ABS DAEWOO NUBIRA 2004 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DAEWOO, Model Year: 2004, Model line: NUBIRA, Model: DAEWOO NUBIRA 2004Pages: 2643, PDF Size: 80.54 MB
Page 1134 of 2643
ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM 4F – 53
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
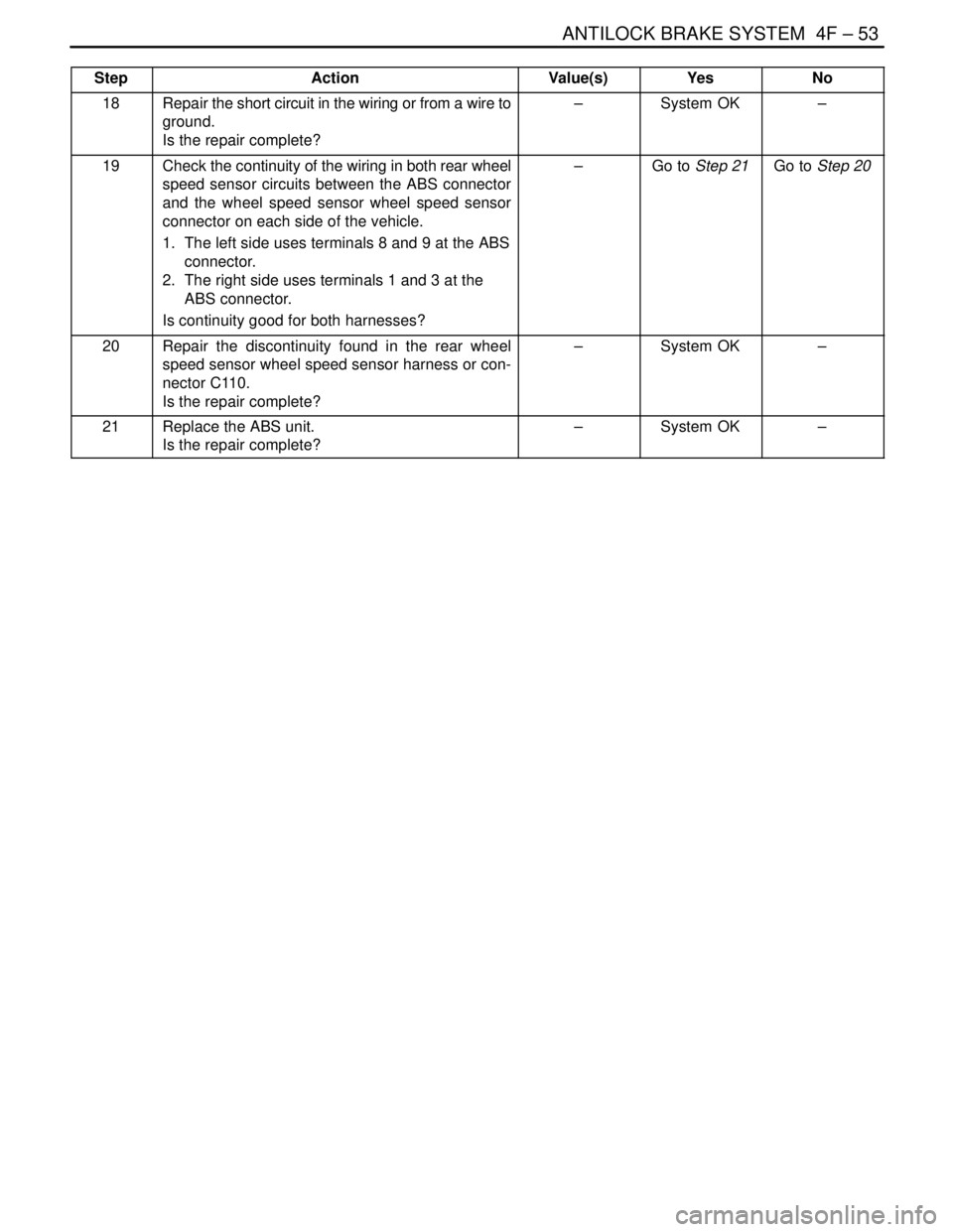
StepNo Yes Value(s) Action
18Repair the short circuit in the wiring or from a wire to
ground.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
19Check the continuity of the wiring in both rear wheel
speed sensor circuits between the ABS connector
and the wheel speed sensor wheel speed sensor
connector on each side of the vehicle.
1. The left side uses terminals 8 and 9 at the ABS
connector.
2. The right side uses terminals 1 and 3 at the
ABS connector.
Is continuity good for both harnesses?–Go to Step 21Go to Step 20
20Repair the discontinuity found in the rear wheel
speed sensor wheel speed sensor harness or con-
nector C110.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
21Replace the ABS unit.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
Page 1135 of 2643
4F – 54IANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
J3B14F04
60A Ef230A Ef5
2
42
C107 C105
2
C110
G106
A19
A13 A1 A14
C110 C202
C202WHT LT GRN
DK
GRN LT GRN/
BLK
BLK
DK BLUDK BLU
PPL/WHT
PPL/WHT ABS
TCS Parking
Brake
Hot at all times
RED REDRED/WHT
Ignition
Switch
RED
RED
I/P Cluster
EBCM8
20
22 2216 41
1211
18 1621
1
C107
10A F410AF11
32 31
43
6 62 C201
C201 C201C201
C110 C202
Hot in Run and Start
30
4
1711
C202
15
B15
DLC
(Data Link
Connector)12
G106
BLK/WHTOil Feeding
Connector
”2” Ter.
