Brake line CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2002 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2002, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2002Pages: 2399, PDF Size: 57.96 MB
Page 57 of 2399

(3) Install driveshaft in hub/bearing and on output
shaft of rear drive line module. Driveshaft is
installed by first sliding the outer joint of the drive-
shaft into the hub/bearing and then compressing the
inner joint on the driveshaft and installing it on the
output shaft the drive line module.
(4) Install rotor on hub/bearing.
(5) Carefully lower disc brake caliper and brake
shoes over rotor and onto caliper adapter by revers-
ing the removal procedure (Fig. 14).CAUTION: When installing guide pin bolts extreme
caution should be taken not to cross-thread the cal-
iper guide pin bolts.
(6) Install the disc brake caliper guide pin bolts
(Fig. 15). Tighten the guide pin bolts to a torque of
35 N´m (26 ft. lbs.).
Fig. 12 Hub/Bearing Removal And Installation
1 - PARK BRAKE BRAKE SHOE
2 - HUB/BEARING
3 - PARK BRAKE BRAKE SHOE
Fig. 13 Hub/Bearing Mounting Bolts
1 - HUB/BEARING
2 - AXLE
3 - MOUNTING BOLTS
4 - CALIPER ADAPTER
Fig. 14 Removing/Installing Caliper (Left Side
Shown)
1 - LIFT THIS END OF CALIPER AWAY FROM ADAPTER FIRST
2 - DISC BRAKE CALIPER
3 - ADAPTER ABUTMENT
4 - OUTBOARD BRAKE SHOE HOLD DOWN CLIP
5 - OUTBOARD BRAKE SHOE
6 - ROTOR
7 - ADAPTER
Fig. 15 Caliper Guide Pin Bolts
1 - STUD PIN BOLTS
2 - DISC BRAKE CALIPER
3 - DRIVESHAFT
4 - AXLE
5 - DISC BRAKE CALIPER ADAPTER
2 - 34 REAR SUSPENSIONRS
HUB / BEARING (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 58 of 2399
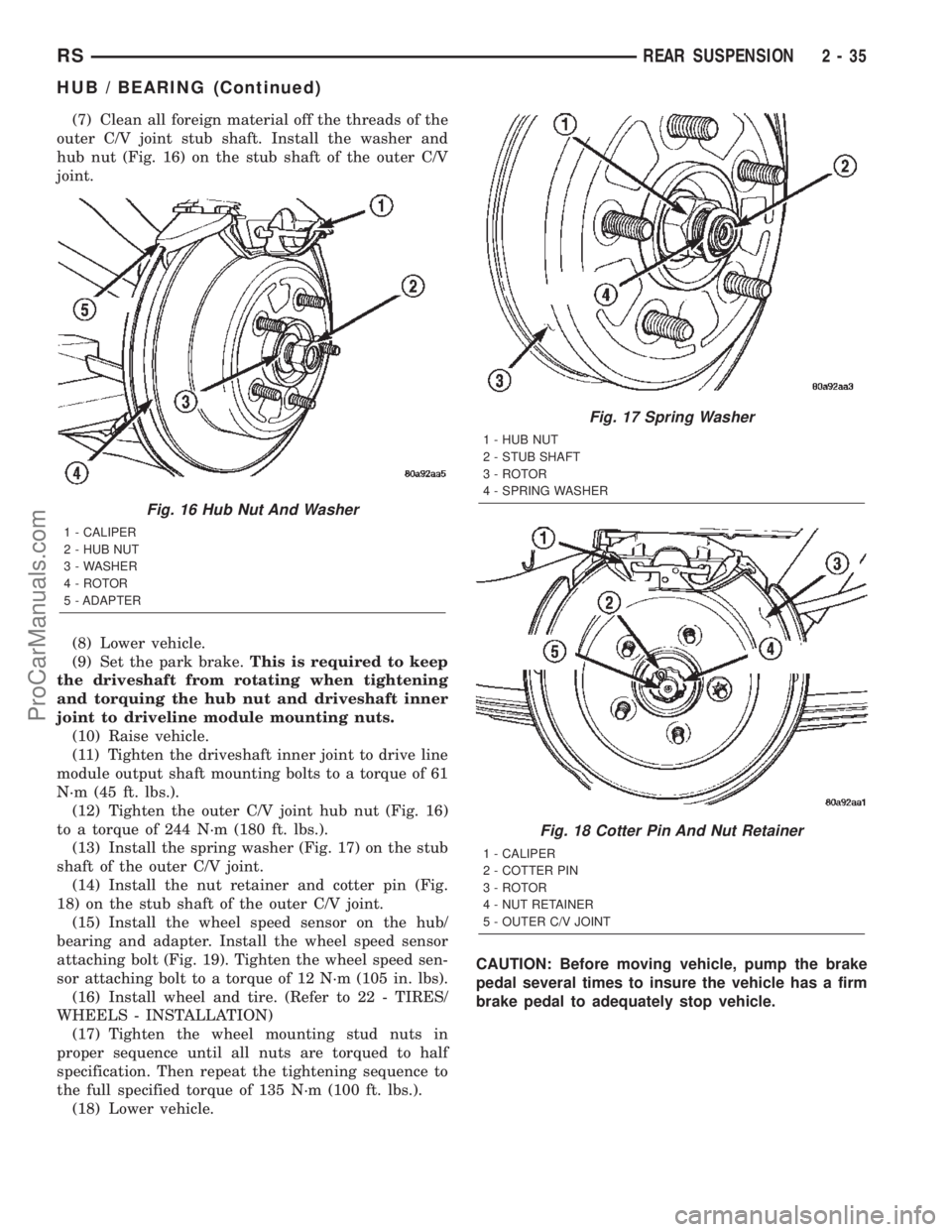
(7) Clean all foreign material off the threads of the
outer C/V joint stub shaft. Install the washer and
hub nut (Fig. 16) on the stub shaft of the outer C/V
joint.
