Gasoline CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2004 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2004, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2004Pages: 2585, PDF Size: 62.54 MB
Page 1509 of 2585

FUEL DELIVERY
DESCRIPTION
The front wheel drive car uses a plastic fuel tank
located rear center of the vehicle.
The Fuel Delivery System consists of: the following
items:
²Electric fuel pump module
²Fuel filter
²Tubes/lines/hoses
²Fuel injectors
The in-tank fuel pump module contains the fuel
pump. The pump is serviced as part of the fuel pump
module. Refer to Fuel Pump Module.
The fuel filter is replaceable only as part of the
fuel pump module.
OPERATION
The fuel system provides fuel pressure by an
in-tank pump module. The Powertrain Control Mod-
ule (PCM) controls the operation of the fuel system
by providing battery voltage to the fuel pump
through the fuel pump relay. The PCM requires only
three inputs and a good ground to operate the fuel
pump relay. The three inputs are:
²Ignition voltage
²Crankshaft Position (CKP) sensor
²Camshaft Position (CMP) sensor
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - FUEL DELIVERY
SYSTEM
(Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic Information)
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FUEL SYSTEM
PRESSURE RELEASE PROCEDURE
(1) Remove Fuel Pump relay from Power Distribu-
tion Center (PDC). For location of relay, refer to label
on underside of PDC cover.
(2) Start and run engine until it stalls.
(3) Attempt restarting engine until it will no
longer run.
(4) Turn ignition key to OFF position.
(5) Return fuel pump relay to PDC.
(6) One or more Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC's)
may have been stored in PCM memory due to fuel
pump relay removal. The DRB IIItscan tool must be
used to erase a DTC.
STANDARD PROCEDURE - DRAINING FUEL
TANK
Two different procedures may be used to drain fuel
tank (lowering tank or using DRBIIItscan tool).The quickest draining procedure involves lowering
the fuel tank.
WARNING: RELEASE FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE
BEFORE SERVICING FUEL SYSTEM COMPONENTS.
SERVICE VEHICLES IN WELL VENTILATED AREAS
AND AVOID IGNITION SOURCES. NEVER SMOKE
WHILE SERVICING THE VEHICLE. THIS MAY
RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY OR DEATH.
As an alternative procedure, the electric fuel pump
may be activated allowing tank to be drained at fuel
rail connection. Refer to DRBIIItscan tool for fuel
pump activation procedures. Before disconnecting
fuel line at fuel rail, release fuel pressure. Refer to
the Fuel System Pressure Release Procedure in this
group for procedures. Disconnect the fuel line at the
fuel rail and remove the plastic retainer from the
fuel rail. Take plastic retainer and install it back into
the fuel line from body. Check the O-ring and make
sure that it is in place and not damaged. Attach end
of special test hose tool number 6539 at fuel line con-
nection from the body line. Position opposite end of
this hose tool to an approved gasoline draining sta-
tion. Activate fuel pump and drain tank until empty.
When done remove the special test hose tool number
6539 from the body line. Remove the plastic retainer
from the special test hose tool number 6539 and rein-
stall it into the fuel line from the body. Check the
O-ring and make sure that it is in place and not
damaged. Install the fuel line to the fuel rail.
If electric fuel pump is not operating, tank must be
lowered for fuel draining. Refer to following proce-
dures.
(1) Remove fuel filler cap.
(2) Perform the Fuel System Pressure Release pro-
cedure.
(3) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(4) Raise vehicle and support.
(5) Certain models are equipped with a separate
grounding wire (strap) connecting the fuel fill tube
assembly to the body. Disconnect wire by removing
screw.
(6) Open fuel fill door and remove screws mount-
ing fuel filler tube assembly to body. Do not discon-
nect rubber fuel fill or vent hoses from tank at this
time.
(7) Place a transmission jack under center of fuel
tank. Apply a slight amount of pressure to fuel tank
with transmission jack.
(8) Remove fuel tank mounting straps.
(9)Lower the tank just enough so that the
filler tube fitting is the highest point of the fuel
tank.
(10) Remove filler tube from fuel tank. Tank will
be drained through this fitting.
14 - 2 FUEL DELIVERYRS
Page 1510 of 2585
NOTE: WRAP SHOP TOWELS AROUND HOSES TO
CATCH ANY GASOLINE SPILLAGE.
(11) Drain fuel tank into holding tank or a prop-
erly labeledGasolinesafety container.
WARNING: GASOLINE OR GASOLINE VAPORS ARE
HIGHLY FLAMMABLE. A FIRE COULD OCCUR IF AN
IGNITION SOURCE IS PRESENT. NEVER DRAIN ORSTORE GASOLINE OR DIESEL FUEL IN AN OPEN
CONTAINER, DUE TO THE POSSIBILITY OF FIRE
OR EXPLOSION. THIS MAY RESULT IN PERSONAL
INJURY OR DEATH.
(12) If fuel pump module removal is necessary,
refer to Fuel Pump Module Removal/Installation in
this section.
SPECIFICATIONS
FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE
400 kpa 34 kpa (58 psi 5 psi)
TORQUE
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Fuel Filler Neck Clamp 3.3 30
Fuel Rail 2.4L 22 195
Fuel Rail 3.3/3.8L 11.8 105
Fuel Tank Strap 54 40
Fuel Tank T Strap 28.2 250
Fuel Filter Bolt 4.5 40
RSFUEL DELIVERY14-3
FUEL DELIVERY (Continued)
Page 1517 of 2585

(6) Remove harness from vehicle.
(7) Remove fuel hose quick connect fitting from the
chassis tube.Refer to Fuel Hoses, Clamps and
Quick Connect Fittings in this Section.Place a
shop towel under the connections to absorb any fuel
spilled from the fitting.
