Grounding DAEWOO LACETTI 2004 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DAEWOO, Model Year: 2004, Model line: LACETTI, Model: DAEWOO LACETTI 2004Pages: 2643, PDF Size: 80.54 MB
Page 339 of 2643
ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 93
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
ENGINE COOLING FAN CIRCUIT CHECK – DUAL FAN
(1.4L/1.6L DOHC)
Circuit Description
The engine cooling fan circuit operates the main cooling
fan and the auxiliary cooling fan. The cooling fans are con-
trolled by the engine control module (ECM) based on in-
puts from the Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor
and the Air Conditioning Pressure (ACP) sensor. The
ECM controls the low speed cooling fan operation by inter-
nally grounding the ECM connector terminal 10. This ener-
gizes the low speed cooling fan relay and operates the
main cooling fan and the auxiliary cooling fan at low speed
as the cooling fans are connected in a series circuit. The
ECM controls the high speed cooling fan operation by in-
ternally grounding the ECM connector terminal 10 and the
ECM connector terminal 9 at the same time. This ener-
gizes the low speed cooling fan relay, the high speed cool-
ing fan relay, and the series/parallel cooling fan relay re-
sulting in high speed fan operation as the cooling fans are
now connected in a parallel circuit.
Diagnostic Aids
S If the owner complained of an overheating problem,
it must be determined if the complaint was due to
an actual boil over, or the engine coolant tempera-
ture gauge indicated overheating. If the engine is
overheating and the cooling fans are on, the cooling
system should be checked.
S If the engine fuse block fuses Ef11 become open
(blown) immediately after installation, inspect for a
short to ground in the wiring of the appropriate cir-
cuit. If the fuses become open (blown) when the
cooling fans are to be turned on by the ECM, sus-
pect a faulty cooling fan motor.
S The ECM will turn the cooling fans on at low speed
when the coolant temperature is 97°C (207°F). The
ECM will turn the cooling fans off when the coolant
temperature is 94°C(201°F).
S The ECM will turn the cooling fans on at high speed
when the coolant temperature is 101°C (214°F).
The ECM will change the cooling fans from high
speed to low speed when the coolant temperature
is 98°C (208°F).S The ECM will turn the cooling fans on at low speed
when the A/C system is on. The ECM will change
the cooling fans from low speed to high speed
when the high side A/C pressure is 1882 kPa (273
psi) then return to low speed when the high side
A/C pressure is 1448 kPa (210 psi). When the A/C
system is on, the ECM will change the cooling fans
from low to high speed when the coolant tempera-
ture reaches 117°C (244°F) then return to low
speed when the coolant temperature reaches
11 4°C (237°F).
S The cooling fan circuit can be checked quickly by
disconnecting the ECM connector 2 and grounding
the connector terminal 10. This should create low
speed cooling fan operation with the ignition ON. By
grounding the ECM connector terminals 10 and 9
and turning the ignition ON, high speed cooling fan
operation should be achieved.
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic
table.
4. This step, along with step 5, checks for the ability of
the ECM to operate the cooling fans.
8. This step, along with step 9, checks for the ability of
the ECM to operate the cooling fans in response to
A/C pressure readings.
16. After confirming battery voltage and the ECM sup-
plying a ground to the coil side of the cooling fan
relay A, by jumpering connector terminals 30 and
87 it will be determined if the relay is at fault or a
wiring problem is present.
31. This step checks for the presence of battery volt-
age to the main cooling fan when the A/C is on. If
battery voltage is present and the cooling fans are
not operating, the problem is in the ground side of
the cooling fan circuit.
37. By directly grounding the ECM connector terminals
10 and 9, the main and auxiliary cooling fans
should run at high speed.
Engine Cooling Fan Circuit Check – Dual Fan (1.4L/1.6L DOHC)
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) system
check.
