check engine CITROEN CX 1988 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CITROEN, Model Year: 1988, Model line: CX, Model: CITROEN CX 1988Pages: 648, PDF Size: 95.8 MB
Page 2 of 648

USE OF THE MANUAL
PRESENTATION
The Repair Manual comes in a binder with a “Mu/to” type
mechanism to facilitate the filing of additive sheets
or the removal of a part for operation in the workshop.
The MECHANICAL COMPONENTS, PART 1 VOLUME (8531) covers operations on the MECHANlCAL
COMPONENTS and the BODYWORK which may be carried out by a general workshop.
It is divided into 15 chapters separated by vinyl tab inserts numbered @ to @
General
Engine
Fuel system-Carburettor
Ignition system
Clutch
Gearbox-Drive shafts
Source and reserve of pressure
Front axle Rear axle
Suspension - wheels - tyres
Steering
Braking system
Electrical equipment and radio
Heater, ventilation and air-conditioning
Bodywork
COMPOSITION OF A CHAPTER
Each chapter includes:
-
the list of operations in it,
-
the operations in numerical order.
OPERATIONS
The operation references are made up as follow: MA 100 - 00 II a
-
a) z T-r TiiTz
a) vehicle code letters: MA
b) three figure number identifying the assembly or the assembly part
c) figure indicating the type of operation:
-
the figures 000 indicate the vehicle specification
- the figures 00 indicate the assembly specification
- the figures 0 indicate checks and adjustments
- the figures 1 indicate removals and refittings
- the figures 2 indicate dismantling and re-assembly
-
the figures 3 indicate reconditioning
d) figure /I,... /2.../... standing for a variant,
e) letter: a, b, standing for an evolution
rious operations are presented:
1’ either through photos, drawings and texts,
hrough photos, drawings and symbols.
‘!%.OSSARY has been placed at the beginning of each volume for this purpose.
e glossary (the one in the Mechanical Components volume is different from the one in
caning for each symbol has been translated into nine languages.
kts in a removable set of “plastic” sheets bound with one manceuvrable me
ion of one or several pages (and obtain photocopies from them, for instance). the Bodywork volur nel,
‘tal r ing to facilitate the
85 31
Page 17 of 648

PROTECTION OF THE ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
PRECAUTIONS TO BE TAKEN WHEN CARRYING OUT AN OPERATION ON THE VEHICLE
It is essential to avoid actrons which may damage the electrical or the electronic equipment or create a short circuit
(wrth subsequent risk of fire or accident).
Battery:
a) First disconnect cable clamp from the battery negative terminal, earthed, then from the positive post.
b 1 Before tightening the negative clamp to the battery (the negative lead should be connected last), ensure that there
is no short circuit (bright sparks or arcs).
Small sparks may occur due to the interior lamp (door open), door locking device, clock or components having
remained in operation.
c 1 Make sure that the terminals are properly connected. Clamps and terminals should be clean and correctly tightened.
d ) When recharging the battery, disconnect the two clamps first.
e) Do not reverse the negative and positive clamps on the battery. (This could destroy the alternator diodes).
Fuses:
a 1 Fit the correct type of fuses: use the fuses specified for the protected devices
b 1 Take the added accessories and the functions into consideration.
Charging circuit:
,a 1 Do not run the alternator unless it is connected to the battery. Do not disconnect the battery when the alternator
is rotating.
b 1 Ensure that the regulator is correctly earthed.
c ) Do not interchange the leads connected to the regulator, (charge detection warning lamp and excitation are specific).
d ) Do not connect a suppressor capacitor to the regulator without taking precautions or following proper
instructions.
e 1 Do not use an electric welding equipment on the vehicle without having first disconnected the alternator, the regula-
tor and the battery (insulate the two terminals).
f 1 Do not R check )) the operation of an alternator by short circuiting the positive and ground terminals, which may
destroy the diodes.