WARNING: WRAP A SHOP TOWEL AROUND HOSES
TO CATCH ANY GASOLINE SPILLAGE.
(8) Remove fuel rail attaching bolts.
(9) Remove fuel rail. Be careful not to damage the
injector O-rings upon removal from their ports.
REMOVAL - 3.3/3.8L
(1) Perform fuel system pressure release procedure
before servicing or starting repairs.Refer to
Fuel System Pressure Release Procedure in this sec-
tion.
(2) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(3) Remove upper intake manifold, refer to the
Engine/Manifolds/Upper Intake for more informa-
tion..
(4) Cover intake manifold with suitable cover
when servicing.
(5) Remove the fuel hose quick connect fitting from
the chassis tube.Refer to Fuel Hoses, Clamps
and Quick Connect Fittings in this Section.
WARNING: WRAP A SHOP TOWEL AROUND HOSES
TO CATCH ANY GASOLINE SPILLAGE.
(6) Remove the fuel rail attaching bolts (Fig. 13).
(7) Remove fuel rail. Be careful not to damage the
injector O-rings upon removal from their ports.
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - 2.4L
(1) Ensure injector holes are clean. Replace
O-rings if damaged.
(2) Lubricate injector O-rings with a drop of clean
engine oil to ease installation.
(3) Put the tip of each injector into their ports.
Push the assembly into place until the injectors are
seated in the ports.
(4) Install the fuel rail mounting bolts. Tighten
bolts to 22 N´m (200 in. lbs.) torque.
(5) Connect the connectors to the fuel injectors.
(6) Install wiring harness to brackets.
(7) Connect the wiring connectors to fuel injectors
harness (Fig. 12).
(8) Connect negative battery cable.
(9) Use the DRBIIItscan tool to pressurize the
fuel system. Check for leaks.
INSTALLATION - 3.3/3.8L
(1) Ensure injector holes are clean. Replace
O-rings if damaged.
(2) Lubricate injector O-rings with a drop of clean
engine oil to ease installation.
(3) Put the tip of each injector into their ports.
Push the assembly into place until the injectors are
seated in the ports.
(4) Install the fuel rail mounting bolts. Tighten
bolts to 22 N´m (200 in. lbs.) torque.
(5) Remove covering on lower intake manifold and
clean surface.
(6) Install the Upper Intake Manifold, refer to
Engine/Manifolds/Upper Intake for more information.
(7) Install fuel hose quick connector fitting to chas-
sis tubes.Refer to Fuel Hoses, Clamps and
Quick Connect Fittings in this Section.Push the
fitting onto the chassis tube until it clicks into place.
Pull on the fitting to ensure complete insertion.
(8) Connect negative cable to battery.
(9) Use the DRBIIItscan tool to pressurize the
fuel system. Check for leaks.
FUEL TANK
DESCRIPTION
The fuel tank is constructed of a plastic material.
Its main functions are for fuel storage and for place-
ment of the fuel pump module. The tank is made
from High density Polyethylene (HDPE) material.If
equipped with ORVR (Onboard Refueling Vapor
Recovery) it has been added to the fuel tank to con-
trol refueling vapor emissions.
Fig. 13 FUEL INJECTORS 3.3/3.8L
14 - 10 FUEL DELIVERYRS
FUEL RAIL (Continued)
Page 1518 of 2585
OPERATION
All models pass a full 360 degree rollover test
without fuel leakage. To accomplish this, fuel and
vapor flow controls are required for all fuel tank con-
nections.
All models are equipped with either one or two
check valves mounted into the top of the fuel tank (or
pump module).
An evaporation control system is connected to the
check valve(s)/control valve(Refer to 25 - EMIS-
SIONS CONTROL/EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS/
ORVR - OPERATION) to reduce emissions of fuel
vapors into the atmosphere, when the tank is vented
due to vapor expansion in the tank. When fuel evap-
orates from the fuel tank, vapors pass through vent
hoses or tubes to a charcoal canister where they are
temporarily held. When the engine is running, the
vapors are drawn into the intake manifold. In addi-
tion, fuel vapors produced during vehicle refueling
are allowed to pass through the vent hoses/tubes to
the charcoal canister(s) for temporary storage (prior
to being drawn into the intake manifold). All models
are equipped with a self-diagnosing system using a
Leak Detection Pump (LDP) or Natural Vacuum
Leak Detection (NVLD). Refer to the Emission Con-
trol System for additional information.
INLET CHECK VALVE
All vehicles have an inlet check valve on the inside
of the fuel tank at the filler inlet
The valve prevents fuel from splashing back on
customer during vehicle refueling. The valve is a
non-serviceable item.
