTION
There are two interchangeable, floating (spring
rotates during operation), valve spring designs. Type
A may be identified by the counterclockwise (spring
spirals down and to the left) appearance, And Type B
may be identified by the clockwise (spring spirals
down and to the right) appearance. Both of the valve
springs are a bee-hive shaped design but have differ-
ent specifications (Fig. 34). The springs are seated on
a steel washer on the cylinder head with retainers
and locks retaining the springs (Fig. 35). The springs
are installed with the smaller diameter against
spring retainer (Fig. 34).
OPERATION
The valve spring returns the valve against its seat
for a positive seal of the combustion chamber.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - CYLINDER HEAD OFF
(1) With the cylinder head on a bench, position
Special Tool C-3422-D with 8464 Adapter on the
valve and spring retainer (Fig. 36).
(2) Compress the spring only enough to remove the
valve retainer locks.
(3) Slowly release the spring tension and remove
the valve spring and retainer.
(4) For removal of the valve stem seal (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/VALVE STEM SEALS -
REMOVAL).
Fig. 32 Intake and Exhaust Valves
1 - MARGIN
2-FACE
3 - STEM
4 - VALVE SPRING RETAINER LOCK GROOVES
Fig. 33 Measuring Valve Guide Wear - Typical
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9 - 109
INTAKE/EXHAUST VALVES & SEATS (Continued)