check engine CHRYSLER TOWN AND COUNTRY 2002 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2002, Model line: TOWN AND COUNTRY, Model: CHRYSLER TOWN AND COUNTRY 2002Pages: 2399, PDF Size: 57.96 MB
Page 1276 of 2399

CLEANING...........................113
INSPECTION..........................113
CAMSHAFT & BEARINGS (IN BLOCK)
DESCRIPTION........................114
OPERATION..........................114
REMOVAL............................114
INSPECTION..........................115
INSTALLATION........................115
CONNECTING ROD BEARINGS
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MEASURING
CONNECTING ROD BEARING
CLEARANCE........................115
CRANKSHAFT
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - 3.3L..................116
DESCRIPTION - 3.8L..................117
OPERATION..........................117
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MEASURING
CRANKSHAFT END PLAY..............117
REMOVAL............................117
INSPECTION..........................118
INSTALLATION........................118
CRANKSHAFT MAIN BEARINGS
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MAIN BEARING
FITTING............................119
REMOVAL - CRANKSHAFT MAIN
BEARINGS..........................121
INSTALLATION - CRANKSHAFT MAIN
BEARINGS..........................121
CRANKSHAFT OIL SEAL - FRONT
REMOVAL............................122
INSTALLATION........................123
CRANKSHAFT OIL SEAL - REAR
REMOVAL............................123
INSTALLATION........................123
CRANKSHAFT REAR OIL SEAL RETAINER
REMOVAL............................124
INSTALLATION........................124
FLEX PLATE
REMOVAL............................124
INSTALLATION........................124
HYDRAULIC LIFTERS (CAM IN BLOCK)
DESCRIPTION........................125
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HYDRAULIC
LIFTERS...........................125
REMOVAL............................126
INSTALLATION........................126
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD
DESCRIPTION........................126
OPERATION..........................126
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FITTING
CONNECTING RODS..................127
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FITTING
PISTONS...........................127
REMOVAL............................127
INSTALLATION........................128PISTON RINGS
STANDARD PROCEDURE - PISTON RING
FITTING............................130
REMOVAL............................131
INSTALLATION........................131
VIBRATION DAMPER
REMOVAL............................132
INSTALLATION........................132
ENGINE MOUNTING
DESCRIPTION........................133
FRONT MOUNT
REMOVAL............................133
INSTALLATION........................133
LEFT MOUNT
REMOVAL............................134
INSTALLATION........................134
REAR MOUNT
REMOVAL............................135
INSTALLATION........................136
RIGHT MOUNT
REMOVAL............................137
INSTALLATION........................137
LUBRICATION
DESCRIPTION........................137
OPERATION..........................137
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE OIL
PRESSURE.........................137
OIL
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE OIL
AND FILTER CHANGE.................138
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE OIL
LEVEL CHECK.......................139
OIL COOLER & LINES
DESCRIPTION........................140
OPERATION..........................140
REMOVAL............................140
INSTALLATION........................140
OIL FILTER
REMOVAL............................140
INSTALLATION........................140
OIL FILTER ADAPTER
REMOVAL............................141
INSTALLATION........................141
OIL PAN
REMOVAL............................141
CLEANING...........................141
INSPECTION.........................142
INSTALLATION........................142
OIL PRESSURE RELIEF VALVE
REMOVAL............................142
INSTALLATION........................143
OIL PRESSURE SWITCH
DESCRIPTION........................143
OPERATION..........................143
REMOVAL............................143
INSTALLATION........................143
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9-75
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1279 of 2399

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE DIAGNOSIS - PERFORMANCE
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
ENGINE WILL NOT START 1. Weak battery. 1. Test battery. Charge or replace
as necessary. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/BATTERY SYSTEM -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING)
2. Corroded or loose battery
connections.2. Clean and tighten battery
connections. Apply a coat of light
mineral grease to terminals.
3. Faulty starter. 3. Test starting system. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/STARTING -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING)
4. Faulty coil(s) or control unit. 4. Test and replace as needed.
(Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic
Information)
5. Incorrect spark plug gap. 5. Set gap. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/IGNITION CONTROL
- SPECIFICATIONS)
6. Contamination in fuel system. 6. Clean system and replace fuel
filter.
