lock CHRYSLER VOYAGER 1996 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 1996, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 1996Pages: 1938, PDF Size: 55.84 MB
Page 1920 of 1938
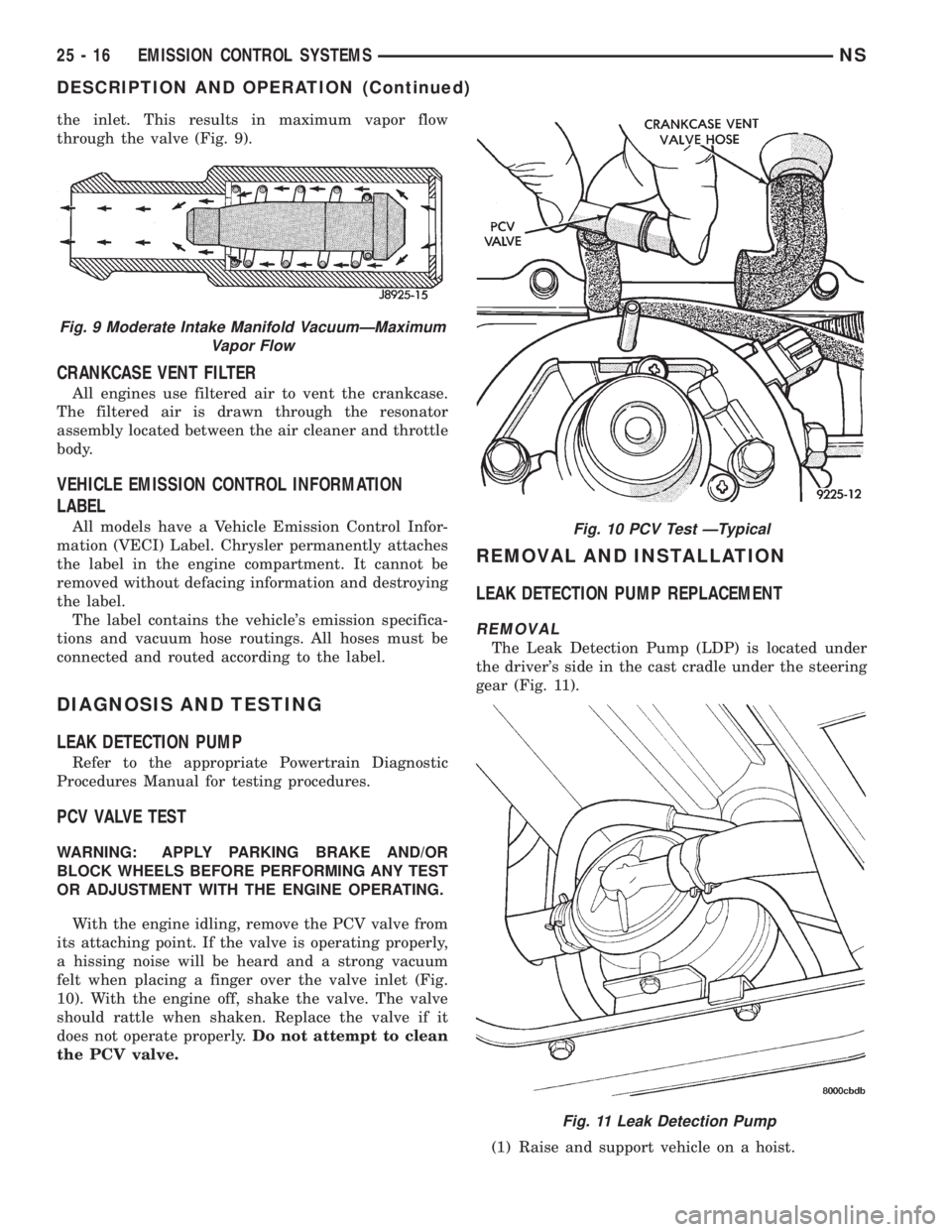
the inlet. This results in maximum vapor flow
through the valve (Fig. 9).
