gas type CHRYSLER VOYAGER 1996 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 1996, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 1996Pages: 1938, PDF Size: 55.84 MB
Page 1257 of 1938

DESCRIPTION...........SPECIFICATIONS
Nominal.................63.005±63.020 mm
±0.25....................62.755±62.770 mm
±0.125...................62.880±62.895 mm
Center Bearing Diameter...................
Nominal.................63.050±63.093 mm
±0.25....................62.800±62.843 mm
±0.125...................62.925±62.968 mm
Clearance Between Journal and Bearing:
0.030±0.088 mm..........................
Rear Journal Diameter.....................
Nominal.................79.980±80.000 mm
±0.25....................79.730±79.750 mm
±0.125...................79.855±79.875 mm
Rear Bearing Diameter.....................
Nominal.................80.045±80.070 mm
±0.25....................79.795±79.820 mm
±0.125...................79.920±79.945 mm
Clearance Between Journal and Bearing:
0.045±0.090 mm (Wear Limit: 0.200 mm).......
Connecting Rod Journal....................
Nominal.................53.940±53.955 mm
±0.25....................53.690±53.705 mm
±0.125...................53.815±53.830 mm
Connecting Rod Bearing....................
Nominal.................53.977±54.016 mm
±0.25....................53.727±53.766 mm
±0.125...................53.852±53.891 mm
Clearance Between Journal and Bearing:
0.022±0.076 mm (Wear Limit: 0.200 mm).......
Crankshaft End Play
End Play.....................0.08±0.21 mm
Adjustment.................Thrust Washers
Thrust Washers Available........2.31±2.36 mm
Thrust Washers Available........2.41±2.46 mm
Thrust Washers Available........2.51±2.56 mm
Main Bearing Carriers
Front....................67.025±67.050 mm
Center...................66.670±66.690 mm
Rear....................85.985±86.005 mm
Liners
Internal Diameter..........92.000±92.010 mm
Protrusion....................0.01±0.06 mm
Adjustment.........................Shims
Available Shims:...................0.15 mm
Available Shims:...................0.17 mm
Available Shims:...................0.20 mm
Available Shims:...................0.23 mm
Available Shims:...................0.25 mm
Cylinder Head
Minimum Thickness..........89.95±90.05 mm
Gasket.............................Steel
Gasket thickness:.......1.4260.1 mm 0 Holes
Gasket thickness:.......1.6260.1 mm 1 HolesDESCRIPTION...........SPECIFICATIONS
Gasket thickness:.......1.5260.1 mm 2 Holes
End Plates
Height.....................89.02±90.00 mm
Connecting Rods
Weight (Without the crank
bearing)..................1129±1195 grams
Small End Bearing Internal Diameter
Minimum.......................30.035 mm
Maximum......................30.050 mm
Crankshaft Bearings Standard Internal
Diameter.................53.997±54.016 mm
Pistons
Skirt Diameter............91.935±91.945 mm
(Measured at approximately 15 mm above the
bottom of the skirt)
Piston Clearance.............0.055±0.075 mm
Top of Piston to Cylinder Head....0.80±0.89 mm
Piston Protrusion.....0.53±0.62 mm Fit Gasket
(1.42), 0 Holes
Piston Protrusion.....0.73±0.82 mm Fit Gasket
(1.62), 1 Hole
Piston Protrusion.....0.63±0.72 mm Fit Gasket
(1.52), 2 Holes
Piston Pins
Type .........................Full Floating
Pin Diameter..............29.990±29.996 mm
Clearance..................0.004±0.014 mm
Piston Rings (Clearance in Groove)
Top .......................0.080±0.130 mm
Second.....................0.070±0.102 mm
Oil Control.................0.040±0.072 mm
Piston Rings (Fitted Gap)
Top .........................0.25±0.50 mm
Second......................0.20±0.35 mm
Oil Control...................0.25±0.58 mm
Camshaft
Journal Diameter Front.....53.460±53.480 mm
Bearing Clearance.............0.06±0.13 mm
Journal Diameter Center....53.460±53.480 mm
Bearing Clearance.............0.06±0.13 mm
Journal Diameter Rear......53.460±53.480 mm
Bearing Clearance.............0.06±0.13 mm
Tappets
Outside Diameter..........22.195±22.212 mm
Rocker Gear
Shaft Diameter.............21.979±22.00 mm
Bushing internal diameter . . . 22.020±22.041 mm
Assembly Clearance..........0.020±0.062 mm
Valves (Intake)
Opens........................26ÉB.T.D.C.
Closes........................58ÉA.B.D.C.
Valves (Exhaust)
Opens........................64ÉB.B.D.C.
Closes........................38ÉA.T.D.C.
NS/GSENGINE 9 - 79
SPECIFICATIONS (Continued)
Page 1265 of 1938

CAUTION: When servicing, care must be exercised
not to dent or bend the bellows of the flex-joint.
Should this occur, the flex-joint will eventually fail
and require the catalytic converter be replaced.
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
INTAKE/EXHAUST MANIFOLDÐ2.4L ENGINE
The intake manifold is a tuned two-piece alumi-
num casting with individual primary runners leading
from a plenum to the cylinders. The manifold is
designed to boost torque which is desired for excel-
lent engine response and usable power output.