7. Faulty fuel pump. 7. Test fuel pump and replace as
needed. (Refer to Appropriate
Diagnostic Information)
8. Incorrect engine timing. 8. Check for a skipped timing
belt/chain.
ENGINE STALLS OR IDLES
ROUGH1. Idle speed too low. 1. Test minimum air flow. (Refer to
Appropriate Diagnostic Information)
2. Incorrect fuel mixture. 2. (Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic
Information)
3. Intake manifold leakage. 3. Inspect intake manifold, manifold
gasket, and vacuum hoses.
4. Faulty ignition coil(s). 4. Test and replace as necessary.
(Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic
Information)
9 - 78 ENGINE 3.3/3.8LRS
ENGINE 3.3/3.8L (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1281 of 2399
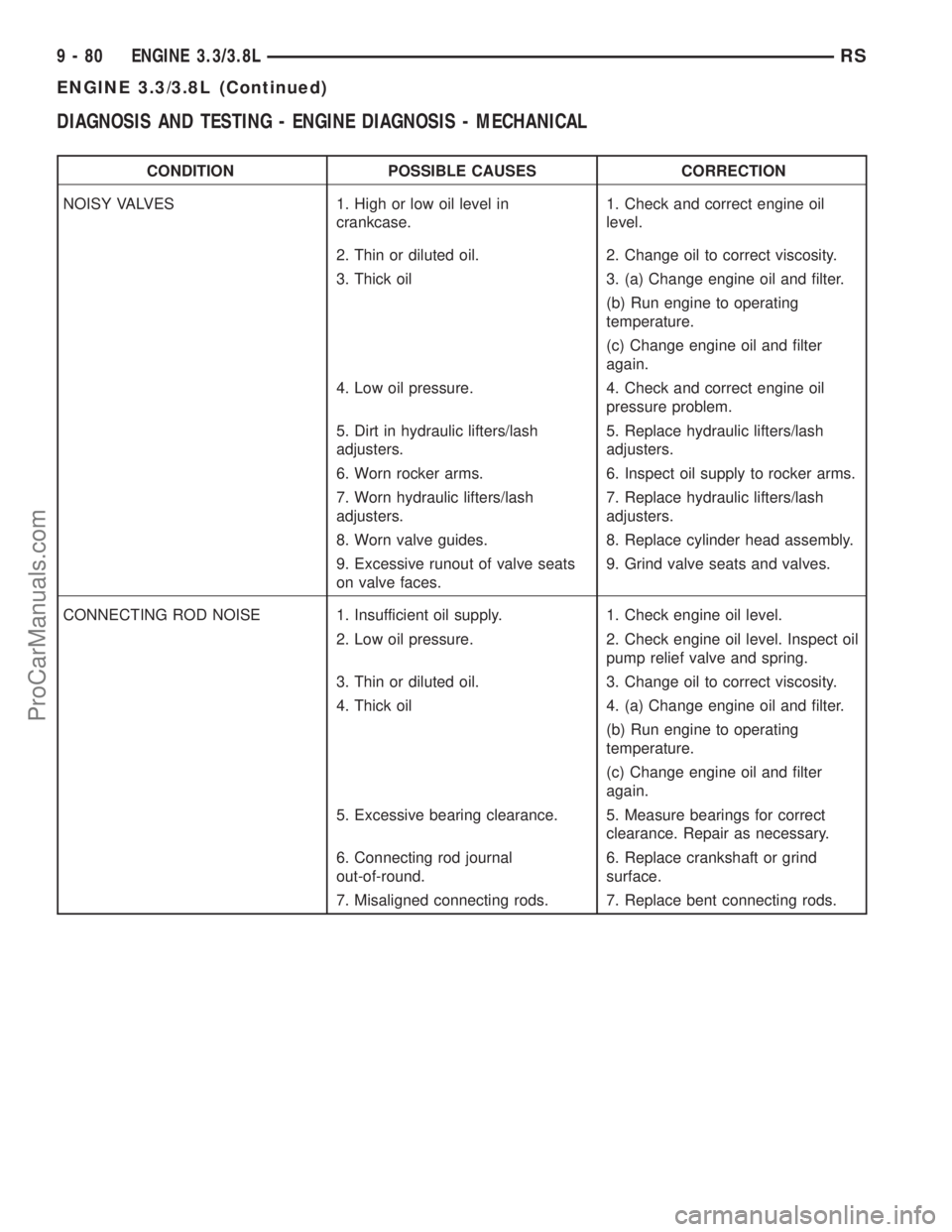
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE DIAGNOSIS - MECHANICAL
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
NOISY VALVES 1. High or low oil level in
crankcase.1. Check and correct engine oil
level.
