ABS CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2005 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 2005, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 2005Pages: 2339, PDF Size: 59.69 MB
Page 203 of 2339

(8) Remove front wheel speed sensor from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Proper installation of wheel speed sen-
sor cables is critical to continued system operation.
Be sure that cables are installed in retainers. Fail-
ure to install cables in retainers as shown in this
section may result in contact with moving parts and
over extension of cables, resulting in an open cir-
cuit.
(1) Connect the front wheel speed sensor cable to
the vehicle wiring harness connector. Be sure speed
sensor cable connector is fully seated and locked into
vehicle wiring harness connector.
(2) Install the bolts attaching the routing clamps
to the body of the vehicle. Tighten the bolts to a
torque of 14 N´m (125 in. lbs.).
(3) Insert speed sensor cable grommets into inter-
mediate bracket on strut.
(4) Install the wheel speed sensor head mounting
bolt (Fig. 1). Tighten the bolt to a torque of 13 N´m
(115 in. lbs.)
(5) Install the wheel and tire assembly on vehicle.
(6) Lower vehicle.
(7) Road test vehicle to ensure proper operation of
the base and ABS brake systems.
REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
-AWD
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE/HOISTING - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE)
CAUTION: When disconnecting speed sensor cable
from vehicle wiring harness be careful not to dam-
age pins on the electrical connectors. Also, inspect
connectors for any signs of previous damage.
(2) Remove grommet from floor pan of vehicle and
disconnect speed sensor cable connector from vehicle
wiring harness.
CAUTION: When removing rear wheel speed sensor
cable from routing clips, be sure not to damage the
routing clips. Routing clips that are molded onto
the brake hose will require replacement of the brake
hose if damaged during removal or installation of
the speed sensor cable.
(3) Carefully remove speed sensor cable from
press-in routing clips along brake hose and tubing.(4) Remove bolt securing wheel speed sensor cable
metal clip to rear of axle. Remove metal clip from
cable if necessary.
CAUTION: If speed sensor head has seized due to
corrosion, do not use pliers on speed sensor head
in an attempt to remove it. Use a hammer and a
punch and tap mounting flange edge side-to-side,
rocking the sensor until free.
(5) Remove wheel speed sensor head attaching
bolt.
(6) Remove wheel speed sensor head from the axle,
and remove sensor from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Proper installation of wheel speed sen-
sor cables is critical to continued system operation.
Be sure that cables are installed in retainers. Fail-
ure to install cables in retainers as indicated may
result in contact with moving parts or over-exten-
sion of cables, resulting in an open circuit.
(1) Install wheel speed sensor head in axle flange.
CAUTION: Prior to installing the speed sensor head
attaching bolt, the plastic anti-rotation pin must be
fully seated into the bearing flange.
(2) Install wheel speed sensor head attaching bolt.
Tighten bolt to a torque 10 N´m (90 in. lbs.).
(3) Check the air gap between the face of the
wheel speed sensor and the top surface of the tone
wheel. (Refer to 5 - BRAKES - SPECIFICATIONS)
CAUTION: When installing wheel speed sensor
cable in the routing clips on rear brake flex hose,
be sure not to damage the routing clips. Routing
clips are molded onto the hose and will require
replacement of the brake hose if damaged.
(4) Install speed sensor cable under leaf spring
onto brake hose and tubing utilizing routing clips to
secure it in place.
(5) Install metal routing clip on speed sensor cable
and mount it to rear of axle with mounting bolt.
Tighten mounting bolt to 16 N´m (140 in. lbs.).
(6) Connect wheel speed sensor cable to vehicle
wiring harness.Be sure speed sensor cable con-
nector is fully seated and locked into vehicle
wiring harness connector.
(7) Install speed sensor cable grommet into the
floor pan, being sure the grommet is fully seated into
the access hole.
(8) Lower vehicle.
(9) Road test vehicle to ensure proper operation of
the base and ABS braking systems.
