engine CITROEN CX 1988 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CITROEN, Model Year: 1988, Model line: CX, Model: CITROEN CX 1988Pages: 648, PDF Size: 95.8 MB
Page 163 of 648
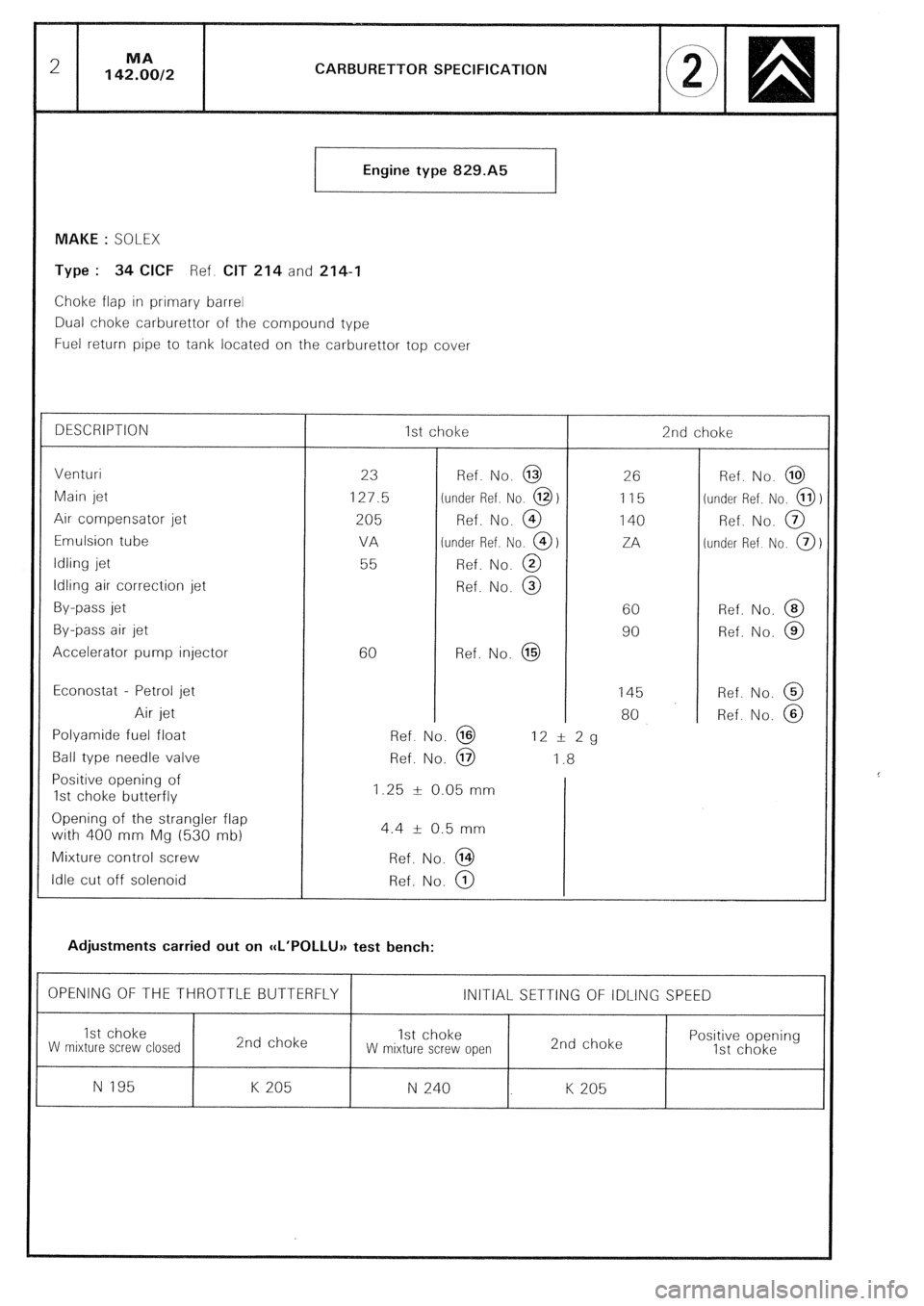
CARBURETTOR SPECIFICATION
Engine type 829.A5
MAKE : SOLEX
Type : 34 CICF Ref. CIT 214 and 214-I
Choke flap in primary barrel
Dual choke carburettor of the compound type
Fuel return pipe to tank located on the carburettor top cover
DESCRIPTION
Venturi
Main jet
Air compensator jet
Emulsion tube
Idling jet
Idling air correction jet
By-pass jet
By-pass air jet
Accelerator pump injector
Econostat - Petrol jet
Air jet
Polyamide fuel float
Ball type needle valve
Positive opening of
1st choke butterfly
Opening of the strangler flap
with 400 mm Mg (530 mb)
Mixture control screw
Idle cut off solenoid 1st choke
23
127.5
205
VA
55
60 Ref. No. @
(under Ref. No. 0)
Ref. No. @
(under Ref. No. @)
Ref. No. @
Ref. No. @
Ref. No. @ 26
115
140
ZA
60
90
145
80 2nd choke
Ref. No. @ 12 I!I 2g
Ref. No. @ 1.8
1.25 k 0.05 mm
4.4 + 0.5 mm
Ref. No. @
Ref. No. @
Adjustments carried out on CCL’POLLUH test bench: Ref. No. @
(under Ref. No. 0
Ref. No. @
[under Ref No. @
Ref. No. @
Ref. No. @
