battery location CHRYSLER CARAVAN 2005 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2005, Model line: CARAVAN, Model: CHRYSLER CARAVAN 2005Pages: 2339, PDF Size: 59.69 MB
Page 469 of 2339

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
Inoperative fuel filler door lockout
mechanismCheck operation of fuel filler door lockout
mechanism.
Inoperative sliding door control module
or BCMDisconnect then reconnect battery negative
cable to reset module. Cycle door, if no
function exists check for loose wire
connections, see Body Diagnostic Manual for
detailed procedures
Inoperative striker Striker misaligned or loose
Striker damaged
Replace striker if necessary
Cables worn and stretched Replace cables as necessary
Binding or sticking of components Establish location of binding and replace
necessary components
Key fob, B-pillar or overhead
console switch does not
operate power sliding doorBlown Fuse Check fuse and replace
Battery voltage low Charge or replace battery
Inoperative latch assembly Check for foreign matter preventing the
operation of latch assembly
Check wire connection
Pawl and/or ratchet switch inoperative
Replace latch if necessary
Wiring problems (system or vehicle) Troubleshoot using the appropriate wiring
information
Inoperative BCM Check electrical connections
Refer to the body diagnostic manual for
additional checks
Replace BCM if necessary
Inoperative key fob Verify inoperative key fob by trying other key
fob functions
Replace key fob battery
Reprogram key fob
Replace key fob if necessary
Inoperative sliding door control module Disconnect then reconnect battery negative
cable to reset module. Cycle door, if no
function exists check for loose wire
connections, see Body Diagnostic Manual for
detailed procedures
Inoperative door motor assembly Check for foreign matter preventing the
operation of gear motor assembly
Check wire connections
Gear motor clutch does not engage, replace
assembly
8N - 46 POWER SLIDING DOOR SYSTEMRS
POWER SLIDING DOOR SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 470 of 2339

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
Full open switch inoperative, replace hold
open latch assembly
Replace motor assembly. if necessary
Door does not stay open Inoperative hold open latch assembly Check wire/cable connections
Replace hold open latch, if necessary
Inoperative hold open latch striker Replace hold open latch striker, if necessary
High inside/outside opening
effortInoperative latch assembly Check wire connections and for blown fuse
Check cable connections
Check for foreign matter preventing the
operation of latch assembly
Troubleshoot using body diagnostic manual
Replace latch assembly, if necessary
Inoperative inside/outside handle
assemblyGo to that9POSSIBLE CAUSE9and review
9CORRECTIONS9
Binding or sticking of components Establish location of binding and replace
necessary components
Door continues to cinch
closed during power modeInoperative latch assembly Check wire connections and for blown fuse
Check for foreign matter preventing the
operation of latch assembly
Troubleshoot using body diagnostic manual