Starting the engine:
Do not use a booster or a 24-volt battery. Only use a correctly charged 12-volt battery (a higher capacity battery may
be utilised). Otherwise, risk of deterioration of the ignition module or any other electronic control units. If the starter
is needed for starting the engine, without running it, it is necessary to disconnect datum and flywheel sensors on the
All Electronic Ignition, or the primary lead of the coil on any other type of ignition.
Ignition:
a 1 Do not connect a suppressor capacitor to the negative terminal of the coil.
b 1 Do not operate the module if its radiator is not connected to the earth.
c 1 Fit the radio suppressor capacitors recommended by the factory.
d 1 Never operate the ignition system while the HT circuit is open. Connect the HT leads to earth
e) Only use rev. counter having a HT sensor, (never puncture HT leads).
0.1. bulb:
a) Never replace a 01. bulb with the headlamp switched on. If the headlamps have been in use, allow them to cool down.
b) Do not touch a 0.1. bulb with bare fingers. Any fingerprints must be cleaned with soapy water and the bulb dried
with a dry lint-free cloth.
Checks :
a) Preferably use a high resistance (> 10 k Q VI voltmeter or a battery-operated ohm-meter
b) Take care not to use instruments taking their power from the mains.
Electronic components:
a) Avoid overvoltages due to a badly insulated charger, electric arcing or connections to the coil.
The units such as regulator, ignition module, tachometer, windscreen wiper timer, flasher unit, clock, radio, oil gauge
unit, door lock control unit, etc. comprising electronic components may be deteriorated.
b) The electronic components should not be placed or operated under a temperature exceeding 80°C.
c) Always switch off instruments or electronic control units before connecting or disconnecting them.
‘
Page 95 of 648

o&ion oi‘i tht: enginr:,
-T.bis (as shown on i/til.irial~oiii,
attaching bracket 6031-
nafu/a//y asp/rafed erg/m with E/7: bracket to bc: fit-
ted on the exhaust pipe, with one screw,
turbo with EN: fit the bracket to the pressure relief
valve outlet,
- tensioner 4061-T (siack).
Place sling 2517-T.bis. under tension, tensioner
4061-T being loosened, Fig. II.
Remove:
- screw (I 1 from the engine bearer, Fig. III.
- nut (3) and screws (4) from the gearbox mounting,
Fig. V (retrieve the shims),
- screw (2) from the torque rod; slacken the other
scl-ew, Fig. IV.
Slightly raise the power unit assembly
Screw tensioner 4061-T fully, Fig. VI and remove
the engine/gearbox assembly:
Before refitting the power unit assembly:
Check the condition of the engine mounting brac-
kets. Replace them if needed.
Adjustment to be tested,
(as per Op.0 MA 733.0/1) Fit the engine crankcase water dralrl plug, fltted with a
~~~in~ torque: 3 mda
Place sling 2517-T.bis, attaching bracket 6031 -T
and tensioner 4061-T; screw the tensioner fully In,
Fig. I and VI.
Engage the engine/gearbox assembly Into Its corr-
partment, Fig. VI.
l-oosen tensioner 4061-T, Fig. II.
Refit: (without tightening)
- engine support bracket
screw (I 1,
- torque rod screw (2)
- gearbox support plate (toyeTher with 1f.s shims).
Tighten:
- the engrne bearer to 10 mdaN, Fig. III
- the torque rod to 9 mdaN, Fig. IV
-. the gearbox support plate fixings, Fig. V:
screws (4): to 3 mdaN
nut (31: to 16.5 mdaN.
Insert the clutch cable into Its ball-joint. Tighten clutch
control support (5). Adjust the clutch , Fig. VII.
Locate, Fig. VIII.
the dual outlet power take off (61.
the oil gauge.
Page 97 of 648

le up the exhaust system. econnect, Fig. IV and V:
- connectors 11 I),
turaily aspirated engines w/th EN, fitted with
seals:
Tighten the flange to 1.6 mda
On the turbocharged engines with EH, fitted with
NEW nuts and seals:
Refit: Fig. I and II, - sensor (12) (with biue /dent mark),
- sensor (13) (with no ident mark),
- HT coil 191 cyls 1 and 4 (with yellow /dent mark),
HT coil i IO) cyls 2 and 3 (w/t/r fro markl,
- the suppressors,
- the reversing larnp switch wrring harness,
- the throttle spindle switch (141,
- knock sensor (I 8).
