change time CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2001 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2001, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2001Pages: 4284, PDF Size: 83.53 MB
Page 1810 of 4284

CD CHANGER
DESCRIPTION
The 4 Disc In-Dash CD Changer (if equipped) is
located in the instrument panel below the radio. The
remote changer does not use a cartridge or magazine
for the CD's. Up to 4 CD's can be directly loaded into
this unit.
OPERATION
Due to its compact design, the CD changer can
carry out only one operation at a time. For example,
you can not load a new disc while playing another at
the same time. Each operation happens sequentially.
The radio unit provides control over all features of
the CD changer with the exception of the CD load
and eject functions, which are controlled by buttons
located on the front of the CD changer. All features
you would expect, such as Disc Up/Down, Track
Up/Down, Random and Scan are controlled by the
radio, which also displays all relevant CD changer
information on the radio display.
The CD changer contains a Load/Eject button and
an indicator LED for each of the four disc positions
as well as an illuminated disc opening. The individ-
ual LED indicates whether a CD is currently loaded
in that particular chamber of the CD changer. Press-
ing the individual Load/Eject button for a particular
chamber will eject a disc currently present in that
chamber. If the chamber is currently empty, actuat-
ing the Load/Eject button will position that chamber
to receive and load a new disc in that chamber.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove screws holding CD changer.
(3) Disconnect the wire connector from the back of
the CD changer.
(4) Remove the CD changer from the vehicle (Fig.
5).
INSTALLATION
(1) Reconnect the wire connector to the CD
changer.
(2) Insert the CD changer into the instrument
panel.
NOTE: Use care when inserting CD changer so that
cable is not pinched or trapped against instrument
panel.
(3) Install screws holding CD changer.
(4) Reconnect the battery negative cable.
CHOKE
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
If the audio system is cutting in and out at higher
volumes, check for continuity across the choke con-
nector. If no continuity, replace the choke assembly.
The choke is located on the junction block/body con-
trol module.
D-PILLAR SPEAKER
REMOVAL
PASSENGER SIDE
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable.
(2) Remove rear header trim.
(3) Remove liftgate scuff plate.
(4) Remove upper seat belt bolt. (Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/RESTRAINTS/SEAT BELT OUT-
BOARD FRONT - REMOVAL).
(5) Partially remove quarter trim panel to access
the D-pillar speaker.
(6) Slide the speaker from the retainer (Fig. 6).
(7) Disconnect the wire harness connector from the
speaker.
DRIVER SIDE
(1) Disconnect and isolate the negative battery
cable.
(2) Remove jack cover.
(3) Remove liftgate scuff plate.
(4) Partially remove quarter trim panel to access
the D-pillar speaker.
Fig. 5 CD - PLAYER
1 - CD-PLAYER
2 - POWER OUTLET
8A - 6 AUDIORS
Page 1821 of 4284

²Engine running at 420 to 480 rpm for 10 sec-
onds
²Oil pressure switch closed to ground for (1 sec-
ond minimum, 2 seconds maximum)
Chime rate: 168 to 192 chimes per minute.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SEAT BELT CHIME
The seat belt chime will sound for 4 to 8 seconds,
when the ignition is turned on and the driver's seat
belt is not buckled (seat belt switch is closed to
ground). This is a reminder to the driver to buckle
the seat belt. The seat belt lamp is controlled by the
ORC. The cluster will also bulb check the seat belt
warning lamp for 6 seconds. Buckling the driver's
seat belt before the time out has expired will cause
the chime to stop immediately. Chime rate: 38 to 62
chimes per minute but the lamp will remain on until
6 seconds have expired.
To test the seat belt warning system, the ignition
switch must be in the OFF position for 1 minute
before starting the test. Turn the ignition switch to
the on position with the driver's seat belt not buck-
led. The seat belt warning lamp should light and the
chime should sound 4 to 8 seconds.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SEAT BELT LAMP
The seat belt lamp in the instrument cluster sig-
nals the vehicle passengers to fasten their seat belts.
The seat belt lamp is illuminated directly by the
instrument cluster for 6 seconds after the instrument
cluster receives the message from the ORC. The seat
belt lamp is therefore illuminated for 6 seconds
whenever the ignition switch is moved to run/start
position.
(1) While ignition is off, the seat belt lamp will not
be illuminated.
(2) The ignition power feed status will be updated
every 250 milliseconds or on change.
