boot CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2005 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2005, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2005Pages: 2339, PDF Size: 59.69 MB
Page 32 of 2339
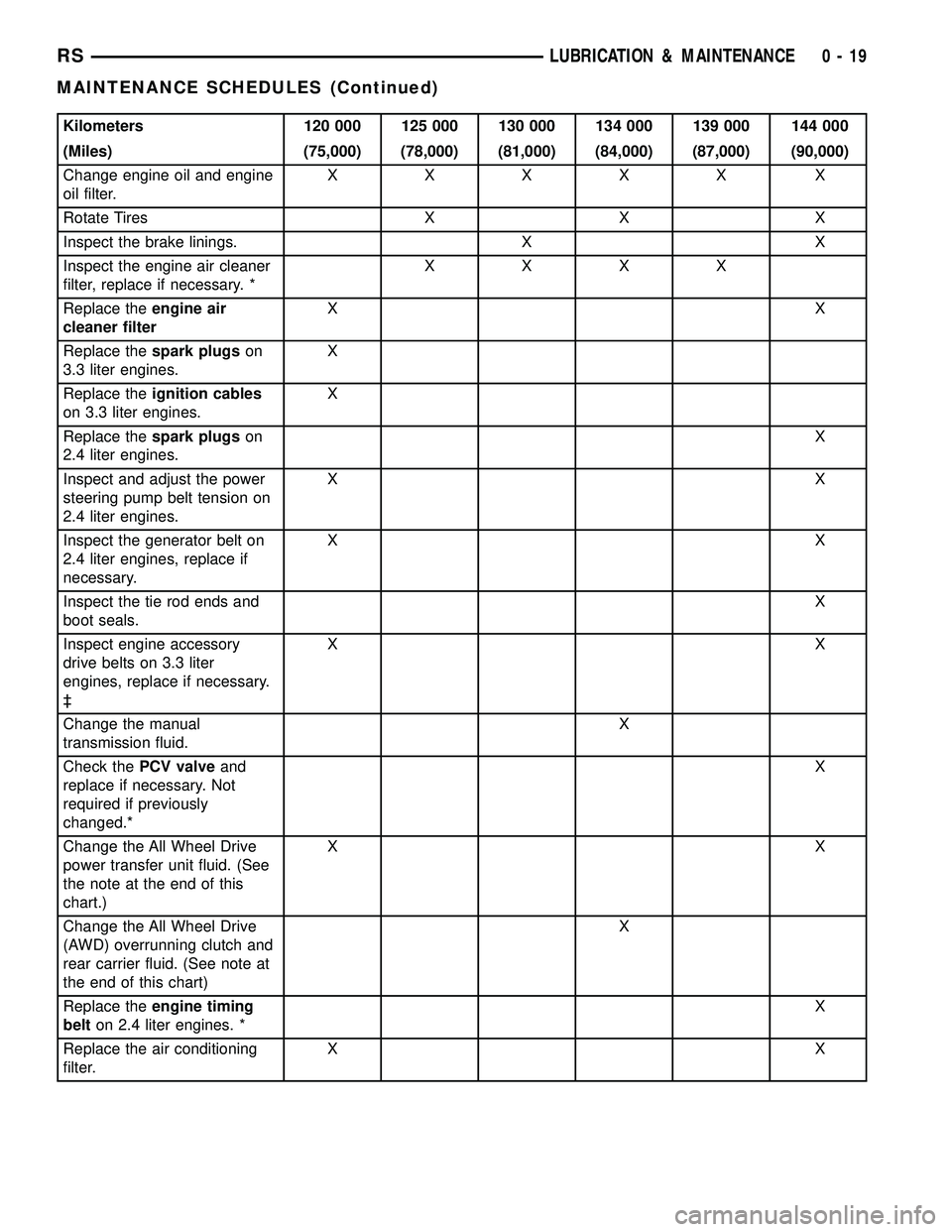
Kilometers 120 000 125 000 130 000 134 000 139 000 144 000
(Miles) (75,000) (78,000) (81,000) (84,000) (87,000) (90,000)
Change engine oil and engine
oil filter.XXXXX X
Rotate Tires X X X
Inspect the brake linings. X X
Inspect the engine air cleaner
filter, replace if necessary. *XXXX
Replace theengine air
cleaner filterXX
Replace thespark plugson
3.3 liter engines.X
Replace theignition cables
on 3.3 liter engines.X
Replace thespark plugson
2.4 liter engines.X
Inspect and adjust the power
steering pump belt tension on
2.4 liter engines.XX
Inspect the generator belt on
2.4 liter engines, replace if
necessary.XX
Inspect the tie rod ends and
boot seals.X
Inspect engine accessory
drive belts on 3.3 liter
engines, replace if necessary.
