oil change CHRYSLER CARAVAN 2005 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2005, Model line: CARAVAN, Model: CHRYSLER CARAVAN 2005Pages: 2339, PDF Size: 59.69 MB
Page 1296 of 2339
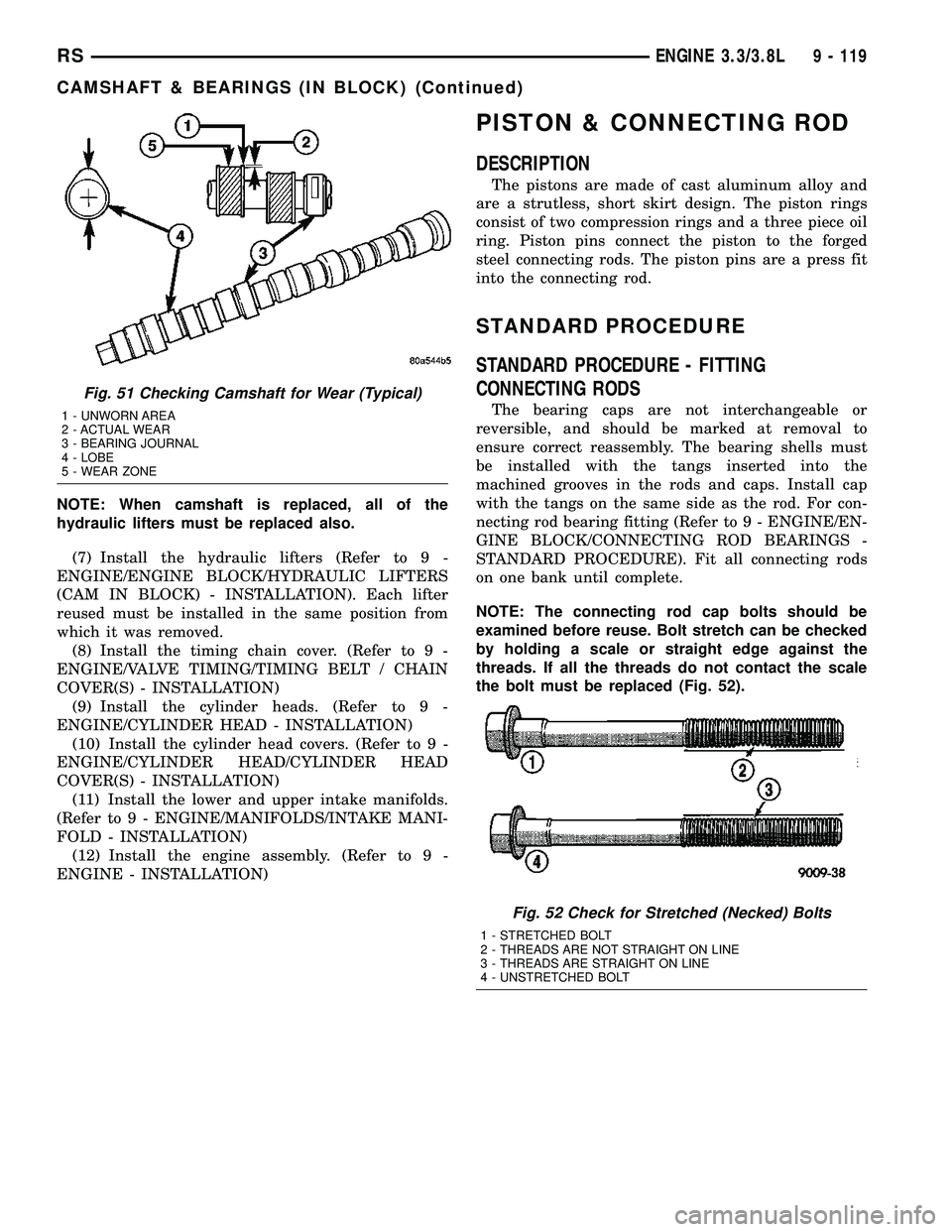
NOTE: When camshaft is replaced, all of the
hydraulic lifters must be replaced also.
(7) Install the hydraulic lifters (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/HYDRAULIC LIFTERS
(CAM IN BLOCK) - INSTALLATION). Each lifter
reused must be installed in the same position from
which it was removed.
(8) Install the timing chain cover. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION)
(9) Install the cylinder heads. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - INSTALLATION)
(10) Install the cylinder head covers. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION)
(11) Install the lower and upper intake manifolds.
