Timing belt DAEWOO LACETTI 2004 Service Manual PDF
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DAEWOO, Model Year: 2004, Model line: LACETTI, Model: DAEWOO LACETTI 2004Pages: 2643, PDF Size: 80.54 MB
Page 184 of 2643
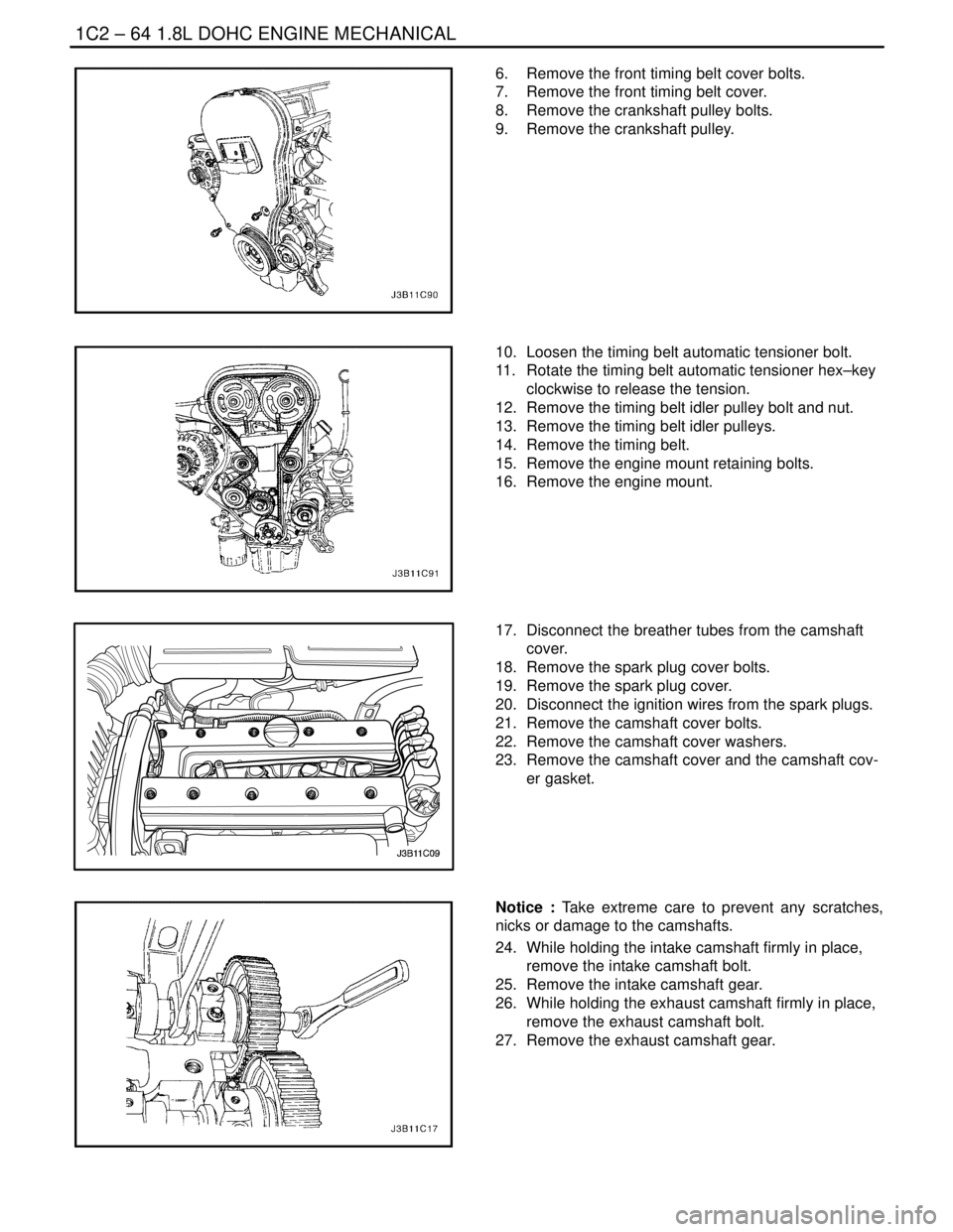
1C2 – 64I1.8L DOHC ENGINE MECHANICAL
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
6. Remove the front timing belt cover bolts.
7. Remove the front timing belt cover.
8. Remove the crankshaft pulley bolts.
9. Remove the crankshaft pulley.
10. Loosen the timing belt automatic tensioner bolt.
11. Rotate the timing belt automatic tensioner hex–key
clockwise to release the tension.