5 - 92 BRAKES - ABSRS
FRONT WHEEL SPEED SENSOR (Continued)
Page 204 of 2339

REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
- FWD
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle. (Refer to LUBRICATION &
MAINTENANCE/HOISTING - STANDARD PROCE-
DURE)
CAUTION: When disconnecting speed sensor cable
from vehicle wiring harness be careful not to dam-
age pins on the electrical connectors. Also, inspect
connectors for any signs of previous damage.
(2) Remove grommet from floor pan of vehicle and
disconnect speed sensor cable connector from vehicle
wiring harness (Fig. 2).
CAUTION: When removing rear wheel speed sensor
cable from routing clips, be sure not to damage the
routing clips. Routing clips that are molded onto
the brake hose will require replacement of the brake
hose if damaged during removal or installation of
the speed sensor cable.
(3) Carefully remove speed sensor cable from
press-in routing clips (Fig. 3).
(4) Remove bolt securing metal routing clip to rear
of axle and remove sensor cable from metal clip (Fig.
3).
(5) Remove secondary (yellow) retaining clip at
rear of wheel speed sensor head (Fig. 4).
(6) Push up on metal retaining clip (Fig. 4) until it
bottoms. This will release wheel speed sensor head
from hub and bearing. While holding metal clip up,
pull back on wheel speed sensor head removing it
from hub and bearing.(7) Remove wheel speed sensor assembly from
vehicle.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Proper installation of wheel speed sen-
sor cable is critical to continued system operation.
Be sure that cable is installed in routing retainers/
clips. Failure to install cable in retainers may result
in contact with moving parts or over extension of
cable, resulting in an open circuit.
CAUTION: It is important that only MoparTWheel
Bearing Grease be used for the following step appli-
cation. Other lubricants may cause sensor failure.
Fig. 2 Wheel Speed Sensor Connector
1 - CONNECTOR
2 - FLOOR PAN
3 - GROMMET
Fig. 3 SPEED SENSOR CABLE ROUTING
1 - METAL CLIP AND MOUNTING BOLT
2 - ROUTING CLIPS
Fig. 4 SENSOR CONNECTION AT HUB AND
BEARING
1 - SECONDARY SENSOR RETAINING CLIP
2 - METAL SENSOR RETAINING CLIP
3 - HUB AND BEARING
RSBRAKES - ABS5-93
Page 205 of 2339
(1) Lubricate the sensor O-ring with Mopar Wheel
Bearing Grease before installation into the Hub And
Bearing.If not lubricated, an improper seal may
result due to rolling of the O-ring.
(2) If metal sensor retaining clip is not in the neu-
tral installed position on hub and bearing cap, install
from the bottom, if necessary, and push clip upward
until it snaps into position.
(3) Install wheel speed sensor head into rear of
hub and bearing aligning index tab with the notch in
the top of the mounting hole. Push the sensor in
until it snaps into place on the metal retaining clip.
(4)
Install secondary (yellow) retaining clip over wheel
speed sensor head and engage the tabs on each side.
(5) Route sensor cable under leaf spring along rear
of axle. Install speed sensor cable into routing clips
on rear brake flex hose (Fig. 3).
(6) Install cable into metal routing clip and attach
it to the rear axle with mounting bolt (Fig. 3).
Tighten mounting bolt to 16 N´m (140 in. lbs.).
(7) Connect wheel speed sensor cable to vehicle
wiring harness (Fig. 2).Be sure speed sensor
cable connector is fully seated and locked into
vehicle wiring harness connector.
(8)
Install speed sensor cable grommet into hole in
floor pan making sure grommet is fully seated into hole.
(9) Lower vehicle.
(10) Road test vehicle to ensure proper operation
of the base and ABS braking systems.
TONE WHEEL
INSPECTION - TONE WHEEL
NOTE: Rear tone wheels for front-wheel-drive vehi-
cles are sealed within the hub and bearing assem-
bly and cannot be inspected or replaced.
Replacement of the hub and bearing is necessary.
Tone wheels can cause erratic wheel speed sensor
signals. Inspect tone wheels for the following possible
causes.