(8) Lower vehicle.
(9) Set the park brake.This is required to keep
the driveshaft from rotating when tightening
and torquing the hub nut and driveshaft inner
joint to driveline module mounting nuts.
(10) Raise vehicle.
(11) Tighten the driveshaft inner joint to drive line
module output shaft mounting bolts to a torque of 61
N´m (45 ft. lbs.).
(12) Tighten the outer C/V joint hub nut (Fig. 16)
to a torque of 244 N´m (180 ft. lbs.).
(13) Install the spring washer (Fig. 17) on the stub
shaft of the outer C/V joint.
(14) Install the nut retainer and cotter pin (Fig.
18) on the stub shaft of the outer C/V joint.
(15) Install the wheel speed sensor on the hub/
bearing and adapter. Install the wheel speed sensor
attaching bolt (Fig. 19). Tighten the wheel speed sen-
sor attaching bolt to a torque of 12 N´m (105 in. lbs).
(16) Install wheel and tire. (Refer to 22 - TIRES/
WHEELS - INSTALLATION)
(17) Tighten the wheel mounting stud nuts in
proper sequence until all nuts are torqued to half
specification. Then repeat the tightening sequence to
the full specified torque of 135 N´m (100 ft. lbs.).
(18) Lower vehicle.CAUTION: Before moving vehicle, pump the brake
pedal several times to insure the vehicle has a firm
brake pedal to adequately stop vehicle.
Fig. 16 Hub Nut And Washer
1 - CALIPER
2 - HUB NUT
3 - WASHER
4 - ROTOR
5 - ADAPTER
Fig. 17 Spring Washer
1 - HUB NUT
2 - STUB SHAFT
3 - ROTOR
4 - SPRING WASHER
Fig. 18 Cotter Pin And Nut Retainer
1 - CALIPER
2 - COTTER PIN
3 - ROTOR
4 - NUT RETAINER
5 - OUTER C/V JOINT
RSREAR SUSPENSION2-35
HUB / BEARING (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 80 of 2399

DIFFERENTIAL & DRIVELINE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
HALF SHAFT - FRONT.....................1
HALF SHAFT - REAR.....................14PROPELLER SHAFT.....................22
REAR DRIVELINE MODULE................24
HALF SHAFT - FRONT
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
HALF SHAFT - FRONT
DESCRIPTION..........................1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HALF SHAFT.....1
REMOVAL.............................2
INSTALLATION..........................4
SPECIFICATIONS - HALF SHAFT - FRONT....6
CV BOOT - INNER
REMOVAL.............................6INSTALLATION..........................6
CV BOOT - OUTER
REMOVAL.............................10
INSTALLATION.........................10
OUTER CV JOINT BEARING SHIELD
REMOVAL.............................13
INSTALLATION.........................13
HALF SHAFT - FRONT
DESCRIPTION
All vehicles use an unequal length half shaft sys-
tem (Fig. 1).
The left half shaft uses a tuned rubber damper
weight. When replacing the left half shaft, be sure
the replacement half shaft has the same damper
weight as the original.
All half shaft assemblies use the same type of
inner and outer joints. The inner joint of both half
shaft assemblies is a tripod joint, and the outer joint
of both half shaft assemblies is a Rzeppa joint. Both
tripod joints and Rzeppa joints are true constant
velocity (CV) joint assemblies. The inner tripod joint
allows for the changes in half shaft length through
the jounce and rebound travel of the front suspen-
sion.
On vehicles equipped with ABS brakes, the outer
CV joint is equipped with a tone wheel used to deter-
mine vehicle speed for ABS brake operation.
The inner tripod joint of both half shafts is splined
into the transaxle side gears. The inner tripod joints
are retained in the side gears of the transaxle using
a snap ring located in the stub shaft of the tripod
joint. The outer CV joint has a stub shaft that issplined into the wheel hub and retained by a steel
hub nut.DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HALF SHAFT
VEHICLE INSPECTION
(1) Check for grease in the vicinity of the inboard
tripod joint and outboard CV joint; this is a sign of
inner or outer joint seal boot or seal boot clamp dam-
age.