12. Remove the timing belt idler pulley bolt and nut.
13. Remove the timing belt idler pulleys.
14. Remove the timing belt.
15. Remove the engine mount retaining bolts.
16. Remove the engine mount.
17. Disconnect the breather tubes from the camshaft
cover.
18. Remove the spark plug cover bolts.
19. Remove the spark plug cover.
20. Disconnect the ignition wires from the spark plugs.
21. Remove the camshaft cover bolts.
22. Remove the camshaft cover washers.
23. Remove the camshaft cover and the camshaft cov-
er gasket.
Notice : Take extreme care to prevent any scratches,
nicks or damage to the camshafts.
24. While holding the intake camshaft firmly in place,
remove the intake camshaft bolt.
25. Remove the intake camshaft gear.
26. While holding the exhaust camshaft firmly in place,
remove the exhaust camshaft bolt.
27. Remove the exhaust camshaft gear.
Page 185 of 2643
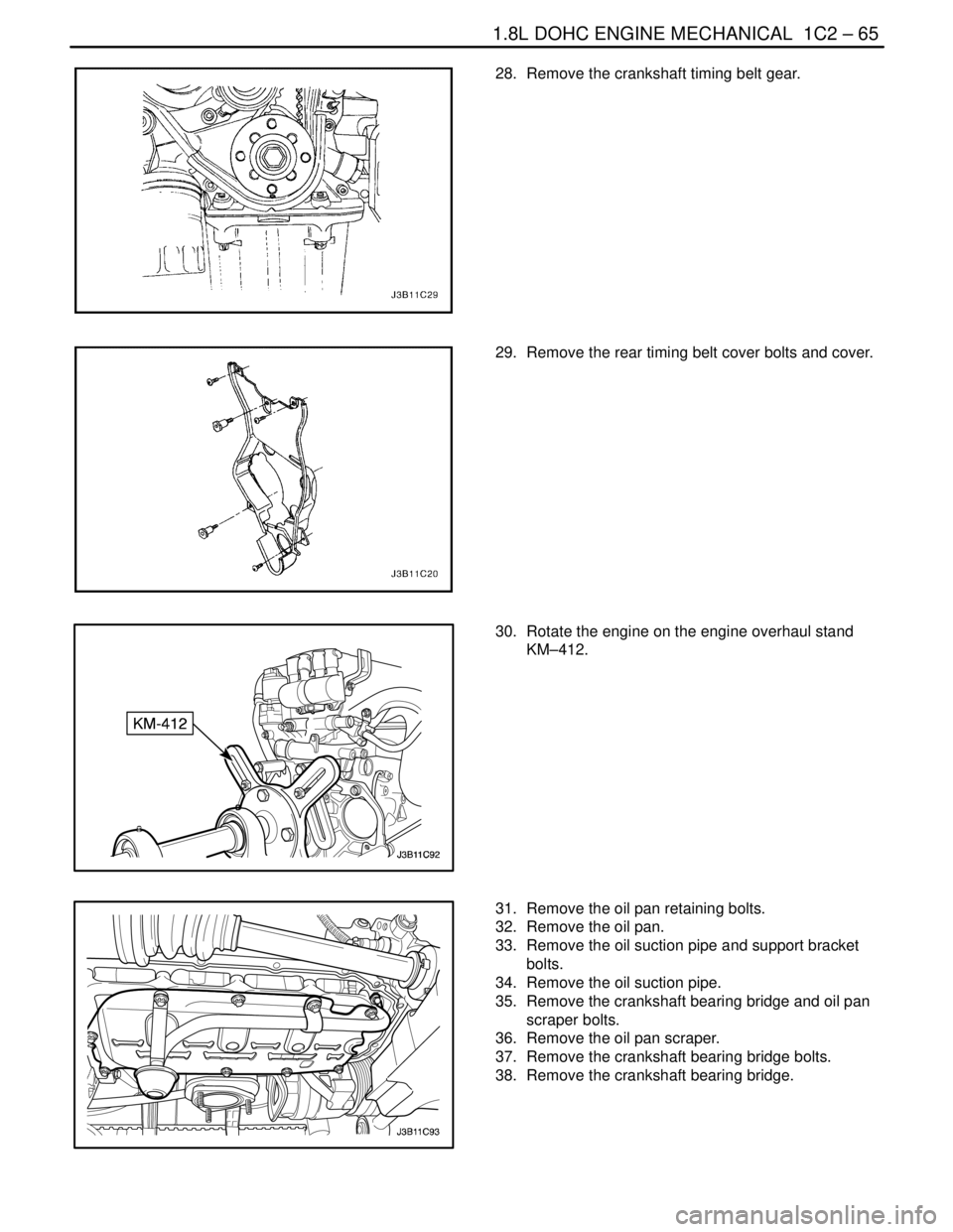
1.8L DOHC ENGINE MECHANICAL 1C2 – 65
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
28. Remove the crankshaft timing belt gear.
29. Remove the rear timing belt cover bolts and cover.
30. Rotate the engine on the engine overhaul stand
KM–412.
