spark plugs replace CHRYSLER VOYAGER 1996 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 1996, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 1996Pages: 1938, PDF Size: 55.84 MB
Page 20 of 1938

52,500 Miles (84 000 km) or at 42 months
²Change engine oil.
²Flush and replace engine coolant if not done at
36 months.
60,000 Miles (96 000 km) or at 48 months
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Replace air cleaner element.
²Check PCV valve and replace, if necessary.
*
²Inspect serpentine drive belt, replace if neces-
sary.
²Inspect tie rod ends and boot seals.
67,500 Miles (108 000 km) or at 54 months
²Change engine oil.
²Inspect brake linings.
75,000 Miles (120 000 km) or at 60 months
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Inspect serpentine drive belt, replace if neces-
sary. This maintenance is not required if belt was
previously replaced.
²Flush and replace engine coolant if it has been
30,000 miles (48 000 km) or 24 months since last
change.
82,500 Miles (132 000 km) or at 66 months
²Change engine oil.
²Flush and replace engine coolant if it has been
30,000 miles (48 000 km) or 24 months since last
change.
90,000 Miles (144 000 km) or at 72 months
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Replace air cleaner element.
²Check PCV valve and replace, if necessary.
Not required if previously changed. *
²Inspect serpentine drive belt, replace if neces-
sary. This maintenance is not required if belt was
previously replaced.
²Inspect tie rod ends and boot seals.
²Inspect brake linings.
97,500 Miles (156 000 km) or at 78 months
²Change engine oil.
100,000 Miles (160,000 km)
²Replace spark plugs on 3.3L and 3.8L
engines.
²Replace ignition cables on 3.3L and 3.8L
engines.
105,000 Miles (168 000 km) or at 84 months
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Inspect serpentine drive belt, replace if neces-
sary. This maintenance is not required if belt was
previously replaced.
²Flush and replace engine coolant if it has been
30,000 miles (48 000 km) or 24 months since last
change.
112,500 Miles (180 000 km) or at 90 months
²Change engine oil.
²Inspect brake linings.
²Flush and replace engine coolant if it has been
30,000 miles (48 000 km) or 24 months since last
change.
120,000 Miles (192 000 km) or at 96 months
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Replace automatic transmission fluid.
²Replace engine air cleaner element.
²Check and replace PCV valve, if necessary.
*
²Inspect serpentine drive belt. Not required if
replaced at 75,000, 90,000 or 105,000 miles.
²Inspect tie rod ends and boot seals.
* This maintenance is recommended by Chrysler to
the owner but is not required to maintain the war-
ranty on the PCV valve.
** If California vehicle, this maintenance is recom-
mended by Chrysler to the owner but is not required
to maintain the warranty of the timing belt.
SCHEDULE ± B
3,000 Miles (5 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
6,000 Miles (10 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
9,000 Miles (14 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Inspect brake linings.
12,000 Miles (19 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
15,000 Miles (24 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Inspect air cleaner element. Replace as
necessary.
0 - 4 LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCENS
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 22 of 1938

²Replace spark plugs.
²Replace ignition cables.
²Inspect serpentine drive belt, replace if neces-
sary. This maintenance is not required if belt was
previously replaced.
²Drain and refill automatic transaxle fluid and
replace filter. Adjust band, if so equipped. (See note)
²Change AWD power transfer unit fluid.
78,000 Miles (125 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
81,000 Miles (130 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Inspect brake linings.
²Flush and replace engine coolant.
84,000 Miles (134 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Change AWD overrunning clutch and rear car-
rier fluid.
87,000 Miles (139 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
90,000 Miles (144 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Replace air cleaner element.
²Check PCV valve and replace if necessary.
Not required if previously changed. *
²Inspect serpentine drive belt, replace if neces-
sary. This maintenance is not required if belt was
previously replaced.
²Drain and refill automatic transmission fluid
and replace filter. Adjust bands, if so equipped. (See
note)
²Change AWD power transfer unit fluid.
²Inspect tie rod ends and boot seals.
²Inspect brake linings.
93,000 Miles (149 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
96,000 Miles (154 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
99,000 Miles (158 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Inspect brake linings.
102,000 Miles (163 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
105,000 Miles (168 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Inspect air cleaner element. Replace as
necessary.
²Inspect serpentine drive belt, replace if neces-
sary. This maintenance is not required if belt was
previously replaced.
²Drain and refill automatic transmission fluid
and filter. Adjust bands, if so equipped. (See note)
²Change AWD power transfer unit fluid.
²Change AWD overrunning clutch and rear car-
rier fluid.
108,000 Miles (173 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Inspect brake linings.
111,000 Miles (178 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Flush and replace engine coolant.
114,000 Miles (182 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
117,000 Miles (187 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Inspect brake linings.
120,000 Miles (192 000 km)
²Change engine oil.
²Replace engine oil filter.
²Replace air cleaner element.
²Inspect PCV valve. Replace as necessary. *
²Inspect serpentine drive belt. Not required if
replaced at 75,000, 90,000 or 105,000 miles.