Replace latch assembly, if necessary
Inoperative sliding door control module
or BCMDisconnect then reconnect battery negative
cable to reset module. Cycle door, if no
function exists check for loose wire
connections, see Body Diagnostic Manual for
detailed procedures
Wiring problems (system or vehicle) Troubleshoot using the appropriate wiring
information
Door continues to open
during power mode (runaway
motor)Inoperative sliding door control module
or BCMDisconnect then reconnect battery negative
cable to reset module. Cycle door, if no
function exists check for loose wire
connections, see Body Diagnostic Manual for
detailed procedures
Inoperative hold open latch assembly Check wire/cable connections
Replace hold open latch, if necessary
Inoperative drive assembly Remove lower drive unit and check for no
drive condition
Wiring problems (system or vehicle) Troubleshoot using electrical schematics.
Refer to wiring diagrams
Door opens very slowly Inoperative door motor assembly Check wire/cable connections
Replace motor assembly, if necessary
RSPOWER SLIDING DOOR SYSTEM8N-47
POWER SLIDING DOOR SYSTEM (Continued)
Page 480 of 2339
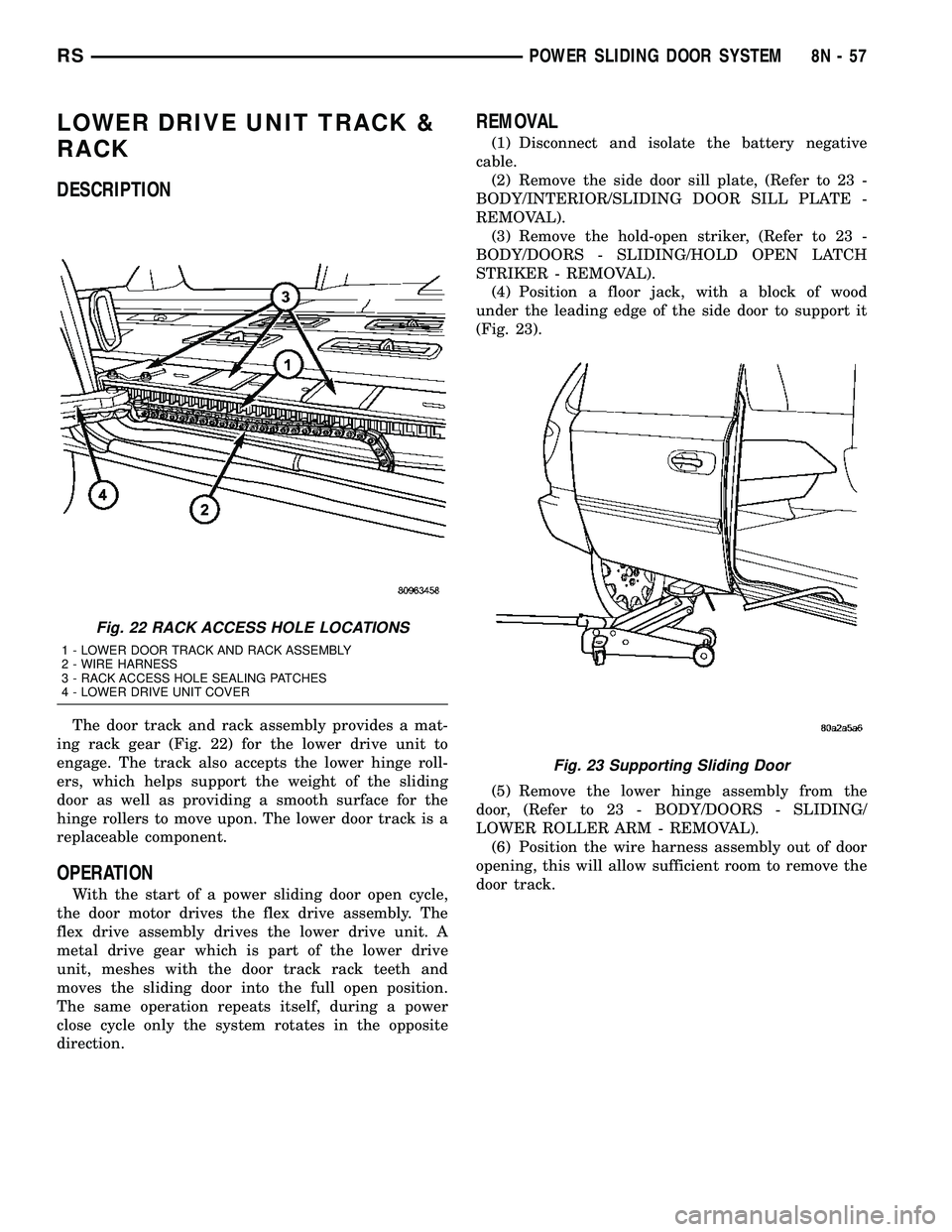
LOWER DRIVE UNIT TRACK &
RACK
DESCRIPTION
The door track and rack assembly provides a mat-
ing rack gear (Fig. 22) for the lower drive unit to
engage. The track also accepts the lower hinge roll-
ers, which helps support the weight of the sliding
door as well as providing a smooth surface for the
hinge rollers to move upon. The lower door track is a
replaceable component.
OPERATION
With the start of a power sliding door open cycle,
the door motor drives the flex drive assembly. The
flex drive assembly drives the lower drive unit. A
metal drive gear which is part of the lower drive
unit, meshes with the door track rack teeth and
moves the sliding door into the full open position.
The same operation repeats itself, during a power
close cycle only the system rotates in the opposite
direction.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove the side door sill plate, (Refer to 23 -
BODY/INTERIOR/SLIDING DOOR SILL PLATE -
REMOVAL).
(3) Remove the hold-open striker, (Refer to 23 -
BODY/DOORS - SLIDING/HOLD OPEN LATCH
STRIKER - REMOVAL).
(4) Position a floor jack, with a block of wood
under the leading edge of the side door to support it
(Fig. 23).
(5) Remove the lower hinge assembly from the
door, (Refer to 23 - BODY/DOORS - SLIDING/
LOWER ROLLER ARM - REMOVAL).
(6) Position the wire harness assembly out of door
opening, this will allow sufficient room to remove the
door track.
Fig. 22 RACK ACCESS HOLE LOCATIONS
1 - LOWER DOOR TRACK AND RACK ASSEMBLY
2 - WIRE HARNESS
3 - RACK ACCESS HOLE SEALING PATCHES
4 - LOWER DRIVE UNIT COVER
Fig. 23 Supporting Sliding Door
RSPOWER SLIDING DOOR SYSTEM8N-57
Page 496 of 2339
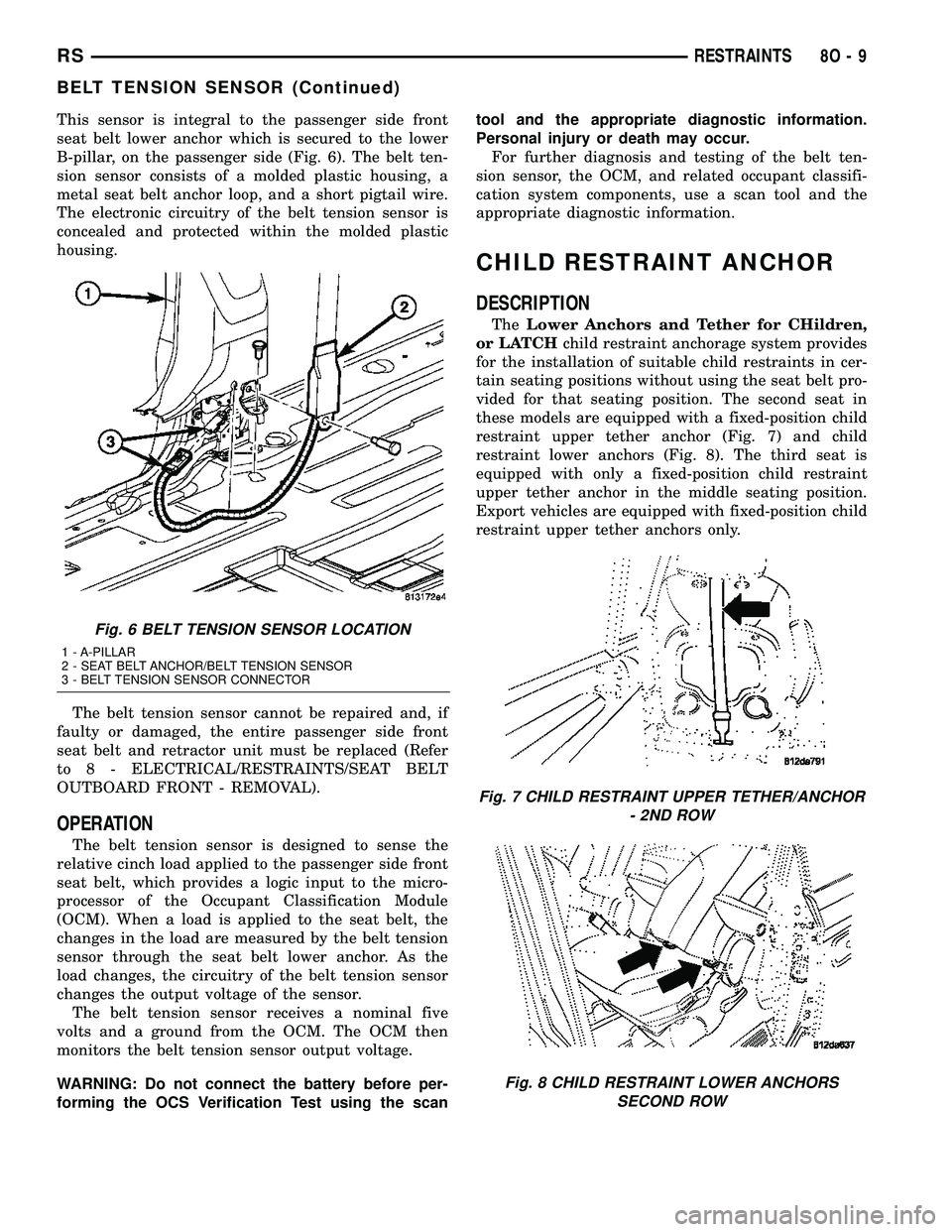
This sensor is integral to the passenger side front
seat belt lower anchor which is secured to the lower
B-pillar, on the passenger side (Fig. 6). The belt ten-
sion sensor consists of a molded plastic housing, a
metal seat belt anchor loop, and a short pigtail wire.