- flexible pipe (2) to the pressure release valve outlet,
- exhaust pipe (4) to the turbo, screws (31, distance
pieces (51,
- screw (6) and adjusting shims.
There should be a 5 mm clearance at least between
the exhaust pipe and the engine crankcase. Recouple, Fig. V and VI:
- the water hoses,
- air circurt pipes (151, (161, (17). (20) and (211,
- petrol circuit pipes (I 9),
- gear shift link rods,
- the accelerator cable.
Tighten, Fig. I and II:
- turbocharger nuts fin the correct sequence), Fig. II,
- flexible hose (2) screws (3) and nuts (I 1 to
2.5 mdaN,
- screw (6) to 5 mdaN. Fit:
- the driveshafts,
(See Op. @ MA 372-l/11
- the radiator,
- the bonnet,
- the battery,
Refit: Fig. Ill
- the pressure regulator and compressor holder (air
conditioning option) together with its shims; tigh-
ten nuts (7) to 5 mdaN. - the protection plate located under the spare
wheel.
Check the oil levels. Top up if necessary.
Vehicles with air-conditioning: Fill up the cooling circuit (wrth the heater open) and
carry out the bleeding operation.
- the compressor belt and protection cover,
- the pressure regulator accumulator, fitted with a
NEW seal,
- the HP pump outlet pope, fitted with a NEW sea/
and its fastenings (8),
- the pipe situated between the pressure regulator
and the brake accumulator, fitted with NEWseals,
- the HP pump rubber suction pipe,
- the horn. (As per Op @ MA 230.0/l/.
Bleed the front brakes.
(Refer to Op. MA 453.0/l/.
Check the gear change.
Lower the vehicle to the ground.
Page 116 of 648

emove:
the I-oati Wi-l~~d,
- the wheelarch lrnrrng,
- the belt protectron covets
Position: Fig. I and II
the valves of cylrnder No. 1 rn the “rocking” ~OSI-
tion (look Into the engine 011 filler),
the flywheel wrth mar-ks- -alrgned,
- camsfraft gear wheel mark A opposite screw 12)
Loosen:
the nuts of the tensioners and compress the spring
of eacir tensloner. Hetighten the nuts.
Remove:
- injection pump belt,
- the trmrng belt
REFITTING
Fit, Fig. II:
the timrng belt- marks t-+-) and i-e-1 on the belt
should face the marks A and B on pinrons (there
are 35 pitches between A and B, passing around
the tensloner roller (I 1).
Loosen the nuts of the tensioner roller.
Install, Fig. III:
- tool 6Q28-T.K. on the roller
- the tool weight over the mark 2 of the rod, Fig 1V. Fitting the injection pump belt:
Run the engrne by 1 turn err the drrectrorr of rotation
until marks--- +- /Ino up, Fig. I
(wrth cylinder No 1 at the rnrtral trmrng
point)
Setting the pump to the injection point:
refer to Op @ MA. 146-011
Fit the InJectron purnf, drrvrng belt with the srde oppo-
site the roller, trght.
Slacken the roller nut. Let the roller- spring react
Tighten the rnut to 2 mdaN.
Rotate the engine by 2 turns in the direction of nor-
rnal rotation and check the pump timrng.
Remove the tools
Start the engine Warrn it up until the electric cooling
fans operate.
Retension the belt while the engine is hot, Fig. IV
Refit:
- the protectron covers,
- the wheelarch lining,
the road wheel
Page 122 of 648
CHECKING AND ADJUSTING
THE ENGINE SUPPORT BRACKETS
-.~ ~.~ -.-... --- >
Page 157 of 648

GENERAL FEATURES OF THE CARBURATION
FITTING. Fig. I:
5. FIN the tamper-proof protective plug (a):
- load gun A,
- screw tool E onto gun A,
- position plug (a) in its housing on the carburettor (make sure it is fitted the right way round Fig. 111,
- actuate the gun until the plug is properly located.
