weight CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2005 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2005, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2005Pages: 2339, PDF Size: 59.69 MB
Page 85 of 2339

(2) Install the shackle mounting nuts on the
hanger pins, but DO NOT TIGHTEN AT THIS
TIME.
(3) AWD only ± Install, BUT DO NOT TIGHTEN,
retaining bolts fastening inner to outer halves of leaf
spring hanger at this time (Fig. 39).
(4) Using a jack, raise the leaf spring into
mounted position.
(5) Install the rear spring mount-to-body bolts
(Fig. 40). Tighten rear spring mount bolts to 61 N´m
(45 ft. lbs.) torque.
(6) Install the lower mounting bolt fastening the
shock absorber to the axle. DO NOT TIGHTEN THE
BOLT AT THIS TIME.
(7) Remove the jack from under axle.(8) Lower the vehicle so that the full weight of the
vehicle is on all four tires (curb height).
CAUTION: AWD only ± In order to avoid bending the
spring shackles, the shackle pin nuts must be tight-
ened to the specified torque before the inboard-to-
outboard shackle half bolts can be tightened.
(9) Tighten shackle mounting nuts to 61 N´m (45
ft. lbs.) torque.
(10) If equipped with AWD, tighten shackle-to-
shackle mounting bolts to 61 N´m (45 ft. lbs.) torque.
(11) Tighten shock absorber lower mounting bolt to
88 N´m (65 ft. lbs.) torque.
SPRING SHACKLE
REMOVAL
(Refer to 2 - SUSPENSION/REAR/SPRING
MOUNTS - REMOVAL)
INSTALLATION
(Refer to 2 - SUSPENSION/REAR/SPRING
MOUNTS - INSTALLATION)
STABILIZER BAR
DESCRIPTION
Some front-wheel-drive models use a stabilizer bar.
It is mounted behind the rear axle. All-wheel-drive
models use a stabilizer bar that is mounted in front
of the rear axle.
The stabilizer bar interconnects both sides of the
rear axle and attaches to the rear frame rails using 2
rubber isolated link arms.
Both type stabilizer bars have the same basic com-
ponents. Attachment to the rear axle tube, and rear
frame rails is through rubber-isolated bushings.
The 2 rubber isolated links are connected to the
rear frame rails by brackets. These brackets are
bolted to the bottom of the frame rails.
OPERATION
Jounce and rebound movements affecting one
wheel are partially transmitted to the opposite wheel
to reduce body roll.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - AWD
(1) Raise vehicle. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE/HOISTING - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE)
Fig. 39 All-Wheel-Drive Rear Suspension
1 - SHACKLE
2 - REAR MOUNT (HANGER)
3 - LEAF SPRING (MULTI-LEAF)
4 - AWD REAR AXLE
Fig. 40 Rear Spring Mount (Typical)
1 - LEAF SPRING MOUNT
2 - 44 REAR SUSPENSIONRS
SPRING MOUNTS - REAR (Continued)
Page 86 of 2339
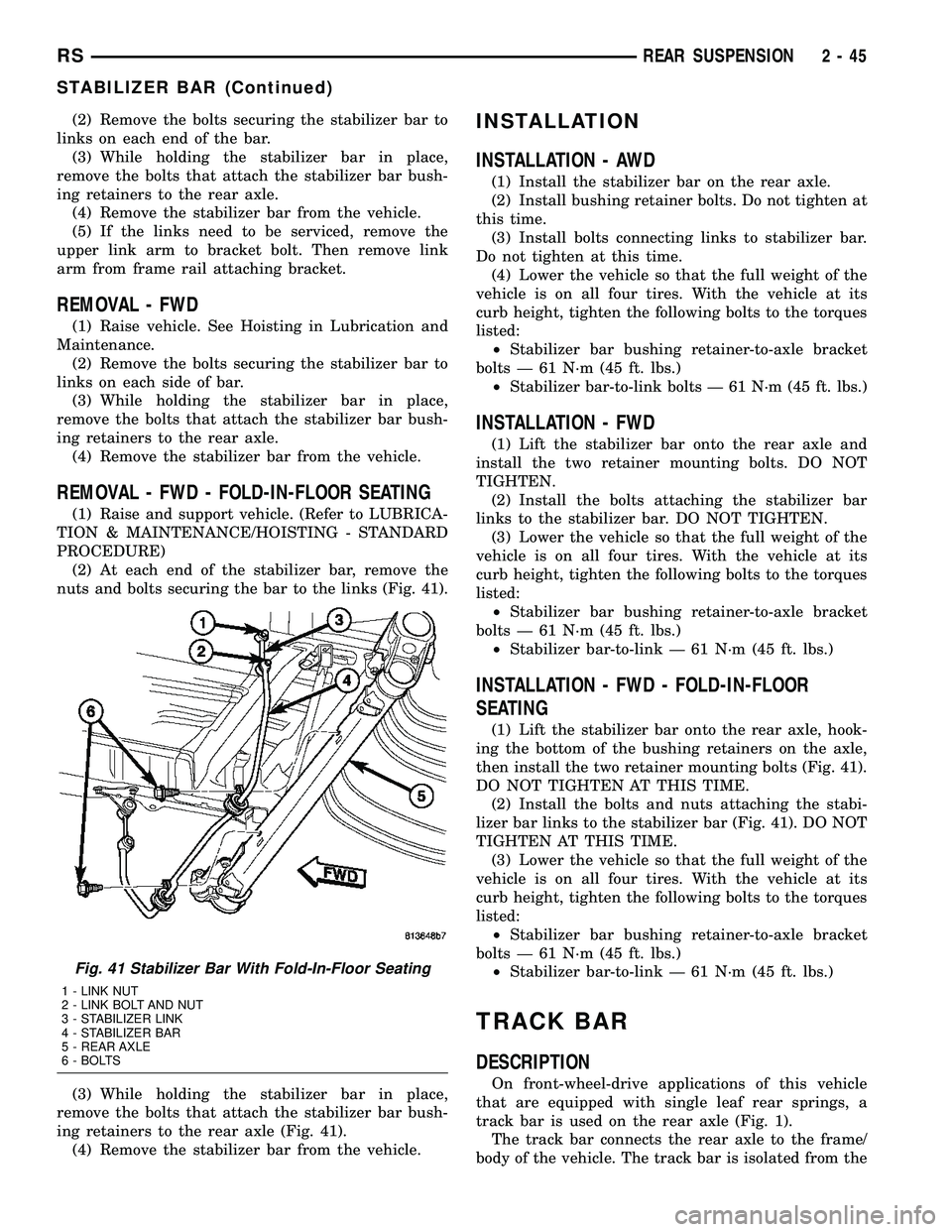
(2) Remove the bolts securing the stabilizer bar to
links on each end of the bar.