²missing, chipped, or broken teeth
²contact with the wheel speed sensor
²wheel speed sensor to tone wheel alignment
²wheel speed sensor to tone wheel clearance
²excessive tone wheel runout
²tone wheel loose on its mounting surface
If a front tone wheel is found to need replacement,
the drive shaft must be replaced. No attempt should
be made to replace just the tone wheel. (Refer to 3 -
DIFFERENTIAL & DRIVELINE/HALF SHAFT -
REMOVAL)
If a rear tone wheel is found to need replacement
on an all-wheel-drive model, the drive shaft must be
replaced. No attempt should be made to replace justthe tone wheel. (Refer to 3 - DIFFERENTIAL &
DRIVELINE/HALF SHAFT - REMOVAL)
If wheel speed sensor to tone wheel contact is evi-
dent, determine the cause and correct it before
replacing the wheel speed sensor or tone wheel.
Check the gap between the speed sensor head and
the tone wheel to ensure it is within specifications.
(Refer to 5 - BRAKES - ABS/ELECTRICAL - SPEC-
IFICATIONS)
Excessive wheel speed sensor runout can cause
erratic wheel speed sensor signals. Refer to SPECI-
FICATIONS in this section of the service manual for
the maximum allowed tone wheel runout (Refer to 5 -
BRAKES - ABS/ELECTRICAL - SPECIFICATIONS).
If tone wheel runout is excessive, determine if it is
caused by a defect in the driveshaft assembly or hub
and bearing. Replace as necessary.
Tone wheels are pressed onto their mounting sur-
faces and should not rotate independently from the
mounting surface. Replacement of the front drive-
shaft, rear driveshaft (AWD only) or rear hub and
bearing is necessary.
TRACTION CONTROL SWITCH
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TRACTION
CONTROL SWITCH
(1) Remove lower steering column shroud. (Refer
to 19 - STEERING/COLUMN/LOWER SHROUD -
REMOVAL)
Fig. 5 Traction Control And Autostick Wiring
Connections
1 - TRACTION CONTROL WIRING CONNECTOR
2 - ROUTING CLIP
3 - AUTOSTICK WIRING CONNECTOR
4 - COLUMN WIRING HARNESS
5 - 94 BRAKES - ABSRS
REAR WHEEL SPEED SENSOR - FWD (Continued)
Page 206 of 2339
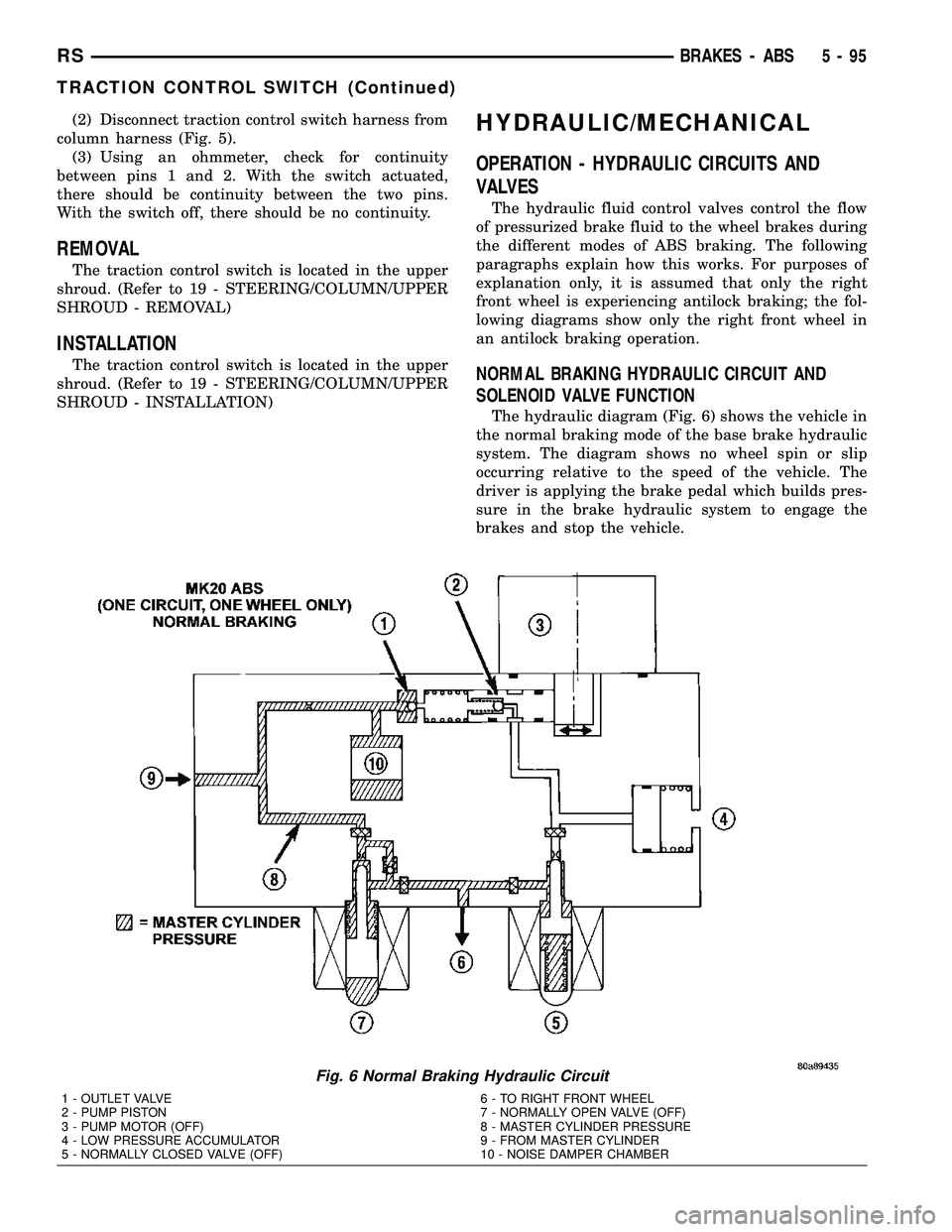
