battery CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2005 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2005, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2005Pages: 2339, PDF Size: 59.69 MB
Page 1576 of 2339
A conventional mechanical interlock system is also
used. This system manually prohibits shifter move-
ment when the ignition switch is in the LOCK or
ACC positions. Solenoid operation is not required in
these key positions.
For intended BTSI system operation, refer to the
following chart:
ACTION EXPECTED RESPONSE
1. Turn key to the9OFF9
position.1. Shifter CAN be shifted
out of park with brake
pedal applied.
2. Turn key to the
9ON/RUN9position.2. Shifter CANNOT be
shifted out of park.
3. Turn key to the
9ON/RUN9position and
depress the brake pedal.3. Shifter CAN be shifted
out of park.
4. Leave shifter in any
gear and try to return key
to the9LOCK9or9ACC9
position.4. Key cannot be
returned to the9LOCK9or
9ACC9position.
5. Return shifter to
9PARK9and try to remove
the key.5. Key can be removed
(after returning to9LOCK9
position).
6. With the key removed,
try to shift out of9PARK9.6. Shifter cannot be
shifted out of9PARK9.
NOTE: Any failure to meet these expected
responses requires system adjustment or repair.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - BRAKE/
TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID
For intended BTSI system operation, refer to the
following chart:
ACTION EXPECTED RESPONSE
1. Turn key to the9OFF9
position.1. Shifter CAN be shifted
out of park with brake
pedal applied.
2. Turn key to the
9ON/RUN9position.2. Shifter CANNOT be
shifted out of park.
3. Turn key to the
9ON/RUN9position and
depress the brake pedal.3. Shifter CAN be shifted
out of park.
4. Leave shifter in any
gear and try to return key
to the9LOCK9or9ACC9
position.4. Key cannot be
returned to the9LOCK9or
9ACC9position.
5. Return shifter to
9PARK9and try to remove
the key.5. Key can be removed
(after returning to9LOCK9
position).
ACTION EXPECTED RESPONSE
6. With the key removed,
try to shift out of9PARK9.6. Shifter cannot be
shifted out of9PARK9.
NOTE: Any failure to meet these expected
responses requires system repair. Refer to the
appropriate Diagnostic Information.
REMOVAL
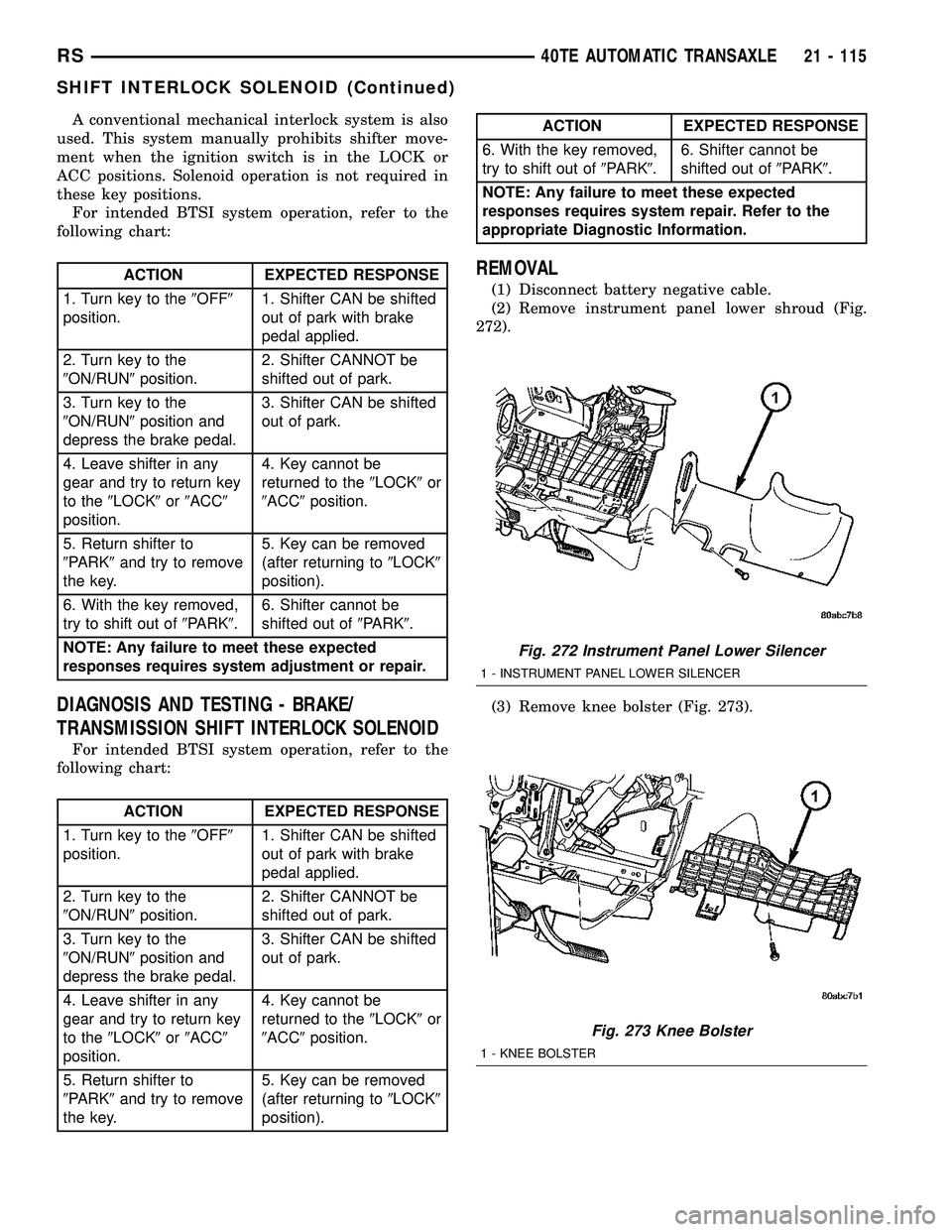
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Remove instrument panel lower shroud (Fig.
