service CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2002 Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2002, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2002Pages: 2399, PDF Size: 57.96 MB
Page 98 of 2399
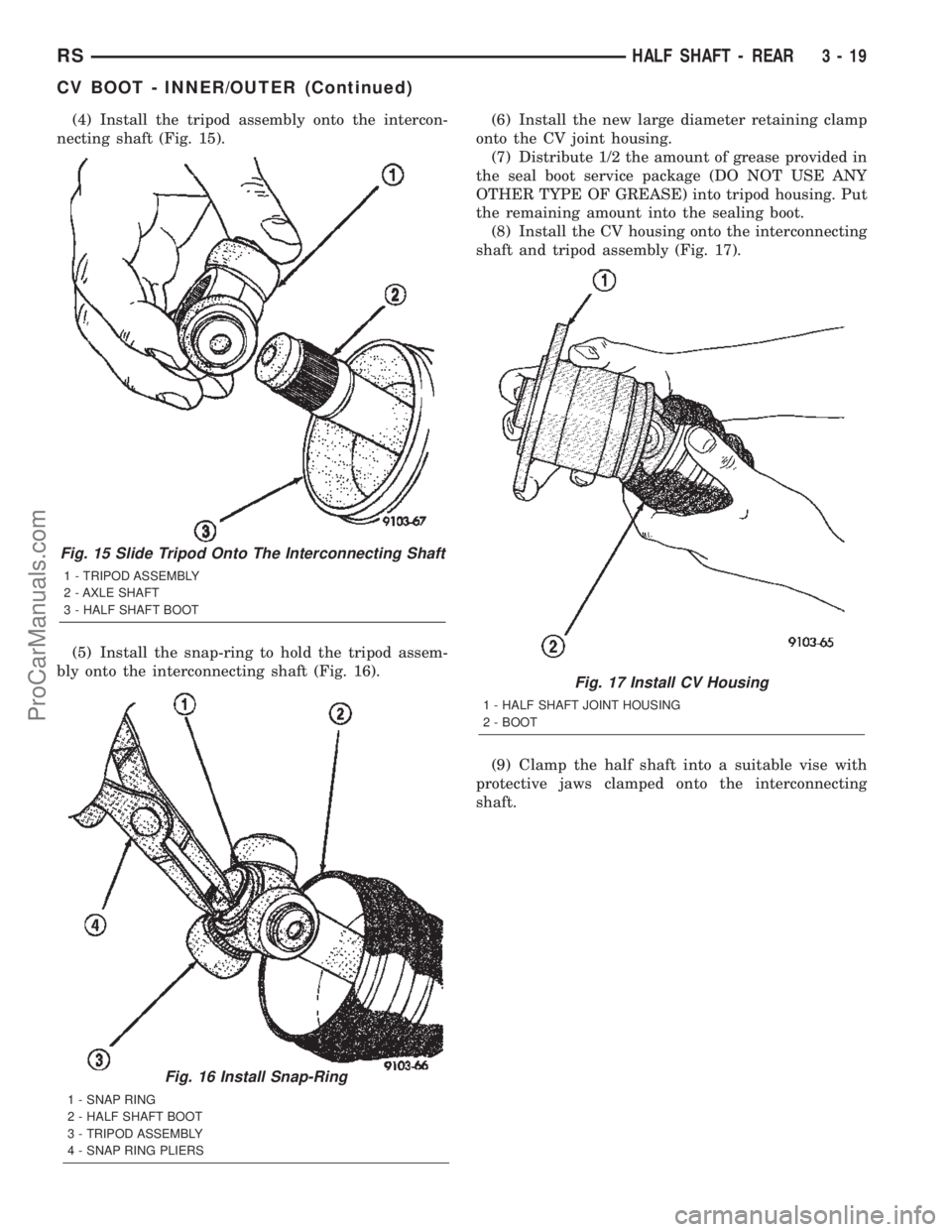
(4) Install the tripod assembly onto the intercon-
necting shaft (Fig. 15).
(5) Install the snap-ring to hold the tripod assem-
bly onto the interconnecting shaft (Fig. 16).(6) Install the new large diameter retaining clamp
onto the CV joint housing.