The electronic circuitry of the belt tension sensor is
concealed and protected within the molded plastic
housing.
The belt tension sensor cannot be repaired and, if
faulty or damaged, the entire passenger side front
seat belt and retractor unit must be replaced (Refer
to 8 - ELECTRICAL/RESTRAINTS/SEAT BELT
OUTBOARD FRONT - REMOVAL).
OPERATION
The belt tension sensor is designed to sense the
relative cinch load applied to the passenger side front
seat belt, which provides a logic input to the micro-
processor of the Occupant Classification Module
(OCM). When a load is applied to the seat belt, the
changes in the load are measured by the belt tension
sensor through the seat belt lower anchor. As the
load changes, the circuitry of the belt tension sensor
changes the output voltage of the sensor.
The belt tension sensor receives a nominal five
volts and a ground from the OCM. The OCM then
monitors the belt tension sensor output voltage.
WARNING: Do not connect the battery before per-
forming the OCS Verification Test using the scantool and the appropriate diagnostic information.
Personal injury or death may occur.
For further diagnosis and testing of the belt ten-
sion sensor, the OCM, and related occupant classifi-
cation system components, use a scan tool and the
appropriate diagnostic information.
CHILD RESTRAINT ANCHOR
DESCRIPTION
TheLower Anchors and Tether for CHildren,
or LATCHchild restraint anchorage system provides
for the installation of suitable child restraints in cer-
tain seating positions without using the seat belt pro-
vided for that seating position. The second seat in
these models are equipped with a fixed-position child
restraint upper tether anchor (Fig. 7) and child
restraint lower anchors (Fig. 8). The third seat is
equipped with only a fixed-position child restraint
upper tether anchor in the middle seating position.
Export vehicles are equipped with fixed-position child
restraint upper tether anchors only.
Fig. 6 BELT TENSION SENSOR LOCATION
1 - A-PILLAR
2 - SEAT BELT ANCHOR/BELT TENSION SENSOR
3 - BELT TENSION SENSOR CONNECTOR
Fig. 7 CHILD RESTRAINT UPPER TETHER/ANCHOR
- 2ND ROW
Fig. 8 CHILD RESTRAINT LOWER ANCHORS
SECOND ROW
RSRESTRAINTS8O-9
BELT TENSION SENSOR (Continued)
Page 501 of 2339
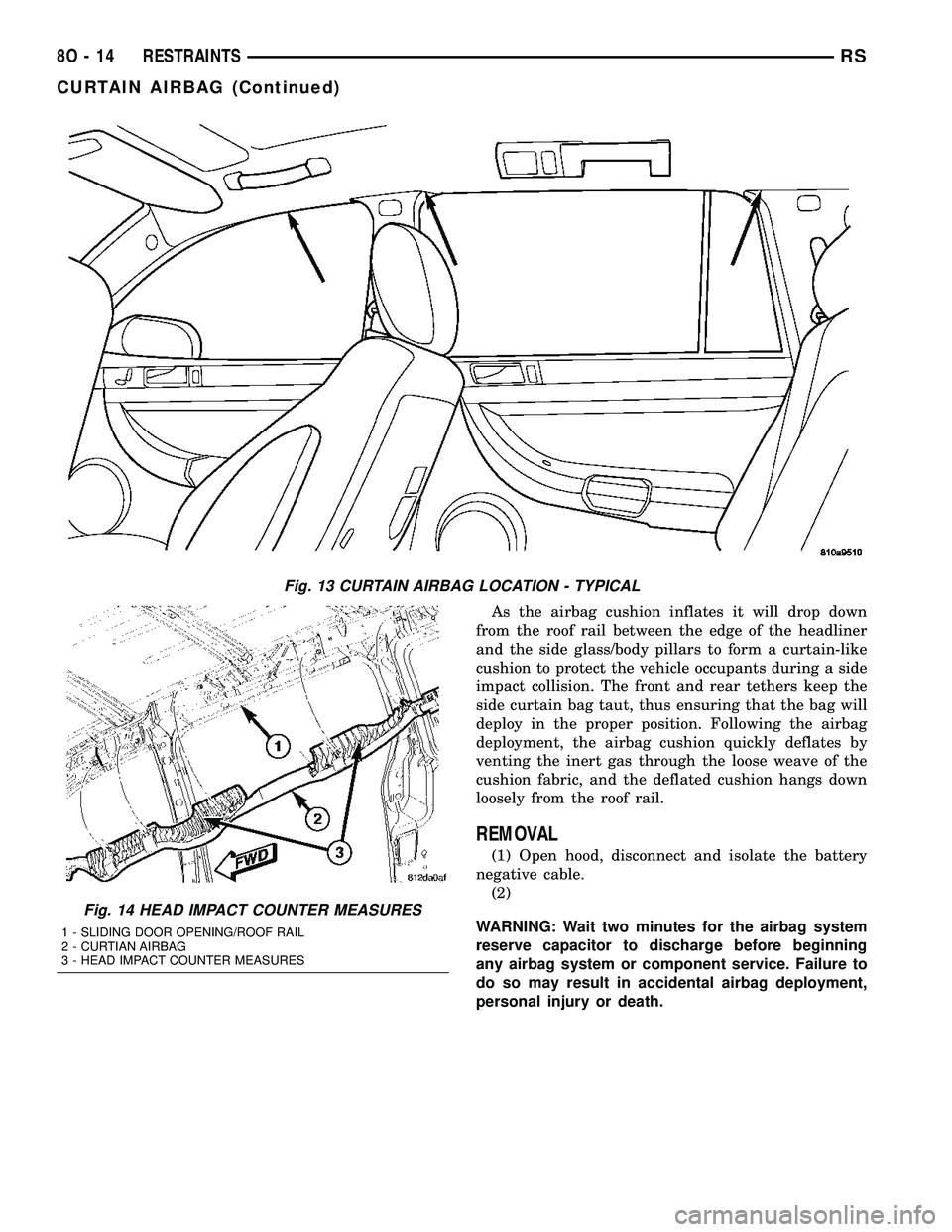
As the airbag cushion inflates it will drop down
from the roof rail between the edge of the headliner
and the side glass/body pillars to form a curtain-like
cushion to protect the vehicle occupants during a side
impact collision. The front and rear tethers keep the
side curtain bag taut, thus ensuring that the bag will
deploy in the proper position. Following the airbag
deployment, the airbag cushion quickly deflates by
venting the inert gas through the loose weave of the
cushion fabric, and the deflated cushion hangs down
loosely from the roof rail.
REMOVAL
(1) Open hood, disconnect and isolate the battery
negative cable.
(2)
WARNING: Wait two minutes for the airbag system
reserve capacitor to discharge before beginning
any airbag system or component service. Failure to
do so may result in accidental airbag deployment,
personal injury or death.
Fig. 13 CURTAIN AIRBAG LOCATION - TYPICAL
Fig. 14 HEAD IMPACT COUNTER MEASURES
1 - SLIDING DOOR OPENING/ROOF RAIL