(2) Disconnect traction control switch harness from
column harness (Fig. 5).
(3) Using an ohmmeter, check for continuity
between pins 1 and 2. With the switch actuated,
there should be continuity between the two pins.
With the switch off, there should be no continuity.
REMOVAL
The traction control switch is located in the upper
shroud. (Refer to 19 - STEERING/COLUMN/UPPER
SHROUD - REMOVAL)
INSTALLATION
The traction control switch is located in the upper
shroud. (Refer to 19 - STEERING/COLUMN/UPPER
SHROUD - INSTALLATION)
HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL
OPERATION - HYDRAULIC CIRCUITS AND
VALVES
The hydraulic fluid control valves control the flow
of pressurized brake fluid to the wheel brakes during
the different modes of ABS braking. The following
paragraphs explain how this works. For purposes of
explanation only, it is assumed that only the right
front wheel is experiencing antilock braking; the fol-
lowing diagrams show only the right front wheel in
an antilock braking operation.
NORMAL BRAKING HYDRAULIC CIRCUIT AND
SOLENOID VALVE FUNCTION
The hydraulic diagram (Fig. 6) shows the vehicle in
the normal braking mode of the base brake hydraulic
system. The diagram shows no wheel spin or slip
occurring relative to the speed of the vehicle. The
driver is applying the brake pedal which builds pres-
sure in the brake hydraulic system to engage the
brakes and stop the vehicle.
Fig. 6 Normal Braking Hydraulic Circuit
1 - OUTLET VALVE
2 - PUMP PISTON
3 - PUMP MOTOR (OFF)
4 - LOW PRESSURE ACCUMULATOR
5 - NORMALLY CLOSED VALVE (OFF)6 - TO RIGHT FRONT WHEEL
7 - NORMALLY OPEN VALVE (OFF)
8 - MASTER CYLINDER PRESSURE
9 - FROM MASTER CYLINDER
10 - NOISE DAMPER CHAMBER
RSBRAKES - ABS5-95
TRACTION CONTROL SWITCH (Continued)
Page 207 of 2339

ABS PRIMARY HYDRAULIC CIRCUIT AND
SOLENOID VALVE FUNCTION (ABS WITHOUT
TRACTION CONTROL)
The hydraulic diagram (Fig. 7) shows the vehicle in
the ABS braking mode. The diagram shows one
wheel is slipping because the driver is attempting to
stop the vehicle at a faster rate than is allowed by
the surface on which the tires are riding.