BRNBRN BRN
BRN PNK PNK PNK
19J1
59B1
ONStart Lock
Acc
IG1
19
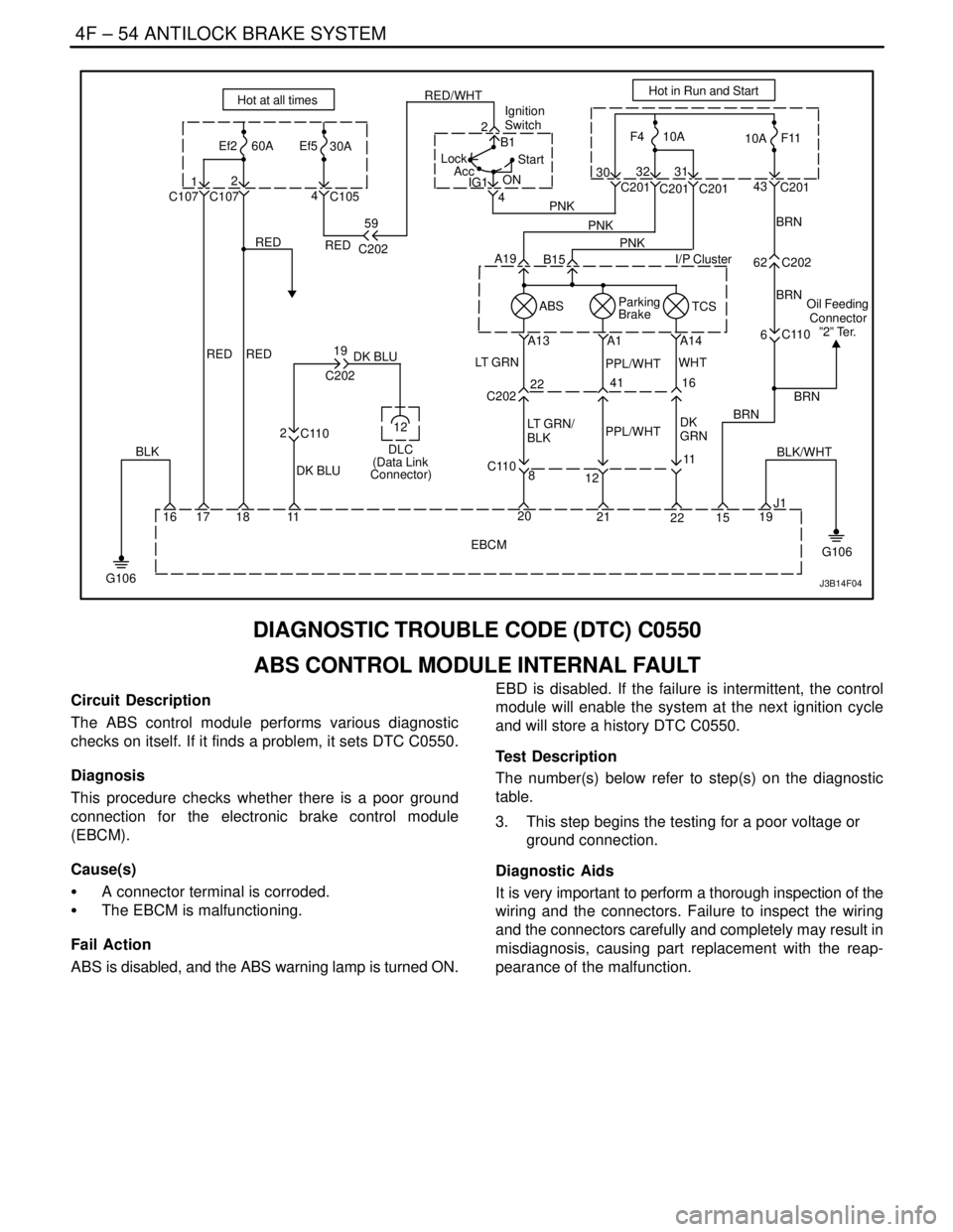
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) C0550
ABS CONTROL MODULE INTERNAL FAULT
Circuit Description
The ABS control module performs various diagnostic
checks on itself. If it finds a problem, it sets DTC C0550.
Diagnosis
This procedure checks whether there is a poor ground
connection for the electronic brake control module
(EBCM).
Cause(s)
S A connector terminal is corroded.
S The EBCM is malfunctioning.
Fail Action
ABS is disabled, and the ABS warning lamp is turned ON.EBD is disabled. If the failure is intermittent, the control
module will enable the system at the next ignition cycle
and will store a history DTC C0550.
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic
table.
