parking brake CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2002 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2002, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2002Pages: 2399, PDF Size: 57.96 MB
Page 1579 of 2399

ASSEMBLY...........................115
SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID
DESCRIPTION........................115
OPERATION..........................115
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BRAKE/
TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK
SOLENOID..........................117
REMOVAL............................117
INSTALLATION........................118
SOLENOID - TCC
DESCRIPTION........................119
OPERATION..........................119
REMOVAL............................119
INSTALLATION........................120
THROTTLE VALVE CABLE
REMOVAL............................120
INSTALLATION........................121
ADJUSTMENTS
THROTTLE VALVE LINKAGE
ADJUSTMENT.......................122
TORQUE CONVERTER
DESCRIPTION........................122
OPERATION..........................126
REMOVAL............................127
INSTALLATION........................127
TRANSFER SYSTEM - OUTPUT SHAFT/GEAR/
BEARING
REMOVAL............................128INSTALLATION........................131
ADJUSTMENTS
ADJUSTMENT - OUTPUT SHAFT BEARING . 135
TRANSFER SYSTEM - TRANSFER SHAFT/
GEAR/BEARING
REMOVAL............................137
INSTALLATION........................141
ADJUSTMENTS
ADJUSTMENT - TRANSFER SHAFT
BEARING...........................145
VALVE BODY
REMOVAL............................146
DISASSEMBLY........................148
CLEANING...........................154
INSPECTION.........................155
ASSEMBLY...........................155
INSTALLATION........................158
ADJUSTMENTS
HYDRAULIC CONTROL PRESSURE
ADJUSTMENTS......................160
VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR/PINION GEAR
REMOVAL............................160
INSTALLATION........................160
31TH AUTOMATIC
TRANSAXLE
DESCRIPTION
This transaxle combines torque converter, three
speed transmission, final drive gearing, and differen-
tial into a front wheel drive system.
Within this transaxle, there are three primary
areas:
(1) Main center line plus valve body.
(2) Transfer shaft center line (includes governor
and parking sprag).
(3) Differential center line.
Center distances between the main rotating parts
in these three areas are held precise to maintain a
low noise level.
The torque converter, transaxle area, and differen-
tial are housed in an integral aluminum die casting.
The differential oil sump is common with the
transaxle sump. Separate filling of the differen-
tial is NOT necessary.
The torque converter is attached to the crankshaft
through a flexible driving plate. Cooling of the con-
verter is accomplished by circulating the transaxle
fluid through a remote cooler. There are two types of
coolers used. An oil-to-water type cooler located in
the radiator side tank and/or an oil-to-air heatexchanger. The torque converter assembly is a sealed
unit that cannot be disassembled.
The transaxle fluid is filtered by an internal filter
attached to the lower side of the valve body assembly.
Engine torque is transmitted to the torque con-
verter and then through the input shaft to multiple-
disc clutches in the transaxle. The power flow
depends on the application of the clutches and bands.
Refer to Elements in Use Chart in Diagnosis and
Tests section.
The transaxle consists of:
²Two multiple-disc clutches
²An overrunning clutch
²Two servos
²A hydraulic accumulator
²Two bands
²Two planetary gear sets
This provides three forward ratios and a reverse
ratio. The common sun gear of the planetary gear
sets is connected to the front clutch by a driving
shell. The driving shell is splined to the sun gear and
front clutch retainer. The hydraulic system consists
of an oil pump and a single valve body which con-
tains all of the valves except the governor valves.
The transaxle sump and differential sump are both
vented through the dipstick. Output torque from the
main center line is delivered through helical gears to
the transfer shaft. This gear set is a factor in the
transaxle final drive (axle) ratio. The shaft also car-
21 - 22 31TH AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1657 of 2399

(8) Start engine and allow to idle for at least one
minute. Then, with parking and service brakes
applied, move selector lever momentarily to each
position, ending in the park or neutral position.
(9) Check the transaxle fluid level and add an
appropriate amount to bring the transaxle fluid level
to 3mm (1/8 in.) below the ªADDº mark on the dip-
stick (Fig. 168).
(10) Recheck the fluid level after the transaxle has
reached normal operating temperature (180ÉF.).
(Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTO-
MATIC - 31TH/FLUID - STANDARD PROCEDURE)(11) To prevent dirt from entering transaxle, make
certain that dipstick is fully seated into the dipstick
opening.
DIPSTICK TUBE FLUID SUCTION METHOD
(ALTERNATIVE)
(1) When performing the fluid suction method,
make sure the transaxle is at full operating temper-
ature.
(2) To perform the dipstick tube fluid suction
method, use a suitable fluid suction device (VaculaŸ
or equivalent).
(3) Insert the fluid suction line into the dipstick
tube.
NOTE: Verify that the suction line is inserted to the
lowest point of the transaxle oil pan. This will
ensure complete evacuation of the fluid in the pan.
(4) Follow the manufacturers recommended proce-
dure and evacuate the fluid from the transaxle.
(5) Remove the suction line from the dipstick tube.
(6) Pour four quarts of MopartATF+4 (Automatic
Transmission FluidÐType 9602) through the dipstick
opening.
(7) Start engine and allow to idle for at least one
minute. Then, with parking and service brakes
applied, move selector lever momentarily to each
position, ending in the park or neutral position.
(8) Check the transaxle fluid level and add an
appropriate amount to bring the transaxle fluid level
to 3mm (1/8 in.) below the ªADDº mark on the dip-
stick (Fig. 168).
(9) Recheck the fluid level after the transaxle has
reached normal operating temperature (180ÉF.).
(Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTO-
MATIC - 31TH/FLUID - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(10) To prevent dirt from entering transaxle, make
certain that dipstick is fully seated into the dipstick
opening.
Fig. 166 Oil Filter Screws
1 - SCREWDRIVER HANDLE
2 - SPECIAL TOOL L-4553
3 - OIL FILTER SCREWS (2)
4 - OIL FILTER
Fig. 167 Oil Filter and Gasket
1 - OIL FILTER
2 - GASKET
3 - VALVE BODY
Fig. 168 Dipstick Markings
1 - TRANSAXLE DIPSTICK
21 - 100 31TH AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
FLUID (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1661 of 2399

ADJUSTMENTS
GEARSHIFT CABLE ADJUSTMENT
Lift and rotate the gearshift hand lever into the
park (P) gate position and remove the ignition key.
This confirms the shift lever is in the gated park (P)
position.
After confirming the park gate position, turn the
ignition switch . If the starter will operate, the park
gate position is correct. Move the shift lever into the
neutral (N) position. If the starter will operate in this
position, the linkage is properly adjusted. If the
starter fails to operate in either position, linkage
adjustment is required.
(1) Park the vehicle on level ground and set the
parking brake.
(2) Place the gearshift lever in park (P) gate posi-
tion and remove key.
(3) Loosen the cable adjustment screw at the
transaxle operating lever (Fig. 181).
(4) Pull the transaxle operating lever fully forward
to the park detent position.
(5) Release the park brake, then rock the vehicle
to assure it is in park lock. Reset the park brake.
(6) Tighten the cable adjustment screw to 8 N´m
(70 in. lbs.). Gearshift cable should now be properly
adjusted.
(7) Verify PRNDL indicator still displays the corre-
sponding gear completely. If not, readjustment of
PRNDL may be required.
(8) Check adjustment by using the preceding pro-
cedure.
GOVERNOR
DESCRIPTION
The governor assembly is fastened to the transaxle
transfer shaft. It consists of a governor body, weight,
valve, and shaft.
OPERATION
The governor meters hydraulic pressure, and this
metered pressure is used to signal the transmission
when it is time for a shift to occur. It does this by
balancing governor pressure on one side of a shift
valve, and throttle pressure on the other. When gov-
ernor pressure increases far enough to overcome the
throttle pressure on the valve, a shift occurs.
With the gearshift selector in a forward driving
range, line pressure flows from the manual valve and
down to the governor valve. When the output shaft
starts to rotate with vehicle motion, the governor
weight assembly will start to move outward due to
centrifugal force. As the weight is moved outward, it
will pull the valve with it until the land of the valve
uncovers the line pressure port. As the port begins to
become uncovered, governor pressure is metered. As
the vehicle's speed continues to increase, the weight
assembly will be at a point at which governor pres-
sure is acting on the left side of the reaction area of
the valve. This produces sufficient force to compress
the spring and allow the outer weight to move out
against the outer governor body retaining ring. At a
very high speed, the governor valve will be opened as
far as possible. In this condition, it is possible for
governor pressure to meet, but not to exceed, line
pressure. Generally governor pressure ranges from
0-100 psi from idle to maximum speed, and rises pro-
portionally with the increase in output shaft speed.
