Knock sensor DAEWOO NUBIRA 2004 Service User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DAEWOO, Model Year: 2004, Model line: NUBIRA, Model: DAEWOO NUBIRA 2004Pages: 2643, PDF Size: 80.54 MB
Page 253 of 2643
ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 7
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
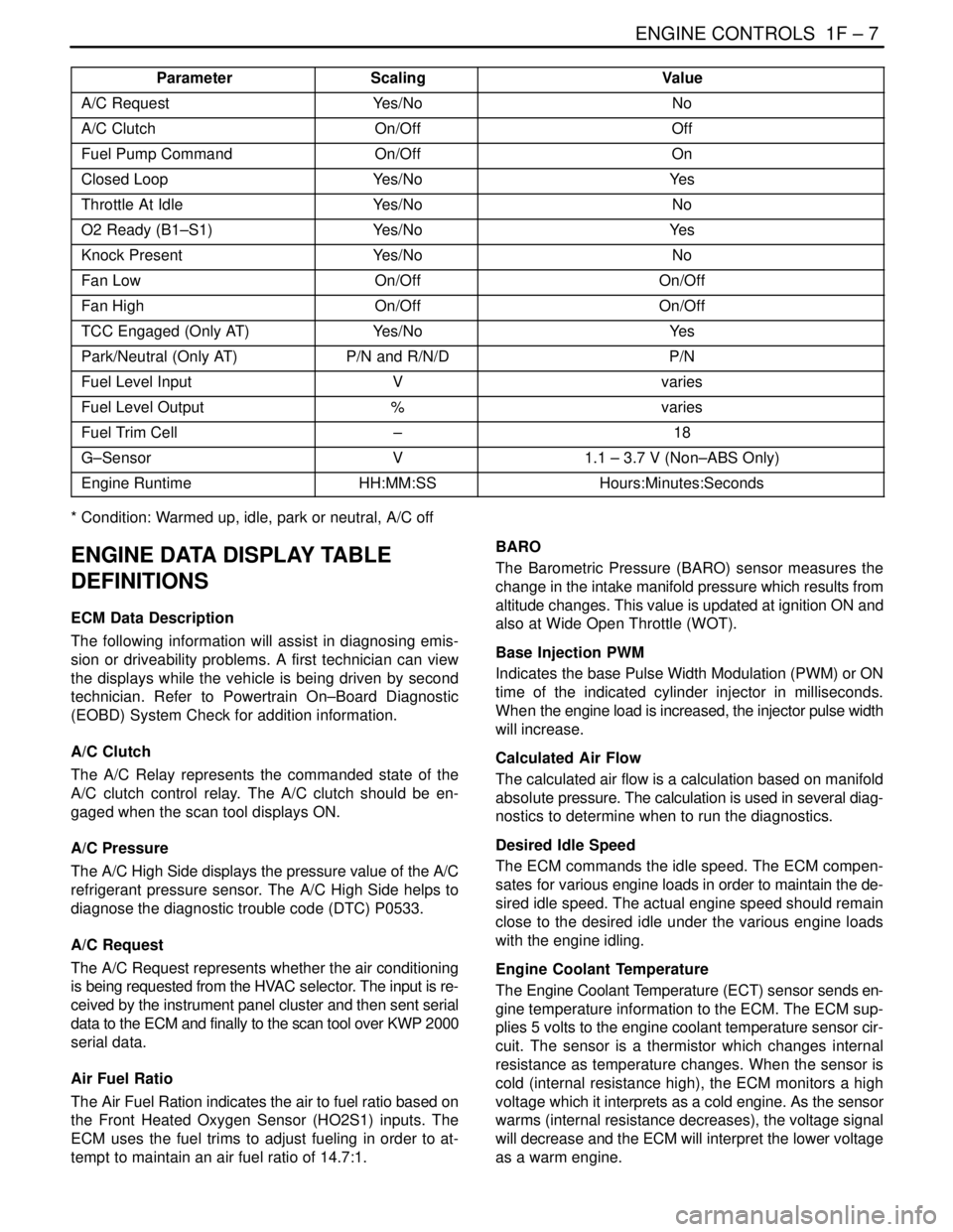
Parameter ValueScaling
A/C RequestYes/NoNo
A/C ClutchOn/OffOff
Fuel Pump CommandOn/OffOn
Closed LoopYes/NoYe s
Throttle At IdleYes/NoNo
O2 Ready (B1–S1)Yes/NoYe s
Knock PresentYes/NoNo
Fan LowOn/OffOn/Off
Fan HighOn/OffOn/Off
TCC Engaged (Only AT)Yes/NoYe s
Park/Neutral (Only AT)P/N and R/N/DP/N
Fuel Level InputVvaries
Fuel Level Output%varies
Fuel Trim Cell–18
G–SensorV1.1 – 3.7 V (Non–ABS Only)
Engine RuntimeHH:MM:SSHours:Minutes:Seconds
* Condition: Warmed up, idle, park or neutral, A/C off
ENGINE DATA DISPLAY TABLE
DEFINITIONS
ECM Data Description
The following information will assist in diagnosing emis-
sion or driveability problems. A first technician can view
the displays while the vehicle is being driven by second
technician. Refer to Powertrain On–Board Diagnostic
(EOBD) System Check for addition information.