³XX
Change the manual
transmission fluid.X
Check thePCV valveand
replace if necessary. Not
required if previously
changed.*X
Change the All Wheel Drive
power transfer unit fluid. (See
the note at the end of this
chart.)XX
Change the All Wheel Drive
(AWD) overrunning clutch and
rear carrier fluid. (See note at
the end of this chart)X
Replace theengine timing
belton 2.4 liter engines. *X
Replace the air conditioning
filter.XX
RSLUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE0-19
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES (Continued)
Page 34 of 2339
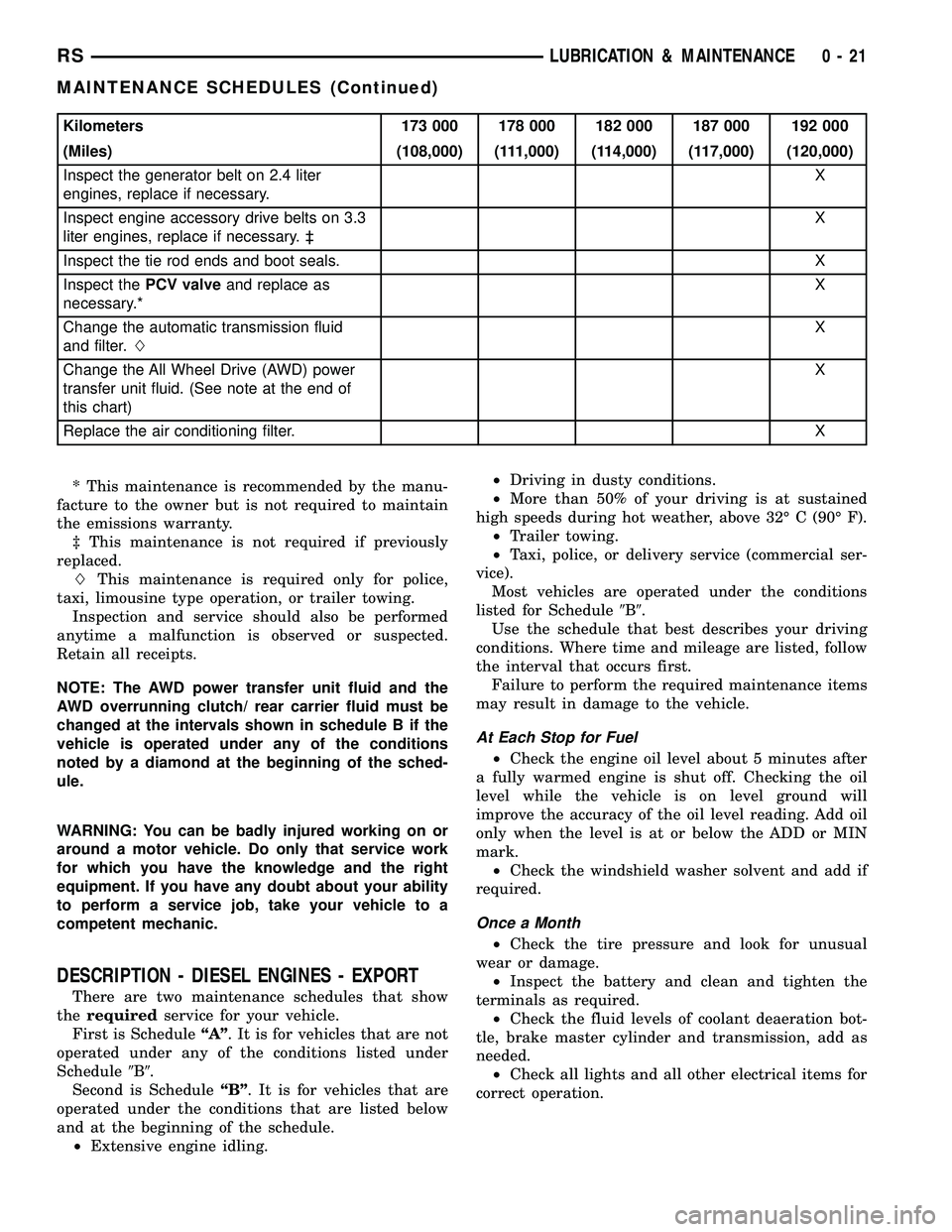
Kilometers 173 000 178 000 182 000 187 000 192 000
(Miles) (108,000) (111,000) (114,000) (117,000) (120,000)
Inspect the generator belt on 2.4 liter
engines, replace if necessary.X
Inspect engine accessory drive belts on 3.3
liter engines, replace if necessary. ³X
Inspect the tie rod ends and boot seals. X
Inspect thePCV valveand replace as
necessary.*X
Change the automatic transmission fluid
and filter.LX
Change the All Wheel Drive (AWD) power
transfer unit fluid. (See note at the end of
this chart)X
Replace the air conditioning filter.X
* This maintenance is recommended by the manu-
facture to the owner but is not required to maintain
the emissions warranty.
³ This maintenance is not required if previously
replaced.
LThis maintenance is required only for police,
taxi, limousine type operation, or trailer towing.
Inspection and service should also be performed
anytime a malfunction is observed or suspected.
Retain all receipts.
NOTE: The AWD power transfer unit fluid and the
AWD overrunning clutch/ rear carrier fluid must be
changed at the intervals shown in schedule B if the
vehicle is operated under any of the conditions
noted by a diamond at the beginning of the sched-
ule.
WARNING: You can be badly injured working on or
around a motor vehicle. Do only that service work
for which you have the knowledge and the right
equipment. If you have any doubt about your ability
to perform a service job, take your vehicle to a
competent mechanic.
DESCRIPTION - DIESEL ENGINES - EXPORT
There are two maintenance schedules that show
therequiredservice for your vehicle.
First is ScheduleªAº. It is for vehicles that are not
operated under any of the conditions listed under
Schedule9B9.
Second is ScheduleªBº. It is for vehicles that are
operated under the conditions that are listed below
and at the beginning of the schedule.
²Extensive engine idling.²Driving in dusty conditions.
²More than 50% of your driving is at sustained
high speeds during hot weather, above 32É C (90É F).
²Trailer towing.
²Taxi, police, or delivery service (commercial ser-
vice).
Most vehicles are operated under the conditions
listed for Schedule9B9.
Use the schedule that best describes your driving
conditions. Where time and mileage are listed, follow
the interval that occurs first.
Failure to perform the required maintenance items
may result in damage to the vehicle.
At Each Stop for Fuel
²Check the engine oil level about 5 minutes after
a fully warmed engine is shut off. Checking the oil
level while the vehicle is on level ground will
improve the accuracy of the oil level reading. Add oil
only when the level is at or below the ADD or MIN
mark.
²Check the windshield washer solvent and add if
required.
Once a Month
²Check the tire pressure and look for unusual
wear or damage.
²Inspect the battery and clean and tighten the
terminals as required.
²Check the fluid levels of coolant deaeration bot-
tle, brake master cylinder and transmission, add as
needed.
²Check all lights and all other electrical items for
correct operation.
RSLUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE0-21
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES (Continued)
Page 35 of 2339
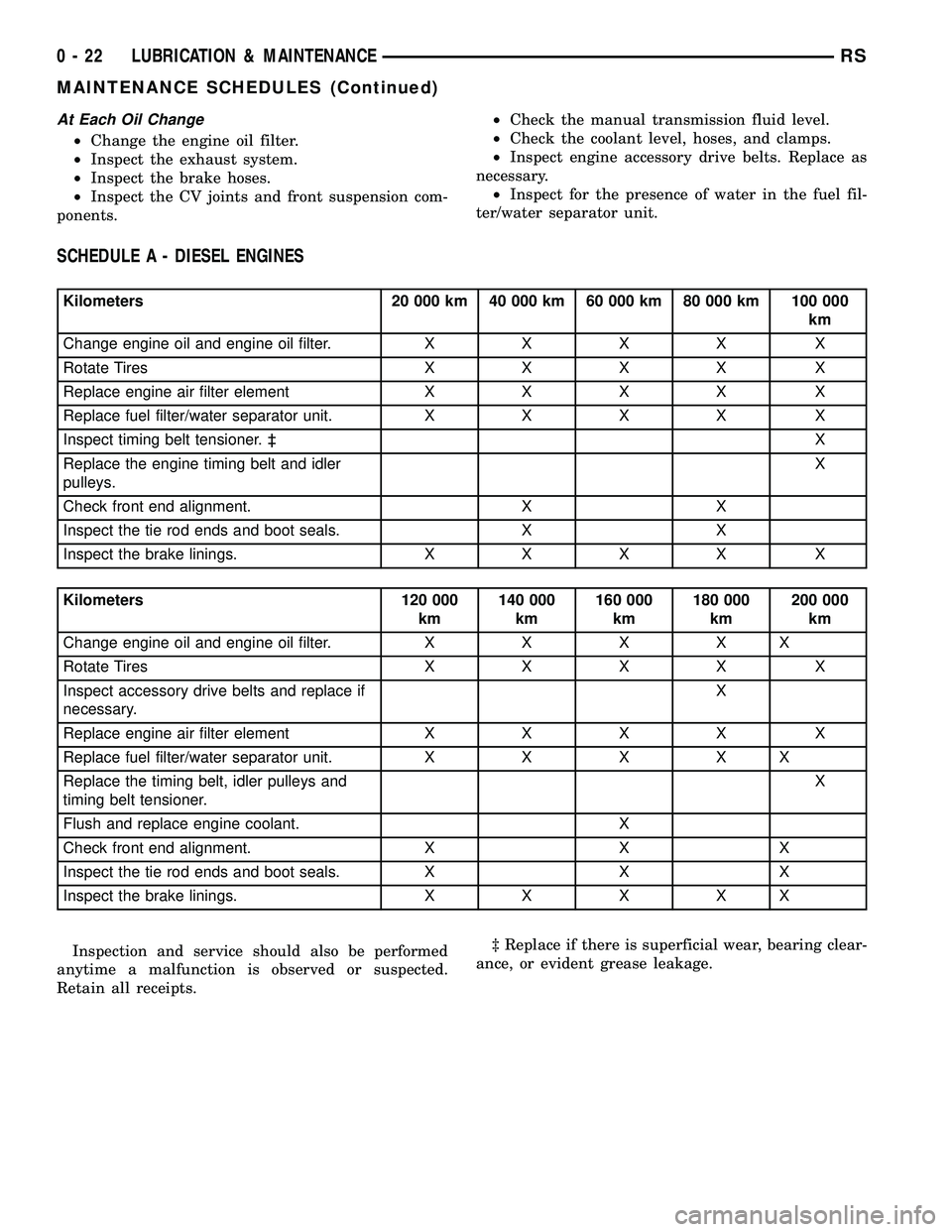
At Each Oil Change
²Change the engine oil filter.
²Inspect the exhaust system.
²Inspect the brake hoses.
²Inspect the CV joints and front suspension com-
ponents.²Check the manual transmission fluid level.
²Check the coolant level, hoses, and clamps.
²Inspect engine accessory drive belts. Replace as
necessary.
²Inspect for the presence of water in the fuel fil-
ter/water separator unit.
SCHEDULE A - DIESEL ENGINES
Kilometers 20 000 km 40 000 km 60 000 km 80 000 km 100 000
km
Change engine oil and engine oil filter.XXXX X
Rotate TiresXXXX X
Replace engine air filter elementXXXX X
Replace fuel filter/water separator unit.XXXX X
Inspect timing belt tensioner. ³X
Replace the engine timing belt and idler
pulleys.X
Check front end alignment. X X
Inspect the tie rod ends and boot seals. X X
Inspect the brake linings.XXXX X
Kilometers 120 000
km140 000
km160 000
km180 000
km200 000
km
Change engine oil and engine oil filter.XXXXX
Rotate TiresXXXX X
Inspect accessory drive belts and replace if
necessary.X
Replace engine air filter elementXXXX X
Replace fuel filter/water separator unit.XXXXX
Replace the timing belt, idler pulleys and
timing belt tensioner.X
Flush and replace engine coolant. X
Check front end alignment. X X X
Inspect the tie rod ends and boot seals. X X X
Inspect the brake linings.XXXXX
Inspection and service should also be performed
anytime a malfunction is observed or suspected.
Retain all receipts.³ Replace if there is superficial wear, bearing clear-
ance, or evident grease leakage.
0 - 22 LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCERS
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES (Continued)
Page 36 of 2339
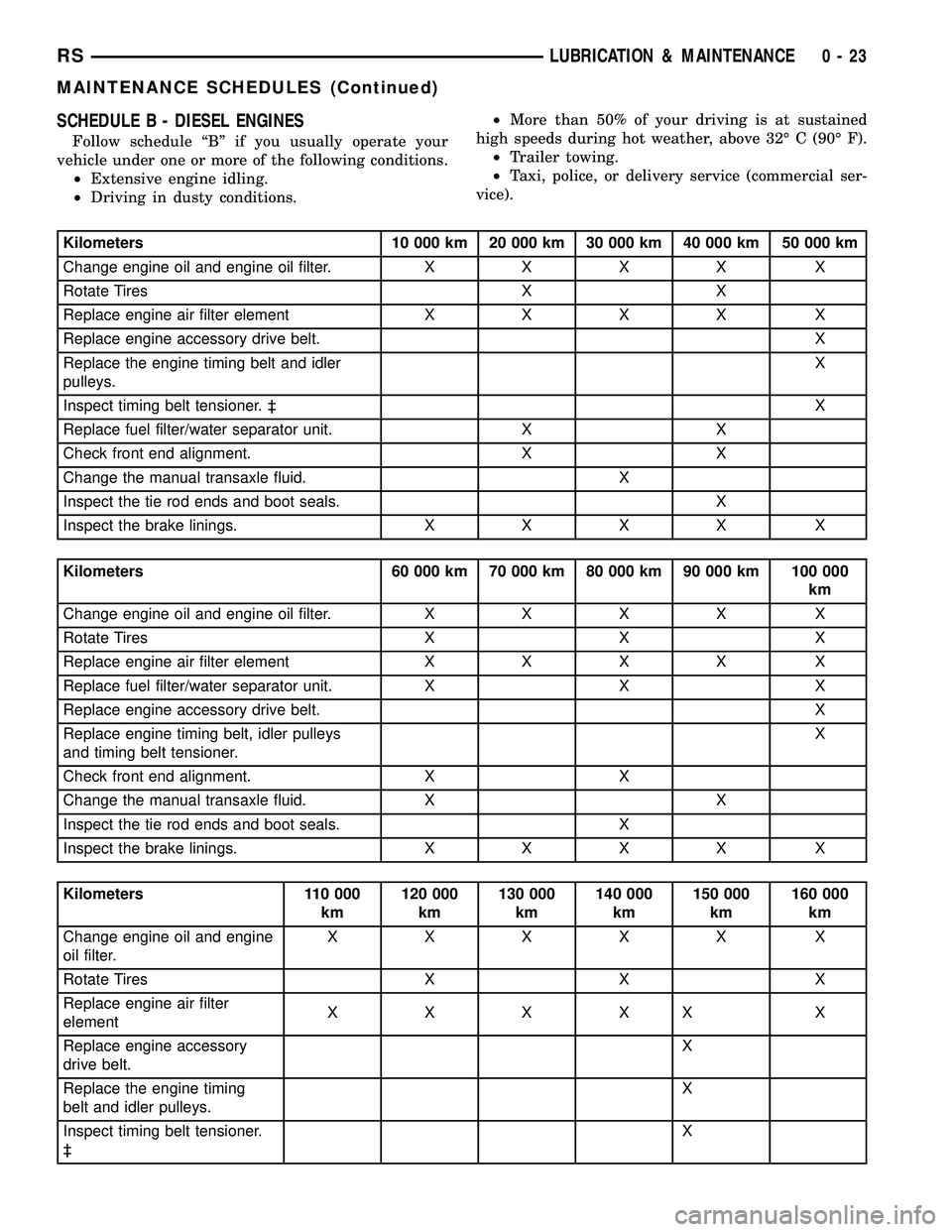
SCHEDULE B - DIESEL ENGINES
Follow schedule ªBº if you usually operate your
vehicle under one or more of the following conditions.
²Extensive engine idling.
²Driving in dusty conditions.²More than 50% of your driving is at sustained
high speeds during hot weather, above 32É C (90É F).
²Trailer towing.
²Taxi, police, or delivery service (commercial ser-
vice).
Kilometers 10 000 km 20 000 km 30 000 km 40 000 km 50 000 km
Change engine oil and engine oil filter.XXXX X
Rotate Tires X X
Replace engine air filter elementXXXX X
Replace engine accessory drive belt. X
Replace the engine timing belt and idler
pulleys.X
Inspect timing belt tensioner. ³X
Replace fuel filter/water separator unit. X X
Check front end alignment. X X
Change the manual transaxle fluid. X
Inspect the tie rod ends and boot seals. X
Inspect the brake linings.XXXX X
Kilometers 60 000 km 70 000 km 80 000 km 90 000 km 100 000
km
Change engine oil and engine oil filter.XXXX X
Rotate Tires X X X
Replace engine air filter elementXXXX X
Replace fuel filter/water separator unit. X X X
Replace engine accessory drive belt. X
Replace engine timing belt, idler pulleys
and timing belt tensioner.X
Check front end alignment. X X