The exhaust manifold is made of nodular cast iron
for strength and high temperatures.
INTAKE/EXHAUST MANIFOLDÐ3.0L ENGINE
The aluminum alloy manifold is a cross type with
long runners to improve air flow. The runners,
attaching below at the cylinder head, also attach
above and support an air plenum. The air plenum
chamber absorbs air pulsations created during the
suction phase of each cylinder.Both exhaust manifolds are a log style made of
ductile cast iron. Exhaust gasses, collected from the
front cylinder bank, leave the front manifold through
an end outlet and are fed through an upper crossover
tube to the rear manifold. The collected exhaust from
both manifolds are combined at the exhaust outlet, to
the exhaust pipe.
INTAKE/EXHAUST MANIFOLDÐ3.3/3.8L ENGINES
The intake manifold is a tuned two-piece semi-per-
manent mold aluminum casting with individual pri-
mary runners leading from a plenum to the
cylinders. The manifold is designed to boost torque in
the 3600 rpm range and contributes to the engine's
broad, flat torque curve, which was desired for excel-
lent engine tractability, response and usable power
output.
The intake manifold is also cored with upper level
EGR passages for balanced cylinder to cylinder EGR
distribution.
The exhaust manifolds are log type with a cross-
over and are attached directly to the cylinder heads.
They are made from nodular cast iron.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
EXHAUST SYSTEM
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
EXCESSIVE EXHAUST
NOISE (UNDER HOOD)1. Exhaust manifold cracked or broken. 1. Replace manifold.
2. Manifold to cylinder head leak. 2. Tighten manifold and/or replace gasket.
3. EGR Valve to manifold gasket leakage. 3. Tighten fasteners or replace gasket.
4. EGR Valve to EGR tube gasket
leakage.4. Tighten fasteners or replace gasket.
5. EGR tube to manifold tube leakage. 5. Tighten tube nut.
6. Exhaust flex-joint to manifold leak. 6. Tighten joint fasteners and/or replace
gasket.
7. Exhaust flex-joint. 7. Replace catalytic converter assembly.
8. Pipe and shell noise from front exhaust
pipe.8. Characteristic of single wall pipe.
EXCESSIVE EXHAUST
NOISE1. Leak at exhaust pipe joints. 1. Tighten clamps at leaking joints.
2. Burned or rusted out muffler assembly
or exhaust pipe.2. Replace muffler resonator tailpipe
assembly or exhaust pipe with catalytic
converter assembly.
3. Burned or rusted out resonator. 3. Replace muffler resonator tailpipe
assembly.
4. Restriction in exhaust system. 4. Remove restriction, if possible, or
replace as necessary.
5. Converter material in muffler. 5. Replace muffler and converter
assemblies. Check fuel injection and
ignition systems for proper operation.
NSEXHAUST SYSTEM AND INTAKE MANIFOLD 11 - 3
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 1296 of 1938

GASOLINE/OXYGENATE BLENDS
Some fuel suppliers blend unleaded gasoline with
materials that contain oxygen such as alcohol, MTBE
(Methyl Tertiary Butyl Ether) and ETBE (Ethyl Ter-
tiary Butyl Ether). Oxygenates are required in some
areas of the country during winter months to reduce
carbon monoxide emissions. The type and amount of
oxygenate used in the blend is important.
The following are generally used in gasoline
blends:
Ethanol- (Ethyl or Grain Alcohol) properly
blended, is used as a mixture of 10 percent ethanol
and 90 percent gasoline. Gasoline blended with etha-
nol may be used in your vehicle.
MTBE/ETBE- Gasoline and MTBE (Methyl Ter-
tiary Butyl Ether) blends are a mixture of unleaded
gasoline and up to 15 percent MTBE. Gasoline and
ETBE (Ethyl Tertiary Butyl Ether) are blends of gas-
oline and up to 17 percent ETBE. Gasoline blended
with MTBE or ETBE may be used in your vehicle.
Methanol- Methanol (Methyl or Wood Alcohol) is
used in a variety of concentrations blended with
unleaded gasoline. You may encounter fuels contain-
ing 3 percent or more methanol along with other
alcohols called cosolvents.
DO NOT USE GASOLINES CONTAINING
METHANOL.
Use of methanol/gasoline blends may result in
starting and driveability problems and damage criti-
cal fuel system components.
Problems that are the result of using methanol/
gasoline blends are not the responsibility of Chrysler
Corporation and may not be covered by the vehicle
warranty.
Reformulated Gasoline
Many areas of the country are requiring the use of
cleaner-burning fuel referred to asReformulated
Gasoline. Reformulated gasolines are specially
blended to reduce vehicle emissions and improve air
quality.
Chrysler Corporation strongly supports the use of
reformulated gasolines whenever available. Although
your vehicle was designed to provide optimum perfor-
mance and lowest emissions operating on high qual-
ity unleaded gasoline, it will perform equally well
and produce even lower emissions when operating on
reformulated gasoline.
Materials Added to Fuel
Indiscriminate use of fuel system cleaning agents
should be avoided. Many of these materials intended
for gum and varnish removal may contain active sol-
vents of similar ingredients that can be harmful to
fuel system gasket and diaphragm materials.