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANI-
FOLD - INSTALLATION)
(12) Install the engine assembly. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE - INSTALLATION)
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD
DESCRIPTION
The pistons are made of cast aluminum alloy and
are a strutless, short skirt design. The piston rings
consist of two compression rings and a three piece oil
ring. Piston pins connect the piston to the forged
steel connecting rods. The piston pins are a press fit
into the connecting rod.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FITTING
CONNECTING RODS
The bearing caps are not interchangeable or
reversible, and should be marked at removal to
ensure correct reassembly. The bearing shells must
be installed with the tangs inserted into the
machined grooves in the rods and caps. Install cap
with the tangs on the same side as the rod. For con-
necting rod bearing fitting (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/EN-
GINE BLOCK/CONNECTING ROD BEARINGS -
STANDARD PROCEDURE). Fit all connecting rods
on one bank until complete.
NOTE: The connecting rod cap bolts should be
examined before reuse. Bolt stretch can be checked
by holding a scale or straight edge against the
threads. If all the threads do not contact the scale
the bolt must be replaced (Fig. 52).
Fig. 51 Checking Camshaft for Wear (Typical)
1 - UNWORN AREA
2 - ACTUAL WEAR
3 - BEARING JOURNAL
4 - LOBE
5 - WEAR ZONE
Fig. 52 Check for Stretched (Necked) Bolts
1 - STRETCHED BOLT
2 - THREADS ARE NOT STRAIGHT ON LINE
3 - THREADS ARE STRAIGHT ON LINE
4 - UNSTRETCHED BOLT
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9 - 119
CAMSHAFT & BEARINGS (IN BLOCK) (Continued)
Page 1298 of 2339
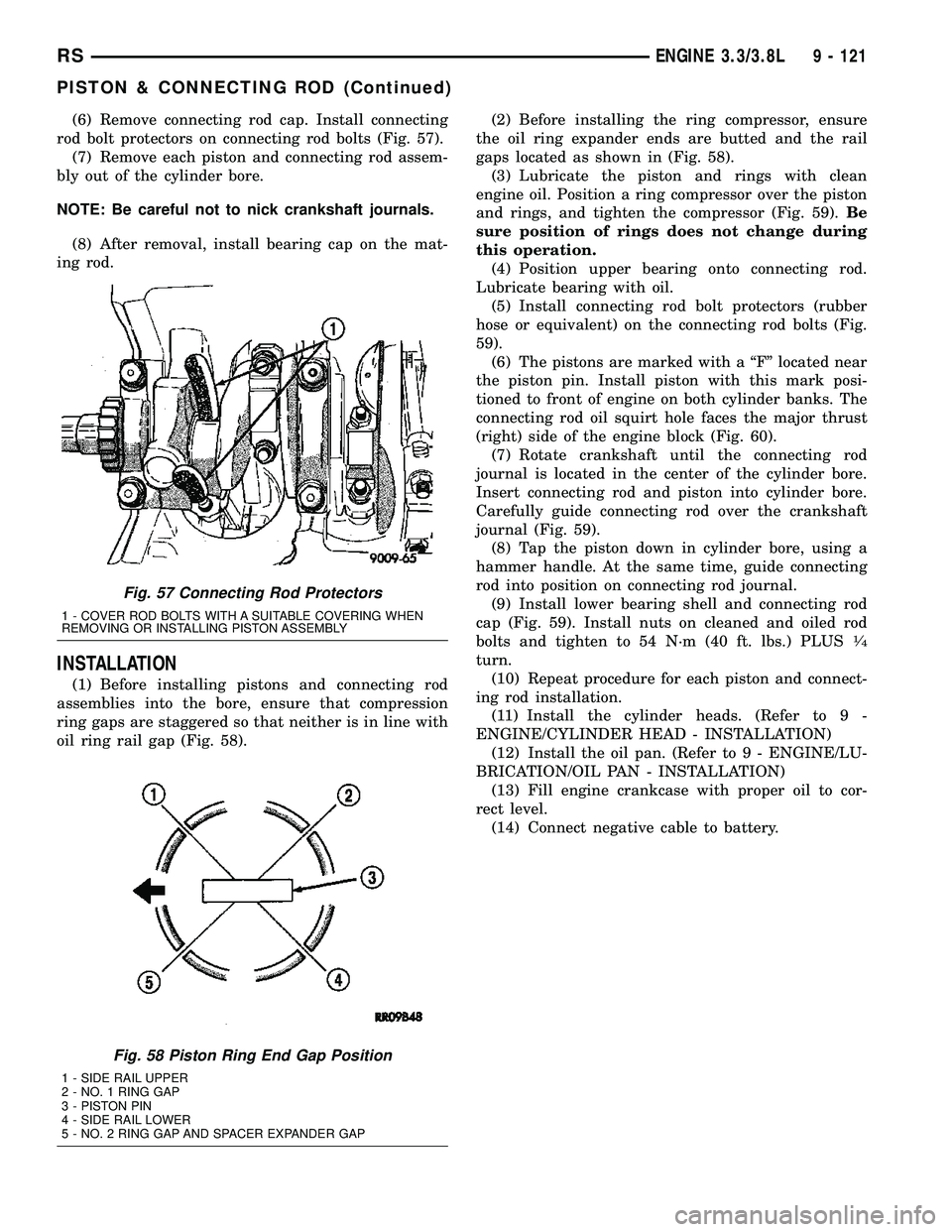
(6) Remove connecting rod cap. Install connecting
rod bolt protectors on connecting rod bolts (Fig. 57).