(3) This lamp will be checked by the instrument
cluster for 6 seconds with every run/start cycle of the
ignition switch.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TURN SIGNAL ON
CHIME
The turn signal on chime will warn the driver that
the turn signals have been left on. When the body
control module receives a turn signal input for 1/4.0
mile, vehicle speed is greater than 24 km/h (15 mph),
the chime will sound continuously until the turn sig-nal is turned OFF. If vehicle speed drops below 24
km/h (15 mph) prior to the warning being activated,
the accumulated distance traveled will be reset. The
turn signal chime is not activated when the emer-
gency flashers are turned on. Chime rate: 50612
chimes per minute.
For the turn signal warning system to operate:
²Must have input from either the right or left
turn signal lamps. Creates a voltage change between
0 and battery voltage.
²The vehicle speed sensor sends a message to the
Powertrain Control Module that vehicle has exceeded
24 km/h (15 mph) for 1/4.0 mile).
²When the above two conditions are met, the
chime will sound. The chime will stop when no fur-
ther voltage change is detected.
²If hazard warning signals are pulsing, no chime
will sound.
²If speed drops below 24 km/h (15 mph) before
the warning is issued, the warning will not be issued
and the distance counter will be reset.
²If turn signal lamps are not working properly,
the chime will not sound.
²When using the scan tool, refer to the proper
Body Diagnostic Manual for the procedure.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - WARNING LAMP
ANNOUNCEMENT CHIME
The warning lamp announcement chime will warn
the driver to scan the instrument cluster to observe
which warning lamp is illuminated. Whenever the
volts, low fuel, airbag, door ajar or gate ajar lamps
are first illuminated, the chime will sound one tone.
The door/liftgate ajar warning lamp announcement
chime sounds only if the vehicle speed is above 4
m.p.h.
Two seconds after ignition switch is turned ON or
until the seat belt warning chime ends, all warning
announcement chimes will be consolidated into one
warning announcement. This will occur 2 seconds
after the seat belt warning chime ends. If a warning
announcement should occur while another warning
chime in progress (turn signal, low oil pressure or
high speed warnings), no additional chimes will
sound after the chime in progress ends. All associ-
ated lamps will be illuminated, and the active chime
will be the warning announcement.
RSCHIME/BUZZER8B-3
CHIME/BUZZER (Continued)
Page 1834 of 4284

(M) Check Engine Lamp (MIL) will illuminate during engine operation if this Diagnostic Trouble Code was recorded.
(G) Generator Lamp Illuminated
GENERIC SCAN
TOOL CODEDRB SCAN TOOL DISPLAY DESCRIPTION OF DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE
P0071 Ambient Temp Sensor Preformance Ambient change less than 3É C in 200 Miles
P0106 (M) Barometric Pressure Out of Range MAP sensor input voltage out of an acceptable range
detected during reading of barometric pressure at key-on.
P0107 (M) Map Sensor Voltage Too Low MAP sensor input below minimum acceptable voltage.
P0108 (M) Map Sensor Voltage Too High MAP sensor input above maximum acceptable voltage.
P0111 (M) Intake Air Temp Sensor Preformance Intake Air change less than 3É C in 200 Miles
P0112 (M) Intake Air Temp Sensor Voltage Low Intake air (charge) temperature sensor input below the
minimum acceptable voltage.
P0113 (M) Intake Air Temp Sensor Voltage High Intake air (charge) temperature sensor input above the
maximum acceptable voltage.
P0116 Engine Coolant Temp Performance A rationatilty error has been detected in the coolant temp
sensor.
P0117 (M) ECT Sensor Voltage Too Low Engine coolant temperature sensor input below the minimum
acceptable voltage.
P0118 (M) ECT Sensor Voltage Too High Engine coolant temperature sensor input above the
maximum acceptable voltage.
P0121 (M) TPS Voltage Does Not Agree With
MAPTPS signal does not correlate to MAP sensor signal.
P0122 (M) Throttle Position Sensor Voltage
LowThrottle position sensor input below the acceptable voltage
range.
P0123 (M) Throttle Position Sensor Voltage
HighThrottle position sensor input above the maximum
acceptable voltage.
P0125 (M) Engine Coolant Temp Not Reached Time to enter Closed Loop Operation (Fuel Control) is
excessive.
P0130 1/1 O2 Sensor Heater Relay Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the ASD or CNG
shutoff relay control ckt.
P0131 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Shorted To Ground Oxygen sensor input voltage maintained below normal
operating range.
P0132 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Shorted To Voltage Oxygen sensor input voltage maintained above normal
operating range.
P0133 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Slow Response Oxygen sensor response slower than minimum required
switching frequency.
P0134 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Stays at Center Neither rich or lean condition is detected from the oxygen
sensor input.
P0135 (M) 1/1 O2 Sensor Heater Failure Oxygen sensor heater element malfunction.