Ref. No. @
Ref. No. @
OPENING OF THE THROTTLE BUTTERFLY 1 INITIAL SETTING OF IDLING SPEED
I
1st choke
W mixture screw closed 2nd choke 1st choke
W mixture screw open 2nd choke
I
Positive opening
1st choke
N 195 K 205 N 240 K 205
Page 166 of 648
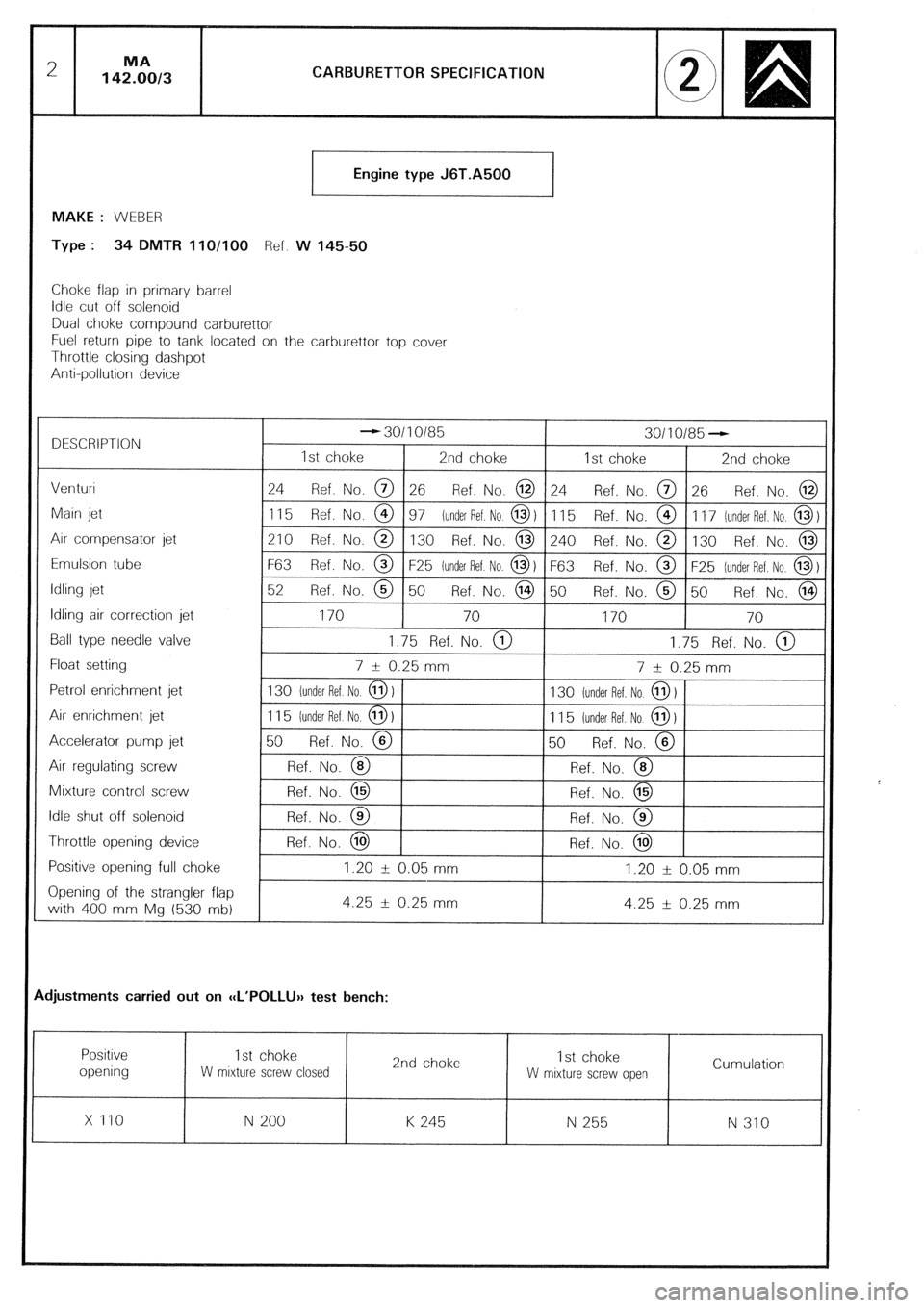
CARBURETTOR SPECIFICATION
Engine type J6T.A500
MAKE : WEBER
Type : 34 DMTR 11 O/100 Ref. W 14550
Choke flap in primary barrel
Idle cut off solenoid
Dual choke compound carburettor
Fuel return pipe to tank located on the carburettor top cover
Throttle closing dashpot
Anti-pollution device
DESCRIPTION - 30110185
30110185 -
1st choke 2nd choke
1st choke 2nd choke
Venturi 24
Ref. No. @ 26 Ref. No. @ 24 Ref. No. @ 26 Ref. No. @
Main jet
1 15 Ref. No. @ 97 (under Ref. No @ 1 11 5 Ref. No. @ 1 17 lunder Ref. No. @ 1
Arr compensator jet
210 Ref. No. @ 130 Ref. No. @ 240 Ref. No. @ 130 Ref. No. @
Emulsion tube
F63 Ref. No. @ F25 iunder Ref No. 0) F63 Ref. No. @ F25 [under Ref. No, 0)
Idling jet 52
Ref. No. @ 50 Ref. No. @ 50 Ref. No. @ 50 Ref. No. @
Idling air correction jet
170 70
170 70
Ball type needle valve
1.75 Ref. No. @ 1.75 Ref. No. @
Float setting
7 i 0.25 mm
7 AI 0.25 mm
Petrol enrichment jet 130 (under Ref No. @ )