A/C Clutch
The A/C Relay represents the commanded state of the
A/C clutch control relay. The A/C clutch should be en-
gaged when the scan tool displays ON.
A/C Pressure
The A/C High Side displays the pressure value of the A/C
refrigerant pressure sensor. The A/C High Side helps to
diagnose the diagnostic trouble code (DTC) P0533.
A/C Request
The A/C Request represents whether the air conditioning
is being requested from the HVAC selector. The input is re-
ceived by the instrument panel cluster and then sent serial
data to the ECM and finally to the scan tool over KWP 2000
serial data.
Air Fuel Ratio
The Air Fuel Ration indicates the air to fuel ratio based on
the Front Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S1) inputs. The
ECM uses the fuel trims to adjust fueling in order to at-
tempt to maintain an air fuel ratio of 14.7:1.BARO
The Barometric Pressure (BARO) sensor measures the
change in the intake manifold pressure which results from
altitude changes. This value is updated at ignition ON and
also at Wide Open Throttle (WOT).
Base Injection PWM
Indicates the base Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) or ON
time of the indicated cylinder injector in milliseconds.
When the engine load is increased, the injector pulse width
will increase.
Calculated Air Flow
The calculated air flow is a calculation based on manifold
absolute pressure. The calculation is used in several diag-
nostics to determine when to run the diagnostics.
Desired Idle Speed
The ECM commands the idle speed. The ECM compen-
sates for various engine loads in order to maintain the de-
sired idle speed. The actual engine speed should remain
close to the desired idle under the various engine loads
with the engine idling.
Engine Coolant Temperature
The Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) sensor sends en-
gine temperature information to the ECM. The ECM sup-
plies 5 volts to the engine coolant temperature sensor cir-
cuit. The sensor is a thermistor which changes internal
resistance as temperature changes. When the sensor is
cold (internal resistance high), the ECM monitors a high
voltage which it interprets as a cold engine. As the sensor
warms (internal resistance decreases), the voltage signal
will decrease and the ECM will interpret the lower voltage
as a warm engine.
Page 254 of 2643

1F – 8IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
EGR Desired Position
The desired exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) position is
the commanded EGR position. The ECM calculates the
desired EGR position. The higher the percentage, the lon-
ger the ECM is commanding the EGR valve ON.
Engine Load
Indicates engine load based on manifold absolute pres-
sure. The higher the percentage, the more load the engine
is under.
Engine Run Time
The engine run time is a measure of how long the engine
has been running. When the engine stops running, the tim-
er resets to zero.
Engine Speed
Engine Speed is computed by the ECM from the fuel con-
trol reference input. It should remain close to desired idle
under the various engine loads with the engine idling.
Fan
The Fan Control (FC) Relay is commanded by the ECM.
The FC Relay displays the command as ON or OFF.
Fuel Level Sensor
The Fuel Level Sensor monitors the fuel level in the tank.
The Fuel Level Sensor monitors the rate of change of the
air pressure in the EVAP system. Several of the Enhanced
EVAP System diagnostics are dependent upon the correct
fuel level.
Fuel System Status
The Closed Loop is displayed indicating that the ECM is
controlling the fuel delivery according to the Front Heated
Oxygen Sensor (HO2S1) voltage as close to an air/fuel ra-
tio of 14.7 to 1 as possible.
IAC Position
The scan tool displays the ECM command for the Idle Air
Control (IAC) pintle position in counts. The higher the
number of counts, the greater the commanded idle speed
reads. The Idle Air Control responds to changes in the en-
gine load in order to maintain the desired idle rpm.
Ignition 1 (Voltage)
The ignition volts represent the system voltage measured
by the ECM at the ignition feed circuit.
Intake Air Temperature
The ECM converts the resistance of the Intake Air Tem-
perature (IAT) sensor to degrees in the same manner as
the engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor. In take air
temperature is used by the ECM to adjust fuel delivery and
spark timing according to incoming air density.Knock Present
The KS Noise Channel indicates when the ECM detects
the KS signal. The ECM should display NO at idle.
Long Term FT
The Long Term Fuel Trim (FT) is derived from the short
term fuel trim value. The Long Term FT is used for the long
term correction of the fuel delivery. A value of 128 counts
(0%) indicates that the fuel delivery requires no com-
pensation in order to maintain a 14.7:1 air to fuel ratio. A
value below 128 counts means that the fuel system is too
rich and the fuel delivery is being reduced. The ECM is de-
creasing the injector pulse width. A value above 128
counts indicates that a lean condition exists for which the
ECM is compensating.
MAP
The Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) sensor measures
the change in the intake manifold pressure which results
from engine load and speed changes. As the intake man-
ifold pressure increases, the air density in the intake also
increases and the additional fuel is required.