E-85 GENERAL INFORMATION
The information in this section is for Flexible Fuel
Vehicles (FFV) only. These vehicles can be identified
by the unique Fuel Filler Door Label that states
Ethanol (E-85) or Unleaded Gasoline Only. This sec-
tion only covers those subjects that are unique to
these vehicles. Please refer to the other sections of
this manual for information on features that are
common between Flexible Fuel and gasoline only
powered vehicles.
ETHANOL FUEL (E-85)
E-85 is a mixture of approximately 85% fuel etha-
nol and 15% unleaded gasoline.
WARNING: Ethanol vapors are extremely flammable
and could cause serious personal injury. Never
have any smoking materials lit in or near the vehi-
cle when removing the fuel filler tube cap (gas cap)
or filling the tank. Do not use E-85 as a cleaning
agent and never use it near an open flame.
FUEL REQUIREMENTS
Your vehicle will operate on both unleaded gasoline
with an octane rating of 87, or E-85 fuel, or any mix-
ture of these two.
For best results, a refueling pattern that alternates
between E-85 and unleaded gasoline should be
avoided. When you do switch fuels, it is recom-
mended that
²you do not switch when the fuel gauge indicates
less than 1/4 full
²you do not add less than 5 gallons when refuel-
ing
²you operate the vehicle immediately after refuel-
ing for a period of at least 5 minutes
Observing these precautions will avoid possible
hard starting and/or significant deterioration in driv-
ability during warm up.
NOTE: When the ambient temperature is above
90ÉF, you may experience hard starting and rough
idle following start up even if the above recommen-
dations are followed.
STARTING
The characteristics of E-85 fuel make it unsuitable
for use when ambient temperatures fall below 0ÉF. In
the range of 0ÉF to 32ÉF, you may experience an
increase in the time it takes for your engine to start,
and a deterioration in drivability (sags and/or hesita-
tions) until the engine is fully warmed up.
14 - 2 FUEL SYSTEMNS
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 1300 of 1938
hydrocarbons. Vapors from the fuel tank are collected
in a charcoal filled canister. The vapors are held in
the canister until the engine is operating. When the
engine is running, the vapors are drawn through the
intake manifold into the combustion chambers.
PRESSURE-VACUUM FILLER CAP
The loss of any fuel or vapor out of the filler neck
is prevented by the use of a safety filler cap. The cap
will release pressure only under significant pressure
of 10.9 to 13.45 kPa (1.58 to 1.95 psi). The vacuum
release for all gas caps is between 0.97 and 2.0 kPa
(0.14 and 0.29 psi). The cap must be replaced by a
similar unit if replacement is necessary.
WARNING: REMOVE FILLER CAP TO RELIEVE
TANK PRESSURE BEFORE REMOVING OR REPAIR-
ING FUEL SYSTEM COMPONENTS.
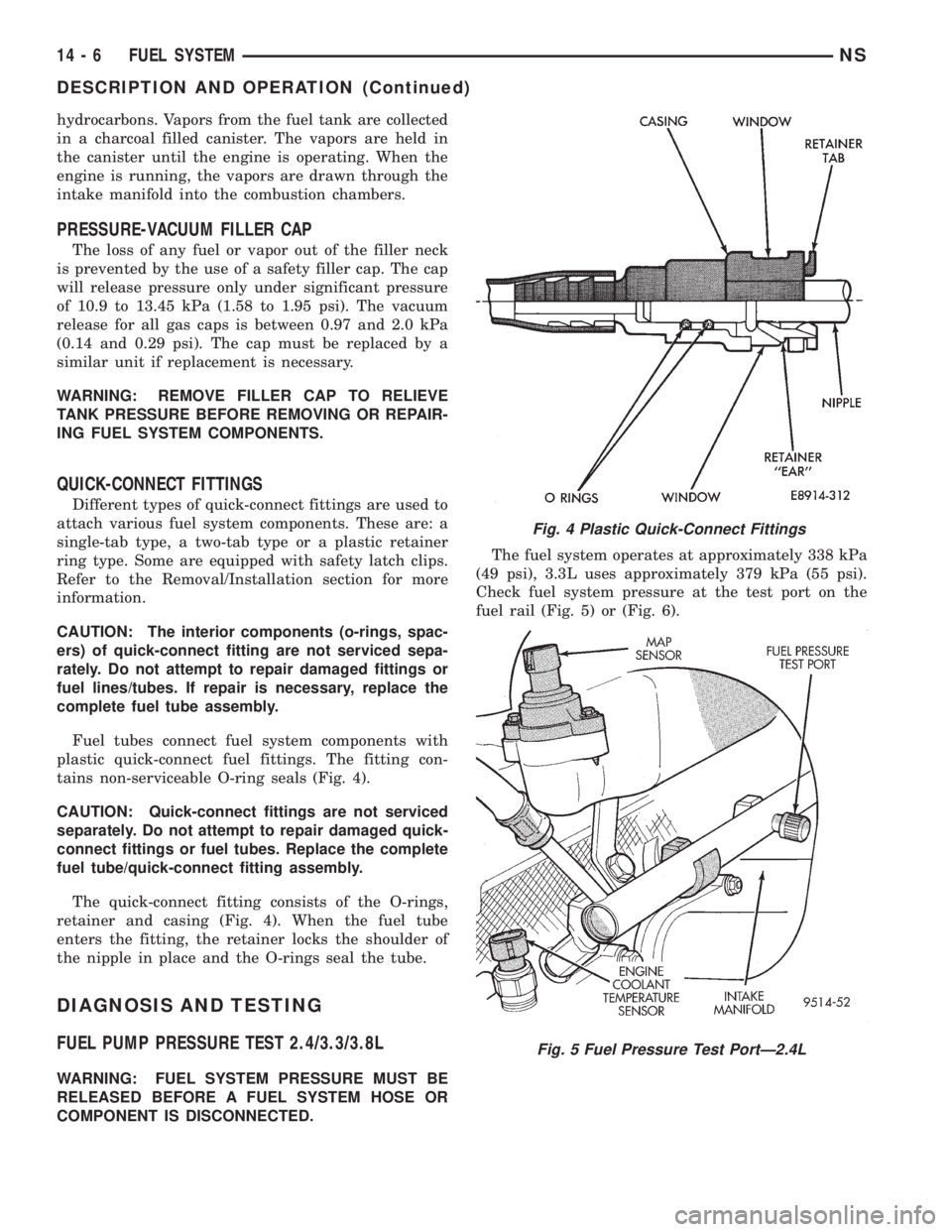
QUICK-CONNECT FITTINGS
Different types of quick-connect fittings are used to
attach various fuel system components. These are: a
single-tab type, a two-tab type or a plastic retainer
ring type. Some are equipped with safety latch clips.
Refer to the Removal/Installation section for more
information.
CAUTION: The interior components (o-rings, spac-
ers) of quick-connect fitting are not serviced sepa-
rately. Do not attempt to repair damaged fittings or
fuel lines/tubes. If repair is necessary, replace the
complete fuel tube assembly.
Fuel tubes connect fuel system components with
plastic quick-connect fuel fittings. The fitting con-