²Drain and refill automatic transmission fluid
and replace filter. Adjust bands, if so equipped.
²Change AWD power transfer unit fluid.
²Inspect tie rod ends and boot seals.
* This maintenance is recommended by Chrysler to
the owner but is not required to maintain the war-
ranty on the PCV valve.
** If California vehicle, this maintenance is recom-
mended by Chrysler to the owner but is not required
to maintain the warranty of the timing belt.
NOTE: Operating vehicle more than 50% in heavy
traffic during hot weather, above 90ÉF (32ÉC), using
vehicle for police, taxi, limousine type operation or
trailer towing require the more frequent transaxle
service noted in Schedule ± B. Perform these ser-
vices if vehicle is usually operated under these con-
ditions.
Inspection and service should also be performed
anytime a malfunction is observed or suspected.
0 - 6 LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCENS
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 300 of 1938
²available manifold vacuum
²barometric pressure
²engine coolant temperature
²engine RPM
²intake air temperature (2.4L only)
²throttle position
The PCM also regulates the fuel injection system.
Refer to the Fuel Injection sections of Group 14.
IGNITION SYSTEM
NOTE: The 2.4, 3.0 and 3.3/3.8L engines use a fixed
ignition timing system. Basic ignition timing is not
adjustable. All spark advance is determined by the
Powertrain Control Module (PCM).
The distributorless ignition system used on 2.4 and
3.3/3.8L engines is refered to as the Direct Ignition
System (DIS). The system's three main components
are the coil pack, crankshaft position sensor, and
camshaft position sensor. The crankshaft position
sensor and camshaft position sensor are hall effect
devices.
The 3.0L engine uses a distributor, crankshaft sen-
sor and ignition coil. The system's main components
are the distributor, distributor pickup, camshaft sig-
nal, crankshaft signal and ignition coil.
SPARK PLUGSÐ2.4/3.0L
All engines use resistor spark plugs. They have
resistance values ranging from 6,000 to 20,000 ohms
when checked with at least a 1000 volt spark plug
tester.Do not use an ohm meter to check the resis-
tance of the spark plugs. This will give an inac-
curate reading.
Remove the spark plugs and examine them for
burned electrodes and fouled, cracked or broken por-
celain insulators. Keep plugs arranged in the order
in which they were removed from the engine. An iso-
lated plug displaying an abnormal condition indicates
that a problem exists in the corresponding cylinder.
Replace spark plugs at the intervals recommended in
Group O - Lubrication and Maintenance.
Spark plugs that have low mileage may be cleaned
and reused if not otherwise defective, carbon or oil
fouled. Refer to the Spark Plug Condition section of
this group. After cleaning, file the center electrode
flat with a small flat point file or jewelers file. Adjust
the gap between the electrodes (Fig. 2) to the dimen-
sions specified in the chart at the end of this section.
Special care should be used when installing spark
plugs in the 2.4L cylinder head spark plug wells. Be
sure the plugs do not drop into the wells, damage to
the electrodes can occur.
Always tighten spark plugs to the specified torque.
Over tightening can cause distortion resulting in a
change in the spark plug gap. Overtightening can