REMOVAL
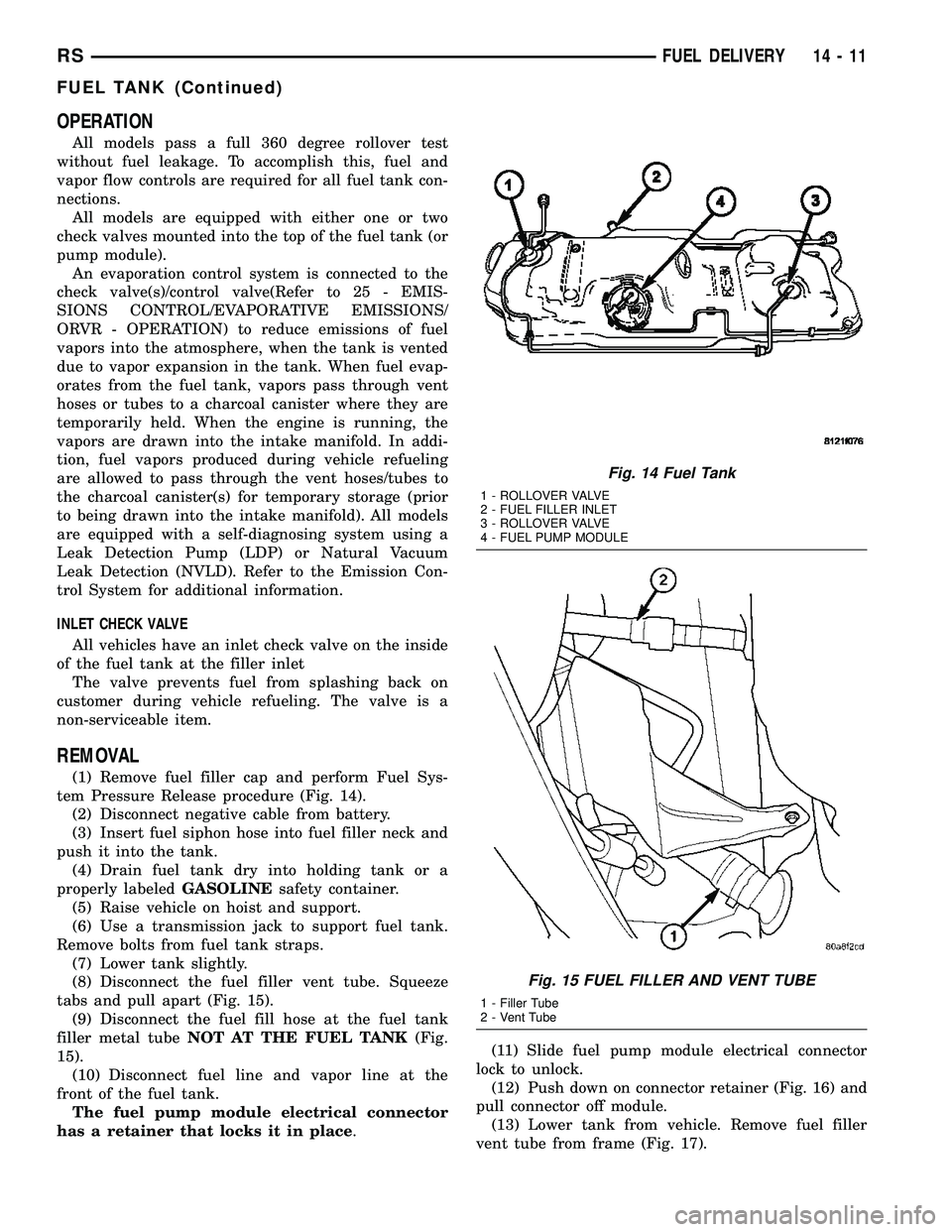
(1) Remove fuel filler cap and perform Fuel Sys-
tem Pressure Release procedure (Fig. 14).
(2) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(3) Insert fuel siphon hose into fuel filler neck and
push it into the tank.
(4) Drain fuel tank dry into holding tank or a
properly labeledGASOLINEsafety container.
(5) Raise vehicle on hoist and support.
(6) Use a transmission jack to support fuel tank.
Remove bolts from fuel tank straps.
(7) Lower tank slightly.
(8) Disconnect the fuel filler vent tube. Squeeze
tabs and pull apart (Fig. 15).
(9) Disconnect the fuel fill hose at the fuel tank
filler metal tubeNOT AT THE FUEL TANK(Fig.
15).
(10) Disconnect fuel line and vapor line at the
front of the fuel tank.
The fuel pump module electrical connector
has a retainer that locks it in place.(11) Slide fuel pump module electrical connector
lock to unlock.
(12) Push down on connector retainer (Fig. 16) and
pull connector off module.
(13) Lower tank from vehicle. Remove fuel filler
vent tube from frame (Fig. 17).
Fig. 14 Fuel Tank
1 - ROLLOVER VALVE
2 - FUEL FILLER INLET
3 - ROLLOVER VALVE
4 - FUEL PUMP MODULE
Fig. 15 FUEL FILLER AND VENT TUBE
1 - Filler Tube
2 - Vent Tube
RSFUEL DELIVERY14-11
FUEL TANK (Continued)
Page 2097 of 2585
white letters. To remove the protective coating, apply
warm water and let it soak for a few minutes. After-
wards, scrub the coating away with a soft bristle
brush. Steam cleaning may also be used to remove
the coating.
CAUTION: DO NOT use gasoline, mineral oil, oil-
based solvent or a wire brush for cleaning.
WHEELS
DESCRIPTION - WHEEL
Original equipment wheels are designed for proper
operation at all loads up to the specified maximum
vehicle capacity.