P0136 1/2 O2 Sensor Heater Relay Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the ASD or CNG
shutoff relay control ckt.
P0137 (M) 1/2 O2 Sensor Shorted To Ground Oxygen sensor input voltage maintained below normal
operating range.
P0138 (M) 1/2 O2 Sensor Shorted To Voltage Oxygen sensor input voltage maintained above normal
operating range.
P0139 (M) 1/2 O2 Sensor Slow Response Oxygen sensor response not as expected.
8E - 10 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULESRS
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 1837 of 4284

(M) Check Engine Lamp (MIL) will illuminate during engine operation if this Diagnostic Trouble Code was recorded.
(G) Generator Lamp Illuminated
GENERIC SCAN
TOOL CODEDRB SCAN TOOL DISPLAY DESCRIPTION OF DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE
P0350 Ignition Coil Draws Too Much
CurrentA coil (1-5) is drawing too much current.
P0351 (M) Ignition Coil # 1 Primary Circuit Peak primary circuit current not achieved with maximum
dwell time.
P0352 (M) Ignition Coil # 2 Primary Circuit Peak primary circuit current not achieved with maximum
dwell time.
P0353 (M) Ignition Coil # 3 Primary Circuit Peak primary circuit current not achieved with maximum
dwell time.
P0354 (M) Ignition Coil # 4 Primary Circuit Peak primary circuit current not achieved with maximum
dwell time (High Impedance).
P0355 (M) Ignition Coil # 5 Primary Circuit Peak primary circuit current not achieved with maximum
dwell time (High Impedance).
P0356 (M) Ignition Coil # 6 Primary Circuit Peak primary circuit current not achieved with maximum
dwell time (high impedance).
P0357 Ignition Coil # 7 Primary Circuit Peak primary circuit current not achieved with maximum
dwell time (high impedance).
P0358 Ignition Coil # 8 Primary Circuit Peak primary circuit current not achieved with maximum
dwell time (high impedance).
P0401 (M) EGR System Failure Required change in air/fuel ration not detected during
diagnostic test.
P0403 (M) EGR Solenoid Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the EGR solenoid
control circuit.
P0404 (M) EGR Position Sensor Rationality EGR position sensor signal does not correlate to EGR duty
cycle.
P0405 (M) EGR Position Sensor Volts Too Low EGR position sensor input below the acceptable voltage
range.
P0406 (M) EGR Position Sensor Volts Too High EGR position sensor input above the acceptable voltage
range.
P0412 Secondary Air Solenoid Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the secondary air
(air switching/aspirator) solenoid control circuit.
P0420 (M) 1/1 Catalytic Converter Efficiency Catalyst 1/1 efficiency below required level.
P0432 (M) 1/2 Catalytic Converter Efficiency Catalyst 2/1 efficiency below required level.
P0441 (M) Evap Purge Flow Monitor Insufficient or excessive vapor flow detected during
evaporative emission system operation.
P0442 (M) Evap Leak Monitor 0.040 Leak
DetectedA 0.040 leak has been detected in the evaporative system.
P0443 (M) Evap Purge Solenoid Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the EVAP purge
solenoid control circuit.
P0455 (M) Evap Leak Monitor Large Leak
DetectedA large leak has been detected in the evaporative system.
P0456 Evap Leak Monitor 0.020 Leak
DetectedA 0.020 leak has been detected in the evaporative system.
P0460 Fuel Level Unit No Change Over
MilesNo movement of fuel level sender detected.
RSELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES8E-13
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 1838 of 4284
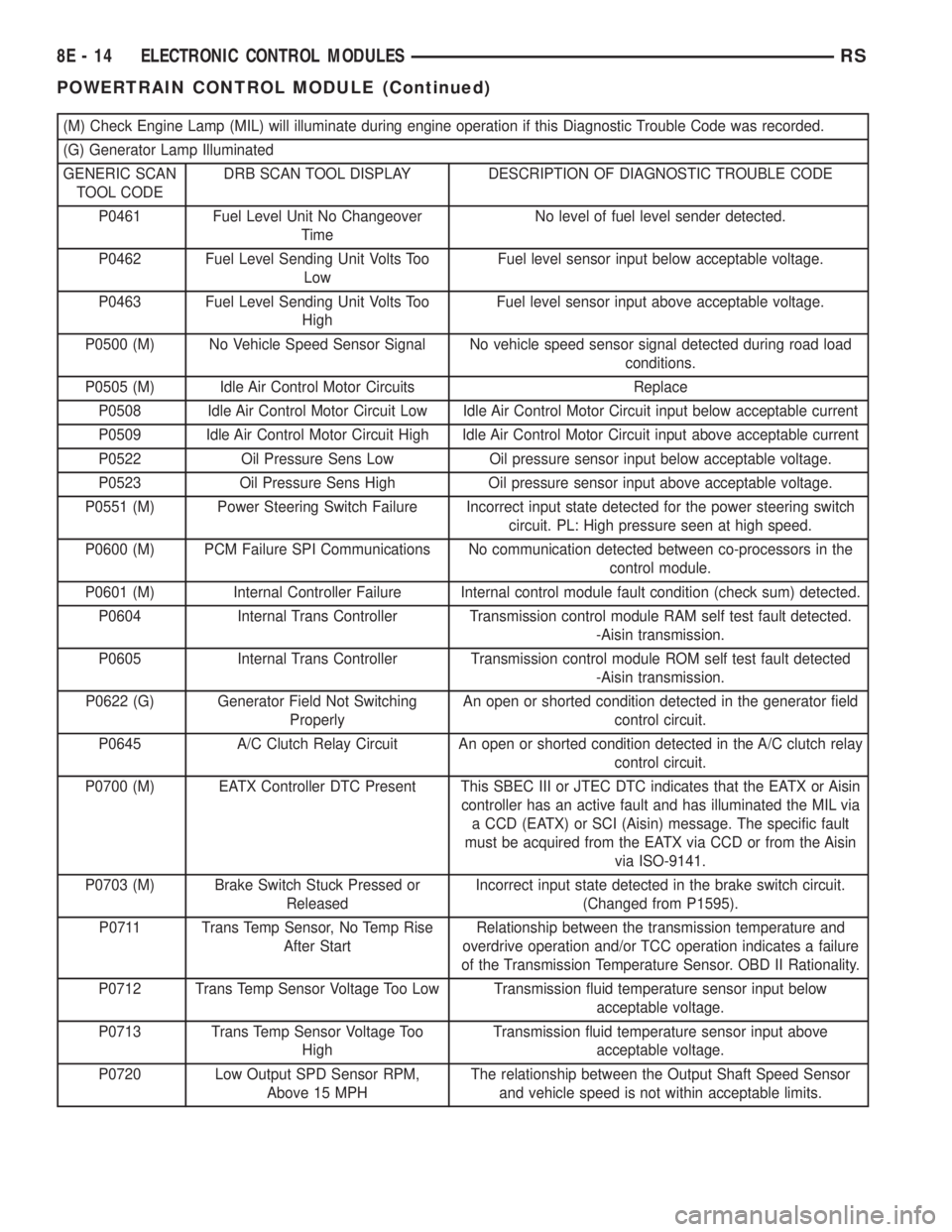
(M) Check Engine Lamp (MIL) will illuminate during engine operation if this Diagnostic Trouble Code was recorded.
(G) Generator Lamp Illuminated
GENERIC SCAN
TOOL CODEDRB SCAN TOOL DISPLAY DESCRIPTION OF DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE
P0461 Fuel Level Unit No Changeover
TimeNo level of fuel level sender detected.
P0462 Fuel Level Sending Unit Volts Too
LowFuel level sensor input below acceptable voltage.
P0463 Fuel Level Sending Unit Volts Too
HighFuel level sensor input above acceptable voltage.
P0500 (M) No Vehicle Speed Sensor Signal No vehicle speed sensor signal detected during road load
conditions.
P0505 (M) Idle Air Control Motor Circuits Replace
P0508 Idle Air Control Motor Circuit Low Idle Air Control Motor Circuit input below acceptable current
P0509 Idle Air Control Motor Circuit High Idle Air Control Motor Circuit input above acceptable current
P0522 Oil Pressure Sens Low Oil pressure sensor input below acceptable voltage.
P0523 Oil Pressure Sens High Oil pressure sensor input above acceptable voltage.
P0551 (M) Power Steering Switch Failure Incorrect input state detected for the power steering switch
circuit. PL: High pressure seen at high speed.
P0600 (M) PCM Failure SPI Communications No communication detected between co-processors in the
control module.
P0601 (M) Internal Controller Failure Internal control module fault condition (check sum) detected.
P0604 Internal Trans Controller Transmission control module RAM self test fault detected.
-Aisin transmission.
P0605 Internal Trans Controller Transmission control module ROM self test fault detected
-Aisin transmission.
P0622 (G) Generator Field Not Switching
ProperlyAn open or shorted condition detected in the generator field
control circuit.
P0645 A/C Clutch Relay Circuit An open or shorted condition detected in the A/C clutch relay
control circuit.
