ECU CHRYSLER CARAVAN 2005 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2005, Model line: CARAVAN, Model: CHRYSLER CARAVAN 2005Pages: 2339, PDF Size: 59.69 MB
Page 324 of 2339

REMOVAL
The battery cables on this vehicle may include por-
tions of wiring circuits for the generator and other
components on the vehicle. If battery cable replace-
ment is required, it will be necessary to extract the
cables out of the engine wire harness assembly. Use
care not to damage the other wires and circuits
which are also packaged into the engine wire harness
assembly.
(1) Turn the ignition switch to the Off position. Be
certain that all electrical accessories are turned off.
(2) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(3) Remove the battery thermowrap (if equipped)
from the battery tray.
(4) Remove the tape from the engine wire harness
assembly, to access the desired battery cable.
(5) One at a time, trace and disconnect the battery
cable retaining fasteners and routing clips until the
desired cable is free from the vehicle.
(6) Feed the battery cable out of the vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the battery cable in the vehicle.
(2) One at a time, trace and install the battery
cable retaining fasteners and routing clips until the
desired cable is properly installed in the engine wire
harness assembly.
(3) Install the tape on the engine wire harness
assembly.
(4) Install the battery thermowrap (if equipped) on
the battery tray.
(5) Connect the battery negative cable.
BATTERY TRAY
DESCRIPTION
The battery is mounted in a molded plastic battery
tray and support unit located in the left front corner
of the engine compartment. The battery tray and
support unit is secured with two nuts, one is located
directly under the battery and the other is located on
the right side of the tray which also serves as a cool-
ant bottle neck retaining bolt. An additional bolt is
located directly under the battery.
The battery tray and support unit also includes a
engine vacuum reservoir, located in the rear of the
unit (Fig. 17). And a drainage hose, located in the
front of the unit (Fig. 17).
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Disconnect and isolate the battery positive
cable.(3) Remove the battery from the vehicle. (Refer to
8 - ELECTRICAL/BATTERY SYSTEM/BATTERY -
REMOVAL).
(4) Remove the battery tray retaining fasteners
(Fig. 18).
Fig. 17 RS BATTERY TRAY
1 - ENGINE VACUUM RESERVOIR
2 - BATTERY TRAY ASSEMBLY
3 - DRAINAGE HOSE
Fig. 18 BATTERY TRAY POSITION & ORIENTATION
1 - BATTERY TRAY RETAINING FASTENERS
RSBATTERY SYSTEM8F-19
BATTERY CABLES (Continued)
Page 347 of 2339

OPERATION
When the rear window defogger button is
depressed to the On position, current is directed to
the rear defogger grid lines and the heated power
mirrors (if equipped). The heated grid lines heat the
glass to help clear the rear window and side mirror
surfaces of fog or frost.
The electric backlight (EBL) system is controlled
by a momentary switch located in the A/C-heater
control on the instrument panel. A yellow indicator in
the switch will illuminate to indicate when the sys-
tem is turned on. The integrated power module (IPM)
contains the EBL system control circuitry.
NOTE: The rear window defogger turns off automat-
ically after approximately 10 minutes of initial oper-
ation. Each following activation cycle of the
defogger system will last approximately five min-
utes.
The EBL system will be automatically turned off
after a programmed time interval of about ten min-
utes. After the initial time interval has expired, if the
defogger switch is turned on again during the same
ignition cycle, the defogger system will automatically
turn off after about five minutes.
The EBL system will automatically shut off if the
ignition switch is turned to the Off position, or it can
be turned off manually by depressing the defogger
switch a second time.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
ELECTRIC BACKLIGHT (EBL) SYSTEM
NOTE: Illumination of the defogger switch indicator
lamp means that there is electrical current available
at the output of the rear window defogger logic cir-
cuitry, but does not confirm that the electrical cur-
rent is reaching the rear glass heating grid lines.
NOTE: For circuit descriptions and diagrams of the
rear window defogger system, refer to 8W - WIRING
DIAGRAM INFORMATION.
Operation of the electrical backlight (EBL) system
can be confirmed by the following:(1) Turn the ignition switch to the On position. Set
the defogger switch in the On position. The rear win-
dow defogger operation can be checked by feeling the
rear window glass. A distinct difference in tempera-
ture between the grid lines and the adjacent clear
glass can be detected within three to four minutes of
operation.
(2) If a temperature difference is not detected, use
a 12-volt DC voltmeter and contact the rear glass
heating grid terminal B with the negative lead, and
terminal A with the positive lead (Fig. 2). The volt-
meter should read battery voltage. If the voltmeter
does not read battery voltage, check the following:
²Confirm that the ignition switch is in the On
position.
²Make sure that the rear glass heating grid feed
wire and ground wire are connected to the terminals.
Confirm that the ground wire has continuity to
ground.
²Check that fuse 13 (40 amp) in the integrated
power module (IPM) is OK. The fuse must be tight in
it's receptacle and all electrical connections must be
secure.
(3) When the above steps have been completed and
the rear glass heating grid is still inoperative, one or
more of the following is faulty. It may be necessary to
connect a DRBIIItscan tool to perform further diag-
nostics. Refer to Body Diagnostic Procedures.
²Rear window defogger switch in the A/C-heater
control.
²J1850 bus communication between the A/C-
heater control and the front control module (FCM).