CRANKCASE VENT FILTER
All engines use filtered air to vent the crankcase.
The filtered air is drawn through the resonator
assembly located between the air cleaner and throttle
body.
VEHICLE EMISSION CONTROL INFORMATION
LABEL
All models have a Vehicle Emission Control Infor-
mation (VECI) Label. Chrysler permanently attaches
the label in the engine compartment. It cannot be
removed without defacing information and destroying
the label.
The label contains the vehicle's emission specifica-
tions and vacuum hose routings. All hoses must be
connected and routed according to the label.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
LEAK DETECTION PUMP
Refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic
Procedures Manual for testing procedures.
PCV VALVE TEST
WARNING: APPLY PARKING BRAKE AND/OR
BLOCK WHEELS BEFORE PERFORMING ANY TEST
OR ADJUSTMENT WITH THE ENGINE OPERATING.
With the engine idling, remove the PCV valve from
its attaching point. If the valve is operating properly,
a hissing noise will be heard and a strong vacuum
felt when placing a finger over the valve inlet (Fig.
10). With the engine off, shake the valve. The valve
should rattle when shaken. Replace the valve if it
does not operate properly.Do not attempt to clean
the PCV valve.
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
LEAK DETECTION PUMP REPLACEMENT
REMOVAL
The Leak Detection Pump (LDP) is located under
the driver's side in the cast cradle under the steering
gear (Fig. 11).
(1) Raise and support vehicle on a hoist.
Fig. 9 Moderate Intake Manifold VacuumÐMaximum
Vapor Flow
Fig. 10 PCV Test ÐTypical
Fig. 11 Leak Detection Pump
25 - 16 EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMSNS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1921 of 1938
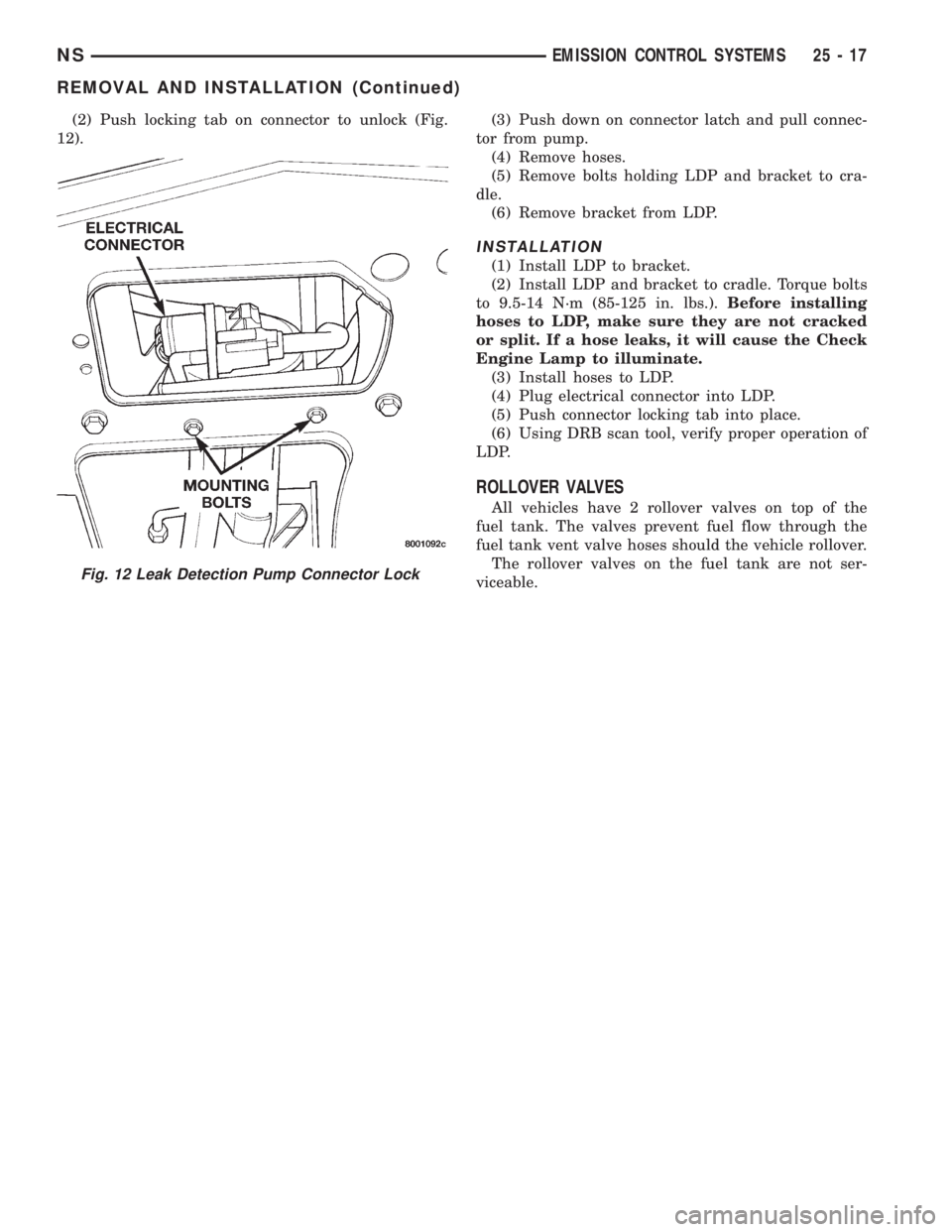
(2) Push locking tab on connector to unlock (Fig.
12).(3) Push down on connector latch and pull connec-
tor from pump.
(4) Remove hoses.
(5) Remove bolts holding LDP and bracket to cra-
dle.
(6) Remove bracket from LDP.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install LDP to bracket.