also damage the cylinder head. Tighten spark plugs
to 28 N´m (20 ft. lbs.) torque.SPARK PLUGSÐ3.3/3.8L
The 3.3/3.8L engines utilize platinum spark plugs.
Refer to the maintenance schedule in Group 0 of this
service manual.
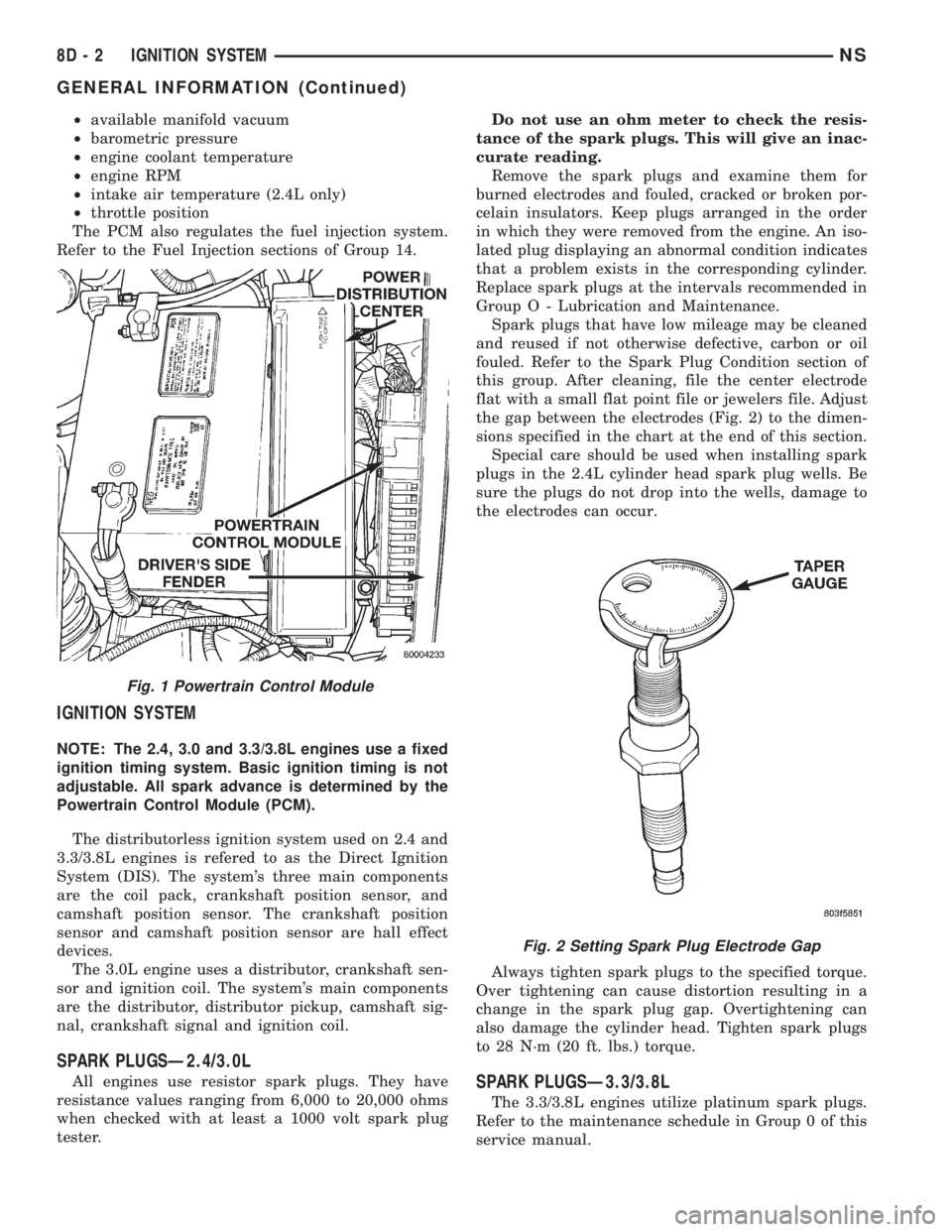
Fig. 1 Powertrain Control Module
Fig. 2 Setting Spark Plug Electrode Gap
8D - 2 IGNITION SYSTEMNS
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 301 of 1938

All engines use resistor spark plugs. They have
resistance values ranging from 6,000 to 20,000 ohms
when checked with at least a 1000 volt spark plug
tester.
Do not use an ohm meter to check the resis-
tance of the spark plugs. This will give an inac-
curate reading.
Remove the spark plugs and examine them for
burned electrodes and fouled, cracked or broken por-
celain insulators. Keep plugs arranged in the order
in which they were removed from the engine. An iso-
lated plug displaying an abnormal condition indicates
that a problem exists in the corresponding cylinder.
Replace spark plugs at the intervals recommended in
Group O - Lubrication and Maintenance.
Spark plugs that have low mileage may be cleaned
and reused if not otherwise defective, carbon or oil
fouled. Refer to the Spark Plug Condition section of
this group.
The spark plugs are double platinum and have a
recommended service life of 100,000 miles for normal
driving conditions per schedule A in this manual. The
spark plugs have a recommended service life of
75,000 miles for serve driving conditions per schedule
B in this manual. A thin platinum pad is welded to
both electrode ends as show in (Fig. 3). Extreme care
must be used to prevent spark plug cross threading,
mis-gaping and ceramic insulator damage during
plug removal and installation.
CAUTION: Never attempt to file the electrodes or
use a wire brush for cleaning platinum plugs. This
would damage the platinum pads which would
shorten spark plug life.
Apply a very small amount of anti-seize compound
to the threads when reinstalling the vehicle's original
spark plugs that have been determined good.Do not
apply anti-seize compound to new spark plugs.
NOTE: Anti-seize compound is electrically conduc-
tive and can cause engine misfires if not applied
correctly. It is extremely important that the anti-
seize compound doesn't make contact with the
spark plug electrodes or ceramic insulator.
Never force a gap gauge between the platinum
electrodes or adjust the gap on platinum spark plugs
without reading the 3.3/3.8L Spark Plug Gap Mea-
surement procedures in this section.
Always tighten spark plugs to the specified torque.
Over tightening can cause distortion resulting in a
change in the spark plug gap. Overtightening can
also damage the cylinder head. Tighten spark plugs
to 28 N´m (20 ft. lbs.) torque.
Due to the engine packaging environment for the
3.3/3.8L engines, extreme care should be used wheninstalling the spark plugs to avoid cross threading
problems.
3.3/3.8L SPARK PLUG GAP MEASUREMENT
CAUTION: The Platinum pads can be damaged dur-
ing the measurement of checking the gap if extreme
care is not used.
²USE ONLY A TAPER GAP GAUGE (Fig. 2)
²Never force the gap gauge through the platinum
pads. Only apply enough force until resistance is felt.
²Never use a wire brush or spark plug cleaner
machine to clean platinum spark plugs
²Use an OSHA approved air nozzle when drying
gas fouled spark plugs.