2. Thin or diluted oil. 2. Change oil to correct viscosity.
3. Thick oil 3. (a) Change engine oil and filter.
(b) Run engine to operating
temperature.
(c) Change engine oil and filter
again.
4. Low oil pressure. 4. Check and correct engine oil
pressure problem.
5. Dirt in hydraulic lifters/lash
adjusters.5. Replace hydraulic lifters/lash
adjusters.
6. Worn rocker arms. 6. Inspect oil supply to rocker arms.
7. Worn hydraulic lifters/lash
adjusters.7. Replace hydraulic lifters/lash
adjusters.
8. Worn valve guides. 8. Replace cylinder head assembly.
9. Excessive runout of valve seats
on valve faces.9. Grind valve seats and valves.
CONNECTING ROD NOISE 1. Insufficient oil supply. 1. Check engine oil level.
2. Low oil pressure. 2. Check engine oil level. Inspect oil
pump relief valve and spring.
3. Thin or diluted oil. 3. Change oil to correct viscosity.
4. Thick oil 4. (a) Change engine oil and filter.
(b) Run engine to operating
temperature.
(c) Change engine oil and filter
again.
5. Excessive bearing clearance. 5. Measure bearings for correct
clearance. Repair as necessary.
6. Connecting rod journal
out-of-round.6. Replace crankshaft or grind
surface.
7. Misaligned connecting rods. 7. Replace bent connecting rods.
9 - 80 ENGINE 3.3/3.8LRS
ENGINE 3.3/3.8L (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1282 of 2399

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
MAIN BEARING NOISE 1. Insufficient oil supply. 1. Check engine oil level.
2. Low oil pressure. 2. Check engine oil level. Inspect oil
pump relief valve and spring.
3. Thin or diluted oil. 3. Change oil to correct viscosity.
4. Thick oil 4. (a) Change engine oil and filter.
(b) Run engine to operating
temperature.
(c) Change engine oil and filter
again.
5. Excessive bearing clearance. 5. Measure bearings for correct
clearance. Repair as necessary.
6. Excessive end play. 6. Check thrust bearing for wear on
flanges.
7. Crankshaft journal out-of-round
or worn.7. Replace crankshaft or grind
journals.
8. Loose flywheel or torque
converter.8. Tighten to correct torque.
OIL PRESSURE DROP 1. Low oil level. 1. Check engine oil level.
2. Faulty oil pressure sensor/switch. 2. Replace oil pressure sensor/
switch.
3. Low oil pressure. 3. Check oil pressure sensor/switch
and main bearing oil clearance.
4. Clogged oil filter. 4. Install new oil filter.
5. Worn parts in oil pump. 5. Replace worn parts or pump.
6. Thin or diluted oil. 6. Change oil to correct viscosity.
7. Oil pump relief valve stuck. 7. Remove valve and inspect, clean,
or replace.
8. Oil pump suction tube loose. 8. Remove oil pan and install new
tube or clean, if necessary.
9. Oil pump cover warped or
cracked.9. Install new oil pump.
10. Excessive bearing clearance. 10. Measure bearings for correct
clearance.
OIL LEAKS 1. Misaligned or deteriorated
gaskets.1. Replace gasket(s).
2. Loose fastener, broken or porous
metal part.2. Tighten, repair or replace the
part.
