Engine Systems CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2002 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2002, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2002Pages: 2399, PDF Size: 57.96 MB
Page 409 of 2399

(3) To disable the ignition and fuel systems, dis-
connect the Automatic Shutdown Relay (ASD). The
ASD relay is located in the Power Distribution Cen-
ter (PDC). Refer to the PDC cover for proper relay
location.
(4) Verify that all lights and accessories are OFF,
and the transmission shift selector is in the PARK
and SET parking brake.
CAUTION: Do not overheat the starter motor or
draw the battery voltage below 9.6 volts during
cranking operations.
(5) Rotate and hold the ignition switch in the
START position. Observe the volt-ampere tester (Fig.
3).
²If voltage reads above 9.6 volts, and amperage
draw reads above 280 amps, check for engine seizing
or faulty starter.
²If voltage reads 12.4 volts or greater and amper-
age reads 0 to 10 amps, check for corroded cables
and/or bad connections.
²Voltage below 9.6 volts and amperage draw
above 300 amps, the problem is the starter. Replace
the starter refer to starter removal.
(6) After the starting system problems have been
corrected, verify the battery state-of-charge and
charge battery if necessary. Disconnect all testing
equipment and connect ASD relay. Start the vehicle
several times to assure the problem has been cor-
rected.SPECIFICATIONS
STARTER
MANUFACTURER NIPPONDENSO
Engine Application 2.4L /3.3/3.8L
Power rating 1.2 Kw
Voltage 12 VOLTS
No. of Fields 4
No. of Poles 4
Brushes 4
Drive Conventional Gear Train
Free running Test
Voltage 11
Amperage Draw 73 Amp
Minimum Speed 3401 RPM
SolenoidClosing Voltage 7.5 Volts
Cranking Amperage Draw
test150 - 200 Amps.
Engine should be up to operating temperature.
Extremely heavy oil or tight engine will increase
starter amperage draw.
Torques
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Starter Mounting Bolts 47.4 35
Starter Solenoid Battery
Nut11.3 8.3 100
8F - 34 STARTINGRS
STARTING (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 412 of 2399

ENGINE SYSTEMS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
BATTERY SYSTEM......................... 1
CHARGING.............................. 20STARTING............................... 31
BATTERY SYSTEM
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
BATTERY SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION..........................1
OPERATION............................2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BATTERY
SYSTEM.............................2
CLEANING.............................5
INSPECTION...........................6
SPECIFICATIONS........................6
SPECIAL TOOLS
BATTERY SYSTEM SPECIAL TOOLS.......7
BATTERY
DESCRIPTION..........................7
OPERATION............................9
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BATTERY.......9
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - SPIRAL PLATE
BATTERY CHARGING..................10
STANDARD PROCEDURE -
CONVENTIONAL BATTERY CHARGING.....11
STANDARD PROCEDURE - OPEN-CIRCUIT
VOLTAGE TEST.......................13
STANDARD PROCEDURE - IGNITION-OFF
DRAW TEST.........................13
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CHECKING
BATTERY ELECTROLYTE LEVEL.........14REMOVAL - BATTERY...................15
INSTALLATION.........................15
BATTERY HOLDDOWN
DESCRIPTION.........................15
OPERATION...........................15
REMOVAL.............................16
INSTALLATION.........................16
BATTERY CABLES
DESCRIPTION.........................16
OPERATION...........................16
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BATTERY CABLE . 16
REMOVAL.............................18
INSTALLATION.........................18
BATTERY TRAY
DESCRIPTION.........................18
OPERATION...........................19
REMOVAL.............................19
INSTALLATION.........................19
THERMOWRAP
DESCRIPTION.........................19
OPERATION...........................19
REMOVAL.............................19
INSTALLATION.........................19
BATTERY SYSTEM
DESCRIPTION
A single 12-volt battery system is standard factory-
installed equipment on this model. All of the compo-
nents of the battery system are located within the
engine compartment of the vehicle. The service infor-
mation for the battery system in this vehicle coversthe following related components, which are covered
in further detail elsewhere in this service manual:
²Battery- The storage battery provides a reli-
able means of storing a renewable source of electrical
energy within the vehicle.
²Battery Cable- The battery cables connect the
battery terminal posts to the vehicle electrical sys-
tem.
RGENGINE SYSTEMS8Fa-1
ProCarManuals.com
Page 413 of 2399

²Battery Holddown- The battery holddown
hardware secures the battery in the battery tray in
the engine compartment.