If gap adjustment is required of platinum plug,
bend only the ground electrode. DO NOT TOUCH
the platinum pads. Use only a proper gapping tool
and check with a taper gap gauge.
CAUTION: Cleaning of the platinum plug may dam-
age the platinum tip.
SPARK PLUG CABLE
Spark Plug cables are sometimes referred to as
secondary ignition wires. The wires transfer electri-
cal current from the ignition coil pack, distributor
(3.0L), to individual spark plugs at each cylinder. The
resistive spark plug cables are of nonmetallic con-
struction. The cables provide suppression of radio fre-
quency emissions from the ignition system.
Check the spark plug cable connections for good
contact at the coil, distributor cap towers (3.0L), and
spark plugs. Terminals should be fully seated. The
insulators should be in good condition and should fit
tightly on the coil, distributor (3.0L) and spark plugs.
Spark plug cables with insulators that are cracked or
torn must be replaced.
Fig. 3 Platinum Pads
NSIGNITION SYSTEM 8D - 3
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 302 of 1938

Clean Spark Plug cables with a cloth moistened
with a non-flammable solvent. Wipe the cables dry.
Check for brittle or cracked insulation.
SPARK PLUG CABLESÐ3.3/3.8L
The spark plug cables and spark plug boots are
made from high temperature silicone materials. The
spark plug boots utilize metal heat shields for ther-
mal protection from the exhaust manifold. The heat
shields slide over the spark plug boots. The notches
on the heat shields ensure the spark plug boot and
shield twist together during spark plug boot removal.
They also identify proper heat shield installation on
the boot for service.Refer to 3.3/3.8L Spark Plug
Cable removal and installation.All spark plug
cable leads are properly identified with cylinder num-
bers. The inside of the spark plug boot is coated with
a special high temperature silicone grease for greater
sealing and to minimize boot bonding to the spark
plug insulator. The convoluted tubing on the rear
plug cables are made of a high temperature plastic
material. Under normal driving conditions, the spark
plug cables have a recommended service life of a
100,000 miles. The spark plugs have a recommended
service life of 75,000 miles for severe driving condi-
tions per schedule B in this manual.
The spark plug heat shield can be reused if an
ignition cable is replaced due to failure. Never reuse
heat shield's that have heat shield anti-twist, side or
spark plug attachment tabs bent or missing. Ensure
that the heat shield is properly attached to the spark
plug to avoid RFI problems. The bottom of the spark
plug heat shield must make contact with the spark
plug hex.
The front ignition cables must not make contact
with the oil dip stick tube and #5 cable must not
touch the coil mounting bolt to avoid abrasion/dielec-
tric failures.
IGNITION COIL
WARNING: THE DIRECT IGNITION SYSTEM GEN-
ERATES APPROXIMATELY 40,000 VOLTS. PER-
SONAL INJURY COULD RESULT FROM CONTACT
WITH THIS SYSTEM.
The ignition coil assembly consists of 3 indepen-
dent coils molded together (Fig. 4). The coil assembly
is mounted on the intake manifold. Spark plug cables
route to each cylinder from the coil. The coil fires two
spark plugs every power stroke. One plug is the cyl-
inder under compression, the other cylinder fires on
the exhaust stroke. The Powertrain Control Module
(PCM) determines which of the coils to charge and
fire at the correct time.
Coil 1 fires cylinders 1 and 4, coil 2 fires cylinders
2 and 5, coil 3 fires cylinders 3 and 6.The Auto Shutdown (ASD) relay provides battery
voltage to the ignition coil. The PCM provides a
ground contact (circuit) for energizing the coil. When
the PCM breaks the contact, the energy in the coil
primary transfers to the secondary causing the
spark. The PCM will de-energize the ASD relay if it
does not receive the crankshaft position sensor and
camshaft position sensor inputs. Refer to Auto Shut-
down (ASD) RelayÐPCM Output, in this section for
relay operation.
AUTOMATIC SHUTDOWN (ASD) RELAY
The Powertrain Control Module (PCM) operates
the Auto Shutdown (ASD) relay by switching the
ground path on and off.
The ASD relay supplies battery voltage to the fuel
injectors, electronic ignition coil and the heating ele-
ments in the oxygen sensors.
The PCM controls the relay by switching the
ground path for the solenoid side of the relay on and
off. The PCM turns the ground path off when the
ignition switch is in the Off position unless the 02
Heater Monitor test is being run. Refer to Group 25,
On-Board Diagnostics. When the ignition switch is in
the On or Crank position, the PCM monitors the
crankshaft position sensor and camshaft position sen-
sor signals to determine engine speed and ignition
timing (coil dwell). If the PCM does not receive the
crankshaft position sensor and camshaft position sen-
sor signals when the ignition switch is in the Run
position, it will de-energize the ASD relay.
The ASD relay is located in the Power Distribution
Center (PDC). The PDC is located on the driver's
side inner fender well (Fig. 5). A label on the under-
side of the PDC cover identifies the relays and fuses
in the PDC.