Change the manual transaxle fluid. X X
Inspect the tie rod ends and boot seals. X
Inspect the brake linings.XXXX X
Kilometers 110 000
km120 000
km130 000
km140 000
km150 000
km160 000
km
Change engine oil and engine
oil filter.XXXXX X
Rotate Tires X X X
Replace engine air filter
elementXXXXX X
Replace engine accessory
drive belt.X
Replace the engine timing
belt and idler pulleys.X
Inspect timing belt tensioner.
³X
RSLUBRICATION & MAINTENANCE0-23
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES (Continued)
Page 37 of 2339
Kilometers 110 000
km120 000
km130 000
km140 000
km150 000
km160 000
km
Replace fuel filter/water
separator unit.XX X
Flush and replace engine
coolant.X
Check front end alignment. X X X
Inspect the tie rod ends and
boot seals.XX
Inspect the brake linings. XXXXX X
Inspection and service should also be performed
anytime a malfunction is observed or suspected.
Retain all receipts.
³ Replace if there is superficial wear, bearing clear-
ance, or evident grease leakage.
WARNING: You can be badly injured working on or
around a motor vehicle. Do only that service work
for which you have the knowledge and the right
equipment. If you have any doubt about your ability
to perform a service job, take your vehicle to a
competent mechanic.
HOISTING
STANDARD PROCEDURE - HOISTING
Refer to Owner's Manual provided with vehicle for
proper emergency jacking procedures.
WARNING: THE HOISTING AND JACK LIFTING
POINTS PROVIDED ARE FOR A COMPLETE VEHI-
CLE. WHEN THE ENGINE OR REAR SUSPENSION
IS REMOVED FROM A VEHICLE, THE CENTER OF
GRAVITY IS ALTERED MAKING SOME HOISTING
CONDITIONS UNSTABLE. PROPERLY SUPPORT OR
SECURE VEHICLE TO HOISTING DEVICE WHEN
THESE CONDITIONS EXIST.CAUTION: Do not position hoisting device on any
suspension component, including the front suspen-
sion crossmember, the rear leaf springs, and the
rear axle. Do not hoist on the front and rear
bumpers, the lower liftgate crossmember, the lower
radiator crossmember, the down standing flanges
on the sill or the front engine mount.
FOR PROPER HOIST PLACEMENT REFER
TO (Fig. 5).
The hoisting points are identified by S.A.E.
inverted triangle hoisting symbols (Fig. 5). The front
hoisting points are at the bottom of the font rail
below the hoisting symbol approximately 250 mm
behind the front suspension crossmember. When
using outboard lift hoists, verify that the hoist lift
pads have been properly adjusted to eliminate con-
tact between the hoist arm and the down standing
flange on the sill. The rear hoisting points are the
leaf spring front mounting brackets. The hoist pad
must be positioned to pick up the flanges on the
bracket, not the leaf spring.
When servicing the leaf springs or the leaf spring
mounting brackets, special provisions are required to
support the rear of the vehicle. Position the rear
hoist pads under the horizontal surface on the bot-
tom of the sill, inboard adjacent to the flange and
centered fore/aft between the jacking indicator tabs
on the lower flange.DO NOT HOIST ON THE
FLANGE.Place a soft pad between the hoist and the
painted surface on the sill to avoid scratching the fin-
ish.