(7) Distribute 1/2 the amount of grease provided in
the seal boot service package (DO NOT USE ANY
OTHER TYPE OF GREASE) into tripod housing. Put
the remaining amount into the sealing boot.
(8) Install the CV housing onto the interconnecting
shaft and tripod assembly (Fig. 17).
(9) Clamp the half shaft into a suitable vise with
protective jaws clamped onto the interconnecting
shaft.
Fig. 16 Install Snap-Ring
1 - SNAP RING
2 - HALF SHAFT BOOT
3 - TRIPOD ASSEMBLY
4 - SNAP RING PLIERS
Fig. 15 Slide Tripod Onto The Interconnecting Shaft
1 - TRIPOD ASSEMBLY
2 - AXLE SHAFT
3 - HALF SHAFT BOOT
Fig. 17 Install CV Housing
1 - HALF SHAFT JOINT HOUSING
2 - BOOT
RSHALF SHAFT - REAR3-19
CV BOOT - INNER/OUTER (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 101 of 2399

PROPELLER SHAFT
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
PROPELLER SHAFT
DESCRIPTION.........................22
OPERATION...........................22REMOVAL.............................23
INSTALLATION.........................23
SPECIFICATIONS - PROPELLER SHAFT.....23
PROPELLER SHAFT
DESCRIPTION
WARNING: Due to propeller shaft imbalance con-
cerns, the propeller shaft can only be serviced as
an assembly.
AWD models utilize a ªtwo-pieceº propeller shaft
(Fig. 1) to transmit power to the rear driveline mod-
ule assembly. This two-piece design consists of:
²Front and rear shaft segments.
²Plunging center CV joint²Center support bearing
²Rubber coupler at driveline module flange
The front shaft segment utilizes a CV joint at the
power transfer unit connection, and a plunging CV
joint at the center bearing location.
The rear shaft segment utilizes a center support
bearing at the forward position, and a rubber coupler
at the driveline module flange.
OPERATION
The propeller shaft (Fig. 1) is used to transmit
torque from the transaxle power transfer unit (PTU)
Fig. 1 Propeller Shaft Removal/Installation
1 - PTU FLANGE 3 - REAR DRIVELINE MODULE 5 - BOLT-CENTER SUPPORT BEARING-TO-
CROSSMEMBER
2 - CROSSMEMBER 4 - BOLT-PROPELLER SHAFT COUPLER-
T0-DRIVELINE MODULE6 - PROPELLER SHAFT ASSEMBLY
3 - 22 PROPELLER SHAFTRS
ProCarManuals.com
Page 103 of 2399

REAR DRIVELINE MODULE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
REAR DRIVELINE MODULE
DESCRIPTION.........................24
OPERATION...........................24
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REAR
DRIVELINE MODULE NOISE.............25
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REAR
DRIVELINE MODULE OPERATION........27
REMOVAL.............................27
DISASSEMBLY.........................28
ASSEMBLY............................30
INSTALLATION.........................34
SPECIFICATIONS - REAR DRIVELINE
MODULE............................35
SPECIAL TOOLS.......................35
BI-DIRECTIONAL OVERRUNNING CLUTCH
DESCRIPTION.........................36
OPERATION...........................38
DIFFERENTIAL ASSEMBLY
DESCRIPTION.........................41OPERATION...........................41
FLUID - DIFFERENTIAL ASSEMBLY
STANDARD PROCEDURE - DIFFERENTIAL
ASSEMBLY FLUID DRAIN AND FILL.......42
FLUID
STANDARD PROCEDURE - OVERRUNNING
CLUTCH HOUSING FLUID CHANGE.......43
VISCOUS COUPLER
DESCRIPTION.........................44
OPERATION...........................44
TORQUE ARM
REMOVAL.............................46
INSTALLATION.........................46
INPUT FLANGE SEAL
REMOVAL.............................46
INSTALLATION.........................47
OUTPUT FLANGE SEAL
REMOVAL.............................48
INSTALLATION.........................49
REAR DRIVELINE MODULE
DESCRIPTION
The rear driveline module assembly (Fig. 1) con-
sists of four main components:
²Bi-Directional Overrunning Clutch (BOC)
²Viscous Coupling
²Differential Assembly
²Torque Arm
The viscous coupling and bi-directional overrun-
ning clutch are contained within an overrunning
clutch housing, which fastens to the differential
assembly. The overrunning clutch housing and differ-
ential assembly have unique fluid sumps, each
requiring their own type and capacity of fluid. The
overrunning clutch housing requires MopartATF+4
(Automatic Transmission FluidÐType 9602) or equiv-
alent. The differential assembly requires
Driveline module service is limited to the following
components:
²Differential Assembly (serviced only as assem-
bly)
²Viscous Coupling
²Bi-Directional Overrunning Clutch (BOC)
²Overrunning Clutch Housing
²Seals (Input Flange, Output Flange, Overrun-
ning Clutch Housing O-rings)²Input Flange/Shield
²Torque Arm
²Vents
²Fasteners
OPERATION
The primary benefits of All Wheel Drive are:
²Superior straight line acceleration, and corner-
ing on all surfaces
²Better traction and handling under adverse con-
ditions, resulting in improved hill climbing ability
and safer driving.