Is the check completed?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
21. Check the engine fuse block fuse Ef11.
2. Replace the fuse as needed.
Is the fuse OK?–Go to Step 3Go to
”Diagnostic
Aids”
Page 346 of 2643
1F – 100IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
ENGINE COOLING FAN CIRCUIT CHECK – DUAL FAN
(1.8L DOHC)
Circuit Description
The engine cooling fan circuit operates the main cooling
fan and the auxiliary cooling fan. The cooling fans are con-
trolled by the engine control module (ECM) based on in-
puts from the Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor
and the Air Conditioning Pressure (ACP) sensor. The
ECM controls the low speed cooling fan operation by inter-
nally grounding the ECM connector terminal K28. This en-
ergizes the low speed cooling fan relay and operates the
main cooling fan and the auxiliary cooling fan at low speed
as the cooling fans are connected in a series circuit. The
ECM controls the high speed cooling fan operation by in-
ternally grounding the ECM connector terminal K28 and
the ECM connector terminal K12 at the same time. This
energizes the low speed cooling fan relay, the high speed
cooling fan relay, and the series/parallel cooling fan relay
resulting in high speed fan operation as the cooling fans
are now connected in a parallel circuit.
Diagnostic Aids
S If the owner complained of an overheating problem,
it must be determined if the complaint was due to
an actual boil over, or the engine coolant tempera-
ture gauge indicated overheating. If the engine is
overheating and the cooling fans are on, the cooling
system should be checked.
S If the engine fuse block fuses Ef21, Ef6, Ef8 be-
come open (blown) immediately after installation,
inspect for a short to ground in the wiring of the ap-
propriate circuit. If the fuses become open (blown)
when the cooling fans are to be turned on by the
ECM, suspect a faulty cooling fan motor.
S The ECM will turn the cooling fans on at low speed
when the coolant temperature is 97°C (207°F). The
ECM will turn the cooling fans off when the coolant
temperature is 94°C(201°F).
S The ECM will turn the cooling fans on at high speed
when the coolant temperature is 101°C (214°F).
The ECM will change the cooling fans from high
speed to low speed when the coolant temperature
is 98°C (208°F).S The ECM will turn the cooling fans on at low speed
when the A/C system is on. The ECM will change
the cooling fans from low speed to high speed
when the high side A/C pressure is 1882 kPa (273
psi) then return to low speed when the high side
A/C pressure is 1448 kPa (210 psi). When the A/C
system is on, the ECM will change the cooling fans
from low to high speed when the coolant tempera-
ture reaches 117°C (244°F) then return to low
speed when the coolant temperature reaches
11 4°C (237°F).
S The cooling fan circuit can be checked quickly by
disconnecting the ECM connector 2 and grounding
the connector terminal K28. This should create low
speed cooling fan operation with the ignition ON. By
grounding the ECM connector terminals K28 and
K12 and turning the ignition ON, high speed cooling
fan operation should be achieved.
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic
table.
4. This step, along with step 5, checks for the ability of
the ECM to operate the cooling fans.
8. This step, along with step 9, checks for the ability of
the ECM to operate the cooling fans in response to
A/C pressure readings.
16. After confirming battery voltage and the ECM sup-
plying a ground to the coil side of the cooling fan
relay A, by jumpering connector terminals 30 and
87 it will be determined if the relay is at fault or a
wiring problem is present.
31. This step checks for the presence of battery volt-
age to the main cooling fan when the A/C is on. If
battery voltage is present and the cooling fans are
not operating, the problem is in the ground side of
the cooling fan circuit.
37. By directly grounding the ECM connector terminals
K28 and K12, the main and auxiliary cooling fans
should run at high speed.
Engine Cooling Fan Circuit Check – Dual Fan (1.8L DOHC)
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) system
check.
Is the check completed?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
21. Check the I/P fuse block fuse F2.
2. Replace the fuse as needed.
Is the fuse OK?–Go to Step 3Go to
”Diagnostic
Aids”
Page 491 of 2643
ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 245
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0480
LOW SPEED COOLING FAN RELAY CIRCUIT FAULT
(1.4L DOHC)
Circuit Description
Ignition voltage is supplied directly to the cooling fan relay
coil. The engine control module(ECM) controls the relay
by grounding the control circuit via an internal switch called
a driver. The primary function of the driver is supply the
ground for the component being controlled. Each driver
has a fault line which is monitored by the ECM. When the
ECM is commanding a component ON, the voltage of the
control circuit should be low (near 0volts). When the ECM
is commanding the control circuit to a component OFF, the
voltage potential of the circuit should be high(near battery
voltage). If the fault detection circuit senses a voltage oth-
er than what is expected, the fault line status will change
causing the DTC to set.
The relay is used to control the high current flow to the
cooling fan motors. This allows the ECM driver to only
have to handle the relatively low current used by the relay.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S The low speed cooling fan control circuit is an open
or a short to battery to ground condition exist.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will not illumi-
nate after three consecutive trip with a fail.S The ECM will record operating conditions ant the
time the diagnostic fail. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for 10 sec-
onds.