31. Remove the oil pan retaining bolts.
32. Remove the oil pan.
33. Remove the oil suction pipe and support bracket
bolts.
34. Remove the oil suction pipe.
35. Remove the crankshaft bearing bridge and oil pan
scraper bolts.
36. Remove the oil pan scraper.
37. Remove the crankshaft bearing bridge bolts.
38. Remove the crankshaft bearing bridge.
Page 190 of 2643
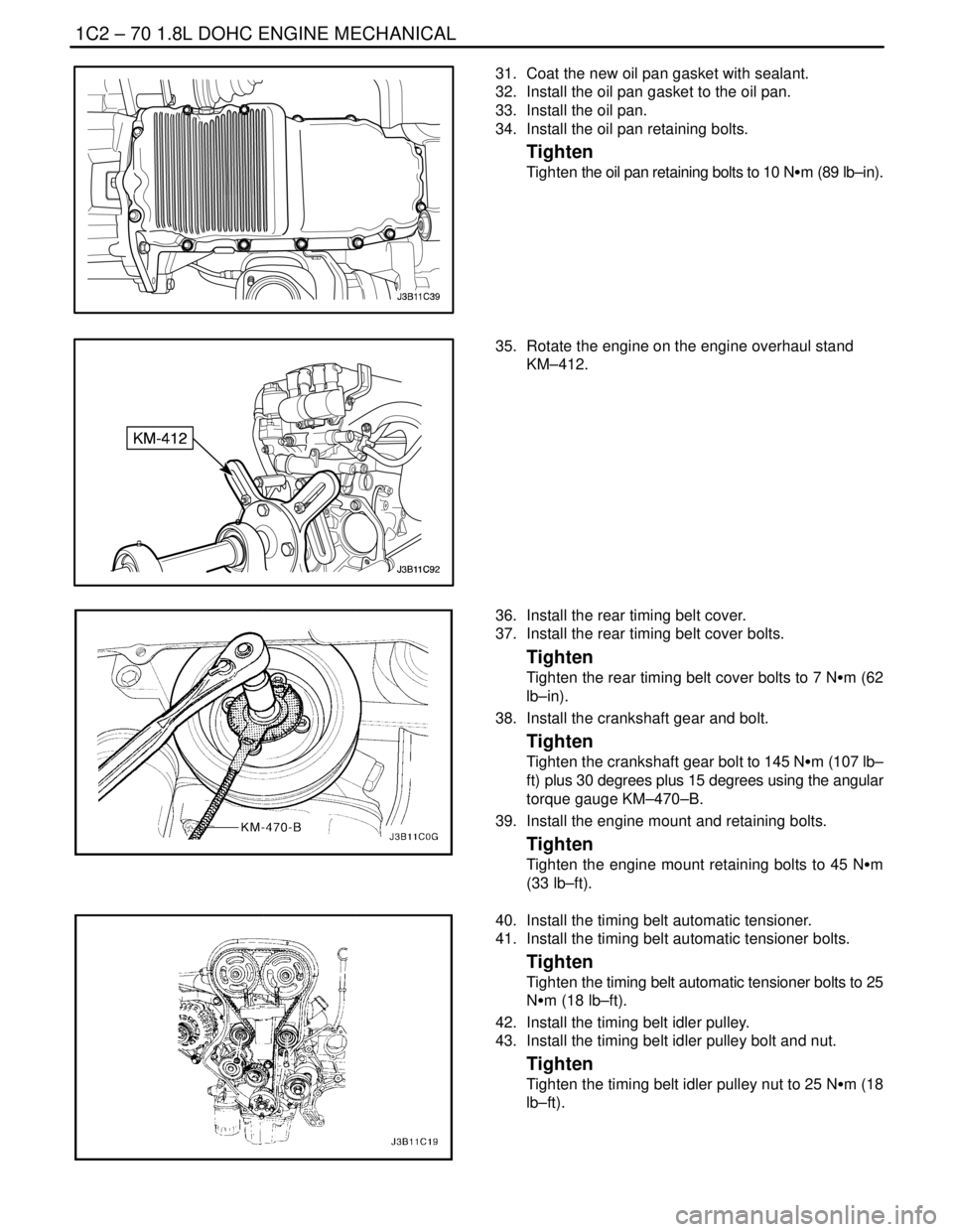
1C2 – 70I1.8L DOHC ENGINE MECHANICAL
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
31. Coat the new oil pan gasket with sealant.
32. Install the oil pan gasket to the oil pan.
33. Install the oil pan.
34. Install the oil pan retaining bolts.
Tighten
Tighten the oil pan retaining bolts to 10 NSm (89 lb–in).