(2) Install LDP and bracket to cradle. Torque bolts
to 9.5-14 N´m (85-125 in. lbs.).Before installing
hoses to LDP, make sure they are not cracked
or split. If a hose leaks, it will cause the Check
Engine Lamp to illuminate.
(3) Install hoses to LDP.
(4) Plug electrical connector into LDP.
(5) Push connector locking tab into place.
(6) Using DRB scan tool, verify proper operation of
LDP.
ROLLOVER VALVES
All vehicles have 2 rollover valves on top of the
fuel tank. The valves prevent fuel flow through the
fuel tank vent valve hoses should the vehicle rollover.
The rollover valves on the fuel tank are not ser-
viceable.
Fig. 12 Leak Detection Pump Connector Lock
NSEMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS 25 - 17
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1923 of 1938

the amount of EGR supplied to the engine. This pro-
vides the correct amount of exhaust gas recirculation
for different operating conditions.
This system does not allow EGR at idle. The EGR
systems can operate at all coolant temperatures
above 60ÉF as long as the battery ambient tempera-
ture is above 7ÉF.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
EGR SYSTEM ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS
The PCM performs an on-board diagnostic check of
the EGR system. The diagnostic system uses the
electronic EGR transducer for the system tests.
The diagnostic check activates only during selected
engine/driving conditions. When the conditions are
met, the PCM energizes the transducer solenoid to
disable the EGR. The PCM checks for a change in
the heated oxygen sensor signal. If the air-fuel mix-
ture goes lean, the PCM will attempt to enrichen the
mixture. The PCM registers a Diagnostic Trouble
Code (DTC) if the EGR system is not operating cor-
rectly. After registering a DTC, the PCM turns on the
malfunction indicator (Check Engine) lamp after 2
consecutive trips. There are 2 types of failures sensed
by the PCM. The first is a short or open in the elec-
trical solenoid circuit. The second is a mechanical
failure or loss of vacuum. The Malfunction Indicator
Lamp (MIL) indicates the need for service.