Diagnostic Aids
Using Freeze Frame and/or failure records data may aid
in locating an intermittent condition. If the DTC cannot be
duplicated, the information included in the Freeze Frame
and/or failure records data can be useful in determining
how many miles since the DTC set. The fail counter and
Pass Counter can also be used to determine how many
ignition cycles the diagnostics reported a Freeze Frame
conditions (rpm, load, vehicle speed, temperature, etc.)
that .are noted. This will isolate when the DTC failed.
DTC P0480 – Low Speed Cooling Fan Relay Circuit Fault
(1.4L DOHC)
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an Euro On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD)
System Check.
Is the system check complete?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
21. Turn the ignition switch to ON with the engine
OFF.
2. Install a scan tool.
3. Command the relay ON and OFF.
Does the relay turn ON and OFF when command-
ed?–Go to Step 3Go to Step 5
31. Turn the ignition switch to LOCK.
2. Disconnect the engine control module (ECM)
connector.
3. Turn the ignition switch to ON.
4. Using a digital voltmeter(DVM), measure the
current in low speed relay control circuit, at ter-
minal 10 to ground for 2 minutes.
Does the amperage measure less than the specified
value?0.75 ampsGo to
”Diagnostic
Aids”Go to Step 6
Page 494 of 2643
1F – 248IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0480
LOW SPEED COOLING FAN RELAY CIRCUIT FAULT
(1.6L DOHC)
Circuit Description
Ignition voltage is supplied directly to the cooling fan relay
coil. The engine control module(ECM) controls the relay
by grounding the control circuit via an internal switch called
a driver. The primary function of the driver is supply the
ground for the component being controlled. Each driver
has a fault line which is monitored by the ECM. When the
ECM is commanding a component ON, the voltage of the
control circuit should be low (near 0volts). When the ECM
is commanding the control circuit to a component OFF, the
voltage potential of the circuit should be high(near battery
voltage). If the fault detection circuit senses a voltage oth-
er than what is expected, the fault line status will change
causing the DTC to set.
The relay is used to control the high current flow to the
cooling fan motors. This allows the ECM driver to only
have to handle the relatively low current used by the relay.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S The low speed cooling fan control circuit is an open
or a short to battery or a short to ground condition
exist.
Action Taken When the DTC SetsS The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will not illumi-
nate.
S The ECM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Failure Records data
only.
S This information will not be stored in the Freeze
Frame data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
Using Freeze Frame and/or failure records data may aid
in locating an intermittent condition. If the DTC cannot be
duplicated, the information included in the Freeze Frame
and/or failure records data can be useful in determining
how many miles since the DTC set. The fail counter and
Pass Counter can also be used to determine how many
ignition cycles the diagnostics reported a Freeze Frame
conditions (rpm, load, vehicle speed, temperature, etc.)
that .are noted. This will isolate when the DTC failed.
DTC P0480 – Low Speed Cooling Fan Relay Circuit Fault
(1.6L DOHC)
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an Euro On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD)
System Check.
Is the system check complete?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
21. Turn the ignition switch to ON with the engine
OFF.
2. Install a scan tool.
3. Command the relay ON and OFF.
Does the relay turn ON and OFF when command-
ed?–Go to Step 3Go to Step 5
31. Turn the ignition switch to LOCK.
2. Disconnect the engine control module (ECM)
connector.
3. Turn the ignition switch to ON.
4. Using a digital voltmeter(DVM), measure the
current in low speed relay control circuit, at ter-
minal 10 to ground for 2 minutes.
Does the amperage measure less than the specified
value?0.75 ampsGo to
”Diagnostic
Aids”Go to Step 6
Page 497 of 2643
ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 251
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0481
HIGH SPEED COOLING FAN RELAY CIRCUIT FAULT
(1.4L DOHC)
Circuit Description
Ignition voltage is supplied directly to the cooling fan relay
coil. The engine control module(ECM) controls the relay
by grounding the control circuit via an internal switch called
a driver. The primary function of the driver is supply the
ground for the component being controlled. Each driver
has a fault line which is monitored by the ECM. When the
ECM is commanding a component ON, the voltage of the
control circuit should be low (near 0volts). When the ECM
is commanding the control circuit to a component OFF, the
voltage potential of the circuit should be high(near battery
voltage). If the fault detection circuit senses a voltage oth-
er than what is expected, the fault line status will change
causing the DTC to set.