The heart of the system is an inter-axle viscous
coupling. The vehicle retains predominantly front-
wheel drive characteristics, but the All Wheel Drive
capability takes effect when the front wheels start to
slip. Under normal level road, straight line driving,
100% of the torque is allocated to the front wheels.
The viscous coupling controls and distributes torque/
power to the rear wheels. The viscous coupling trans-
mits torque to the rear wheels in proportion of the
amount of the slippage at the front wheels. Thais
variable torque distribution is automatic with no
driver inputs required. The coupling is similar to a
multi-plate clutch. It consists of a series of closely
spaced discs, which are alternately connected to the
front and rear drive units. The unit is totally sealed
and partially filled with silicone fluid. There is no
3 - 24 REAR DRIVELINE MODULERS
ProCarManuals.com
Page 107 of 2399

DISASSEMBLY
WARNING: Differential is only to be serviced as an
assembly, and no disassembly is required.
(1) Remove six torque arm-to-differential case
bolts and remove torque arm assembly (Fig. 4).
(2) Remove input flange nut and washer using
Tool 6958 and a breaker bar (Fig. 5).(3) Remove input flange (Fig. 6).
(4) Remove input flange seal from overrunning
clutch housing using suitable screwdriver (Fig. 7).
Fig. 4 Torque Arm Fasteners
1 - TORQUE ARM ASSEMBLY
2 - BOLT (SIX)
Fig. 5 Input Flange Nut
1 - INPUT FLANGE
2 - TOOL 6958
Fig. 6 Input Flange
1 - INPUT FLANGE/SHIELD
Fig. 7 Input Flange Seal Removal
1 - INPUT FLANGE SEAL
2 - SCREWDRIVER
3 - 28 REAR DRIVELINE MODULERS
REAR DRIVELINE MODULE (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 133 of 2399

come in contact with a hub mounted drum (drum for
disc/drum brakes or drum-in-hat for disc/disc brakes)
and hold it in place.
WARNING
WARNING: DUST AND DIRT ACCUMULATING ON
BRAKE PARTS DURING NORMAL USE MAY CON-
TAIN ASBESTOS FIBERS FROM PRODUCTION OR
AFTERMARKET BRAKE LININGS. BREATHING
EXCESSIVE CONCENTRATIONS OF ASBESTOS
FIBERS CAN CAUSE SERIOUS BODILY HARM.
EXERCISE CARE WHEN SERVICING BRAKE
PARTS. DO NOT SAND OR GRIND BRAKE LINING
UNLESS EQUIPMENT USED IS DESIGNED TO CON-
TAIN THE DUST RESIDUE. DO NOT CLEAN BRAKE
PARTS WITH COMPRESSED AIR OR BY DRY
BRUSHING. CLEANING SHOULD BE DONE BY
DAMPENING THE BRAKE COMPONENTS WITH A
FINE MIST OF WATER, THEN WIPING THE BRAKE
COMPONENTS CLEAN WITH A DAMPENED CLOTH.