(3) While holding the stabilizer bar in place,
remove the bolts that attach the stabilizer bar bush-
ing retainers to the rear axle.
(4) Remove the stabilizer bar from the vehicle.
(5) If the links need to be serviced, remove the
upper link arm to bracket bolt. Then remove link
arm from frame rail attaching bracket.
REMOVAL - FWD
(1) Raise vehicle. See Hoisting in Lubrication and
Maintenance.
(2) Remove the bolts securing the stabilizer bar to
links on each side of bar.
(3) While holding the stabilizer bar in place,
remove the bolts that attach the stabilizer bar bush-
ing retainers to the rear axle.
(4) Remove the stabilizer bar from the vehicle.
REMOVAL - FWD - FOLD-IN-FLOOR SEATING
(1) Raise and support vehicle. (Refer to LUBRICA-
TION & MAINTENANCE/HOISTING - STANDARD
PROCEDURE)
(2) At each end of the stabilizer bar, remove the
nuts and bolts securing the bar to the links (Fig. 41).
(3) While holding the stabilizer bar in place,
remove the bolts that attach the stabilizer bar bush-
ing retainers to the rear axle (Fig. 41).
(4) Remove the stabilizer bar from the vehicle.
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - AWD
(1) Install the stabilizer bar on the rear axle.
(2) Install bushing retainer bolts. Do not tighten at
this time.
(3) Install bolts connecting links to stabilizer bar.
Do not tighten at this time.
(4) Lower the vehicle so that the full weight of the
vehicle is on all four tires. With the vehicle at its
curb height, tighten the following bolts to the torques
listed:
²Stabilizer bar bushing retainer-to-axle bracket
bolts Ð 61 N´m (45 ft. lbs.)
²Stabilizer bar-to-link bolts Ð 61 N´m (45 ft. lbs.)
INSTALLATION - FWD
(1) Lift the stabilizer bar onto the rear axle and
install the two retainer mounting bolts. DO NOT
TIGHTEN.
(2) Install the bolts attaching the stabilizer bar
links to the stabilizer bar. DO NOT TIGHTEN.
(3) Lower the vehicle so that the full weight of the
vehicle is on all four tires. With the vehicle at its
curb height, tighten the following bolts to the torques
listed:
²Stabilizer bar bushing retainer-to-axle bracket
bolts Ð 61 N´m (45 ft. lbs.)
²Stabilizer bar-to-link Ð 61 N´m (45 ft. lbs.)
INSTALLATION - FWD - FOLD-IN-FLOOR
SEATING
(1) Lift the stabilizer bar onto the rear axle, hook-
ing the bottom of the bushing retainers on the axle,
then install the two retainer mounting bolts (Fig. 41).
DO NOT TIGHTEN AT THIS TIME.
(2) Install the bolts and nuts attaching the stabi-
lizer bar links to the stabilizer bar (Fig. 41). DO NOT
TIGHTEN AT THIS TIME.
(3) Lower the vehicle so that the full weight of the
vehicle is on all four tires. With the vehicle at its
curb height, tighten the following bolts to the torques
listed:
²Stabilizer bar bushing retainer-to-axle bracket
bolts Ð 61 N´m (45 ft. lbs.)
²Stabilizer bar-to-link Ð 61 N´m (45 ft. lbs.)
TRACK BAR
DESCRIPTION
On front-wheel-drive applications of this vehicle
that are equipped with single leaf rear springs, a
track bar is used on the rear axle (Fig. 1).
The track bar connects the rear axle to the frame/
body of the vehicle. The track bar is isolated from the
Fig. 41 Stabilizer Bar With Fold-In-Floor Seating
1 - LINK NUT
2 - LINK BOLT AND NUT
3 - STABILIZER LINK
4 - STABILIZER BAR
5 - REAR AXLE
6 - BOLTS
RSREAR SUSPENSION2-45
STABILIZER BAR (Continued)
Page 87 of 2339
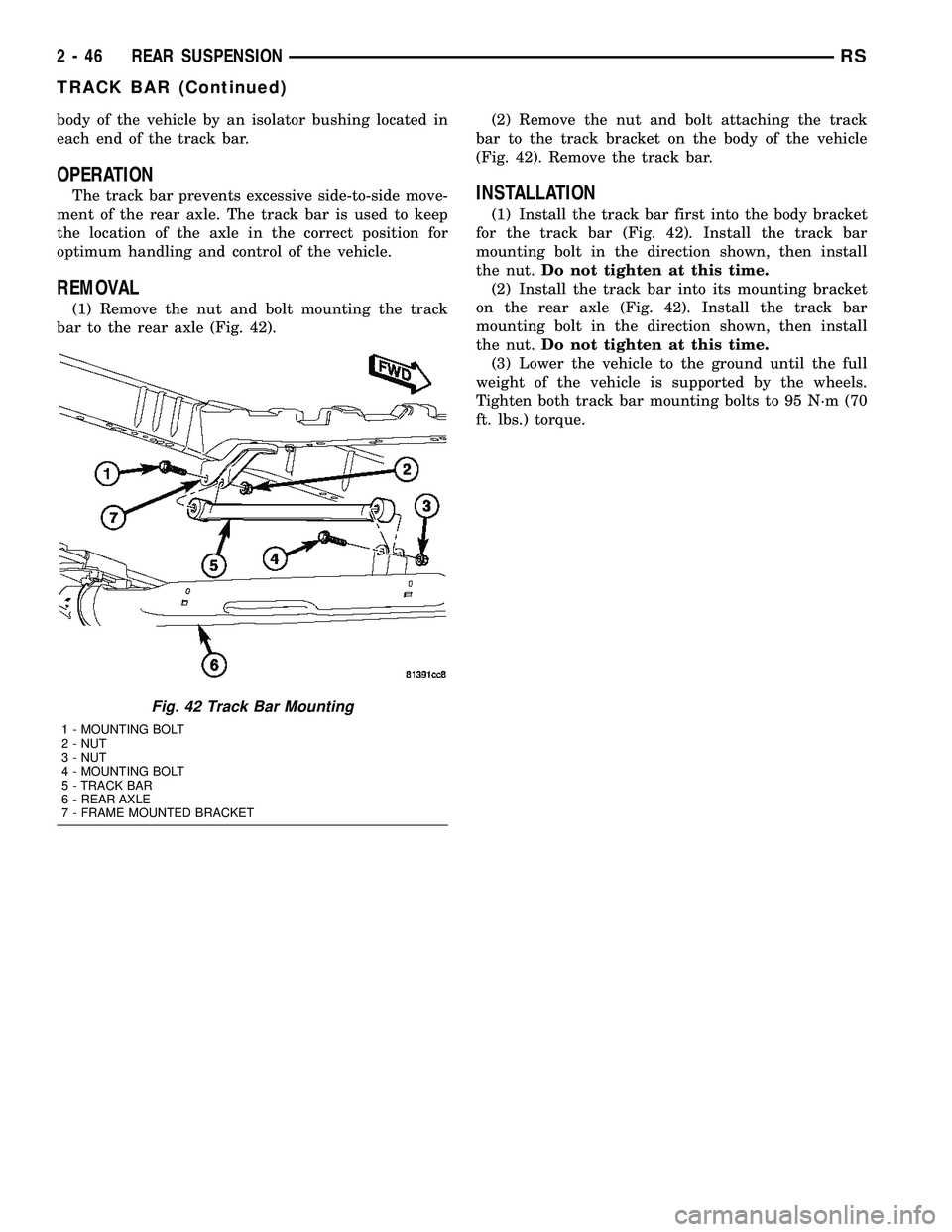
body of the vehicle by an isolator bushing located in
each end of the track bar.
OPERATION
The track bar prevents excessive side-to-side move-
ment of the rear axle. The track bar is used to keep