²The normally open and normally closed valves
modulate (build/decay) the brake hydraulic pressure
as required.
²The pump/motor is switched on so that the
brake fluid from the low pressure accumulators is
returned to the master cylinder circuits.
²The brake fluid is routed to either the master
cylinder or the wheel brake depending on the posi-
tion of the normally open valve.
Fig. 7 ABS Without Traction Control - Primary Hydraulic Circuit
1 - OUTLET VALVE
2 - PUMP PISTON
3 - PUMP MOTOR (ON)
4 - LOW PRESSURE ACCUMULATOR PRESSURE
5 - LOW PRESSURE ACCUMULATOR
6 - NORMALLY CLOSED VALVE (MODULATING)
7 - TO RIGHT FRONT WHEEL8 - NORMALLY OPEN VALVE (MODULATING)
9 - FROM MASTER CYLINDER
10 - MASTER CYLINDER PRESSURE
11 - CONTROLLED WHEEL PRESSURE
12 - PUMP INTERSTAGE PRESSURE
13 - NOISE DAMPER CHAMBER
5 - 96 BRAKES - ABSRS
HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL (Continued)
Page 208 of 2339
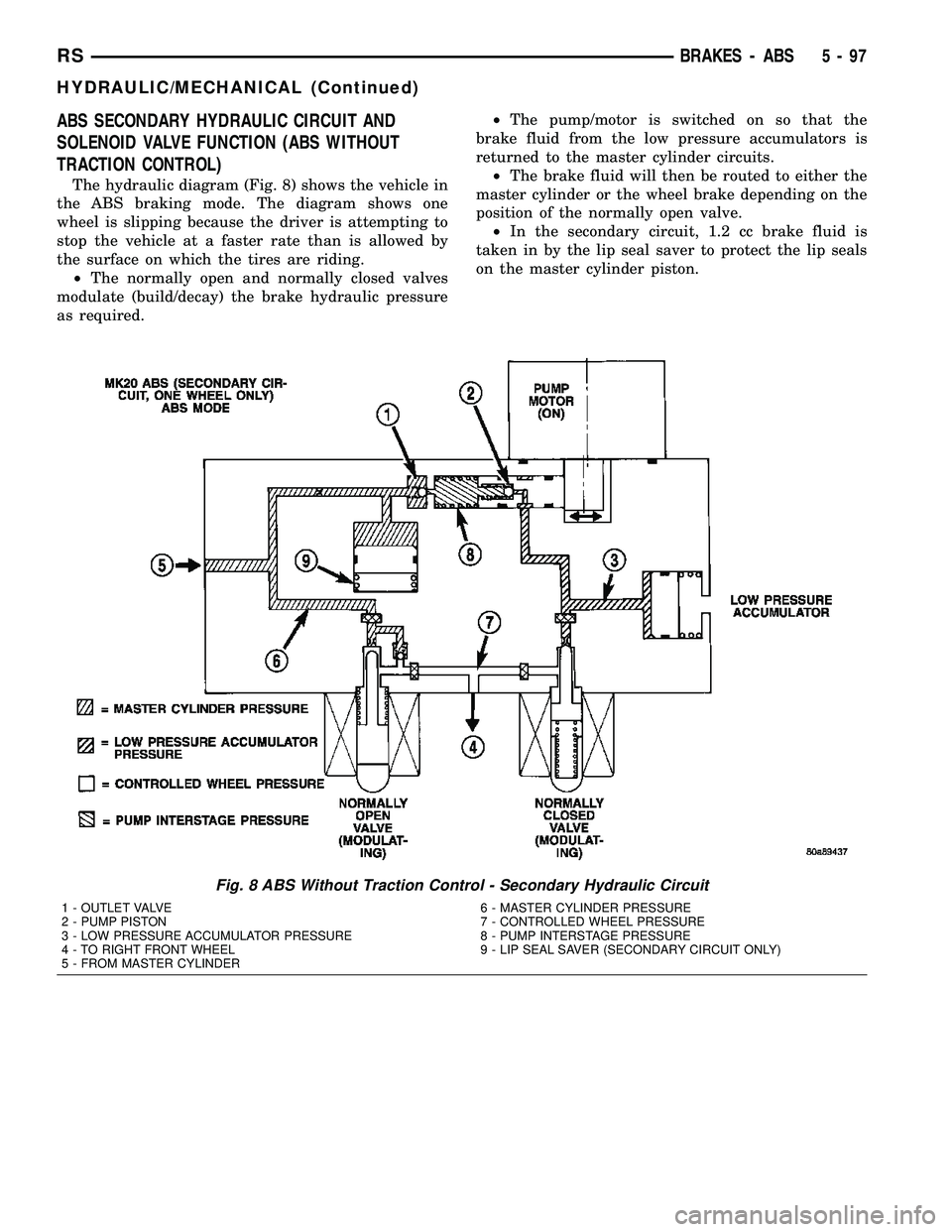
ABS SECONDARY HYDRAULIC CIRCUIT AND
SOLENOID VALVE FUNCTION (ABS WITHOUT
TRACTION CONTROL)
The hydraulic diagram (Fig. 8) shows the vehicle in
the ABS braking mode. The diagram shows one
wheel is slipping because the driver is attempting to
stop the vehicle at a faster rate than is allowed by
the surface on which the tires are riding.
²The normally open and normally closed valves
modulate (build/decay) the brake hydraulic pressure