²Battery Thermowrap- The battery ther-
mowarp insulates the battery to protect it from
engine compartment temperature extremes.
²Battery Tray- The battery tray provides a
secure mounting location in the vehicle for the bat-
tery and an anchor point for the battery holddown
hardware.
For battery system maintenance schedules and
jump starting procedures, see the owner's manual in
the vehicle glove box. Optionally, refer to Lubrication
and Maintenance for the recommended battery main-
tenance schedules and for the proper battery jump
starting procedures. While battery charging can be
considered a maintenance procedure, the battery
charging procedures and related information are
located in the standard procedures section of this ser-
vice manual. This was done because the battery must
be fully-charged before any battery system diagnosis
or testing procedures can be performed. Refer to
Standard procedures for the proper battery charging
procedures.
OPERATION
The battery system is designed to provide a safe,
efficient, reliable and mobile means of delivering and
storing electrical energy. This electrical energy is
required to operate the engine starting system, as
well as to operate many of the other vehicle acces-
sory systems for limited durations while the engine
and/or the charging system are not operating. The
battery system is also designed to provide a reserve
of electrical energy to supplement the charging sys-
tem for short durations while the engine is running
and the electrical current demands of the vehicle
exceed the output of the charging system. In addition
to delivering, and storing electrical energy for the
vehicle, the battery system serves as a capacitor and
voltage stabilizer for the vehicle electrical system. It
absorbs most abnormal or transient voltages caused
by the switching of any of the electrical components
or circuits in the vehicle.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BATTERY SYSTEM
The battery, starting, and charging systems in the
vehicle operate with one another and must be tested
as a complete system. In order for the engine to start
and the battery to maintain its charge properly, all of
the components that are used in these systems must
perform within specifications. It is important that
the battery, starting, and charging systems be thor-
oughly tested and inspected any time a battery needs
to be charged or replaced. The cause of abnormal bat-
tery discharge, overcharging or early battery failure
must be diagnosed and corrected before a battery is
replaced and before a vehicle is returned to service.
The service information for these systems has been
separated within this service manual to make it eas-
ier to locate the specific information you are seeking.
However, when attempting to diagnose any of these
systems, it is important that you keep their interde-
pendency in mind.
The diagnostic procedures used for the battery,
starting, and charging systems include the most
basic conventional diagnostic methods, to the more
sophisticated On-Board Diagnostics (OBD) built into
the Powertrain Control Module (PCM). Use of an
induction-type milliampere ammeter, a volt/ohmme-
ter, a battery charger, a carbon pile rheostat (load
tester) and a 12-volt test lamp may be required. All
OBD-sensed systems are monitored by the PCM.
Each monitored circuit is assigned a Diagnostic Trou-
ble Code (DTC). The PCM will store a DTC in elec-
tronic memory for any failure it detects. Refer to
Charging System for the proper charging system on-
board diagnostic test procedures.
MICRO 420 ELECTRICAL SYSTEM TESTER
The Micro 420 automotive battery system tester is
designed to help the dealership technicians diagnose
the cause of a defective battery. Follow the instruc-
tion manual supplied with the tester to properly
diagnose a vehicle. If the instruction manual is not
available refer to the standard procedure in this sec-
tion, which includes the directions for using the
Micro 420 electrical system tester.
8Fa - 2 BATTERY SYSTEMRG
BATTERY SYSTEM (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 419 of 2399
nal resistance and also increases the active material
surface area.
WARNING: NEVER EXCEED 14.4 VOLTS WHEN
CHARGING A SPIRAL PLATE BATTERY. PERSONAL
INJURY AND/OR BATTERY DAMAGE MAY RESULT.
Due to the maintanance-free design, distilled water
cannot be added to this battery. Therefore, if more
than 14.4 volts are used during the spiral plate bat-
tery charging process, water vapor can be exhausted
through the pressure-sensitive battery vents and lost
for good. This can permanently damage the spiral
plate battery. Never exceed 14.4 volts when charging
a spiral plate battery. Personal injury and/or battery
damage may result.
CONVENTIONAL BATTERY - GASOLINE ENGINE
Low-maintenance batteriesare used on vehicles
equipped with a gasoline engine, these batteries have
removable battery cell caps (Fig. 5). Watercanbe
added to this battery. Under normal service, the com-
position of this battery reduces gassing and water
loss at normal charge rates. However these batteries
may require additional distilled water after years of
service.