²Rear window defogger (EBL) relay in the IPM.
²Rear window defogger (EBL) relay control circu-
ity in the IPM.
²Check for a loose wire connector or a wire
pushed out of a connector.
²Rear window grid lines (all grid lines would
have to be broken, or the power feed or ground wire
not connected, for the entire heating grid to be inop-
erative).
(4) If the system operation has been verified but
defogger switch LED indicator does not illuminate,
replace the A/C-heater control.
8G - 2 HEATED GLASSRS
HEATED GLASS (Continued)
Page 355 of 2339
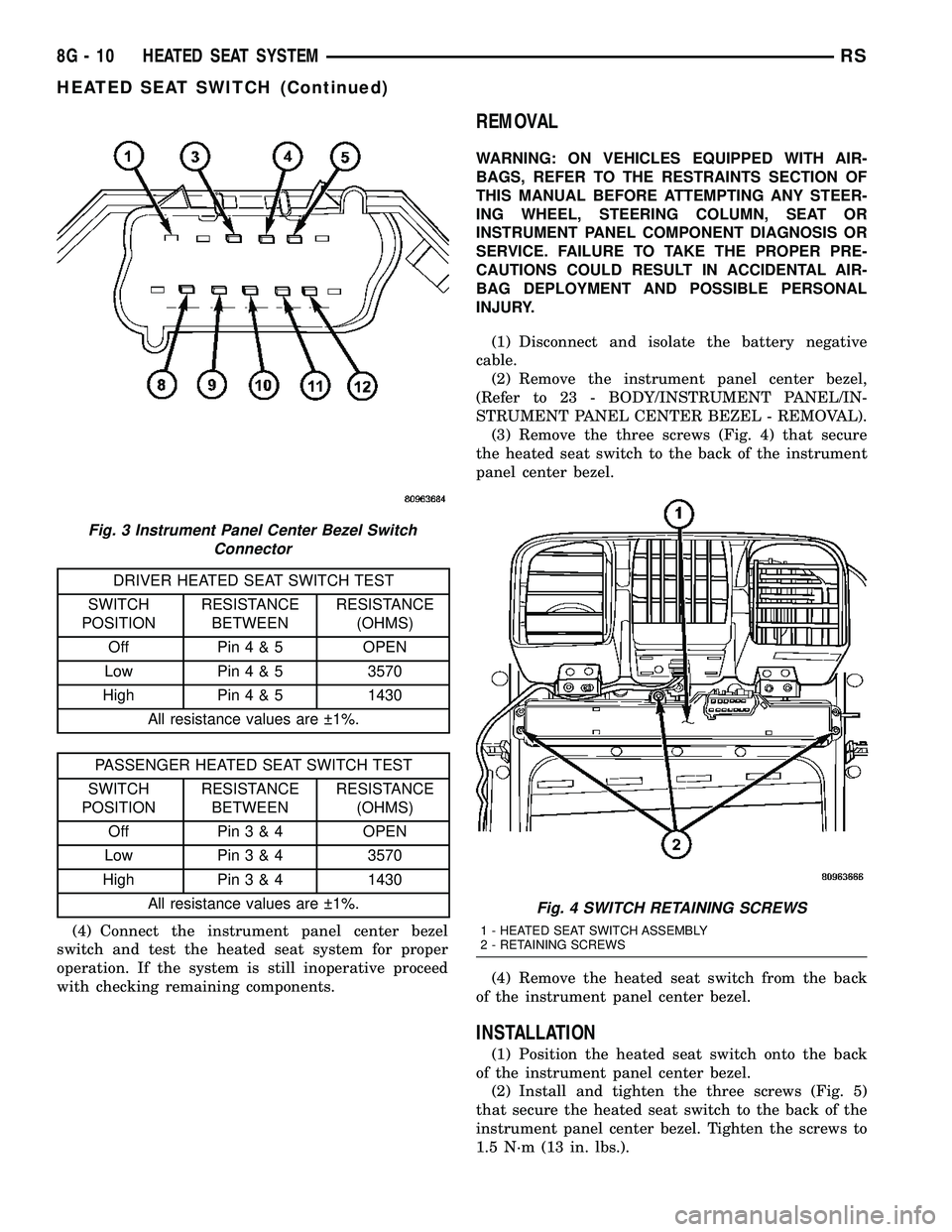
DRIVER HEATED SEAT SWITCH TEST
SWITCH
POSITIONRESISTANCE
BETWEENRESISTANCE
(OHMS)
Off Pin4&5OPEN
Low Pin4&53570
High Pin4&51430
All resistance values are 1%.
PASSENGER HEATED SEAT SWITCH TEST
SWITCH
POSITIONRESISTANCE
BETWEENRESISTANCE
(OHMS)
Off Pin3&4OPEN
Low Pin3&43570
High Pin3&41430
All resistance values are 1%.
(4) Connect the instrument panel center bezel
switch and test the heated seat system for proper
operation. If the system is still inoperative proceed
with checking remaining components.
REMOVAL
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAGS, REFER TO THE RESTRAINTS SECTION OF
THIS MANUAL BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY STEER-
ING WHEEL, STEERING COLUMN, SEAT OR
INSTRUMENT PANEL COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS OR
SERVICE. FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRE-
CAUTIONS COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIR-
BAG DEPLOYMENT AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL
INJURY.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the instrument panel center bezel,
(Refer to 23 - BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/IN-
STRUMENT PANEL CENTER BEZEL - REMOVAL).