P0700 (M) EATX Controller DTC Present This SBEC III or JTEC DTC indicates that the EATX or Aisin
controller has an active fault and has illuminated the MIL via
a CCD (EATX) or SCI (Aisin) message. The specific fault
must be acquired from the EATX via CCD or from the Aisin
via ISO-9141.
P0703 (M) Brake Switch Stuck Pressed or
ReleasedIncorrect input state detected in the brake switch circuit.
(Changed from P1595).
P0711 Trans Temp Sensor, No Temp Rise
After StartRelationship between the transmission temperature and
overdrive operation and/or TCC operation indicates a failure
of the Transmission Temperature Sensor. OBD II Rationality.
P0712 Trans Temp Sensor Voltage Too Low Transmission fluid temperature sensor input below
acceptable voltage.
P0713 Trans Temp Sensor Voltage Too
HighTransmission fluid temperature sensor input above
acceptable voltage.
P0720 Low Output SPD Sensor RPM,
Above 15 MPHThe relationship between the Output Shaft Speed Sensor
and vehicle speed is not within acceptable limits.
8E - 14 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULESRS
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 1843 of 4284

OPERATION - SENSOR RETURN - PCM INPUT
The sensor return circuit provides a low electrical
noise ground reference for all of the systems sensors.
The sensor return circuit connects to internal ground
circuits within the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM).
OPERATION - SCI RECEIVE - PCM INPUT
SCI Receive is the serial data communication
receive circuit for the DRB scan tool. The Powertrain
Control Module (PCM) receives data from the DRB
through the SCI Receive circuit.
OPERATION - IGNITION SENSE - PCM INPUT
The ignition sense input informs the Powertrain
Control Module (PCM) that the ignition switch is in
the crank or run position.
OPERATION - PCM GROUND
Ground is provided through multiple pins of the
PCM connector. Depending on the vehicle there may
be as many as three different ground pins. There are
power grounds and sensor grounds.
The power grounds are used to control the ground
side of any relay, solenoid, ignition coil or injector.
The signal ground is used for any input that uses
sensor return for ground, and the ground side of any
internal processing component.
The SBEC III case is shielded to prevent RFI and
EMI. The PCM case is grounded and must be firmly
attached to a good, clean body ground.
Internally all grounds are connected together, how-
ever there is noise suppression on the sensor ground.
For EMI and RFI protection the case is also
grounded separately from the ground pins.
OPERATION - 8-VOLT SUPPLY - PCM OUTPUT
The PCM supplies 8 volts to the crankshaft posi-
tion sensor, camshaft position sensor.
OPERATION - 5 VOLT SUPPLY - PCM OUTPUT
The PCM supplies 5 volts to the following sensors:
²A/C pressure transducer
²Engine coolant temperature sensor
²Manifold absolute pressure sensor
²Throttle position sensor
²Linear EGR solenoid
OPERATION - MODES OF OPERATION
As input signals to the PCM change, the PCM
adjusts its response to output devices. For example,
the PCM must calculate a different injector pulse
width and ignition timing for idle than it does for
Wide Open Throttle (WOT). There are several differ-
ent modes of operation that determine how the PCM
responds to the various input signals.There are two different areas of operation, OPEN
LOOP and CLOSED LOOP.
During OPEN LOOP modes the PCM receives
input signals and responds according to preset PCM
programming. Inputs from the upstream and down-
stream heated oxygen sensors are not monitored dur-
ing OPEN LOOP modes, except for heated oxygen
sensor diagnostics (they are checked for shorted con-
ditions at all times).
During CLOSED LOOP modes the PCM monitors
the inputs from the upstream and downstream
heated oxygen sensors. The upstream heated oxygen
sensor input tells the PCM if the calculated injector
pulse width resulted in the ideal air-fuel ratio of 14.7
to one. By monitoring the exhaust oxygen content
through the upstream heated oxygen sensor, the
PCM can fine tune injector pulse width. Fine tuning
injector pulse width allows the PCM to achieve opti-
mum fuel economy combined with low emissions.
For the PCM to enter CLOSED LOOP operation,
the following must occur:
(1) Engine coolant temperature must be over 35ÉF.
²If the coolant is over 35É the PCM will wait 44
seconds.
²If the coolant is over 50ÉF the PCM will wait 38
seconds.
²If the coolant is over 167ÉF the PCM will wait
11 seconds.
(2) For other temperatures the PCM will interpo-
late the correct waiting time.
(3) O2 sensor must read either greater than 0.745
volts or less than 0.1 volt.