130 lunder Ref. No @ 1
Air enrichment jet
1 15 [under Ref No. 0) 1 1 5 [under Ref. No. @ 1
Accelerator pump jet 50
Ref. No. @ 50 Ref. No. @
Air regulating screw
Ref. No. @ Ref. No. @
Mixture control screw Ref. No. @
Ref. No. @
Idle shut off solenoid
Ref. No. @ Ref. No. @
Throttle opening device Ref. No. @
Ref. No. @
Positive opening full choke
1.20 i 0.05 mm 1.20 -fr 0.05 mm
Opening of the strangler flap
with 400 mm Mg (530 mb) 4.25 + 0.25 mm
4.25 --lr 0.25 mm
djustments carried out on ccL’POLLU>) test bench:
Positive
1st choke
2nd choke 1st choke
opening
W mrxture screw closed
W mixture screw open Cumulation
x 110
N 200 K 245 N 255
N 310
Page 169 of 648
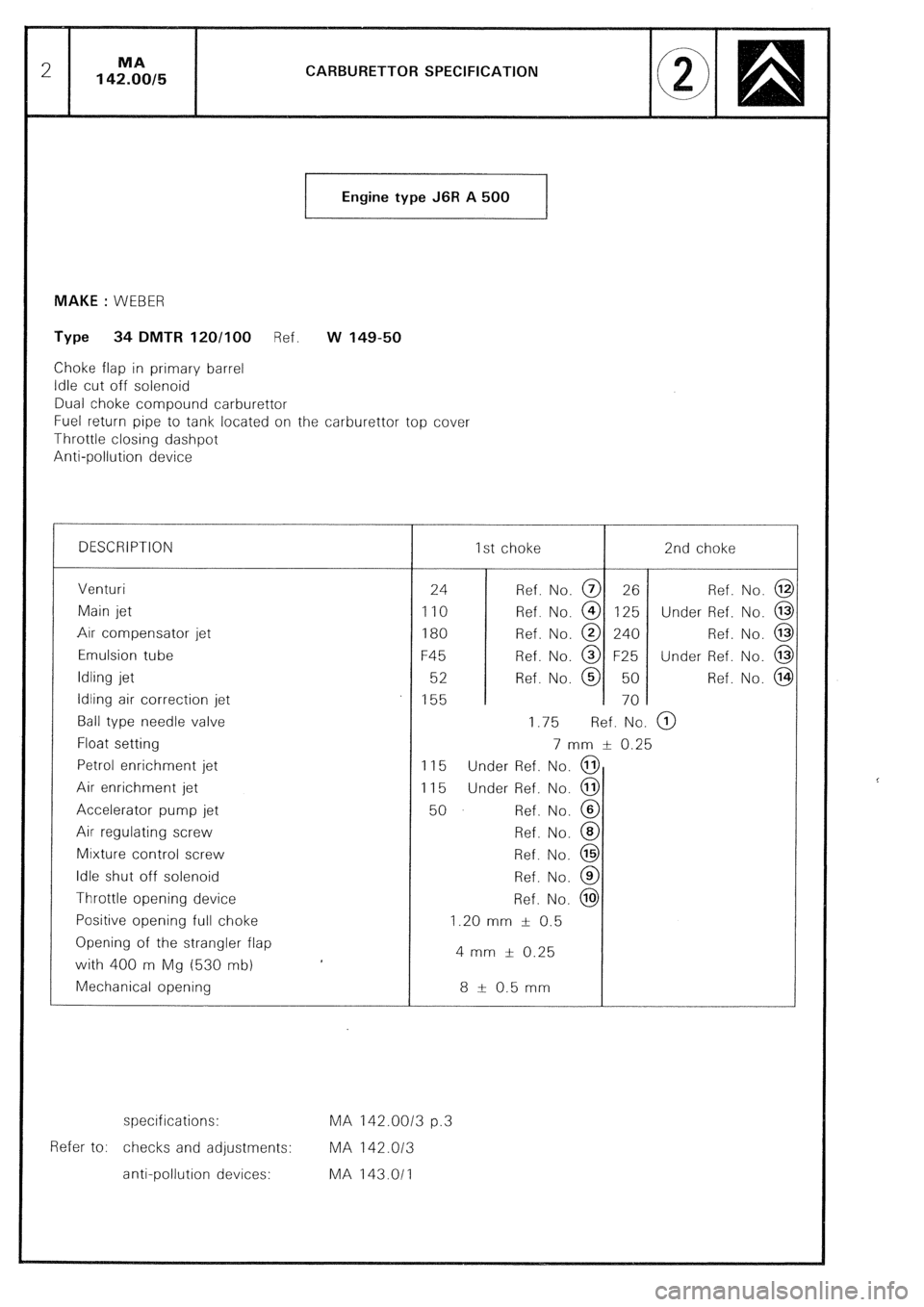
CARBURETTOR SPECIFICATION
Engine type J6R A 500
1 MAKE : WEBER
Type 34 DMTR 120/100 Ref. w 149-50
Choke flap in primary barrel
Idle cut off solenoid
Dual choke compound carburettor
Fuel return pipe to tank located on the carburettor top cover
Throttle closing dashpot
Anti-oollution device
DESCRIPTION 1st choke 2nd choke
Venturi
Main jet
Air compensator jet
Emulsion tube
Idling jet
Idling air correction jet
Ball type needle valve
Float setting
Petrol enrichment jet