NOISE AND/OR VIBRATION IN TURNS
A clicking noise and/or a vibration in turns could
be caused by one of the following conditions:
²Damaged outer CV or inner tripod joint seal
boot or seal boot clamps. This will result in the loss
and/or contamination of the joint grease, resulting in
inadequate lubrication of the joint.
²Noise may also be caused by another component
of the vehicle coming in contact with the half shafts.
CLUNKING NOISE DURING ACCELERATION
This noise may be a result of one of the following
conditions:
²A torn seal boot on the inner or outer joint of the
half shaft assembly.
RSDIFFERENTIAL & DRIVELINE3-1
ProCarManuals.com
Page 93 of 2399

HALF SHAFT - REAR
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
HALF SHAFT - REAR
DESCRIPTION.........................14
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HALF SHAFT....14
REMOVAL.............................15
INSTALLATION.........................15SPECIFICATIONS - HALF SHAFT - FRONT . . . 16
CV BOOT - INNER/OUTER
REMOVAL.............................17
INSTALLATION.........................18
HALF SHAFT - REAR
DESCRIPTION
The inner and outer joints of both half shaft
assemblies are tripod joints. The tripod joints are
true constant velocity (CV) joint assemblies, which
allow for the changes in half shaft length through
the jounce and rebound travel of the rear suspension.
On vehicles equipped with ABS brakes, the outer
CV joint is equipped with a tone wheel used to deter-
mine vehicle speed for ABS brake operation.
The inner tripod joint of both half shafts is bolted
rear differential assembly's output flanges. The outer
CV joint has a stub shaft that is splined into the
wheel hub and retained by a steel hub nut.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HALF SHAFT
VEHICLE INSPECTION
(1) Check for grease in the vicinity of the inboard
tripod joint and outboard CV joint; this is a sign of
inner or outer joint seal boot or seal boot clamp dam-
age.
NOISE AND/OR VIBRATION IN TURNS
A clicking noise and/or a vibration in turns could
be caused by one of the following conditions:
²Damaged outer CV or inner tripod joint seal
boot or seal boot clamps. This will result in the loss
and/or contamination of the joint grease, resulting in
inadequate lubrication of the joint.²Noise may also be caused by another component
of the vehicle coming in contact with the half shafts.
CLUNKING NOISE DURING ACCELERATION
This noise may be a result of one of the following
conditions:
²A torn seal boot on the inner or outer joint of the
half shaft assembly.
²A loose or missing clamp on the inner or outer
joint of the half shaft assembly.
²A damaged or worn half shaft CV joint.
SHUDDER OR VIBRATION DURING ACCELERATION
This problem could be a result of:
²A worn or damaged half shaft inner tripod joint.
²A sticking tripod joint spider assembly (inner tri-
pod joint only).
²Improper wheel alignment. (Refer to 2 - SUS-
PENSION/WHEEL ALIGNMENT - STANDARD
PROCEDURE)
VIBRATION AT HIGHWAY SPEEDS
This problem could be a result of:
²Foreign material (mud, etc.) packed on the back-
side of the wheel(s).
²Out of balance tires or wheels. (Refer to 22 -
TIRES/WHEELS - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
²Improper tire and/or wheel runout. (Refer to 22 -
TIRES/WHEELS - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING)
3 - 14 HALF SHAFT - REARRS
ProCarManuals.com
Page 115 of 2399

BI-DIRECTIONAL
OVERRUNNING CLUTCH
DESCRIPTION
The bi-directional overrunning clutch (BOC) (Fig.
28) works as a mechanical disconnect between the
front and rear axles, preventing torque from being
transferred from the rear axle to the front. The BOC
is a simply an overrunning clutch which works in
both clockwise and counter-clockwise rotations. This
means that when the output (the rear axle) is rotat-
ing faster in one direction than the input (front axle),
there is no torque transmission. But when the input
speed is equal to the output speed, the unit becomes
locked. The BOC provides significant benefits regard-
ing braking stability, handling, and driveline durabil-
ity. Disconnecting the front and the rear driveline
during braking helps to maintain the braking stabil-
ity of an AWD vehicle. In an ABS/braking event, the
locking of the rear wheels must be avoided for stabil-
ity reasons. Therefore brake systems are designed to
lock the front wheels first. Any torque transfer from
the rear axle to the front axle disturbs the ABS/brak-
ing system and causes potential instabilities on aslippery surface. The BOC de-couples the rear driv-
eline as soon the rear wheels begin to spin faster
than the front wheels (front wheels locked) in order
to provide increased braking stability. Furthermore
the BOC also reduces the likelihood of throttle off
over-steer during cornering. In a throttle off maneu-
ver, the BOC once again de-couples the rear driveline
forcing all the engine brake torque to the front
wheels. This eliminates the chance of lateral slip on
the rear axle and increases it on the front. The vehi-
cle will therefore tend to understeer, a situation
which is considered easier to manage in most circum-
stances. During this maneuver, and during the ABS
braking event, the BOC does not transmit torque
through to the rear wheels. The rear driveline mod-
ule, with the BOC, will perform the same as a front
wheel drive vehicle during these events. The gear
ratio offset between the front and rear differentials
force the BOC into the overrunning mode most of the
time. This allows BOC to significantly reduce the
rolling resistance of the vehicle, which improves fuel
consumption, allows the downsizing of the driveline
components, and prevents the PTU and propshaft
joints from overheating.