(4) The multi-port fuel injection systems has the
following modes of operation:
²Ignition switch ON (Zero RPM)
²Engine start-up
²Engine warm-up
²Cruise
²Idle
²Acceleration
²Deceleration
²Wide Open Throttle
²Ignition switch OFF
(5) The engine start-up (crank), engine warm-up,
deceleration with fuel shutoff and wide open throttle
modes are OPEN LOOP modes. Under most operat-
ing conditions, the acceleration, deceleration (with
A/C on), idle and cruise modes,with the engine at
operating temperatureare CLOSED LOOP modes.IGNITION SWITCH ON (ZERO RPM) MODE
When the ignition switch activates the fuel injec-
tion system, the following actions occur:
²The PCM monitors the engine coolant tempera-
ture sensor and throttle position sensor input. The
RSELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES8E-19
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 1845 of 4284

²Fuel system monitor
²EGR monitor
²Purge system monitor
²All inputs monitored for proper voltage range.
²All monitored components (refer to the Emission
section for On-Board Diagnostics).
The PCM compares the upstream and downstream
heated oxygen sensor inputs to measure catalytic
convertor efficiency. If the catalyst efficiency drops
below the minimum acceptable percentage, the PCM
stores a diagnostic trouble code in memory.
During certain idle conditions, the PCM may enter
a variable idle speed strategy. During variable idle
speed strategy the PCM adjusts engine speed based
on the following inputs.
²A/C sense
²Battery voltage
²Battery temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²Engine run time
²Inlet/Intake air temperature
²Vehicle mileage
ACCELERATION MODE
This is a CLOSED LOOP mode. The PCM recog-
nizes an abrupt increase in Throttle Position sensor
output voltage or MAP sensor output voltage as a
demand for increased engine output and vehicle
acceleration. The PCM increases injector pulse width
in response to increased fuel demand.
DECELERATION MODE
This is a CLOSED LOOP mode. During decelera-
tion the following inputs are received by the PCM:
²A/C sense
²Battery voltage
²Inlet/Intake air temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²Crankshaft position (engine speed)
²Exhaust gas oxygen content (upstream heated
oxygen sensor)
²Knock sensor
²Manifold absolute pressure
²Throttle position
²IAC motor control changes in response to MAP
sensor feedback
The PCM may receive a closed throttle input from
the Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) when it senses an
abrupt decrease in manifold pressure. This indicates
a hard deceleration. In response, the PCM may
momentarily turn off the injectors. This helps
improve fuel economy, emissions and engine braking.
WIDE-OPEN-THROTTLE MODE
This is an OPEN LOOP mode. During wide-open-
throttle operation, the following inputs are used by
the PCM:
²Inlet/Intake air temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²Engine speed
²Knock sensor
²Manifold absolute pressure
²Throttle position
When the PCM senses a wide-open-throttle condi-
tion through the Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) it de-
energizes the A/C compressor clutch relay. This
disables the air conditioning system.
The PCM does not monitor the heated oxygen sen-
sor inputs during wide-open-throttle operation except
for downstream heated oxygen sensor and both
shorted diagnostics. The PCM adjusts injector pulse
width to supply a predetermined amount of addi-
tional fuel.
IGNITION SWITCH OFF MODE
When the operator turns the ignition switch to the
OFF position, the following occurs:
²All outputs are turned off, unless 02 Heater
Monitor test is being run. Refer to the Emission sec-
tion for On-Board Diagnostics.
²No inputs are monitored except for the heated
oxygen sensors. The PCM monitors the heating ele-
ments in the oxygen sensors and then shuts down.
STANDARD PROCEDURES - OBTAINING
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
BULB CHECK
Each time the ignition key is turned to the ON
position, the malfunction indicator (check engine)
lamp on the instrument panel should illuminate for
approximately 2 seconds then go out. This is done for
a bulb check. When the key is in the power on, but
engine off position, the MIL will remain illuminated
for regulatory purposes.
OBTAINING DTC'S USING DRB SCAN TOOL
(1) Connect the DRB scan tool to the data link
(diagnostic) connector. This connector is located in
the passenger compartment; at the lower edge of
instrument panel; near the steering column.
(2) Turn the ignition switch on and access the
ªRead Faultº screen.
(3) Record all the DTC's and ªfreeze frameº infor-
mation shown on the DRB scan tool.
RSELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES8E-21
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 1850 of 4284

2:1. In direct drive (3rd gear), the gear ratio changes
to 1:1. The gear ratio changes as clutches are applied
and released. By monitoring the length of time it
takes for the gear ratio to change following a shift
request, the TCM can determine the volume of fluid
used to apply or release a friction element.