35. Rotate the engine on the engine overhaul stand
KM–412.
36. Install the rear timing belt cover.
37. Install the rear timing belt cover bolts.
Tighten
Tighten the rear timing belt cover bolts to 7 NSm (62
lb–in).
38. Install the crankshaft gear and bolt.
Tighten
Tighten the crankshaft gear bolt to 145 NSm (107 lb–
ft) plus 30 degrees plus 15 degrees using the angular
torque gauge KM–470–B.
39. Install the engine mount and retaining bolts.
Tighten
Tighten the engine mount retaining bolts to 45 NSm
(33 lb–ft).
40. Install the timing belt automatic tensioner.
41. Install the timing belt automatic tensioner bolts.
Tighten
Tighten the timing belt automatic tensioner bolts to 25
NSm (18 lb–ft).
42. Install the timing belt idler pulley.
43. Install the timing belt idler pulley bolt and nut.
Tighten
Tighten the timing belt idler pulley nut to 25 NSm (18
lb–ft).
Page 191 of 2643

1.8L DOHC ENGINE MECHANICAL 1C2 – 71
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
Notice : Take extreme care to prevent any scratches,
nicks or damage to the camshafts.
44. Install the intake camshaft gear.
45. Install the intake camshaft gear bolt while holding
the intake camshaft firmly in place.
Tighten
Tighten the intake camshaft gear bolt to 50 NSm (37
lb–ft) plus 60 degrees and 15 degrees using the angu-
lar torque gauge KM–470–B.
46. Install the exhaust camshaft gear.
47. Install the exhaust camshaft gear bolt while holding
the exhaust camshaft firmly in place.
Tighten
Tighten the exhaust camshaft gear bolt to 50 NSm (37
lb–ft) plus 60 degrees and 15 degrees using the angu-
lar torque gauge KM–470–B.
48. Install the timing belt. Refer to ”Timing Belt” in this
section.
49. Adjust the timing belt tension. Refer to ”Timing Belt
Check and Adjust” in this section.
50. Apply a small amount of gasket sealant to the cor-
ners of the front camshaft caps and to the top of
the rear camshaft cover to cylinder head seal.
51. Install the camshaft cover and the camshaft cover
gasket.
52. Install the camshaft cover washers.
53. Install the camshaft cover bolts.
Tighten
Tighten the camshaft cover bolts to 8 NSm (71 lb–in).
54. Connect the ignition wires to the spark plugs.
55. Install the spark plug cover.
56. Install the spark plug cover bolts.
Tighten
Tighten the spark plug cover bolts to 8 NSm (71 lb–in).
57. Connect the breather tube to the camshaft cover.
58. Install the front timing belt cover.
59. Install the front timing belt cover bolts.
Tighten
Tighten the front timing belt cover bolts to 8 NSm (71
lb–in).
60. Install the engine lifting device.
61. Remove the engine from the engine overhaul stand
KM–412.
Page 195 of 2643

1.8L DOHC ENGINE MECHANICAL 1C2 – 75
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
AND SYSTEM OPERATION
CYLINDER HEAD AND GASKET
The cylinder head is made of an aluminum alloy. The cylin-
der head uses cross–flow intake and exhaust ports. A
spark plug is located in the center of each combustion
chamber. The cylinder head houses the dual camshafts.
CRANKSHAFT
The crankshaft has eight integral weights which are cast
with it for balancing. Oil holes run through the center of the
crankshaft to supply oil to the connecting rods, the bear-
ings, the pistons, and the other components. The end
thrust load is taken by the thrust washers installed at the
center journal.
TIMING BELT
The timing belt coordinates the crankshaft and the dual
overhead camshafts and keeps them synchronized. The
timing belt also turns the coolant pump. The timing belt
and the pulleys are toothed so that there is no slippage be-
tween them. There are two idler pulleys. An automatic ten-
sioner pulley maintains the timing belt’s correct tension.
The timing belt is made of a tough reinforced rubber similar
to that used on the serpentine drive belt. The timing belt
requires no lubrication.