the location of the axle in the correct position for
optimum handling and control of the vehicle.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the nut and bolt mounting the track
bar to the rear axle (Fig. 42).(2) Remove the nut and bolt attaching the track
bar to the track bracket on the body of the vehicle
(Fig. 42). Remove the track bar.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install the track bar first into the body bracket
for the track bar (Fig. 42). Install the track bar
mounting bolt in the direction shown, then install
the nut.Do not tighten at this time.
(2) Install the track bar into its mounting bracket
on the rear axle (Fig. 42). Install the track bar
mounting bolt in the direction shown, then install
the nut.Do not tighten at this time.
(3) Lower the vehicle to the ground until the full
weight of the vehicle is supported by the wheels.
Tighten both track bar mounting bolts to 95 N´m (70
ft. lbs.) torque.
Fig. 42 Track Bar Mounting
1 - MOUNTING BOLT
2 - NUT
3 - NUT
4 - MOUNTING BOLT
5 - TRACK BAR
6 - REAR AXLE
7 - FRAME MOUNTED BRACKET
2 - 46 REAR SUSPENSIONRS
TRACK BAR (Continued)
Page 93 of 2339
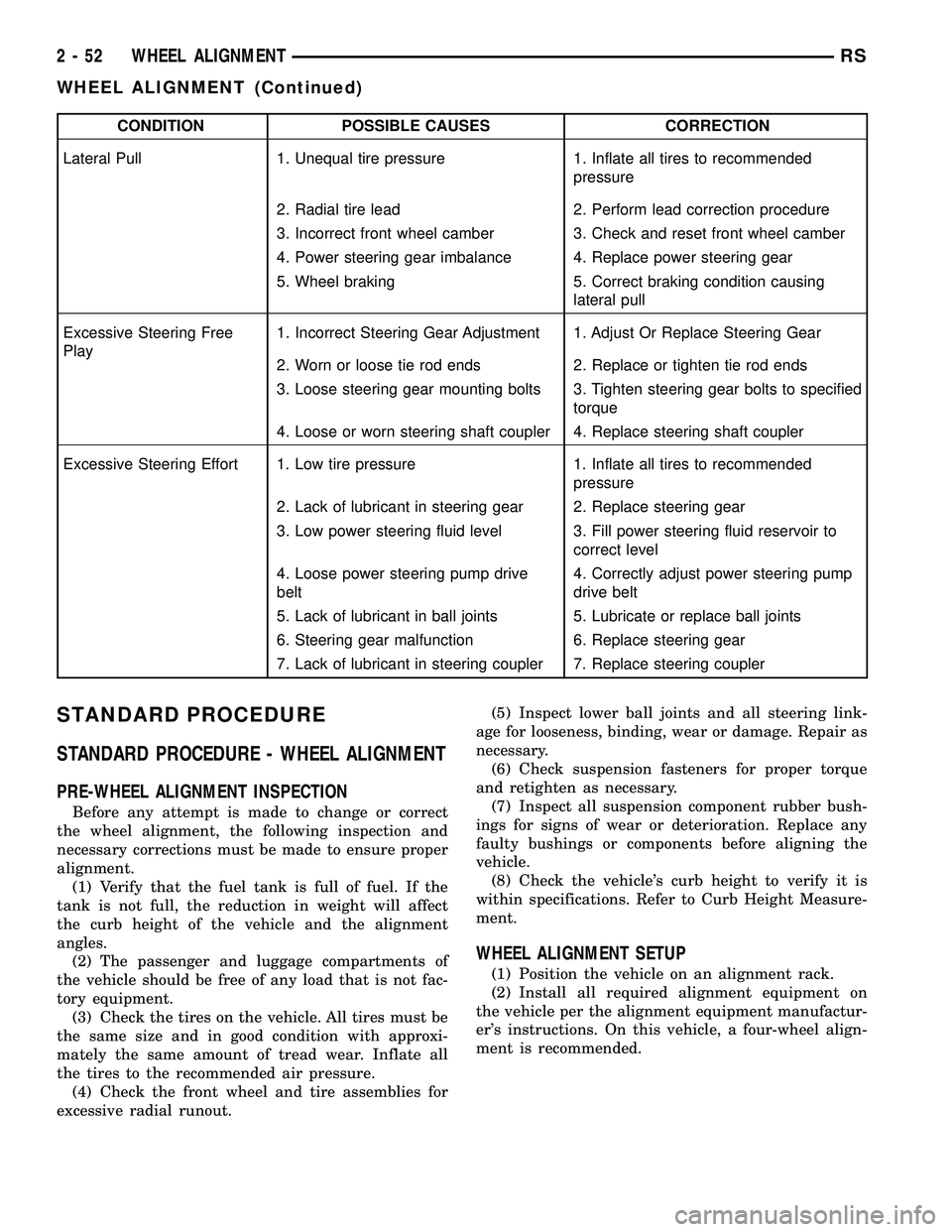
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
Lateral Pull 1. Unequal tire pressure 1. Inflate all tires to recommended
pressure
2. Radial tire lead 2. Perform lead correction procedure
3. Incorrect front wheel camber 3. Check and reset front wheel camber
4. Power steering gear imbalance 4. Replace power steering gear
5. Wheel braking 5. Correct braking condition causing
lateral pull
Excessive Steering Free
Play1. Incorrect Steering Gear Adjustment 1. Adjust Or Replace Steering Gear
2. Worn or loose tie rod ends 2. Replace or tighten tie rod ends
3. Loose steering gear mounting bolts 3. Tighten steering gear bolts to specified
torque
4. Loose or worn steering shaft coupler 4. Replace steering shaft coupler
Excessive Steering Effort 1. Low tire pressure 1. Inflate all tires to recommended
pressure
2. Lack of lubricant in steering gear 2. Replace steering gear
3. Low power steering fluid level 3. Fill power steering fluid reservoir to
correct level
4. Loose power steering pump drive
belt4. Correctly adjust power steering pump
drive belt
5. Lack of lubricant in ball joints 5. Lubricate or replace ball joints
6. Steering gear malfunction 6. Replace steering gear
7. Lack of lubricant in steering coupler 7. Replace steering coupler
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - WHEEL ALIGNMENT
PRE-WHEEL ALIGNMENT INSPECTION
Before any attempt is made to change or correct
the wheel alignment, the following inspection and
necessary corrections must be made to ensure proper
alignment.
(1) Verify that the fuel tank is full of fuel. If the
tank is not full, the reduction in weight will affect
the curb height of the vehicle and the alignment
angles.
(2) The passenger and luggage compartments of
the vehicle should be free of any load that is not fac-
tory equipment.
(3) Check the tires on the vehicle. All tires must be
the same size and in good condition with approxi-
mately the same amount of tread wear. Inflate all
the tires to the recommended air pressure.
(4) Check the front wheel and tire assemblies for
excessive radial runout.(5) Inspect lower ball joints and all steering link-
age for looseness, binding, wear or damage. Repair as
necessary.
(6) Check suspension fasteners for proper torque
and retighten as necessary.
(7) Inspect all suspension component rubber bush-
ings for signs of wear or deterioration. Replace any