0 - 24 LUBRICATION & MAINTENANCERS
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES (Continued)
Page 42 of 2339

SUSPENSION
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
FRONT SUSPENSION.....................1
REAR SUSPENSION......................26WHEEL ALIGNMENT.....................47
FRONT SUSPENSION
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
FRONT SUSPENSION
DESCRIPTION - FRONT SUSPENSION.......2
OPERATION - FRONT SUSPENSION.........2
STANDARD PROCEDURE - LUBRICATION....2
SPECIFICATIONS
FRONT SUSPENSION FASTENER TORQUE . . 3
SPECIAL TOOLS
FRONT SUSPENSION...................3
BUSHINGS
REMOVAL - STABILIZER BAR CUSHION......4
INSTALLATION - STABILIZER BAR CUSHION . . . 4
HUB / BEARING
DESCRIPTION..........................5
OPERATION............................5
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HUB AND
BEARING............................5
REMOVAL.............................5
INSTALLATION..........................5
KNUCKLE
DESCRIPTION..........................6
OPERATION............................7
REMOVAL - STEERING KNUCKLE...........7
INSPECTION - STEERING KNUCKLE.........9
INSTALLATION - STEERING KNUCKLE.......9
LOWER BALL JOINT
DESCRIPTION.........................10
OPERATION...........................10
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - LOWER BALL
JOINT..............................10
LOWER BALL JOINT SEAL BOOT
DESCRIPTION - EXPORT.................10
REMOVAL
REMOVAL...........................11
REMOVAL - EXPORT...................11INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION.......................11
INSTALLATION - EXPORT...............11
LOWER CONTROL ARM
DESCRIPTION.........................12
OPERATION...........................12
REMOVAL - LOWER CONTROL ARM........12
DISASSEMBLY
DISASSEMBLY - LOWER CONTROL ARM
(REAR BUSHING - STANDARD)..........13
DISASSEMBLY - LOWER CONTROL ARM
(REAR BUSHING - HYDRO).............13
INSPECTION - LOWER CONTROL ARM......14
ASSEMBLY
ASSEMBLY - LOWER CONTROL ARM
(REAR BUSHING - STANDARD)..........14
ASSEMBLY - LOWER CONTROL ARM
(REAR BUSHING - HYDRO).............15
INSTALLATION - LOWER CONTROL ARM....15
STABILIZER BAR
DESCRIPTION.........................16
OPERATION...........................16
REMOVAL.............................17
INSPECTION..........................17
INSTALLATION.........................17
STRUT
DESCRIPTION - STRUT ASSEMBLY.........19
OPERATION - STRUT ASSEMBLY..........19
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - STRUT
ASSEMBLY..........................20
REMOVAL - STRUT ASSEMBLY............20
DISASSEMBLY - STRUT ASSEMBLY........21
ASSEMBLY - STRUT ASSEMBLY...........23
INSTALLATION - STRUT ASSEMBLY........25
RSSUSPENSION2-1
Page 51 of 2339
(6) Install tie rod end into knuckle steering arm.
Start nut onto stud of tie rod end. While holding stud
of tie rod end stationary using a socket (Fig. 11),
tighten tie rod end to steering knuckle attaching nut.
Tighten the tie rod end nut to a torque of 75 N´m (55
ft. lbs.).
(7) If equipped with antilock brakes, install wheel
speed sensor and mounting bolt on steering knuckle
(Fig. 13). Tighten the speed sensor bolt to a torque of
7 N´m (60 in. lbs.).
(8) Install brake rotor on hub and bearing (Fig. 9).
(9) Install disc brake caliper and adapter assembly
on steering knuckle. Install adapter amounting bolts
and tighten to 169 N´m (125 ft. lbs.).
(10) Clean any debris from the threads of the
outer C/V joint stub axle.
(11) Install the washer and hub nut on stub axle.
(12) Have a helper apply the vehicle's brakes to
keep hub from turning, then tighten hub nut to a
torque of 244 N´m (180 ft. lbs.).
(13) Install the spring wave washer on the end of
the stub axle.
(14) Install the hub nut lock, and anewcotter pin
(Fig. 8). Wrap cotter pin prongs tightly around the
hub nut lock.
(15) Install wheel and tire assembly. Install and
tighten the wheel mounting nuts in proper sequence
until all nuts are torqued to half the required speci-
fication. Then repeat the tightening sequence to the
full specified torque of 135 N´m (100 ft. lbs.).
(16) Lower vehicle.
(17) Set front wheel alignment camber and toe as
necessary. (Refer to 2 - SUSPENSION/WHEEL
ALIGNMENT - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
LOWER BALL JOINT
DESCRIPTION
The ball joint is an integral part of the lower con-
trol arm (Fig. 1). The ball joint has a tapered stud
that is pressed into the aluminum knuckle. The ball
joint stud is threaded on the end for a retainer nut.
The ball joint has a non-vented seal boot. The seal
boot has an integrated heat shield.
The ball joint used in the lower control arm of this
vehicle is a sealed-for-life ball joint and requires no
maintenance lubrication. The ball joint has been
lubricated-for-life during the manufacturing process.
A special fitting cap is installed on the fill port. This
cap must not be removed and replaced with a com-
mon zirc fitting. The special cap is there to eliminate
the possibility of lubrication latter during the ball
joints life, thus damaging the non-vented seal boot.
NOTE: The ball joint does not require any type of
additional lubrication for the life of the vehicle. No
attempt should be made to ever add any lubrication
to the lower ball joint.
OPERATION
The ball joint is a pivotal joint on the lower control
arm that allows the knuckle to move up and down,
and turn with ease.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - LOWER BALL
JOINT
With the weight of the vehicle resting on the road
wheels, grasp the special fitting cap on the bottom of
the ball joint and with no mechanical assistance or
added force, attempt to rotate the grease fitting.
If the ball joint is worn, the grease fitting will
rotate easily. If movement is noted, replacement of
the control arm is recommended.
LOWER BALL JOINT SEAL
BOOT
DESCRIPTION - EXPORT
The lower ball joint seal boot is a two piece unit. It
consists of the seal boot, plus a separate shield that
is located in a groove at the top of the seal boot.
NOTE: The seal boot should only be replaced if
damaged during vehicle service. The entire lower
control arm should be replaced if the joint has been
contaminated.