as required.²The pump/motor is switched on so that the
brake fluid from the low pressure accumulators is
returned to the master cylinder circuits.
²The brake fluid will then be routed to either the
master cylinder or the wheel brake depending on the
position of the normally open valve.
²In the secondary circuit, 1.2 cc brake fluid is
taken in by the lip seal saver to protect the lip seals
on the master cylinder piston.
Fig. 8 ABS Without Traction Control - Secondary Hydraulic Circuit
1 - OUTLET VALVE
2 - PUMP PISTON
3 - LOW PRESSURE ACCUMULATOR PRESSURE
4 - TO RIGHT FRONT WHEEL
5 - FROM MASTER CYLINDER6 - MASTER CYLINDER PRESSURE
7 - CONTROLLED WHEEL PRESSURE
8 - PUMP INTERSTAGE PRESSURE
9 - LIP SEAL SAVER (SECONDARY CIRCUIT ONLY)
RSBRAKES - ABS5-97
HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL (Continued)
Page 209 of 2339

NORMAL BRAKING HYDRAULIC CIRCUIT,
SOLENOID VALVE, AND SHUTTLE VALVE
FUNCTION (ABS WITH TRACTION CONTROL)
The hydraulic diagram (Fig. 9) shows a vehicle
with traction control in the normal braking mode.
The diagram shows no wheel spin or slip occurring
relative to the speed of the vehicle. The driver is
applying the brake pedal which builds pressure in
the brake hydraulic system to engage the brakes and
stop the vehicle. the hydraulic shuttle valve closes
with every brake pedal application so pressure is not
created at the inlet to the pump/motor.