OIL PUMP
The oil pump draws engine oil from the oil pan and feeds
it under pressure to the various parts of the engine. An oil
strainer is mounted before the inlet of the oil pump to re-
move impurities which could clog or damage the oil pump
or other engine components. When the crankshaft ro-
tates, the oil pump driven gear rotates. This causes the
space between the gears to constantly open and narrow,
pulling oil in from the oil pan when the space opens and
pumping the oil out to the engine as it narrows.
At high engine speeds, the oil pump supplies a much high-
er amount of oil than required for lubrication of the engine.
The oil pressure regulator prevents too much oil from en-
tering the engine lubrication passages. During normal oil
supply, a coil spring and valve keep the bypass closed, di-
recting all of the oil pumped to the engine. When the
amount of oil being pumped increases, the pressure be-
comes high enough to overcome the force of the spring.This opens the valve of the oil pressure regulator, allowing
the excess oil to flow through the valve and drain back to
the oil pan.
OIL PAN
The engine oil pan is mounted to the bottom of the cylinder
block. The engine oil pan houses the crankcase and is
made of cast aluminum.
Engine oil is pumped from the oil pan by the oil pump. After
it passes through the oil filter, it is fed through two paths
to lubricate the cylinder block and cylinder head. In one
path, the oil is pumped through oil passages in the crank-
shaft to the connecting rods, then to the pistons and cylin-
ders. It then drains back to the oil pan. In the second path,
the oil is pumped through passages to the camshaft. The
oil passes through the internal passageways in the cam-
shafts to lubricate the valve assemblies before draining
back to the oil pan.
EXHAUST MANIFOLD
A single four–port, rear–takedown manifold is used with
this engine. The manifold is designed to direct escaping
exhaust gases out of the combustion chambers with a
minimum of back pressure. The oxygen sensor is
mounted to the exhaust manifold.
INTAKE MANIFOLD
The intake manifold has four independent long ports and
utilizes an inertial supercharging effect to improve engine
torque at low and moderate speeds.
CAMSHAFTS
This engine is a dual overhead camshaft (DOHC) type,
which means there are two camshafts. One camshaft op-
erates the intake valves, and the other camshaft operates
the exhaust valves. The camshafts sit in journals on the
top of the engine (in the cylinder head) and are held in
place by camshaft caps. The camshaft journals of the cyl-
inder head are drilled for oil passages. Engine oil travels
to the camshafts under pressure where it lubricates each
camshaft journal. The oil returns to the oil pan through
drain holes in the cylinder head. The camshaft lobes are
machined into the solid camshaft to precisely open and
close the intake and the exhaust valves the correct