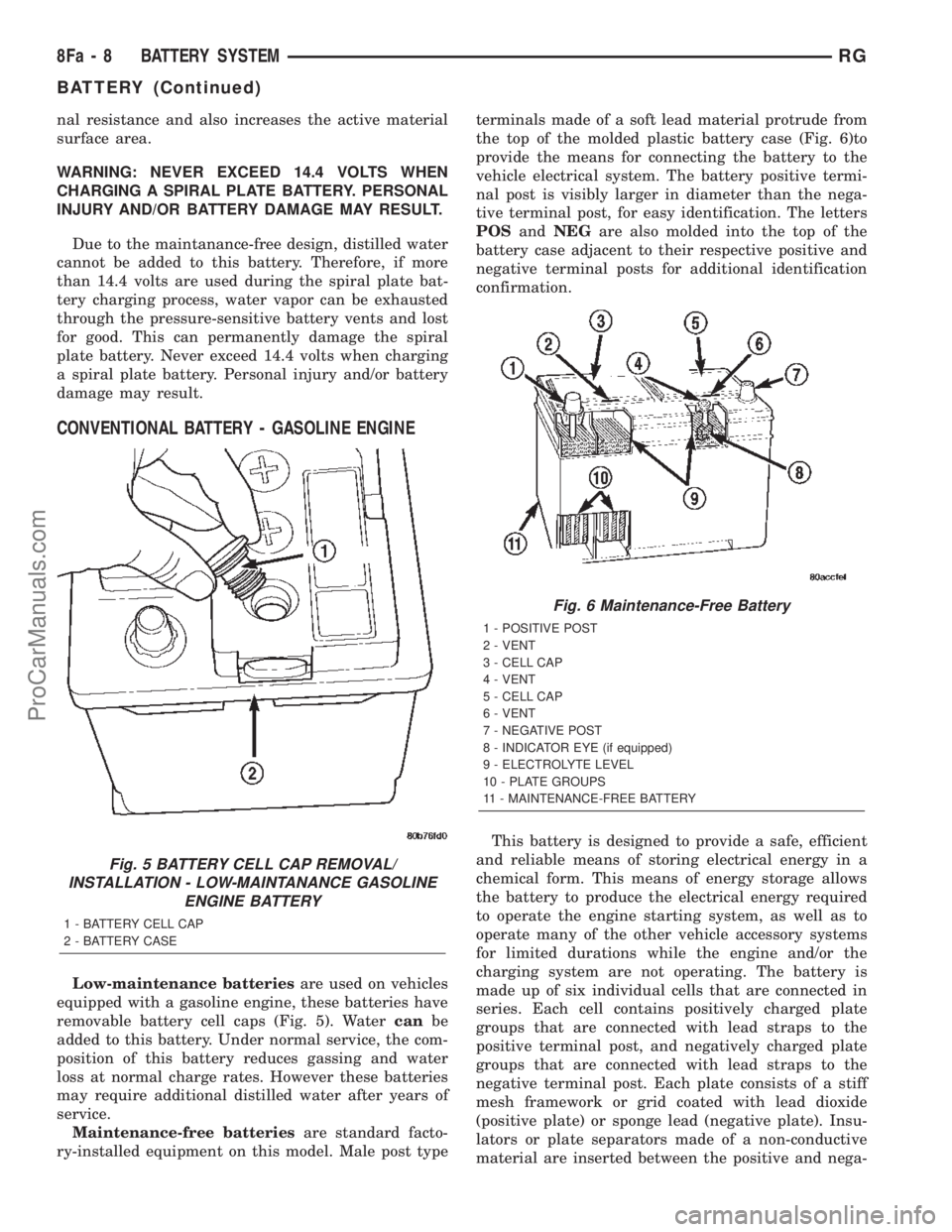
Maintenance-free batteriesare standard facto-
ry-installed equipment on this model. Male post typeterminals made of a soft lead material protrude from
the top of the molded plastic battery case (Fig. 6)to
provide the means for connecting the battery to the
vehicle electrical system. The battery positive termi-
nal post is visibly larger in diameter than the nega-
tive terminal post, for easy identification. The letters
POSandNEGare also molded into the top of the
battery case adjacent to their respective positive and
negative terminal posts for additional identification
confirmation.