Air enrichment jet
Accelerator pump jet
Air regulating screw
Mixture control screw
Idle shut off solenoid
Throttle opening device
Positive opening full choke
Opening of the strangler flap
with 400 m Mg (530 mb)
Mechanical opening 24 Ref. No. @ 26 Ref. No. @
110 Ref. No. @ 125 Under Ref. No. @
180 Ref. No. @ 240 Ref. No. @
F45 Ref. No. @ F25 Under Ref. No. @
52 Ref. No. @ 50 Ref. No. @
155 70
1.75 Ref. No. @)
7 mm & 0.25
115 Under Ref. No. @
115 Under Ref. No. @
50 Ref. No. @
Ref. No. @
Ref. No. @
Ref. No. @
Ref. No. @
1.20 mm f 0.5
4 mm f 0.25
8 t- 0.5 mm
specifications: MA 142.0013 p.3
Refer to: checks and adjustments: MA 142.013
anti-pollution devices: MA 143.011
Page 185 of 648
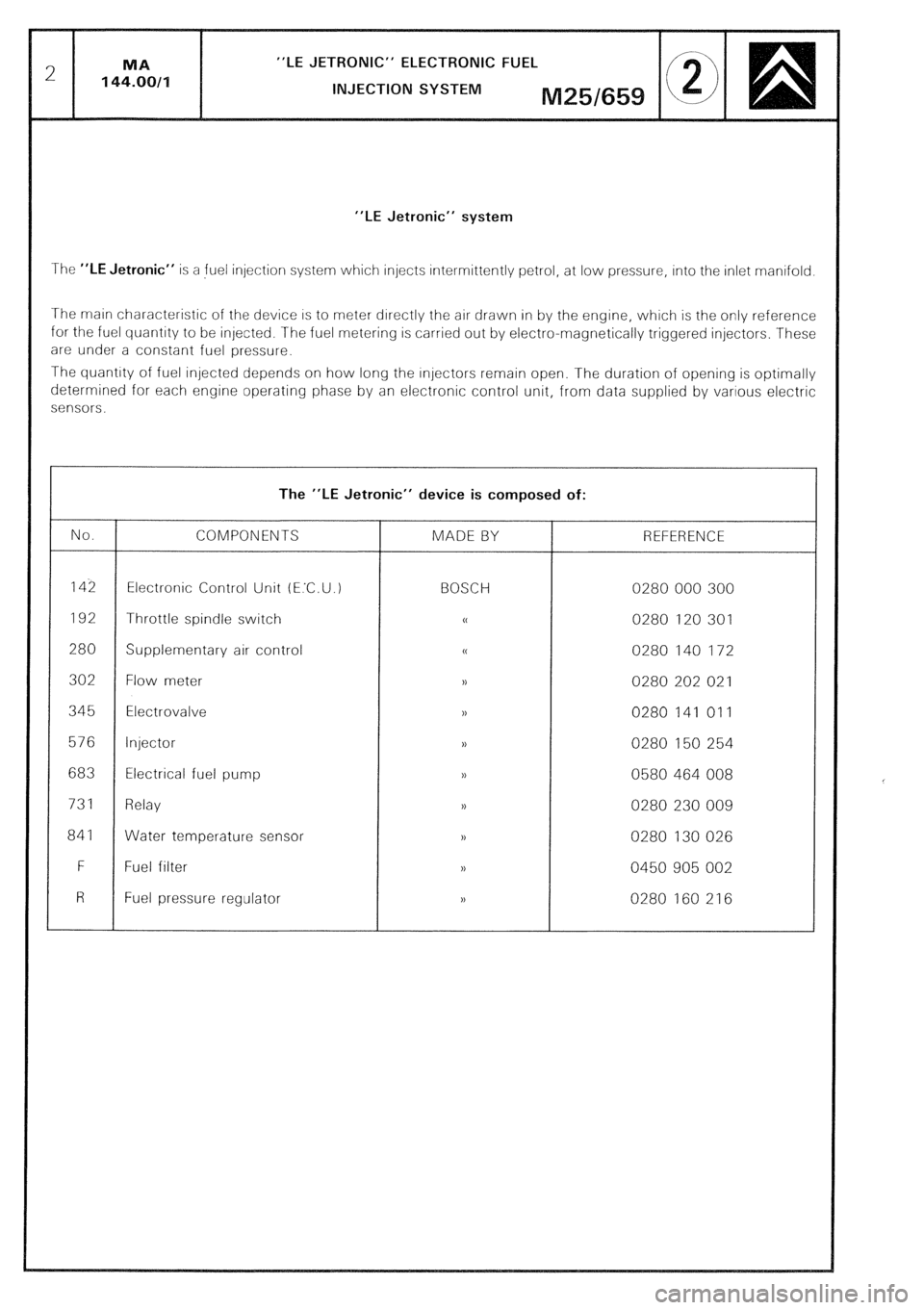
“LE JETRONIC” ELECTRONIC FUEL
INJECTION SYSTEM
“LE Jetronic” system
The “LE Jetronic” IS a fuel injectiorl system which injects Intermittently petrol, at low pressure, into the inlet rnanifold
The main characteristic of the device IS to rneter drrectly the air drawn in by the engine, which is the only reference
for the fuel quantity to be injected. The fuel metering IS carried out by electro-magnetically triggered injectors. These
are under a constant fuel pressure.