amount at the correct time. The camshaft lobes are oiled
by splash action from pressurized oil escaping from the
camshaft journals.
Page 199 of 2643
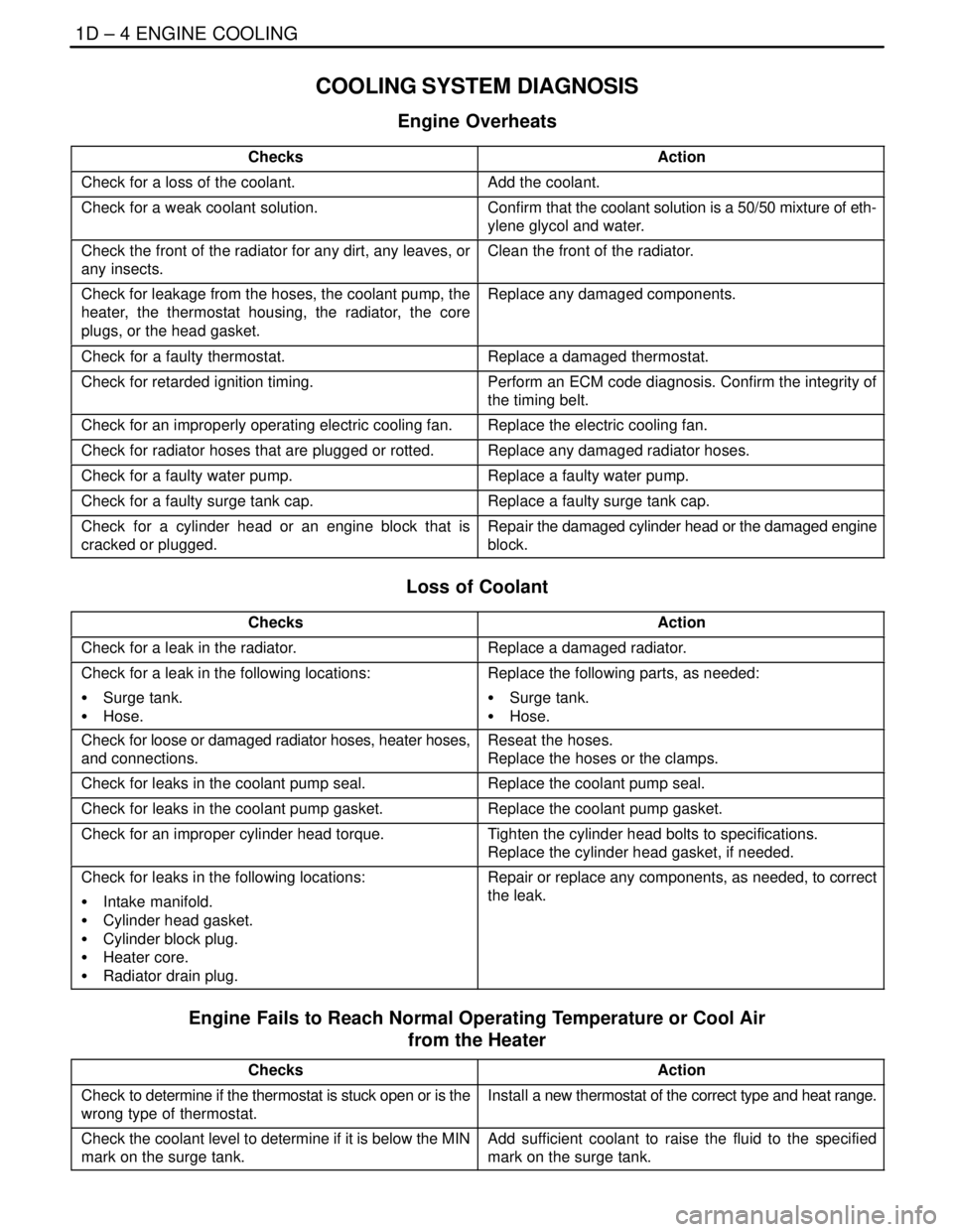
1D – 4IENGINE COOLING
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
COOLING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
Engine Overheats
ChecksAction
Check for a loss of the coolant.Add the coolant.
Check for a weak coolant solution.Confirm that the coolant solution is a 50/50 mixture of eth-
ylene glycol and water.
Check the front of the radiator for any dirt, any leaves, or
any insects.Clean the front of the radiator.
Check for leakage from the hoses, the coolant pump, the
heater, the thermostat housing, the radiator, the core
plugs, or the head gasket.Replace any damaged components.
Check for a faulty thermostat.Replace a damaged thermostat.
Check for retarded ignition timing.Perform an ECM code diagnosis. Confirm the integrity of
the timing belt.
Check for an improperly operating electric cooling fan.Replace the electric cooling fan.
Check for radiator hoses that are plugged or rotted.Replace any damaged radiator hoses.
Check for a faulty water pump.Replace a faulty water pump.
Check for a faulty surge tank cap.Replace a faulty surge tank cap.
Check for a cylinder head or an engine block that is
cracked or plugged.Repair the damaged cylinder head or the damaged engine
block.
Loss of Coolant
ChecksAction
Check for a leak in the radiator.Replace a damaged radiator.
Check for a leak in the following locations:
S Surge tank.
S Hose.Replace the following parts, as needed:
S Surge tank.
S Hose.
Check for loose or damaged radiator hoses, heater hoses,
and connections.Reseat the hoses.
Replace the hoses or the clamps.
Check for leaks in the coolant pump seal.Replace the coolant pump seal.
Check for leaks in the coolant pump gasket.Replace the coolant pump gasket.
Check for an improper cylinder head torque.Tighten the cylinder head bolts to specifications.
Replace the cylinder head gasket, if needed.
Check for leaks in the following locations:
S Intake manifold.
S Cylinder head gasket.
S Cylinder block plug.
S Heater core.
S Radiator drain plug.Repair or replace any components, as needed, to correct
the leak.
Engine Fails to Reach Normal Operating Temperature or Cool Air
from the Heater
ChecksAction
Check to determine if the thermostat is stuck open or is the
wrong type of thermostat.Install a new thermostat of the correct type and heat range.
Check the coolant level to determine if it is below the MIN
mark on the surge tank.Add sufficient coolant to raise the fluid to the specified
mark on the surge tank.
Page 206 of 2643

ENGINE COOLING 1D – 11
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
Installation Procedure
1. Install the thermostat into the thermostat housing
by pressing the thermostat mounting flange down-
ward and then rotating the flange counterclockwise.