faulty bushings or components before aligning the
vehicle.
(8) Check the vehicle's curb height to verify it is
within specifications. Refer to Curb Height Measure-
ment.
WHEEL ALIGNMENT SETUP
(1) Position the vehicle on an alignment rack.
(2) Install all required alignment equipment on
the vehicle per the alignment equipment manufactur-
er's instructions. On this vehicle, a four-wheel align-
ment is recommended.
2 - 52 WHEEL ALIGNMENTRS
WHEEL ALIGNMENT (Continued)
Page 94 of 2339

NOTE: Prior to reading the vehicle's alignment
readouts, the front and rear of vehicle should be
jounced. Induce jounce (rear first, then front) by
grasping the center of the bumper and jouncing
each end of vehicle an equal number of times. The
bumper should always be released when vehicle is
at the bottom of the jounce cycle.
(3) Read the vehicle's current front and rear align-
ment settings. Compare the vehicle's current align-
ment settings to the vehicle specifications for camber,
caster and toe-in. (Refer to 2 - SUSPENSION/
WHEEL ALIGNMENT - SPECIFICATIONS)
(4) If front camber and caster are not within spec-
ifications, proceed to CAMBER AND CASTER below.
If caster and camber are within specifications, pro-
ceed to TOE which can be found following CAMBER
AND CASTER. Rear camber, caster and toe are not
adjustable. If found not to be within specifications,
reinspect for damaged suspension or body compo-
nents and replace as necessary.
CAMBER AND CASTER
Camber and caster settings on this vehicle are
determined at the time the vehicle is designed, by
the location of the vehicle's suspension components.
This is referred to as NET BUILD. The result is no
required adjustment of camber and caster after the
vehicle is built or when servicing the suspension
components. Thus, when performing a wheel align-
ment, caster and camber are not normally considered
adjustable angles. Camber and caster should be
checked to ensure they meet vehicle specifications.
If front camber is found not to meet alignment
specifications, it can be adjusted using an available
camber adjustment bolt package. Before installing a
camber adjustment bolt package on a vehicle found
to be outside the specifications, inspect the suspen-
sion components for any signs of damage or bending.
CAUTION: Do not attempt to adjust the vehicles
wheel alignment by heating, bending or by perform-
ing any other modification to the vehicle's front
suspension components or body.
If camber readings are not within specifications,
use the following procedure to install the front cam-
ber adjustment bolt package and then adjust front
camber.
CAMBER ADJUSTMENT BOLT PACKAGE INSTALLATION
The camber adjustment bolt package contains 2
flange bolts, 2 cam bolts, 2 dog bone washers, and 4
nuts. This package services both sides of the vehicle.
Use the package to attach the strut clevis bracket to
the steering knuckle after the strut clevis brackethas been modified. To install and adjust the camber
adjustment bolt package, follow the procedure below.
(1) Raise the vehicle until its tires are not support-
ing the weight of the vehicle.
(2) Remove the front tire and wheel assemblies.
CAUTION: When removing the steering knuckle
from the strut clevis bracket, do not put a strain on
the brake flex hose. Also, do not let the weight of
the steering knuckle assembly be supported by the
brake flex hose when removed from the strut
assembly. If necessary use a wire hanger to sup-
port the steering knuckle assembly or if required
remove the brake flex hose from the caliper assem-
bly.