If a problem is indicated by the MIL and a DTC for
the EGR system is set, check for proper operation of
the EGR system. Use the System Test, EGR Gas
Flow Test. If the EGR system tests properly, check
the system using the DRB scan tool. Refer to
On-Board Diagnosis sections in this Group. Also,
refer to the DRB scan tool and the appropriate Pow-
ertrain Diagnostics Procedure manual.
EGR SYSTEM TEST
WARNING: APPLY PARKING BRAKE AND/OR
BLOCK WHEELS BEFORE TESTING THE EGR SYS-
TEM.
(1) Check the condition of all EGR system hoses
and tubes for leaks, cracks, kinks and hardening of
rubber hoses. Repair and correct these conditions
before performing any tests.
(2) Be sure the hoses at both the EGR valve and
EGR valve control are connected to the proper fit-
tings (Fig. 4).
(3) Be sure the electrical connector is firmly con-
nected at the valve control.
(4) To check EGR system operation, connect the
DRB scan tool to the 16±way data link connector.
The data link connector is located on the lower edge
of the instrument panel near the steering column.
Refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic Pro-
cedures service manual for operation of the DRB
scan tool when diagnosing the EGR system.
(5) After checking the system with the DRB scan
tool, proceed to the following EGR Valve Leakage and
EGR Valve Control Tests and repair as necessary.
Fig. 3 Electric EGR Transducer Assembly
Fig. 4 EGR Value and EGR Value ÐTypical
NSEMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS 25 - 19
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1934 of 1938

²An EGR Solenoid. The EGR solenoid is located
in the engine compartment next to the PDC (Fig. 3).
The EGR solenoid opens and closes the vaccum sup-
ply that opens and closes the EGR valve. The
amount of time the EGR solenoid is held open is con-
trolled by the PCM. This is referred to as the ªon
timeº of the EGR valve.
²An EGR tube (Fig. 2) connecting a passage in
the EGR valve to the rear of the exhaust manifold.
²The vacuum pump, which supplies vacuum for
the EGR Solenoid valve. This pump also supplies
vacuum for operation of the power brake booster. The
pump is located internally in the front of the engine
block (Fig. 4) and is driven by the crankshaft gear.
²Vacuum lines and hoses to connect the various
components.
When the PCM supplies a ªonº or ªoffº signal to the
EGR Solenoid by grounding the circuit, EGR system
operation starts to occur. The PCM will monitor var-
ious engine conditions and determine when to supply
and remove this ground signal. Some of the engine
conditions that are monitored are the engine coolant
temperature, throttle position and engine speed sen-
sors.
When the ground signal is supplied to the EGR
Solenoid, vacuum from the vacuum pump will be
allowed to pass to the EGR valve via a connecting
hose.
Exhaust gas recirculation will begin in this order
when:
²The PCM determines that EGR system opera-
tion is necessary.²The engine is running to operate the vacuum
pump.
²A ground signal is supplied to the EVM.
²Vacuum passes to the EGR valve.
²The inlet seat (poppet valve) at the bottom of
the EGR valve opens to dilute and recirculate
exhaust gas back into the intake manifold.
The EGR system will be shut down by the PCM
after 60 seconds of continuous engine idling to
improve idle quality.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
EGR GAS FLOW TEST
Use the following test procedure to determine if
exhaust gas is flowing through the EGR valve. It can
also be used to determine if the EGR tube is plugged,
or the system passages in the intake or exhaust man-
ifolds are plugged.
This is not to be used as a complete test of the
EGR system.
The engine must be started, running and warmed
to operating temperature for this test.
(1) All EGR valves are equipped with a vacuum
supply fitting located on the EGR valve vacuum
motor (Fig. 2).
(2) Disconnect the rubber hose from the vacuum
supply fitting (Fig. 2).
(3) Connect a hand±held vacuum pump to this fit-
ting.
(4) Start the engine.
Fig. 3 EGR Solenoid
Fig. 4 Internal Vacuum Pump
25 - 6 EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMNS/GS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)