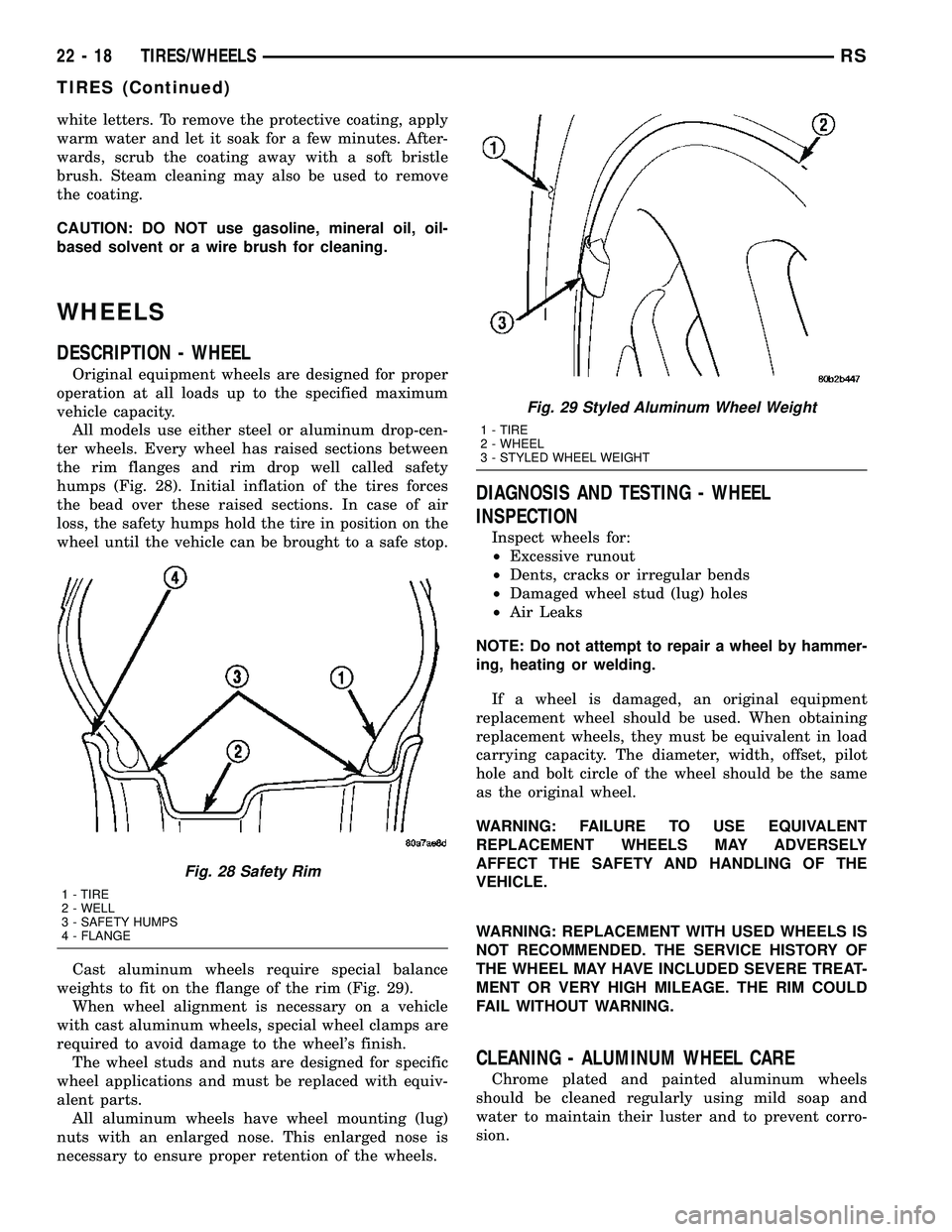
All models use either steel or aluminum drop-cen-
ter wheels. Every wheel has raised sections between
the rim flanges and rim drop well called safety
humps (Fig. 28). Initial inflation of the tires forces
the bead over these raised sections. In case of air
loss, the safety humps hold the tire in position on the
wheel until the vehicle can be brought to a safe stop.
Cast aluminum wheels require special balance
weights to fit on the flange of the rim (Fig. 29).
When wheel alignment is necessary on a vehicle
with cast aluminum wheels, special wheel clamps are
required to avoid damage to the wheel's finish.
The wheel studs and nuts are designed for specific
wheel applications and must be replaced with equiv-
alent parts.
All aluminum wheels have wheel mounting (lug)
nuts with an enlarged nose. This enlarged nose is
necessary to ensure proper retention of the wheels.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - WHEEL
INSPECTION
Inspect wheels for:
²Excessive runout
²Dents, cracks or irregular bends
²Damaged wheel stud (lug) holes
²Air Leaks
NOTE: Do not attempt to repair a wheel by hammer-
ing, heating or welding.
If a wheel is damaged, an original equipment
replacement wheel should be used. When obtaining
replacement wheels, they must be equivalent in load
carrying capacity. The diameter, width, offset, pilot
hole and bolt circle of the wheel should be the same
as the original wheel.
WARNING: FAILURE TO USE EQUIVALENT
REPLACEMENT WHEELS MAY ADVERSELY
AFFECT THE SAFETY AND HANDLING OF THE
VEHICLE.
WARNING: REPLACEMENT WITH USED WHEELS IS
NOT RECOMMENDED. THE SERVICE HISTORY OF
THE WHEEL MAY HAVE INCLUDED SEVERE TREAT-
MENT OR VERY HIGH MILEAGE. THE RIM COULD
FAIL WITHOUT WARNING.
CLEANING - ALUMINUM WHEEL CARE
Chrome plated and painted aluminum wheels
should be cleaned regularly using mild soap and
water to maintain their luster and to prevent corro-
sion.
Fig. 28 Safety Rim
1 - TIRE
2 - WELL
3 - SAFETY HUMPS
4 - FLANGE
Fig. 29 Styled Aluminum Wheel Weight
1 - TIRE
2 - WHEEL
3 - STYLED WHEEL WEIGHT
22 - 18 TIRES/WHEELSRS
TIRES (Continued)
Page 2111 of 2585

CLEANING - TIRES
Before delivery of a vehicle, remove the protective
coating on the tires with white sidewalls or raised
white letters. To remove the protective coating, apply
warm water and let it soak for a few minutes. After-
wards, scrub the coating away with a soft bristle
brush. Steam cleaning may also be used to remove
the coating. CAUTION: DO NOT use gasoline, mineral oil, oil-
based solvent or a wire brush for cleaning.