CAUTION: The knuckle to strut assembly attaching
bolt shanks are serrated and must not be turned
during removal. Remove the nuts while holding the
bolts stationary.
(3) Remove the top and bottom, strut clevis
bracket to steering knuckle attaching bolts (Fig.
7)and discard. Separate the steering knuckle from
the strut clevis bracket and position steering knuckle
so it is out of the way of the strut.
CAUTION: When slotting the bottom mounting hole
on the strut clevis bracket, do not enlarge the hole
beyond the indentations on the sides of the strut
clevis bracket (Fig. 8).
Fig. 7 Clevis Bracket To Steering Knuckle Attaching
Bolts
1 - STRUT CLEVIS BRACKET
2 - ATTACHING BOLTS
3 - TIE ROD END
4 - ROTOR
5 - STEERING KNUCKLE
RSWHEEL ALIGNMENT2-53
WHEEL ALIGNMENT (Continued)
Page 98 of 2339

DIFFERENTIAL & DRIVELINE
HALF SHAFT - FRONT
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
HALF SHAFT - FRONT
DESCRIPTION..........................1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HALF SHAFT.....1
REMOVAL.............................2
INSTALLATION..........................4
SPECIFICATIONS - HALF SHAFT - FRONT....6CV BOOT - INNER
REMOVAL.............................6
INSTALLATION..........................7
CV BOOT - OUTER
REMOVAL.............................10
INSTALLATION.........................11
HALF SHAFT - FRONT
DESCRIPTION
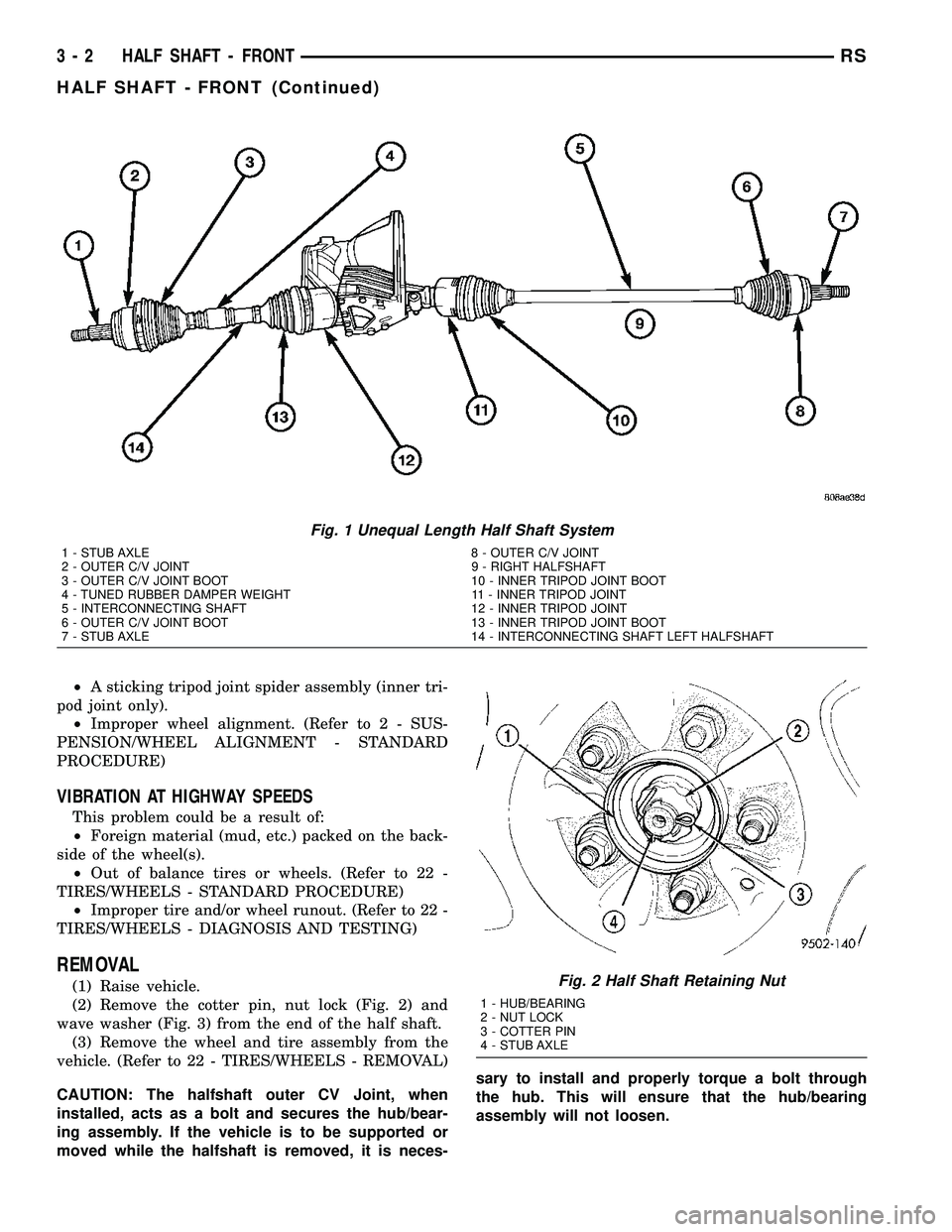
All vehicles use an unequal length half shaft sys-
tem (Fig. 1).
The left half shaft uses a tuned rubber damper
weight. When replacing the left half shaft, be sure
the replacement half shaft has the same damper
weight as the original.
All half shaft assemblies use the same type of
inner and outer joints. The inner joint of both half
shaft assemblies is a tripod joint, and the outer joint
of both half shaft assemblies is a Rzeppa joint. Both
tripod joints and Rzeppa joints are true constant
velocity (CV) joint assemblies. The inner tripod joint
allows for the changes in half shaft length through
the jounce and rebound travel of the front suspen-
sion.
On vehicles equipped with ABS brakes, the outer
CV joint is equipped with a tone wheel used to deter-
mine vehicle speed for ABS brake operation.