3. This step begins the testing for a poor voltage or
ground connection.
Diagnostic Aids
It is very important to perform a thorough inspection of the
wiring and the connectors. Failure to inspect the wiring
and the connectors carefully and completely may result in
misdiagnosis, causing part replacement with the reap-
pearance of the malfunction.
Page 1136 of 2643
ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM 4F – 55
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
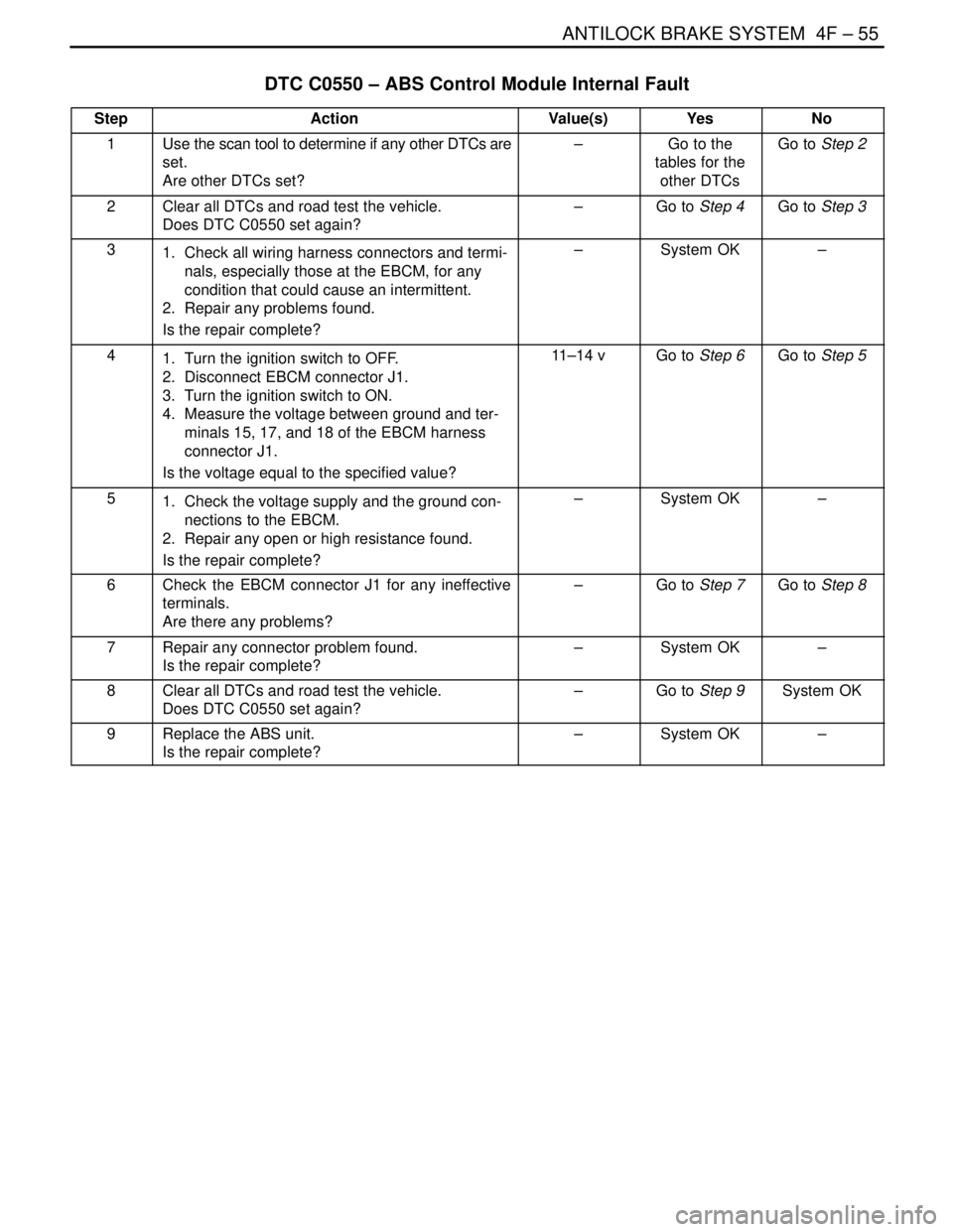
DTC C0550 – ABS Control Module Internal Fault
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Use the scan tool to determine if any other DTCs are
set.
Are other DTCs set?–Go to the
tables for the
other DTCsGo to Step 2
2Clear all DTCs and road test the vehicle.
Does DTC C0550 set again?–Go to Step 4Go to Step 3
31. Check all wiring harness connectors and termi-
nals, especially those at the EBCM, for any
condition that could cause an intermittent.
2. Repair any problems found.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
41. Turn the ignition switch to OFF.
2. Disconnect EBCM connector J1.
3. Turn the ignition switch to ON.
4. Measure the voltage between ground and ter-
minals 15, 17, and 18 of the EBCM harness
connector J1.
Is the voltage equal to the specified value?11–14 vGo to Step 6Go to Step 5
51. Check the voltage supply and the ground con-
nections to the EBCM.