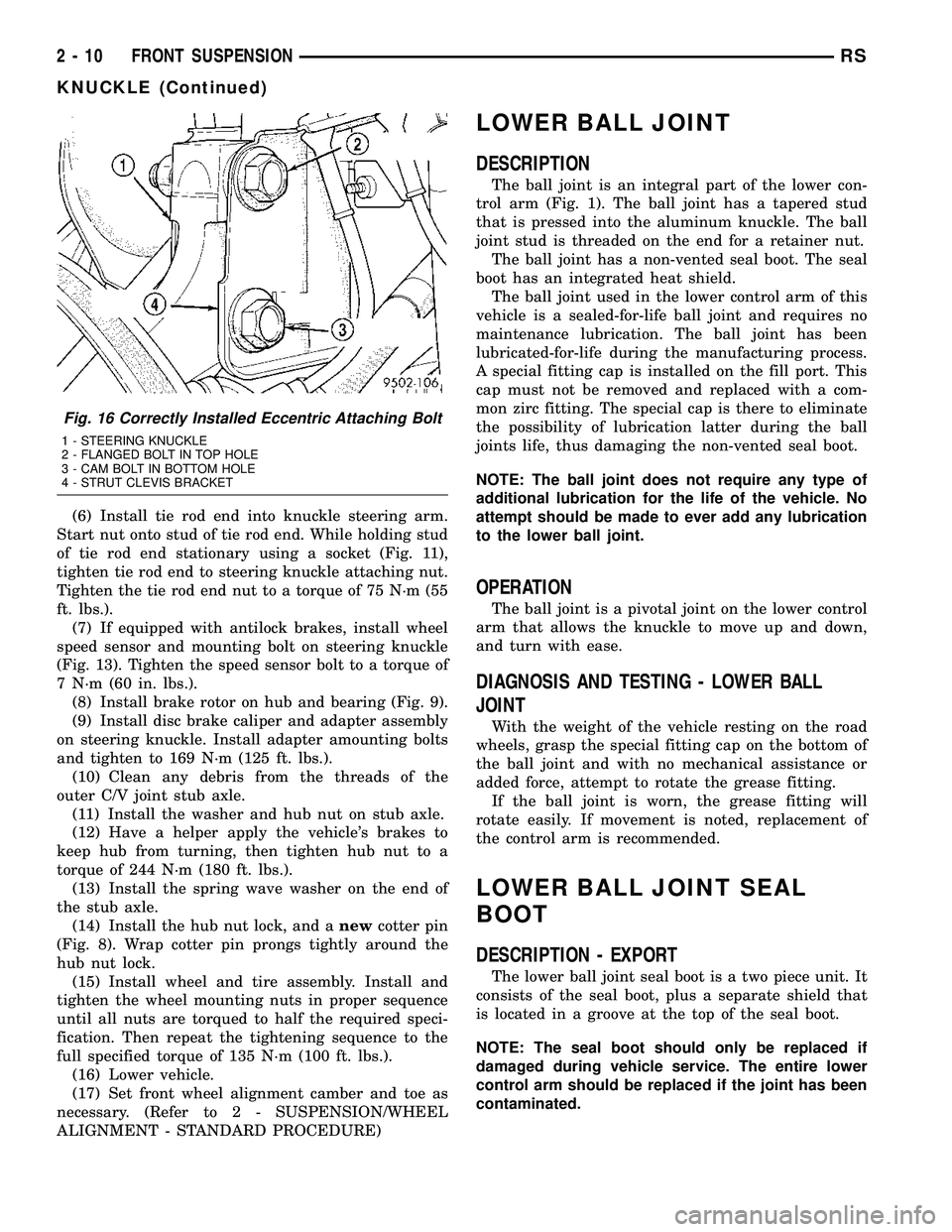
Fig. 16 Correctly Installed Eccentric Attaching Bolt
1 - STEERING KNUCKLE
2 - FLANGED BOLT IN TOP HOLE
3 - CAM BOLT IN BOTTOM HOLE
4 - STRUT CLEVIS BRACKET
2 - 10 FRONT SUSPENSIONRS
KNUCKLE (Continued)
Page 52 of 2339

REMOVAL
REMOVAL
(1) Remove steering knuckle from vehicle. (Refer
to 2 - SUSPENSION/FRONT/KNUCKLE -
REMOVAL)
(2) Using a screwdriver or other suitable tool, pry
seal boot off of ball joint (Fig. 17).
(3) Inspect ball joint for evidence of dirt or water
intrusion and wipe clean as necessary. If dirt or
water intrusion is extreme and joint cannot be prop-
erly cleaned, lower control arm will need to be
replaced. (Refer to 2 - SUSPENSION/FRONT/
LOWER CONTROL ARM - REMOVAL)
REMOVAL - EXPORT
(1) Remove steering knuckle from vehicle. (Refer
to 2 - SUSPENSION/FRONT/KNUCKLE -
REMOVAL)
(2) Remove shield from seal boot by gently pulling
on it.
(3) Using a screw driver or other suitable tool, pry
seal boot off lower ball joint.
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION
(1) Place a liberal dab of MopartWheel Bearing
Grease around base of ball joint stud at socket.(2) Install aNEWseal boot by hand as far as pos-
sible on ball joint. Ensure seal boot shield is posi-
tioned outward from control arm as shown (Fig. 18).
CAUTION: Do not use an arbor press to install seal
boot on ball joint. Damage to seal boot will occur if
excessive pressure is applied while it is being
installed.
(3) Place Installer, Special Tool 6758, over top of
seal boot and squarely align it with bottom edge of
seal boot (Fig. 19). Apply hand pressure (or gently
tap with a hammer if necessary) to top of Installer
until seal boot is pressed squarely down against top
surface of lower control arm.
(4) Wipe any grease off ball joint stem using a
clean shop towel with MopartBrake Parts Cleaner
applied to it.
CAUTION: Do not attempt to install a normal grease
zirc in ball joint in an effort to lubricate joint
through zirc fitting.
(5) Install steering knuckle on vehicle. (Refer to 2 -
SUSPENSION/FRONT/KNUCKLE - INSTALLA-
TION)
INSTALLATION - EXPORT
(1) Place a liberal dab of MopartWheel Bearing
Grease around the base of the ball joint stem at the
socket.
(2) Install aNEWseal boot by hand as far as pos-
sible on the ball joint.