The relay is used to control the high current flow to the
cooling fan motors. This allows the ECM driver to only
have to handle the relatively low current used by the relay.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S The high speed cooling fan control circuit is an
open or a short to battery or a short to ground con-
dition exist.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will not illumi-
nate after three consecutive trip with a fail.S The ECM will record operating conditions ant the
time the diagnostic fail. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for 10 sec-
onds.
Diagnostic Aids
Using Freeze Frame and/or failure records data may aid
in locating an intermittent condition. If the DTC cannot be
duplicated, the information included in the Freeze Frame
and/or failure records data can be useful in determining
how many miles since the DTC set. The fail counter and
Pass Counter can also be used to determine how many
ignition cycles the diagnostics reported a Freeze Frame
conditions (rpm, load, vehicle speed, temperature, etc.)
that .are noted. This will isolate when the DTC failed.
DTC P0481 – High Speed Cooling Fan Relay Circuit Fault
(1.4L DOHC)
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an Euro On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD)
System Check.
Is the system check complete?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
21. Turn the ignition switch to ON with the engine
OFF.
2. Install a scan tool.
3. Command the relay ON and OFF.
Does the relay turn ON and OFF when command-
ed?–Go to Step 3Go to Step 5
31. Turn the ignition switch to LOCK.
2. Disconnect the engine control module (ECM)
connector.
3. Turn the ignition switch to ON.
4. Using a digital voltmeter(DVM), measure the
current in high speed relay control circuit, at
terminal 9 to ground for 2 minutes.
Does the amperage measure less than the specified
value?0.75 ampsGo to
”Diagnostic
Aids”Go to Step 6
Page 500 of 2643
1F – 254IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0481
HIGH SPEED COOLING FAN RELAY CIRCUIT FAULT
(1.6L DOHC)
Circuit Description
Ignition voltage is supplied directly to the cooling fan relay
coil. The engine control module(ECM) controls the relay
by grounding the control circuit via an internal switch called
a driver. The primary function of the driver is supply the
ground for the component being controlled. Each driver
has a fault line which is monitored by the ECM. When the
ECM is commanding a component ON, the voltage of the
control circuit should be low (near 0volts). When the ECM
is commanding the control circuit to a component OFF, the
voltage potential of the circuit should be high(near battery
voltage). If the fault detection circuit senses a voltage oth-
er than what is expected, the fault line status will change
causing the DTC to set.
The relay is used to control the high current flow to the
cooling fan motors. This allows the ECM driver to only
have to handle the relatively low current used by the relay.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S The high speed cooling fan control circuit is an
open or a short to battery or a short to ground con-
dition exist.
Action Taken When the DTC SetsS The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will not illumi-
nate.
S The ECM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Failure Records data
only.
S This information will not be stored in the Freeze
Frame data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
Using Freeze Frame and/or failure records data may aid
in locating an intermittent condition. If the DTC cannot be
duplicated, the information included in the Freeze Frame
and/or failure records data can be useful in determining
how many miles since the DTC set. The fail counter and
Pass Counter can also be used to determine how many
ignition cycles the diagnostics reported a Freeze Frame
conditions (rpm, load, vehicle speed, temperature, etc.)
that .are noted. This will isolate when the DTC failed.
DTC P0481 – High Speed Cooling Fan Relay Circuit Fault
(1.6L DOHC)
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an Euro On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD)
System Check.
Is the system check complete?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
21. Turn the ignition switch to ON with the engine
OFF.
2. Install a scan tool.
3. Command the relay ON and OFF.
Does the relay turn ON and OFF when command-
ed?–Go to Step 3Go to Step 5
31. Turn the ignition switch to LOCK.
2. Disconnect the engine control module (ECM)
connector.
3. Turn the ignition switch to ON.
4. Using a digital voltmeter(DVM), measure the
current in high speed relay control circuit, at
terminal 9 to ground for 2 minutes.