2. Repair any open or high resistance found.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
6Check the EBCM connector J1 for any ineffective
terminals.
Are there any problems?–Go to Step 7Go to Step 8
7Repair any connector problem found.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
8Clear all DTCs and road test the vehicle.
Does DTC C0550 set again?–Go to Step 9System OK
9Replace the ABS unit.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
Page 1137 of 2643
4F – 56IANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
J3B14F04
60A Ef230A Ef5
2
42
C107 C105
2
C110
G106
A19
A13 A1 A14
C110 C202
C202WHT LT GRN
DK
GRN LT GRN/
BLK
BLK
DK BLUDK BLU
PPL/WHT
PPL/WHT ABS
TCS Parking
Brake
Hot at all times
RED REDRED/WHT
Ignition
Switch
RED
RED
I/P Cluster
EBCM8
20
22 2216 41
1211
18 1621
1
C107
10A F410AF11
32 31
43
6 62 C201
C201 C201C201
C110 C202
Hot in Run and Start
30
4
1711
C202
15
B15
DLC
(Data Link
Connector)12
G106
BLK/WHTOil Feeding
Connector
”2” Ter.
BRNBRN BRN
BRN PNK PNK PNK
19J1
59B1
ONStart Lock
Acc
IG1
19
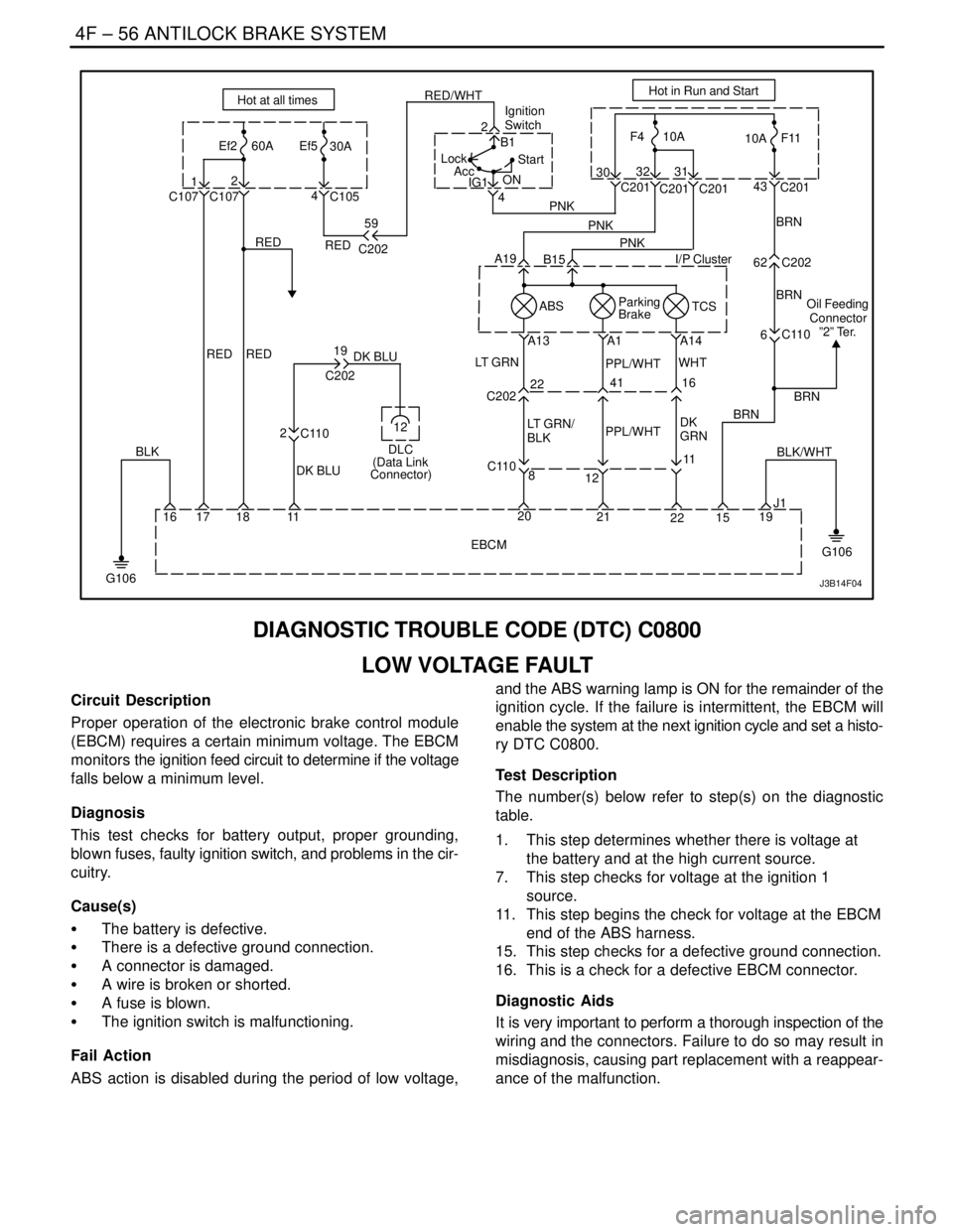
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) C0800
LOW VOLTAGE FAULT
Circuit Description
Proper operation of the electronic brake control module
(EBCM) requires a certain minimum voltage. The EBCM
monitors the ignition feed circuit to determine if the voltage
falls below a minimum level.