This battery is designed to provide a safe, efficient
and reliable means of storing electrical energy in a
chemical form. This means of energy storage allows
the battery to produce the electrical energy required
to operate the engine starting system, as well as to
operate many of the other vehicle accessory systems
for limited durations while the engine and/or the
charging system are not operating. The battery is
made up of six individual cells that are connected in
series. Each cell contains positively charged plate
groups that are connected with lead straps to the
positive terminal post, and negatively charged plate
groups that are connected with lead straps to the
negative terminal post. Each plate consists of a stiff
mesh framework or grid coated with lead dioxide
(positive plate) or sponge lead (negative plate). Insu-
lators or plate separators made of a non-conductive
material are inserted between the positive and nega-
Fig. 5 BATTERY CELL CAP REMOVAL/
INSTALLATION - LOW-MAINTANANCE GASOLINE
ENGINE BATTERY
1 - BATTERY CELL CAP
2 - BATTERY CASE
Fig. 6 Maintenance-Free Battery
1 - POSITIVE POST
2 - VENT
3 - CELL CAP
4 - VENT
5 - CELL CAP
6 - VENT
7 - NEGATIVE POST
8 - INDICATOR EYE (if equipped)
9 - ELECTROLYTE LEVEL
10 - PLATE GROUPS
11 - MAINTENANCE-FREE BATTERY
8Fa - 8 BATTERY SYSTEMRG
BATTERY (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 431 of 2399

CHARGING
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
CHARGING
DESCRIPTION - CHARGING SYSTEM.......20
OPERATION - CHARGING SYSTEM.........20
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ON-BOARD
DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM.................21
SPECIFICATIONS
GENERATOR........................22
TORQUE............................22
SPECIAL TOOLS.......................22
BATTERY TEMPERATURE SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................23
OPERATION...........................23
REMOVAL.............................23
GENERATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................23
OPERATION...........................23
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - 2.4L......................23REMOVAL - 2.5L......................24
REMOVAL - 3.3/3.8L...................25
REMOVAL - 3.5L......................26
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 2.4L..................27
INSTALLATION - 2.5L..................28
INSTALLATION - 3.3/3.8L................28
INSTALLATION - 3.5L..................28
GENERATOR DECOUPLER PULLEY
DESCRIPTION.........................28
OPERATION...........................28
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - GENERATOR
DECOUPLER PULLEY..................29
REMOVAL.............................29
INSTALLATION.........................30
VOLTAGE REGULATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................30
OPERATION...........................30
CHARGING
DESCRIPTION - CHARGING SYSTEM
The charging system consists of:
²Generator
²Decoupler Pulley (If equipped)
²Electronic Voltage Regulator (EVR) circuitry
within the Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
²Ignition switch (refer to the Ignition System sec-
tion for information)
²Battery (refer to the Battery section for informa-
tion)
²Inlet Air Temperature (calculated battery tem-
perature)
²Voltmeter (refer to the Instrument Cluster sec-
tion for information if equipped)
²Wiring harness and connections (refer to the
Wiring section for information)
²Accessory drive belt (refer to the Cooling section
for more information)
OPERATION - CHARGING SYSTEM
The charging system is turned on and off with the
ignition switch. The system is on when the engine is
running and the ASD relay is energized. The ASD
relay is energized when the PCM grounds the ASD
control circuit. This voltage is connected through the
PCM or IPM (intelligent power module) (if equipped)and supplied to one of the generator field terminals
(Gen. Source +) at the back of the generator.
The generator is driven by the engine through a
serpentine belt and pulley or decoupler pulley
arrangement.
The amount of DC current produced by the gener-
ator is controlled by the EVR (field control) circuitry
contained within the PCM. This circuitry is con-
nected in series with the second rotor field terminal
and ground.
An Inlet air temperature sensor is used to calcu-
late the temperature near the battery. This tempera-
ture data, along with data from monitored line
voltage (battery voltage sense circuit), is used by the
PCM to vary the battery charging rate. This is done
by cycling the ground path to control the strength of
the rotor magnetic field. The PCM then compensates
and regulates generator current output accordingly
to maintain system voltage at the targeted system
voltage based on battery temperature.
All vehicles are equipped with On-Board Diagnos-
tics (OBD). All OBD-sensed systems, including EVR
(field control) circuitry, are monitored by the PCM.