(7) Remove each piston and connecting rod assem-
bly out of the cylinder bore.
NOTE: Be careful not to nick crankshaft journals.
(8) After removal, install bearing cap on the mat-
ing rod.
INSTALLATION
(1) Before installing pistons and connecting rod
assemblies into the bore, ensure that compression
ring gaps are staggered so that neither is in line with
oil ring rail gap (Fig. 58).(2) Before installing the ring compressor, ensure
the oil ring expander ends are butted and the rail
gaps located as shown in (Fig. 58).
(3) Lubricate the piston and rings with clean
engine oil. Position a ring compressor over the piston
and rings, and tighten the compressor (Fig. 59).Be
sure position of rings does not change during
this operation.
(4) Position upper bearing onto connecting rod.
Lubricate bearing with oil.
(5) Install connecting rod bolt protectors (rubber
hose or equivalent) on the connecting rod bolts (Fig.
59).
(6) The pistons are marked with a ªFº located near
the piston pin. Install piston with this mark posi-
tioned to front of engine on both cylinder banks. The
connecting rod oil squirt hole faces the major thrust
(right) side of the engine block (Fig. 60).
(7) Rotate crankshaft until the connecting rod
journal is located in the center of the cylinder bore.
Insert connecting rod and piston into cylinder bore.
Carefully guide connecting rod over the crankshaft
journal (Fig. 59).
(8) Tap the piston down in cylinder bore, using a
hammer handle. At the same time, guide connecting
rod into position on connecting rod journal.
(9) Install lower bearing shell and connecting rod
cap (Fig. 59). Install nuts on cleaned and oiled rod
bolts and tighten to 54 N´m (40 ft. lbs.) PLUS
1¤4
turn.
(10) Repeat procedure for each piston and connect-
ing rod installation.
(11) Install the cylinder heads. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD - INSTALLATION)
(12) Install the oil pan. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LU-
BRICATION/OIL PAN - INSTALLATION)
(13) Fill engine crankcase with proper oil to cor-
rect level.
(14) Connect negative cable to battery.
Fig. 57 Connecting Rod Protectors
1 - COVER ROD BOLTS WITH A SUITABLE COVERING WHEN
REMOVING OR INSTALLING PISTON ASSEMBLY
Fig. 58 Piston Ring End Gap Position
1 - SIDE RAIL UPPER
2 - NO. 1 RING GAP
3 - PISTON PIN
4 - SIDE RAIL LOWER
5 - NO. 2 RING GAP AND SPACER EXPANDER GAP
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9 - 121
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD (Continued)
Page 1300 of 2339

CONNECTING ROD BEARINGS
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MEASURING
CONNECTING ROD BEARING CLEARANCE
The bearing caps are not interchangeable and
should be marked at removal to ensure correct
assembly. The bearing shells must be installed with
the tangs inserted into the machined grooves in the
rods and caps. Install cap with the tangs on the same
side as the rod. Fit all rods on one bank until com-
plete. Connecting rod bearings are available in the
standard size and the following undersizes: 0.025
mm (0.001 in.) and 0.250 mm (0.010 in.).
CAUTION: Install the bearings in pairs. Do not use a
new bearing half with an old bearing half. Do not
file the rods or bearing caps.