Misfire History #1–4
Indicates the number of misfires that have occurred after
195 current misfires have been counted. The current mis-
fire counter will add its misfires to the history misfire count-
er after 195 total misfires have taken place. If 1 cylinder is
misfiring, the misfiring current counter will have 195 mis-
fires counted before adding to its history counter. If 2 cylin-
ders are misfiring, the misfiring current counter will add to
their history counters after 97 misfires. The counter incre-
ments only after a misfire diagnostic trouble code (DTC)
has been set.
Front Heated Oxygen Sensor
The pre–converter Front Heated Oxygen Sensor
(HO2S1) reading represents the exhaust oxygen sensor
output voltage. This voltage will fluctuate constantly be-
tween 100 mv (lean exhaust) and 900 mv (rich exhaust)
when the system is operating in a Closed Loop.
Rear Heated Oxygen Sensor
The post–converter Rear Heated Oxygen Sensor
(HO2S2) represents the exhaust oxygen output voltage
past the catalytic converter. This voltage remains inactive,
or the voltage will appear lazy within a range of 100 mv
(lean exhaust) and 900 mv (rich exhaust) when operating
in a Closed Loop.
Short Term FT
The Short Term FT represents a short term correction to
fuel delivery by the ECM in response to the amount of time
the oxygen sensor voltage spends above or below the 450
mv threshold. If the oxygen sensor has mainly been below
450 mv, indicating a lean air/fuel mixture, short term fuel
trim will increase to tell the ECM to add fuel. If the oxygen
sensor voltage stays mainly above the threshold, the ECM
will reduce fuel delivery to compensate for the indicated
rich condition.
Page 256 of 2643
1F – 10IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
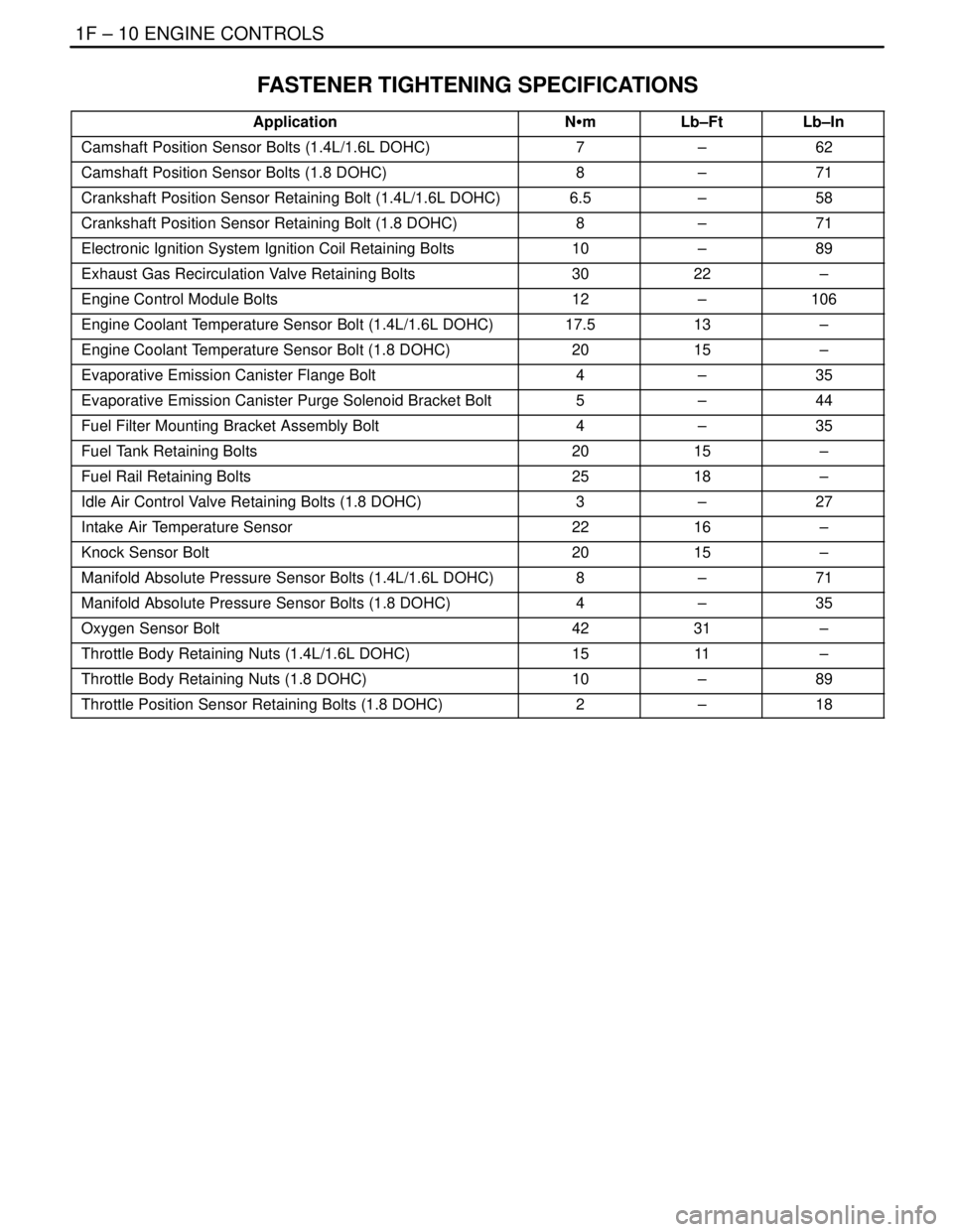
FASTENER TIGHTENING SPECIFICATIONS
ApplicationNSmLb–FtLb–In
Camshaft Position Sensor Bolts (1.4L/1.6L DOHC)7–62
Camshaft Position Sensor Bolts (1.8 DOHC)8–71
Crankshaft Position Sensor Retaining Bolt (1.4L/1.6L DOHC)6.5–58
Crankshaft Position Sensor Retaining Bolt (1.8 DOHC)8–71
Electronic Ignition System Ignition Coil Retaining Bolts10–89
Exhaust Gas Recirculation Valve Retaining Bolts3022–
Engine Control Module Bolts12–106
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor Bolt (1.4L/1.6L DOHC)17.513–
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor Bolt (1.8 DOHC)2015–