Governor pressure and throttle pressure are acting
upon the shift valves to determine when a shift will
occur. Governor pressure is a direct indication of road
speed, and throttle pressure is an indication of
engine load. When both parameters have been met
by the throttle and governor pressures, an upshift or
downshift will occur.
CLEANING
Thoroughly clean all the governor parts in a suit-
able cleaning solution but do not use any type of
caustic cleaning agents.
The governor weight components and the governor
valve, must slide freely in their bores when clean and
dry. Minor surface scratches and burrs can be
smoothed with crocus cloth.
INSPECTION
The aluminum governor valve and outer weight
have a hard coating on them. Check condition of this
Fig. 181 Gearshift Cable Adjustment
1 - SHIFT CABLE ADJUSTMENT
2 - SHIFT CABLE
21 - 104 31TH AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1806 of 2399

FLUID
STANDARD PROCEDURE
FLUID LEVEL AND CONDITION CHECK
NOTE: Only transmission fluid of the type labeled
Mopar ATF+4 (Automatic Transmission Fluid±Type
9602) should be used in this transaxle.
FLUID LEVEL CHECK
The transmission sump has a fluid level indicator
(dipstick) to check oil similar to most automatic
transmissions. It is located on the left side of the
engine. Be sure to wipe all dirt from dipstick handle
before removing.
The torque converter fills in both the P Park and N
Neutral positions. Place the selector lever in P Park
to be sure that the fluid level check is accurate.The
engine should be running at idle speed for at
least one minute, with the vehicle on level
ground.At normal operating temperature 82É C
(180É F), the fluid level is correct if it is in the HOT
region on the oil level indicator (Fig. 210). The fluid
level should be within the COLD region of the dip-
stick at 27É C (80É F) fluid temperature.
FLUID LEVEL CHECK USING DRB
NOTE: Engine and Transaxle should be at normal
operating temperature before performing this proce-
dure.
(1) Start engine and apply parking brake.
(2)
Hook up DRB scan tool and select transmission.
(3) Select sensors.
(4) Read the transmission temperature value.
(5) Compare the fluid temperature value with the
fluid temperature chart (Fig. 211).
Fig. 210 Fluid Level Indicator
1 - FLUID LEVEL INDICATOR
Fig. 211 Transmission Fluid Temperature Chart
1 - MAX. LEVEL
2 - MIN. LEVEL
RS41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 249
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1807 of 2399

(6) Adjust transmission fluid level shown on the
indicator according to the chart.
(7) Check transmission for leaks.
Low fluid level can cause a variety of conditions
because it allows the pump to take in air along with
the fluid. As in any hydraulic system, air bubbles
make the fluid spongy, therefore, pressures will be
low and build up slowly.
Improper filling can also raise the fluid level too
high. When the transaxle has too much fluid, the
gears churn up foam and cause the same conditions
which occur with a low fluid level.
In either case, air bubbles can cause overheating
and/or fluid oxidation, and varnishing. This can
interfere with normal valve, clutch, and accumulator
operation. Foaming can also result in fluid escaping
from the transaxle vent where it may be mistaken
for a leak.
FLUID CONDITION
Along with fluid level, it is important to check the
condition of the fluid. When the fluid smells burned,
and is contaminated with metal or friction material
particles, a complete transaxle recondition is proba-
bly required. Be sure to examine the fluid on the dip-
stick closely. If there is any doubt about its condition,
drain out a sample for a double check.
MopartATF+4 (Automatic Transmission Fluid-
Type 9602) when new is red in color. The ATF is dyed
red so it can be identified from other fluids used in
the vehicle such as engine oil or antifreeze. The red
color is not permanent and is not an indicator of fluid
condition. As the vehicle is driven, the ATF will begin
to look darker in color and may eventually become
brown.This is normal.ATF+4 also has a unique
odor that may change with age. Consequently,odor
and color cannot be used to indicate the fluid
condition or the need for a fluid change.