272).
(3) Remove knee bolster (Fig. 273).
Fig. 272 Instrument Panel Lower Silencer
1 - INSTRUMENT PANEL LOWER SILENCER
Fig. 273 Knee Bolster
1 - KNEE BOLSTER
RS40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 115
SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID (Continued)
Page 1578 of 2339

(3) Install steering column lower shroud.
(4) Install knee bolster (Fig. 278).
(5) Install instrument panel lower silencer (Fig.
279).
(6) Connect battery negative cable.
(7) Verify proper shift interlock system operation.
(Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTO-
MATIC - 31TH/SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID -
OPERATION)SOLENOID/PRESSURE
SWITCH ASSY
DESCRIPTION
The Solenoid/Pressure Switch Assembly (Fig. 280)
is external to the transaxle and mounted to the
transaxle case. The assembly consists of four sole-
noids that control hydraulic pressure to the LR/CC,
2/4, OD, and UD friction elements. The reverse
clutch is controlled by line pressure from the manual
valve in the valve body. The solenoids are contained
within the Solenoid/Pressure Switch Assembly, and
can only be serviced by replacing the assembly.
The solenoid assembly also contains pressure
switches that monitor and send hydraulic circuit
information to the PCM/TCM. Likewise, the pressure
switches can only be service by replacing the assem-
bly.
Fig. 278 Knee Bolster
1 - KNEE BOLSTER
Fig. 279 Instrument Panel Lower Silencer
1 - INSTRUMENT PANEL LOWER SILENCERFig. 280 Solenoid/Pressure Switch Assembly
1 - SOLENOID AND PRESSURE SWITCH ASSEMBLY
RS40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 117
SHIFT INTERLOCK SOLENOID (Continued)
Page 1579 of 2339

OPERATION
SOLENOIDS
The solenoids receive electrical power from the
Transmission Control Relay through a single wire.
The PCM/TCM energizes or operates the solenoids
individually by grounding the return wire of the sole-
noid needed. When a solenoid is energized, the sole-
noid valve shifts, and a fluid passage is opened or
closed (vented or applied), depending on its default
operating state. The result is an apply or release of a
frictional element.
The 2/4 and UD solenoids are normally applied,
which by design allow fluid to pass through in their
relaxed or ªoffº state. This allows transaxle limp-in
(P,R,N,2) in the event of an electrical failure.
The continuity of the solenoids and circuits are
periodically tested. Each solenoid is turned on or off
depending on its current state. An inductive spike
should be detected by the PCM/TCM during this test.
It no spike is detected, the circuit is tested again to
verify the failure. In addition to the periodic testing,
the solenoid circuits are tested if a speed ratio or
pressure switch error occurs.
PRESSURE SWITCHES
The PCM/TCM relies on three pressure switches to
monitor fluid pressure in the L/R, 2/4, and OD
hydraulic circuits. The primary purpose of these
switches is to help the PCM/TCM detect when clutch
circuit hydraulic failures occur. The range for the
pressure switch closing and opening points is 11-23
psi. Typically the switch opening point will be
approximately one psi lower than the closing point.