3. Misaligned or deteriorated cup or
threaded plug.3. Replace as necessary.
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9-81
ENGINE 3.3/3.8L (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1283 of 2399

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
OIL CONSUMPTION OR SPARK
PLUGS FOULED1. PCV system malfunction. 1. Check system and repair as
necessary. (Refer to 25 -
EMISSIONS CONTROL/
EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS/PCV
VALVE - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING)
2. Worn, scuffed or broken rings. 2. Hone cylinder bores. Install new
rings.
3. Carbon in oil ring slots. 3. Install new rings.
4. Rings fitted too tightly in grooves. 4. Remove rings and check
grooves. If groove is not proper
width, replace piston.
5. Worn valve guide(s). 5. Replace cylinder head assembly.
6. Valve stem seal(s) worn or
damaged.6. Replace seal(s).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ENGINE OIL LEAK
INSPECTION
Begin with a thorough visual inspection of the
engine, particularly at the area of the suspected leak.
If an oil leak source is not readily identifiable, the
following steps should be followed:
(1) Do not clean or degrease the engine at this
time because some solvents may cause rubber to
swell, temporarily stopping the leak.
(2) Add an oil soluble dye (use as recommended by
manufacturer). Start the engine and let idle for
approximately 15 minutes. Check the oil dipstick to
make sure the dye is thoroughly mixed as indicated
with a bright yellow color under a black light.
(3) Using a black light, inspect the entire engine
for fluorescent dye, particularly at the suspected area
of oil leak. If the oil leak is found and identified,
repair as necessary.
(4) If dye is not observed, drive the vehicle at var-
ious speeds for approximately 24 km (15 miles), and
repeat inspection.
(5)If the oil leak source is not positively
identified at this time, proceed with the air leak
detection test method as follows:
²Disconnect the fresh air hose (make-up air) at
the cylinder head cover and plug or cap the nipple on
the cover.
²Remove the PCV valve hose from the cylinder
head cover. Cap or plug the PCV valve nipple on the
cover.
²Attach an air hose with pressure gauge and reg-
ulator to the dipstick tube.
CAUTION: Do not subject the engine assembly to
more than 20.6 kpa (3 PSI) of test pressure.²Gradually apply air pressure from 1 psi to 2.5
psi maximum while applying soapy water at the sus-
pected source. Adjust the regulator to the suitable
test pressure that provides the best bubbles which
will pinpoint the leak source. If the oil leak is
detected and identified, repair per service manual
procedures.
²If the leakage occurs at the crankshaft rear oil
seal area, refer to the section, Inspection for Rear
Seal Area Leak.
(6) If no leaks are detected, turn off the air supply.
Remove the air hose, all plugs, and caps. Install the
PCV valve and fresh air hose (make-up air). Proceed
to next step.
(7) Clean the oil off the suspect oil leak area using
a suitable solvent. Drive the vehicle at various
speeds approximately 24 km (15 miles). Inspect the
engine for signs of an oil leak by using a black light.
NOTE: If oil leakage is observed at the dipstick tube
to block location; remove the tube, clean and reseal
using MoparTStud & Bearing Mount (press fit tube
applications only), and for O-ring style tubes,
remove tube and replace the O-ring seal.
INSPECTION FOR REAR SEAL AREA LEAKS
Since it is sometimes difficult to determine the
source of an oil leak in the rear seal area of the
engine, a more involved inspection is necessary. The
following steps should be followed to help pinpoint
the source of the leak.
If the leakage occurs at the crankshaft rear oil seal
area:
(1) Disconnect the battery.
(2) Raise the vehicle.
9 - 82 ENGINE 3.3/3.8LRS
ENGINE 3.3/3.8L (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1284 of 2399

(3) Remove torque converter or clutch housing
cover and inspect rear of block for evidence of oil.
Use a black light to check for the oil leak. If a leak is
present in this area, remove transmission for further
inspection.
(a) Circular spray pattern generally indicates
seal leakage or crankshaft damage.