After the fluid has been checked, seat the dipstick
fully to seal out water and dirt.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID AND FILTER
SERVICE
NOTE: Refer to the maintenance schedules in
LUBRICATION and MAINTENANCE, or the vehicle
owner's manual, for the recommended maintenance
(fluid/filter change) intervals for this transaxle.
NOTE: Only fluids of the type labeled MoparTATF+4
(Automatic Transmission Fluid) Type 9602 should
be used. A filter change should be made at the time
of the transmission oil change. The magnet (on the
inside of the oil pan) should also be cleaned with a
clean, dry cloth.NOTE: If the transaxle is disassembled for any rea-
son, the fluid and filter should be changed.
FLUID/FILTER SERVICE (RECOMMENDED)
(1) Raise vehicle on a hoist. Refer to LUBRICA-
TION and MAINTENANCE for proper procedures.
Place a drain container with a large opening, under
transaxle oil pan.
(2) Loosen pan bolts and tap the pan at one corner
to break it loose allowing fluid to drain, then remove
the oil pan.
(3) Install a new filter and o-ring on bottom of the
valve body (Fig. 212).
(4) Clean the oil pan and magnet. Reinstall pan
using new Mopar Silicone Adhesive sealant. Tighten
oil pan bolts to 19 N´m (165 in. lbs.).
(5) Pour four quarts of MopartATF+4 (Automatic
Transmission Fluid) Type 9602 through the dipstick
opening.
(6) Start engine and allow to idle for at least one
minute. Then, with parking and service brakes
applied, move selector lever momentarily to each
position, ending in the park or neutral position.
Fig. 212 Filter and O-Ring
1 - OIL FILTER
2 - O-RING
21 - 250 41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
FLUID (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1808 of 2399
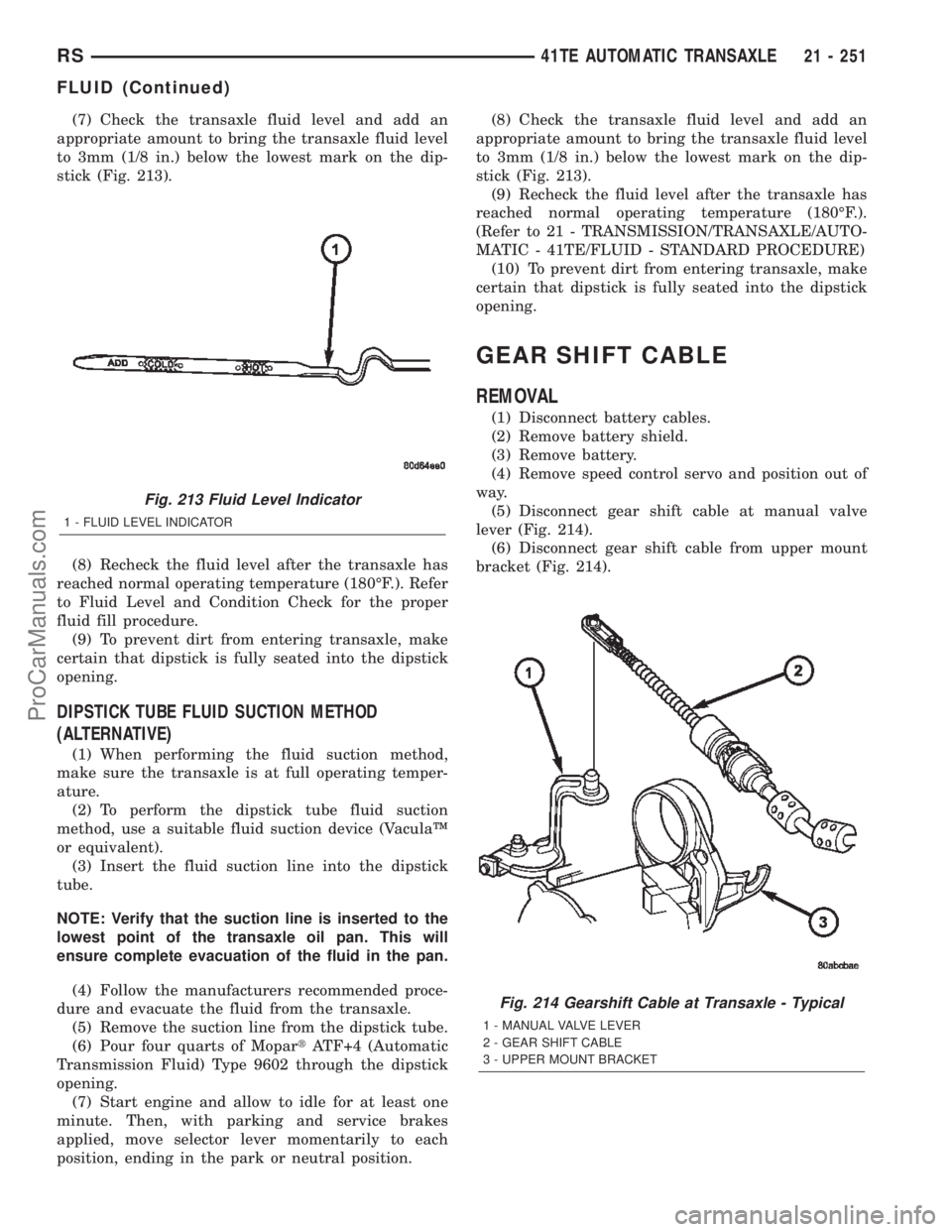
(7) Check the transaxle fluid level and add an
appropriate amount to bring the transaxle fluid level
to 3mm (1/8 in.) below the lowest mark on the dip-
stick (Fig. 213).
(8) Recheck the fluid level after the transaxle has
reached normal operating temperature (180ÉF.). Refer
to Fluid Level and Condition Check for the proper
fluid fill procedure.
(9) To prevent dirt from entering transaxle, make
certain that dipstick is fully seated into the dipstick
opening.
DIPSTICK TUBE FLUID SUCTION METHOD
(ALTERNATIVE)
(1) When performing the fluid suction method,
make sure the transaxle is at full operating temper-