22s - 10 TIRESRS
TIRES (Continued)
Page 2459 of 2585

PLUMBING - FRONT
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
PLUMBING - FRONT
DESCRIPTION - REFRIGERANT LINE.......65
OPERATION- REFRIGERANT LINES........65
WARNING
ENGINE COOLING SYSTEM.............65
A/C SYSTEM.........................65
CAUTION
A/C SYSTEM.........................66
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REFRIGERANT
SYSTEM LEAKS......................66
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SYSTEM
CHARGE LEVEL TEST - GASOLINE
ENGINES............................67
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SYSTEM
CHARGE LEVEL TEST - 2.5L DIESEL......68
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - HANDLING
TUBING AND FITTINGS.................70
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT
SYSTEM SERVICE EQUIPMENT..........70
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT
RECOVERY..........................71
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT
SYSTEM EVACUATE...................72
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT
SYSTEM CHARGE.....................72
A/C COMPRESSOR
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - A/C COMPRESSOR.......73
DESCRIPTION - HIGH PRESSURE RELIEF
VALVE..............................73
OPERATION
OPERATION - A/C COMPRESSOR........73
OPERATION - HIGH PRESSURE RELIEF
VALVE..............................73
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - COMPRESSOR
NOISE DIAGNOSIS....................74
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - COMPRESSOR.............74
REMOVAL - A/C COMPRESSOR MOUNTING
BRACKET - 2.4L ENGINE...............75
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION.......................76
INSTALLATION - A/C COMPRESSOR
MOUNTING BRACKET - 2.4L ENGINE......76
A/C CONDENSER
DESCRIPTION.........................76
OPERATION...........................76REMOVAL.............................77
INSTALLATION.........................78
A/C DISCHARGE LINE
REMOVAL.............................79
INSTALLATION.........................80
A/C EVAPORATOR
DESCRIPTION.........................80
OPERATION...........................80
REMOVAL.............................80
INSTALLATION.........................80
EXPANSION VALVE
DESCRIPTION.........................81
OPERATION...........................81
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - A/C EXPANSION
VALVE ..............................81
REMOVAL.............................82
INSTALLATION.........................82
HEATER CORE
DESCRIPTION.........................83
OPERATION...........................83
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - HEATER CORE TUBES.......83
REMOVAL - HEATER CORE.............84
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - HEATER CORE TUBES....85
INSTALLATION - HEATER CORE..........85
HEATER INLET HOSE
REMOVAL.............................85
INSTALLATION.........................86
HEATER RETURN HOSE
REMOVAL.............................86
INSTALLATION.........................87
LIQUID LINE
REMOVAL.............................88
INSTALLATION.........................90
RECEIVER / DRIER
DESCRIPTION.........................91
OPERATION...........................91
REMOVAL.............................91
INSTALLATION.........................92
REFRIGERANT
DESCRIPTION.........................92
OPERATION...........................92
REFRIGERANT OIL
DESCRIPTION.........................92
OPERATION...........................92
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT
OIL LEVEL...........................93
24 - 64 PLUMBING - FRONTRS
Page 2462 of 2585

present. If system will not maintain vacuum level,
proceed with this procedure.
(2) Prepare a 0.284 Kg. (10 oz.) refrigerant charge
to be injected into the system.
(3) Connect and dispense 0.284 Kg. (10 oz.) of
refrigerant into the evacuated refrigerant system
(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/
PLUMBING - FRONT/REFRIGERANT - STANDARD
PROCEDURE - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM
CHARGE).
(4) Proceed to the SYSTEM LOW procedures.
SYSTEM LOW
(1) Position the vehicle in a wind-free work area.
This will aid in detecting small leaks.
(2) Bring the refrigerant system up to operating
temperature and pressure. This is done by allowing
the engine to run for five minutes with the system
set to the following:
²Transaxle in Park
²Engine idling
²Rear A/C Off (if equipped)
²A/C controls set to 100 percent outside air
²Blower switch in the highest speed position
²A/C in the ON position
²Front windows open
CAUTION: A leak detector designed for R-12 refrig-
erant (only) will not detect leaks in a R-134a refrig-
erant system.
(3) Shut off the vehicle and wait 2 to 7 minutes.
Then use an Electronic Leak Detector that is
designed to detect R-134a type refrigerant and search
for leaks. Fittings, lines, or components that appear
to be oily usually indicates a refrigerant leak. To
inspect the evaporator core for leaks, insert the leak
detector probe into the drain tube opening or a heat
duct. A R-134a dye is available to aid in leak detec-
tion, use only DaimlerChrysler approved refrigerant
dye.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - SYSTEM CHARGE
LEVEL TEST - GASOLINE ENGINES
WARNING: REFER TO THE APPLICABLE WARN-
INGS AND CAUTIONS FOR THIS SYSTEM BEFORE
PERFORMING THE FOLLOWING OPERATION (Refer
to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
FRONT - WARNING - A/C PLUMBING) and (Refer to
24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
FRONT - CAUTION - A/C PLUMBING).
NOTE: The proper amount of R-134a refrigerant for
the refrigerant system in this model is:²Single or Dual Zone (Front Unit Only) - 0.96
kilograms (2.13 pounds or 34 ounces)
²Three Zone (Front and Rear Units) - 1.31 kilo-
grams (2.88 pounds or 46 ounces)
The procedure that follows should be used to deter-
mine whether the refrigerant system contains the
proper refrigerant charge. Symptoms of an improper
refrigerant charge (low) include: poor air conditioner
performance, fog emitted from the air conditioner
outlets, a hissing sound from the expansion valve/
evaporator area. There are two different methods
with which the refrigerant charge level may be
tested:
1. Using a DRBIIItscan tool, a thermocouple and
the Charge Determination Chart (Fig. 1). Refer to
the appropriate diagnostic information.
2. Using a manifold gauge set, a thermocouple and
the Charge Determination Chart (Fig. 1).
A temperature probe is required to measure liquid
line temperature. The clamp-on, Type K thermocou-
ple temperature probe used in this procedure is
available through the DaimlerChrysler Professional
Service Equipment (PSE) program. This probe (PSE
#66-324-0014 or #80PK-1A) is compatible with tem-
perature-measuring instruments that accept Type K
thermocouples, and have a miniature connector
input. Other temperature probes are available
through aftermarket sources; however, all references
in this procedure will reflect the use of the probe
made available through the PSE program.