Fig. 4 Ignition Coil Pack
8D - 4 IGNITION SYSTEMNS
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 307 of 1938

sure that the spark plugs are firing. Inspect the dis-
tributor rotor, cap, spark plug cables, and spark
plugs. If they are in proper working order, the igni-
tion system is not the reason why the engine will not
start. Inspect the fuel system and engine for proper
operation.
CHECK COIL TESTÐ2.4L
Coil one fires cylinders 1 and 4, coil two fires
cylinders 2 and 3. Each coil tower is labeled
with the number of the corresponding cylinder.
(1) Remove ignition cables and measure the resis-
tance of the cables. Resistance must be within the
range shown in the Cable Resistance Chart in Spec-
ifications. Replace any cable not within tolerance.
(2) Disconnect the electrical connector from the
coil pack.
(3) Measure the primary resistance of each coil. At
the coil, connect an ohmmeter between the B+ pin
and the pin corresponding to the cylinders in ques-
tion (Fig. 17). Resistance on the primary side of each
coil should be 0.45 - 0.65 ohm at (70É to 80É F).
Replace the coil if resistance is not within tolerance.
(4) Remove ignition cables from the secondary tow-
ers of the coil. Measure the secondary resistance of
the coil between the towers of each individual coil
(Fig. 18). Secondary resistance should be 7,000 to
15,800 ohms. Replace the coil if resistance is not
within tolerance.
CHECK COIL TESTÐ3.3/3.8L
Coil 1 fires cylinders 1 and 4, coil 2 fires cyl-
inders 2 and 5, and coil 3 fires cylinders 3 and
6. Each coil tower is labeled with the number of
the corresponding cylinder.
(1) Disconnect the electrical connector from the
coil pack (Fig. 19).
(2) Measure the primary resistance of each coil. At
the coil, connect an ohmmeter between the B+ pinand the pin corresponding to the cylinders in ques-
tion (Fig. 20). Resistance on the primary side of each
coil should be 0.45 - 0.65 ohm at 21É to 27ÉC (70É to
80ÉF). A coil that has not been allowed to cool off,
would result in inaccurate measurement results.
Replace the coil if resistance is not within tolerance.
Fig. 17 Terminal Identification
Fig. 18 Checking Ignition Coil Secondary
Resistance
Fig. 19 Ignition Coil Electrical Connector
Fig. 20 Ignition Coil Terminal Identification
NSIGNITION SYSTEM 8D - 9
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 309 of 1938

either the crankshaft position sensor/camshaft posi-
tion sensor 8 volt supply circuit, or the camshaft
position sensor output or ground circuits. Use the
DRB scan tool to test the camshaft position sensor
and the sensor circuits. Refer to the appropriate Pow-
ertrain Diagnostics Procedure Manual. Refer to the
wiring diagrams section for circuit information.
IGNITION TIMING PROCEDURE
The engines for this vehicle, use a fixed ignition
system. The PCM regulates ignition timing. Basic
ignition timing is not adjustable.
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE (MAP) SENSOR
TEST
Refer to Group 14, Fuel System for Diagnosis and
Testing.
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR AND CRANKSHAFT
POSITION SENSOR
The output voltage of a properly operating cam-
shaft position sensor or crankshaft position sensor
switches from high (5.0 volts) to low (0.3 volts). By
connecting an Moper Diagonostic System (MDS) and
engine analyzer to the vehicle, technicians can view
the square wave pattern.
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR
Refer to Group 14, Fuel System for Diagnosis and
Testing.
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR
Refer to Group 14, Fuel System, for Diagnosis and
Testing.
SPARK PLUG CONDITION
NORMAL OPERATING CONDITIONS
The few deposits present will be probably light tan
or slightly gray in color with most grades of commer-
cial gasoline (Fig. 23). There will not be evidence of
electrode burning. Gap growth will not average more
than approximately 0.025 mm (.001 in) per 1600 km
(1000 miles) of operation for non platinum spark
plugs. Non-platnium spark plugs that have normal
wear can usually be cleaned, have the electrodes filed
and regapped, and then reinstalled.
CAUTION: Never attempt to file the electrodes or
use a wire brush for cleaning platinum spark plugs.
This would damage the platinum pads which would
shorten spark plug life.
Some fuel refiners in several areas of the United
States have introduced a manganese additive (MMT)
for unleaded fuel. During combustion, fuel with MMT
may coat the entire tip of the spark plug with a rustcolored deposit. The rust color deposits can be misdi-
agnosed as being caused by coolant in the combustion
chamber. Spark plug performance is not affected by
MMT deposits.
COLD FOULING (CARBON FOULING)
Cold fouling is sometimes referred to as carbon
fouling because the deposits that cause cold fouling
are basically carbon (Fig. 23). A dry, black deposit on
one or two plugs in a set may be caused by sticking
valves or misfire conditions. Cold (carbon) fouling of
the entire set may be caused by a clogged air cleaner.
Cold fouling is normal after short operating peri-
ods. The spark plugs do not reach a high enough
operating temperature during short operating peri-
ods.Replace carbon fouled plugs with new
spark plugs.