Each monitored circuit is assigned a Diagnostic Trou-
ble Code (DTC). The PCM will store a DTC in elec-
tronic memory for certain failures it detects and
illuminate the (MIL) lamp. Refer to On-Board Diag-
nostics in the Electronic Control Modules(Refer to 8 -
ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CONTROL MOD-
8Fa - 20 CHARGINGRG
ProCarManuals.com
Page 445 of 2399

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
STARTER
ENGAGES,
SPINS OUT
BEFORE
ENGINE
STARTS.1. BROKEN TEETH ON
STARTER RING GEAR.1. REMOVE STARTER. INSPECT RING GEAR AND REPLACE
IF NECESSARY.
2. STARTER ASSEMBLY
FAULTY.2. IF ALL OTHER STARTING SYSTEM COMPONENTS AND
CIRCUITS CHECK OK, REPLACE STARTER ASSEMBLY.
STARTER DOES
NOT
DISENGAGE.1. STARTER
IMPROPERLY
INSTALLED.1. INSTALL STARTER. TIGHTEN STARTER MOUNTING
HARDWARE TO CORRECT TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS.
2. STARTER RELAY
FAULTY.2. REFER TO RELAY TEST, IN THIS SECTION. REPLACE
RELAY, IF NECESSARY.
3. IGNITION SWITCH
FAULTY.3. REFER TO IGNITION SWITCH TEST, IN THE STEERING
SECTION. REPLACE SWITCH, IF NECESSARY.
4. STARTER ASSEMBLY
FAULTY.4. IF ALL OTHER STARTING SYSTEM COMPONENTS AND
CIRCUITS CHECK OK, REPLACE STARTER ASSEMBLY.
5. FAULTY TEETH ON
RING GEAR.5. ROTATE FLYWHEEL 360É, AND INSPECT TEETH AND RING
GEAR REPLACED IF DAMAGED.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - CONTROL
CIRCUIT TEST
The starter control circuit has:
²Starter motor with integral solenoid
²Starter relay
²Transmission range sensor, or Park/Neutral
Position switch with automatic transmissions
²Ignition switch
²Battery
²All related wiring and connections
²Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
CAUTION: Before performing any starter tests, the
ignition and fuel systems must be disabled.
²To disable ignition and fuel systems, disconnect
the Automatic Shutdown Relay (ASD). The ASD relay
is located in the Power Distribution Center (PDC).
Refer to the PDC cover for the proper relay location.
STARTER SOLENOID
WARNING: CHECK TO ENSURE THAT THE TRANS-
MISSION IS IN THE PARK POSITION WITH THE
PARKING BRAKE APPLIED.
(1) Verify battery condition. Battery must be in
good condition with a full charge before performing
any starter tests. Refer to Battery Tests.
(2) Perform Starter Solenoid test BEFORE per-
forming the starter relay test.(3) Perform a visual inspection of the starter/
starter solenoid for corrosion, loose connections or
faulty wiring.
(4) Locate and remove the starter relay from the
Power Distribution Center (PDC). Refer to the PDC
label for relay identification and location.
(5) Connect a remote starter switch or a jumper
wire between the remote battery positive post and
terminal 87 of the starter relay connector.
(a) If engine cranks, starter/starter solenoid is
good. Go to the Starter Relay Test.
(b) If engine does not crank or solenoid chatters,
check wiring and connectors from starter relay to
starter solenoid for loose or corroded connections.
Particularly at starter terminals.
(c) Repeat test. If engine still fails to crank prop-
erly, trouble is within starter or starter mounted
solenoid, and replace starter. Inspect the ring gear
teeth.
STARTER RELAY
WARNING: CHECK TO ENSURE THAT THE TRANS-
MISSION IS IN THE PARK/NEUTRAL POSITION
WITH THE PARKING BRAKE APPLIED.
RELAY TEST
The starter relay is located in the Power Distribu-
tion Center (PDC) in the engine compartment. Refer
to the PDC label for relay identification and location.
8Fa - 34 STARTINGRG
STARTING (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 447 of 2399

tion. If that checks OK check for continuity between
PCM and the terminal 85. Repair open circuit as
required. If OK, the PCM may be defective.
SAFETY SWITCHES
For diagnostics of the Transmission Range Sensor,
refer to the Transaxle section for more information.
If equipped with Clutch Interlock/Upstop Switch,
refer to Diagnosis and Testing in the Clutch section.
IGNITION SWITCH
After testing starter solenoid and relay, test igni-
tion switch and wiring. Refer to the Ignition Section
or Wiring Diagrams for more information. Check all
wiring for opens or shorts, and all connectors for
being loose or corroded.
BATTERY
For battery diagnosis and testing, refer to the Bat-
tery section for procedures.