For example, a switch may close at 18 psi and open
at 17 psi. The switches are continuously monitored
by the PCM/TCM for the correct states (open or
closed) in each gear as shown in the following chart:
PRESSURE SWITCH STATES
GEAR L/R 2/4 OD
ROPOPOP
P/N CL OP OP
1st CL OP OP
2nd OP CL OP
DOPOPCL
OD OP CL CL
OP = OPEN
CL = CLOSED
A Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) will set if the
PCM/TCM senses any switch open or closed at the
wrong time in a given gear.The PCM/TCM also tests the 2/4 and OD pressure
switches when they are normally off (OD and 2/4 are
tested in 1st gear, OD in 2nd gear, and 2/4 in 3rd
gear). The test simply verifies that they are opera-
tional, by looking for a closed state when the corre-
sponding element is applied. Immediately after a
shift into 1st, 2nd, or 3rd gear with the engine speed
above 1000 rpm, the PCM/TCM momentarily turns
on element pressure to the 2/4 and/or OD clutch cir-
cuits to identify that the appropriate switch has
closed. If it doesn't close, it is tested again. If the
switch fails to close the second time, the appropriate
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) will set.
REMOVAL
NOTE: If solenoid/pressure switch assembly is
being replaced, the ªQuick-Learnº procedure must
be performed. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/ELEC-
TRONIC CONTROL MODULES/TRANSMISSION
CONTROL MODULE - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Remove air cleaner assembly.
(3) Disconnect solenoid/pressure switch assembly
connector (Fig. 281).
(4) Disconnect input speed sensor connector (Fig.
281).
Fig. 281 Transmission Connectors
1 - SOLENOID PACK CONNECTOR
2 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR CONNECTOR
3 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR CONNECTOR
4 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR CONNECTOR
21 - 118 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
SOLENOID/PRESSURE SWITCH ASSY (Continued)
Page 1580 of 2339
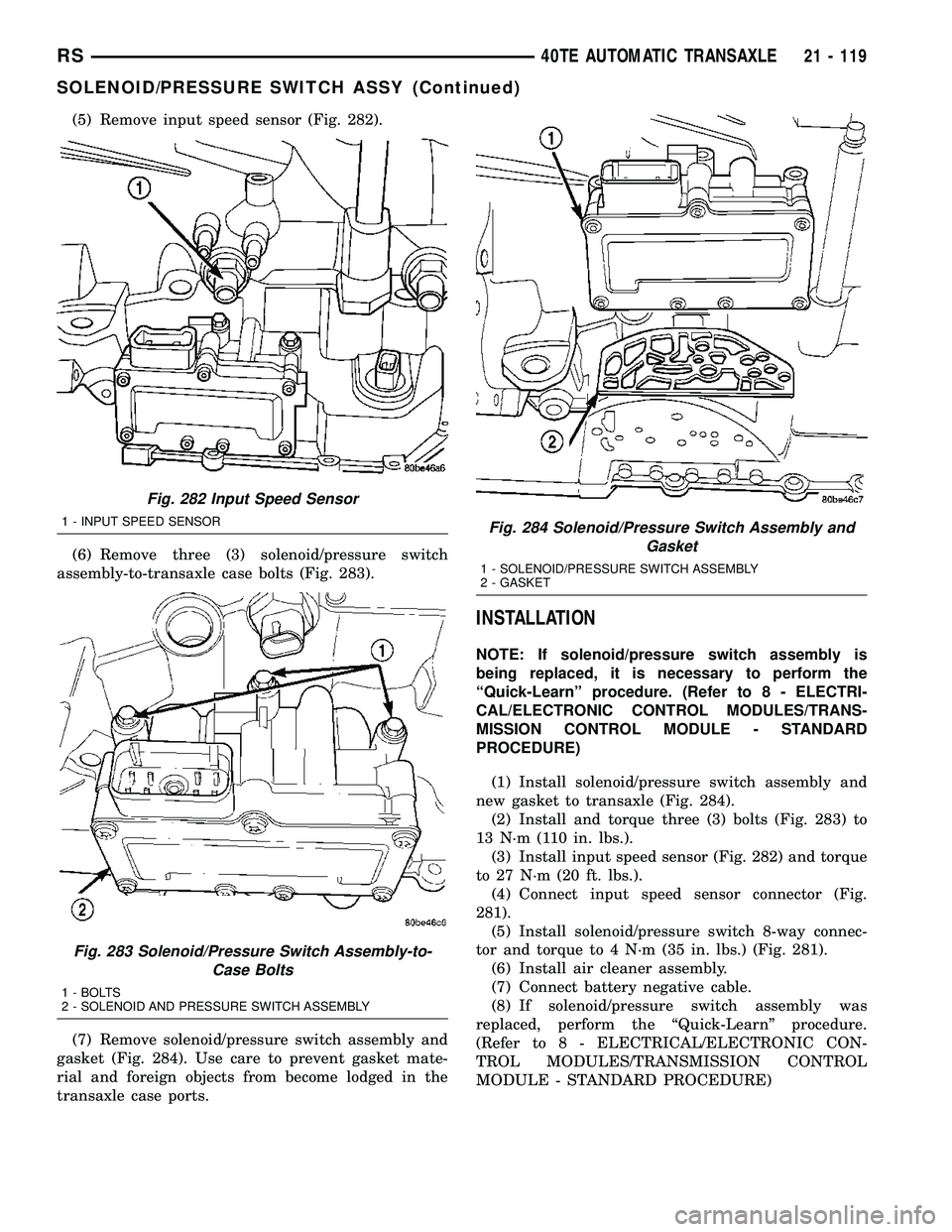
(5) Remove input speed sensor (Fig. 282).