DISPOSE OF CLOTH AND ALL RESIDUE CONTAIN-
ING ASBESTOS FIBERS IN AN IMPERMEABLE
CONTAINER WITH THE APPROPRIATE LABEL. FOL-
LOW PRACTICES PRESCRIBED BY THE OCCUPA-
TIONAL SAFETY AND HEALTH ADMINISTRATION
(OSHA) AND THE ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
AGENCY (EPA) FOR THE HANDLING, PROCESSING,
AND DISPOSING OF DUST OR DEBRIS THAT MAY
CONTAIN ASBESTOS FIBERS.
CAUTION
CAUTION: During service procedures, grease or
any other foreign material must be kept off brake
shoe assemblies, and braking surfaces of brake
rotor or drum, and external surfaces of hub and
bearing assembly.
CAUTION: Handling of brake rotors and calipers
must be done in such a way as to avoid damage to
the rotor and scratching or nicking of brake lining
on the brake shoes.
CAUTION: At no time when servicing a vehicle, can
a sheet metal screw, bolt or other metal fastener be
installed in the shock tower to take the place of an
original plastic clip. Also, NO holes can be drilled
into the front shock tower in the area shown in (Fig.1), for the installation of any metal fasteners into
the shock tower. Because of the minimum clear-
ance in this area (Fig. 1), installation of metal fas-
teners could damage the coil spring coating and
lead to a corrosion failure of the spring. If a plastic
clip is missing, or is lost or broken during servicing
a vehicle, replace only with the equivalent part
listed in the Mopar parts catalog.
CAUTION: Only the recommended jacking or hoist-
ing positions for this vehicle are to be used when-
ever it is necessary to lift a vehicle. Failure to raise
a vehicle from the recommended locations could
result in lifting a vehicle by the hydraulic control
unit mounting bracket. Lifting a vehicle by the
hydraulic control unit mounting bracket will result
in damage to the mounting bracket and the hydrau-
lic control unit.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BASE BRAKE
SYSTEM
NOTE: There are three diagnosis charts following
that cover the RED BRAKE WARNING INDICATOR
LAMP, BRAKE NOISE and OTHER BRAKE CONDI-
TIONS.
Fig. 1 Shock Tower To Spring Minimum Clearance
Area
1 - SHOCK TOWER
2 - COIL SPRING