Does the amperage measure less than the specified
value?0.75 ampsGo to
”Diagnostic
Aids”Go to Step 6
Page 1093 of 2643
4F – 12IANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
J3B14F04
60A Ef230A Ef5
2
42
C107 C105
2
C110
G106
A19
A13 A1 A14
C110 C202
C202WHT LT GRN
DK
GRN LT GRN/
BLK
BLK
DK BLUDK BLU
PPL/WHT
PPL/WHT ABS
TCS Parking
Brake
Hot at all times
RED REDRED/WHT
Ignition
Switch
RED
RED
I/P Cluster
EBCM8
20
22 2216 41
1211
18 1621
1
C107
10A F410AF11
32 31
43
6 62 C201
C201 C201C201
C110 C202
Hot in Run and Start
30
4
1711
C202
15
B15
DLC
(Data Link
Connector)12
G106
BLK/WHTOil Feeding
Connector
”2” Ter.
BRNBRN BRN
BRN PNK PNK PNK
19J1
59B1
ONStart Lock
Acc
IG1
19
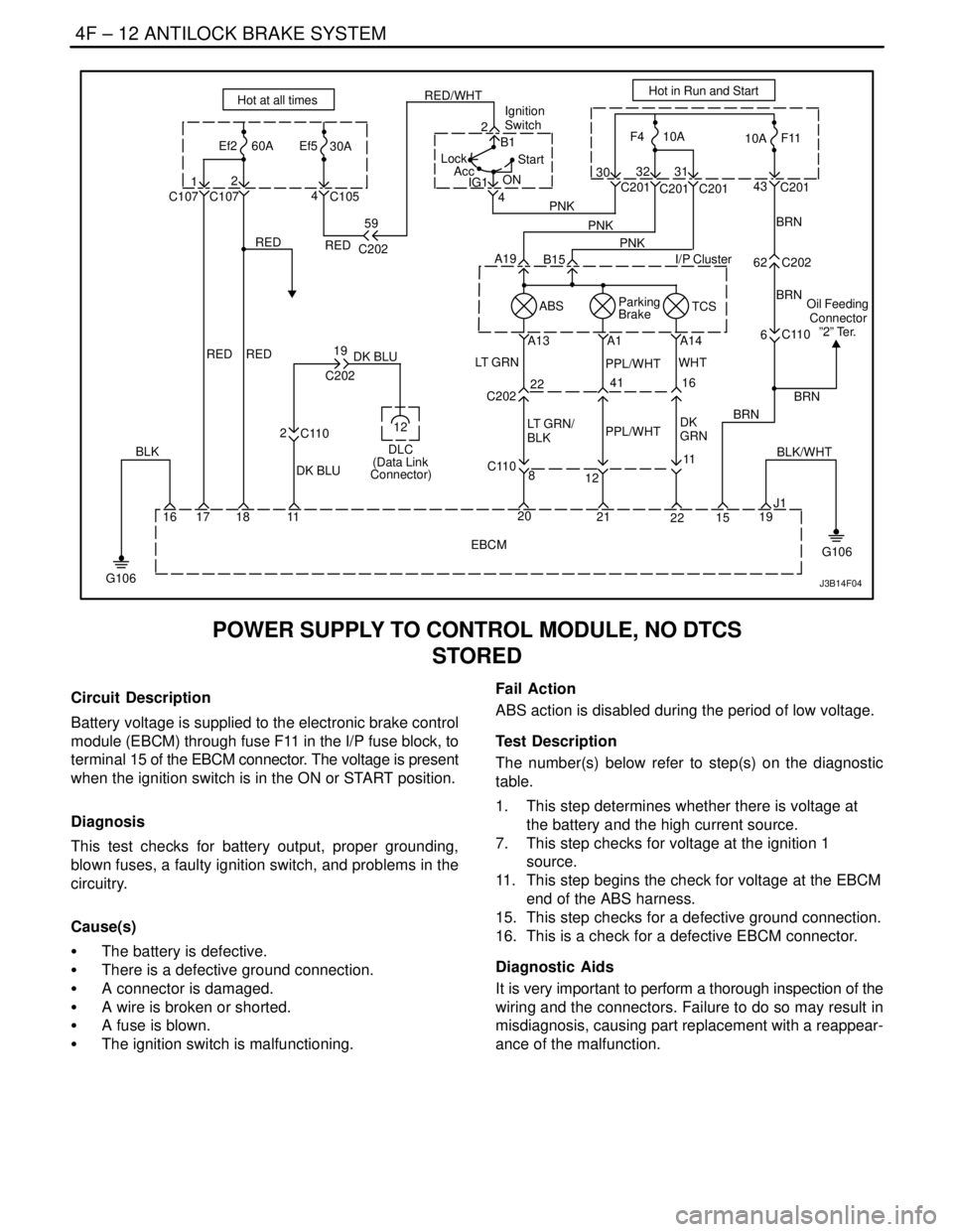
POWER SUPPLY TO CONTROL MODULE, NO DTCS
STORED
Circuit Description
Battery voltage is supplied to the electronic brake control
module (EBCM) through fuse F11 in the I/P fuse block, to
terminal 15 of the EBCM connector. The voltage is present
when the ignition switch is in the ON or START position.