(6) Remove three (3) solenoid/pressure switch
assembly-to-transaxle case bolts (Fig. 283).
(7) Remove solenoid/pressure switch assembly and
gasket (Fig. 284). Use care to prevent gasket mate-
rial and foreign objects from become lodged in the
transaxle case ports.
INSTALLATION
NOTE: If solenoid/pressure switch assembly is
being replaced, it is necessary to perform the
ªQuick-Learnº procedure. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRI-
CAL/ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES/TRANS-
MISSION CONTROL MODULE - STANDARD
PROCEDURE)
(1) Install solenoid/pressure switch assembly and
new gasket to transaxle (Fig. 284).
(2) Install and torque three (3) bolts (Fig. 283) to
13 N´m (110 in. lbs.).
(3) Install input speed sensor (Fig. 282) and torque
to 27 N´m (20 ft. lbs.).
(4) Connect input speed sensor connector (Fig.
281).
(5) Install solenoid/pressure switch 8-way connec-
tor and torque to 4 N´m (35 in. lbs.) (Fig. 281).
(6) Install air cleaner assembly.
(7) Connect battery negative cable.
(8) If solenoid/pressure switch assembly was
replaced, perform the ªQuick-Learnº procedure.
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CON-
TROL MODULES/TRANSMISSION CONTROL
MODULE - STANDARD PROCEDURE)
Fig. 282 Input Speed Sensor
1 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR
Fig. 283 Solenoid/Pressure Switch Assembly-to-
Case Bolts
1 - BOLTS
2 - SOLENOID AND PRESSURE SWITCH ASSEMBLY
Fig. 284 Solenoid/Pressure Switch Assembly and
Gasket
1 - SOLENOID/PRESSURE SWITCH ASSEMBLY
2 - GASKET
RS40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 119
SOLENOID/PRESSURE SWITCH ASSY (Continued)
Page 1582 of 2339
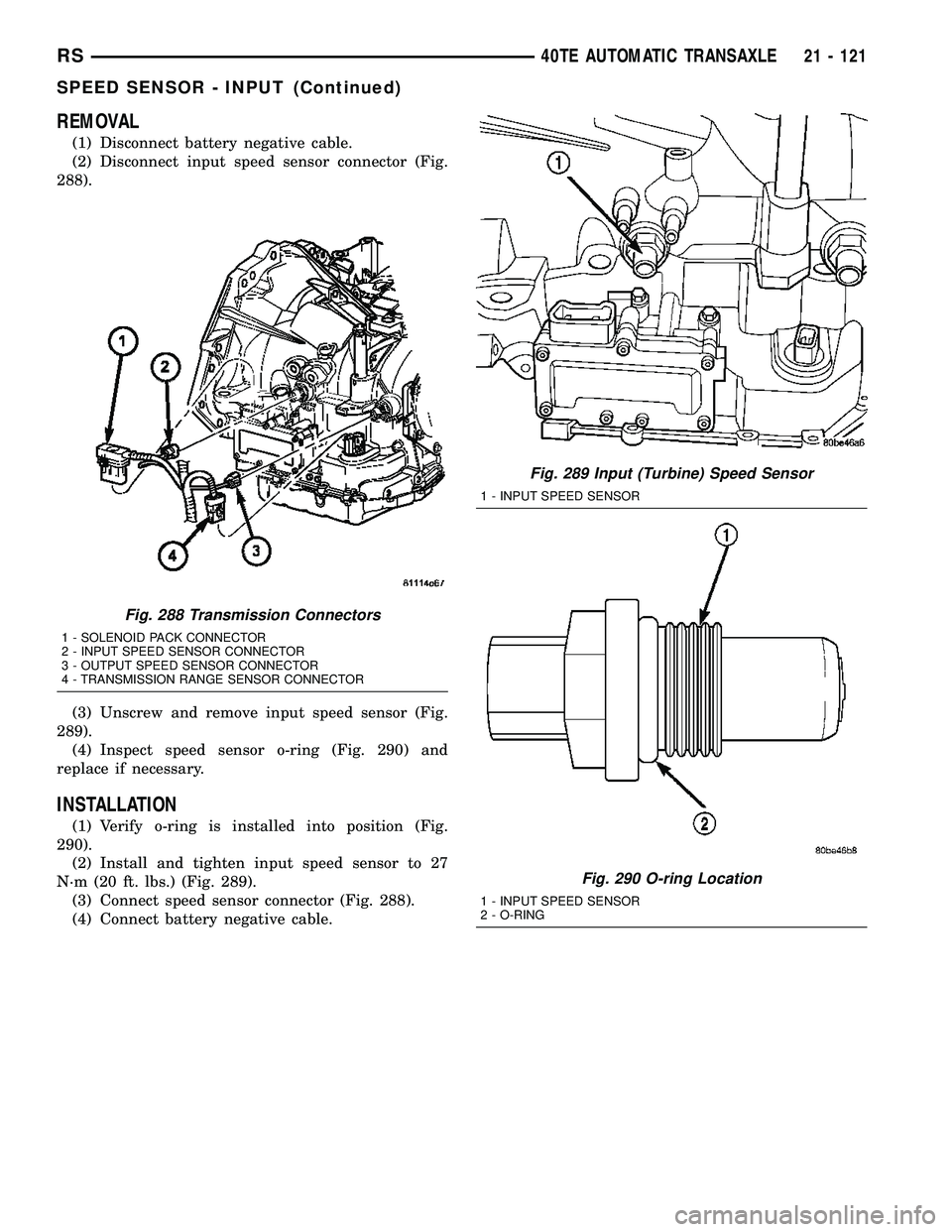
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Disconnect input speed sensor connector (Fig.