Evaporative Emission Canister Flange Bolt4–35
Evaporative Emission Canister Purge Solenoid Bracket Bolt5–44
Fuel Filter Mounting Bracket Assembly Bolt4–35
Fuel Tank Retaining Bolts2015–
Fuel Rail Retaining Bolts2518–
Idle Air Control Valve Retaining Bolts (1.8 DOHC)3–27
Intake Air Temperature Sensor2216–
Knock Sensor Bolt2015–
Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor Bolts (1.4L/1.6L DOHC)8–71
Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor Bolts (1.8 DOHC)4–35
Oxygen Sensor Bolt4231–
Throttle Body Retaining Nuts (1.4L/1.6L DOHC)1511–
Throttle Body Retaining Nuts (1.8 DOHC)10–89
Throttle Position Sensor Retaining Bolts (1.8 DOHC)2–18
Page 274 of 2643

1F – 28IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
COMPONENT LOCATOR
COMPONENT LOCATOR (1.4L/1.6L DOHC)
Components on ECM Harness
11. Engine Control Module (ECM)
12. Data Link Connector (DLC)
13. Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL)
14. ECM/ABS Harness Ground
15. Fuse Panel (2)
ECM Controlled Devices
20. Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Valve
21. Fuel Injector (4)
22. Main Throttle Idle Actuator (MTIA)
23. Fuel Pump Relay
24. Cooling Fan Relays (High)
25. Cooling Fan Control Relay (A/C Only)
26. Electronic Ignition System Ignition Coil
27. Evaporative Emission (EVAP) Control Purge Sole-
noid
28. Main Relay
29. A/C Compressor Relay30. Cooling Fan Relays (Low)
Information Sensors
31. Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
32. Front Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S1)
33. Variable Geometry Induction System (VGIS) Sole-
noid
34. Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
35. Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor
36. Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS)
38. Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor
39. Knock Sensor
40. Rear Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S2)
41. Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor
Not PCM/ECM Connected
42. Evaporative Emission Canister (under vehicle, be-
hind right rear wheel)
43. Engine Oil Pressure Switch
44. Air Cleaner
Page 275 of 2643
ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 29
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
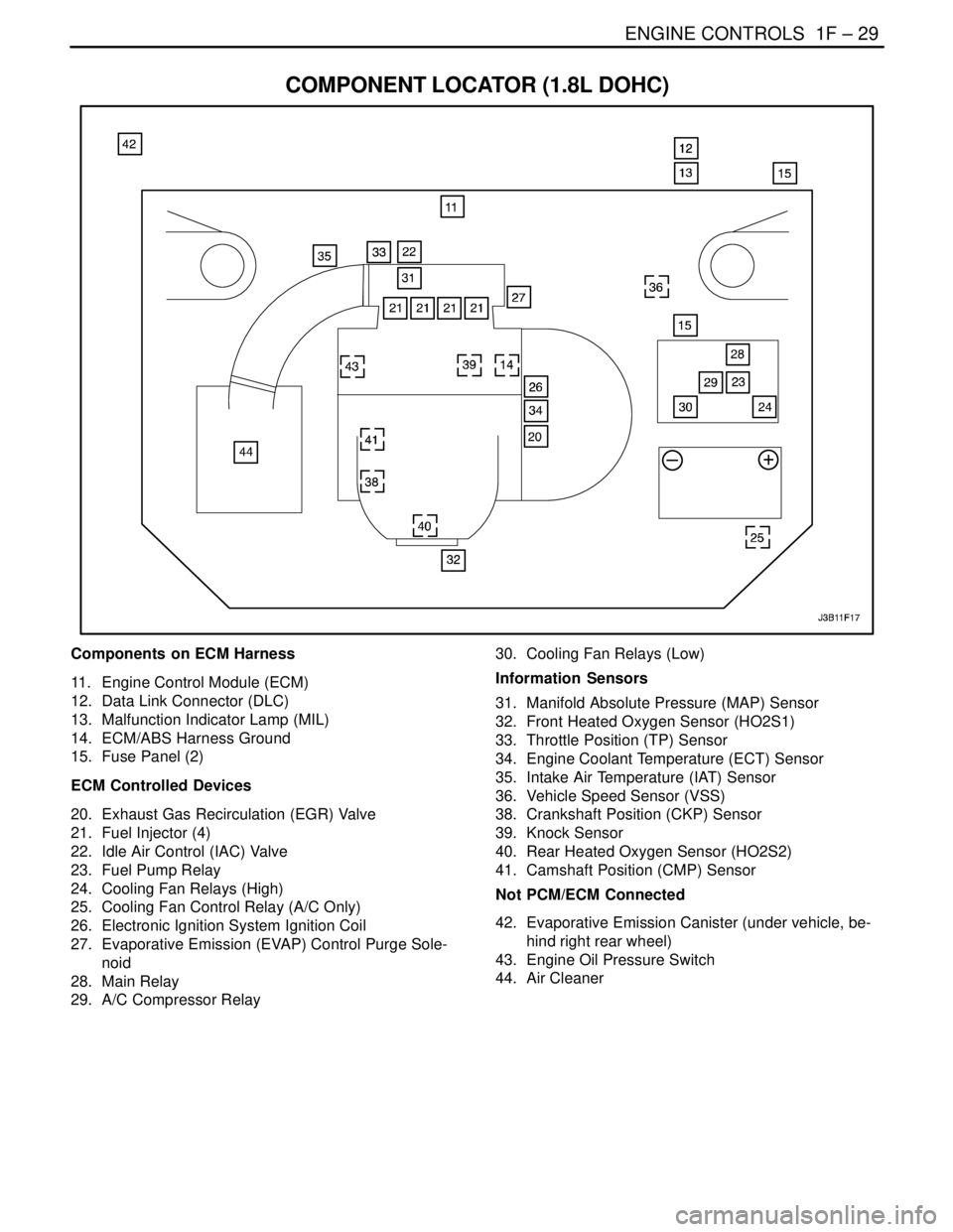
COMPONENT LOCATOR (1.8L DOHC)
Components on ECM Harness
11. Engine Control Module (ECM)
12. Data Link Connector (DLC)
13. Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL)
14. ECM/ABS Harness Ground
15. Fuse Panel (2)
ECM Controlled Devices
20. Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Valve
21. Fuel Injector (4)
22. Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve
23. Fuel Pump Relay
24. Cooling Fan Relays (High)
25. Cooling Fan Control Relay (A/C Only)
26. Electronic Ignition System Ignition Coil
27. Evaporative Emission (EVAP) Control Purge Sole-
noid
28. Main Relay
29. A/C Compressor Relay30. Cooling Fan Relays (Low)
Information Sensors
31. Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
32. Front Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S1)
33. Throttle Position (TP) Sensor
34. Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
35. Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor
36. Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS)
38. Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor
39. Knock Sensor
40. Rear Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S2)
41. Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor
Not PCM/ECM Connected
42. Evaporative Emission Canister (under vehicle, be-
hind right rear wheel)
43. Engine Oil Pressure Switch
44. Air Cleaner
Page 358 of 2643
1F – 112IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
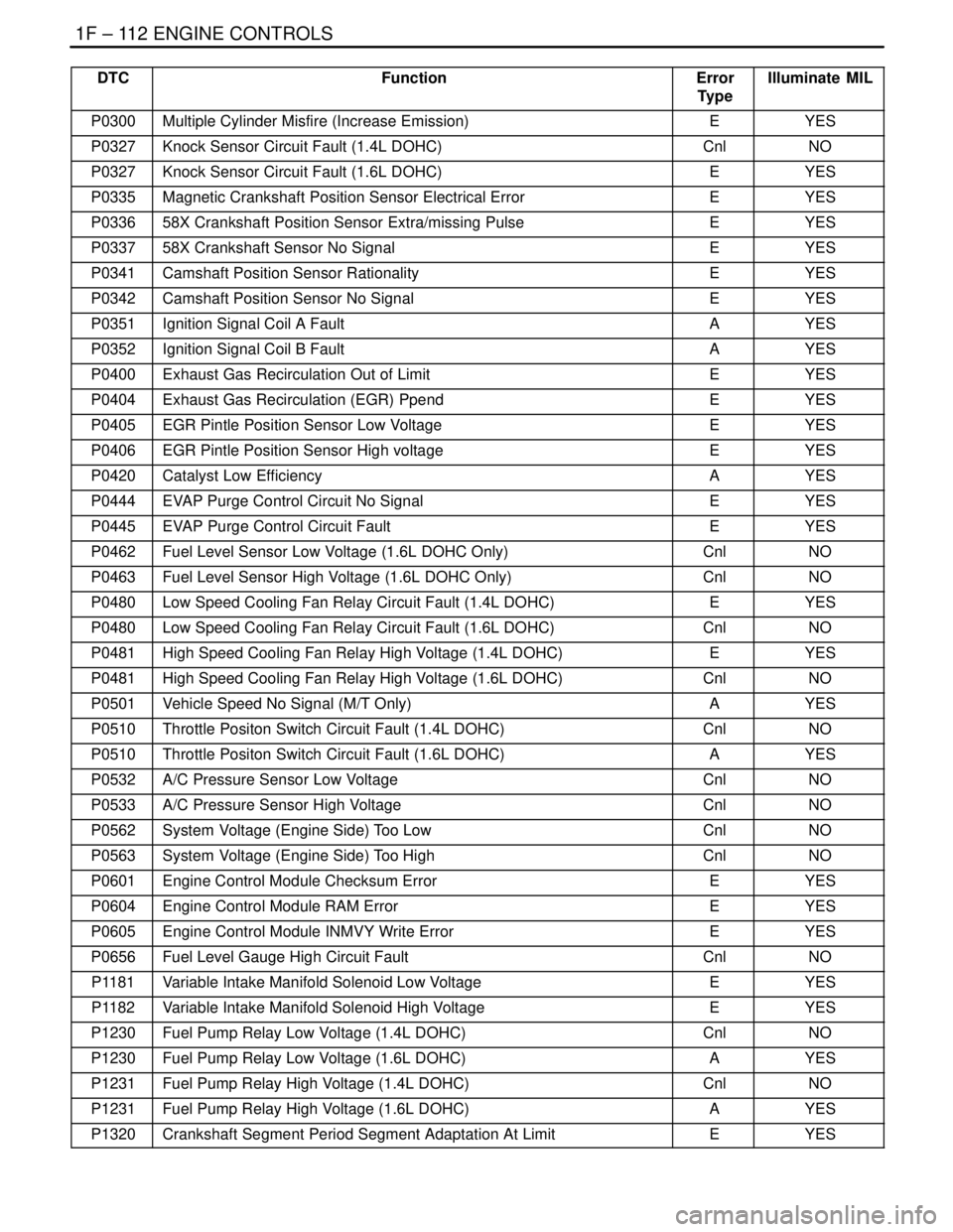
DTCIlluminate MIL Error
Type Function
P0300Multiple Cylinder Misfire (Increase Emission)EYES
P0327Knock Sensor Circuit Fault (1.4L DOHC)CnlNO
P0327Knock Sensor Circuit Fault (1.6L DOHC)EYES
P0335Magnetic Crankshaft Position Sensor Electrical ErrorEYES
P033658X Crankshaft Position Sensor Extra/missing PulseEYES
P033758X Crankshaft Sensor No SignalEYES
P0341Camshaft Position Sensor RationalityEYES
P0342Camshaft Position Sensor No SignalEYES
P0351Ignition Signal Coil A FaultAYES
P0352Ignition Signal Coil B FaultAYES
P0400Exhaust Gas Recirculation Out of LimitEYES
P0404Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) PpendEYES
P0405EGR Pintle Position Sensor Low VoltageEYES
P0406EGR Pintle Position Sensor High voltageEYES
P0420Catalyst Low EfficiencyAYES
P0444EVAP Purge Control Circuit No SignalEYES
P0445EVAP Purge Control Circuit FaultEYES
P0462Fuel Level Sensor Low Voltage (1.6L DOHC Only)CnlNO
P0463Fuel Level Sensor High Voltage (1.6L DOHC Only)CnlNO
P0480Low Speed Cooling Fan Relay Circuit Fault (1.4L DOHC)EYES