3 - NO SHEET METAL SCREWS, BOLTS, OR ANY OTHER
METAL FASTENERS ARE TO BE INSTALLED INTO SHOCK
TOWER IN THIS AREA. ALSO, NO HOLES ARE TO BE DRILLED
INTO SHOCK TOWER IN THIS SAME AREA.
5 - 4 BRAKES - BASERS
BRAKES - BASE (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 135 of 2399
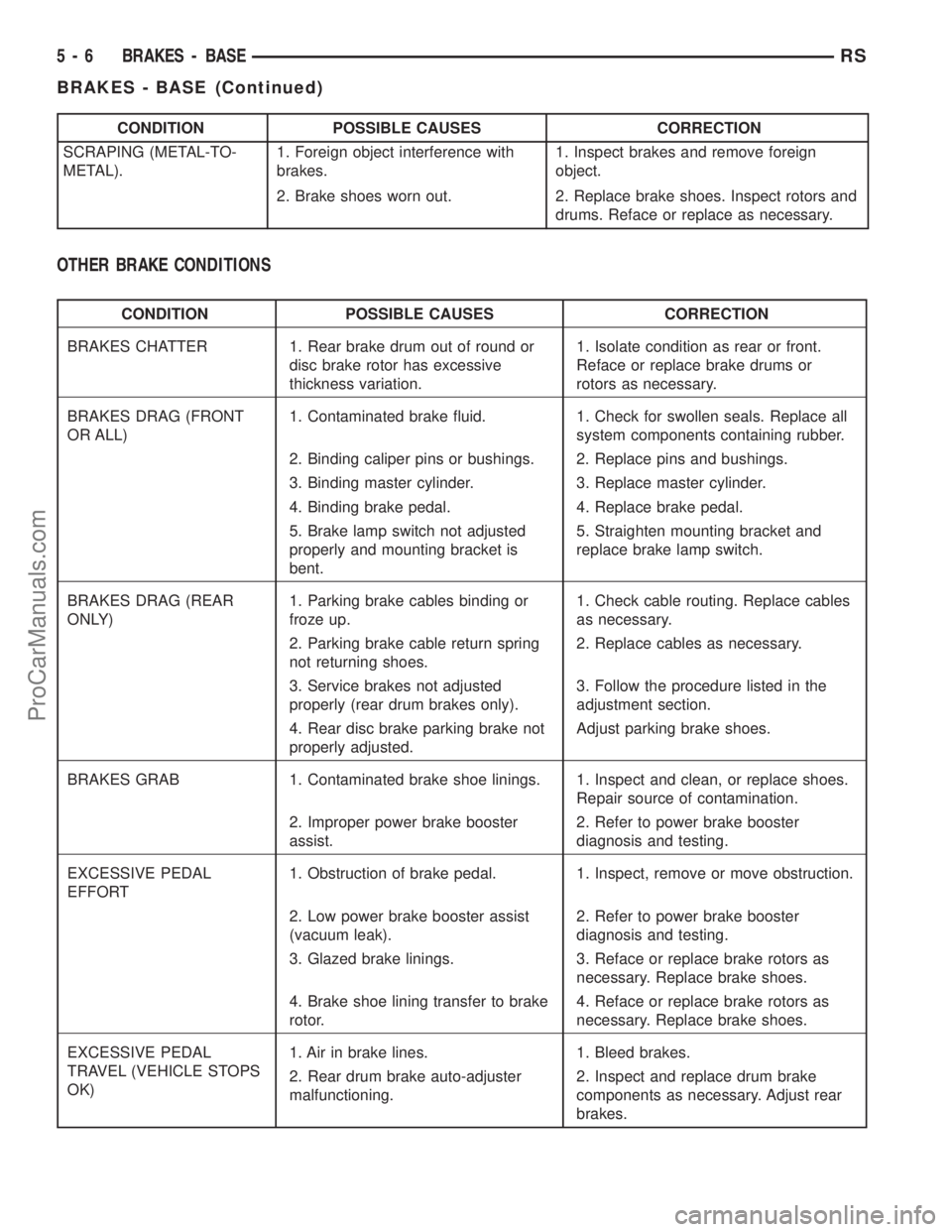
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
SCRAPING (METAL-TO-
METAL).1. Foreign object interference with
brakes.1. Inspect brakes and remove foreign
object.
2. Brake shoes worn out. 2. Replace brake shoes. Inspect rotors and
drums. Reface or replace as necessary.
OTHER BRAKE CONDITIONS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
BRAKES CHATTER 1. Rear brake drum out of round or
disc brake rotor has excessive
thickness variation.1. Isolate condition as rear or front.
Reface or replace brake drums or
rotors as necessary.
BRAKES DRAG (FRONT
OR ALL)1. Contaminated brake fluid. 1. Check for swollen seals. Replace all
system components containing rubber.
2. Binding caliper pins or bushings. 2. Replace pins and bushings.
3. Binding master cylinder. 3. Replace master cylinder.
4. Binding brake pedal. 4. Replace brake pedal.
5. Brake lamp switch not adjusted
properly and mounting bracket is
bent.5. Straighten mounting bracket and
replace brake lamp switch.
BRAKES DRAG (REAR
ONLY)1. Parking brake cables binding or
froze up.1. Check cable routing. Replace cables
as necessary.
2. Parking brake cable return spring
not returning shoes.2. Replace cables as necessary.
3. Service brakes not adjusted
properly (rear drum brakes only).3. Follow the procedure listed in the
adjustment section.
4. Rear disc brake parking brake not
properly adjusted.Adjust parking brake shoes.
BRAKES GRAB 1. Contaminated brake shoe linings. 1. Inspect and clean, or replace shoes.
Repair source of contamination.
2. Improper power brake booster
assist.2. Refer to power brake booster
diagnosis and testing.
EXCESSIVE PEDAL
EFFORT1. Obstruction of brake pedal. 1. Inspect, remove or move obstruction.
2. Low power brake booster assist
(vacuum leak).2. Refer to power brake booster
diagnosis and testing.