tains non-serviceable O-ring seals (Fig. 4).
CAUTION: Quick-connect fittings are not serviced
separately. Do not attempt to repair damaged quick-
connect fittings or fuel tubes. Replace the complete
fuel tube/quick-connect fitting assembly.
The quick-connect fitting consists of the O-rings,
retainer and casing (Fig. 4). When the fuel tube
enters the fitting, the retainer locks the shoulder of
the nipple in place and the O-rings seal the tube.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
FUEL PUMP PRESSURE TEST 2.4/3.3/3.8L
WARNING: FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE MUST BE
RELEASED BEFORE A FUEL SYSTEM HOSE OR
COMPONENT IS DISCONNECTED.The fuel system operates at approximately 338 kPa
(49 psi), 3.3L uses approximately 379 kPa (55 psi).
Check fuel system pressure at the test port on the
fuel rail (Fig. 5) or (Fig. 6).
Fig. 4 Plastic Quick-Connect Fittings
Fig. 5 Fuel Pressure Test PortÐ2.4L
14 - 6 FUEL SYSTEMNS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1371 of 1938

FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEMÐ2.5L DIESEL ENGINE
INDEX
page page
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
FUEL DRAIN TUBES..................... 7
FUEL FILTER/WATER SEPARATOR.......... 4
FUEL GAUGE SENDING UNIT.............. 4
FUEL HEATER RELAY.................... 8
FUEL HEATER.......................... 8
FUEL INJECTION PUMP.................. 5
FUEL INJECTORS....................... 6
FUEL SHUTDOWN SOLENOID............. 5
FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE WARNING....... 3
FUEL TANK MODULE.................... 4
FUEL TANK............................ 3
FUEL TUBES/LINES/HOSES AND CLAMPSÐ
LOW-PRESSURE TYPE................. 6
HIGH-PRESSURE FUEL LINES............. 7
INTRODUCTION........................ 3
QUICK-CONNECT FITTINGSÐLOW PRESSURE
TYPE............................... 7
WASTEGATE (TURBOCHARGER)........... 8
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
AIR IN FUEL SYSTEM................... 11
FUEL HEATER RELAY TEST.............. 12
FUEL INJECTION PUMP TEST............. 12
FUEL INJECTOR SENSOR TEST........... 12
FUEL INJECTOR TEST.................. 12
FUEL SHUTDOWN SOLENOID TEST........ 13
FUEL SUPPLY RESTRICTIONS............ 13GENERAL INFORMATION................. 9
HIGH-PRESSURE FUEL LINE LEAK TEST.... 14
VISUAL INSPECTION..................... 9
WASTEGATE (TURBOCHARGER).......... 14
SERVICE PROCEDURES
AIR BLEED PROCEDURES............... 14
FUEL INJECTION PUMP TIMING........... 15
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
ACCELERATOR PEDAL.................. 16
AIR CLEANER ELEMENT................. 16
FUEL DRAIN TUBES.................... 16
FUEL FILTER/WATER SEPARATOR......... 16
FUEL HEATER RELAY................... 17
FUEL HEATER......................... 17
FUEL INJECTION PUMP................. 19
FUEL INJECTORS...................... 22
FUEL LEVEL SENSOR................... 18
FUEL RESERVOIR MODULE.............. 25
FUEL SHUTDOWN SOLENOID............ 23
FUEL TANK........................... 23
HIGH-PRESSURE LINES................. 26
SPECIFICATIONS
FUEL INJECTOR FIRING SEQUENCE....... 27
FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE............... 27
FUEL TANK CAPACITY.................. 27
IDLE SPEED.......................... 27
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
INTRODUCTION
This Fuel Delivery section will cover components
not controlled by the PCM. For components con-
trolled by the PCM, refer to the Fuel Injection Sys-
temÐ2.5L Diesel Engine section of this group.