(b) Where leakage tends to run straight down,
possible causes are a porous block, oil gallery cup
plug, bedplate to cylinder block mating surfaces
and seal bore. See proper repair procedures for
these items.
(4) If no leaks are detected, pressurize the crank-
case as previously described.
CAUTION: Do not exceed 20.6 kPa (3 psi).
(5) If the leak is not detected, very slowly turn the
crankshaft and watch for leakage. If a leak is
detected between the crankshaft and seal while
slowly turning the crankshaft, it is possible the
crankshaft seal surface is damaged. The seal area on
the crankshaft could have minor nicks or scratches
that can be polished out with emery cloth.
CAUTION: Use extreme caution when crankshaft
polishing is necessary to remove minor nicks and
scratches. The crankshaft seal flange is especially
machined to complement the function of the rear oil
seal.
(6) For bubbles that remain steady with shaft
rotation, no further inspection can be done until dis-
assembled.
(7) After the oil leak root cause and appropriate
corrective action have been identified, replace compo-
nent(s) as necessary.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMPRESSION PRESSURE TEST
The results of a cylinder compression pressure test
can be utilized to diagnose several engine malfunc-
tions.
Ensure the battery is completely charged and the
engine starter motor is in good operating condition.
Otherwise the indicated compression pressures may
not be valid for diagnosis purposes.
(1) Check engine oil level and add oil if necessary.
(2) Drive the vehicle until engine reaches normal
operating temperature. Select a route free from traf-
fic and other forms of congestion, observe all traffic
laws, and accelerate through the gears several times
briskly.
(3) Remove all spark plugs from engine. As spark
plugs are being removed, check electrodes for abnor-
mal firing indicators fouled, hot, oily, etc. Record cyl-
inder number of spark plug for future reference.(4) Remove the Auto Shutdown (ASD) relay from
the PDC.
(5) Be sure throttle blade is fully open during the
compression check.
(6) Insert compression gauge adaptor Special Tool
8116 or the equivalent, into the #1 spark plug hole in
cylinder head. Connect the 0±500 psi (Blue) pressure
transducer (Special Tool CH7059) with cable adap-
tors to the DRBIIIt. For Special Tool identification,
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIAL TOOLS).
(7) Crank engine until maximum pressure is
reached on gauge. Record this pressure as #1 cylin-
der pressure.
(8) Repeat the previous step for all remaining cyl-
inders.
(9) Compression should not be less than 689 kPa
(100 psi) and not vary more than 25 percent from cyl-
inder to cylinder.
(10) If one or more cylinders have abnormally low
compression pressures, repeat the compression test.
(11) If the same cylinder or cylinders repeat an
abnormally low reading on the second compression
test, it could indicate the existence of a problem in
the cylinder in question.The recommended com-
pression pressures are to be used only as a
guide to diagnosing engine problems. An engine
should not be disassembled to determine the
cause of low compression unless some malfunc-
tion is present.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CYLINDER
COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE TEST
The combustion pressure leakage test provides an
accurate means for determining engine condition.
Combustion pressure leakage testing will detect:
²Exhaust and intake valve leaks (improper seat-
ing).
²Leaks between adjacent cylinders or into water
jacket.
²Any causes for combustion/compression pressure
loss.
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE PRESSURE CAP
WITH THE SYSTEM HOT AND UNDER PRESSURE
BECAUSE SERIOUS BURNS FROM COOLANT CAN
OCCUR.
Check the coolant level and fill as required. DO
NOT install the pressure cap.
Start and operate the engine until it attains nor-
mal operating temperature, then turn the engine
OFF.
Clean spark plug recesses with compressed air.
Remove the spark plugs.
Remove the oil filler cap.
Remove the air cleaner.
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9-83
ENGINE 3.3/3.8L (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1285 of 2399

Calibrate the tester according to the manufactur-
er's instructions. The shop air source for testing
should maintain 483 kPa (70 psi) minimum, 1,379
kPa (200 psi) maximum, with 552 kPa (80 psi) rec-
ommended.
Perform the test procedures on each cylinder
according to the tester manufacturer's instructions.