Rotate the thermostat mounting flange until it is
seated in the thermostat housing recesses.
2. Coat the sealing surface of a new seal ring with
Lubriplater®.
3. Install a new seal ring into the recess in the thermo-
stat housing.
4. Install the thermostat housing to the cylinder head.
5. Secure the thermostat housing to the cylinder head
with the mounting bolts.
Tighten
Tighten the thermostat housing mounting bolts to 15
NSm (11 lb–ft).
6. Connect the upper radiator hose to the thermostat
housing.
7. Secure the upper radiator hose to the thermostat
housing with a hose clamp.
8. Refill the engine cooling system. Refer to ”Draining
and Refilling the Cooling System” in this section.
WATER PUMP
Removal Procedure
1. Drain the engine cooling system to a level below
the thermostat housing. Refer to ”Draining and Re-
filling the Cooling System” in this section.
2. Remove the timing belt. Refer to Section 1C DOHC
Engine Mechanical.
3. Remove the timing belt tension roller retaining bolt.
4. Remove the timing belt tension roller.
Page 207 of 2643
1D – 12IENGINE COOLING
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
5. Remove the water pump mounting bolts.
6. Remove the water pump from the engine block.
7. Remove the ring seal from the water pump.
Inspection Cleaning Procedure
1. Inspect the water pump body for cracks and leaks.
2. Inspect the water pump bearing for play or abnor-
mal noise.
3. Inspect the water pump pulley for excessive wear.
If the water pump is defective, replace the water
pump as a unit.
4. Clean the mating surfaces of the water pump and
the engine block.
Installation Procedure
1. Install a new ring seal to the water pump.
2. Coat the sealing surface of the ring seal with Lubri-
plater®.
3. Install the water pump to the engine block with the
flange aligned with the recess of the rear timing belt
cover.
4. Secure the water pump to the engine block with the
mounting bolts.
Tighten
Tighten the water pump mounting bolts to 25 NSSm
(18 lb–ft).
5. Install the timing belt tension roller to the oil pump
with the flange inserted into the recess of the oil
pump.
6. Install the timing belt tension roller bolt. Do not
tighten the bolt at this time.
7. Install the timing belt. Refer to Section 1C, DOHC
Engine Mechanical.
8. Refill the engine cooling system. Refer to ”Draining
and Refilling the Cooling System” in this section.
Page 213 of 2643

1D – 18IENGINE COOLING
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
AND SYSTEM OPERATION
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The cooling system maintains the engine temperature at
an efficient level during all engine operating conditions.
When the engine is cold, the cooling system cools the en-
gine slowly or not at all. This slow cooling of the engine al-
lows the engine to warm up quickly.
The cooling system includes a radiator and recovery sub-
system, cooling fans, a thermostat and housing, a coolant
pump, and a coolant pump drive belt. The timing belt
drives the coolant pump.
All components must function properly in order for the
cooling system to operate. The coolant pump draws the
coolant from the radiator. The coolant then circulates
through water jackets in the engine block, the intake man-
ifold, and the cylinder head. When the coolant reaches the
operating temperature of the thermostat, the thermostat
opens. The coolant then goes back to the radiator where
it cools.
This system directs some coolant through the hoses to the
heater core. This provides for heating and defrosting. The
surge tank is connected to the radiator to recover the cool-
ant displaced by expansion from the high temperatures.
The surge tank maintains the correct coolant level.
The cooling system for this vehicle has no radiator cap or
filler neck. The coolant is added to the cooling system
through the surge tank.
RADIATOR
This vehicle has a lightweight tube–and–fin aluminum ra-
diator. Plastic tanks are mounted on the right and the left
sides of the radiator core.
On vehicles equipped with automatic transaxles, the
transaxle fluid cooler lines run through the left radiator
tank. A radiator drain cock is on this radiator.
To drain the cooling system, open the drain cock.
SURGE TANK
The surge tank is a transparent plastic reservoir, similar to
the windshield washer reservoir.
The surge tank is connected to the radiator by a hose and
to the engine cooling system by another hose. As the ve-
hicle is driven, the engine coolant heats and expands. The
portion of the engine coolant displaced by this expansion
flows from the radiator and the engine into the surge tank.
The air trapped in the radiator and the engine is degassed
into the surge tank.When the engine stops, the engine coolant cools and con-
tracts. The displaced engine coolant is then drawn back
into the radiator and the engine. This keeps the radiator
filled with the coolant to the desired level at all times and
increases the cooling efficiency.