ALL RELATED WIRING AND CONNECTORS
Refer to Wiring Diagrams for more information.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FEED CIRCUIT
RESISTANCE TEST
Before proceeding with this operation, review Diag-
nostic Preparation and Starter Feed Circuit Tests.
The following operation will require a voltmeter,
accurate to 1/10 of a volt.
CAUTION: Ignition and Fuel systems must be dis-
abled to prevent engine start while performing the
following tests.
(1) To disable the Ignition and Fuel systems, dis-
connect the Automatic Shutdown Relay (ASD). The
ASD relay is located in the Power Distribution Cen-
ter (PDC). Refer to the PDC cover for proper relay
location.
(2) Gain access to battery terminals.
(3) With all wiring harnesses and components
properly connected, perform the following:
(a) Connect the negative lead of the voltmeter to
the battery negative post, and positive lead to the
battery negative cable clamp. Rotate and hold the
ignition switch in the START position. Observe the
voltmeter. If voltage is detected, correct poor con-
tact between cable clamp and post.
(b) Connect positive lead of the voltmeter to the
battery positive post, and negative lead to the bat-
tery positive cable clamp. Rotate and hold the igni-
tion switch key in the START position. Observe the
voltmeter. If voltage is detected, correct poor con-
tact between the cable clamp and post.(c) Connect negative lead of voltmeter to battery
negative terminal, and positive lead to engine
block near the battery cable attaching point.
Rotate and hold the ignition switch in the START
position. If voltage reads above 0.2 volt, correct
poor contact at ground cable attaching point. If
voltage reading is still above 0.2 volt after correct-
ing poor contacts, replace ground cable.
(4) Connect positive voltmeter lead to the starter
motor housing and the negative lead to the battery
negative terminal. Hold the ignition switch key in
the START position. If voltage reads above 0.2 volt,
correct poor starter to engine ground.
(a) Connect the positive voltmeter lead to the
battery positive terminal, and negative lead to bat-
tery cable terminal on starter solenoid. Rotate and
hold the ignition switch in the START position. If
voltage reads above 0.2 volt, correct poor contact at
battery cable to solenoid connection. If reading is
still above 0.2 volt after correcting poor contacts,
replace battery positive cable.
(b) If resistance tests do not detect feed circuit
failures, replace the starter motor.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FEED CIRCUIT
TEST
NOTE: The following results are based upon the
vehicle being at room temperature.
The following procedure will require a suitable
volt-ampere tester (Fig. 3).
CAUTION: Before performing any starter tests, the
ignition and fuel systems must be disabled.
(1) Check battery before performing this test. Bat-
tery must be fully charged.
(2) Connect a volt-ampere tester to the battery ter-
minals. Refer to the operating instructions provided
with the tester being used.
Fig. 3 Volt Ampere Tester
8Fa - 36 STARTINGRG
STARTING (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 448 of 2399

(3) To disable the ignition and fuel systems, dis-
connect the Automatic Shutdown Relay (ASD). The
ASD relay is located in the Power Distribution Cen-
ter (PDC). Refer to the PDC cover for proper relay
location.
(4) Verify that all lights and accessories are OFF,
and the transmission shift selector is in the PARK
and SET parking brake.
CAUTION: Do not overheat the starter motor or
draw the battery voltage below 9.6 volts during
cranking operations.
(5) Rotate and hold the ignition switch in the
START position. Observe the volt-ampere tester (Fig.
3).
²If voltage reads above 9.6 volts, and amperage
draw reads above 280 amps, check for engine seizing
or faulty starter.
²If voltage reads 12.4 volts or greater and amper-
age reads 0 to 10 amps, check for corroded cables
and/or bad connections.
²Voltage below 9.6 volts and amperage draw
above 300 amps, the problem is the starter. Replace
the starter refer to starter removal.
(6) After the starting system problems have been
corrected, verify the battery state-of-charge and
charge battery if necessary. Disconnect all testing
equipment and connect ASD relay. Start the vehicle
several times to assure the problem has been cor-
rected.SPECIFICATIONS
STARTER
MANUFACTURER NIPPONDENSO
Engine Application 2.4L /3.3/3.8L
Power rating 1.2 Kw
Voltage 12 VOLTS
No. of Fields 4
No. of Poles 4
Brushes 4
Drive Conventional Gear Train
Free running Test
Voltage 11
Amperage Draw 73 Amp
Minimum Speed 3401 RPM
SolenoidClosing Voltage 7.5 Volts
Cranking Amperage Draw
test150 - 200 Amps.