Measure connecting rod journal for taper and out-
of-round. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/
CRANKSHAFT - INSPECTION)The connecting rod bearing clearances can be
determined by use of Plastigage or the equivalent.
The following is the recommended procedure for the
use of Plastigage:
(1) Rotate the crankshaft until the connecting rod
to be checked is at the bottom of its stroke.
(2) Remove oil film from surface to be checked.
Plastigage is soluble in oil.
(3) Place a piece of Plastigage across the entire
width of the bearing shell in the bearing cap approx-
imately 6.35 mm (1/4 in.) off center and away from
the oil hole. In addition, suspect areas can be
checked by placing Plastigage in that area.
(4) Assemble the rod cap with Plastigage in place.
Tighten the rod cap to the specified torque.Do not
rotate the crankshaft while assembling the cap
or the Plastigage may be smeared, giving inac-
curate results.
(5) Remove the bearing cap and compare the
width of the flattened Plastigage with the scale pro-
vided on the package (Fig. 61). Locate the band clos-
est to the same width. This band indicates the
Fig. 60 Piston and Connecting Rod Positioning (Front View of Engine)
1 - MAJOR THRUST SIDE OF PISTON2 - OIL SQUIRT HOLE
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9 - 123
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD (Continued)
Page 1302 of 2339

(3) Install upper side rail first and then the lower
side rail.
(4) Install No. 2 piston ring and then No. 1 piston
ring (Fig. 66).
(5) Position piston ring end gaps as shown in (Fig.
67).
(6) Position oil ring expander gap at least 45É
from the side rail gaps butnoton the piston pin cen-
ter or on the thrust direction. Staggering ring gap is
important for oil control.
CRANKSHAFT MAIN
BEARINGS
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MAIN BEARING
FITTING
Bearing caps are not interchangeable and should
be marked at removal to insure correct assembly
(Fig. 68). Upper and lower bearing halves are NOT
interchangeable. Lower main bearing halves of 1, 3
and 4 are interchangeable. Upper main bearing
halves of 1, 3 and 4 are interchangeable.
Fig. 64 Piston Ring Installation
1 - NO. 1 PISTON RING
2 - NO. 2 PISTON RING
3 - SIDE RAIL
4 - OIL RING
5 - SPACER EXPANDER
Fig. 65 Oil Ring Side Rail - Typical
1 - SIDE RAIL END
Fig. 66 Piston Ring Installation
Fig. 67 Piston Ring End Gap Position
1 - GAP OF LOWER SIDE RAIL
2 - NO. 1 RING GAP
3 - GAP OF UPPER SIDE RAIL
4 - NO. 2 RING GAP AND SPACER EXPANDER GAP
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9 - 125
PISTON RINGS (Continued)
Page 1303 of 2339

Upper and lower number 2 bearing halves are
flanged to carry the crankshaft thrust loads and are
NOT interchangeable with any other bearing halves
in the engine (Fig. 69). All bearing cap bolts removed
during service procedures are to be cleaned and
lubricated with engine oil before installation. Bearing
shells are available in standard and the following
undersizes: 0.025 mm (0.001 in.) and 0.254 mm
(0.010 in). Never install an undersize bearing that
will reduce clearance below specifications.
CRANKSHAFT BEARING OIL CLEARANCE
Inspect the crankshaft bearing journals. (Refer to 9
- ENGINE/ENGINE BLOCK/CRANKSHAFT -
INSPECTION)
Engine crankshaft bearing clearances can be deter-
mined by use of Plastigage or the equivalent. The fol-
lowing is the recommended procedures for the use ofPlastigage with the engine in the vehicle or engine
on a repair stand.
PLASTIGAGE METHODÐENGINE IN-VEHICLE
NOTE: The total clearance of the main bearings can
only be determined with the engine in the vehicle
by removing the weight of the crankshaft. This can
be accomplished by either of two following meth-
ods:
(1) Preferred method:
a. Shim the bearings adjacent to the bearing to be
checked in order to remove the clearance between
upper bearing shell and the crankshaft. This can be
accomplished by placing a minimum of 0.254 mm
(0.010 in.) shim (e. g. cardboard, matchbook cover,
etc.) between the bearing shell and the bearing cap
on the adjacent bearings and tightening bolts to
14±20 N´m (10±15 ft. lbs.).
²When checking #1 main bearing shim #2 main
bearing.
²When checking #2 main bearing shim #1 & #3
main bearing.
²When checking #3 main bearing shim #2 & #4
main bearing.