FUEL FOULING
A spark plug that is coated with excessive wet fuel
is called fuel fouled. This condition is normally
observed during hard start periods.Clean fuel
fouled spark plugs with compressed air and
reinstall them in the engine.
OIL FOULING
A spark plug that is coated with excessive wet oil
is oil fouled. In older engines, wet fouling can be
caused by worn rings or excessive cylinder wear.
Break-in fouling of new engines may occur before
normal oil control is achieved.Replace oil fouled
spark plugs with new ones.
OIL OR ASH ENCRUSTED
If one or more plugs are oil or ash encrusted, eval-
uate the engine for the cause of oil entering the com-
bustion chambers (Fig. 24). Sometimes fuel additives
can cause ash encrustation on an entire set of spark
Fig. 23 Normal Operation and Cold (Carbon) Fouling
NSIGNITION SYSTEM 8D - 11
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 310 of 1938
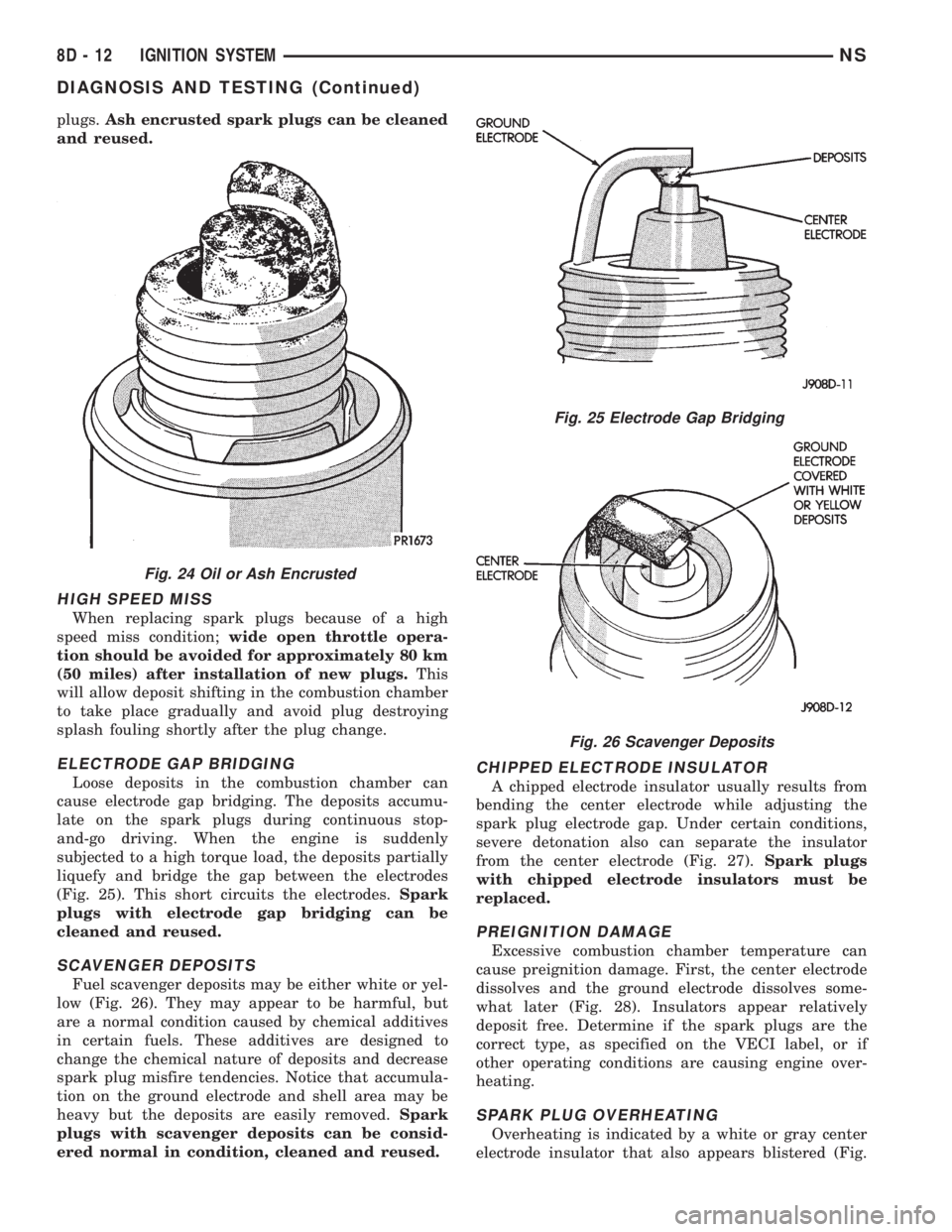
plugs.Ash encrusted spark plugs can be cleaned
and reused.
HIGH SPEED MISS
When replacing spark plugs because of a high
speed miss condition;wide open throttle opera-
tion should be avoided for approximately 80 km
(50 miles) after installation of new plugs.This
will allow deposit shifting in the combustion chamber
to take place gradually and avoid plug destroying
splash fouling shortly after the plug change.