3. Glazed brake linings. 3. Reface or replace brake rotors as
necessary. Replace brake shoes.
4. Brake shoe lining transfer to brake
rotor.4. Reface or replace brake rotors as
necessary. Replace brake shoes.
EXCESSIVE PEDAL
TRAVEL (VEHICLE STOPS
OK)1. Air in brake lines. 1. Bleed brakes.
2. Rear drum brake auto-adjuster
malfunctioning.2. Inspect and replace drum brake
components as necessary. Adjust rear
brakes.
5 - 6 BRAKES - BASERS
BRAKES - BASE (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 144 of 2399

front brakes utilize the familiar internally-vented hat
style rotor. Internally-vented refers to the fact that
the inner most diameter of the braking disc vents to
the inboard side of the rotor (Fig. 16).
CAUTION: TRW and Continental Teves brake rotors
are not interchangeable. If brake rotors are inter-
changed, noise and wear problems can result.
DESCRIPTION - DISC BRAKES (REAR)
There are several distinctive features to the rear
disc brakes on this vehicle (Fig. 17). The single pis-
ton, floating caliper rear disc brake system includes a
hub and bearing assembly, adapter, rotor, caliper, and
brake shoes.
This vehicle is equipped with a caliper having a 42
mm (1.65 in.) piston and uses a 15 inch solid non-
vented brake rotor. The brake rotor is described as a
drum-in-hat style because of its dual role as a brak-
ing disc and parking brake drum.
The parking brake system on vehicles equipped
with rear disc brakes consists of a small duo-servo
drum brake mounted to the caliper adapter and uses
the interior of the rear disc brake rotor as a drum
(hat section of drum-in-hat style brake rotor).
The outboard rear disc brake shoes (pads) are side-
oriented. The shoes are marked indicating which side
they belong on.
DESCRIPTION - DISC BRAKES (EXPORT)
All vehicles are equipped with Four-Wheel-Disc
brakes. Both 15º (BRE) and 16º (BR3) disc/disc brake
systems are available. The disc brakes are manufac-
tured by Continental Teves. The BR3 system is stan-
dard equipment on all-wheel drive and all right-hand
drive models. It is optional on other models.
The BR3 system features larger, externally vented
front brake rotors.
Although there are different disc/disc systems, they
are serviced using the same service procedures. Some
specifications differ.
Fig. 15 ANTI-RATTLE DEVICES ON CALIPERS
1 - CONTINENTAL TEVES CALIPER
2 - TRW CALIPER
3 - ANTI-RATTLE CLIP
4 - ANTI-RATTLE CLIP
Fig. 16 Externally and Internally Vented Rotors
(Cross-Sectional View)
1 - EXTERNAL VENTS (TRW)
2 - INTERNAL VENTS (Continetal Teves)
Fig. 17 Rear Disc Brakes
1 - CALIPER
2 - COTTER PIN
3 - ROTOR
4 - NUT RETAINER
5 - OUTER C/V JOINT
RSBRAKES - BASE5-15
HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 145 of 2399

DESCRIPTION - DRUM BRAKES (REAR)
This vehicle's rear wheel drum brakes are a two-
shoe, internal-expanding type with an automatic
adjuster screw. The automatic adjuster screw is
located directly below the wheel cylinder that is
mounted near the top of the brake assembly (Fig.
18). These and two brake shoes (and attaching parts)
are mounted to a support plate at each rear wheel. A
brake drum covers each brake assembly.
OPERATION
OPERATION - DISC BRAKES (FRONT)
When the brakes are applied, fluid pressure is sent
to each brake caliper. The pressure at the caliper is
exerted equally against the caliper piston. The pres-
sure applied to the piston is transmitted directly to
the inboard brake shoe. This forces the shoe lining
against the inner surface of the brake rotor. At the
same time, fluid pressure within the caliper piston
bore forces the caliper to slide inward on its guide
pins. This action brings the outboard shoe lining into
contact with the outer surface of the brake rotor.
This pressure on both sides of the brake rotor causes
friction, bringing the vehicle to a stop.
When the brake pedal is released, so is the fluid
pressure. The piston seal inside the caliper is
designed to pull the piston back into the bore of the
caliper when the brake pedal is released (Fig. 19).