(3) Remove the three screws (Fig. 4) that secure
the heated seat switch to the back of the instrument
panel center bezel.
(4) Remove the heated seat switch from the back
of the instrument panel center bezel.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the heated seat switch onto the back
of the instrument panel center bezel.
(2) Install and tighten the three screws (Fig. 5)
that secure the heated seat switch to the back of the
instrument panel center bezel. Tighten the screws to
1.5 N´m (13 in. lbs.).
Fig. 3 Instrument Panel Center Bezel Switch
Connector
Fig. 4 SWITCH RETAINING SCREWS
1 - HEATED SEAT SWITCH ASSEMBLY
2 - RETAINING SCREWS
8G - 10 HEATED SEAT SYSTEMRS
HEATED SEAT SWITCH (Continued)
Page 358 of 2339

(2) Connect the new heating element electrical
connectors (Fig. 8).Passenger seat shown, driver
seat similar.
(3) Connect the battery negative cable.
(4) Verify heated seat system operation.
(5) Install the appropriate seat cushion or seat
back trim cover.
NOTE: Make certain the seat wire harness is cor-
rectly routed through the seat and seat back. The
excess wire between the cushion and back ele-
ments should be securely tucked between the rear
of the cushion foam and the rear carpet flap of the
trim cover.HEATED SEAT SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
Two heated seat sensors are used per vehicle, one
in each front seat cushion heating element. The
heated seat temperature sensor is a Negative Tem-
perature Coefficient (NTC) thermistor.
The heated seat sensors cannot be repaired or
adjusted and if found to be faulty, the complete
heated seat cushion element must be replaced.
OPERATION
The temperature sensor is a Negative Temperature
Coefficient (NTC) thermistor. When the temperature
of the seat cushion cover rises, the resistance of the
sensor decreases. The heated seat module supplies a
five-volt current to one side of each sensor, and mon-
itors the voltage drop through the sensor on a return
circuit. The heated seat module uses this tempera-
ture sensor input to monitor the temperature of the
seat, and regulates the current flow to the seat heat-
ing elements accordingly.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
HEATED SEAT SENSOR
Refer to the appropriate wiring information for
complete circuit schematic or connector pin-out infor-
mation.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable. Disconnect the green 4-way heated seat mod-
ule wire harness connector.
(2) Using an ohmmeter, check the resistance
between cavities 2 and 3. The sensor resistance
should be between 50 kilohms at 15É C (60É F) and 2
kilohms at 30É C (85É F). If not OK, replace the
faulty seat element and sensor assembly.
Fig. 8 HEATED SEAT WIRE HARNESS ROUTING
1 - SEAT BACK HEATED SEAT WIRE HARNESS
2 - PASSENGER SEAT BACK
3 - SEAT BACK ELEMENT CONNECTOR
4 - SEAT CUSHION ELEMENT CONNECTOR
RSHEATED SEAT SYSTEM8G-13
HEATED SEAT ELEMENTS (Continued)
Page 373 of 2339

REMOVAL
When replacing the spark plugs and spark plug
cables, route the cables correctly and secure them in
the appropriate retainers. Failure to route the cables
properly can cause the radio to reproduce ignition
noise, cross ignition of the spark plugs orshort cir-
cuit the cables to ground.
Always remove cables by grasping at the boot,
rotating the boot 1/2 turn, and pulling straight back
in a steady motion.
(1) Prior to removing the spark plug, spray com-
pressed air around the spark plug hole and the area
around the spark plug.
(2) Remove the spark plug using a quality socket
with a foam insert.
(3) Inspect the spark plug condition.
INSTALLATION
When replacing the spark plugs and spark plug
cables, route the cables correctly and secure them in
the appropriate retainers. Failure to route the cables
properly can cause the radio to reproduce ignition
noise, cross ignition of the spark plugs orshort cir-
cuit the cables to ground.
(1) Coat threads of spark plug with anti-seize. Be
sure not to get anti-seizeANYWHERE BUT ON
THE THREADS OF THE SPARK PLUG as
shown in (Fig. 13).
(2) To avoid cross threading, start the spark plug
into the cylinder head by hand.
(3) Tighten spark plugs to 17.5 N´m (13 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(4) Install spark plug cables over spark plugs. A
click will be heard and felt when the cable properly
attaches to the spark plug.
SPARK PLUG CABLE
DESCRIPTION
Spark Plug cables are sometimes referred to as
secondary ignition wires. The wires transfer electri-
cal current from the ignition coil pack to individualspark plugs at each cylinder. The resistive spark plug
cables are of nonmetallic construction. The cables
provide suppression of radio frequency emissions
from the ignition system.
Check the spark plug cable connections for good
contact at the coil, and spark plugs. Terminals should
be fully seated. The insulators should be in good con-
dition and should fit tightly on the coil, and spark
plugs. Spark plug cables with insulators that are
cracked or torn must be replaced.
Clean Spark Plug cables with a cloth moistened
with a non-flammable solvent. Wipe the cables dry.
Check for brittle or cracked insulation. The spark
plug cables and spark plug boots are made from high
temperature materials.