ature.
(2) To perform the dipstick tube fluid suction
method, use a suitable fluid suction device (VaculaŸ
or equivalent).
(3) Insert the fluid suction line into the dipstick
tube.
NOTE: Verify that the suction line is inserted to the
lowest point of the transaxle oil pan. This will
ensure complete evacuation of the fluid in the pan.
(4) Follow the manufacturers recommended proce-
dure and evacuate the fluid from the transaxle.
(5) Remove the suction line from the dipstick tube.
(6) Pour four quarts of MopartATF+4 (Automatic
Transmission Fluid) Type 9602 through the dipstick
opening.
(7) Start engine and allow to idle for at least one
minute. Then, with parking and service brakes
applied, move selector lever momentarily to each
position, ending in the park or neutral position.(8) Check the transaxle fluid level and add an
appropriate amount to bring the transaxle fluid level
to 3mm (1/8 in.) below the lowest mark on the dip-
stick (Fig. 213).
(9) Recheck the fluid level after the transaxle has
reached normal operating temperature (180ÉF.).
(Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTO-
MATIC - 41TE/FLUID - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(10) To prevent dirt from entering transaxle, make
certain that dipstick is fully seated into the dipstick
opening.
GEAR SHIFT CABLE
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery cables.
(2) Remove battery shield.
(3) Remove battery.
(4) Remove speed control servo and position out of
way.
(5) Disconnect gear shift cable at manual valve
lever (Fig. 214).
(6) Disconnect gear shift cable from upper mount
bracket (Fig. 214).
Fig. 213 Fluid Level Indicator
1 - FLUID LEVEL INDICATOR
Fig. 214 Gearshift Cable at Transaxle - Typical
1 - MANUAL VALVE LEVER
2 - GEAR SHIFT CABLE
3 - UPPER MOUNT BRACKET
RS41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 251
FLUID (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1811 of 2399

(6) Install gear shift cable to transaxle upper
mount bracket (Fig. 223). An audible ªclickº should
be heard.
(7) Connect gear shift cable end to transaxle man-
ual valve lever (Fig. 223).
(8) Adjust gearshift cable. (Refer to 21 - TRANS-
MISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC - 41TE/GEAR
SHIFT CABLE - ADJUSTMENTS)
(9) Install speed control servo into position.
(10) Install battery.
(11) Install battery shield.
(12) Connect battery cables.