This action helps maintain the proper brake shoe-to-
rotor clearance.
As disc brake shoe linings wear, master cylinder
reservoir brake fluid level will drop. Adjust as neces-sary. Fluid level should always be checked after
replacing shoes.
OPERATION - DISC BRAKES (REAR)
The rear disc brakes operate similarly to front disc
brakes, however, there are some features that require
different service procedures.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - DRUM BRAKE
AUTOMATIC ADJUSTER
The rear drum brakes on this vehicle automatically
adjust when required during the normal operation of
the vehicle every time the brakes are applied. Use
the following procedure to test the operation of the
automatic adjuster.
Place the vehicle on a hoist with a helper in the
driver's seat to apply the brakes. Remove the access
plug from the adjustment hole in each brake support
plate to provide visual access of the brake adjuster
star wheel.
To eliminate the condition where maximum adjust-
ment of the rear brake shoes does not allow the auto-
matic adjuster to operate when tested, back the star
wheel off approximately 30 notches. It will be neces-
sary to hold the adjuster lever away from the star
wheel to permit this adjustment.
Have the helper apply the brakes. Upon applica-
tion of the brake pedal, the adjuster lever should
move down, turning the adjuster star wheel. Thus, a
definite rotation of the adjuster star wheel can be
observed if the automatic adjuster is working prop-
erly. If one or more adjusters do not function prop-
erly, the respective drum must be removed for
adjuster servicing.
Fig. 18 Drum Brake Assembly (Right Shown)
1 - WHEEL CYLINDER
2 - BRAKE SHOE UPPER RETURN SPRING
3 - AUTOMATIC ADJUSTER LEVER
4 - TENSION CLIP
5 - AUTOMATIC ADJUSTER ASSEMBLY
Fig. 19 Caliper Piston Seal Function For Automatic
Adjustment
1 - PISTON
2 - CYLINDER BORE
3 - PISTON SEAL BRAKE PRESSURE OFF
4 - CALIPER HOUSING
5 - DUST BOOT
6 - PISTON SEAL BRAKE PRESSURE ON
5 - 16 BRAKES - BASERS
HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 146 of 2399

BRAKE LINES
DESCRIPTION - BRAKE TUBES AND HOSES
The brake tubes are steel with a corrosion-resis-
tant nylon coating applied to the external surfaces.
The flex hoses are made of reinforced rubber with fit-
tings at each end.
The primary and secondary brake tubes leading
from the master cylinder to the ABS ICU Hydraulic
Control Unit (HCU) or the non-ABS junction block
have a special flexible section. This flexible section is
required due to cradle movement while the vehicle is
in motion (The ICU and non-ABS junction block are
mounted to the cradle).If replacement of these
lines is necessary, only the original factory
brake line containing the flexible section must
be used.
OPERATION - BRAKE TUBES AND HOSES
The purpose of the chassis brake tubes and flex
hoses is to transfer the pressurized brake fluid devel-
oped by the master cylinder to the wheel brakes of
the vehicle. The flex hoses are made of rubber to
allow for the movement of the vehicle's suspension.
INSPECTION - BRAKE TUBES AND HOSES
Flexible rubber hose is used at both front brakes
and at the rear axle. Inspection of brake hoses
should be performed whenever the brake system is
serviced and every 7,500 miles or 12 months, which-
ever comes first (every engine oil change). Inspect
hydraulic brake hoses for surface cracking, scuffing,
or worn spots. If the fabric casing of the rubber hose
becomes exposed due to cracks or abrasions in the
rubber hose cover, the hose should be replaced imme-
diately. Eventual deterioration of the hose can take
place with possible burst failure. Faulty installation
can cause twisting, resulting in wheel, tire, or chassis
interference.
The brake tubing should be inspected periodically
for evidence of physical damage or contact with mov-
ing or hot components.
The flexible brake tube sections used on this vehi-
cle in the primary and secondary tubes from the
master cylinder to the ABS hydraulic control unit
connections must also be inspected. This flexible tub-
ing must be inspected for kinks, fraying and contact
with other components or with the body of the vehi-
cle.