The inner tripod joint of both half shafts is splined
into the transaxle side gears. The inner tripod joints
are retained in the side gears of the transaxle using
a snap ring located in the stub shaft of the tripod
joint. The outer CV joint has a stub shaft that is
splined into the wheel hub and retained by a steel
hub nut.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - HALF SHAFT
VEHICLE INSPECTION
(1) Check for grease in the vicinity of the inboard
tripod joint and outboard CV joint; this is a sign of
inner or outer joint seal boot or seal boot clamp dam-
age.
NOISE AND/OR VIBRATION IN TURNS
A clicking noise and/or a vibration in turns could
be caused by one of the following conditions:
²Damaged outer CV or inner tripod joint seal
boot or seal boot clamps. This will result in the loss
and/or contamination of the joint grease, resulting in
inadequate lubrication of the joint.
²Noise may also be caused by another component
of the vehicle coming in contact with the half shafts.
CLUNKING NOISE DURING ACCELERATION
This noise may be a result of one of the following
conditions:
²A torn seal boot on the inner or outer joint of the
half shaft assembly.
²A loose or missing clamp on the inner or outer
joint of the half shaft assembly.
²A damaged or worn half shaft CV joint.
SHUDDER OR VIBRATION DURING ACCELERATION
This problem could be a result of:
²A worn or damaged half shaft inner tripod joint.
RSDIFFERENTIAL & DRIVELINE3-1
Page 99 of 2339
²A sticking tripod joint spider assembly (inner tri-
pod joint only).
²Improper wheel alignment. (Refer to 2 - SUS-
PENSION/WHEEL ALIGNMENT - STANDARD
PROCEDURE)
VIBRATION AT HIGHWAY SPEEDS
This problem could be a result of:
²Foreign material (mud, etc.) packed on the back-
side of the wheel(s).
²Out of balance tires or wheels. (Refer to 22 -
TIRES/WHEELS - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
²Improper tire and/or wheel runout. (Refer to 22 -
TIRES/WHEELS - DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING)
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle.
(2) Remove the cotter pin, nut lock (Fig. 2) and
wave washer (Fig. 3) from the end of the half shaft.
(3) Remove the wheel and tire assembly from the
vehicle. (Refer to 22 - TIRES/WHEELS - REMOVAL)
CAUTION: The halfshaft outer CV Joint, when
installed, acts as a bolt and secures the hub/bear-
ing assembly. If the vehicle is to be supported or
moved while the halfshaft is removed, it is neces-sary to install and properly torque a bolt through
the hub. This will ensure that the hub/bearing
assembly will not loosen.
Fig. 1 Unequal Length Half Shaft System
1 - STUB AXLE 8 - OUTER C/V JOINT
2 - OUTER C/V JOINT 9 - RIGHT HALFSHAFT
3 - OUTER C/V JOINT BOOT 10 - INNER TRIPOD JOINT BOOT
4 - TUNED RUBBER DAMPER WEIGHT 11 - INNER TRIPOD JOINT
5 - INTERCONNECTING SHAFT 12 - INNER TRIPOD JOINT
6 - OUTER C/V JOINT BOOT 13 - INNER TRIPOD JOINT BOOT
7 - STUB AXLE 14 - INTERCONNECTING SHAFT LEFT HALFSHAFT
Fig. 2 Half Shaft Retaining Nut
1 - HUB/BEARING
2 - NUT LOCK
3 - COTTER PIN
4 - STUB AXLE
3 - 2 HALF SHAFT - FRONTRS
HALF SHAFT - FRONT (Continued)
Page 126 of 2339
BRAKE PADS/SHOES - FRONT
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - FRONT DISC BRAKE SHOES
(CONTINENTAL TEVES BRAKES)
(1) Raise the vehicle. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE/HOISTING - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE).
(2) Remove both front wheel and tire assemblies.
(3) Begin on one side of the vehicle.
(4) Remove the anti-rattle clip from the outboard
side of the caliper and adapter.
(5) Remove the two caliper guide pin bolts.
(6) Remove caliper from caliper adapter and brake
rotor.
CAUTION: Supporting weight of caliper by the flex-
ible brake fluid hose can damage the hose.
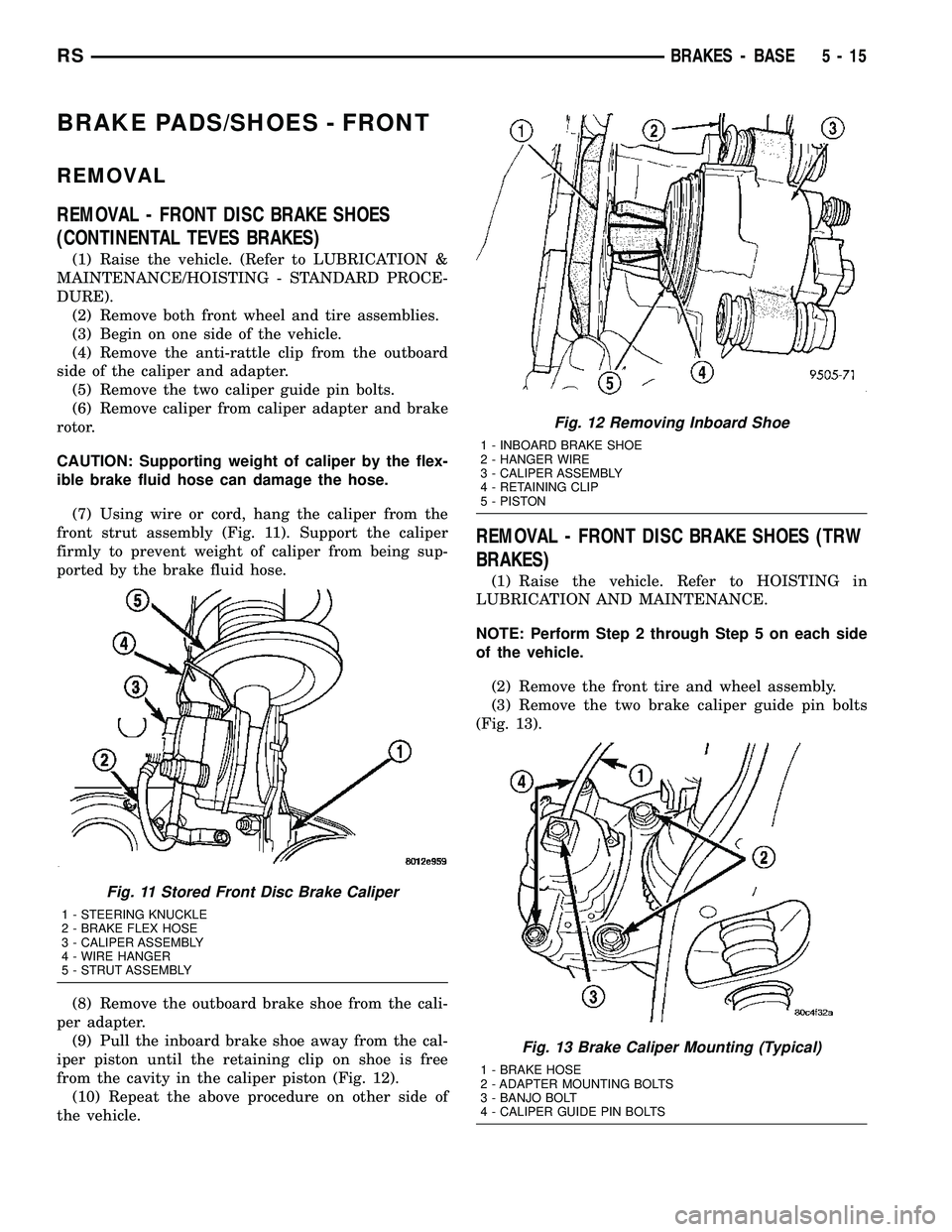
(7) Using wire or cord, hang the caliper from the
front strut assembly (Fig. 11). Support the caliper
firmly to prevent weight of caliper from being sup-
ported by the brake fluid hose.