The fuel heater relay, fuel heater and fuel gauge
are not operated by the PCM. These components are
controlled by the ignition (key) switch. All other fuel
system electrical components necessary to operate
the engine are controlled or regulated by the PCM.
FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE WARNING
WARNING: HIGH±PRESSURE FUEL LINES DELIVER
DIESEL FUEL UNDER EXTREME PRESSURE FROM
THE INJECTION PUMP TO THE FUEL INJECTORS.
THIS MAY BE AS HIGH AS 45,000 KPA (6526 PSI).
USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN INSPECTING FORHIGH±PRESSURE FUEL LEAKS. INSPECT FOR
HIGH±PRESSURE FUEL LEAKS WITH A SHEET OF
CARDBOARD (Fig. 1). HIGH FUEL INJECTION
PRESSURE CAN CAUSE PERSONAL INJURY IF
CONTACT IS MADE WITH THE SKIN.
FUEL TANK
The fuel tank and tank mounting used with the
diesel powered engine is the same as used with gas-
oline powered models, although the fuel tank module
is different.
The fuel tank contains the fuel tank module and
two rollover valves. Two fuel lines are routed to the
fuel tank module. One line is used for fuel supply to
the fuel filter/water separator. The other is used to
return excess fuel back to the fuel tank.
The fuel tank module contains the fuel gauge elec-
trical sending unit.An electrical fuel pump is not
used with the diesel engine.
NS/GSFUEL SYSTEMÐ2.5L DIESEL ENGINE/2.0L GAS ENGINE 14 - 3
Page 1373 of 1938

For periodic draining of water from the bowl, refer
to Fuel Filter/Water Separator Removal/Installation
in this group.
FUEL SHUTDOWN SOLENOID
The fuel shutdown solenoid is controlled and
operated by the PCM.
The fuel shutdown (shut-off) solenoid is used to
electrically shut off the diesel fuel supply to the high-
pressure fuel injection pump. The solenoid is
mounted to the rear of the injection pump (Fig. 4).
The solenoid controls starting and stopping of the
engine regardless of the position of the accelerator
pedal. When the ignition (key) switch is OFF, the
solenoid is shut off and fuel flow is not allowed to the
fuel injection pump. When the key is placed in the
ON or START positions, fuel supply is allowed at the
injection pump.
FUEL INJECTION PUMP
The fuel injection pump is a mechanical distribu-
tor±type, Bosch VP36 series (Fig. 5). A gear on the
end of the injection pump shaft meshes with the
drive gear at the front of engine. The pump is
mechanically timed, relative to the position of the
cam and crankshaft. The PCM can make adjust-
ments to the timing of the injection pump.
The injection pump contains the fuel shutdown
solenoid, fuel temperature sensor, control sleeve sen-
sor, fuel quantity actuator and the fuel timing sole-
noid (Fig. 5).In the electronically controlled injection pump, the
pump plunger works the same as the pump plunger
in a mechanically controlled injection pump, but the
amount of fuel and the time the fuel is injected is
controlled by the vehicle's PCM, instead of by a
mechanical governor assembly. A solenoid controlled
by the PCM is used in place of the mechanical gov-
ernor assembly, and it moves a control sleeve inside
the pump that regulates the amount of fuel being
injected. There is no mechanical connection between
the accelerator pedal and the electronically controlled
injection pump. Instead, a sensor connected to the
accelerator pedal sends a signal to the PCM that rep-
resents the actual position of the accelerator pedal.
The PCM uses this input, along with input from
other sensors to move the control sleeve to deliver
the appropriate amount of fuel. This system is known
as ªDrive-By-Wireº
The actual time that the fuel is delivered is very
important to the diesel combustion process. The PCM
monitors outputs from the engine speed sensor (fly-
wheel position in degrees), and the fuel injector sen-
sor (mechanical movement within the #1 cylinder
fuel injector). Outputs from the Accelerator Pedal
Position sensor, engine speed sensor (engine rpm)
and engine coolant temperature sensor are also used.
The PCM will then compare its set values to these
outputs to electrically adjust the amount of fuel tim-
ing (amount of advance) within the injection pump.
This is referred to as ªClosed Loopº operation. The
PCM monitors fuel timing by comparing its set value
to when the injector #1 opens. If the value is greater
than a preset value a fault will be set.
Fig. 4 Fuel Shutdown Solenoid and Overflow Valve
Location
Fig. 5 Fuel Injection Pump
NS/GSFUEL SYSTEMÐ2.5L DIESEL ENGINE/2.0L GAS ENGINE 14 - 5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1374 of 1938
Actual electric fuel timing (amount of advance) is
accomplished by the fuel timing solenoid mounted to
the bottom of the injection pump (Fig. 5). Fuel timing
will be adjusted by the PCM, which controls the fuel
timing solenoid.