REMOVAL - 2.0/2.4L
Failure to route the cables properly could cause the
radio to reproduce ignition noise, cross ignition of the
spark plugs or short circuit the cables to ground.
Remove spark plug cable from coil first.
Always remove the spark plug cable by grasping
the top of the spark plug insulator, turning the boot
1/2 turn and pulling straight up in a steady motion.
INSTALLATION - 2.0/2.4L
Failure to route the cables properly could cause the
radio to reproduce ignition noise, cross ignition of the
spark plugs or short circuit the cables to ground.
Install spark plug insulators over spark plugs.
Ensure the top of the spark plug insulator covers the
upper end of the spark plug tube, then connect the
other end to coil pack.
8I - 10 IGNITION CONTROLRS
SPARK PLUG (Continued)
Page 377 of 2339
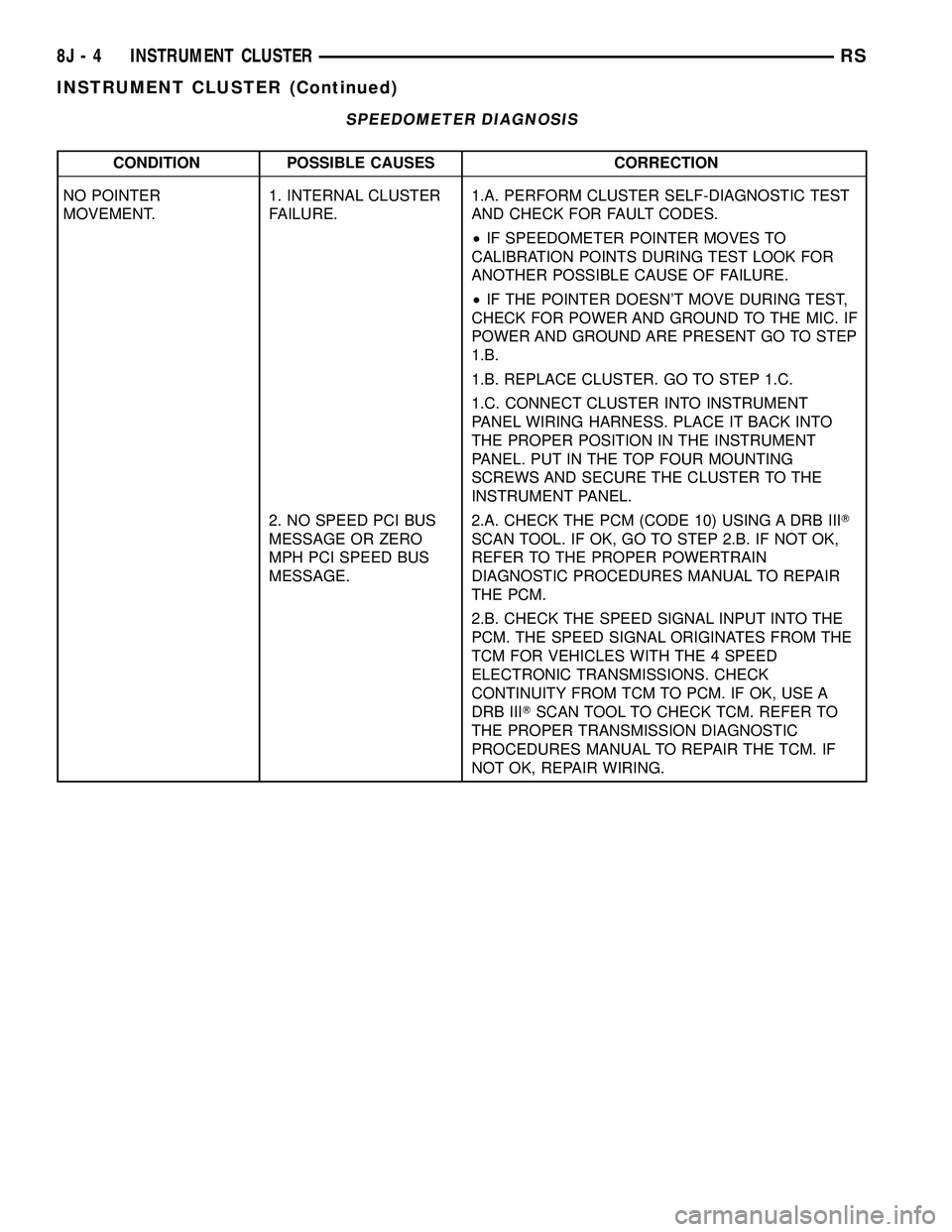
SPEEDOMETER DIAGNOSIS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
NO POINTER
MOVEMENT.1. INTERNAL CLUSTER
FAILURE.1.A. PERFORM CLUSTER SELF-DIAGNOSTIC TEST
AND CHECK FOR FAULT CODES.
²IF SPEEDOMETER POINTER MOVES TO
CALIBRATION POINTS DURING TEST LOOK FOR
ANOTHER POSSIBLE CAUSE OF FAILURE.
²IF THE POINTER DOESN'T MOVE DURING TEST,
CHECK FOR POWER AND GROUND TO THE MIC. IF
POWER AND GROUND ARE PRESENT GO TO STEP
1.B.
1.B. REPLACE CLUSTER. GO TO STEP 1.C.