ELECTRODE GAP BRIDGING
Loose deposits in the combustion chamber can
cause electrode gap bridging. The deposits accumu-
late on the spark plugs during continuous stop-
and-go driving. When the engine is suddenly
subjected to a high torque load, the deposits partially
liquefy and bridge the gap between the electrodes
(Fig. 25). This short circuits the electrodes.Spark
plugs with electrode gap bridging can be
cleaned and reused.
SCAVENGER DEPOSITS
Fuel scavenger deposits may be either white or yel-
low (Fig. 26). They may appear to be harmful, but
are a normal condition caused by chemical additives
in certain fuels. These additives are designed to
change the chemical nature of deposits and decrease
spark plug misfire tendencies. Notice that accumula-
tion on the ground electrode and shell area may be
heavy but the deposits are easily removed.Spark
plugs with scavenger deposits can be consid-
ered normal in condition, cleaned and reused.
CHIPPED ELECTRODE INSULATOR
A chipped electrode insulator usually results from
bending the center electrode while adjusting the
spark plug electrode gap. Under certain conditions,
severe detonation also can separate the insulator
from the center electrode (Fig. 27).Spark plugs
with chipped electrode insulators must be
replaced.
PREIGNITION DAMAGE
Excessive combustion chamber temperature can
cause preignition damage. First, the center electrode
dissolves and the ground electrode dissolves some-
what later (Fig. 28). Insulators appear relatively
deposit free. Determine if the spark plugs are the
correct type, as specified on the VECI label, or if
other operating conditions are causing engine over-
heating.
SPARK PLUG OVERHEATING
Overheating is indicated by a white or gray center
electrode insulator that also appears blistered (Fig.
Fig. 24 Oil or Ash Encrusted
Fig. 25 Electrode Gap Bridging
Fig. 26 Scavenger Deposits
8D - 12 IGNITION SYSTEMNS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 316 of 1938

REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
SPARK PLUG CABLE SERVICEÐ2.4L
The cables insulate the spark plugs and covers the
top of the spark plug tube (Fig. 6). To remove the
cables, lightly grasp the top of the cable. Rotate the
insulator 90É and pull straight up. To replace the
cables, disconnect the cable from the ignition coil.
Ensure the #1 and #4 cables run under the #2
and #3 ignition coil towers. Keep #4 cable away
from the oil fill cap.
SPARK PLUG SERVICE
When replacing the spark plugs and spark plug
cables, route the cables correctly and secure them inthe appropriate retainers. Failure to route the cables
properly can cause the radio to reproduce ignition
noise, cross ignition of the spark plugs orshort cir-
cuit the cables to ground.
Never Wire Brush Spark Plugs.The spark plug
insulator tip is harder than the bristles of wire
brushes. Bristles of wire brushes can leave a conduc-
tive, metallic film on the insulator which could lead
to conductive deposits. Conductive deposits can cause
spark plug failure and engine misfire. Use a jewelers
file to remove deposits from the electrode gap or use
a spark plug cleaning machine to clean spark plugs.
REMOVAL
Always remove cables by grasping at the boot,
rotating the boot 1/2 turn, and pulling straight back
in a steady motion.
(1) Prior to removing the spark plug, spray com-
pressed air around the spark plug hole and the area
around the spark plug.
(2) Remove the spark plug using a quality socket
with a foam insert.
(3) Inspect the spark plug condition. Refer to
Spark Plug Condition in this section.
INSTALLATION
(1) To avoid cross threading, start the spark plug
into the cylinder head by hand.
(2) Tighten spark plugs to 28 N´m (20 ft. lbs.)
torque.
(3) Install spark plug cables over spark plugs. A
click will be heard and felt when the cable properly
attaches to the spark plug.
IGNITION COILÐ2.4L
REMOVAL
REMOVAL
(1) Remove spark plug cables from coil (Fig. 7).
Always twist the coil boots to break the seal with the
coil and pull straight back on the boot.
(2) Remove ignition coil electrical connector.
(3) Remove ignition coil mounting bolts, throttle
cable bracket or clip.
(4) Remove ignition coil.
INSTALLATION
(1) Reverse the above procedure for installation.
Tighten mounting screws to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs.)
torque.
(2) Transfer ignition cables to new coil pack. The
coil pack towers and cables are numbered with cylin-
der identification.