P0480Low Speed Cooling Fan Relay Circuit Fault (1.6L DOHC)CnlNO
P0481High Speed Cooling Fan Relay High Voltage (1.4L DOHC)EYES
P0481High Speed Cooling Fan Relay High Voltage (1.6L DOHC)CnlNO
P0501Vehicle Speed No Signal (M/T Only)AYES
P0510Throttle Positon Switch Circuit Fault (1.4L DOHC)CnlNO
P0510Throttle Positon Switch Circuit Fault (1.6L DOHC)AYES
P0532A/C Pressure Sensor Low VoltageCnlNO
P0533A/C Pressure Sensor High VoltageCnlNO
P0562System Voltage (Engine Side) Too LowCnlNO
P0563System Voltage (Engine Side) Too HighCnlNO
P0601Engine Control Module Checksum ErrorEYES
P0604Engine Control Module RAM ErrorEYES
P0605Engine Control Module INMVY Write ErrorEYES
P0656Fuel Level Gauge High Circuit FaultCnlNO
P1181Variable Intake Manifold Solenoid Low VoltageEYES
P1182Variable Intake Manifold Solenoid High VoltageEYES
P1230Fuel Pump Relay Low Voltage (1.4L DOHC)CnlNO
P1230Fuel Pump Relay Low Voltage (1.6L DOHC)AYES
P1231Fuel Pump Relay High Voltage (1.4L DOHC)CnlNO
P1231Fuel Pump Relay High Voltage (1.6L DOHC)AYES
P1320Crankshaft Segment Period Segment Adaptation At LimitEYES
Page 441 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 195
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0327
KNOCK SENSOR CIRCUIT FAULT (1.4L DOHC)
Circuit Description
The knock sensor (KS) system is used to detect engine
detonation, allowing the engine control module (ECM) to
retard ignition control spark timing based on the KS signal
being received. The KS produces an AC signal so that un-
der a no knock condition the signal on the KS circuit mea-
sures about 0.007V AC. The KS signal’s amplitude and
frequency depend upon the amount of knock being experi-
enced. The ECM contains a non–replaceable knock filter
module called a signal–to–noise enhancement filter
(SNEF) module. This filter module in the ECM determines
whether knock is occurring by comparing the signal level
on the KS circuit with the voltage level on the noise chan-
nel. The noise channel allows the ECM to reject any false
knock signal by knowing the amount of normal engine me-
chanical noise present. Normal engine noise varies de-
pending on engine speed and load. When the ECM deter-
mines that an abnormally low noise channel voltage level
is being experienced, a DTC P0327 will set.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S The knock sensor SPI bus in failure during 8 sec-
onds.