288).
(3) Unscrew and remove input speed sensor (Fig.
289).
(4) Inspect speed sensor o-ring (Fig. 290) and
replace if necessary.
INSTALLATION
(1) Verify o-ring is installed into position (Fig.
290).
(2) Install and tighten input speed sensor to 27
N´m (20 ft. lbs.) (Fig. 289).
(3) Connect speed sensor connector (Fig. 288).
(4) Connect battery negative cable.
Fig. 288 Transmission Connectors
1 - SOLENOID PACK CONNECTOR
2 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR CONNECTOR
3 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR CONNECTOR
4 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR CONNECTOR
Fig. 289 Input (Turbine) Speed Sensor
1 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR
Fig. 290 O-ring Location
1 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR
2 - O-RING
RS40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 121
SPEED SENSOR - INPUT (Continued)
Page 1584 of 2339

VEHICLE SPEED SIGNAL
The vehicle speed signal is taken from the Output
Speed Sensor. The PCM converts this signal into a
pulse per mile signal and sends the vehicle speed
message across the communication bus to the BCM.
The BCM sends this signal to the Instrument Cluster
to display vehicle speed to the driver. The vehicle
speed signal pulse is roughly 8000 pulses per mile.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(3) Disconnect output speed sensor connector (Fig.
294).
(4) Unscrew and remove output speed sensor (Fig.
295).
(5) Inspect speed sensor o-ring (Fig. 296) and
replace if necessary.
INSTALLATION
(1) Verify o-ring is installed into position (Fig.
296).
(2) Install and tighten input speed sensor to 27
N´m (20 ft. lbs.).
(3) Connect speed sensor connector (Fig. 294).
(4) Connect battery negative cable.
Fig. 294 Transmission Connectors
1 - SOLENOID PACK CONNECTOR
2 - INPUT SPEED SENSOR CONNECTOR
3 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR CONNECTOR
4 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR CONNECTOR
Fig. 295 Output Speed Sensor
1 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR
Fig. 296 O-ring Location
1 - OUTPUT SPEED SENSOR
2 - O-RING
RS40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 123
SPEED SENSOR - OUTPUT (Continued)
Page 1591 of 2339

TRANSMISSION CONTROL
RELAY
DESCRIPTION
The transmission control relay (Fig. 306) is located
in the Intelligent Power Module (IPM), which is
located on the left side of the engine compartment
between the battery and left fender.
OPERATION
The relay is supplied fused B+ voltage, energized by
the PCM/TCM, and is used to supply power to the sole-
noid pack when the transmission is in normal operating
mode. When the relay is ªoffº, no power is supplied to
the solenoid pack and the transmission is in ªlimp-inº
mode. After a controller reset (ignition key turned to the
ªrunº position or after cranking engine), the PCM/TCM
energizes the relay. Prior to this, the PCM/TCM verifies
that the contacts are open by checking for no voltage at
the switched battery terminals. After this is verified,
the voltage at the solenoid pack pressure switches is
checked. After the relay is energized, the PCM/TCM
monitors the terminals to verify that the voltage is
greater than 3 volts.
TRANSMISSION RANGE
SENSOR
DESCRIPTION
The Transmission Range Sensor (TRS) is mounted
to the top of the valve body inside the transaxle andcan only be serviced by removing the valve body. The
electrical connector extends through the transaxle
case (Fig. 307).
The Transmission Range Sensor (TRS) has four
switch contacts that monitor shift lever position and
send the information to the PCM/TCM.