3 - 36 REAR DRIVELINE MODULERS
ProCarManuals.com
Page 116 of 2399
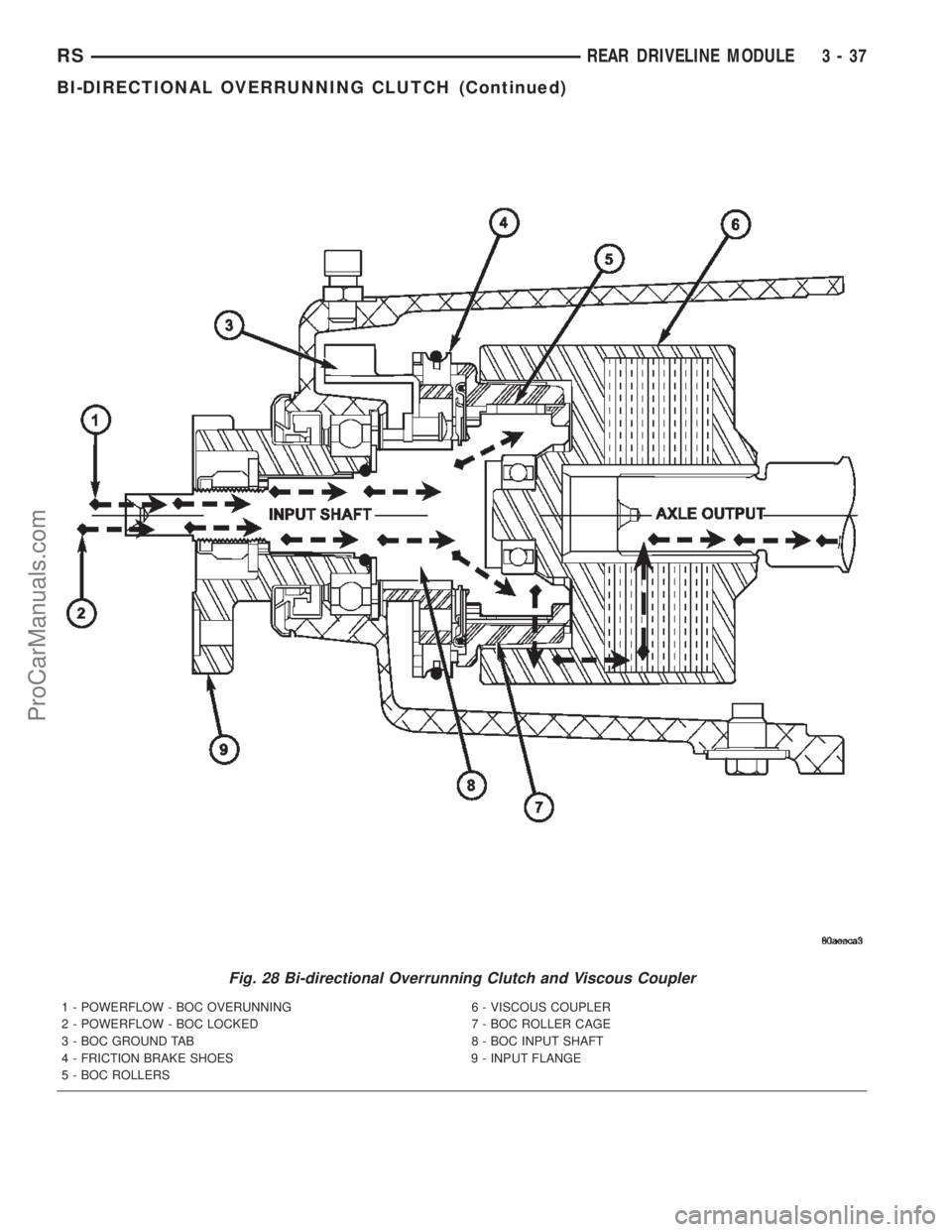
Fig. 28 Bi-directional Overrunning Clutch and Viscous Coupler
1 - POWERFLOW - BOC OVERUNNING 6 - VISCOUS COUPLER
2 - POWERFLOW - BOC LOCKED 7 - BOC ROLLER CAGE
3 - BOC GROUND TAB 8 - BOC INPUT SHAFT
4 - FRICTION BRAKE SHOES 9 - INPUT FLANGE
5 - BOC ROLLERS
RSREAR DRIVELINE MODULE3-37
BI-DIRECTIONAL OVERRUNNING CLUTCH (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 118 of 2399
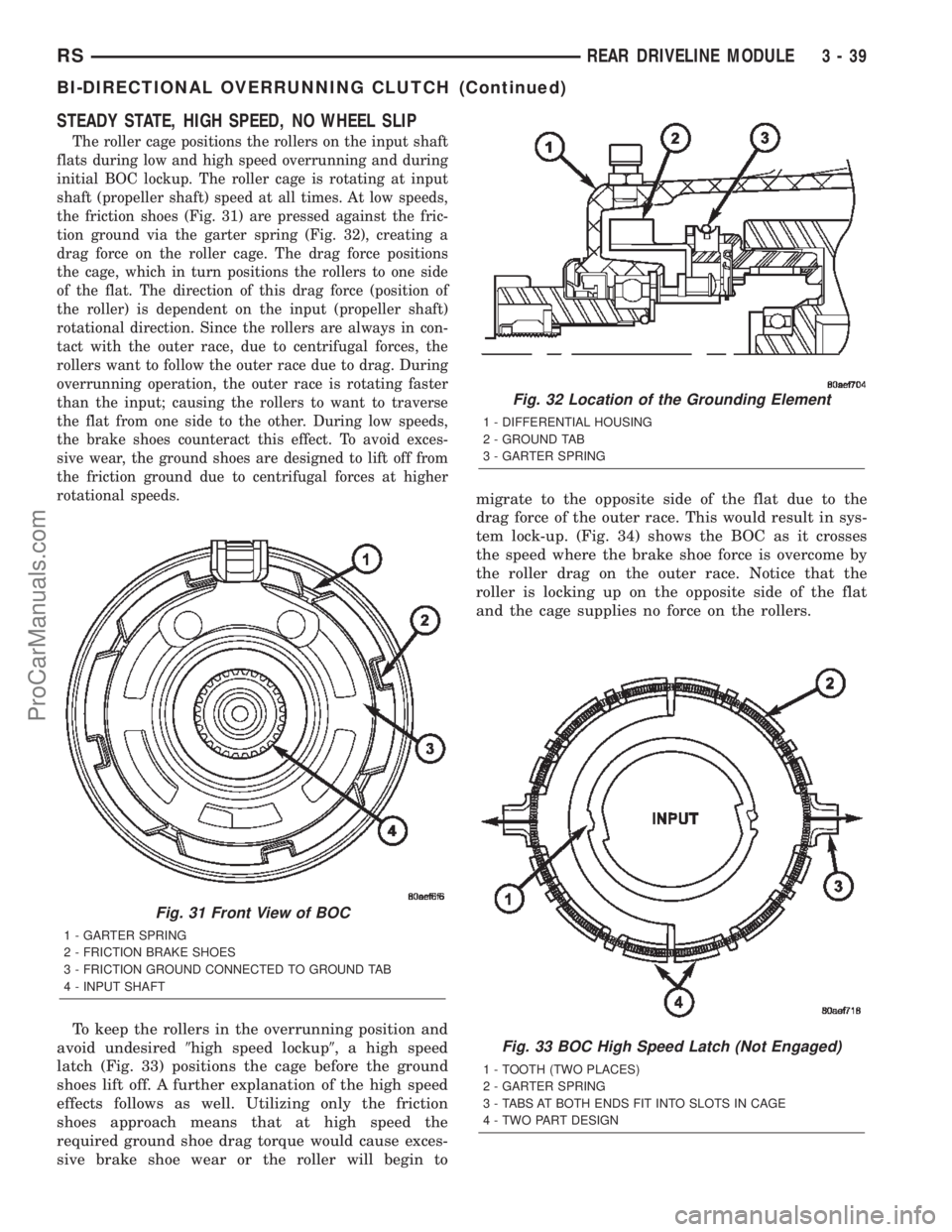
STEADY STATE, HIGH SPEED, NO WHEEL SLIP
The roller cage positions the rollers on the input shaft
flats during low and high speed overrunning and during
initial BOC lockup. The roller cage is rotating at input
shaft (propeller shaft) speed at all times. At low speeds,
the friction shoes (Fig. 31) are pressed against the fric-
tion ground via the garter spring (Fig. 32), creating a
drag force on the roller cage. The drag force positions
the cage, which in turn positions the rollers to one side
of the flat. The direction of this drag force (position of
the roller) is dependent on the input (propeller shaft)
rotational direction. Since the rollers are always in con-
tact with the outer race, due to centrifugal forces, the
rollers want to follow the outer race due to drag. During
overrunning operation, the outer race is rotating faster
than the input; causing the rollers to want to traverse
the flat from one side to the other. During low speeds,
the brake shoes counteract this effect. To avoid exces-
sive wear, the ground shoes are designed to lift off from
the friction ground due to centrifugal forces at higher
rotational speeds.