Or
S The knock sensor voltage is less than 0.3V.
S The engine coolant temperature is greater than
60°C (145°F).
S The engine speed is greater than 1,500 rpm.
S The mass air flow is higer than 180mg/tdc.
Or
S When difference between a original signal valve
and filtering valve is less than 5%.S The engine coolant temperature is greater than
60°C (145°F).
S The mass air flow is greater than 180mg/tdc.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will not illumi-
nate.
S The ECM will store wnditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Failure Records data
only.
S This information will not be stored in the Freeze
Frame data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
Check and correct any abnormal engine noise before us-
ing the diagnostic table.
Any circuitry that is suspected as causing engine noise
complaint should be thoroughly checked for the following
conditions :
S Backed–out terminals
S Improper mating
S Broken locks
S Improperly formed
S Damaged terminals
S Poor terminal–to–wire connection
S Physical damage to the wiring harness
Page 442 of 2643
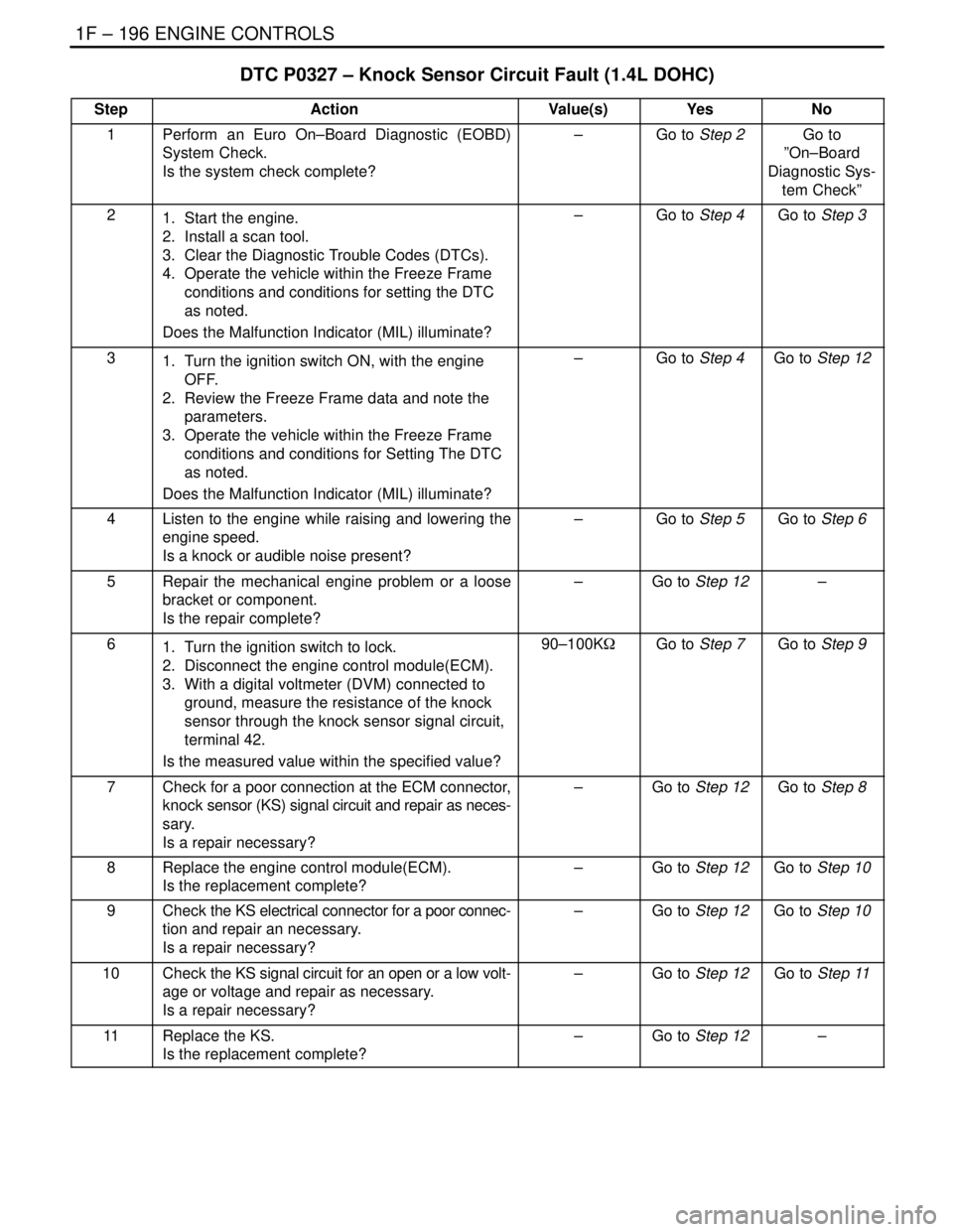
1F – 196IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DTC P0327 – Knock Sensor Circuit Fault (1.4L DOHC)
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an Euro On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD)
System Check.