1.C. CONNECT CLUSTER INTO INSTRUMENT
PANEL WIRING HARNESS. PLACE IT BACK INTO
THE PROPER POSITION IN THE INSTRUMENT
PANEL. PUT IN THE TOP FOUR MOUNTING
SCREWS AND SECURE THE CLUSTER TO THE
INSTRUMENT PANEL.
2. NO SPEED PCI BUS
MESSAGE OR ZERO
MPH PCI SPEED BUS
MESSAGE.2.A. CHECK THE PCM (CODE 10) USING A DRB IIIT
SCAN TOOL. IF OK, GO TO STEP 2.B. IF NOT OK,
REFER TO THE PROPER POWERTRAIN
DIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURES MANUAL TO REPAIR
THE PCM.
2.B. CHECK THE SPEED SIGNAL INPUT INTO THE
PCM. THE SPEED SIGNAL ORIGINATES FROM THE
TCM FOR VEHICLES WITH THE 4 SPEED
ELECTRONIC TRANSMISSIONS. CHECK
CONTINUITY FROM TCM TO PCM. IF OK, USE A
DRB IIITSCAN TOOL TO CHECK TCM. REFER TO
THE PROPER TRANSMISSION DIAGNOSTIC
PROCEDURES MANUAL TO REPAIR THE TCM. IF
NOT OK, REPAIR WIRING.
8J - 4 INSTRUMENT CLUSTERRS
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER (Continued)
Page 387 of 2339

LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR
DESCRIPTION
LAMP SYSTEMS
Lighting circuits are protected by fuses. Lighting
circuits require an overload protected power and high
side drivers source, ON/OFF device, lamps and body
grounds to operate properly. Plastic lamps require a
wire in the harness to supply body ground to the
lamp socket. Replace sockets and bulbs that are cor-
roded.
Some of the interior and exterior lighting functions
are governed by the Body Control Module (BCM).
The headlamp, dome, and the door ajar switches pro-
vide signals to the BCM. The BCM in turn sends a
Programmable Communication Interface (PCI) bus
message to the Front Control Module (FCM) to
enable the necessary drivers to set the required illu-
mination configuration.
Wire connectors can make intermittent contact or
become corroded. Before coupling wire connectors,
inspect the terminals inside the connector. Male ter-
minals should not be bent or disengaged from the
insulator. Female terminals should not be sprung
open or disengaged from the insulator. Bent and
sprung terminals can be repaired using needle nose
pliers and pick tool. Corroded terminals appear
chalky or green. Corroded terminals should be
replaced to avoid recurrence of the problem symp-
toms.
Begin electrical system failure diagnosis by testing
related fuses in the fuse block and intelligent power
module. Verify that bulbs are in good condition and
test continuity of the circuit ground. Refer to the
appropriate wiring information.
AUTOMATIC HEADLAMP SYSTEM
The Automatic Headlamp system turns the instru-
mentation and exterior illumination lamps ON when
the ambient light levels are Night and the engine
RPM is 450 or above, and OFF when light levels are
Day.
DAYTIME RUNNING LAMPS
Operating the high-beam headlamps at reduced
power provides daytime running lamps, which are
required on all new Canadian vehicles. Daytime run-
ning lamps are functional when 450 rpm's are
reached.
HEADLAMPS ON WITH WINDSHIELD WIPERS
For vehicles equipped with the Automatic Head-
lamp System, the instrumentation and exterior illu-
mination lamps will be turned ON when the
headlamp switch is in the AUTO position, RPM >450 and the windshield wipers have been in the
intermittent, low or high mode of operation for more
than ten seconds. When the windshield wipers are
turned OFF the Body Control Module will determine
if the instrumentation and exterior illumination
lamps should remain ON base upon the current
ambient light level.
HEADLAMP SYSTEM
The configuration of the headlamp system of head-
lamps, park lamps and fog lamps is determined by
the BCM. The BCM determines the lighting configu-
ration as a result of the inputs from the ignition
switch, headlamp switch and multi-function switch. A
PCI bus is transmitted from the BCM to the FCM to
enable the necessary drivers to set the illumination
configuration. Four wires are connected between the
headlamp switch and the BCM. The first wire con-
tains information regarding the position of the head-
lamp switch (Off, Automatic Headlamps, Automatic
Headlamp switch fog, Park with Fog, Head, or Head
with Fog Lamps). The second wire contains informa-
tion regarding the position of the dimmer switch
(Dome Lamp, Daytime Brightness, Dimming Level or
Off). The third wire is a dedicated signal return
(ground) wire. The fourth wire provides power to the
front fog lamp indicator.
HEADLAMP TIME DELAY SYSTEM
The headlamp time delay system is controlled by
the Body Control Module (BCM) via a PCI bus mes-
sage transmitted by the BCM to the FCM to turn off
the headlamps.
OPERATION
AUTOMATIC HEADLAMP SYSTEM
Automatic headlamps are controlled by the Body
Control Module (BCM). With the headlamp switch in
the AUTO position, the BCM will control the head-
lamp, parking, side marker, tail and instrumentation
lamps based on ambient light levels. Ambient light
levels are monitored by the BCM using the Day/
Night signal and Electrochromatic Mirror (ECM)
present from the Compass Mini Trip (CMTC) located
on the front windshield in front of the rear view mir-
ror ECM. Ambient light readings are averaged to
limit cycling the lamps ON and OFF when passing
through areas with varying light levels. The auto-
matic headlamps will only function when the engine
is running with RPM > 450. When the headlamp
switch is in the AUTO position (Automatic mode), the
Headlamp Time Delay system will function when the
ignition switch is placed in any position other than
run/start.