Fig. 5 Intake Air Temperature Sensor
Fig. 6 Spark Plug Cables
8D - 18 IGNITION SYSTEMNS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 325 of 1938
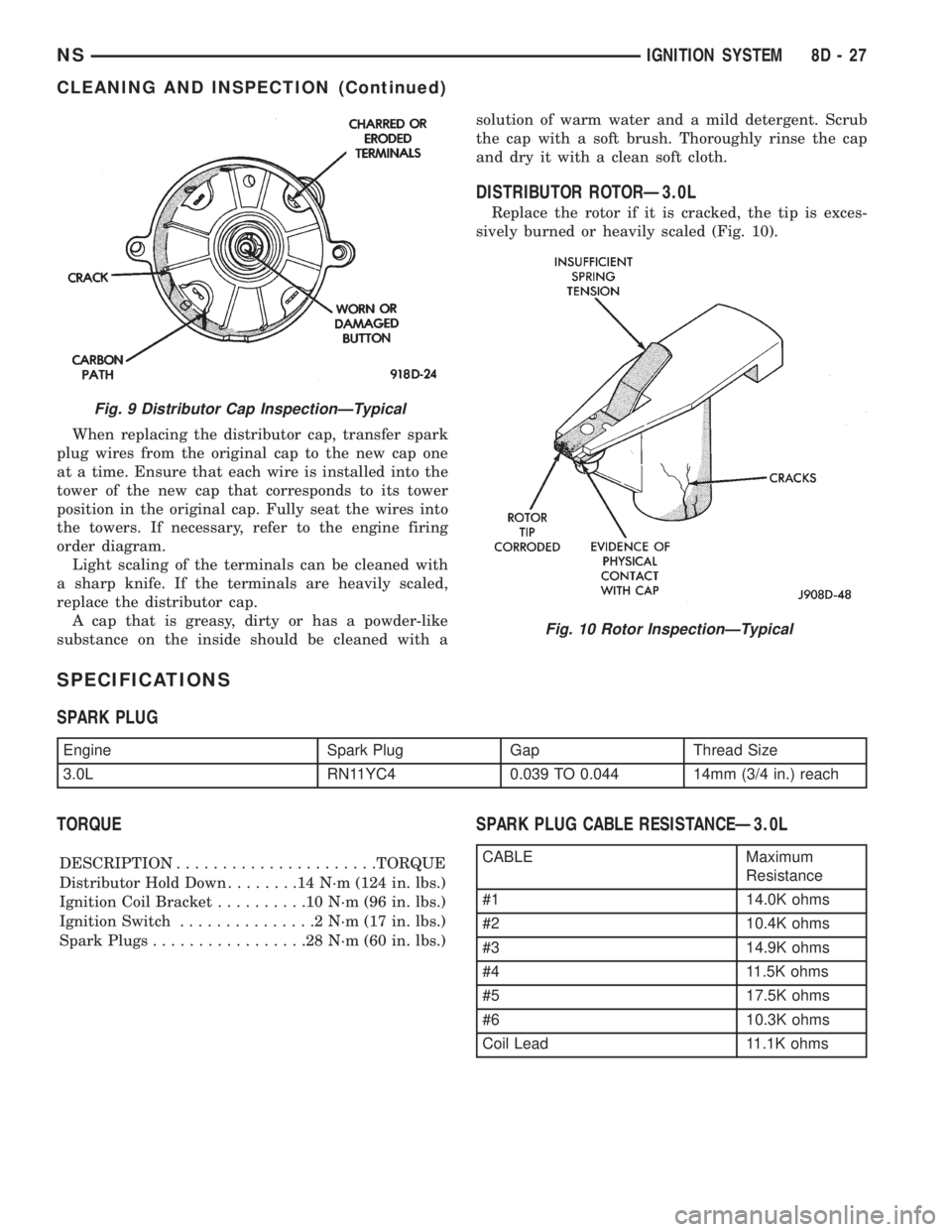
When replacing the distributor cap, transfer spark
plug wires from the original cap to the new cap one
at a time. Ensure that each wire is installed into the
tower of the new cap that corresponds to its tower
position in the original cap. Fully seat the wires into
the towers. If necessary, refer to the engine firing
order diagram.
Light scaling of the terminals can be cleaned with
a sharp knife. If the terminals are heavily scaled,
replace the distributor cap.
A cap that is greasy, dirty or has a powder-like
substance on the inside should be cleaned with asolution of warm water and a mild detergent. Scrub
the cap with a soft brush. Thoroughly rinse the cap
and dry it with a clean soft cloth.
DISTRIBUTOR ROTORÐ3.0L
Replace the rotor if it is cracked, the tip is exces-
sively burned or heavily scaled (Fig. 10).
SPECIFICATIONS
SPARK PLUG
TORQUE
DESCRIPTION......................TORQUE
Distributor Hold Down........14N´m(124 in. lbs.)
Ignition Coil Bracket..........10N´m(96in.lbs.)
Ignition Switch...............2N´m(17in.lbs.)
Spark Plugs.................28N´m(60in.lbs.)
SPARK PLUG CABLE RESISTANCEÐ3.0L
Fig. 9 Distributor Cap InspectionÐTypical
Fig. 10 Rotor InspectionÐTypical
Engine Spark Plug Gap Thread Size
3.0L RN11YC4 0.039 TO 0.044 14mm (3/4 in.) reach
CABLE Maximum
Resistance
#1 14.0K ohms
#2 10.4K ohms
#3 14.9K ohms
#4 11.5K ohms
#5 17.5K ohms
#6 10.3K ohms
Coil Lead 11.1K ohms
NSIGNITION SYSTEM 8D - 27
CLEANING AND INSPECTION (Continued)