The volume of transmission fluid needed to apply
the friction elements are continuously updated for
adaptive controls. As friction material wears, the vol-
ume of fluid need to apply the element increases.Certain mechanical problems within the clutch
assemblies (broken return springs, out of position
snap rings, excessive clutch pack clearance, improper
assembly, etc.) can cause inadequate or out-of-range
clutch volumes. Also, defective Input/Output Speed
Sensors and wiring can cause these conditions. The
following chart identifies the appropriate clutch vol-
umes and when they are monitored/updated:
CLUTCH VOLUMES
ClutchWhen Updated
Proper Clutch
Volume
Shift Sequence Oil Temperature Throttle Angle
L/R2-1 or 3-1 coast
downshift>70É <5É 35to83
2/4 1-2 shift
> 110É5 - 54É20 to 77
OD 2-3 shift 48 to 150
UD 4-3 or 4-2 shift > 5É 24 to 70
SHIFT SCHEDULES
As mentioned earlier, the TCM has programming
that allows it to select a variety of shift schedules.
Shift schedule selection is dependent on the follow-
ing:
²Shift lever position
²Throttle position²Engine load
²Fluid temperature
²Software level
As driving conditions change, the TCM appropri-
ately adjusts the shift schedule. Refer to the follow-
ing chart to determine the appropriate operation
expected, depending on driving conditions.
Schedule Condition Expected Operation
Extreme ColdOil temperature at start-up below
-16É FPark, Reverse, Neutral and 2nd
gear only (prevents shifting which
may fail a clutch with frequent
shifts)
ColdOil temperature at start-up above
-12É F and below 36É F± Delayed 2-3 upshift
(approximately 22-31 mph)
± Delayed 3-4 upshift (45-53 mph)
± Early 4-3 costdown shift
(approximately 30 mph)
± Early 3-2 coastdown shift
(approximately 17 mph)
± High speed 4-2, 3-2, 2-1 kickdown
shifts are prevented
± No EMCC
WarmOil temperature at start-up above
36É F and below 80 degree F± Normal operation (upshift,
kickdowns, and coastdowns)
± No EMCC
8E - 26 ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULESRS
TRANSMISSION CONTROL MODULE (Continued)
Page 1862 of 4284

battery discharges, a gradual chemical change takes
place within each cell. The sulfuric acid in the elec-
trolyte combines with the plate materials, causing
both plates to slowly change to lead sulfate. At the
same time, oxygen from the positive plate material
combines with hydrogen from the sulfuric acid, caus-
ing the electrolyte to become mainly water. The
chemical changes within the battery are caused by
the movement of excess or free electrons between the
positive and negative plate groups. This movement of
electrons produces a flow of electrical current
through the load device attached to the battery ter-
minals.
As the plate materials become more similar chem-
ically, and the electrolyte becomes less acid, the volt-
age potential of each cell is reduced. However, by
charging the battery with a voltage higher than that
of the battery itself, the battery discharging process
is reversed. Charging the battery gradually changes
the sulfated lead plates back into sponge lead and
lead dioxide, and the water back into sulfuric acid.
This action restores the difference in the electron
charges deposited on the plates, and the voltage
potential of the battery cells. For a battery to remain
useful, it must be able to produce high-amperage cur-
rent over an extended period. A battery must also be
able to accept a charge, so that its voltage potential
may be restored.
The battery is vented to release excess hydrogen
gas that is created when the battery is being charged
or discharged. However, even with these vents,
hydrogen gas can collect in or around the battery. If
hydrogen gas is exposed to flame or sparks, it may
ignite. If the electrolyte level is low, the battery may
arc internally and explode. If the battery is equipped
with removable cell caps, add distilled water when-
ever the electrolyte level is below the top of the
plates. If the battery cell caps cannot be removed, the
battery must be replaced if the electrolyte level
becomes low.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BATTERY
The battery must be completely charged and the
top, posts and terminal clamps should be properly
cleaned and inspected before diagnostic procedures
are performed. Refer to Battery System Cleaning for
the proper cleaning procedures, and Battery System
Inspection for the proper battery inspection proce-
dures. Refer to Standard Procedures for the proper
battery charging procedures.
WARNING: IF THE BATTERY SHOWS SIGNS OF
FREEZING, LEAKING OR LOOSE POSTS, DO NOT
TEST, ASSIST-BOOST, OR CHARGE. THE BATTERY
MAY ARC INTERNALLY AND EXPLODE. PERSONAL
INJURY AND/OR VEHICLE DAMAGE MAY RESULT.WARNING: EXPLOSIVE HYDROGEN GAS FORMS IN
AND AROUND THE BATTERY. DO NOT SMOKE,
USE FLAME, OR CREATE SPARKS NEAR THE BAT-
TERY. PERSONAL INJURY AND/OR VEHICLE DAM-
AGE MAY RESULT.