2 - CURTIAN AIRBAG
3 - HEAD IMPACT COUNTER MEASURES
8O - 14 RESTRAINTSRS
CURTAIN AIRBAG (Continued)
Page 503 of 2339

INSTALLATION
(1) Position curtain airbag over retaining holes in
roof rail and firmly snap into place (Fig. 17).
(2) Install the curtain airbag retaining bolts (Fig.
17).
(3) Engage the side curtain airbag front tether in
the A-pillar and install retaining bolt (Fig. 16).
(4) Install the bolt in the curtain airbag inflator
mounting bracket (Fig. 18).
(5) Install the retaining bolts at the d-pillar (Fig.
19).
(6) Connect the curtain airbag squib connector
(Fig. 15).
(7) Install the headliner into the vehicle (Refer to
23 - BODY/INTERIOR/HEADLINER - INSTALLA-
TION).
WARNING: Do not connect the battery negative
cable (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/RESTRAINTS -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AIRBAG SYSTEM). Per-
sonal injury or death may result if the system test
is not performed first.
(8) Verify vehicle and system operation.
(9) Close hood.
DRIVER AIRBAG
DESCRIPTION
The injection molded, thermoplastic driver airbag
protective trim cover is the most visible part of the
driver airbag. The driver airbag is located in the cen-
ter of the steering wheel, where it is secured to the
steering wheel armature. Concealed beneath the
driver airbag trim cover are the horn switch, thefolded airbag cushion, the airbag cushion retainer,
the airbag housing, the airbag inflator, and the
retainers that secure the inflator to the airbag hous-
ing. The airbag cushion, housing, and inflator are
secured within an integral receptacle molded into the
back of the trim cover.
The resistive membrane-type horn switch is
secured with heat stakes to the inside surface of the
driver airbag trim cover, between the trim cover and
the folded airbag cushion. The horn switch ground
pigtail wire has a female spade terminal connector
that receives a path to ground through a male spade
terminal that is integral to the driver airbag housing
stamping and is located near the upper right corner
on the back of the housing. The horn switch feed pig-
tail wire has a white, molded plastic insulator that is
secured by an integral retainer to a mounting hole
located near the lower left corner on the back of the
housing, and is connected to the vehicle electrical
system through a take out and connector of the steer-
ing wheel wire harness.
The airbag is a multistage unit that deploys with
less force than those previously used. The airbag
inflator is a dual-initiator, non-azide, pyrotechnic-
type unit with four mounting studs and is secured to
the stamped metal airbag housing using four hex
nuts with washers. Two keyed and color-coded con-
nector receptacles on the driver airbag inflator con-
nect the two inflator initiators to the vehicle
electrical system through two yellow or black-jack-
eted, two-wire pigtail harnesses of the clockspring.
The driver airbag, trim cover, and horn switch unit
cannot be repaired, and must be replaced if deployed
or in any way damaged.
OPERATION
The Driver Airbag Trim Cover contains the horn
switch, inflator device, and a fabric bag. The driver
airbag trim cover/horn switch is not serviced sepa-
rately from the driver airbag components.