Maintain the coolant level between the MIN and the MAX
marks on the surge tank when the system is cold.
WATER PUMP
The belt–driven centrifugal water pump consists of an im-
peller, a drive shaft, and a belt pulley. The water pump is
mounted on the front of the transverse–mounted engine,
and is driven by the timing belt.
The impeller is supported by a completely sealed bearing.
The water pump is serviced as an assembly and, there-
fore, cannot be disassembled.
THERMOSTAT
A wax pellet–type thermostat controls the flow of the en-
gine coolant through the engine cooling system. The ther-
mostat is mounted in the thermostat housing to the front
of the cylinder head.
The thermostat stops the flow of the engine coolant from
the engine to the radiator in order to provide faster warm–
up, and to regulate the coolant temperature. The thermo-
stat remains closed while the engine coolant is cold, pre-
venting circulation of the engine coolant through the
radiator. At this point, the engine coolant is allowed to cir-
culate only throughout the heater core to warm it quickly
and evenly.
As the engine warms, the thermostat opens. This allows
the engine coolant to flow through the radiator, where the
heat is dissipated through the radiator. This opening and
closing of the thermostat permits enough engine coolant
to enter the radiator to keep the engine within proper en-
gine temperature operating limits.
The wax pellet in the thermostat is hermetically sealed in
a metal case. The wax element of the thermostat expands
when it is heated and contracts when it is cooled.
As the vehicle is driven and the engine warms, the engine
coolant temperature increases. When the engine coolant
reaches a specified temperature, the wax pellet element
in the thermostat expands and exerts pressure against the
metal case, forcing the valve open. This allows the engine
coolant to flow through the engine cooling system and cool
the engine.
As the wax pellet cools, the contraction allows a spring to
close the valve.
The thermostat begins to open at 87°C (189°F) and is fully
open at 102°C (216°F). The thermostat closes at 86°C
(187°F).
Page 286 of 2643
1F – 40IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
ENGINE CRANKS BUT WILL NOT RUN (1.4L/1.6L DOHC)
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic
table.
1. The On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System Check
prompts the technician to complete some basic
checks and store the freeze frame and failure re-
cords data on the scan tool if applicable. This
creates an electronic copy of the data taken when
the occurred. The information is then stored on the
scan tool for later reference.
2. By performing a compression test, it can be deter-
mined if the engine has the mechanical ability to
run.
3. It is important to check for the presence of sparkfrom all of the ignition wires. If spark is present from
one to three of the ignition coil terminals, the Crank-
shaft Position (CKP) sensor is OK.
19. In checking the engine control module (ECM) out-
puts for the electronic spark timing signal, it recom-
mended to use an oscilloscope to view the varying
voltage signals. In measuring these outputs with a
voltmeter, intermittent errors may occur that cannot
be seen by a voltmeter.
35. This step checks for proper operation of the ECM’s
control of the fuel pump circuit.
59. This step checks for a ground signal being supplied
by the ECM to operate the fuel injectors. If there is
no ground present during the cranking of the en-
gine, and the fuel injector wiring is OK, the ECM is
at fault.
Engine Cranks But Will Not Run (1.4L/1.6L DOHC)
CAUTION : Use only electrically insulated pliers when
handling ignition wires with the engine running to
prevent an electrical shock.
CAUTION : Do not pinch or restrict nylon fuel lines.Damage to the lines could cause a fuel leak, resulting
in possible fire or personal injury.
Step
ActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an Euro On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD)
System Check.
Is the check complete.–Go to Step 2Go to
”Euro On–
Board Diagnos-
tic System
Check”
2Crank the engine.
Does the engine start and continue to run?–System OKGo to Step 3
3Perform a cylinder compression test.
Is the cylinder compression for all of the cylinders at
or above the value specified?689 kPa
(100 psi)Go to Step 7Go to Step 4
4Inspect the timing belt alignment.
Is the timing belt in alignment?–Go to Step 6Go to Step 5
5Align or replace the timing belt as needed.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 2–
6Repair internal engine damage as needed.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 2–
7Inspect the fuel pump fuse.
Is the problem found?–Go to Step 8Go to Step 9
8Replace the fuse.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 2–
9Check for the presence of spark from all of the igni-
tion wires while cranking the engine.
Is spark present from all of the ignition wires?–Go to Step 23Go to Step 10
101. Measure the resistance of the ignition wires.
2. Replace any of the ignition wire(s) with a resist-
ance above the value specified.
3. Check for the presence of spark from all of the
ignition wire.
Is spark present from all of the ignition wires?30000 WGo to Step 2Go to Step 11