Diagnosis
This test checks for battery output, proper grounding,
blown fuses, a faulty ignition switch, and problems in the
circuitry.
Cause(s)
S The battery is defective.
S There is a defective ground connection.
S A connector is damaged.
S A wire is broken or shorted.
S A fuse is blown.
S The ignition switch is malfunctioning.Fail Action
ABS action is disabled during the period of low voltage.
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic
table.
1. This step determines whether there is voltage at
the battery and the high current source.
7. This step checks for voltage at the ignition 1
source.
11. This step begins the check for voltage at the EBCM
end of the ABS harness.
15. This step checks for a defective ground connection.
16. This is a check for a defective EBCM connector.
Diagnostic Aids
It is very important to perform a thorough inspection of the
wiring and the connectors. Failure to do so may result in
misdiagnosis, causing part replacement with a reappear-
ance of the malfunction.
Page 1100 of 2643
ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM 4F – 19
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
EBD System Indicator Lamp Inoperative
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Install the scan tool and check for any DTCs.
Is any DTC set?–Go to the chart
for the DTCGo to Step 2
21. Turn the ignition switch to LOCK.
2. Disconnect the scan tool.
3. Release the parking brake fully.
4. Push the brake pedal.
5. Turn the ignition switch to ON.
6. Observe the EBD indicator lamp.
Does the lamp illuminate for about 4 seconds, then
turn off?–Go to ”Intermit-
tents and Poor
Connections”Go to Step 3
3With the ignition still ON, observe the oil pressure
lamp.
Is the oil pressure lamp illuminated?–Go to Step 4Go to Step 19
41. Turn the ignition switch to LOCK.
2. Disconnect connector from the EBCM.
3. Connect a jumper from terminal 21 to the
grounding bar in the connector.
4. Turn the ignition switch to ON.
Does the EBD indicator illuminate?–Go to Step 5Go to Step 8
5S Turn the ignition switch to LOCK.
S Examine terminals 19 and 21 at the EBCM
connector on both the ABS wiring harness and
on the EBCM.
Is there a poor connection at any of these terminals?–Go to Step 6Go to Step 7
6Repair the faulty terminals or replace the ABS unit
as required.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
7Replace the ABS unit.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
8S Turn the ignition switch to LOCK.
S Disconnect the wire from the negative battery
terminal.
S Measure the resistance between the negative
battery wire, which is attached to ground, and
the shorting bar in the EBCM connector.
Does the resistance match the specified value?0 WGo to Step 10Go to Step 9
9Repair the open or high resistance in the circuit from
EBCM connector, terminal 19 to ground G106.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
101. Remove the I/P cluster.
2. Remove and check the EBD indicator bulb.
Is the bulb burned out?–Go to Step 11Go to Step 12
111. Replace the EBD indicator bulb.
2. Install the I/P cluster.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
12Check the continuity at the I/P cluster connector ter-
minal A1.