Fig. 17 Ball Joint Seal Boot Removal
1 - BALL JOINT STUD
2 - SCREWDRIVER
3 - SEAL BOOT
Fig. 18 Ball Joint Seal Boot Installed Position
1 - BALL JOINT STUD
2 - LOWER CONTROL ARM
3 - SEAL BOOT SHIELD
RSFRONT SUSPENSION2-11
LOWER BALL JOINT SEAL BOOT (Continued)
Page 53 of 2339
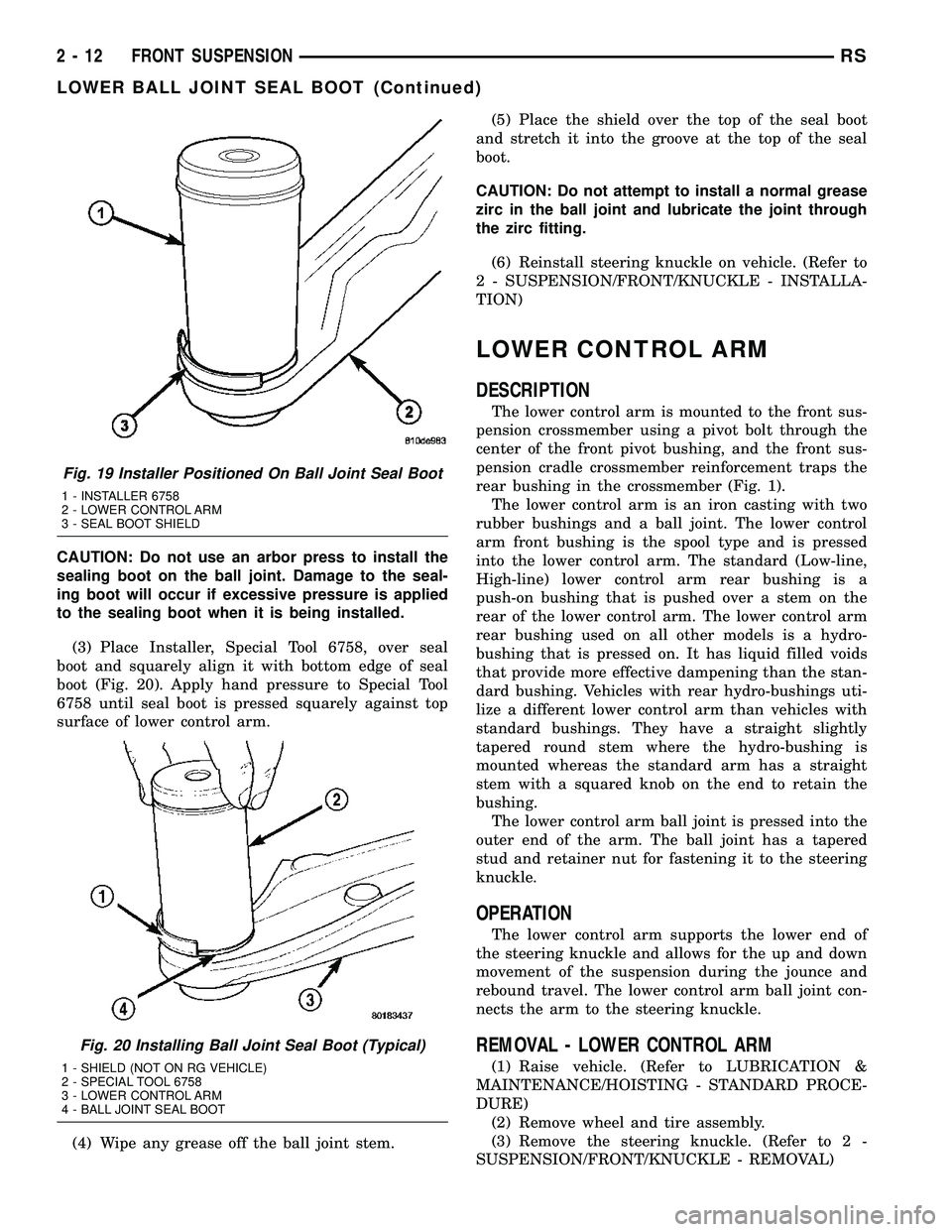
CAUTION: Do not use an arbor press to install the
sealing boot on the ball joint. Damage to the seal-
ing boot will occur if excessive pressure is applied
to the sealing boot when it is being installed.
(3) Place Installer, Special Tool 6758, over seal
boot and squarely align it with bottom edge of seal
boot (Fig. 20). Apply hand pressure to Special Tool
6758 until seal boot is pressed squarely against top
surface of lower control arm.
(4) Wipe any grease off the ball joint stem.(5) Place the shield over the top of the seal boot
and stretch it into the groove at the top of the seal
boot.
CAUTION: Do not attempt to install a normal grease
zirc in the ball joint and lubricate the joint through
the zirc fitting.
(6) Reinstall steering knuckle on vehicle. (Refer to
2 - SUSPENSION/FRONT/KNUCKLE - INSTALLA-
TION)
LOWER CONTROL ARM
DESCRIPTION
The lower control arm is mounted to the front sus-
pension crossmember using a pivot bolt through the
center of the front pivot bushing, and the front sus-
pension cradle crossmember reinforcement traps the
rear bushing in the crossmember (Fig. 1).
The lower control arm is an iron casting with two
rubber bushings and a ball joint. The lower control
arm front bushing is the spool type and is pressed
into the lower control arm. The standard (Low-line,
High-line) lower control arm rear bushing is a
push-on bushing that is pushed over a stem on the
rear of the lower control arm. The lower control arm
rear bushing used on all other models is a hydro-
bushing that is pressed on. It has liquid filled voids
that provide more effective dampening than the stan-
dard bushing. Vehicles with rear hydro-bushings uti-
lize a different lower control arm than vehicles with
standard bushings. They have a straight slightly
tapered round stem where the hydro-bushing is
mounted whereas the standard arm has a straight
stem with a squared knob on the end to retain the
bushing.
The lower control arm ball joint is pressed into the
outer end of the arm. The ball joint has a tapered
stud and retainer nut for fastening it to the steering
knuckle.
OPERATION
The lower control arm supports the lower end of
the steering knuckle and allows for the up and down
movement of the suspension during the jounce and
rebound travel. The lower control arm ball joint con-
nects the arm to the steering knuckle.