WARNING: THE BATTERY CONTAINS SULFURIC
ACID, WHICH IS POISONOUS AND CAUSTIC. AVOID
CONTACT WITH THE SKIN, EYES, OR CLOTHING.
IN THE EVENT OF CONTACT, FLUSH WITH WATER
AND CALL A PHYSICIAN IMMEDIATELY. KEEP OUT
OF THE REACH OF CHILDREN.
WARNING: IF THE BATTERY IS EQUIPPED WITH
REMOVABLE CELL CAPS, BE CERTAIN THAT EACH
OF THE CELL CAPS ARE IN PLACE AND TIGHT
BEFORE THE BATTERY IS RETURNED TO SER-
VICE. PERSONAL INJURY AND/OR VEHICLE DAM-
AGE MAY RESULT FROM LOOSE OR MISSING
CELL CAPS.
The condition of a battery is determined by two cri-
teria:
²State-Of-Charge- This can be determined by
checking the specific gravity of the battery electrolyte
(built-in indicator test or hydrometer test), or by
checking the battery voltage (open-circuit voltage
test).
²Cranking Capacity- This can be determined
by performing a battery load test, which measures
the ability of the battery to supply high-amperage
current.
First, determine the battery state-of-charge. This
can be done in one of three ways. If the battery has a
built-in test indicator, perform the built-in indicator
test to determine the state-of-charge. If the battery
has no built-in test indicator but does have remov-
able cell caps, perform the hydrometer test to deter-
mine the state-of-charge. If the battery cell caps are
not removable, or a hydrometer is not available, per-
form the open-circuit voltage test to determine the
state-of-charge. Refer to open-circuit voltage test in
the Standard Procedures section of this group.
Second, determine the battery cranking capacity by
performing a load test. The battery must be charged
before proceeding with a load test if:
²The battery built-in test indicator has a black or
dark color visible.
²The temperature corrected specific gravity of the
battery electrolyte is less than 1.235.
²The battery open-circuit voltage is less than 12.4
volts.
A battery that will not accept a charge is faulty,
and must be replaced. Further testing is not
required. A fully-charged battery must be load tested
8F - 8 BATTERY SYSTEMRS
BATTERY (Continued)
Page 1928 of 4284

INSTRUMENT CLUSTER DTC'S
DTC DESCRIPTION
100.00 LOOP-BACK FAILURE
100.1 ABS COMMUNICATION FAULT
100.2 BCM COMMUNICATION FAULT
100.3 EATX COMMUNICATION FAULT
100.4 PCM COMMUNICATION FAULT
100.5 ORC COMMUNICATION FAULT
100.6 SBEC/DEC/MCM COMMUNICATION
FAULT
200.0 AIRBAG LED SHORT
200.1 AIRBAG LED OPEN
200.2 ABS LED SHORT
200.3 ABS LED OPEN
200.6 EL INVERTER TIME-OUT
200.7 EATX MISMATCH
DIM TEST
When CHEC-0 is displayed in the odometer win-
dow, the cluster's Vacuum Fluorescent (VF) displays
will dim down. If the VF display brightness does not
change, a problem exists in the cluster.
CALIBRATION TEST
When CHEC-1 is displayed in the odometer win-
dow, each of the cluster's gauge pointers will move
sequentially through each calibration point. The
table contains the proper calibration points for each
gauge. If the gauge pointers are not calibrated, a
problem exists in the cluster. If any gauge is out of
calibration, replace the cluster.
CLUSTER CALIBRATION
SPEEDOMETER CALIBRATION POINT
1 0 MPH (0 KM/H)
2 20 MPH (40 KM/H)
3 60 MPH (100 KM/H)
4 100 MPH (160 KM/H)
TACHOMETER
1 0 RPM
2 1000 RPM
3 3000 RPM
4 6000 RPM
FUEL GAUGE
1 EMPTY
2 1/4 FILLED
3 1/2 FILLED
4 FULL
TEMPERATURE
GAUGE
1 COLD
2 1/4
3 3/4
4 HOT
ODOMETER SEGMENT TEST
When CHEC-2 is displayed in the odometer win-
dow, each digit of the odometer will illuminate
sequentially. If a segment in the odometer does not
illuminate normally, a problem exists in the display.
ELECTRONIC TRANSMISSION RANGE INDICATOR
SEGMENT TEST
When CHEC-3 is displayed in the odometer win-
dow, each segment of the transmission range indica-
tor will illuminate sequentially. If a segment in the
transmission range indicator does not illuminate nor-
mally, a problem exists in the display board.
8J - 2 INSTRUMENT CLUSTERRS
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER (Continued)