When the front airbag system is deployed, the fol-
lowingMUSTbe replaced:
²Complete Steering Column Assembly
²Lower Steering Column Coupler
²Steering Wheel.
²Clockspring.
²Driver Airbag
²Passenger Airbag
²Knee Blocker Airbag
²Upper Instrument Panel with Pad
²Front Seat Belt Buckles, both driver and passen-
ger with integral tensioners.
Fig. 19 CURTAIN AIRBAG D-PILLAR ATTACHMENT
1 - CURTAIN AIRBAG D-PILLAR ATTACHMENT LOCATIONS
2 - D-PILLAR
3 - ROOF RAIL AT REAR QUARTER GLASS
8O - 16 RESTRAINTSRS
CURTAIN AIRBAG (Continued)
Page 506 of 2339
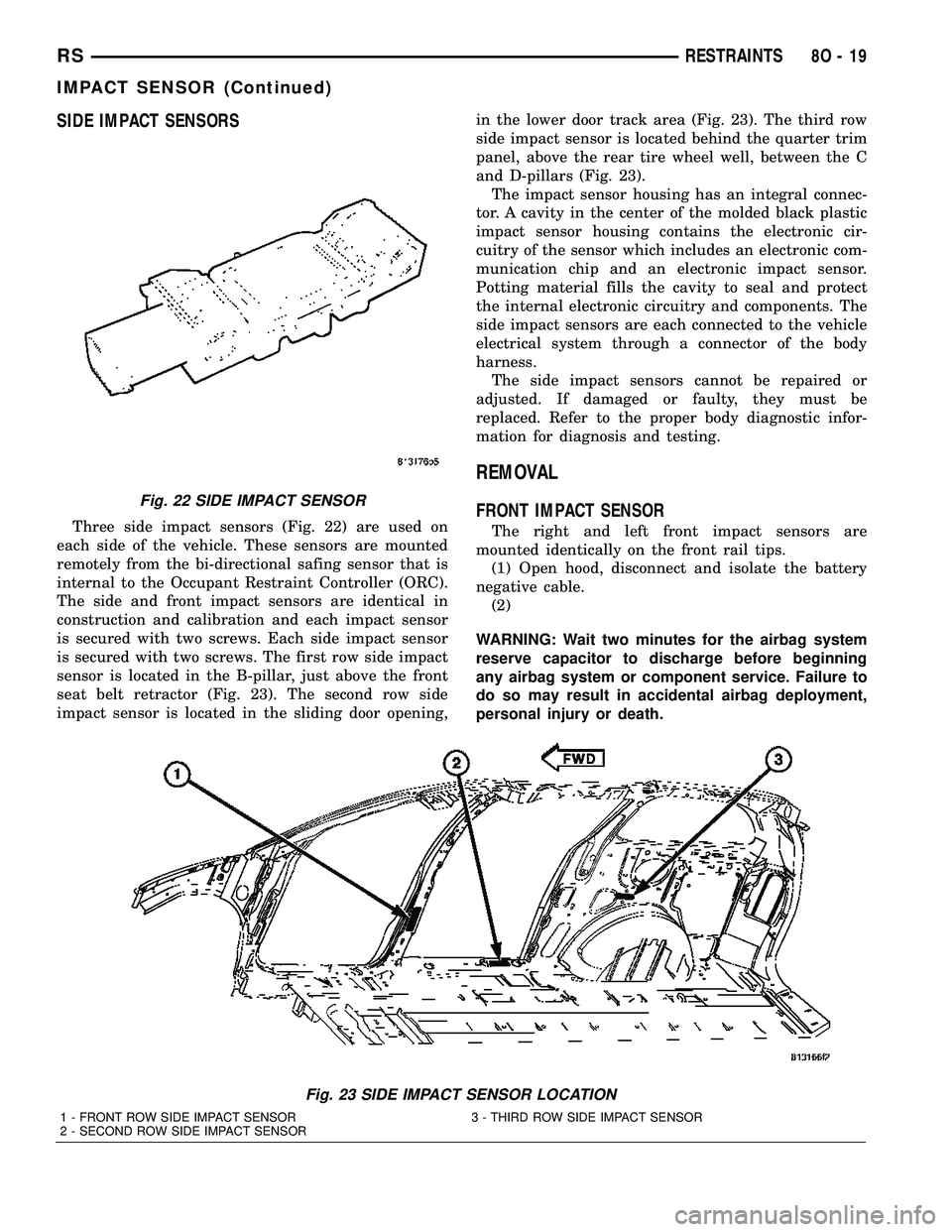
SIDE IMPACT SENSORS
Three side impact sensors (Fig. 22) are used on
each side of the vehicle. These sensors are mounted
remotely from the bi-directional safing sensor that is
internal to the Occupant Restraint Controller (ORC).
The side and front impact sensors are identical in
construction and calibration and each impact sensor
is secured with two screws. Each side impact sensor
is secured with two screws. The first row side impact
sensor is located in the B-pillar, just above the front
seat belt retractor (Fig. 23). The second row side
impact sensor is located in the sliding door opening,in the lower door track area (Fig. 23). The third row
side impact sensor is located behind the quarter trim
panel, above the rear tire wheel well, between the C
and D-pillars (Fig. 23).
The impact sensor housing has an integral connec-
tor. A cavity in the center of the molded black plastic
impact sensor housing contains the electronic cir-
cuitry of the sensor which includes an electronic com-
munication chip and an electronic impact sensor.
Potting material fills the cavity to seal and protect
the internal electronic circuitry and components. The
side impact sensors are each connected to the vehicle
electrical system through a connector of the body
harness.
The side impact sensors cannot be repaired or
adjusted. If damaged or faulty, they must be
replaced. Refer to the proper body diagnostic infor-
mation for diagnosis and testing.
REMOVAL
FRONT IMPACT SENSOR
The right and left front impact sensors are
mounted identically on the front rail tips.