An overflow valve is attached into the fuel return
line at the rear of the fuel injection pump (Fig. 4).
This valve serves two purposes. One is to ensure that
a certain amount of residual pressure is maintained
within the pump when the engine is switched off.
This will prevent the fuel timing mechanism within
the injection pump from returning to its zero posi-
tion. The other purpose is to allow excess fuel to be
returned to the fuel tank through the fuel return
line. The pressure values within this valve are preset
and can not be adjusted.
The fuel injection pump supplies high±pressure
fuel of approximately 45,000 kPa (6526 psi) to each
injector in precise metered amounts at the correct
time.
For mechanical injection pump timing, refer to
Fuel Injection Pump Timing in the Service Proce-
dures section of this group.
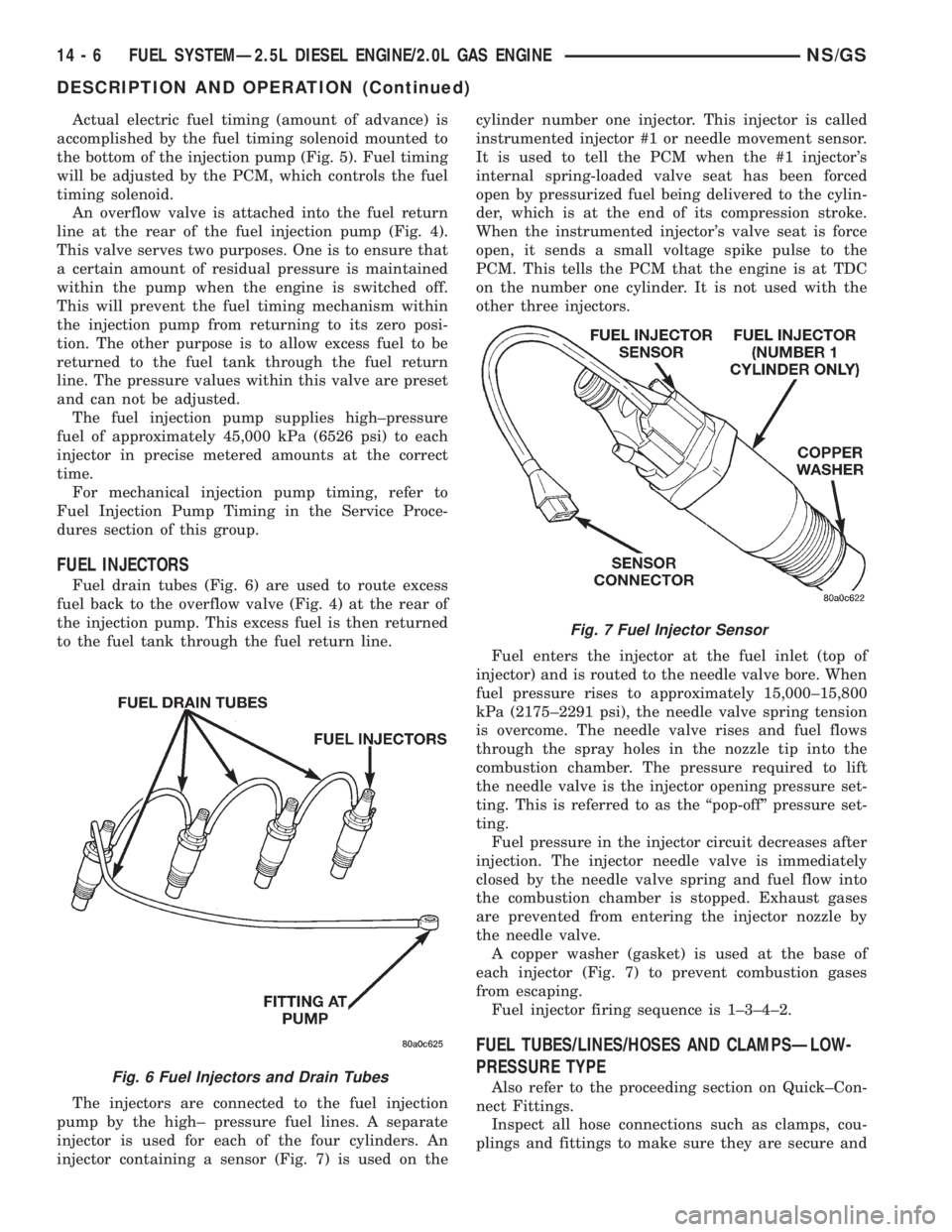
FUEL INJECTORS
Fuel drain tubes (Fig. 6) are used to route excess
fuel back to the overflow valve (Fig. 4) at the rear of
the injection pump. This excess fuel is then returned
to the fuel tank through the fuel return line.
The injectors are connected to the fuel injection
pump by the high± pressure fuel lines. A separate
injector is used for each of the four cylinders. An
injector containing a sensor (Fig. 7) is used on thecylinder number one injector. This injector is called
instrumented injector #1 or needle movement sensor.
It is used to tell the PCM when the #1 injector's
internal spring-loaded valve seat has been forced
open by pressurized fuel being delivered to the cylin-
der, which is at the end of its compression stroke.