Does the ohmmeter show the specified value?0 WGo to Step 14Go to Step 13
Page 1137 of 2643
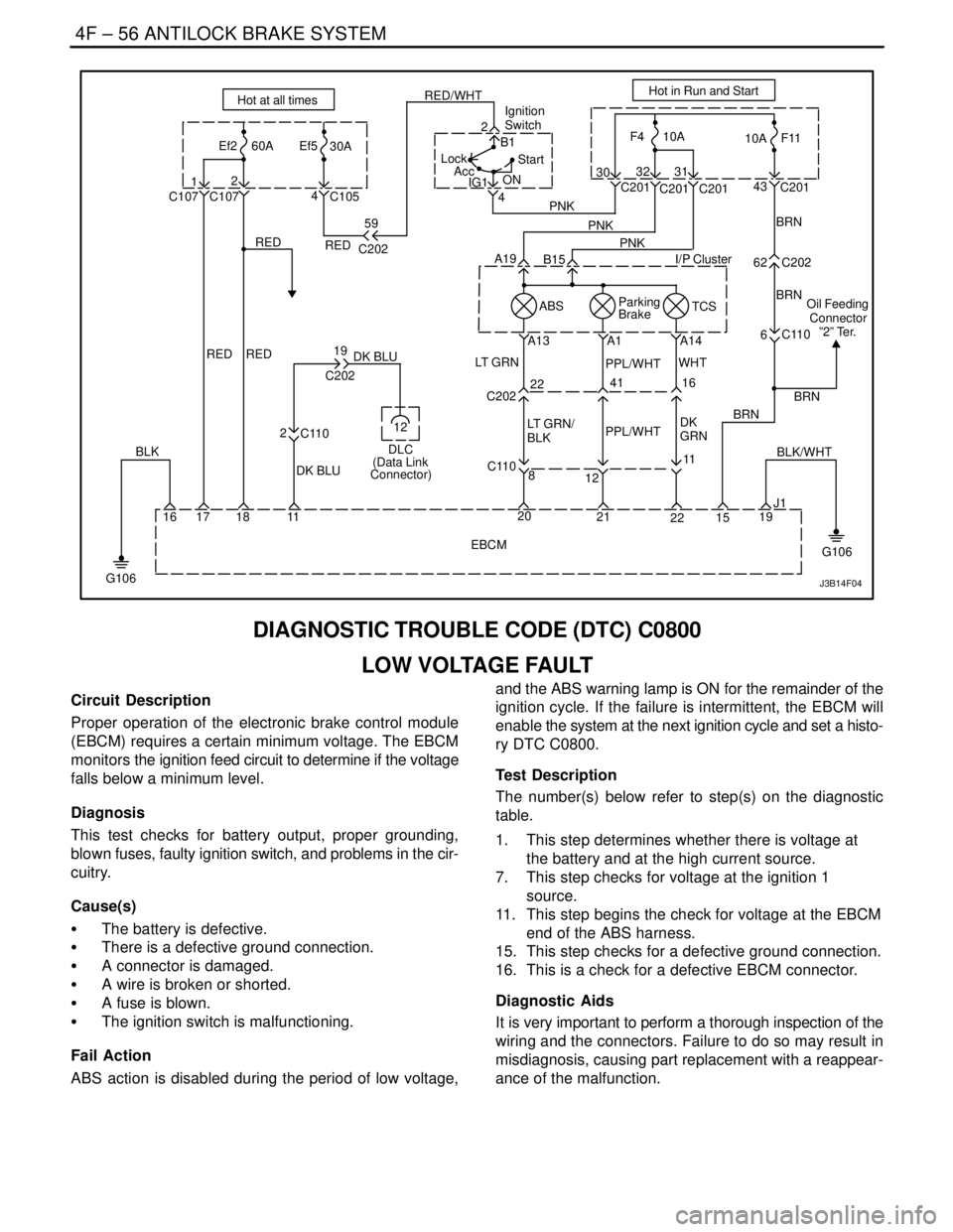
4F – 56IANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
J3B14F04
60A Ef230A Ef5
2
42
C107 C105
2
C110
G106
A19
A13 A1 A14
C110 C202
C202WHT LT GRN
DK
GRN LT GRN/
BLK
BLK
DK BLUDK BLU
PPL/WHT
PPL/WHT ABS
TCS Parking
Brake
Hot at all times
RED REDRED/WHT
Ignition
Switch
RED
RED
I/P Cluster
EBCM8
20
22 2216 41
1211
18 1621
1
C107
10A F410AF11
32 31
43
6 62 C201
C201 C201C201
C110 C202
Hot in Run and Start
30
4
1711
C202
15
B15
DLC
(Data Link
Connector)12
G106
BLK/WHTOil Feeding
Connector
”2” Ter.
BRNBRN BRN
BRN PNK PNK PNK
19J1
59B1
ONStart Lock
Acc
IG1
19
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) C0800
LOW VOLTAGE FAULT
Circuit Description
Proper operation of the electronic brake control module
(EBCM) requires a certain minimum voltage. The EBCM
monitors the ignition feed circuit to determine if the voltage
falls below a minimum level.
Diagnosis
This test checks for battery output, proper grounding,
blown fuses, faulty ignition switch, and problems in the cir-
cuitry.
Cause(s)
S The battery is defective.
S There is a defective ground connection.