8L - 2 LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIORRS
Page 392 of 2339

(3) Install the retaining screws.
(4) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
FRONT FOG LAMP
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FRONT FOG LAMP
When a vehicle experiences problems with the
front fog lamp system, verify the condition of the bat-
tery connections, fuses, charging system, fog lamp
bulbs, wire connectors, relay, high beam switch, and
headlamp switch. Refer to the appropriate wiring
information.
Each vehicle is equipped with various lamp assem-
blies. A good ground is necessary for proper lighting
operation. Grounding is provided by the lamp socket
when it comes in contact with the metal body, or
through a separate ground wire.
When changing lamp bulbs check the socket for
corrosion. If corrosion is present, clean it with a wire
brush.
When it is necessary to remove components to ser-
vice another, it should not be necessary to apply
excessive force or bend a component to remove it.
Before damaging a trim component, verify hidden
fasteners or captured edges are not holding the com-
ponent in place.
FRONT FOG LAMP DIAGNOSIS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
FOG LAMPS ARE DIM
WITH ENGINE IDLING
OR IGNITION TURNED
OFF.1. Loose or corroded battery
cables.1. Clean and secure battery cable clamps and
posts.
2. Loose or worn generator drive
belt.2. Adjust or replace generator drive belt.
3. Charging system output too low. 3. Test and repair charging system. Refer to
Electrical, Charging,
4. Battery has insufficient charge. 4. Test battery state-of-charge. Refer to
Electrical, Battery System.
5. Battery is sulfated or shorted. 5. Load test battery. Refer to Electrical, Battery
System.
6. Poor lighting circuit Z349/Z248
ground.6. Test for voltage drop across Z349/248
ground locations. Refer to Electrical, Wiring
Information.
FOG LAMP BULBS
BURN OUT
FREQUENTLY1. Charging system output too
high.1. Test and repair charging system. Refer to
Electrical, Charging.
2. Loose or corroded terminals or
splices in circuit.2. Inspect and repair all connectors and splices.
Refer to Electrical, Wiring Information.
Fig. 7 CHMSL ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
1 - CHMSL UNIT
2 - CHMSL ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
RSLAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR8L-7
CENTER HIGH MOUNTED STOP LAMP UNIT (Continued)
Page 396 of 2339
HEADLAMP
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HEADLAMP
When a vehicle experiences problems with the
headlamp system, verify the condition of the battery
connections, fuses, charging system, headlamp bulbs,
wire connectors, relay, high beam switch, dimmer
switch, and headlamp switch. Refer to the appropri-
ate wiring information.
Each vehicle is equipped with various lamp assem-
blies. A good ground is necessary for proper lighting
operation. Grounding is provided by the lamp socketwhen it comes in contact with the metal body, or
through a separate ground wire.
When changing lamp bulbs check the socket for
corrosion. If corrosion is present, clean it with a wire
brush.
When it is necessary to remove components to ser-
vice another, it should not be necessary to apply
excessive force or bend a component to remove it.
Before damaging a trim component, verify hidden
fasteners or captured edges are not holding the com-
ponent in place.
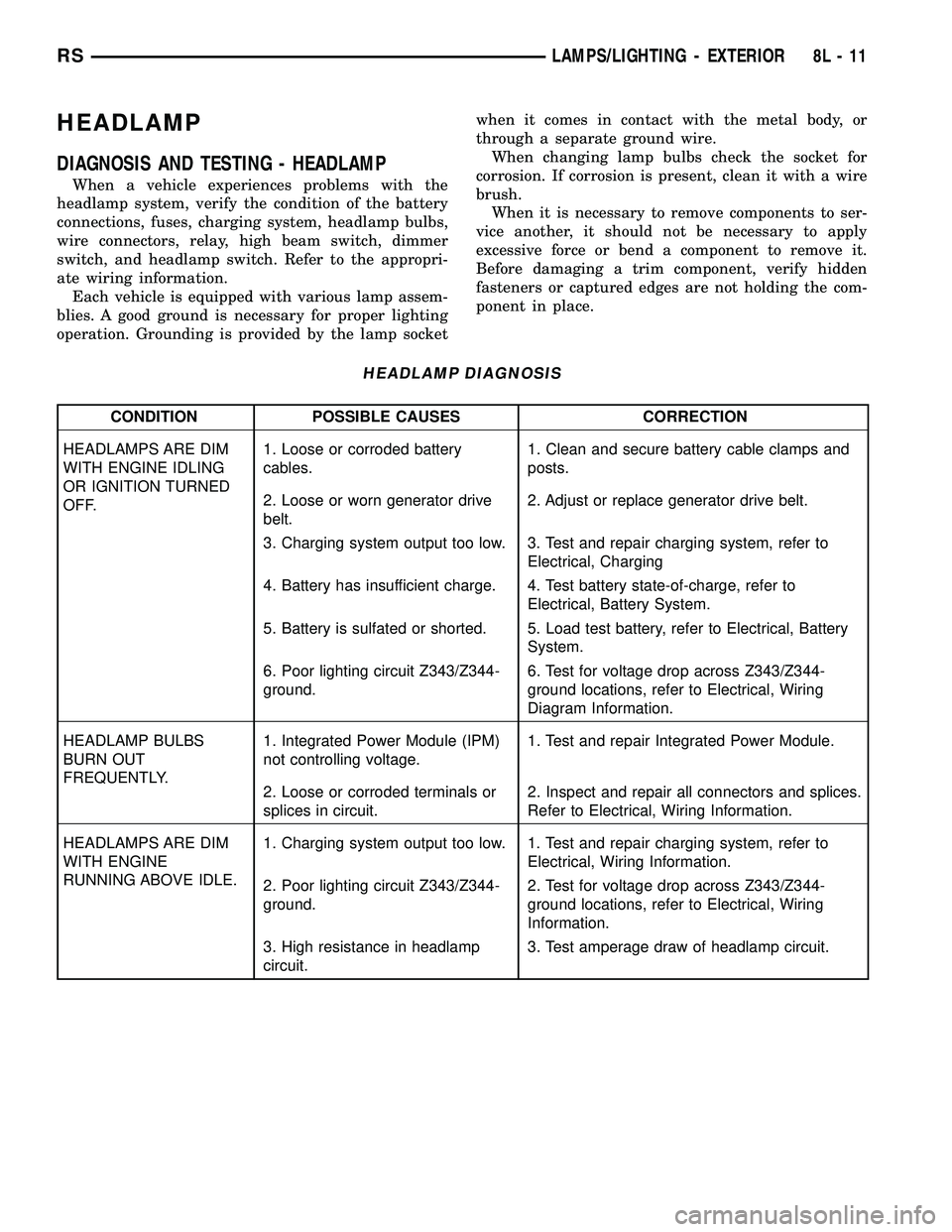
HEADLAMP DIAGNOSIS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
HEADLAMPS ARE DIM