Diagnosis
This test checks for battery output, proper grounding,
blown fuses, faulty ignition switch, and problems in the cir-
cuitry.
Cause(s)
S The battery is defective.
S There is a defective ground connection.
S A connector is damaged.
S A wire is broken or shorted.
S A fuse is blown.
S The ignition switch is malfunctioning.
Fail Action
ABS action is disabled during the period of low voltage,and the ABS warning lamp is ON for the remainder of the
ignition cycle. If the failure is intermittent, the EBCM will
enable the system at the next ignition cycle and set a histo-
ry DTC C0800.
Test Description
The number(s) below refer to step(s) on the diagnostic
table.
1. This step determines whether there is voltage at
the battery and at the high current source.
7. This step checks for voltage at the ignition 1
source.
11. This step begins the check for voltage at the EBCM
end of the ABS harness.
15. This step checks for a defective ground connection.
16. This is a check for a defective EBCM connector.
Diagnostic Aids
It is very important to perform a thorough inspection of the
wiring and the connectors. Failure to do so may result in
misdiagnosis, causing part replacement with a reappear-
ance of the malfunction.
Page 1138 of 2643
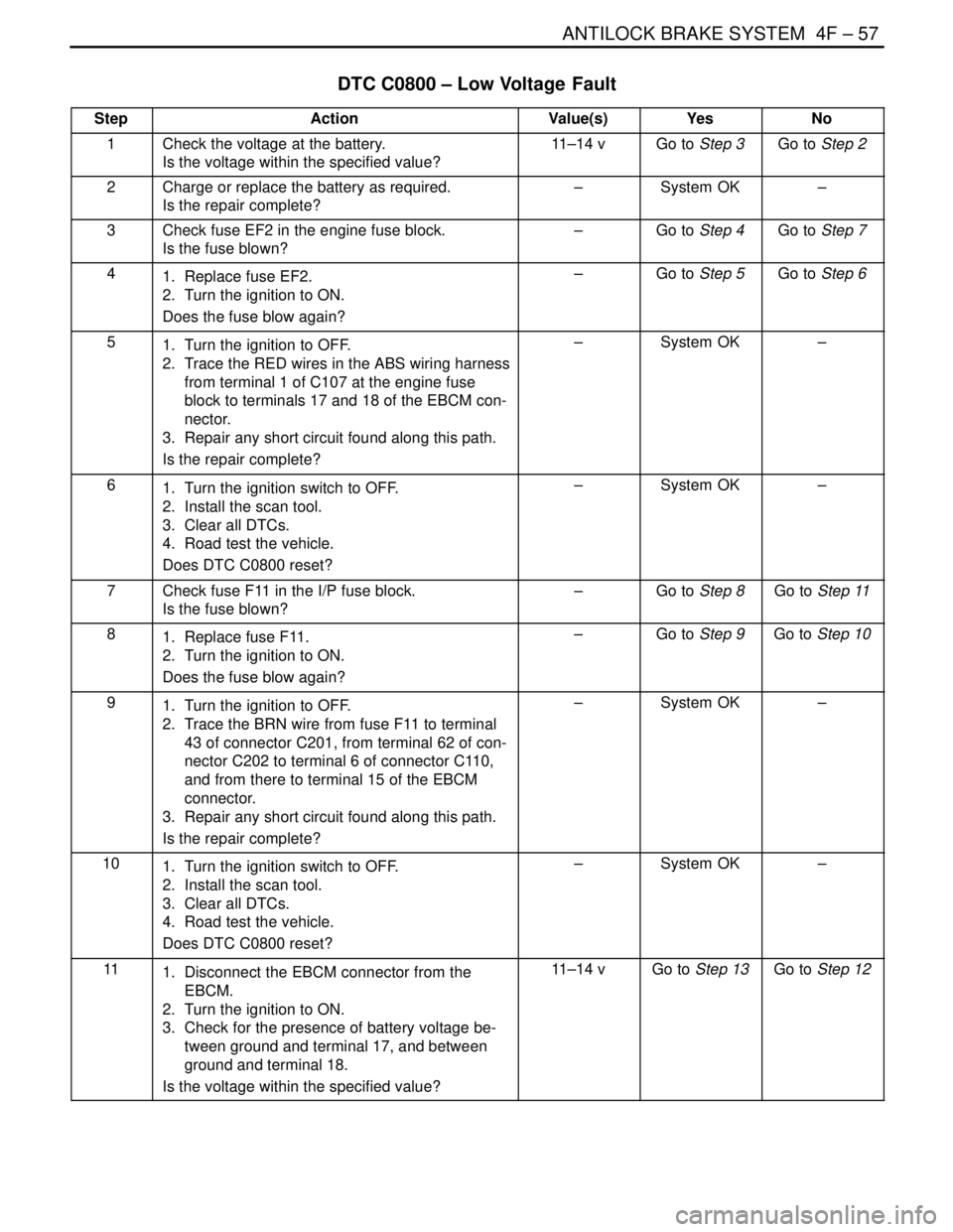
ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM 4F – 57
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DTC C0800 – Low Voltage Fault
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Check the voltage at the battery.