²When checking #4 main bearing shim #3 main
bearing.
NOTE: Remove all shims before reassembling
engine.
(2) Alternative Method:
a. Support the weight of the crankshaft with a
jack under the counterweight adjacent to the bearing
being checked.
(3) Remove oil film from surface to be checked.
Plastigage is soluble in oil.
(4) Place a piece of Plastigage across the entire
width of the bearing shell in the cap approximately
6.35 mm (1/4 in.) off center and away from the oil
holes (Fig. 70). (In addition, suspected areas can be
checked by placing the Plastigage in the suspected
area). Torque the bearing cap bolts of the bearing
being checked to the proper specifications.
(5) Remove the bearing cap and compare the width
of the flattened Plastigage (Fig. 71) with the scale
provided on the package. Locate the band closest to
the same width. This band shows the amount of
clearance in thousandths. Differences in readings
between the ends indicate the amount of taper
present. Record all readings taken. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE - SPECIFICATIONS)Plastigage gener-
ally is accompanied by two scales. One scale is
in inches, the other is a metric scale.
Fig. 68 Main Bearing Cap Identification
Fig. 69 Main Bearing Identification
1 - OIL GROOVES
2 - OIL HOLES
3 - UPPER BEARINGS
4 - LOWER BEARINGS
9 - 126 ENGINE 3.3/3.8LRS
CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARINGS (Continued)
Page 1316 of 2339
OIL
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE OIL AND
FILTER CHANGE
Change engine oil at mileage and time intervals
described in the Maintenance Schedule. (Refer to
LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE/MAINTE-
NANCE SCHEDULES - DESCRIPTION)
WARNING: NEW OR USED ENGINE OIL CAN BE
IRRITATING TO THE SKIN. AVOID PROLONGED OR
REPEATED SKIN CONTACT WITH ENGINE OIL.
CONTAMINANTS IN USED ENGINE OIL, CAUSED BY
INTERNAL COMBUSTION, CAN BE HAZARDOUS TO
YOUR HEALTH. THOROUGHLY WASH EXPOSED
SKIN WITH SOAP AND WATER. DO NOT WASH
SKIN WITH GASOLINE, DIESEL FUEL, THINNER, OR
SOLVENTS, HEALTH PROBLEMS CAN RESULT. DO
NOT POLLUTE, DISPOSE OF USED ENGINE OIL
PROPERLY. CONTACT YOUR DEALER OR GOVERN-
MENT AGENCY FOR LOCATION OF COLLECTION
CENTER IN YOUR AREA.Run engine until achieving normal operating tem-
perature.
(1) Position the vehicle on a level surface and turn
engine off.
(2) Open hood, remove oil fill cap (Fig. 97).
(3) Hoist and support vehicle on safety stands.
Refer to Hoisting and Jacking Recommendations.
(Refer to LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE/HOIST-
ING - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(4) Place a suitable drain pan under crankcase
drain (Fig. 96).
(5) Remove drain plug from crankcase (Fig. 96)
and allow oil to drain into pan. Inspect drain plug
threads for stretching or other damage. Replace
drain plug and gasket if damaged.
(6) Remove oil filter. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LUBRI-
CATION/OIL FILTER - REMOVAL)
(7) Install and tighten drain plug in crankcase.
(8) Install new oil filter. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/LU-
BRICATION/OIL FILTER - INSTALLATION)
(9) Lower vehicle and fill crankcase with specified
type and amount of engine oil. (Refer to LUBRICA-
TION & MAINTENANCE/FLUID TYPES -
DESCRIPTION)
(10) Install oil fill cap.