In order to use the temperature probe, a digital
thermometer will also be required. If a digital ther-
mometer is not available, an adapter is available
through the PSE program that will convert any stan-
dard digital multimeter into a digital thermometer.
This adapter is designed to accept any standard Type
K thermocouple. If a digital multimeter is not avail-
able, this tool is also available through the PSE pro-
gram.
NOTE: When connecting the service equipment
couplings to the refrigerant system service ports,
be certain that the valve of each coupling is fully
closed. This will reduce the amount of effort
required to make the connection.
(1) Remove the caps from the refrigerant system
service ports and attach a manifold gauge set or a
R-134a refrigerant recovery/recycling/charging sta-
tion that meets SAE Standard J2210 to the refriger-
ant system.
(2) Attach a clamp-on thermocouple to the liquid
line. The thermocouple must be placed as close to the
A/C pressure transducer as possible to accurately
observe liquid line temperature.
(3) Bring the refrigerant system up to operating
temperature and pressure. This is done by allowing
RSPLUMBING - FRONT24-67
PLUMBING - FRONT (Continued)
Page 2468 of 2585

CHARGING PROCEDURE
CAUTION: A small amount of refrigerant oil is
removed from the A/C system each time the refrig-
erant system is recovered and evacuated. Before
charging the A/C system, you MUST replenish any
oil lost during the recovery process. Refer the
equipment manufacturer instructions for more infor-
mation.
(1) Evacuate the refrigerant system. (Refer to 24 -
HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMBING -
FRONT/REFRIGERANT - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE - REFRIGERANT SYSTEM EVACUATE).
(2) A manifold gauge set and a R-134a refrigerant
recovery/recycling/charging station that meets SAE
Standard J2210 should still be connected to the
refrigerant system.
(3) Measure the proper amount of refrigerant and
heat it to 52É C (125É F) with the charging station.
See the operating instructions supplied by the equip-
ment manufacturer for proper use of this equipment.
(4) Open both the suction and discharge valves,
then open the charge valve to allow the heated
refrigerant to flow into the system.
(5) When the transfer of refrigerant has stopped,
close both the suction and discharge valves.
(6) If all of the refrigerant charge did not transfer
from the dispensing device, open all of the windows
in the vehicle and set the heater-air conditioner con-
trols so that the compressor is engaged and the
blower motor is operating at its lowest speed setting.
Run the engine at a steady high idle (about 1400
rpm). If the compressor will not engage, test the com-
pressor clutch control circuit and repair as required.
(7) Open the suction valve to allow the remaining
refrigerant to transfer to the refrigerant system.
WARNING: TAKE CARE NOT TO OPEN THE DIS-
CHARGE (HIGH PRESSURE) VALVE AT THIS TIME.
(8) Close the suction valve and test the system
performance. (Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR CON-
DITIONING - STANDARD PROCEDURE - A/C PER-
FORMANCE TEST).
(9) Disconnect the charging station and manifold
gauge set from the refrigerant system service ports.
(10) Reinstall the caps onto the refrigerant system
service ports.
(11) Run the HVAC Control Cooldown test to ver-
ify proper operation(Refer to 24 - HEATING & AIR
CONDITIONING - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING).A/C COMPRESSOR
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTION - A/C COMPRESSOR
Vehicles equipped with the 2.5L diesel, 3.3L and
3.8L gasoline engines use the Denso 10S20 A/C com-
pressor. Vehicles equipped with the 2.4L gasoline
engine use the Denso 10S17 A/C compressor. Both
A/C compressors include an integral high pressure
relief valve. The A/C compressor is secured to a
mounting bracket on the 2.4L gasoline engine and
directly to the cylinder block on the 2.5L diesel, 3.3L
and 3.8L gasoline engines.
DESCRIPTION - HIGH PRESSURE RELIEF
VALVE
A high pressure relief valve is located on the rear
of the A/C compressor. This mechanical valve is
designed to vent refrigerant from the A/C system to
protect against damage to the compressor and other
system components, caused by condenser air flow
restriction or an overcharge of refrigerant.
OPERATION
OPERATION - A/C COMPRESSOR
The A/C compressor is driven by the engine
through an electric clutch, drive pulley and belt
arrangement. The compressor is lubricated by refrig-
erant oil that is circulated throughout the refrigerant
system with the refrigerant.
The compressor draws in low-pressure refrigerant
vapor from the evaporator through its suction port. It
then compresses the refrigerant into a high-pressure,
high-temperature refrigerant vapor. The compressor
pumps the high-pressure refrigerant vapor to the
condenser through the compressor discharge port.
The compressor cannot be repaired. If faulty or
damaged, the entire compressor assembly must be
replaced. The compressor clutch, pulley and clutch
coil are available for service.
OPERATION - HIGH PRESSURE RELIEF VALVE
The high pressure relief valve vents the system
when a discharge pressure of 3445 to 4135 kPa (500
to 600 psi) or above is reached. The valve closes
when a minimum discharge pressure of 2756 kPa
(400 psi) is reached.
The high pressure relief valve vents only enough
refrigerant to reduce the system pressure, and then
re-seats itself. The majority of the refrigerant is con-
served in the system. If the valve vents refrigerant, it
does not mean that the valve is faulty.