WITH ENGINE IDLING
OR IGNITION TURNED
OFF.1. Loose or corroded battery
cables.1. Clean and secure battery cable clamps and
posts.
2. Loose or worn generator drive
belt.2. Adjust or replace generator drive belt.
3. Charging system output too low. 3. Test and repair charging system, refer to
Electrical, Charging
4. Battery has insufficient charge. 4. Test battery state-of-charge, refer to
Electrical, Battery System.
5. Battery is sulfated or shorted. 5. Load test battery, refer to Electrical, Battery
System.
6. Poor lighting circuit Z343/Z344-
ground.6. Test for voltage drop across Z343/Z344-
ground locations, refer to Electrical, Wiring
Diagram Information.
HEADLAMP BULBS
BURN OUT
FREQUENTLY.1. Integrated Power Module (IPM)
not controlling voltage.1. Test and repair Integrated Power Module.
2. Loose or corroded terminals or
splices in circuit.2. Inspect and repair all connectors and splices.
Refer to Electrical, Wiring Information.
HEADLAMPS ARE DIM
WITH ENGINE
RUNNING ABOVE IDLE.1. Charging system output too low. 1. Test and repair charging system, refer to
Electrical, Wiring Information.
2. Poor lighting circuit Z343/Z344-
ground.2. Test for voltage drop across Z343/Z344-
ground locations, refer to Electrical, Wiring
Information.
3. High resistance in headlamp
circuit.3. Test amperage draw of headlamp circuit.
RSLAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR8L-11
Page 420 of 2339
NOTE: If a new CMTC module has been installed,
the compass will have to be calibrated and the vari-
ance set. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/OVERHEAD
CONSOLE - STANDARD PROCEDURE - COMPASS
CALIBRATION).
UNIVERSAL TRANSMITTER
DESCRIPTION
A Universal Transmitter transceiver is available on
some vehicles. The universal transmitter transceiver
is integral to the Electronic Vehicle Information Cen-
ter (EVIC) and the Compass Mini-Trip Computer
(CMTC) modules, which are located in the overhead
console. The only visible component of the universal
transmitter are the three transmitter push buttons
centered between the modules push buttons located
just rearward of the display screen in the overhead
console. The three universal transmitter push but-
tons are identified with one, two or three light indi-
cators so that they can be easily identified.
Each of the three universal transmitter push but-
tons controls an independent radio transmitter chan-
nel. Each of these three channels can be trained to
transmit a different radio frequency signal for the
remote operation of garage door openers, motorized
gate openers, home or office lighting, security sys-
tems or just about any other device that can be
equipped with a radio receiver in the 286 to 399
MegaHertz (MHz) frequency range for remote opera-
tion. The universal transmitter is capable of operat-
ing systems using either rolling code or non-rolling
code technology.
The electronics module displays messages and a
small house-shaped icon with one, two or three dots
corresponding to the three transmitter buttons to
indicate the status of the universal transmitter. The
EVIC messages are:
²Cleared Channels- Indicates that all of the
transmitter codes stored in the universal transmitter
have been successfully cleared.
²Training- Indicates that the universal trans-
mitter is in its transmitter learning mode.
²Trained- Indicates that the universal transmit-
ter has successfully acquired a new transmitter code.
²Transmit- Indicates that a trained universal
transmitter button has been depressed and that the
universal transmitter is transmitting.