ADJUSTMENTS
GEARSHIFT CABLE ADJUSTMENT
VERIFICATION
(1) Place gearshift lever in gated park (P).
(2) Attempt to move vehicle by rocking back and
forth on level ground. If vehicle does not move,
attempt to start engine. If engine starts, the park
position is correct.
(3) Set parking brake.
(4) Turn key to on/run and depress brake pedal.
Place gearshift lever in neutral (N).(5) Attempt to start engine. If engine starts in
both neutral (N) or park (P), gearshift cable is
adjusted properly. No adjustment is required.
(6) If engine does not start in either park (P) or
neutral (N), perform adjustment procedure.
ADJUSTMENT
(1) Park the vehicle on level ground and set the
parking brake.
(2) Place the gearshift lever in gated park (P) and
remove ignition key.
(3) Loosen the cable adjustment screw at the
transaxle manual valve lever (Fig. 224).
(4) Pull the gearshift lever fully forward to the
park detent position.
(5) Release the park brake, then rock the vehicle
to assure it is in park. Reset the park brake.
(6) Tighten the cable adjustment screw to 8 N´m
(70 in. lbs.). Gearshift cable should now be properly
adjusted.
(7) Verify adjustment by using the verification pro-
cedure.
Fig. 223 Gearshift Cable at Transaxle
1 - MANUAL VALVE LEVER
2 - GEAR SHIFT CABLE
3 - UPPER MOUNT BRACKET
Fig. 224 Gearshift Cable Adjustment
1 - GEARSHIFT CABLE ADJUSTMENT SCREW
2 - GEARSHIFT CABLE
21 - 254 41TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
GEAR SHIFT CABLE (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 1996 of 2399

MOPARTSPRAY WHITE LUBE OR EQUIVALENT
²Door Check Straps
²Liftgate Latches
²Liftgate Prop Pivots
²Ash Receiver
²Fuel Filler Door Remote Control Latch Mecha-
nism
²Parking Brake Mechanism
²Sliding Seat Tracks
²Liftgate Latch
MOPARTMultipurpose GREASE OR EQUIVALENT
²All Other Hood Mechanisms
MOPARTLOCK CYLINDER LUBRICANT OR
EQUIVALENT
²Door Lock Cylinders
²Liftgate Lock Cylinder
SPECIAL TOOLS
BODY
INDEX
DESCRIPTION FIGURE
STICK, TRIM C 4755 16
REMOVER, MOLDINGS C-4829 17
PLIERS, HEADLINER CLIP 6967 18
Fig. 16 STICK, TRIM C 4755
Fig. 17 REMOVER, MOLDINGS C-4829
Fig. 18 PLIERS, HEADLINER CLIP 6967
RSBODY23-13
BODY (Continued)
ProCarManuals.com
Page 2376 of 2399

PCV VALVE
DESCRIPTION
The PCV valve contains a spring loaded plunger.
The plunger meters the amount of crankcase vapors
routed into the combustion chamber based on intake
manifold vacuum (Fig. 7) or (Fig. 8).
OPERATION
When the engine is not operating or during an
engine backfire, the spring forces the plunger back
against the seat. This prevents vapors from flowing
through the valve (Fig. 9).
When the engine is at idle or cruising, high mani-
fold vacuum is present. At these times manifold vac-
uum is able to completely compress the spring and
pull the plunger to the top of the valve (Fig. 10). In
this position there is minimal vapor flow through the
valve.
During periods of moderate intake manifold vac-
uum the plunger is only pulled part way back from
the inlet. This results in maximum vapor flow
through the valve (Fig. 11).
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - PCV SYSTEM
WARNING: APPLY PARKING BRAKE AND/OR
BLOCK WHEELS BEFORE PERFORMING ANY TEST
OR ADJUSTMENT WITH THE ENGINE OPERATING.
(1) With engine idling, remove the hose from the
PCV valve. If the valve is not plugged, a hissing
Fig. 7 PCV VALVE 2.4L
1 - PCV Valve
Fig. 8 PCV VALVE 3.3/3.8L
Fig. 9 Engine Off or Engine Backfire No Vapor Flow
Fig. 10 High Intake Manifold Vacuum Minimal Vapor
Flow
Fig. 11 Moderate Intake Manifold Vacuum Maximum
Vapor Flow
RSEVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS25-17
ProCarManuals.com