The TRS also has an integrated temperature sen-
sor (thermistor) that communicates transaxle tem-
perature to the TCM and PCM (Fig. 308).
Fig. 306 Transmission Control Relay Location
1 - TRANSMISSION CONTROL RELAY
2 - LEFT FENDER
3 - INTELLIGENT POWER MODULE (IPM)
4 - BATTERY
Fig. 307 Transmission Range Sensor (TRS)
Location
1 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR
Fig. 308 Transmission Temperature Sensor
1 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR
2 - TEMPERATURE SENSOR
21 - 130 40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLERS
Page 1592 of 2339

OPERATION
The Transmission Range Sensor (TRS) (Fig. 307)
communicates shift lever position (SLP) to the PCM/
TCM as a combination of open and closed switches.
Each shift lever position has an assigned combina-
tion of switch states (open/closed) that the PCM/TCM
receives from four sense circuits. The PCM/TCM
interprets this information and determines the
appropriate transaxle gear position and shift sched-
ule.
Since there are four switches, there are 16 possible
combinations of open and closed switches (codes).
Seven of these codes are related to gear position and
three are recognized as ªbetween gearº codes. This
results in six codes which should never occur. These
are called ªinvalidº codes. An invalid code will result
in a DTC, and the PCM/TCM will then determine the
shift lever position based on pressure switch data.
This allows reasonably normal transmission opera-
tion with a TRS failure.
TRS SWITCH STATES
SLP T42 T41 T3 T1
PCL CL CL OP
RCL OP OP OP
NCL CL OP CL
ODOP OP OP CL
3OP OP CL OP
LCL OP CL CL
TRANSMISSION TEMPERATURE SENSOR
The TRS has an integrated thermistor (Fig. 308)
that the PCM/TCM uses to monitor the transmis-
sion's sump temperature. Since fluid temperature
can affect transmission shift quality and convertor
lock up, the PCM/TCM requires this information to
determine which shift schedule to operate in. The
PCM also monitors this temperature data so it can
energize the vehicle cooling fan(s) when a transmis-
sion ªoverheatº condition exists. If the thermistor cir-
cuit fails, the PCM/TCM will revert to calculated oil
temperature usage.
CALCULATED TEMPERATURE
A failure in the temperature sensor or circuit will
result in calculated temperature being substituted for
actual temperature. Calculated temperature is a pre-dicted fluid temperature which is calculated from a
combination of inputs:
²Battery (ambient) temperature
²Engine coolant temperature
²In-gear run time since start-up
REMOVAL
(1) Remove valve body assembly from transaxle.
(Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTO-
MATIC - 41TE/VALVE BODY - REMOVAL)
(2) Remove transmission range sensor retaining
screw and remove sensor from valve body (Fig. 309).
(3) Remove TRS from manual shaft.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install transmission range sensor (TRS) to the
valve body and torque retaining screw (Fig. 309) to 5
N´m (45 in. lbs.).
(2) Install valve body to transaxle. (Refer to 21 -
TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC -
41TE/VALVE BODY - INSTALLATION)
Fig. 309 Remove Transmission Range Sensor
1 - TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR
2 - MANUAL VALVE CONTROL PIN
3 - RETAINING SCREW
RS40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 131
TRANSMISSION RANGE SENSOR (Continued)
Page 1594 of 2339
MANUAL VALVE
The manual valve is operated by the mechanical
shift linkage. Its primary responsibility is to send
line pressure to the appropriate hydraulic circuits
and solenoids. The valve has three operating ranges
or positions.
CONVERTER CLUTCH SWITCH VALVE
The main responsibility of the converter clutch
switch valve is to control hydraulic pressure applied
to the front (off) side of the converter clutch piston.
Line pressure from the regulator valve is fed to the
torque converter regulator valve, where it passes
through the valve, and is slightly regulated. The
pressure is then directed to the converter clutch
switch valve and to the front side of the converter
clutch piston. This pressure pushes the piston back
and disengages the converter clutch.
CONVERTER CLUTCH CONTROL VALVE
The converter clutch control valve controls the
back (on) side of the torque converter clutch. When
the PCM/TCM energizes or modulates the LR/CC
solenoid to apply the converter clutch piston, both
the converter clutch control valve and the converter
control valve move, allowing pressure to be applied to
the back side of the clutch.
T/C REGULATOR VALVE
The torque converter regulator valve slightly regu-
lates the flow of fluid to the torque converter.
LOW/REVERSE SWITCH VALVE
The low/reverse clutch is applied from different
sources, depending on whether low (1st) gear or
reverse is selected. The low/reverse switch valve
alternates positions depending on from which direc-
tion fluid pressure is applied. By design, when the
valve is shifted by fluid pressure from one channel,
the opposing channel is blocked. The switch valve
alienates the possibility of a sticking ball check, thus
providing consistent application of the low/reverse
clutch under all operating conditions.