While testing, listen for pressurized air escaping
through the throttle body, tailpipe and oil filler cap
opening. Check for bubbles in the coolant.
All gauge pressure indications should be equal,
with no more than 25% leakage per cylinder.
FOR EXAMPLE:At 552 kPa (80 psi) input pres-
sure, a minimum of 414 kPa (60 psi) should be main-
tained in the cylinder.
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MEASURING
BEARING CLEARANCE USING PLASTIGAGE
Engine crankshaft bearing clearances can be deter-
mined by use of Plastigage or equivalent. The follow-
ing is the recommended procedure for the use of
Plastigage:
(1) Remove oil film from surface to be checked.
Plastigage is soluble in oil.
(2) Place a piece of Plastigage across the entire
width of the bearing shell in the cap approximately
6.35 mm (1/4 in.) off center and away from the oil
holes (Fig. 3). (In addition, suspected areas can be
checked by placing the Plastigage in the suspected
area). Torque the bearing cap bolts of the bearing
being checked to the proper specifications.(3) Remove the bearing cap and compare the
width of the flattened Plastigage with the metric
scale provided on the package. Locate the band clos-
est to the same width. This band shows the amount
of clearance in thousandths of a millimeter. Differ-
ences in readings between the ends indicate the
amount of taper present. Record all readings taken.
Compare clearance measurements to specs found in
engine specifications (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - SPECI-
FICATIONS).Plastigage generally is accompa-
nied by two scales. One scale is in inches, the
other is a metric scale.
NOTE: Plastigage is available in a variety of clear-
ance ranges. Use the most appropriate range for
the specifications you are checking.
(4) Install the proper crankshaft bearings to
achieve the specified bearing clearances.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FORM-IN-PLACE
GASKETS AND SEALERS
There are numerous places where form-in-place
gaskets are used on the engine. Care must be taken
when applying form-in-place gaskets to assure
obtaining the desired results.Do not use form-in-
place gasket material unless specified.Bead size,
continuity, and location are of great importance. Too
thin a bead can result in leakage while too much can
result in spill-over which can break off and obstruct
fluid feed lines. A continuous bead of the proper
width is essential to obtain a leak-free gasket.
There are numerous types of form-in-place gasket
materials that are used in the engine area. Mopart
Engine RTV GEN II, MopartATF-RTV, and Mopart
Gasket Maker gasket materials, each have different
properties and can not be used in place of the other.
MOPARtENGINE RTV GEN IIis used to seal
components exposed to engine oil. This material is a
specially designed black silicone rubber RTV that
retains adhesion and sealing properties when
exposed to engine oil. Moisture in the air causes the
material to cure. This material is available in three
ounce tubes and has a shelf life of one year. After one
year this material will not properly cure. Always
inspect the package for the expiration date before
use.
MOPARtATF RTVis a specifically designed
black silicone rubber RTV that retains adhesion and
sealing properties to seal components exposed to
automatic transmission fluid, engine coolants, and
moisture. This material is available in three ounce
tubes and has a shelf life of one year. After one year
this material will not properly cure. Always inspect
the package for the expiration date before use.
Fig. 3 Plastigage Placed in Lower ShellÐTypical
1 - PLASTIGAGE
9 - 84 ENGINE 3.3/3.8LRS
ENGINE 3.3/3.8L (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1287 of 2399

STANDARD PROCEDURE - HYDROSTATIC
LOCKED ENGINE
When an engine is suspected to be hydrostatically
locked, regardless of what caused the problem, the
following steps should be used.
CAUTION: DO NOT use starter motor to rotate the
engine, severe damage may occur.
(1) Inspect air cleaner, induction system and
intake manifold to insure system is dry and clear of
foreign material.
(2) Remove negative battery cable.
(3) Place a shop towel around the spark plugs
when removing them from the engine. This will catch
any fluid that may possibly be in the cylinder under
pressure.
(4) With all spark plugs removed, rotate engine
crankshaft using a breaker bar and socket.
(5) Identify the fluid in the cylinder(s) (i.e., cool-
ant, fuel, oil or other).