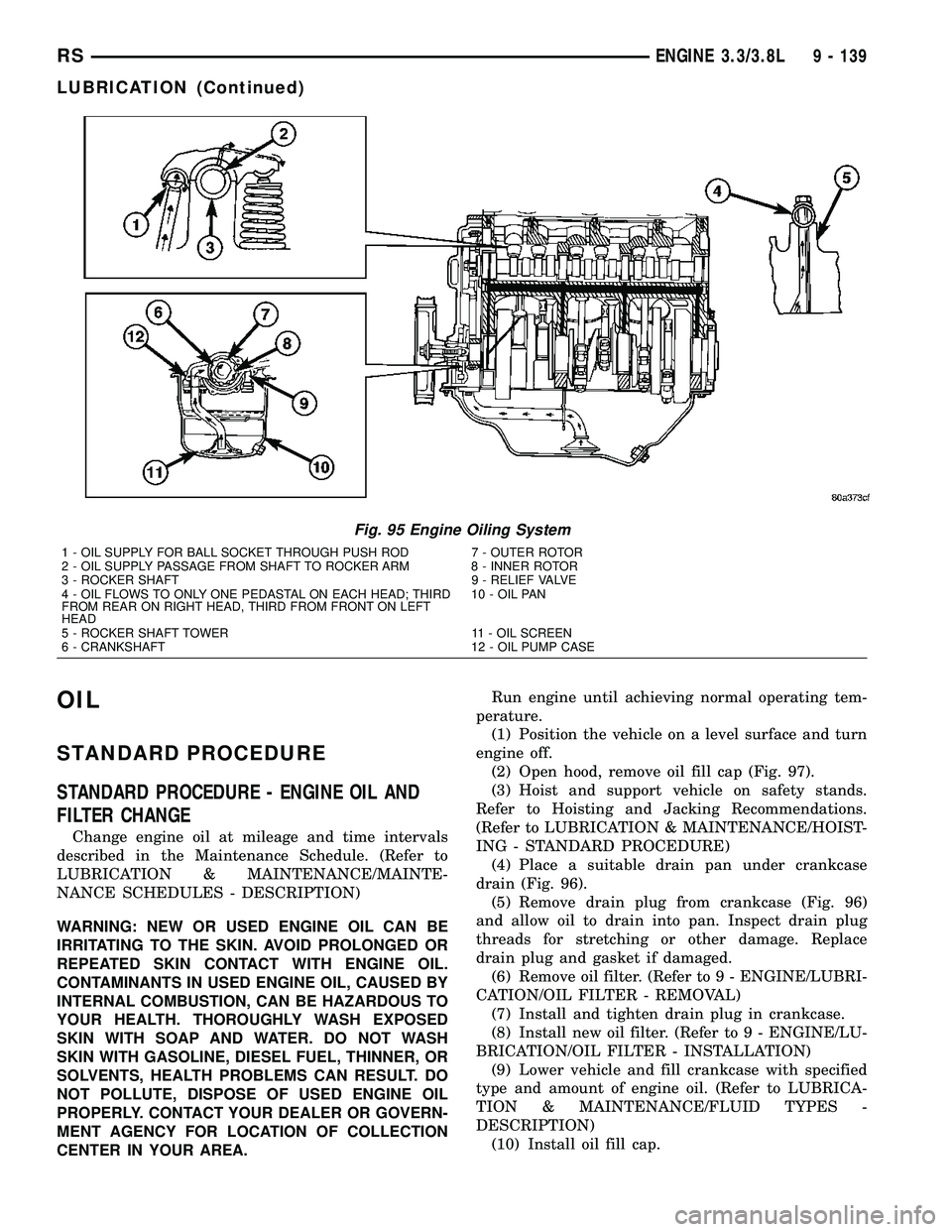
Fig. 95 Engine Oiling System
1 - OIL SUPPLY FOR BALL SOCKET THROUGH PUSH ROD 7 - OUTER ROTOR
2 - OIL SUPPLY PASSAGE FROM SHAFT TO ROCKER ARM 8 - INNER ROTOR
3 - ROCKER SHAFT 9 - RELIEF VALVE
4 - OIL FLOWS TO ONLY ONE PEDASTAL ON EACH HEAD; THIRD
FROM REAR ON RIGHT HEAD, THIRD FROM FRONT ON LEFT
HEAD10 - OIL PAN
5 - ROCKER SHAFT TOWER 11 - OIL SCREEN
6 - CRANKSHAFT 12 - OIL PUMP CASE
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9 - 139
LUBRICATION (Continued)
Page 1324 of 2339
(2) Install timing chain cover (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION) and oil pan (Refer to 9
- ENGINE/VALVE TIMING/TIMING BELT / CHAIN
COVER(S) - INSTALLATION).
INTAKE MANIFOLD
DESCRIPTION
The intake system is made up of an upper and
lower intake manifold. The upper intake manifold is
made of a composite for both the 3.3L engine and for
the 3.8L engine (Fig. 118). The lower intake manifold
is common between the two engines (Fig. 122). It also
provides coolant crossover between cylinder heads
and houses the coolant thermostat (Fig. 122).
The intake manifold utilizes a compact design with
very low restriction and outstanding flow balance.
This design allows the engine to perform with a wide
torque curve while increasing higher rpm horse-
power.