Fig. 9 ABS With Traction Control - Normal Braking Hydraulic Circuit
1 - OUTLET VALVE
2 - PUMP PISTON
3 - PUMP MOTOR (OFF)
4 - SUCTION VALVE
5 - LOW PRESSURE ACCUMULATOR
6 - NORMALLY CLOSED VALVE (OFF)
7 - TO RIGHT FRONT WHEEL8 - NORMALLY OPEN VALVE (OFF)
9 - NORMALLY OPEN ASR VALVE (OFF)
10 - FROM MASTER CYLINDER
11 - HYDRAULIC SHUTTLE VALVE
12 - MASTER CYLINDER PRESSURE
13 - NOISE DAMPER CHAMBER
5 - 98 BRAKES - ABSRS
HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL (Continued)
Page 210 of 2339

ABS BRAKING HYDRAULIC CIRCUIT, SOLENOID
VALVE, AND SHUTTLE VALVE FUNCTION (ABS
WITH TRACTION CONTROL)
The hydraulic diagram (Fig. 10) shows the vehicle
in the ABS braking mode. The diagram shows one
wheel is slipping because the driver is attempting to
stop the vehicle at a faster rate than is allowed by
the surface on which the tires are riding.
²The hydraulic shuttle valve closes upon brake
application so that the pump/motor cannot siphon
brake fluid from the master cylinder.²The normally open and normally closed valves
modulate (build/decay) the brake hydraulic pressure
as required.
²The pump/motor is switched on so that the
brake fluid from the low pressure accumulators is
returned to the master cylinder circuits.
²The brake fluid is routed to either the master
cylinder or the wheel brake depending on the posi-
tion of the normally open valve.
Fig. 10 ABS With Traction Control - ABS Braking Hydraulic Circuit
1 - OUTLET VALVE
2 - PUMP PISTON
3 - PUMP MOTOR (ON)
4 - SUCTION VALVE
5 - LOW PRESSURE ACCUMULATOR
6 - NORMALLY CLOSED VALVE (MODULATING)
7 - TO RIGHT FRONT WHEEL
8 - NORMALLY OPEN VALVE (MODULATING)9 - NORMALLY OPEN ASR VALVE (OFF)
10 - FROM MASTER CYLINDER
11 - HYDRAULIC SHUTTLE VALVE
12 - MASTER CYLINDER PRESSURE
13 - CONTROLLED WHEEL PRESSURE
14 - LOW PRESSURE ACCUMULATOR PRESSURE
15 - PUMP INTERSTAGE PRESSURE
16 - NOISE DAMPER CHAMBER
RSBRAKES - ABS5-99
HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL (Continued)
Page 211 of 2339

ABS TRACTION CONTROL HYDRAULIC CIRCUIT,
SOLENOID VALVE, AND SHUTTLE VALVE
FUNCTION (ABS WITH TRACTION CONTROL)
The hydraulic diagram (Fig. 11) shows the vehicle
in the ABS braking mode. The diagram shows a drive
wheel is spinning and brake pressure is required to
reduce its speed.
²The normally open ASR valve is energized to iso-
late the brake fluid being pumped from the master
cylinder and to isolate the driven wheel.
²The normally open ASR valve bypasses the
pump output back to the master cylinder at a fixed
pressure setting.
²The normally open and normally closed valves
modulate (build/decay) the brake pressure as
required to the spinning wheel.
HCU (HYDRAULIC CONTROL
UNIT)
DESCRIPTION
The hydraulic control unit (HCU) is mounted to
the CAB as part of the ICU (Fig. 22). The HCU con-
trols the flow of brake fluid to the brakes using a
series of valves and accumulators. A pump/motor is
mounted on the HCU to supply build pressure to the
brakes during an ABS stop.
The HCU on a vehicle equipped with ABS and
traction control has a valve block housing that is
approximately 1 inch longer on the low pressure fluid
accumulators side than a HCU on a vehicle that is
equipped with only ABS.