To keep the rollers in the overrunning position and
avoid undesired9high speed lockup9, a high speed
latch (Fig. 33) positions the cage before the ground
shoes lift off. A further explanation of the high speed
effects follows as well. Utilizing only the friction
shoes approach means that at high speed the
required ground shoe drag torque would cause exces-
sive brake shoe wear or the roller will begin tomigrate to the opposite side of the flat due to the
drag force of the outer race. This would result in sys-
tem lock-up. (Fig. 34) shows the BOC as it crosses
the speed where the brake shoe force is overcome by
the roller drag on the outer race. Notice that the
roller is locking up on the opposite side of the flat
and the cage supplies no force on the rollers.
Fig. 31 Front View of BOC
1 - GARTER SPRING
2 - FRICTION BRAKE SHOES
3 - FRICTION GROUND CONNECTED TO GROUND TAB
4 - INPUT SHAFT
Fig. 32 Location of the Grounding Element
1 - DIFFERENTIAL HOUSING
2 - GROUND TAB
3 - GARTER SPRING
Fig. 33 BOC High Speed Latch (Not Engaged)
1 - TOOTH (TWO PLACES)
2 - GARTER SPRING
3 - TABS AT BOTH ENDS FIT INTO SLOTS IN CAGE
4 - TWO PART DESIGN
RSREAR DRIVELINE MODULE3-39
BI-DIRECTIONAL OVERRUNNING CLUTCH (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 124 of 2399
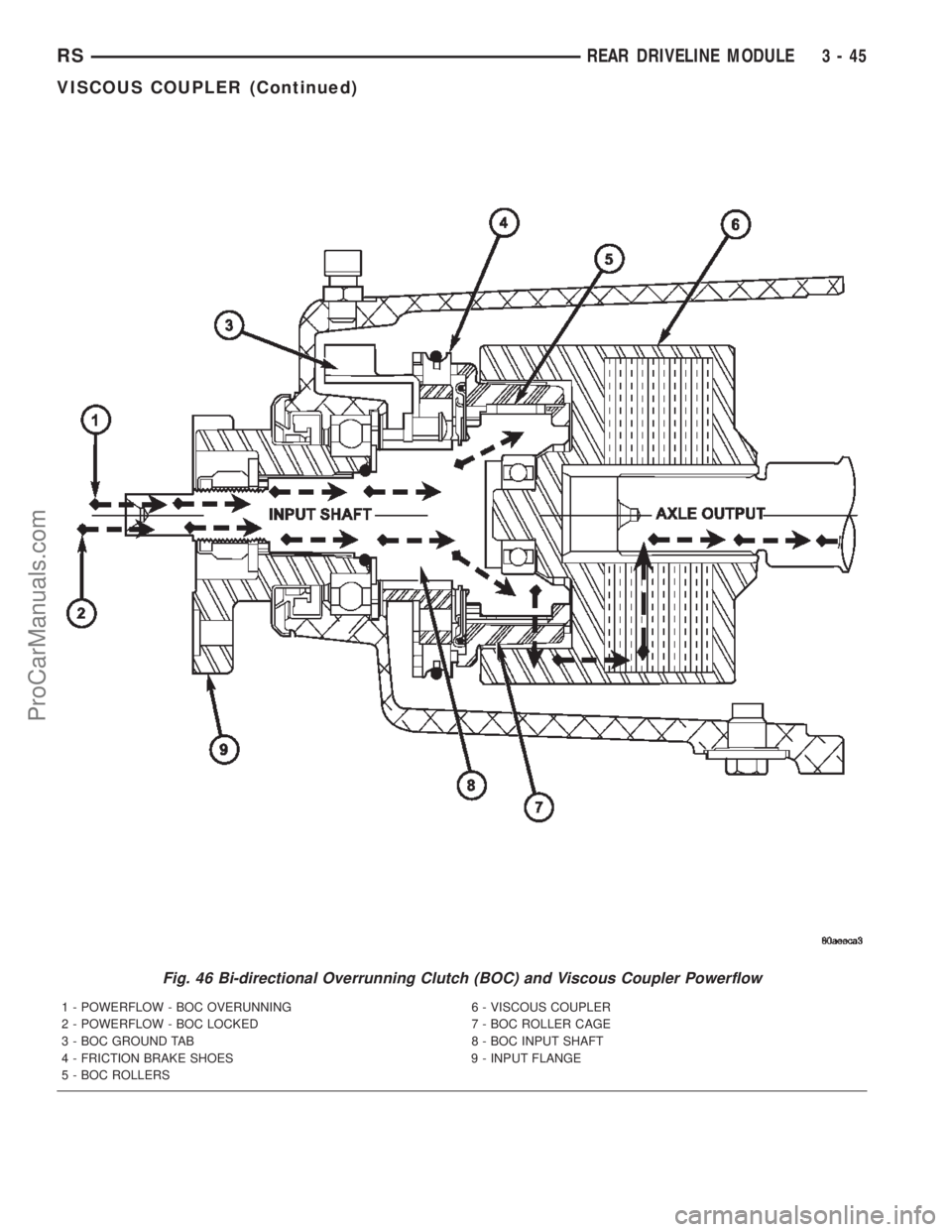
Fig. 46 Bi-directional Overrunning Clutch (BOC) and Viscous Coupler Powerflow
1 - POWERFLOW - BOC OVERUNNING 6 - VISCOUS COUPLER
2 - POWERFLOW - BOC LOCKED 7 - BOC ROLLER CAGE
3 - BOC GROUND TAB 8 - BOC INPUT SHAFT
4 - FRICTION BRAKE SHOES 9 - INPUT FLANGE
5 - BOC ROLLERS
RSREAR DRIVELINE MODULE3-45
VISCOUS COUPLER (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 130 of 2399

BRAKES
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
BRAKES - BASE........................... 1BRAKES - ABS........................... 85
BRAKES - BASE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
BRAKES - BASE
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - BASE BRAKES...........3
DESCRIPTION - BASE BRAKES (EXPORT) . . . 3
OPERATION - BASE BRAKES..............3
WARNING.............................4
CAUTION..............................4
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BASE BRAKE
SYSTEM.............................4
STANDARD PROCEDURE - BASE BRAKE
BLEEDING............................7