The quantrty of fuel injected depends on how long the Injectors remain open. The duration of opening is optimally
determined for each engine operating phase by an electronic control unit, from data supplied by various electric
sensors.
The “LE Jetronic” device is composed of:
No.
COMPONENTS MADE BY REFERENCE
142 Electronic Control Unit (E.C. U.) BOSCH 0280 000 300
192 Throttle spindle switch cc 0280 120 301
280 Supplementary air control (C 0280 140 172
302 Flow meter ,, 0280 202 021
345 Electrovalve ,) 0280 141 011
576 Injector n 0280 150 254
683 Electrical fuel pump
)> 0580 464 008
731 Relay D 0280 230 009
841 Water temperature sensor D 0280 130 026
F Fuel filter N 0450 905 002
R Fuel regulator pressure ,) 0280 160 216
Page 194 of 648
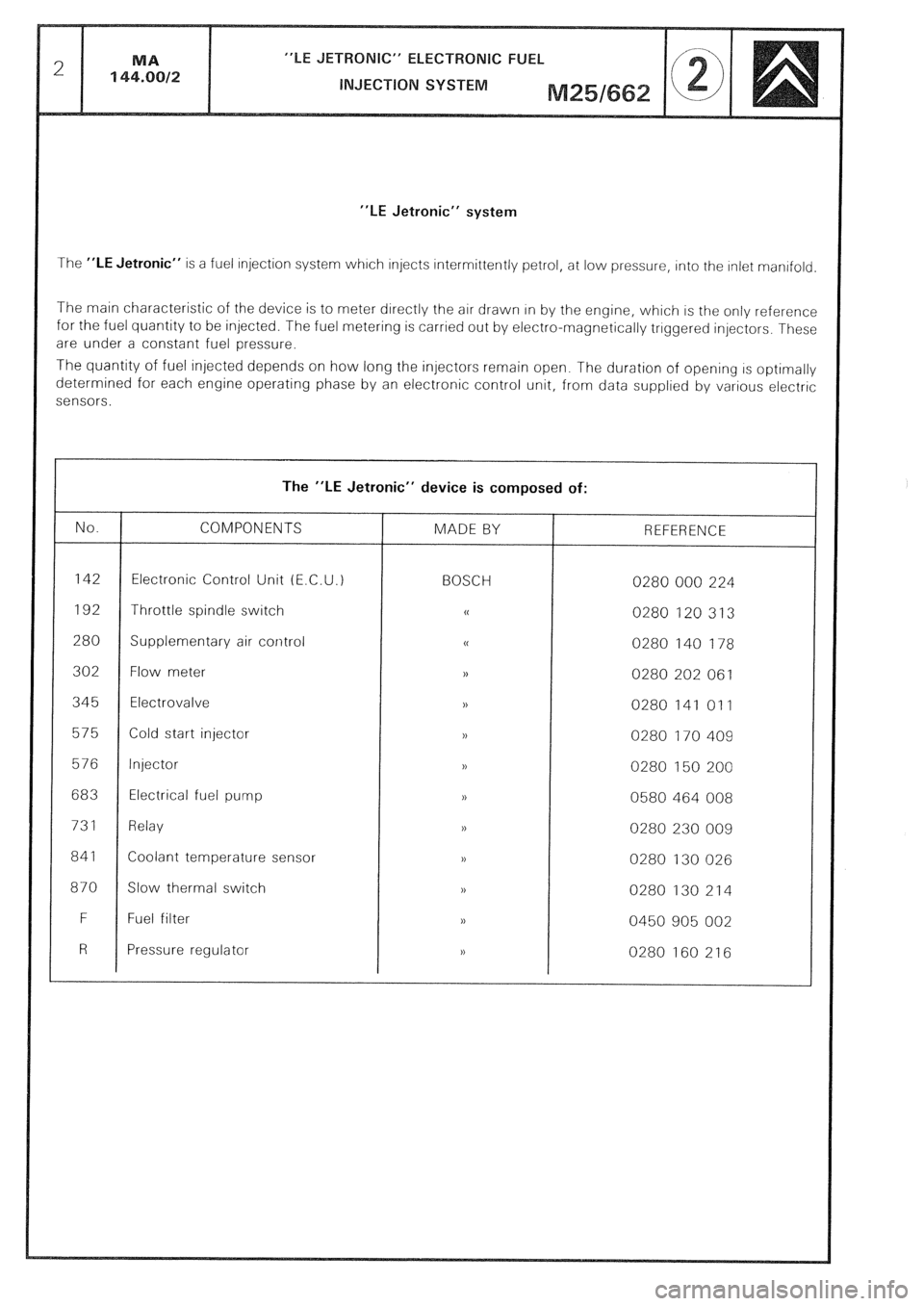
“LE Jetronic” system
The “LE Jetronic” is a fuel injection system whrch injects intermittently petrol, at low pressure, into the Inlet manrfold
The main characteristic of the device is to meter directly the air drawn In by the engine, which is the only reference
for the fuel quantity to be injected. The fuel metering is carried out by electro-magnetically triggered injectors. These
are under a constant fuel pressure.