EXHAUST EMISSION CONTROL
In order to comply with current regulations, the checking and adjustment of the exhaust emission from vehicles
with a petrol engine must, without fail, be performed after the following operations:
I. ENGINE REPLACEMENT.
II. CARBURETTOR REPLACEMENT.
Ill. WORK ON THE CARBURETTOR.
Replacement of parts of the carburettor.
Carburettor adjustment.
Work on the carburettor controls.
IV. WORK ON THE INLET MANIFOLD.
Replacement or removal of:
- the inlet manifold,
- the air filter,
- crankcase gas recirculation system
V. WORK ON THE ENGINE.
Rocker adjustment.
Replacement or removal of:
- the cylinder head,
- the camshaft,
- the rockers,
- the valves,
- the liners and pistons.
VI. WORK ON THE IGNITION.
Replacement or reconditioning of the distributor (wholly or partially)
Adjustment or replacement of the sparking plugs.
Adjustment of the ignition timing.
VII. WORK ON EXHAUST SYSTEM.
Replacement or removal of:
- the exhaust manifold,
- the silencer or any part of the exhaust.
VIII. WORK ON THE EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM.
When the vehicle is fitted with a specific equipment (e.g. on vehicles of SWEDEN, AUSTRALlA or JAPAN type)
Page 169 of 648
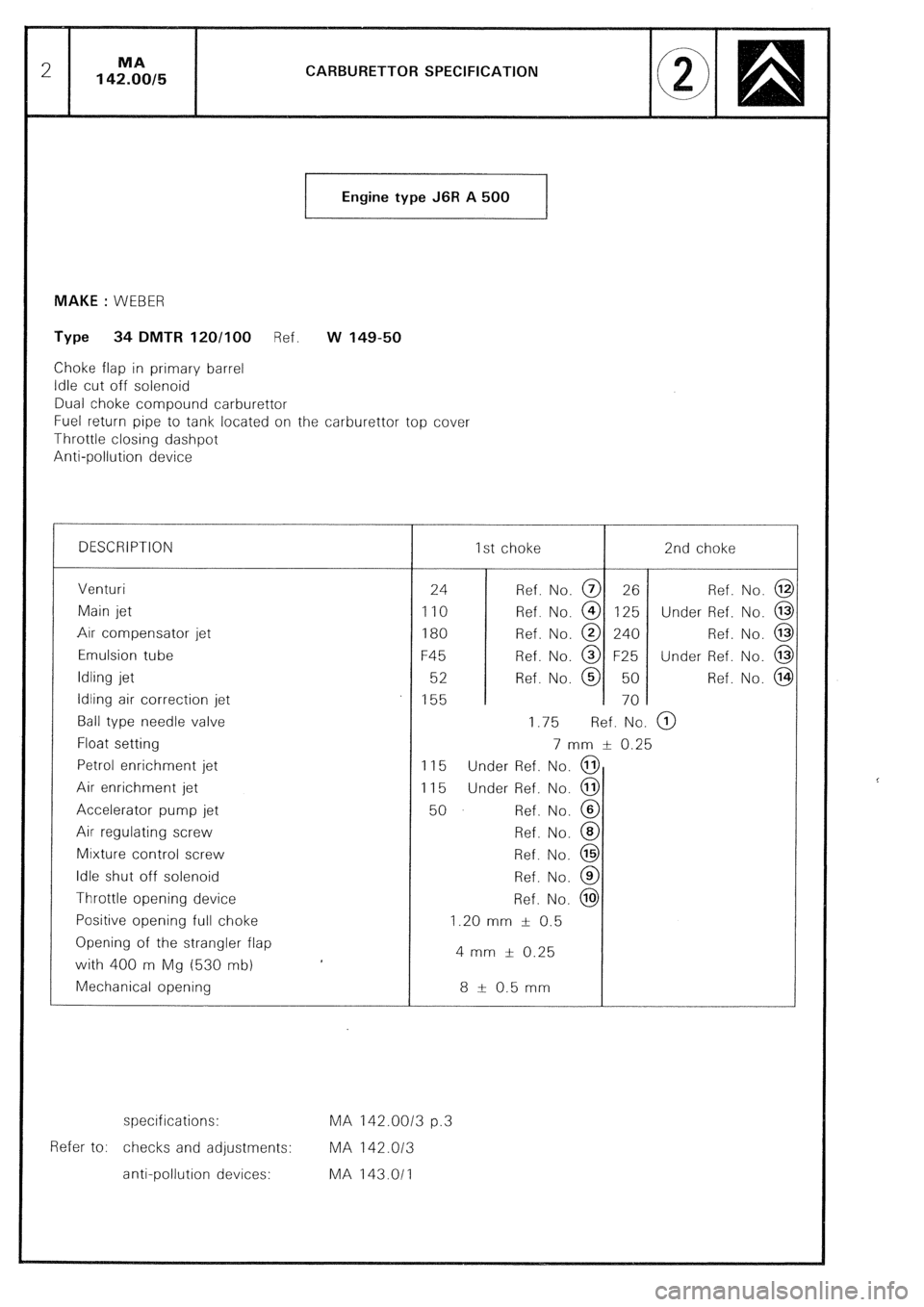
CARBURETTOR SPECIFICATION
Engine type J6R A 500
1 MAKE : WEBER
Type 34 DMTR 120/100 Ref. w 149-50
Choke flap in primary barrel
Idle cut off solenoid
Dual choke compound carburettor
Fuel return pipe to tank located on the carburettor top cover
Throttle closing dashpot
Anti-oollution device
DESCRIPTION 1st choke 2nd choke
Venturi
Main jet
Air compensator jet
Emulsion tube
Idling jet
Idling air correction jet
Ball type needle valve
Float setting
Petrol enrichment jet
Air enrichment jet
Accelerator pump jet