Is the voltage within the specified value?11–14 vGo to Step 3Go to Step 2
2Charge or replace the battery as required.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
3Check fuse EF2 in the engine fuse block.
Is the fuse blown?–Go to Step 4Go to Step 7
41. Replace fuse EF2.
2. Turn the ignition to ON.
Does the fuse blow again?–Go to Step 5Go to Step 6
51. Turn the ignition to OFF.
2. Trace the RED wires in the ABS wiring harness
from terminal 1 of C107 at the engine fuse
block to terminals 17 and 18 of the EBCM con-
nector.
3. Repair any short circuit found along this path.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
61. Turn the ignition switch to OFF.
2. Install the scan tool.
3. Clear all DTCs.
4. Road test the vehicle.
Does DTC C0800 reset?–System OK–
7Check fuse F11 in the I/P fuse block.
Is the fuse blown?–Go to Step 8Go to Step 11
81. Replace fuse F11.
2. Turn the ignition to ON.
Does the fuse blow again?–Go to Step 9Go to Step 10
91. Turn the ignition to OFF.
2. Trace the BRN wire from fuse F11 to terminal
43 of connector C201, from terminal 62 of con-
nector C202 to terminal 6 of connector C110,
and from there to terminal 15 of the EBCM
connector.
3. Repair any short circuit found along this path.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
101. Turn the ignition switch to OFF.
2. Install the scan tool.
3. Clear all DTCs.
4. Road test the vehicle.
Does DTC C0800 reset?–System OK–
111. Disconnect the EBCM connector from the
EBCM.
2. Turn the ignition to ON.
3. Check for the presence of battery voltage be-
tween ground and terminal 17, and between
ground and terminal 18.