BRAKE PADS/SHOES - FRONT
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - FRONT DISC BRAKE SHOES
(DISC/DISC BRAKES)
(1) Raise the vehicle. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE/HOISTING - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE).
(2) Remove both front wheel and tire assemblies.
(3) Begin on one side of the vehicle.
(4) Remove the anti-rattle clip from the outboard
side of the caliper and adapter.
(5) Remove the two caliper guide pin bolts.
(6) Remove caliper from caliper adapter and brake
rotor.
CAUTION: Supporting weight of caliper by the flex-
ible brake fluid hose can damage the hose.
(7) Using wire or cord, hang the caliper from the
front strut assembly (Fig. 20). Support the caliper
firmly to prevent weight of caliper from being sup-
ported by the brake fluid hose.
(8) Remove the outboard brake shoe from the cali-
per adapter.
(9) Pull the inboard brake shoe away from the cal-
iper piston until the retaining clip on shoe is free
from the cavity in the caliper piston (Fig. 21).
(10) Repeat the above procedure on other side of
the vehicle.
Fig. 20 Stored Front Disc Brake Caliper
1 - STEERING KNUCKLE
2 - BRAKE FLEX HOSE
3 - CALIPER ASSEMBLY
4 - WIRE HANGER
5 - STRUT ASSEMBLY
RSBRAKES - BASE5-17
ProCarManuals.com
Page 163 of 2399

DISC BRAKE CALIPER
ADAPTER
REMOVAL - FRONT DISC BRAKE CALIPER
ADAPTER
(1) Raise vehicle. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE/HOISTING - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE)
(2) Remove front wheel and tire assembly, disc
brake caliper and brake shoes. (Refer to 5 - BRAKES/
HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL/BRAKE PADS/SHOES
- REMOVAL)
(3) Remove two bolts fastening adapter to steering
knuckle, then remove disc brake caliper adapter.
INSTALLATION - FRONT DISC BRAKE CALIPER
ADAPTER
(1) Place adapter over brake rotor and align
adapter mounting holes to knuckle.
CAUTION: Adapter mounting bolts have a special
DacrometTcoating applied to resist corrosion. If
mounting bolts need to be replaced, use only
MoparTreplacement parts.
(2) Install adapter mounting bolts and tighten to
169 N´m (125 ft. lbs.) torque.
(3) Install brake shoes, disc brake caliper and
wheel and tire assembly. (Refer to 5 - BRAKES/HY-
DRAULIC/MECHANICAL/BRAKE PADS/SHOES -
INSTALLATION)
(4) Lower vehicle.
(5) Pump the brake pedal several times to set the
pads to the brake rotor.
(6) Check and adjust brake fluid level as neces-
sary.
DISC BRAKE CALIPER GUIDE
PINS
REMOVAL - DISC BRAKE CALIPER GUIDE PINS
(DISC/DRUM BRAKES)
(1) Raise the vehicle. Refer to HOISTING in
LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE.
(2) Remove the front tire and wheel assembly.
(3) Remove the two brake caliper guide pin bolts
(Fig. 51).
(4) Remove the disc brake caliper from the disc
brake caliper adapter and hang it out of the way
using wire or a bungee cord. Use care not to overex-
tend the brake hose when doing this.
(5) Remove the guide pins and boots from the
adapter as shown (Fig. 52).
INSTALLATION - DISC BRAKE CALIPER GUIDE
PINS (DISC/DRUM BRAKES)
(1) Lubricate the guide pins and inside the boots
with the packet supplied with the service kit, Syth-
eso GLK-1 lubricant or equivalent.
(2) Install the guide pins and boots in the adapter
as shown (Fig. 52). The boots have grooves built into
their inner lips to fit onto the pins and adapter.
CAUTION: Use care when installing the caliper onto
the disc brake adapter to avoid damaging the boots
on the caliper guide pins.
Fig. 51 Brake Caliper Mounting
1 - BRAKE HOSE
2 - ADAPTER MOUNTING BOLTS
3 - BANJO BOLT
4 - CALIPER GUIDE PIN BOLTS
Fig. 52 Guide Pins And Boots
1 - PINS
2 - BOOTS
5 - 34 BRAKES - BASERS
ProCarManuals.com