(1) Open hood, disconnect and isolate the battery
negative cable.
(2)
WARNING: Wait two minutes for the airbag system
reserve capacitor to discharge before beginning
any airbag system or component service. Failure to
do so may result in accidental airbag deployment,
personal injury or death.
Fig. 23 SIDE IMPACT SENSOR LOCATION
1 - FRONT ROW SIDE IMPACT SENSOR 3 - THIRD ROW SIDE IMPACT SENSOR
2 - SECOND ROW SIDE IMPACT SENSOR
Fig. 22 SIDE IMPACT SENSOR
RSRESTRAINTS8O-19
IMPACT SENSOR (Continued)
Page 510 of 2339
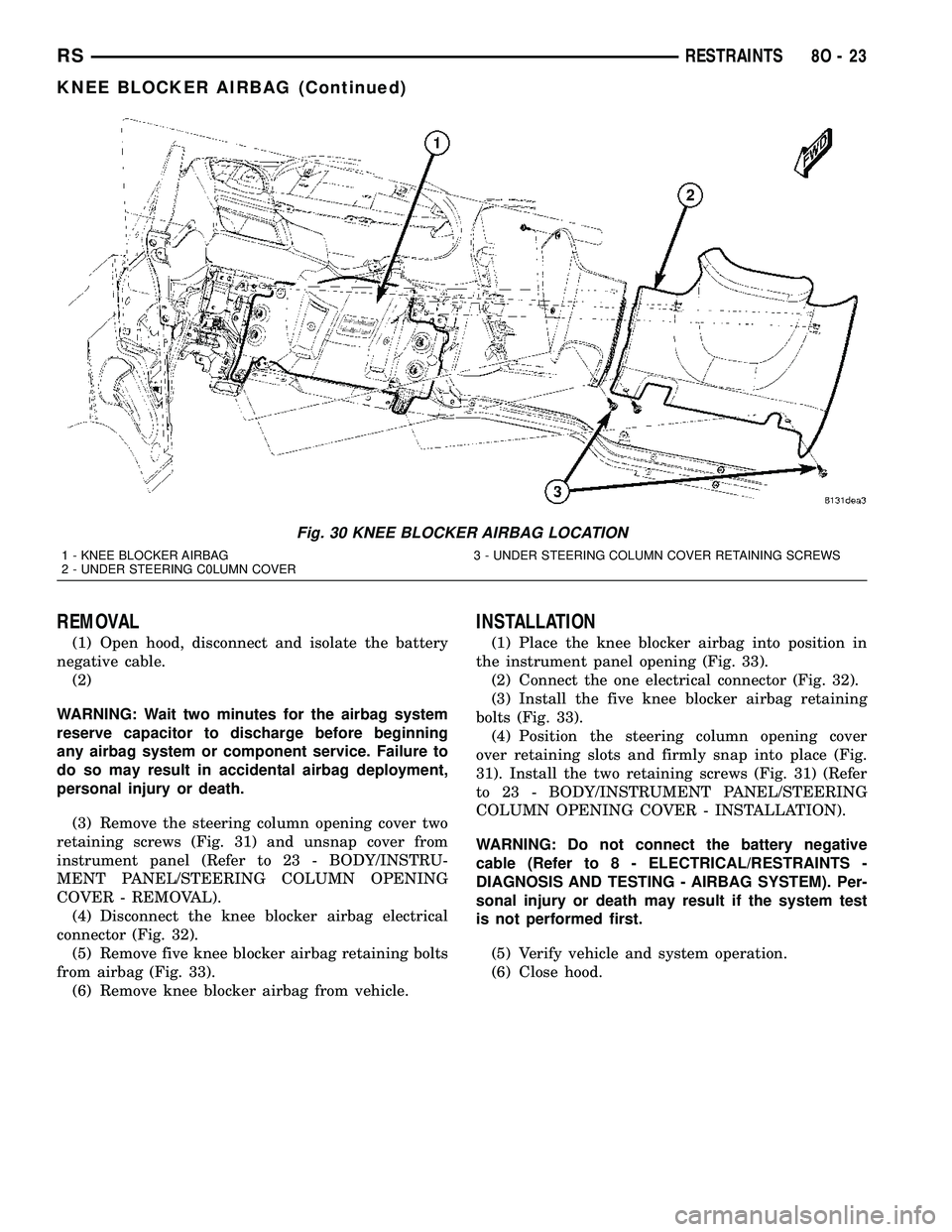
REMOVAL
(1) Open hood, disconnect and isolate the battery
negative cable.
(2)
WARNING: Wait two minutes for the airbag system
reserve capacitor to discharge before beginning
any airbag system or component service. Failure to
do so may result in accidental airbag deployment,
personal injury or death.
(3) Remove the steering column opening cover two
retaining screws (Fig. 31) and unsnap cover from
instrument panel (Refer to 23 - BODY/INSTRU-
MENT PANEL/STEERING COLUMN OPENING
COVER - REMOVAL).
(4) Disconnect the knee blocker airbag electrical
connector (Fig. 32).
(5) Remove five knee blocker airbag retaining bolts
from airbag (Fig. 33).
(6) Remove knee blocker airbag from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Place the knee blocker airbag into position in
the instrument panel opening (Fig. 33).
(2) Connect the one electrical connector (Fig. 32).
(3) Install the five knee blocker airbag retaining
bolts (Fig. 33).
(4) Position the steering column opening cover
over retaining slots and firmly snap into place (Fig.
31). Install the two retaining screws (Fig. 31) (Refer
to 23 - BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/STEERING
COLUMN OPENING COVER - INSTALLATION).
WARNING: Do not connect the battery negative
cable (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/RESTRAINTS -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AIRBAG SYSTEM). Per-
sonal injury or death may result if the system test
is not performed first.
(5) Verify vehicle and system operation.
(6) Close hood.