(6) Make sure all fluid has been removed from the
cylinders. Inspect engine for damage (i.e., connecting
rods, pistons, valves, etc.)
(7) Repair engine or components as necessary to
prevent this problem from re-occurring.
CAUTION: Squirt approximately one teaspoon of oil
into the cylinders, rotate engine to lubricate the cyl-
inder walls to prevent damage on restart.
(8) Install new spark plugs.
(9) Drain engine oil and remove oil filter.
(10) Install a new oil filter.
(11) Fill engine with specified amount of approved
oil.
(12) Connect negative battery cable.
(13) Start engine and check for any leaks.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REPAIR OF
DAMAGED OR WORN THREADS
Damaged or worn threads (excluding spark plug
and camshaft bearing cap attaching threads) can be
repaired. Essentially, this repair consists of drilling
out worn or damaged threads, tapping the hole with
a special Heli-Coil Tap, (or equivalent) and installing
an insert into the tapped hole. This brings the hole
back to its original thread size.CAUTION: Be sure that the tapped holes maintain
the original center line.
Heli-Coil tools and inserts are readily available
from automotive parts jobbers.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - ENGINE CORE AND
OIL GALLERY PLUGS
Using a blunt tool such as a drift and a hammer,
strike the bottom edge of the cup plug. With the cup
plug rotated, grasp firmly with pliers or other suit-
able tool and remove plug (Fig. 5).
CAUTION: Do not drive cup plug into the casting as
restricted cooling can result and cause serious
engine problems.
Thoroughly clean inside of cup plug hole in cylin-
der block or head. Be sure to remove old sealer.
Lightly coat inside of cup plug hole with Mopart
Stud and Bearing Mount. Make certain the new plug
is cleaned of all oil or grease. Using proper drive
plug, drive plug into hole so that the sharp edge of
the plug is at least 0.5 mm (0.020 in.) inside the
lead-in chamfer.
It is not necessary to wait for curing of the sealant.
The cooling system can be refilled and the vehicle
placed in service immediately.
Fig. 5 Core Hole Plug Removal
1 - CYLINDER BLOCK
2 - REMOVE PLUG WITH PLIERS
3 - STRIKE HERE WITH HAMMER
4 - DRIFT PUNCH
5 - CUP PLUG
9 - 86 ENGINE 3.3/3.8LRS
ENGINE 3.3/3.8L (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1301 of 2399

INSTALLATION
(1) Install air box into vehicle and onto the locat-
ing pin.
(2) Install bolt to hold air box to the upper radia-
tor cross member.
(3) Install the inlet hose to the throttle body.
(4) Connect the inlet air temperature sensor (Fig.
16).
(5) Connect the negative battery cable.
CYLINDER HEAD
DESCRIPTION
The aluminum cylinder heads (Fig. 17) are
designed to create high flow combustion chambers to
improve performance, while minimizing the change
to the burn rate in the chamber. The cylinder head
incorporates the combustion chamber. Two valves
per-cylinder are used with inserted valve seats and
guides. A multi-layer steel (MLS) type gasket is used
between the cylinder head and engine block.
OPERATION
The cylinder head closes the combustion chamber,
allowing the pistons to compress the fuel/air mixture
for ignition. The valves are actuated by the lobe pro-
files on the camshaft to open and close at specified
duration to either allow clean air in the combustion
chamber or the exhaust gases out; depending on the
stroke of the engine.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTINGÐCYLINDER HEAD
GASKET
A cylinder head gasket leak can be located between
adjacent cylinders or between a cylinder and the
adjacent water jacket.
Possible indications of the cylinder head gasket
leaking between adjacent cylinders are:
²Loss of engine power
²Engine misfiring
²Poor fuel economy
Possible indications of the cylinder head gasket
leaking between a cylinder and an adjacent water
jacket are:
²Engine overheating
²Loss of coolant
²Excessive steam (white smoke) emitting from
exhaust
²Coolant foaming
CYLINDER-TO-CYLINDER LEAKAGE TEST
To determine if an engine cylinder head gasket is
leaking between adjacent cylinders, follow the proce-
dures in Cylinder Compression Pressure Test (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING). An
engine cylinder head gasket leaking between adja-
cent cylinders will result in approximately a 50±70%
reduction in compression pressure.