When the instrumented injector's valve seat is force
open, it sends a small voltage spike pulse to the
PCM. This tells the PCM that the engine is at TDC
on the number one cylinder. It is not used with the
other three injectors.
Fuel enters the injector at the fuel inlet (top of
injector) and is routed to the needle valve bore. When
fuel pressure rises to approximately 15,000±15,800
kPa (2175±2291 psi), the needle valve spring tension
is overcome. The needle valve rises and fuel flows
through the spray holes in the nozzle tip into the
combustion chamber. The pressure required to lift
the needle valve is the injector opening pressure set-
ting. This is referred to as the ªpop-offº pressure set-
ting.
Fuel pressure in the injector circuit decreases after
injection. The injector needle valve is immediately
closed by the needle valve spring and fuel flow into
the combustion chamber is stopped. Exhaust gases
are prevented from entering the injector nozzle by
the needle valve.
A copper washer (gasket) is used at the base of
each injector (Fig. 7) to prevent combustion gases
from escaping.
Fuel injector firing sequence is 1±3±4±2.
FUEL TUBES/LINES/HOSES AND CLAMPSÐLOW-
PRESSURE TYPE
Also refer to the proceeding section on Quick±Con-
nect Fittings.
Inspect all hose connections such as clamps, cou-
plings and fittings to make sure they are secure andFig. 6 Fuel Injectors and Drain Tubes
Fig. 7 Fuel Injector Sensor
14 - 6 FUEL SYSTEMÐ2.5L DIESEL ENGINE/2.0L GAS ENGINENS/GS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1375 of 1938

leaks are not present. The component should be
replaced immediately if there is any evidence of deg-
radation that could result in failure.
Never attempt to repair a plastic fuel line/tube or a
quick±connect fitting. Replace complete line/tube as
necessary.
Avoid contact of any fuel tubes/hoses with other
vehicle components that could cause abrasions or
scuffing. Be sure that the fuel lines/tubes are prop-
erly routed to prevent pinching and to avoid heat
sources.
The lines/tubes/hoses are of a special construction.
If it is necessary to replace these lines/tubes/hoses,
use only original equipment type.
The hose clamps used to secure the rubber hoses
are of a special rolled edge construction. This con-
struction is used to prevent the edge of the clamp
from cutting into the hose. Only these rolled edge
type clamps may be used in this system. All other
types of clamps may cut into the hoses and cause
fuel leaks.
Where a rubber hose is joined to a metal tube
(staked), do not attempt to repair. Replace entire
line/tube assembly.
Use new original equipment type hose clamps.
Tighten hose clamps to 2 N´m (20 in. lbs.) torque.
QUICK-CONNECT FITTINGSÐLOW PRESSURE
TYPE
Different types of quick-connect fittings are used to
attach various fuel system components. These are: a
single-tab type, a two-tab type or a plastic retainer
ring type (Fig. 8). Refer to Quick-Connect Fittings in
the Removal/Installation section for more informa-
tion.
CAUTION: The interior components (o-rings, spac-
ers) of quick-connect fitting are not serviced sepa-
rately, but new pull tabs are available for some
types. Do not attempt to repair damaged fittings or
fuel lines/tubes. If repair is necessary, replace the
complete fuel tube assembly.
HIGH-PRESSURE FUEL LINES
CAUTION: The high±pressure fuel lines must be
held securely in place in their holders. The lines
cannot contact each other or other components. Do
not attempt to weld high±pressure fuel lines or to
repair lines that are damaged. Only use the recom-
mended lines when replacement of high±pressure
fuel line is necessary.
High±pressure fuel lines deliver fuel under pres-
sure of up to approximately 45,000 kPa (6526 PSI)
from the injection pump to the fuel injectors. Thelines expand and contract from the high±pressure
fuel pulses generated during the injection process. All
high±pressure fuel lines are of the same length and
inside diameter. Correct high±pressure fuel line
usage and installation is critical to smooth engine
operation.
WARNING: USE EXTREME CAUTION WHEN
INSPECTING FOR HIGH±PRESSURE FUEL LEAKS.
INSPECT FOR HIGH±PRESSURE FUEL LEAKS WITH
A SHEET OF CARDBOARD. HIGH FUEL INJECTION
PRESSURE CAN CAUSE PERSONAL INJURY IF
CONTACT IS MADE WITH THE SKIN.
FUEL DRAIN TUBES
These rubber tubes are low±pressure type.
Some excess fuel is continually vented from the
fuel injection pump. During injection, a small amount
of fuel flows past the injector nozzle and is not
injected into the combustion chamber. This fuel
drains into the fuel drain tubes (Fig. 9) and back to
the tee banjo fitting, which is connected to the same
line as the overflow valve, which allows a variable
quantity to return to the fuel tank. The overflow
valve is calibrated to open at a preset pressure.
Excess fuel not required by the pump to maintain the
minimum pump cavity pressure is then returned
through the overflow valve and on to the fuel tank
through the fuel return line.