If, for some reason, the molded-in vacuum ports
break, the composite manifold can be salvaged. The
vacuum ports are designed to break at the shoulder,
if overloaded. Additional material in the shoulder
area provides sufficient stock to repair. For more
information and procedure, (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/
MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANIFOLD - STANDARD
PROCEDURE). Also, if the special screws that attach
the MAP sensor, power steering reservoir, throttle
cable bracket, and the EGR tube become stripped, an
oversized screw is available to repair the stripped-out
condition. For more information and procedure,
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANI-
FOLD - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - INTAKE
MANIFOLD LEAKS
An intake manifold air leak is characterized by
lower than normal manifold vacuum. Also, one or
more cylinders may not be functioning.
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN THE
ENGINE IS OPERATING. DO NOT STAND IN A
DIRECT LINE WITH THE FAN. DO NOT PUT YOUR
HANDS NEAR THE PULLEYS, BELTS OR THE FAN.
DO NOT WEAR LOOSE CLOTHING.
(1) Start the engine.
(2) Spray a small stream of water (Spray Bottle) at
the suspected leak area.
(3) If engine RPM'S change, the area of the sus-
pected leak has been found.
(4) Repair as required.
INTAKE MANIFOLD - UPPER
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MANIFOLD
STRIPPED THREAD REPAIR
The composite upper intake manifold thread
bosses, if stripped out, can be repaired by utilizing a
repair screw available through Mopartparts. Repair
screws are available for the following manifold
attached components:
²MAP sensor
²Power steering reservoir
²EGR tube
²Throttle cable bracket
The repair screws require a unique tightening
torque specification from the original screw. Refer to
the following chart for specification.
DESCRIPTION TORQUE*
STRIP-OUT REPAIR SCREWS ONLY
MAP Sensor Repair
Screw4 N´m (35 in. lbs.)
Power Steering Reservoir
Repair Screw9 N´m (80 in. lbs.)
EGR Tube Attaching
Repair Screw9 N´m (80 in. lbs.)
Throttle Cable Bracket
Repair Screw9 N´m (80 in. lbs.)
*Install Slowly Using Hand Tools Only
Fig. 113 Oil Pressure Relief Valve
1 - RELIEF VALVE
2 - SPRING
3 - RETAINER CAP
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9 - 147
OIL PUMP (Continued)
Page 1398 of 2339

IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTOR
DESCRIPTION
The idle air control valve is mounted on the throt-
tle body. The PCM operates the idle air control valve
(Fig. 15) or (Fig. 16).
OPERATION
The PCM adjusts engine idle speed through the
idle air control valve to compensate for engine load,
coolant temperature or barometric pressure changes.The throttle body has an air bypass passage that
provides air for the engine during closed throttle idle.
The idle air control valve regulates air flow through
the bypass passage.
The PCM controls engine idle speed by adjusting
the position of the idle air control valve. The adjust-
ments are based on inputs the PCM receives. The
inputs are from the throttle position sensor, crank-
shaft position sensor, coolant temperature sensor,
MAP sensor, vehicle speed sensor and various switch
operations (brake, park/neutral, air conditioning).
When engine rpm is above idle speed, the IAC is
used for the following functions:
²Off-idle dashpot
²Deceleration air flow control
²A/C compressor load control (also opens the pas-
sage slightly before the compressor is engaged so
that the engine rpm does not dip down when the
compressor engages)
Target Idle
Target idle is determined by the following inputs:
²Gear position
²ECT Sensor
²Battery voltage
²Ambient/Battery Temperature Sensor
²VSS
²TPS
²MAP Sensor
REMOVAL
When servicing throttle body components, always
reassemble components with new O-rings and seals
where applicable. If assembly of component is diffi-
cult, a light coat of engine oil may be applied to the
O-RINGS ONLY to aid assembly. Use care when
removing hoses to prevent damage to hose or hose
nipple.
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove electrical connector from idle air con-
trol valve (Fig. 17).
(3) Remove idle air control valve mounting screw.
(4) Remove valve from throttle body. Ensure the
O-rings is removed with the valve.
INSTALLATION
When servicing throttle body components, always
reassemble components with new O-rings and seals
where applicable. If assembly of component is diffi-
cult,a light coat of engine oil may be applied to
the O-RINGS ONLY (Fig. 18)to aid assembly. Use
care when removing hoses to prevent damage to hose
or hose nipple.
(1) Carefully place idle air control motor into
throttle body.