REMOVAL
NOTE: If valve body is replaced or reconditioned,
the ªQuick-Learnº Procedure must be performed.
(Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CONTROL
MODULES/TRANSMISSION CONTROL MODULE -
STANDARD PROCEDURE)
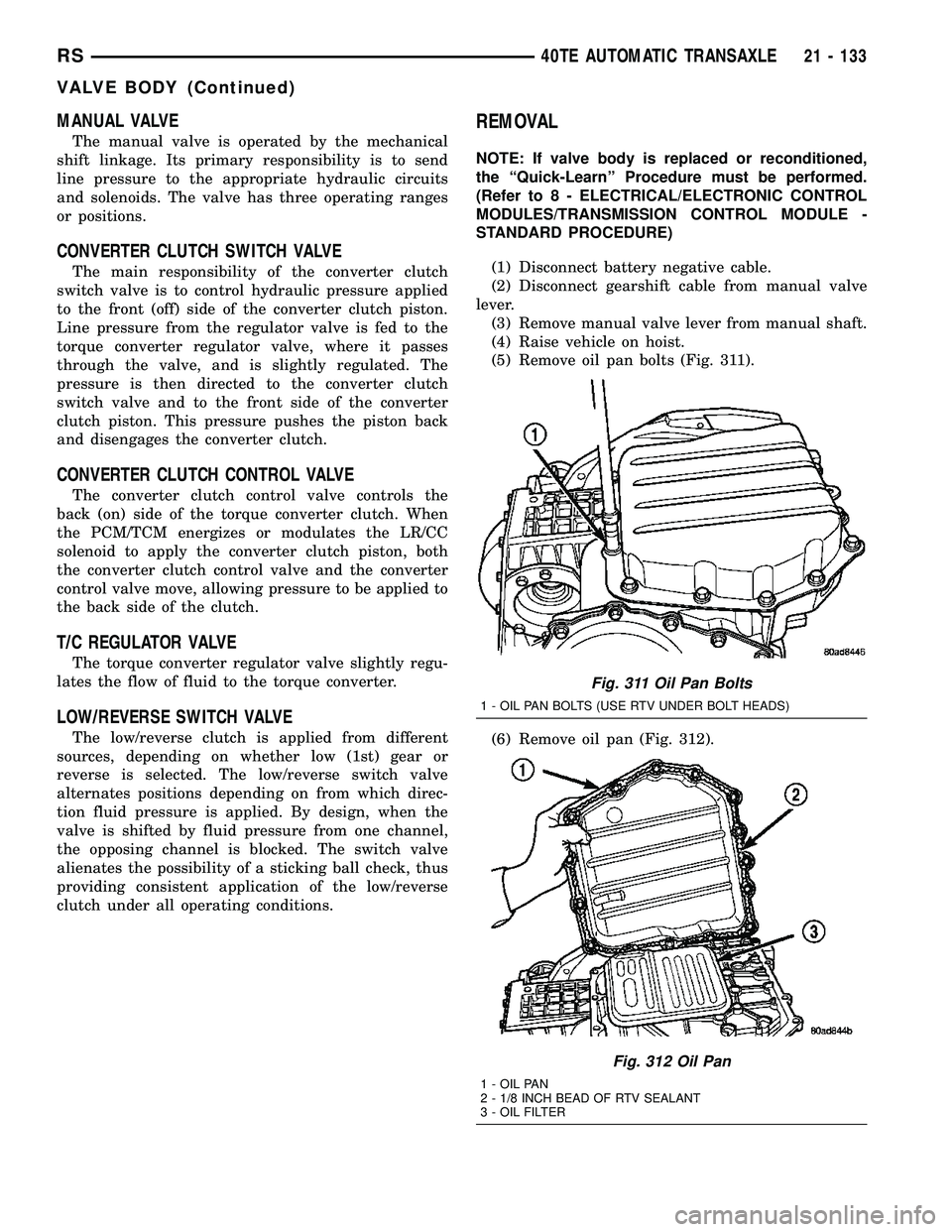
(1) Disconnect battery negative cable.
(2) Disconnect gearshift cable from manual valve
lever.
(3) Remove manual valve lever from manual shaft.
(4) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(5) Remove oil pan bolts (Fig. 311).
(6) Remove oil pan (Fig. 312).