Fig. 8 Plastic Retainer Ring-Type Fitting
NS/GSFUEL SYSTEMÐ2.5L DIESEL ENGINE/2.0L GAS ENGINE 14 - 7
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1384 of 1938
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
ACCELERATOR PEDAL
CAUTION: Be careful not to damage or kink the
cable core wire (within the cable sheathing) while
servicing the accelerator pedal or throttle cable.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect electrical connector.
(2) Remove accelerator pedal mounting bracket
nuts. Remove accelerator pedal assembly.
INSTALLATION
(1) Place accelerator pedal assembly over studs
protruding from floor pan. Tighten mounting nuts to
5 N´m (46 in. lbs.) torque.
(2) Connect electrical connector.
(3) Before starting the engine, operate the acceler-
ator pedal to check for any binding.
AIR CLEANER ELEMENT
REMOVAL
(1) Remove hose clamp at Mass Air Flow Sensor.
(2) Remove hose from Mass Air Flow Sensor.(3) Loosen 2 clamps holding air cleaner housing
halves together.
(4) Remove left side of air cleaner housing.
(5) Remove element from air cleaner housing.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install a new element in housing.
(2) Position left side of housing.
(3) Snap clamps into place.
(4) Install hoses and clamps.
FUEL DRAIN TUBES
The fuel drain tubes (Fig. 28) are low±pressure
type.
Pull each tube from the injector for removal. Push
on for installation. Clamps are not required for these
tubes.
FUEL FILTER/WATER SEPARATOR
The fuel filter/water separator is located in the
engine compartment on the right side near the shock
tower. (Fig. 29).
The fuel filter/water separator assembly contains
the fuel filter, fuel heater element, and fuel drain
valve (Fig. 29).
DRAINING WATER FROM FILTER BOWL
Moisture (water) collects at the bottom of the filter/
separator in a plastic bowl. Water entering the fuel
injection pump can cause serious damage to the
pump.Note that the bulb will be illuminated for
approximately 2 seconds each time the key is
initially placed in the ON position. This is done
for a bulb check.
Fig. 27 Accelerator Pedal Mounting-Typical
Fig. 28 Fuel Drain Tubes
14 - 16 FUEL SYSTEMÐ2.5L DIESEL ENGINE/2.0L GAS ENGINENS/GS
Page 1390 of 1938

(14) Gauge reading should be at 0.60 mm. If not,
the pump must be rotated for adjustment:
(a) Loosen the three injection pump mounting
nuts at the mounting flanges. These flanges are
equipped with slotted holes. The slotted holes are
used to rotate and position the injection pump for
fuel timing. Loosen the three nuts just enough to
rotate the pump.
(b) Rotate the pumpclockwise(as viewed from
front) until .60 mm is indicated on the dial indica-
tor gauge.
(c) Tighten the three pump mounting nuts to 30
N´m (22 ft. lbs.) torque.
(d) Recheck the dial indicator after tightening
the pump mounting nuts. Gauge should still be
reading 0.60 mm. Loosen pump mounting nuts and
readjust if necessary.
(15) Remove dial indicator and adapter tools.
(16) Install access plug and washer to rear of
injection pump.
(17) Install plug at timing gear cover.
(18) Remove dial indicator from valve stem.
(19) Install valve spring and keepers.
(20) Install rocker arm assembly and tighten nuts.
(21) Install and connect the four high±pressure
fuel lines to the fuel injection pump. Also connect
fuel lines at the fuel injectors. For procedures, refer
to High±Pressure Fuel Lines in this group.
(22) Install electrical connector at engine coolant
temperature sensor.
(23) Connect electrical connector at fuel shutdown
solenoid.(24) Connect the main engine wiring harness to
the glow plugs.
(25) Connect the fuel timing solenoid pigtail har-
ness to the engine wiring harness.
(26) Connect the overflow valve/banjo fitting (fuel
return line assembly). Replace copper gaskets before
installing.
(27) Connect the rubber fuel return and supply
hoses to metal lines at pump. Tighten hose clamps to
2 N´m (20 in. lbs.) torque.
(28) Install generator assembly.
(29) Install engine accessory drive belt. Refer to
Group 7, Cooling System for procedures.
(30) Install negative battery cable to battery.
(31) Start the engine and bring to normal operat-
ing temperature.
(32) Check for fuel leaks.
FUEL INJECTORS
Four fuel injectors are used on each engine. Of these
four, two different types are used. The fuel injector used
on cylinder number one is equipped with a fuel injector
sensor (Fig. 47). The other three fuel injectors are iden-
tical.
Do not place the fuel injector equipped with
the fuel injector sensor into any other location
except the cylinder number one position.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable at battery.
(2) Thoroughly clean the area around the injector
with compressed air.
(3) Remove the fuel drain hoses (tubes) at each
injector (Fig. 48) being serviced. Each of these hoses
is slip±fit to the fitting on injector.
(4) Remove the high±pressure fuel line at injector
being removed. Refer to High±Pressure Fuel Lines in
this group for procedures.
(5) Remove the injector using special socket tool
number VM.1012A. When removing cylinder number
Fig. 46 Installing Dial Indicator and Special Adapter
Tools
Fig. 47 Fuel Injector SensorÐNumber±1 Cylinder
14 - 22 FUEL SYSTEMÐ2.5L DIESEL ENGINE/2.0L GAS ENGINENS/GS
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)