Fig. 30 KNEE BLOCKER AIRBAG LOCATION
1 - KNEE BLOCKER AIRBAG 3 - UNDER STEERING COLUMN COVER RETAINING SCREWS
2 - UNDER STEERING C0LUMN COVER
RSRESTRAINTS8O-23
KNEE BLOCKER AIRBAG (Continued)
Page 515 of 2339
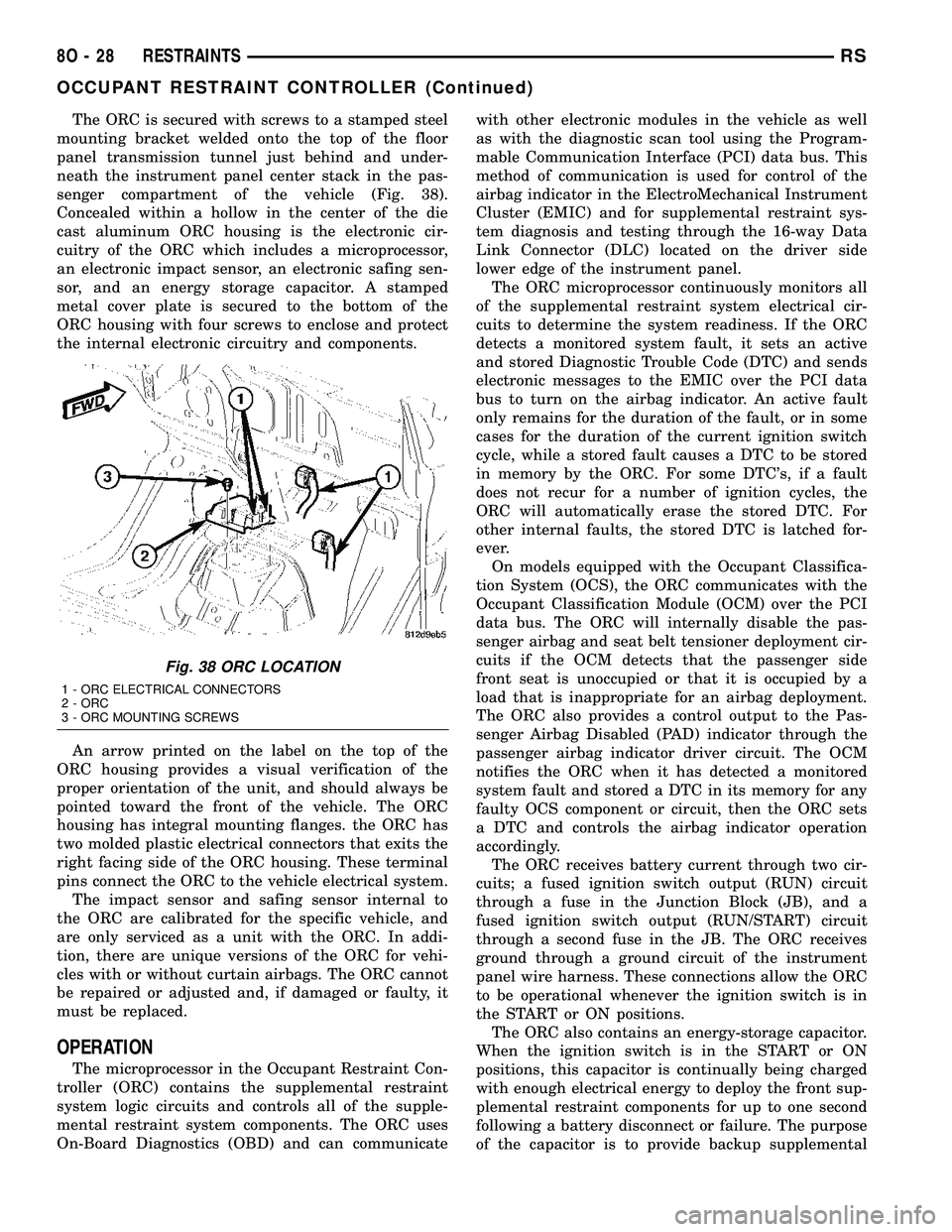
The ORC is secured with screws to a stamped steel
mounting bracket welded onto the top of the floor
panel transmission tunnel just behind and under-
neath the instrument panel center stack in the pas-
senger compartment of the vehicle (Fig. 38).
Concealed within a hollow in the center of the die
cast aluminum ORC housing is the electronic cir-
cuitry of the ORC which includes a microprocessor,
an electronic impact sensor, an electronic safing sen-
sor, and an energy storage capacitor. A stamped
metal cover plate is secured to the bottom of the
ORC housing with four screws to enclose and protect
the internal electronic circuitry and components.
An arrow printed on the label on the top of the
ORC housing provides a visual verification of the
proper orientation of the unit, and should always be
pointed toward the front of the vehicle. The ORC
housing has integral mounting flanges. the ORC has
two molded plastic electrical connectors that exits the
right facing side of the ORC housing. These terminal
pins connect the ORC to the vehicle electrical system.
The impact sensor and safing sensor internal to
the ORC are calibrated for the specific vehicle, and
are only serviced as a unit with the ORC. In addi-
tion, there are unique versions of the ORC for vehi-
cles with or without curtain airbags. The ORC cannot
be repaired or adjusted and, if damaged or faulty, it
must be replaced.
OPERATION
The microprocessor in the Occupant Restraint Con-
troller (ORC) contains the supplemental restraint
system logic circuits and controls all of the supple-
mental restraint system components. The ORC uses
On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) and can communicatewith other electronic modules in the vehicle as well
as with the diagnostic scan tool using the Program-
mable Communication Interface (PCI) data bus. This
method of communication is used for control of the
airbag indicator in the ElectroMechanical Instrument
Cluster (EMIC) and for supplemental restraint sys-
tem diagnosis and testing through the 16-way Data
Link Connector (DLC) located on the driver side
lower edge of the instrument panel.