CYLINDER-TO-WATER JACKET LEAKAGE TEST
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN THE
ENGINE IS OPERATING WITH COOLANT PRES-
SURE CAP REMOVED.
VISUAL TEST METHOD
With the engine cool, remove the coolant pressure
cap. Start the engine and allow it to warm up until
thermostat opens.
If a large combustion/compression pressure leak
exists, bubbles will be visible in the coolant.
COOLING SYSTEM TESTER METHOD
WARNING: WITH COOLING SYSTEM TESTER IN
PLACE, PRESSURE WILL BUILD UP FAST. EXCES-
SIVE PRESSURE BUILT UP, BY CONTINUOUS
ENGINE OPERATION, MUST BE RELEASED TO A
SAFE PRESSURE POINT. NEVER PERMIT PRES-
SURE TO EXCEED 138 kPa (20 psi).
Install Cooling System Tester 7700 or equivalent to
pressure cap neck. Start the engine and observe the
tester's pressure gauge. If gauge pulsates with every
power stroke of a cylinder a combustion pressure
leak is evident.
CHEMICAL TEST METHOD
Combustion leaks into the cooling system can also
be checked by using Bloc-Chek Kit C-3685-A or
equivalent. Perform test following the procedures
supplied with the tool kit.
REMOVAL - CYLINDER HEAD
(1) Drain the cooling system. (Refer to 7 - COOL-
ING - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(2) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(3) Remove upper and lower intake manifolds.
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/INTAKE MANI-
FOLD - REMOVAL)
WARNING: INTAKE MANIFOLD GASKET IS MADE
OF VERY THIN METAL AND MAY CAUSE PER-
SONAL INJURY, HANDLE WITH CARE.
9 - 100 ENGINE 3.3/3.8LRS
AIR CLEANER HOUSING (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1302 of 2399

(4) Remove the cylinder head covers. (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/CYLINDER HEAD
COVER(S) - REMOVAL)
(5) Remove the spark plugs from cylinder head.
(6) Remove the dipstick and tube (Fig. 18).
(7) Remove exhaust manifold(s). (Refer to 9 -
ENGINE/MANIFOLDS/EXHAUST MANIFOLD -
REMOVAL)
(8) Remove rocker arm and shaft assemblies.(Refer
to 9 - ENGINE/CYLINDER HEAD/ROCKER ARMS -
REMOVAL) Remove push rods andmark positions
to ensure installation in original locations.
(9) Remove the eight head bolts from each cylinder
head and remove cylinder heads (Fig. 22).
CLEANING
To ensure engine gasket sealing, proper surface
preparation must be performed, especially with the
use of aluminum engine components and multi-layer
steel cylinder head gaskets.NOTE: Multi-Layer Steel (MLS) head gaskets require
a scratch free sealing surface.
Remove all gasket material from cylinder head and
block (Refer to 9 - ENGINE - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE). Be careful not to gouge or scratch the alumi-
num head sealing surface.
Clean all engine oil passages.
INSPECTION
(1) Before cleaning, check for leaks, damage and
cracks.
(2) Clean cylinder head and oil passages.
(3) Check cylinder head for flatness (Fig. 19).
(4) Cylinder head must be flat within:
²Standard dimension = less than 0.05 mm (0.002
inch.)
²Service Limit = 0.2 mm (0.008 inch.)
²Grinding Limit = Maximum of 0.2 mm (0.008
inch.) is permitted.
Fig. 17 Cylinder Head and Components
1 - VALVE LOCKS 5 - SPRING SEATS
2 - RETAINERS 6 - CYLINDER HEAD
3 - VALVE SPRINGS 7 - VALVE - EXHAUST
4 - VALVE STEM SEALS 8 - VALVE - INTAKE
RSENGINE 3.3/3.8L9 - 101
CYLINDER HEAD (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com