Fig. 15 TPS/IAC 2.4L
1 - Idle Air Control Valve
2 - Throttle Position Sensor
Fig. 16 TPS/IAC 3.3/3.8L
1 - Idle Air Control Valve
2 - Throttle Position Sensor
RSFUEL INJECTION14-33
Page 1433 of 2339

GEAR
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
GEAR
DESCRIPTION.........................26
OPERATION...........................26
WARNING
WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS.............26
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - LHD GEAR.................26
REMOVAL - RHD GEAR................29INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - LHD GEAR.............31
INSTALLATION - RHD GEAR.............33
SPECIAL TOOLS
POWER STEERING GEAR..............34
OUTER TIE ROD
REMOVAL.............................34
INSTALLATION.........................35
GEAR
DESCRIPTION
This vehicle is equipped with a rack and pinion
power steering gear (Fig. 1). It is mounted to the
underside of the front suspension cradle/crossmem-
ber.
The steering column is attached to the gear
through the use of an intermediate shaft and cou-
plers. The outer ends of the power steering gear's
outer tie rods connect to the steering knuckles.
NOTE: The power steering gear should NOT be ser-
viced or adjusted unless DaimlerChrysler Corpora-
tion authorizes. If a malfunction or oil leak occurs,
the complete steering gear should be replaced.
Only the outer tie rods may be replaced separately
from the rest of the gear.
OPERATION
Turning of the steering wheel is converted into lin-
ear (side-to-side) travel through the meshing of the
helical pinion teeth with the rack teeth in the steer-
ing gear. This travel pushes and pulls the tie rods to
change the direction of the vehicle's front wheels.
Power assist steering provided by the power steer-
ing pump is controlled by an open center, rotary type
control valve which directs oil from the pump to
either side of the integral rack piston upon demand.
Road feel is controlled by the diameter of a torsion
bar which initially steers the vehicle. As required
steering effort increases, as in a turn, the torsion bar
twists, causing relative rotary motion between the
rotary valve body and the valve spool. This move-
ment directs oil behind the integral rack piston
which, in turn, builds hydraulic pressure and assists
in the turning effort.Manual steering control of the vehicle can be main-
tained if power steering assist is lost. However,
under this condition, steering effort is significantly
increased.
WARNING
WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS
WARNING: POWER STEERING FLUID, ENGINE
PARTS AND EXHAUST SYSTEM MAY BE
EXTREMELY HOT IF ENGINE HAS BEEN RUNNING.
DO NOT START ENGINE WITH ANY LOOSE OR DIS-
CONNECTED HOSES. DO NOT ALLOW HOSES TO
TOUCH HOT EXHAUST MANIFOLD OR CATALYST.
WARNING: FLUID LEVEL SHOULD BE CHECKED
WITH THE ENGINE OFF TO PREVENT PERSONAL
INJURY FROM MOVING PARTS.
CAUTION: When the system is open, cap all open
ends of the hoses, power steering pump fittings or
power steering gear ports to prevent entry of for-
eign material into the components.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - LHD GEAR
(1) Remove cap from power steering fluid reser-
voir.
(2) Using a siphon pump, remove as much fluid as
possible from the power steering fluid reservoir.Use
care not to damage the filter mesh below the
fluid surface.
19 - 26 GEARRS
Page 1476 of 2339

(14) Measure input shaft end play. Place transaxle
so input shaft is vertical. Set up end play set and
dial indicator as shown in (Fig. 27).Input shaft end
play should be within 0.13-0.64 mm (0.005-0.025
in.)If outside of this range, a #4 thrust plate change
is required. Record indicator reading for reference
upon reassembly.(15) Remove oil pump-to-case bolts (Fig. 28).
CAUTION: Be sure input speed sensor is removed
before removing oil pump.
(16) Install pullers Tool C-3752 as shown in (Fig.
29).
Fig. 26 Low/Reverse Accumulator
1 - PISTON
2 - RETURN SPRINGS
Fig. 27 Measure Input Shaft End Play Using Tool
8266ÐTypical
1 - TOOL 8266±8
2 - TOOL 8266±2
3 - TOOL C-3339
Fig. 28 Remove Oil Pump-to-Case Bolts
1 - PUMP ATTACHING BOLTS
2 - PUMP HOUSING
Fig. 29 Install Tool C-3752
1 - PULLERS TOOL C-3752
2 - PUMP
RS40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21-15
40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE (Continued)