Is the voltage within the specified value?11–14 vGo to Step 13Go to Step 12
Page 1139 of 2643
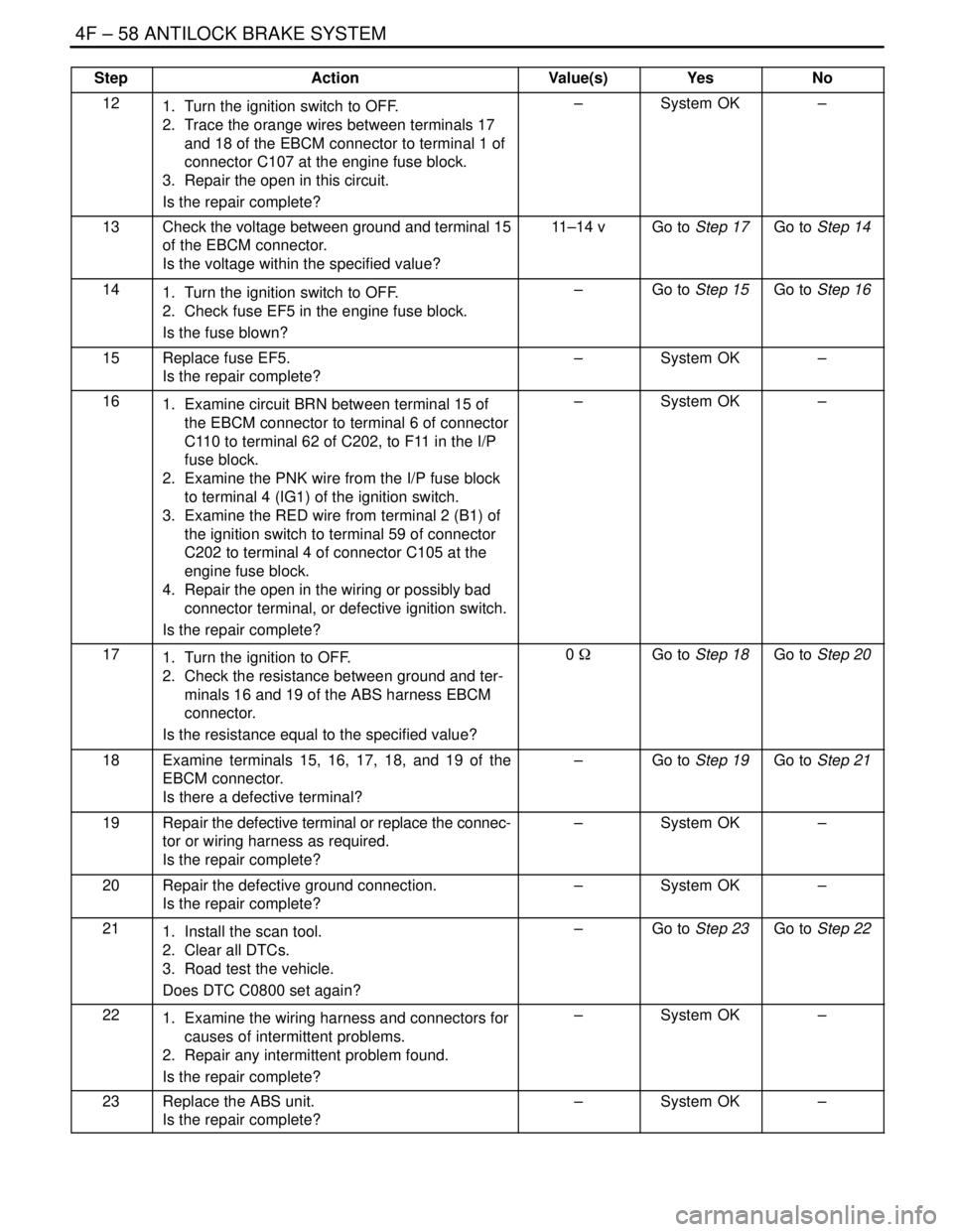
4F – 58IANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
StepNo Yes Value(s) Action
121. Turn the ignition switch to OFF.
2. Trace the orange wires between terminals 17
and 18 of the EBCM connector to terminal 1 of
connector C107 at the engine fuse block.
3. Repair the open in this circuit.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
13Check the voltage between ground and terminal 15
of the EBCM connector.
Is the voltage within the specified value?11–14 vGo to Step 17Go to Step 14
141. Turn the ignition switch to OFF.
2. Check fuse EF5 in the engine fuse block.
Is the fuse blown?–Go to Step 15Go to Step 16
15Replace fuse EF5.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
161. Examine circuit BRN between terminal 15 of
the EBCM connector to terminal 6 of connector
C110 to terminal 62 of C202, to F11 in the I/P
fuse block.
2. Examine the PNK wire from the I/P fuse block
to terminal 4 (IG1) of the ignition switch.
3. Examine the RED wire from terminal 2 (B1) of
the ignition switch to terminal 59 of connector
C202 to terminal 4 of connector C105 at the
engine fuse block.
4. Repair the open in the wiring or possibly bad
connector terminal, or defective ignition switch.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
171. Turn the ignition to OFF.
2. Check the resistance between ground and ter-
minals 16 and 19 of the ABS harness EBCM
connector.
Is the resistance equal to the specified value?0 WGo to Step 18Go to Step 20
18Examine terminals 15, 16, 17, 18, and 19 of the
EBCM connector.
Is there a defective terminal?–Go to Step 19Go to Step 21
19Repair the defective terminal or replace the connec-
tor or wiring harness as required.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
20Repair the defective ground connection.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
211. Install the scan tool.
2. Clear all DTCs.
3. Road test the vehicle.
Does DTC C0800 set again?–Go to Step 23Go to Step 22
221. Examine the wiring harness and connectors for
causes of intermittent problems.
2. Repair any intermittent problem found.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
23Replace the ABS unit.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
Page 1142 of 2643

ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM 4F – 61
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
BLEEDING SYSTEM
Replacement modulators are shipped already filled and
bled. In normal procedures requiring removal of the modu-
lator, such as to replace the EBCM, air will not enter the
modulator, and normal bleeding will be all that is needed.
For this procedure, refer to Section 4A, Hydraulic Brakes.
If air enters the hydraulic modulator, or if an unfilled modu-
lator is installed, use the brake bleeding program in the
scan tool to bleed the modulator. Manual bleeding of the
hydraulic modulator is not possible.
ABS 5.3 ASSEMBLY
(Left–Hand Drive Shown, Right–Hand Drive
Similar)
Removal Procedure
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Disconnect the 31–pin ABS wiring harness connec-
tor from its socket on the EBCM.
3. Cover the connector and the socket with shop
cloths to protect them from brake fluid.
Notice : Take care not to allow air into the hydraulic unit
or into the brake pipes from the master cylinder. If air gets
into the hydraulic unit, it will require a bleeding procedure
using a scan tool programmed for the ABS 5.3 system. As
long as no air enters the hydraulic unit, a simple bleeding
procedure is all the system will require.
4. Remove the brake pipes from the hydraulic unit. It
may be necessary to loosen the brake pipe nuts on
the master cylinder to allow for moving those pipes
out of the way.
5. Loosen the mounting nuts on the hydraulic unit.
6. Move the brake pipes aside far enough to allow for
lifting the ABS 5.3 unit out of the mounting bracket.
7. Tighten the brake pipe nuts on the master cylinder
to avoid leaking brake fluid.
8. Cap the brake pipes.
Installation Procedure
1. Insert the ABS 5.3 hydraulic unit into its mounting
bracket and install the nuts.
Tighten
Tighten the ABS 5.3 mounting nuts to 15 NSm (11 lb–
ft).
2. Remove the screw plugs and install all of the hy-
draulic brake pipes.
Tighten
Tighten the brake pipe nuts to 22 NSm (16 lb–ft).
3. Connect the 31–pin wiring harness connector J1.
4. Connect the negative battery cable.
5. Bleed the hydraulic system. Refer to Section 4A,
Hydraulic Brakes.