RSPLUMBING - FRONT24-73
PLUMBING - FRONT (Continued)
Page 2550 of 2585

CHAIN WEAR - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
MEASURING TIMING..................9-153
CHANGE - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
DIFFERENTIAL ASSEMBLY FLUID.........3-40
CHANGE - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
ENGINE OIL AND FILTER...........9-137,9-53
CHANGE - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
OVERRUNNING CLUTCH HOUSING
FLUID..............................3-41
CHANGE - STANDARD PROCEDURE, PTU
FLUID..............................21-5
CHANGER - DESCRIPTION, CD...........8A-7
CHANGER - INSTALLATION, CD..........8A-8
CHANGER - OPERATION, CD.............8A-7
CHANGER - REMOVAL, CD..............8A-8
CHANNEL - INSTALLATION, WATER.....23-121
CHANNEL - REMOVAL, WATER.........23-121
CHARGE - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
REFRIGERANT SYSTEM...............24-72
CHARGE LEVEL TEST - 2.5L DIESEL -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING, SYSTEM......24-68
CHARGE LEVEL TEST - GASOLINE
ENGINES - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
SYSTEM............................24-67
CHARGING - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
CONVENTIONAL BATTERY..............8F-11
CHARGING - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
SPIRAL PLATE BATTERY...............8F-10
CHARGING SYSTEM - DESCRIPTION.....8F-20
CHARGING SYSTEM - OPERATION.......8F-20
CHARTS - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
STEERING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS...........19-3
CHARTS - SPECIFICATIONS, COLOR
CODE..............................23-84
CHATTER COMPLAINTS - DIAGNOSIS
AND TESTING, CLUTCH.................6-6
CHECK - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
COOLING SYSTEM FLOW................7-3
CHECK - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
EXHAUST SYSTEM RESTRICTION.........11-2
CHECK - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
COOLANT LEVEL.......................7-5
CHECK - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
ENGINE OIL LEVEL...................9-137
CHECK - STANDARD PROCEDURE, FLUID
LEVEL.............................21-71
CHECK, STANDARD PROCEDURE -
ENGINE OIL LEVEL....................9-53
CHECK, STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID
LEVEL AND CONDITION........21-201,21s-102
CHECK STRAP - INSTALLATION.........23-15
CHECK STRAP - REMOVAL.............23-15
CHECKING - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
BRAKE FLUID LEVEL..............5-32,5s-31
CHECKING - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
POWER STEERING FLUID LEVEL........19-44
CHECKING BATTERY ELECTROLYTE
LEVEL - STANDARD PROCEDURE........8F-14
CHECKING ENGINE OIL PRESSURE -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING..............9-52
CHECKING POWER STEERING BELT
TENSION - STANDARD PROCEDURE.......7-8
CHILD RESTRAINT ANCHOR -
DESCRIPTION........................8O-4
CHILD RESTRAINT ANCHOR -
OPERATION..........................8O-4
CHILD SEAT - INSTALLATION, QUAD.....23-89
CHILD SEAT - REMOVAL, QUAD.........23-89
CHILD SEAT MODULE, BENCH SEAT -
REMOVAL..........................23-87
CHIME SYSTEM - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING
............................8B-1
CHIME/BUZZER - DESCRIPTION
..........8B-1
CHIME/BUZZER - OPERATION
............8B-1
CHIME/BUZZER - WARNING
.............8B-1
CHIME/THERMISTOR - DESCRIPTION
....8N-10
CHIME/THERMISTOR - INSTALLATION
....8N-10
CHIME/THERMISTOR - OPERATION
......8N-10
CHIME/THERMISTOR - REMOVAL
.......8N-10
CHIRP PREFERENCE - STANDARD
PROCEDURE, HORN
..............8N-42,8N-5
CIRCUIT - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE SENSOR
......8M-12
CIRCUIT FUNCTIONS - DESCRIPTION
. . 8W-01-6
CIRCUIT INFORMATION - DESCRIPTION
. 8W-01-5
CIRCUIT RESISTANCE TEST -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING, FEED
. . . 8F-32,8F-34CIRCUIT TEST - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, CONTROL..............8F-30,8F-32
CIRCUIT TEST - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, FEED.................8F-33,8F-35
CIRCUITS - OPERATION, NON-
MONITORED.........................25-5
CIRCUITS AND VALVES - OPERATION,
HYDRAULIC..........................5-83
CLAMP - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
HOSES..............................14-7
CLAMPS - DESCRIPTION, FUEL
LINES/HOSES........................14-6
CLAMPS - DESCRIPTION, HOSE...........7-1
CLAMPS - OPERATION, HOSE.............7-2
CLEAN, CLEANING...................21-114
CLEARANCE - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
MEASURING CONNECTING ROD
BEARING...........................9-120
CLEARANCE USING PLASTIGAGE -
STANDARD PROCEDURE, MEASURING
BEARING........................9-12,9-84
CLOCK SPRING - DESCRIPTION..........8O-4
CLOCK SPRING - INSTALLATION.........8O-5
CLOCK SPRING - OPERATION...........8O-4
CLOCK SPRING - REMOVAL.............8O-5
CLOCK SPRING CENTERING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE...............8O-5
CLUSTER - DESCRIPTION, INSTRUMENT . . . 8J-1
CLUSTER - OPERATION, INSTRUMENT.....8J-1
CLUSTER BEZEL - INSTALLATION........23-63
CLUSTER BEZEL - REMOVAL.............23-63
CLUSTER DIAGNOSIS - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING............................8J-2
CLUSTER ILLUMINATION LAMPS -
INSTALLATION.......................8L-21