The universal transmitter cannot be repaired, and
is available for service only as a unit with the EVIC
or CMTC modules. If any of these components is
faulty or damaged, the complete EVIC or CMTC
module must be replaced.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
UNIVERSAL TRANSMITTER
If both the Universal Transmitter and the Elec-
tronic Vehicle Information Center (EVIC) are inoper-
ative, (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/OVERHEAD
CONSOLE/ELECTRONIC VEHICLE INFO CENTER
- DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING). If the Universal
Transmitter is inoperative, but the EVIC is operating
normally, retrain the Transmitter with a known good
transmitter (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/OVERHEAD
CONSOLE/UNIVERSAL TRANSMITTER - STAN-
DARD PROCEDURE - SETTING TRANSMITTER
CODES). If the unit is still inoperative, test the uni-
versal transmitter with the Radio Frequency Detec-
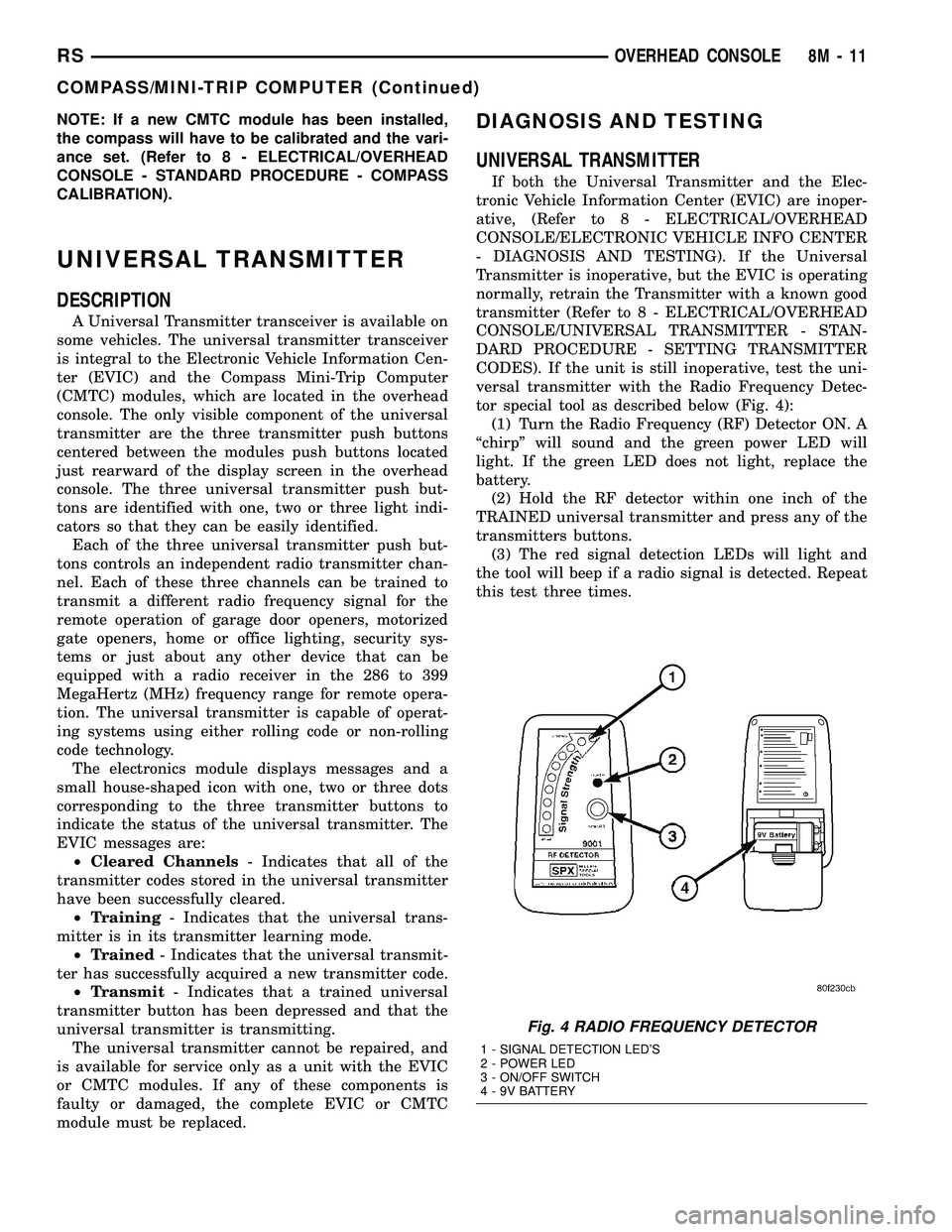
tor special tool as described below (Fig. 4):
(1) Turn the Radio Frequency (RF) Detector ON. A
ªchirpº will sound and the green power LED will
light. If the green LED does not light, replace the
battery.
(2) Hold the RF detector within one inch of the
TRAINED universal transmitter and press any of the
transmitters buttons.
(3) The red signal detection LEDs will light and
the tool will beep if a radio signal is detected. Repeat
this test three times.
Fig. 4 RADIO FREQUENCY DETECTOR
1 - SIGNAL DETECTION LED'S
2 - POWER LED
3 - ON/OFF SWITCH
4 - 9V BATTERY
RSOVERHEAD CONSOLE8M-11
COMPASS/MINI-TRIP COMPUTER (Continued)