Air regulating screw
Mixture control screw
Idle shut off solenoid
Throttle opening device
Positive opening full choke
Opening of the strangler flap
with 400 m Mg (530 mb)
Mechanical opening 24 Ref. No. @ 26 Ref. No. @
110 Ref. No. @ 125 Under Ref. No. @
180 Ref. No. @ 240 Ref. No. @
F45 Ref. No. @ F25 Under Ref. No. @
52 Ref. No. @ 50 Ref. No. @
155 70
1.75 Ref. No. @)
7 mm & 0.25
115 Under Ref. No. @
115 Under Ref. No. @
50 Ref. No. @
Ref. No. @
Ref. No. @
Ref. No. @
Ref. No. @
1.20 mm f 0.5
4 mm f 0.25
8 t- 0.5 mm
specifications: MA 142.0013 p.3
Refer to: checks and adjustments: MA 142.013
anti-pollution devices: MA 143.011
Page 212 of 648

CHECKING AND ADJUSTING
THE INJECTION SYSTEM
II. - INSPECTION AND TIMING OF THE “ROT0-DIESEL” INJECTION PUMP
Raise the LH side of the vehicle and support it on
stands.
Disconnect the battery negative lead.
Engage the 5th gear. Rotate the engine by turning the
wheel.
Set the No. 1 cylinder to the initial timing point,
Fig.1.
(look into the oil filter orifice).
- place cylinder No. 1 valves in the rocking position;
turn the crankshaft by one turn in the normal direc-
tion of engine rotation.
- align marks on the flywheel and on the crankcase
(++I.
- turn the crankshaft back through a quarter of a turn.
Remove either the plug (with a 32 mm ring spanner)
or the inspection plate depending on the type of the
pump.
Refit, Fig II or Ill, according to pump:
- the feeler,
- the support for the dial-gauge.
- the dial-gauge equipped with its right-angled lever.
Finding the pump internal timing point:
- turn the crankshaft in the direction of rotation until
the large pointer on the dial indicator starts moving
in the opposite direction.
- set “0” mark on the dial-gauge in line with the large
pointer.