CLUSTER ILLUMINATION LAMPS -
REMOVAL..........................8L-21
CLUSTER LENS - INSTALLATION........8J-10
CLUSTER LENS - REMOVAL............8J-10
CLUTCH - DESCRIPTION.................6-1
CLUTCH - DESCRIPTION, BI-
DIRECTIONAL OVERRUNNING...........3-34
CLUTCH - OPERATION, BI-DIRECTIONAL
OVERRUNNING.......................3-36
CLUTCH AIR PRESSURE TESTS -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.......21-122,21s-30
CLUTCH ASSEMBLY - ASSEMBLY,
INPUT.....................21-216,21s-116
CLUTCH ASSEMBLY - DISASSEMBLY,
INPUT.....................21-208,21s-107
CLUTCH ASSY - 2.4L GAS -
INSTALLATION, MODULAR..............6-11
CLUTCH ASSY - 2.4L GAS - REMOVAL,
MODULAR...........................6-11
CLUTCH CHATTER COMPLAINTS -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING...............6-6
CLUTCH COIL - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, A/C COMPRESSOR...........24-15
CLUTCH COVER AND DISC RUNOUT -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING...............6-6
CLUTCH DISC AND PRESSURE PLATE -
2.5L TD - INSTALLATION
...............6-12
CLUTCH DISC AND PRESSURE PLATE -
2.5L TD - REMOVAL
...................6-11
CLUTCH HOUSING FLUID CHANGE -
STANDARD PROCEDURE,
OVERRUNNING
.......................3-41
CLUTCH PEDAL INTERLOCK SWITCH -
INSTALLATION
........................6-14
CLUTCH PEDAL INTERLOCK SWITCH -
REMOVAL
...........................6-13
CLUTCH PEDAL UPSTOP SWITCH -
INSTALLATION
........................6-16
CLUTCH PEDAL UPSTOP SWITCH -
REMOVAL
...........................6-15
CLUTCH RELAY - DESCRIPTION, A/C
COMPRESSOR
.......................24-19
CLUTCH RELAY - INSTALLATION, A/C
COMPRESSOR
.......................24-20
CLUTCH RELAY - OPERATION, A/C
COMPRESSOR
.......................24-19
CLUTCH RELAY - REMOVAL, A/C
COMPRESSOR
.......................24-20
CLUTCH RELEASE LEVER AND BEARING
- INSTALLATION
.......................6-7
CLUTCH RELEASE LEVER AND BEARING
- REMOVAL
...........................6-6CLUTCH SYSTEM - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING.............................6-3
CLUTCH/COIL - DESCRIPTION, A/C
COMPRESSOR.......................24-15
CLUTCH/COIL - INSPECTION, A/C
COMPRESSOR.......................24-17
CLUTCH/COIL - INSTALLATION, A/C
COMPRESSOR.......................24-17
CLUTCH/COIL - OPERATION, A/C
COMPRESSOR.......................24-15
CLUTCH/COIL - REMOVAL, A/C
COMPRESSOR.......................24-16
CLUTCHES - DESCRIPTION, DRIVING . . . 21-190,
21s-95
CLUTCHES - DESCRIPTION, HOLDING . . . 21-207,
21s-106
CLUTCHES - OPERATION, DRIVING.....21-190,
21s-95
CLUTCHES - OPERATION, HOLDING....21-207,
21s-106
COAT/CLEARCOAT FINISH -
DESCRIPTION, BASE..................23-85
CODE - DESCRIPTION, PAINT...........23-85
CODE CHARTS - SPECIFICATIONS,
COLOR.............................23-84
CODE PLATE - DESCRIPTION, BODY....Intro.-1
CODES - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
ERASING TRANSMITTER..............8M-11
CODES - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
OBTAINING DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE......8E-15
CODES - STANDARD PROCEDURE,
SETTING TRANSMITTER..............8M-11
COIL - DESCRIPTION, IGNITION............8I-6
COIL - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING, A/C
COMPRESSOR CLUTCH...............24-15
COIL - OPERATION, IGNITION............8I-7
COLLAR - INSTALLATION, STRUCTURAL . . . 9-48
COLLAR - REMOVAL, STRUCTURAL.......9-47
COLOR CODE CHARTS -
SPECIFICATIONS.....................23-84
COLUMN - DESCRIPTION, STEERING.....19-10
COLUMN - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
STEERING..........................19-12
COLUMN COVER - INSTALLATION,
LOWER STEERING...................23-70
COLUMN COVER - INSTALLATION, OVER
STEERING..........................23-70
COLUMN COVER - REMOVAL, LOWER
STEERING..........................23-70
COLUMN COVER - REMOVAL, OVER
STEERING..........................23-70
COLUMN COVER BACKING PLATE -
INSTALLATION, STEERING.............23-70
COLUMN COVER BACKING PLATE -
REMOVAL, STEERING.................23-70
COLUMN TORQUE, SPECIFICATIONS.....19-14
COMBUSTION PRESSURE LEAKAGE
TEST - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING,
CYLINDER........................9-83,9-9
COMMON PROBLEM CAUSES -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.............21-30
COMMUNICATION RECEIVE - PCM INPUT
- OPERATION, DATA BUS..............8E-15
COMMUNICATIONS INTERFACE (PCI)
BUS, OPERATION - PROGRAMMABLE....14-21
COMPASS CALIBRATION - STANDARD
PROCEDURE.........................8M-3
COMPASS DEMAGNETIZING -
STANDARD PROCEDURE...............8M-4
COMPASS MINI-TRIP COMPUTER -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING.............8M-10
COMPASS VARIATION ADJUSTMENT -
STANDARD PROCEDURE...............8M-5
COMPASS/MINI-TRIP COMPUTER -
DESCRIPTION........................8M-9
COMPASS/MINI-TRIP COMPUTER -
INSTALLATION......................8M-10
COMPASS/MINI-TRIP COMPUTER -
OPERATION.........................8M-9
COMPASS/MINI-TRIP COMPUTER -
REMOVAL..........................8M-10
COMPLAINTS - DIAGNOSIS AND
TESTING, CLUTCH CHATTER
..............6-6
COMPRESSION PRESSURE TEST -
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING, CYLINDER
. . 9-83,9-9
COMPRESSOR - DESCRIPTION, A/C
......24-73
COMPRESSOR - OPERATION, A/C
........24-73
COMPRESSOR - REMOVAL
.............24-74
RSINDEX7
Description Group-Page Description Group-Page Description Group-Page