SPECIFICATIONS
BRAKE FASTENER TORQUE.............9
SPECIAL TOOLS
BASE BRAKE SYSTEM..................9
BRAKE FLUID LEVEL SWITCH
DESCRIPTION.........................10
OPERATION...........................10
REMOVAL.............................10
INSTALLATION.........................10
ADJUSTABLE PEDAL SWITCH
DESCRIPTION.........................11
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ADJUSTABLE
PEDAL SWITCH.......................11
REMOVAL.............................11
INSTALLATION.........................12
PEDAL POSITION SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................12
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PEDAL
POSITION SENSOR....................13
REMOVAL.............................13
INSTALLATION.........................13
HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - DISC BRAKES (FRONT) . . . 14
DESCRIPTION - DISC BRAKES (REAR)....15
DESCRIPTION - DISC BRAKES (EXPORT) . . 15DESCRIPTION - DRUM BRAKES (REAR) . . . 16
OPERATION
OPERATION - DISC BRAKES (FRONT).....16
OPERATION - DISC BRAKES (REAR)......16
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - DRUM BRAKE
AUTOMATIC ADJUSTER................16
BRAKE LINES
DESCRIPTION - BRAKE TUBES AND HOSES . 17
OPERATION - BRAKE TUBES AND HOSES . . . 17
INSPECTION - BRAKE TUBES AND HOSES . . . 17
BRAKE PADS/SHOES - FRONT
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - FRONT DISC BRAKE SHOES
(DISC/DISC BRAKES)..................17
REMOVAL - FRONT DISC BRAKE SHOES
(DISC/DRUM BRAKES).................18
CLEANING - DISC BRAKE SHOES..........18
INSPECTION - DISC BRAKE SHOES........18
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - FRONT DISC BRAKE
SHOES.............................19
INSTALLATION - FRONT DISC BRAKE
SHOES (DISC/DRUM BRAKES)...........19
BRAKE PADS/SHOES - REAR DISC
REMOVAL - REAR DISC BRAKE SHOES.....19
CLEANING - DISC BRAKE SHOES..........21
INSPECTION - DISC BRAKE SHOES........21
INSTALLATION - REAR DISC BRAKE SHOES . . 21
BRAKE PADS/SHOES - REAR DRUM
REMOVAL - REAR DRUM BRAKE SHOES....22
INSPECTION - REAR DRUM BRAKE SHOE
LINING..............................25
INSTALLATION - REAR DRUM BRAKE SHOES . 25
ADJUSTMENTS
ADJUSTMENT - REAR DRUM BRAKE
SHOES.............................26
RSBRAKES5-1
ProCarManuals.com
Page 135 of 2399
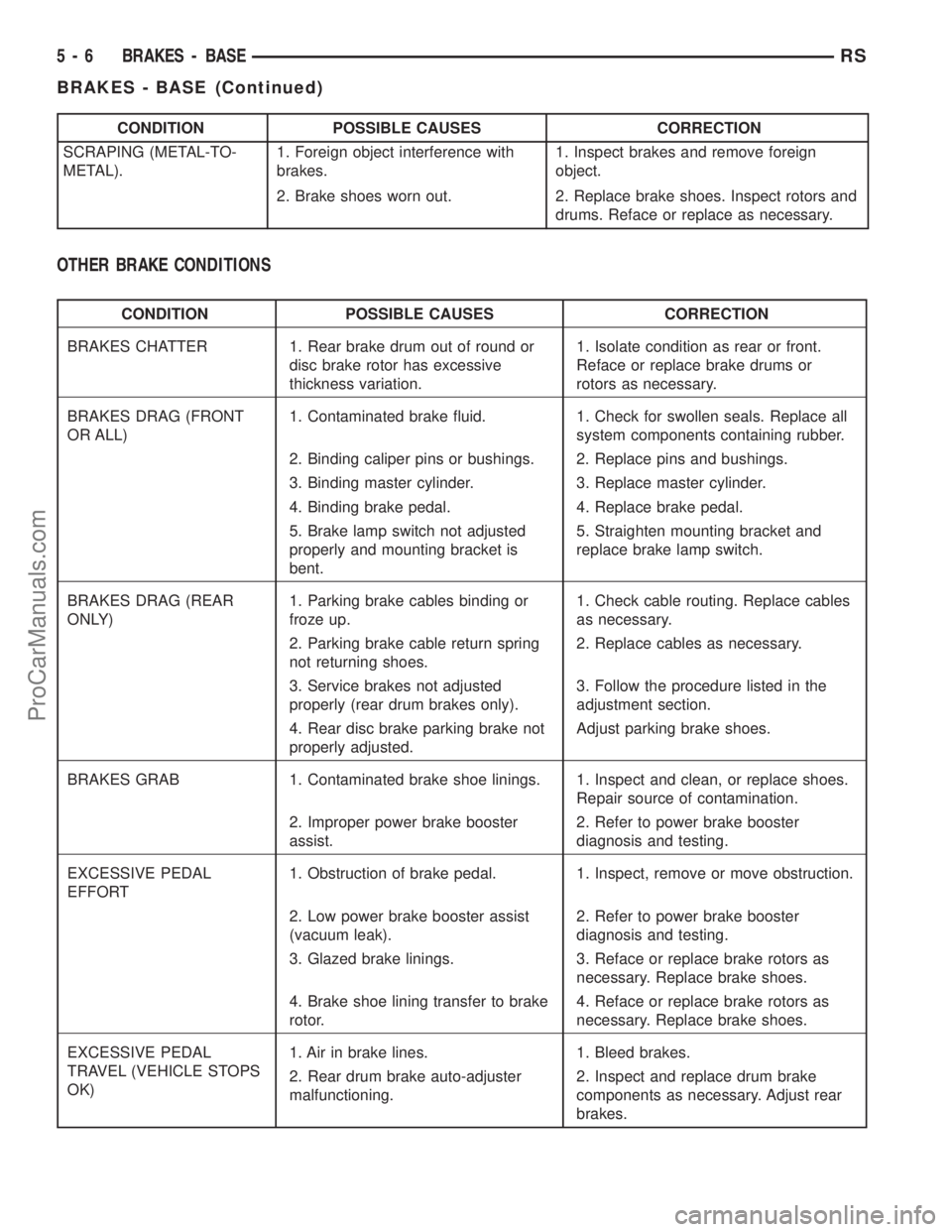