The ORC microprocessor continuously monitors all
of the supplemental restraint system electrical cir-
cuits to determine the system readiness. If the ORC
detects a monitored system fault, it sets an active
and stored Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) and sends
electronic messages to the EMIC over the PCI data
bus to turn on the airbag indicator. An active fault
only remains for the duration of the fault, or in some
cases for the duration of the current ignition switch
cycle, while a stored fault causes a DTC to be stored
in memory by the ORC. For some DTC's, if a fault
does not recur for a number of ignition cycles, the
ORC will automatically erase the stored DTC. For
other internal faults, the stored DTC is latched for-
ever.
On models equipped with the Occupant Classifica-
tion System (OCS), the ORC communicates with the
Occupant Classification Module (OCM) over the PCI
data bus. The ORC will internally disable the pas-
senger airbag and seat belt tensioner deployment cir-
cuits if the OCM detects that the passenger side
front seat is unoccupied or that it is occupied by a
load that is inappropriate for an airbag deployment.
The ORC also provides a control output to the Pas-
senger Airbag Disabled (PAD) indicator through the
passenger airbag indicator driver circuit. The OCM
notifies the ORC when it has detected a monitored
system fault and stored a DTC in its memory for any
faulty OCS component or circuit, then the ORC sets
a DTC and controls the airbag indicator operation
accordingly.
The ORC receives battery current through two cir-
cuits; a fused ignition switch output (RUN) circuit
through a fuse in the Junction Block (JB), and a
fused ignition switch output (RUN/START) circuit
through a second fuse in the JB. The ORC receives
ground through a ground circuit of the instrument
panel wire harness. These connections allow the ORC
to be operational whenever the ignition switch is in
the START or ON positions.
The ORC also contains an energy-storage capacitor.
When the ignition switch is in the START or ON
positions, this capacitor is continually being charged
with enough electrical energy to deploy the front sup-
plemental restraint components for up to one second
following a battery disconnect or failure. The purpose
of the capacitor is to provide backup supplemental
Fig. 38 ORC LOCATION
1 - ORC ELECTRICAL CONNECTORS
2 - ORC
3 - ORC MOUNTING SCREWS
8O - 28 RESTRAINTSRS
OCCUPANT RESTRAINT CONTROLLER (Continued)
Page 516 of 2339

restraint system protection in case there is a loss of
battery current supply to the ORC during an impact.
Two sensors are contained within the ORC, an
electronic impact sensor and a safing sensor. The
ORC also monitors inputs from eight remote impact
sensors. Two front impact sensors are located on each
outboard side of the lower radiator support, and
three side impact sensors are located on each side of
the vehicle at the B-pillar, in the lower sliding door
opening in front of the C-pillar, and over the rear
wheel well between the C and D-pillars. The elec-
tronic impact sensors are accelerometers that sense
the rate of vehicle deceleration, which provides veri-
fication of the direction and severity of an impact.
The safing sensor is an electronic accelerometer
sensor within the ORC that provides an additional
logic input to the ORC microprocessor. The safing
sensor is used to verify the need for a supplemental
restraint deployment by detecting impact energy of a
lesser magnitude than that of the primary electronic
impact sensors, and must exceed a safing threshold
in order for the airbags to deploy. Vehicles equipped
with curtain airbags, there is a second safing sensor
within the ORC to provide confirmation to the ORC
microprocessor of side impact forces. This second saf-
ing sensor is a bi-directional unit that detects impact
forces from either side of the vehicle.
Pre-programmed decision algorithms in the ORC
microprocessor determine when the deceleration rate
as signaled by the impact sensors and the safing sen-
sors indicate an impact that is severe enough to
require supplemental restraint system protection
and, based upon the severity of the monitored
impact, determines the level of front airbag deploy-
ment force required for each front seating position.
When the programmed conditions are met, the ORC
sends the proper electrical signals to deploy the dual
multistage front airbags at the programmed force
levels, the front seat belt tensioners and, if the vehi-
cle is so equipped, either curtain airbag. For vehicles
equipped with the OCS, the passenger front airbag
and seat belt tensioner will be deployed by the ORC
only if enabled by the OCM messages (PAD indicator
OFF) at the time of the impact.
To diagnose and test the ORC and all airbag sys-
tem components, use a scan tool and the appropriate
diagnostic information.
REMOVAL
WARNING: Never replace both the Occupant
Restraint Controller (ORC) and the Occupant Clas-
sification Module (OCM) at the same time. If both
require replacement, replace one, then perform the
Airbag System test (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/RE-
STRAINTS - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - AIRBAGSYSTEM) before replacing the other. Both the ORC
and the OCM store Occupant Classification System
(OCS) calibration data, which they transfer to one
another when one of them is replaced. If both are
replaced at the same time, an irreversible fault will
be set in both modules and the OCS may malfunc-
tion and result in personal injury or death.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2)
WARNING: Wait two minutes for the airbag system
reserve capacitor to discharge before beginning
any airbag system or component service. Failure to
do so may result in accidental airbag deployment,
personal injury or death.
(3) Remove storage bin from instrument panel
(Refer to 23 - BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/STOR-
AGE BIN - REMOVAL).
(4) Remove three bolts holding ORC to floor
bracket (Fig. 39).
(5) Disconnect the wire connectors from the ORC
(Fig. 39).
(6) Remove the ORC from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
WARNING: Do not install ORC if mounting location
is deformed or damaged. This will cause the ORC
to be improperly located and could result in occu-
pant personal injury or death.
WARNING: Use correct screws when installing the
ORC.
Fig. 39 ORC - REMOVE/INSTALL
1 - ORC ELECTRICAL CONNECTORS
2 - ORC
3 - ORC MOUNTING SCREWS
RSRESTRAINTS8O-29
OCCUPANT RESTRAINT CONTROLLER (Continued)