Page 1144 of 2643

ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM 4F – 63
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
FRONT WHEEL SPEED SENSOR
JUMPER HARNESS
(Left–Hand Drive Shown, Right–Hand Drive
Similar)
Removal Procedure
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Disconnect connector from the EBCM.
3. Remove the appropriate terminals from connector:
S Right–side – terminals 4 (WHT) and 5 (GRY).
S Left–side – terminals 6 (BRN) and 7 (LT BLU).
4. Both speed sensor harnesses break out of the ABS
wiring harness just beyond the ABS connector. The
right–side speed sensor harness crosses the top of
the fire wall to the right–side fender area. The left–
side speed sensor harness goes directly to the left–
side fender area.
5. Free the speed sensor harness from the wiring har-
ness.
6. Remove the front wheel speed sensor electrical
connector from the retaining clamps and disconnect
the harness from the sensor connector.
Installation Procedure
1. Install the front wheel speed sensor jumper har-
ness.
2. Connect the front wheel speed sensor electrical
connector and secure it into the clamps.
3. Replace the jumper harness into the wiring har-
ness.
4. Insert the terminals into connector as they had
been removed:
S Right–side – terminals 4 (WHT) and 5 (GRY).
S Left–side – terminals 6 (BRN) and 7 (LT BLU).
5. Connect EBCM connector.
6. Connect the negative battery cable.
Page 1146 of 2643

ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM 4F – 65
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
GENERAL DESCRIPTION AND SYSTEM
OPERATION
BASIC KNOWLEDGE REQUIRED
Before using this section, it is important that you have a ba-
sic knowledge of the following items. Without this knowl-
edge, it will be difficult to use the diagnostic procedures
contained in this section.
S Basic Electrical Circuits : You should understand
the basic theory of electricity and know the mean-
ing of voltage, current (amps), and resistance
(ohms). You should understand what happens in a
circuit with an open or shorted wire. You should be
able to read and understand a wiring diagram.
S Use of Circuit Testing Tools : You should know how
to use a test light and how to bypass components
to test circuits using fused jumper wires. You should
be familiar with a digital multimeter. You should be
able to measure voltage, resistance, and current,
and be familiar with the controls and how to use
them correctly.
ABS SYSTEM COMPONENTS
The ABS 5.3 Antilock Braking System (ABS) consists of
a conventional hydraulic brake system plus antilock com-
ponents. The conventional brake system includes a vacu-
um booster, master cylinder, front disc brakes, rear lead-
ing/trailing drum brakes, interconnecting hydraulic brake
pipes and hoses, brake fluid level sensor and the BRAKE
indicator.
The ABS components include a hydraulic unit, an elec-
tronic brake control module (EBCM), two system fuses,
four wheel speed sensors (one at each wheel), intercon-
necting wiring, the ABS indicator, the EBD indicator (which
is connected to the parking lamp) and the rear disk brakes.
See “ABS Component Locator” in this section for the gen-
eral layout of this system.
The hydraulic unit with the attached EBCM is located be-
tween the surge tank and the fire wall on the left side of the
vehicle.
The basic hydraulic unit configuration consists of hydraulic
check valves, two solenoid valves for each wheel, a hy-
draulic pump, two accumulators, and two damper. The hy-
draulic unit controls hydraulic pressure to the front calipers
and rear wheel cylinders by modulating hydraulic pressure
to prevent wheel lockup.
Nothing in the hydraulic unit or the EBCM is serviceable.
In the event of any failure, the entire ABS unit with at-
tached EBCM must be replaced. For more information, re-
fer to ”Base Braking Mode” and ”Antilock Braking Mode”
in this section.
BASE BRAKING MODE
The baseline braking mode of the ABS 5.3 system used
in this vehicle is a diagonal split system. In this system,
one master cylinder circuit supplies pressure to the right
front and the left rear brakes; the other circuit supplies
pressure to the left front and the right rear brakes. All
valves in the hydraulic modulator are in their normal, non–
energized positions as shown in the drawings found in
”ABS System Components” in this section.
Page 1150 of 2643

ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM 4F – 69
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
EBD (ELECTRONIC BRAKE FORCE
DISTRIBUTION) SYSTEM
As an add–on logic to the ABS base algorithm, EBD works
in a range in which the intervention thresholds for ABS
control are not reached yet.
EBD ensures that the rear wheels are sensitively moni-
tored for slip with respect to the front axle. If slip is de-
tected, the inlet valves for the rear wheels are switched to
pressure hold to prevent a further increase in pressure at
the rear–wheel breaks, thus electronically reproducing a
pressure–reduction function at the rear–wheel brakes.
THE BENEFITS OF EBD
S Elimination of conventional proportioning valve.
S EBD utilizes the existing rear axle wheel speed
sensor to monitor rear wheel slip.
S Based on many variables in algorithm a pressure
hold, increase and/or decrease pulsetrain may be
triggered at the rear wheels insuring vehicle stabil-
ity.
S Vehicle approaches the ideal brake force distribu-
tion. (front to rear)
S Constant brake force distribution during vehicle life-
time.
S EBD function is monitored via ABS safety logic.
(conventional proportioning valves are not monitor-
able)
S ”Keep alive” function.