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
SCRAPING (METAL-TO-
METAL).1. Foreign object interference with
brakes.1. Inspect brakes and remove foreign
object.
2. Brake shoes worn out. 2. Replace brake shoes. Inspect rotors and
drums. Reface or replace as necessary.
OTHER BRAKE CONDITIONS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
BRAKES CHATTER 1. Rear brake drum out of round or
disc brake rotor has excessive
thickness variation.1. Isolate condition as rear or front.
Reface or replace brake drums or
rotors as necessary.
BRAKES DRAG (FRONT
OR ALL)1. Contaminated brake fluid. 1. Check for swollen seals. Replace all
system components containing rubber.
2. Binding caliper pins or bushings. 2. Replace pins and bushings.
3. Binding master cylinder. 3. Replace master cylinder.
4. Binding brake pedal. 4. Replace brake pedal.
5. Brake lamp switch not adjusted
properly and mounting bracket is
bent.5. Straighten mounting bracket and
replace brake lamp switch.
BRAKES DRAG (REAR
ONLY)1. Parking brake cables binding or
froze up.1. Check cable routing. Replace cables
as necessary.
2. Parking brake cable return spring
not returning shoes.2. Replace cables as necessary.
3. Service brakes not adjusted
properly (rear drum brakes only).3. Follow the procedure listed in the
adjustment section.
4. Rear disc brake parking brake not
properly adjusted.Adjust parking brake shoes.
BRAKES GRAB 1. Contaminated brake shoe linings. 1. Inspect and clean, or replace shoes.
Repair source of contamination.
2. Improper power brake booster
assist.2. Refer to power brake booster
diagnosis and testing.
EXCESSIVE PEDAL
EFFORT1. Obstruction of brake pedal. 1. Inspect, remove or move obstruction.
2. Low power brake booster assist
(vacuum leak).2. Refer to power brake booster
diagnosis and testing.
3. Glazed brake linings. 3. Reface or replace brake rotors as
necessary. Replace brake shoes.
4. Brake shoe lining transfer to brake
rotor.4. Reface or replace brake rotors as
necessary. Replace brake shoes.
EXCESSIVE PEDAL
TRAVEL (VEHICLE STOPS
OK)1. Air in brake lines. 1. Bleed brakes.
2. Rear drum brake auto-adjuster
malfunctioning.2. Inspect and replace drum brake
components as necessary. Adjust rear
brakes.
5 - 6 BRAKES - BASERS
BRAKES - BASE (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com