(8) Remove the outboard brake shoe from the cali-
per adapter.
(9) Pull the inboard brake shoe away from the cal-
iper piston until the retaining clip on shoe is free
from the cavity in the caliper piston (Fig. 12).
(10) Repeat the above procedure on other side of
the vehicle.
REMOVAL - FRONT DISC BRAKE SHOES (TRW
BRAKES)
(1) Raise the vehicle. Refer to HOISTING in
LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE.
NOTE: Perform Step 2 through Step 5 on each side
of the vehicle.
(2) Remove the front tire and wheel assembly.
(3) Remove the two brake caliper guide pin bolts
(Fig. 13).
Fig. 11 Stored Front Disc Brake Caliper
1 - STEERING KNUCKLE
2 - BRAKE FLEX HOSE
3 - CALIPER ASSEMBLY
4 - WIRE HANGER
5 - STRUT ASSEMBLY
Fig. 12 Removing Inboard Shoe
1 - INBOARD BRAKE SHOE
2 - HANGER WIRE
3 - CALIPER ASSEMBLY
4 - RETAINING CLIP
5 - PISTON
Fig. 13 Brake Caliper Mounting (Typical)
1 - BRAKE HOSE
2 - ADAPTER MOUNTING BOLTS
3 - BANJO BOLT
4 - CALIPER GUIDE PIN BOLTS
RSBRAKES - BASE5-15
Page 129 of 2339
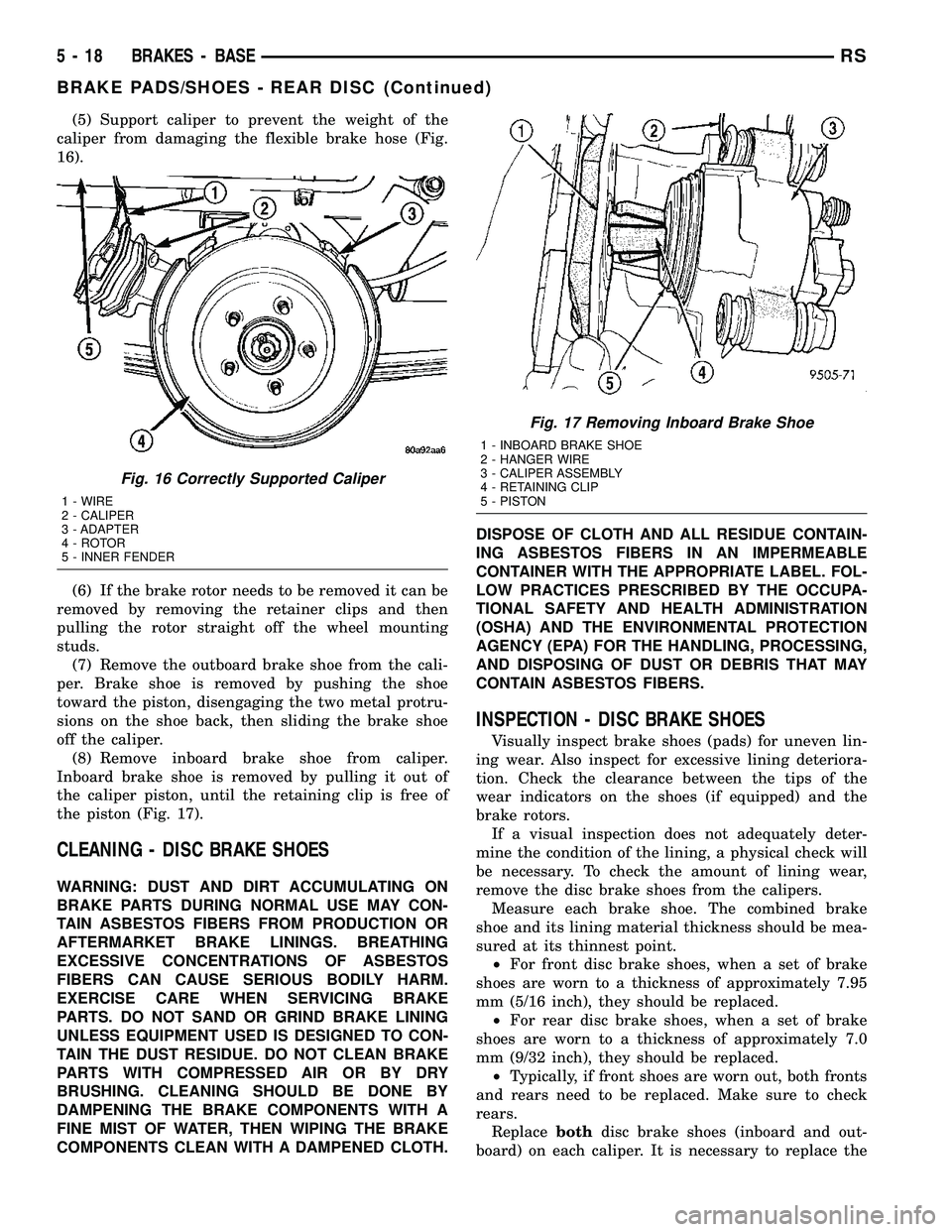
(5) Support caliper to prevent the weight of the
caliper from damaging the flexible brake hose (Fig.