Engine should be up to operating temperature.
Extremely heavy oil or tight engine will increase
starter amperage draw.
Torques
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Starter Mounting Bolts 47.4 35
Starter Solenoid Battery Nut 11.3 8.3 100
RGSTARTING8Fa-37
STARTING (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 503 of 2399

OPERATION - TURN SIGNAL SYSTEM.......21
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - MULTI-
FUNCTION SWITCH...................22
REMOVAL.............................22
INSTALLATION.........................22
PARK/TURN SIGNAL LAMP
REMOVAL.............................22
INSTALLATION.........................22
PARK/TURN SIGNAL LAMP - EXPORT
REMOVAL.............................22
INSTALLATION.........................23
REAR FOG LAMP - EXPORT
DESCRIPTION.........................23REPEATER LAMP - EXPORT
REMOVAL.............................23
INSTALLATION.........................23
TAIL LAMP
REMOVAL.............................23
INSTALLATION.........................23
TAIL LAMP - EXPORT
REMOVAL.............................23
INSTALLATION.........................24
TAIL LAMP UNIT
REMOVAL.............................24
INSTALLATION.........................24
LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIOR
DESCRIPTION
LAMP SYSTEMS
Lighting circuits are protected by fuses. Lighting
circuits require an overload protected power source,
on/off device, lamps and body ground to operate prop-
erly. Plastic lamps require a wire in the harness to
supply body ground to the lamp socket. Replace sock-
ets and bulbs that are corroded.
Some of the interior and exterior lighting functions
are governed by the Body Control Module (BCM).
The headlamp, dome, and the door ajar switches pro-
vide signals to the BCM. The BCM in turn sends a
Programmable Communication Interface (PCI) bus
message to the Front Control Module (FCM) to
enable the necessary drivers to set the required illu-
mination configuration.
Wire connectors can make intermittent contact or
become corroded. Before coupling wire connectors,
inspect the terminals inside the connector. Male ter-
minals should not be bent or disengaged from the
insulator. Female terminals should not be sprung
open or disengaged from the insulator. Bent and
sprung terminals can be repaired using needle nose
pliers and pick tool. Corroded terminals appear
chalky or green. Corroded terminals should be
replaced to avoid recurrence of the problem symp-
toms.
Begin electrical system failure diagnosis by testing
related fuses in the fuse block and intelligent power
module. Verify that bulbs are in good condition and
test continuity of the circuit ground. Refer to the
appropriate wiring information.
AUTOMATIC HEADLAMP SYSTEM
The Automatic Headlamp system turns the instru-
mentation and exterior illumination lamps ON when
the ambient light levels are Night and the engine
RPM is 450 or above, and OFF when light levels are
Day.
DAYTIME RUNNING LAMPS
Operating the high-beam headlamps at reduced
power provides daytime running lamps, which are
required on all new Canadian vehicles.
HEADLAMPS ON WITH WINDSHIELD WIPERS
For vehicles equipped with the Automatic Head-
lamp System, the instrumentation and exterior illu-
mination lamps will be turned ON when the
headlamp switch is in the AUTO position, RPM >
450 and the windshield wipers have been in the
intermittent, low or high mode of operation for more
than ten seconds. When the windshield wipers are
turned OFF the Body Control Module will determine
if the instrumentation and exterior illumination
lamps should remain ON base upon the current
ambient light level.
HEADLAMP SYSTEM
The configuration of the headlamp system of head-
lamps, park lamps and fog lamps is determined by
the BCM. The BCM determines the lighting configu-
ration as a result of the inputs from the ignition
switch, headlamp switch and multi-function switch. A
PCI bus is transmitted from the BCM to the FCM to
enable the necessary drivers to set the illumination
configuration. Four wires are connected between the
headlamp switch and the BCM. The first wire con-
tains information regarding the position of the head-
lamp switch (Off, Automatic Headlamps, Automatic
Headlamp switch fog, Park with Fog, Head, or Head
with Fog Lamps). The second wire contains informa-
tion regarding the position of the dimmer switch
(Dome Lamp, Daytime Brightness, Dimming Level or
Off). The third wire is a dedicated signal return
(ground) wire. The fourth wire provides power to the
front fog lamp indicator.