Checking the injection pump timing:
- rotate the crankshaft by a quarter turn in the oppo-
site direction to its direction of rotation.
- turn back in the normal direction of rotation until the
“0” mark on the dial-gauge has been reached.
- in that position, marks (-1 and (c) should be in line,
Fig. I.
If not, re-check the timing. Timing the injection pump:
- set the engine to the initial trming point, Fig. I.
- turn the crankshaft by 114 turn in the opposite direc-
tion to normal direction of ro’tatron, then turn back
in the direction of rotation to bring marks t-+) and
+-I opposite.
Adjusting the pump timing, Fig. Ill:
Slacken off the injector pipe connections and the 4
attachment points.
Bring the pump to the injection point with the feeler
at the base of V-shaped groove (timing point).
Set the “0” mark on the dial opposite the needle on
the dial-gauge. Orientate the pump casing towards the
engine.
Slowly turn back to the injection point (needle facing
the “0” mark on the dial), by moving the pump
casing away from the engine (in the opposite direc-
tion to engine rotation).
Tighten the pump fixing nuts to 2.4 mdaN. During
this operation, the needle should not move.
Check the pump timing
Remove the timing tools.
Refit the plug, (tighten to 2 mdaN), or the inspec-
tion plate.
Seal the injection pump plug.
Tighten the injector pipe connections to 2 mdaN.
Reconnect the battery negative cable
Switch on the ignition (electrical STOP solenoid exci-
tation) and prime the fuel circuit using the manual
pump (5) located on the filter.
Fully depress the accelerator pedal to facilitate the
engine bleeding and start.
Note: the initial timing point corresponds to:
3.24 -L- 0.05 mm BTDC: M 25/648
4.32 + 0.05 mm BTDC: M 25/660 DPA pump
4.71 f 0.05 mm BTDC: M 25/660 DPC pump
8531
Page 213 of 648

CHECKING AND ADJUSTING
THE INJECTION SYSTEM
III. - ADJUSTING THE ROTO-DIESEL INJECTION PUMP CONTROLS
DPC type pump from engine M 25/648, Fig. I
DPA type pump from engine M 25/660, Fig. II
Checking the fast-idle control
Ensure that lever (7) is against its stop, by pushing
it in the direction of arrow (-).
If not, adjust tension of cab/e by means of cable end
clamp (6). Complete tightening of cable using sheath
tensioner (41.
Checking the fast-idle control
Make sure that the cable is slack.
If not, check the operation of the thermal sensor (101
located on the water outlet duct: the cable must ope-
rate over a range of 6 mm between its “ENGINE
COLD” and “ENGINE WARM” positions.
Adjusting the accelerator control
Engine stopped:
Fully depress the accelerator pedal.
Check that lever (I) is against stop (2).
If not, move pin (3) of accelerator cable.
Make sure that, at idle, lever (I) is against stop (5).
Adjusting the anti-stalling device
Engine running:
Insert a 1.5 mm thick shim (DPC pump, Fig. I)
2 mm thick shim (DPA pump, Fig. II)
between lever (I) and stop-screw (5) at “b”.
Place a 3 mm dia. rod through the hole in lever (7)
at “a” by pushing STOP lever (9) outwards. Set the engine speed to:
800 t 50 rpm (DPC pump)
800 f 25 rpm (DPA pump)
by turning stop screw (5).
Remove the 3 mm dia. rod and the shim
Adjust the idling speed to:
800 + 25 rpm
by turning stop screw (8).
Checking the engine deceleration:
Accelerate the engine to 3.000 rpm, then release the
accelerator lever sharply.
- if the deceleration is too fast (engine often stalling),
unscrew stop-screw (5) by 114 turn,
- if the deceleration is too slow (poor engine braking),
screw up stop-screw (51 by l/4 turn.
In both cases, check the idling speed and adjust if
necessary.
If the malfunction continues to exist, carry out the
adjustments again.
Check the efficiency of the mechanically operated
STOP control (9).
Note: The setting figures are identical if the vehicle
is equipped with air-conditioning and the adjustments
are to be effected with the air-conditioning off.