REMOVAL - LOWER CONTROL ARM
(1) Raise vehicle. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE/HOISTING - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE)
(2) Remove wheel and tire assembly.
(3) Remove the steering knuckle. (Refer to 2 -
SUSPENSION/FRONT/KNUCKLE - REMOVAL)
Fig. 19 Installer Positioned On Ball Joint Seal Boot
1 - INSTALLER 6758
2 - LOWER CONTROL ARM
3 - SEAL BOOT SHIELD
Fig. 20 Installing Ball Joint Seal Boot (Typical)
1 - SHIELD (NOT ON RG VEHICLE)
2 - SPECIAL TOOL 6758
3 - LOWER CONTROL ARM
4 - BALL JOINT SEAL BOOT
2 - 12 FRONT SUSPENSIONRS
LOWER BALL JOINT SEAL BOOT (Continued)
Page 61 of 2339
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - STRUT ASSEMBLY
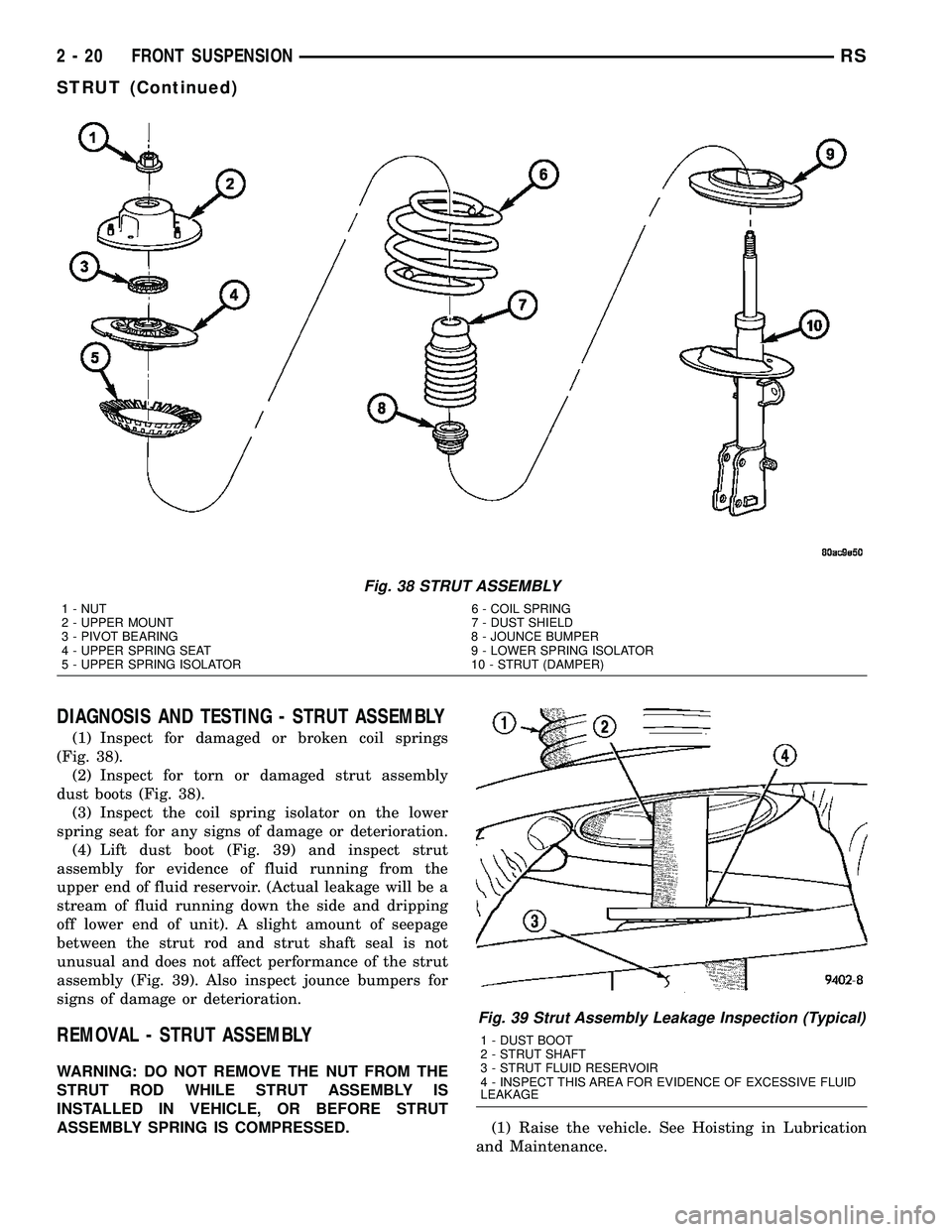
(1) Inspect for damaged or broken coil springs
(Fig. 38).
(2) Inspect for torn or damaged strut assembly
dust boots (Fig. 38).
(3) Inspect the coil spring isolator on the lower
spring seat for any signs of damage or deterioration.
(4) Lift dust boot (Fig. 39) and inspect strut
assembly for evidence of fluid running from the
upper end of fluid reservoir. (Actual leakage will be a
stream of fluid running down the side and dripping
off lower end of unit). A slight amount of seepage
between the strut rod and strut shaft seal is not
unusual and does not affect performance of the strut
assembly (Fig. 39). Also inspect jounce bumpers for
signs of damage or deterioration.
REMOVAL - STRUT ASSEMBLY
WARNING: DO NOT REMOVE THE NUT FROM THE
STRUT ROD WHILE STRUT ASSEMBLY IS
INSTALLED IN VEHICLE, OR BEFORE STRUT
ASSEMBLY SPRING IS COMPRESSED.
(1) Raise the vehicle. See Hoisting in Lubrication
and Maintenance.
Fig. 38 STRUT ASSEMBLY
1 - NUT 6 - COIL SPRING
2 - UPPER MOUNT 7 - DUST SHIELD
3 - PIVOT BEARING 8 - JOUNCE BUMPER
4 - UPPER SPRING SEAT 9 - LOWER SPRING ISOLATOR
5 - UPPER SPRING ISOLATOR 10 - STRUT (DAMPER)
Fig. 39 Strut Assembly Leakage Inspection (Typical)
1 - DUST BOOT
2 - STRUT SHAFT
3 - STRUT FLUID RESERVOIR
4 - INSPECT THIS AREA FOR EVIDENCE OF EXCESSIVE FLUID
LEAKAGE
2 - 20 FRONT SUSPENSIONRS
STRUT (Continued)