S A connector is damaged.
S A wire is broken or shorted.
S A fuse is blown.
S The ignition switch is malfunctioning.
Fail Action
ABS action is disabled during the period of low voltage,and the ABS warning lamp is ON for the remainder of the
ignition cycle. If the failure is intermittent, the EBCM will
enable the system at the next ignition cycle and set a histo-
ry DTC C0800.
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic
table.
1. This step determines whether there is voltage at
the battery and at the high current source.
7. This step checks for voltage at the ignition 1
source.
11. This step begins the check for voltage at the EBCM
end of the ABS harness.
15. This step checks for a defective ground connection.
16. This is a check for a defective EBCM connector.
Diagnostic Aids
It is very important to perform a thorough inspection of the
wiring and the connectors. Failure to do so may result in
misdiagnosis, causing part replacement with a reappear-
ance of the malfunction.
Page 2205 of 2643
SUPPLEMENTAL INFLATABLE RESTRAINTS (SIR) 8B – 101
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
FRONT SEAT BELT
PRETENSIONERS
CAUTION : Tempering with seat belt pretensioner
creates the risk of an injury from unexpected deploy-
ment. Therefore, the driver airbag module should
never be disassembled.
The seat belt pretensioners(with load limiter for some ve-
hicles) are assembled with each front seat belt retractors
to retract the seat belt webbing when accounted frontal
collision. The seat belt pretensioners are controlled by
sensing and diagnostic module(SDM). The seat belt pre-
tensioner contains an igniter charge and a gas generator
to pull the seat belt webbing. The seat belt pretensioner
must be replaced after an accident that causes its activa-
tion.
The seat belt pretensioner also contains a shorting bar to
prevent current from travelling through the seat belt pre-
tensioner during servicing. The shorting bar is disengaged
when the connector is connected.
SENSING AND DIAGNOSTIC
MODULE (SDM)
CAUTION : During the service procedures, be careful
when handling the SDM. Never shake or jar the SDM.
Never apply power to SIR when the SDM is not rigidly
attached to the vehicle. All SDM mounting bolts and
grounding nuts must be fully tightened. Failure to fol-
low these precautions could cause deployment and
result in personal injury.
The SDM is located on the floor beneath the floor console
assembly. The SDM performs the following functions :
S Monitors the supplemental inflatable restraints(SIR)
electrical components and sets a diagnostic trouble
code(DTC) when malfunction is detected.
S Records any faults that are discovered.
S Displays SIR diagnostic trouble codes and system
status information when connected to a scan tool.
S Illuminates the airbag indicator to alert the driver to
any fault.S Provides a reserve power source to deploy the air-
bags and pretensioners if an accident has disabled
the normal power source.
S Monitors vehicle velocity changes to detect frontal
impacts, which are severe enough to warrant de-
ployment.
S Causes current to flow through the airbag modules
and pretensioner to cause deployment if a frontal
impact of sufficient force is detected.
The SDM contains no user–serviceable parts.
AIRBAG WARNING LAMP
The instrument cluster contains an airbag warning indica-
tor and sensing and diagnostic module(SDM). The SDM
performs a turn–on test when the ignition is turned ON.
The SDM flashes the airbag indicator seven times by sup-
plying an intermittent ground to the indicator lamp circuit.
After flashing seven times, the airbag indicator will turn off
if no more malfunctions have been detected.
If the SDM has detected malfunctions in the internal and
external circuits, which could potentially affect the opera-
tion of the supplemental inflatable restraints(SIR), the air-
bag indicator stays on. Some malfunctions could result in
non–deployment when necessary or deployment under
conditions which would not normally result in deployment.
When the SDM is not properly attached to its connector,
the airbag circuit is shorted to ground because there is a
shorting bar in the SDM electrical connector. The shorting
bar is disengaged when proper connection is made, but if
a poor connection exists the SDM connector supplied a
ground to the airbag indicator independently of the SDM,
and the airbag indicator turns on.
CLOCK SPRING
CAUTION : Disassembling the clock spring can cause
injury or cause the clock spring to malfunction.
CAUTION : Over–rotating the clock spring (over 3 and
one quarter turns to one direction) without the steer-
ing wheel in position could damage the clock spring
and result in an inoperative driver airbag.
There is a coil assembly in the steering which is referred
to as a clock spring because of its internal resemblance to
the type of spring used in a mechanical clock. The coil