Fig. 311 Oil Pan Bolts
1 - OIL PAN BOLTS (USE RTV UNDER BOLT HEADS)
Fig. 312 Oil Pan
1 - OIL PAN
2 - 1/8 INCH BEAD OF RTV SEALANT
3 - OIL FILTER
RS40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 133
VALVE BODY (Continued)
Page 1606 of 2339
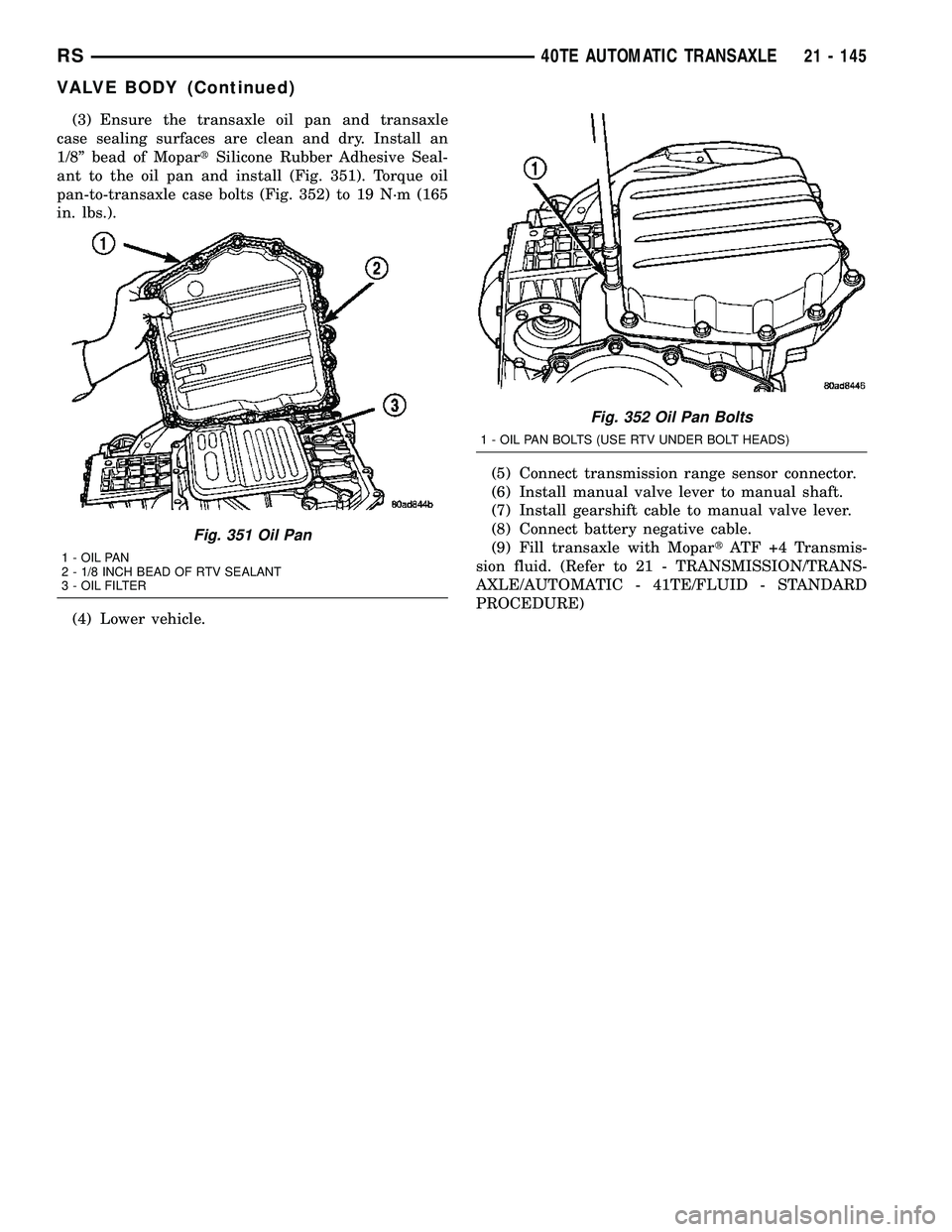
(3) Ensure the transaxle oil pan and transaxle
case sealing surfaces are clean and dry. Install an
1/8º bead of MopartSilicone Rubber Adhesive Seal-
ant to the oil pan and install (Fig. 351). Torque oil
pan-to-transaxle case bolts (Fig. 352) to 19 N´m (165
in. lbs.).
(4) Lower vehicle.(5) Connect transmission range sensor connector.
(6) Install manual valve lever to manual shaft.
(7) Install gearshift cable to manual valve lever.
(8) Connect battery negative cable.
(9) Fill transaxle with MopartATF +4 Transmis-
sion fluid. (Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANS-
AXLE/AUTOMATIC - 41TE/FLUID - STANDARD
PROCEDURE)
Fig. 351 Oil Pan
1 - OIL PAN
2 - 1/8 INCH BEAD OF RTV SEALANT
3 - OIL FILTER
Fig. 352 Oil Pan Bolts
1 - OIL PAN BOLTS (USE RTV UNDER BOLT HEADS)
RS40TE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE21 - 145
VALVE BODY (Continued)