The quantity of fuel injected depends on how long the injectors remain open. The duration of opening IS optimally
determined for each engine operating phase by an electronic control unit, from data supplied by various electric
sensors.
The “LE Jetronic” device is composed of:
No. COMPONENTS MADE BY REFERENCE
142 Electronic Control Unit (E.C.U.) BOSCH 0280 000 224
192 Throttle spindle switch 0
0280 120 313
280 Supplementary air control u
0280 140 178
302 Flow meter ,)
0280 202 061
345 Electrovalve ,,
0280 141 011
575 Cold start injector n
0280 170 409
576 Injector >,
0280 150 200
683 Electrical fuel
pump 1,
0580 464 008
731 Relay >,
0280 230 009
841 Coolant temperature sensor 1)
0280 130 026
870 Slow thermal switch ,>
0280 130 214
F Fuel filter ),
0450 905 002
R Pressure regulator ,)
0280 160 216
Page 206 of 648
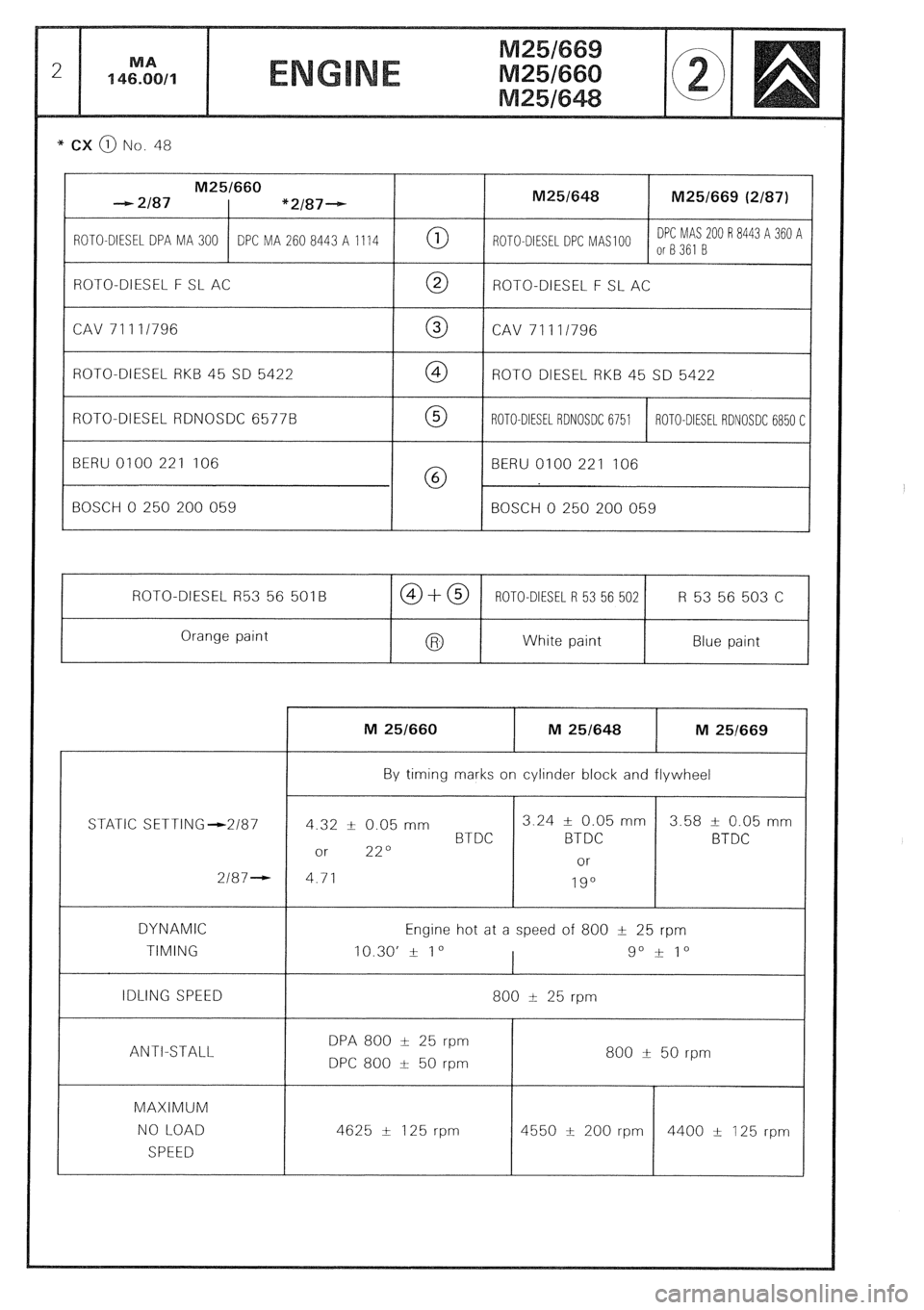
* CX @ No. 48
M25/660
- 2187 “2/87-- M25/648 M25/669 (2/87)
ROTO-DIESEL DPA MA 300 DPC MA 260 8443 A 1114 0 ROTO-DIESEL DPC MAS 100 DPC MAS 200 R 8443 A 360 A
or8361 B
ROTO-DIESEL F SL AC
0 ROTO-DIESEL F SL AC
CAV 71111796 0 CAV 71111796
ROTO-DIESEL RKB 45 SD 5422 @ ROT0 DIESEL RKB 45 SD 5422
ROTO-DIESEL RDNOSDC 6577B 0 ROTO-DIESEL RDNOSDC 6751 ROTO-DIESEL RDNOSDC 6850 C
BERU 0100 221 106
@ BERU 0100 221 106
BOSCH 0 250 200 059 BOSCH 0 250 200 059
ROTO-DIESEL R53 56 501B CO+@ ROTO-DIESEL R 53 56 502 R 53 56 503 C
Orange paint
White paint Blue paint
STATIC SETTING-2187
2187-
DYNAMIC
TIMING
IDLING SPEED
ANTI-STALL
MAXIMUM
NO LOAD
SPEED M 251660 M 25/648 M 251669
By timing marks on cylinder block and flywheel
4 12 k 0.05 mm 3.24 f 0.05 mm 3.58 t- 0.05 mm
BTDC BTDC BTDC
or 22O
or
4.71
19”
Engine hot at a speed of 800 t 25 rpm
10.30’ + 1 o
I go i 1”
800 I 25 rpm
DPA 800 t 25 rpm
DPC 800 t 50 rpm 800 & 50 rpm
4625 & 125 rpm
r
4400 + 125 rpm
Page 212 of 648

CHECKING AND ADJUSTING
THE INJECTION SYSTEM
II. - INSPECTION AND TIMING OF THE “ROT0-DIESEL” INJECTION PUMP
Raise the LH side of the vehicle and support it on
stands.
Disconnect the battery negative lead.
Engage the 5th gear. Rotate the engine by turning the
wheel.
Set the No. 1 cylinder to the initial timing point,
Fig.1.
(look into the oil filter orifice).
- place cylinder No. 1 valves in the rocking position;
turn the crankshaft by one turn in the normal direc-
tion of engine rotation.
- align marks on the flywheel and on the crankcase
(++I.
- turn the crankshaft back through a quarter of a turn.
Remove either the plug (with a 32 mm ring spanner)
or the inspection plate depending on the type of the
pump.
Refit, Fig II or Ill, according to pump:
- the feeler,
- the support for the dial-gauge.
- the dial-gauge equipped with its right-angled lever.
Finding the pump internal timing point:
- turn the crankshaft in the direction of rotation until
the large pointer on the dial indicator starts moving
in the opposite direction.
- set “0” mark on the dial-gauge in line with the large
pointer.
Checking the injection pump timing:
- rotate the crankshaft by a quarter turn in the oppo-
site direction to its direction of rotation.
- turn back in the normal direction of rotation until the
“0” mark on the dial-gauge has been reached.
- in that position, marks (-1 and (c) should be in line,
Fig. I.
If not, re-check the timing. Timing the injection pump:
- set the engine to the initial trming point, Fig. I.
- turn the crankshaft by 114 turn in the opposite direc-
tion to normal direction of ro’tatron, then turn back
in the direction of rotation to bring marks t-+) and
+-I opposite.
Adjusting the pump timing, Fig. Ill:
Slacken off the injector pipe connections and the 4
attachment points.
Bring the pump to the injection point with the feeler
at the base of V-shaped groove (timing point).
Set the “0” mark on the dial opposite the needle on
the dial-gauge. Orientate the pump casing towards the
engine.
Slowly turn back to the injection point (needle facing
the “0” mark on the dial), by moving the pump
casing away from the engine (in the opposite direc-
tion to engine rotation).
Tighten the pump fixing nuts to 2.4 mdaN. During
this operation, the needle should not move.
Check the pump timing
Remove the timing tools.
Refit the plug, (tighten to 2 mdaN), or the inspec-
tion plate.
Seal the injection pump plug.
Tighten the injector pipe connections to 2 mdaN.
Reconnect the battery negative cable
Switch on the ignition (electrical STOP solenoid exci-
tation) and prime the fuel circuit using the manual
pump (5) located on the filter.
Fully depress the accelerator pedal to facilitate the
engine bleeding and start.
Note: the initial timing point corresponds to:
3.24 -L- 0.05 mm BTDC: M 25/648
4.32 + 0.05 mm BTDC: M 25/660 DPA pump
4.71 f 0.05 mm BTDC: M 25/660 DPC pump
8531
Page 213 of 648

CHECKING AND ADJUSTING
THE INJECTION SYSTEM
III. - ADJUSTING THE ROTO-DIESEL INJECTION PUMP CONTROLS
DPC type pump from engine M 25/648, Fig. I
DPA type pump from engine M 25/660, Fig. II
Checking the fast-idle control
Ensure that lever (7) is against its stop, by pushing
it in the direction of arrow (-).
If not, adjust tension of cab/e by means of cable end
clamp (6). Complete tightening of cable using sheath
tensioner (41.