HEADLAMP TIME DELAY SYSTEM
The headlamp time delay system is controlled by
the Body Control Module (BCM) via a PCI bus mes-
8L - 2 LAMPS/LIGHTING - EXTERIORRS
ProCarManuals.com
Page 539 of 2399

ules push buttons located just rearward of the dis-
play screen in the overhead console. The three
universal transmitter push buttons are identified
with one, two or three light indicators so that they be
easily identified by sight or by feel.
Each of the three universal transmitter push but-
tons controls an independent radio transmitter chan-
nel. Each of these three channels can be trained to
transmit a different radio frequency signal for the
remote operation of garage door openers, motorized
gate openers, home or office lighting, security sys-
tems or just about any other device that can be
equipped with a radio receiver in the 286 to 399
MegaHertz (MHz) frequency range for remote opera-
tion. The universal transmitter is capable of operat-
ing systems using either rolling code or non-rolling
code technology.
The electronics module displays messages and a
small house-shaped icon with one, two or three dots
corresponding to the three transmitter buttons to
indicate the status of the universal transmitter. The
EVIC messages are:
²Cleared Channels- Indicates that all of the
transmitter codes stored in the universal transmitter
have been successfully cleared.
²Training- Indicates that the universal trans-
mitter is in its transmitter learning mode.
²Trained- Indicates that the universal transmit-
ter has successfully acquired a new transmitter code.
²Transmit- Indicates that a trained universal
transmitter button has been depressed and that the
universal transmitter is transmitting.
The universal transmitter cannot be repaired, and
is available for service only as a unit with the EVIC
or CMTC modules. If any of these components is
faulty or damaged, the complete EVIC or CMTC
module must be replaced.
OPERATION
The universal transmitter operates on a non-
switched source of battery current so the unit will
remain functional, regardless of the ignition switch
position. For more information on the features, pro-
gramming procedures and operation of the universal
transmitter, see the owner's manual in the vehicle
glove box.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - UNIVERSAL
TRANSMITTER
If the universal transmitter is inoperative, but the
Electronic Vehicle Information Center (EVIC) or
Compass Mini-Trip Computer is operating normally,
see the owner's manual in the vehicle glove box for
instructions on training the universal transmitter.
Retrain the universal transmitter with a known good
transmitter as instructed in the owner's manual andtest the universal transmitter operation again. If the
unit is still inoperative, replace the faulty universal
transmitter and EVIC/CMTC module as a unit. If
both the universal transmitter and the EVIC/CMTC
module are inoperative, refer toOverhead Console
Diagnosis and Testingearlier in this group for fur-
ther diagnosis. For complete circuit diagrams, refer
toOverhead Consolein Wiring Diagrams.
AMBIENT TEMP SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
Ambient air temperature is monitored by the over-
head console through ambient temperature messages
received from the Front Control Module (FCM) over
the Programmable Communications Interface (PCI)
J1850 data bus circuit. The FCM receives a hard
wired input from the ambient temperature sensor.
The ambient temperature sensor is a variable resis-
tor mounted to a bracket that is secured with a screw
to the right side of the headlamp mounting module
grille opening, behind the radiator grille and in front
of the engine compartment.
Refer toFront Control Modulein Electronic
Control Modules. For complete circuit diagrams, refer
to the appropriate wiring information. The ambient
temperature sensor cannot be adjusted or repaired
and, if faulty or damaged, it must be replaced.
OPERATION
The ambient temperature sensor is a variable
resistor that operates on a five-volt reference signal
sent to it by the Front Control Module. The resis-
tance in the sensor changes as temperature changes,
changing the temperature sensor signal circuit volt-
age to the Front Control Module. Based upon the
resistance in the sensor, the Front Control Module
senses a specific voltage on the temperature sensor
signal circuit, which it is programmed to correspond
to a specific temperature. The Front Control Module
then sends the proper ambient temperature mes-
sages to the EVIC, CMTC over the PCI J1850 data
bus.
The thermometer function is supported by the
ambient temperature sensor, a wiring circuit, the
Front Control Module, the Programmable Communi-
cations Interface (PCI) data bus, and a portion of the
Electronics module. If any portion of the ambient
temperature sensor circuit fails, the Front Control
Module will self-diagnose the circuit.
The ambient temperature sensor circuit can also be
diagnosed by referring toDiagnosis and Testing -
Ambient Temperature Sensor, and Diagnosis
and Testing - Ambient Temperature Sensor Cir-
cuit. If the temperature sensor and circuit are con-
8M - 10 MESSAGE SYSTEMSRS
UNIVERSAL TRANSMITTER (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com