Fig. 11 Traction Control Hydraulic Circuit
1 - OUTLET VALVE
2 - PUMP PISTON
3 - PUMP MOTOR (ON)
4 - LOW PRESSURE ACCUMULATOR PRESSURE
5 - LOW PRESSURE ACCUMULATOR
6 - NORMALLY CLOSED VALVE (MODULATING)
7 - TO RIGHT FRONT WHEEL (SPINNING)
8 - NORMALLY OPEN VALVE (MODULATING)
9 - NORMALLY OPEN ASR VALVE ON (REGULATING)10 - FROM MASTER CYLINDER
11 - HYDRAULIC SHUTTLE VALVE
12 - CONTROLLED WHEEL PRESSURE
13 - SUCTION VALVE
14 - PUMP INTERSTAGE PRESSURE
15 - NOISE DAMPER CHAMBER
16 - MASTER CYLINDER PRESSURE
17 - PUMP PRESSURE
5 - 100 BRAKES - ABSRS
HYDRAULIC/MECHANICAL (Continued)
Page 212 of 2339

For more information, (Refer to 5 - BRAKES/HY-
DRAULIC/MECHANICAL/ICU (INTEGRATED CON-
TROL UNIT) - DESCRIPTION)
OPERATION
For information on the operation of the HCU as a
whole, refer to Hydraulic Circuits And Valve Opera-
tion which can be found elsewhere in this section.
For information on the operation of the components
within the HCU, refer to the following three topics.
VALVES AND SOLENOIDS
The valve block contains four inlet valves and four
outlet valves. The inlet valves are spring-loaded in
the open position and the outlet valves are spring-
loaded in the closed position during normal braking.
The fluid is allowed to flow from the master cylinder
to the wheel brakes.
During an ABS stop, these valves cycle to maintain
the proper slip ratio for each wheel. The inlet valve
closes preventing further pressure increase and the
outlet valve opens to provide a path from the wheel
brake to the HCU accumulators and pump/motor.
This releases (decays) pressure from the wheel brake,
thus releasing the wheel from excessive slippage.
Once the wheel is no longer slipping, the outlet valve
is closed and the inlet valve is opened to reapply
(build) pressure.
On vehicles with traction control, there is an extra
set of valves and solenoids. The ASR valves, mounted
in the HCU valve block, are normally in the open
position and close only when the traction control is
applied.
These isolator valves are used to isolate the rear
(non-driving) wheels of the vehicle from the hydraulic
pressure that the HCU pump/motor is sending to the
front (driving) wheels when traction control is being
applied. The rear brakes need to be isolated from the
master cylinder when traction control is being
applied so the rear wheels do not drag. For more
information, refer to Traction Control System in this
section.
BRAKE FLUID ACCUMULATORS
There are two fluid accumulators in the HCU±one
for the primary hydraulic circuit and one for the sec-
ondary hydraulic circuit. Each hydraulic circuit uses
a 5 cc accumulator.
The fluid accumulators temporarily store brake
fluid that is removed from the wheel brakes during
an ABS cycle. This stored fluid is used by the pump/
motor to provide build pressure for the brake hydrau-
lic system. When the antilock stop is complete, the
accumulators are drained by the pump/motor.
On ABS-only vehicles, there is a mini-accumulator
on the secondary hydraulic circuit that protects the
master cylinder seals during an ABS stop, and there
is a noise dampening chamber on the primary circuit.
On ABS with traction control vehicles, there are
two noise dampening chambers in the HCU.
PUMP/MOTOR
There are two pump assemblies in the HCUÐone
for the primary hydraulic circuit and one for the sec-
ondary hydraulic circuit. Both pumps are driven by a
common electric motor. This DC-type motor is inte-
gral to the HCU and is controlled by the CAB.
The pump/motor provides the extra amount of
brake fluid needed during antilock braking. Brake
fluid is released to the accumulators when the outlet
valve is opened during an antilock stop. The pump
mechanism consists of two opposing pistons operated
by an eccentric camshaft. In operation, one piston
draws fluid from the accumulators, and the opposing
piston pumps fluid to the master cylinder circuits.
When the antilock stop is complete, the pump/motor
drains the accumulators.
The CAB may turn on the pump/motor when an
antilock stop is detected. The pump/motor continues
to run during the antilock stop and is turned off after
the stop is complete. Under some conditions, the
pump/motor runs to drain the accumulators during
the next drive-off.
The pump/motor is not a serviceable item; if it
requires replacement, the HCU must be replaced.
RSBRAKES - ABS5 - 101
HCU (HYDRAULIC CONTROL UNIT) (Continued)