Checking the fast-idle control
Make sure that the cable is slack.
If not, check the operation of the thermal sensor (101
located on the water outlet duct: the cable must ope-
rate over a range of 6 mm between its “ENGINE
COLD” and “ENGINE WARM” positions.
Adjusting the accelerator control
Engine stopped:
Fully depress the accelerator pedal.
Check that lever (I) is against stop (2).
If not, move pin (3) of accelerator cable.
Make sure that, at idle, lever (I) is against stop (5).
Adjusting the anti-stalling device
Engine running:
Insert a 1.5 mm thick shim (DPC pump, Fig. I)
2 mm thick shim (DPA pump, Fig. II)
between lever (I) and stop-screw (5) at “b”.
Place a 3 mm dia. rod through the hole in lever (7)
at “a” by pushing STOP lever (9) outwards. Set the engine speed to:
800 t 50 rpm (DPC pump)
800 f 25 rpm (DPA pump)
by turning stop screw (5).
Remove the 3 mm dia. rod and the shim
Adjust the idling speed to:
800 + 25 rpm
by turning stop screw (8).
Checking the engine deceleration:
Accelerate the engine to 3.000 rpm, then release the
accelerator lever sharply.
- if the deceleration is too fast (engine often stalling),
unscrew stop-screw (5) by 114 turn,
- if the deceleration is too slow (poor engine braking),
screw up stop-screw (51 by l/4 turn.
In both cases, check the idling speed and adjust if
necessary.
If the malfunction continues to exist, carry out the
adjustments again.
Check the efficiency of the mechanically operated
STOP control (9).
Note: The setting figures are identical if the vehicle
is equipped with air-conditioning and the adjustments
are to be effected with the air-conditioning off.
Page 216 of 648

Raise the R.H side of the vehicle and support it on
stands.
Disconnect the negative lead from the battery
Engage the highest gear. Using the road wheel, turn
the engine.
Set No. I cylinder to the initial timing point, Fig. I.
(look into the oil filler hole)
- Bring cylinder No. 1 valves into the rocking position
by rotating the engine one turn clockwise.
- Marks- and- should be aligned.
Remove:
- the road wheel,
- the wheelarch lining,
- the belt upper protection cover.
Loosen:
- the injection pump drrvrng pinion nut,
- the belt tensioner nut,
- compress the spring of the tensioner.
Remove:
- the pinion nut,
- the injection pump driving belt. MANDATORY: TO AVOID THE PUMP BEING
DAMAGED INTERNALLY WHEN REMOVING
THE DRIVING PINION, PULLER REF. H AND ITS
NUT J FROM TOOL BOX 6028.T MUST BE
USED.
Fit the nut and clamp of tool 6028.T, Fig. II.
Slacken the nut of tool 6028.T until the injection
pump drive shaft starts moving.
Disconnect the electrical STOP solenoid
Uncouple:
- the accelerator cable,
- the fast idling cable,
- the fuel supply pipe,
- the fuel return pipe.
DPC injection pump, Fig. ill:
Disconnect from the overfuelling circuit:
- the diesel fuel return pipe (21,
- the air pipe (I 1.
Push the diesel fuel filter to one side
Remove:
- the spring,
- the injectors sets of feed pipes,
- the pump fixing nuts (3) Fig. IV.
by means of a 73 mm A/F open spanner
and a 6 mm hexagon Allen key.
Page 218 of 648

REMOVING/REFITTING D.P.A. AND D.P.C.
ROT0 DIESEL INJECTION PUMPS MA
146.1/l 5
REFITTING
Prepare
- the pump (see Op. @ MA 146.0/l/
Fit
- the pump with the mounting studs in the middle of
the slots,
- the pump fixing nuts but do not tighten home.
Assemble, Fig. I:
- the injection pump driving pinion t I); hand tighten
nut (2),
- the pump drive belt with the side opposed to the
tension roller being without slack (take care not to
rotate the pump).
Unscrew, Fig. I:
- tensioner nut (3); let the tensioner load the belt
without assistance.
Retighten, Fig. I:
- tensioner nut (3) to 2 mdaN,
- pinion nut (2) to 5 mdaN.
Carry out the pump timing:
Turn the pump towards the engine to find the point
of injection, (needle facing the “0” mark on the dial).
Screw up, Fig. II, to 2.4 mdaN,
- the pump fixing screws (4); when tightening, the dial
gauge needle should not move.
Check the pump timing (refer to @ MA 146.011)
Remove the tools
Refit:
- either the plug (tighten to 2 mdaN),
- or the inspection plate.
Seal the injection pump plug.
Refit:
- the belt upper protection cover,
- the wheelarch lining,
- the accelerator return spring,
- the injector set of feed pipes.
Tighten to 2.5 mdaN.
Recouple:
- the fast idle cable,
- the accelerator cable,
- the fuel pipe,
- the return pipe, D.P.C. pump, Fig. III.
Connect to the overfuelling circuit,
- the diesel fuel return pipe (61,
- the air pipe (5).
Put the fuel filter back into place.
Reconnect:
- the electric STOP solenoid,
- the negative cable to the battery.
Prime the fuel system using the manually operated
pump located on the filter.
Adjust the injection pump controls and idling speed
as explained in Op. @ MA 146.0/l.
8531