16).
(6) If the brake rotor needs to be removed it can be
removed by removing the retainer clips and then
pulling the rotor straight off the wheel mounting
studs.
(7) Remove the outboard brake shoe from the cali-
per. Brake shoe is removed by pushing the shoe
toward the piston, disengaging the two metal protru-
sions on the shoe back, then sliding the brake shoe
off the caliper.
(8) Remove inboard brake shoe from caliper.
Inboard brake shoe is removed by pulling it out of
the caliper piston, until the retaining clip is free of
the piston (Fig. 17).
CLEANING - DISC BRAKE SHOES
WARNING: DUST AND DIRT ACCUMULATING ON
BRAKE PARTS DURING NORMAL USE MAY CON-
TAIN ASBESTOS FIBERS FROM PRODUCTION OR
AFTERMARKET BRAKE LININGS. BREATHING
EXCESSIVE CONCENTRATIONS OF ASBESTOS
FIBERS CAN CAUSE SERIOUS BODILY HARM.
EXERCISE CARE WHEN SERVICING BRAKE
PARTS. DO NOT SAND OR GRIND BRAKE LINING
UNLESS EQUIPMENT USED IS DESIGNED TO CON-
TAIN THE DUST RESIDUE. DO NOT CLEAN BRAKE
PARTS WITH COMPRESSED AIR OR BY DRY
BRUSHING. CLEANING SHOULD BE DONE BY
DAMPENING THE BRAKE COMPONENTS WITH A
FINE MIST OF WATER, THEN WIPING THE BRAKE
COMPONENTS CLEAN WITH A DAMPENED CLOTH.DISPOSE OF CLOTH AND ALL RESIDUE CONTAIN-
ING ASBESTOS FIBERS IN AN IMPERMEABLE
CONTAINER WITH THE APPROPRIATE LABEL. FOL-
LOW PRACTICES PRESCRIBED BY THE OCCUPA-
TIONAL SAFETY AND HEALTH ADMINISTRATION
(OSHA) AND THE ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
AGENCY (EPA) FOR THE HANDLING, PROCESSING,
AND DISPOSING OF DUST OR DEBRIS THAT MAY
CONTAIN ASBESTOS FIBERS.
INSPECTION - DISC BRAKE SHOES
Visually inspect brake shoes (pads) for uneven lin-
ing wear. Also inspect for excessive lining deteriora-
tion. Check the clearance between the tips of the
wear indicators on the shoes (if equipped) and the
brake rotors.
If a visual inspection does not adequately deter-
mine the condition of the lining, a physical check will
be necessary. To check the amount of lining wear,
remove the disc brake shoes from the calipers.
Measure each brake shoe. The combined brake
shoe and its lining material thickness should be mea-
sured at its thinnest point.
²For front disc brake shoes, when a set of brake
shoes are worn to a thickness of approximately 7.95
mm (5/16 inch), they should be replaced.
²For rear disc brake shoes, when a set of brake
shoes are worn to a thickness of approximately 7.0
mm (9/32 inch), they should be replaced.
²Typically, if front shoes are worn out, both fronts
and rears need to be replaced. Make sure to check
rears.
Replacebothdisc brake shoes (inboard and out-
board) on each caliper. It is necessary to replace the
Fig. 16 Correctly Supported Caliper
1 - WIRE
2 - CALIPER
3 - ADAPTER
4 - ROTOR
5 - INNER FENDER
Fig. 17 Removing Inboard Brake Shoe
1 - INBOARD BRAKE SHOE
2 - HANGER WIRE
3 - CALIPER ASSEMBLY
4 - RETAINING CLIP
5 - PISTON
5 - 18 BRAKES - BASERS
BRAKE PADS/SHOES - REAR DISC (Continued)
Page 191 of 2339

(11) Support caliper to prevent the weight of the
caliper from damaging the flexible brake hose (Fig.
134).
(12) Remove the rotor from the hub/bearing.
(13) Remove the park brake cable mounting bolt to
adapter.
(14) Remove the end of the park brake cable from
the actuator lever on the adapter (Fig. 135).(15) Remove the end of the park brake cable from
the adapter. Park brake cable is removed from
adapter using a 1/2 wrench slipped over the park
brake cable retainer as show in (Fig. 136) to com-
press the locking tabs on the park brake cable
retainer.
(16) AWD only - Remove ABS wheel speed sensor
head from hub/bearing (Fig. 137).
Fig. 134 Correctly Supported Caliper
1 - WIRE
2 - CALIPER
3 - ADAPTER
4 - ROTOR
5 - INNER FENDER
Fig. 135 Park Brake Cable Attachment To Actuator
1 - ADAPTER
2 - PARK BRAKE CABLE
3 - ACTUATOR
4 - AXLE
5 - DRIVESHAFT
6 - PARK BRAKE CABLE RETAINER
7 - HORSESHOE CLIP
Fig. 136 Park Brake Cable Removal From Adapter
1 - DRIVESHAFT
2 - 1/2º WRENCH
3 - PARK BRAKE CABLE
4 - PARK BRAKE CABLE RETAINER
5 - ADAPTER
Fig. 137 Speed Sensor Attaching Bolt (AWD)
1 - ADAPTER
2 - TONE WHEEL
3 - WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
4 - AXLE
5 - BOLT
6 - DRIVESHAFT
5 - 80 BRAKES - BASERS
SHOES - PARKING BRAKE (Continued)