Is the system check complete?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
21. Start the engine.
2. Install a scan tool.
3. Clear the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs).
4. Operate the vehicle within the Freeze Frame
conditions and conditions for setting the DTC
as noted.
Does the Malfunction Indicator (MIL) illuminate?–Go to Step 4Go to Step 3
31. Turn the ignition switch ON, with the engine
OFF.
2. Review the Freeze Frame data and note the
parameters.
3. Operate the vehicle within the Freeze Frame
conditions and conditions for Setting The DTC
as noted.
Does the Malfunction Indicator (MIL) illuminate?–Go to Step 4Go to Step 12
4Listen to the engine while raising and lowering the
engine speed.
Is a knock or audible noise present?–Go to Step 5Go to Step 6
5Repair the mechanical engine problem or a loose
bracket or component.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 12–
61. Turn the ignition switch to lock.
2. Disconnect the engine control module(ECM).
3. With a digital voltmeter (DVM) connected to
ground, measure the resistance of the knock
sensor through the knock sensor signal circuit,
terminal 42.
Is the measured value within the specified value?90–100KWGo to Step 7Go to Step 9
7Check for a poor connection at the ECM connector,
knock sensor (KS) signal circuit and repair as neces-
sary.
Is a repair necessary?–Go to Step 12Go to Step 8
8Replace the engine control module(ECM).
Is the replacement complete?–Go to Step 12Go to Step 10
9Check the KS electrical connector for a poor connec-
tion and repair an necessary.
Is a repair necessary?–Go to Step 12Go to Step 10
10Check the KS signal circuit for an open or a low volt-
age or voltage and repair as necessary.
Is a repair necessary?–Go to Step 12Go to Step 11
11Replace the KS.
Is the replacement complete?–Go to Step 12–
Page 444 of 2643

1F – 198IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0327
KNOCK SENSOR CIRCUIT FAULT (1.6L DOHC)
Circuit Description
The knock sensor (KS) system is used to detect engine
detonation, allowing the transaxle control module
(TCM)/engine control module (ECM) to retard ignition con-
trol spark timing based on the KS signal being received.
The KS produces an AC signal so that under a no knock
condition the signal on the KS circuit measures about
0.007V AC. The KS signal’s amplitude and frequency de-
pend upon the amount of knock being experienced. The
ECM contains a non–replaceable knock filter module
called a signal–to–noise enhancement filter (SNEF) mod-
ule. This filter module in the ECM determines whether
knock is occurring by comparing the signal level on the KS
circuit with the voltage level on the noise channel. The
noise channel allows the ECM to reject any false knock
signal by knowing the amount of normal engine mechani-
cal noise present. Normal engine noise varies depending
on engine speed and load. When the ECM determines that
an abnormally low noise channel voltage level is being ex-
perienced, a DTC P0327 will set.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S The knock sensor SPI bus in failure during 10 sec-
onds.
Or
S The knock sensor voltage is less than 0.3V.
S The engine coolant temperature is greater than
60°C(145°F).
S The engine speed is greater than 1,500rpm.
S The mass air flow is higer than 180mg/tdc.
Or
S When difference between a original signal valve
and filtering valve is less than 5%.S The engine coolant temperature is greater than
60°C(145°F).
S The mass air flow is greater than 170mg/tdc.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illuminate
after three consecutive trip with a fail.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fail. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
Check and correct any abnormal engine noise before us-
ing the diagnostic table.
Any circuitry that is suspected as causing engine noise
complaint should be thoroughly checked for the following
conditions :
S Backed–out terminals
S Improper mating
S Broken locks
S Improperly formed
S Damaged terminals
S Poor terminal–to–wire connection
S Physical damage to the wiring harness
Page 445 of 2643
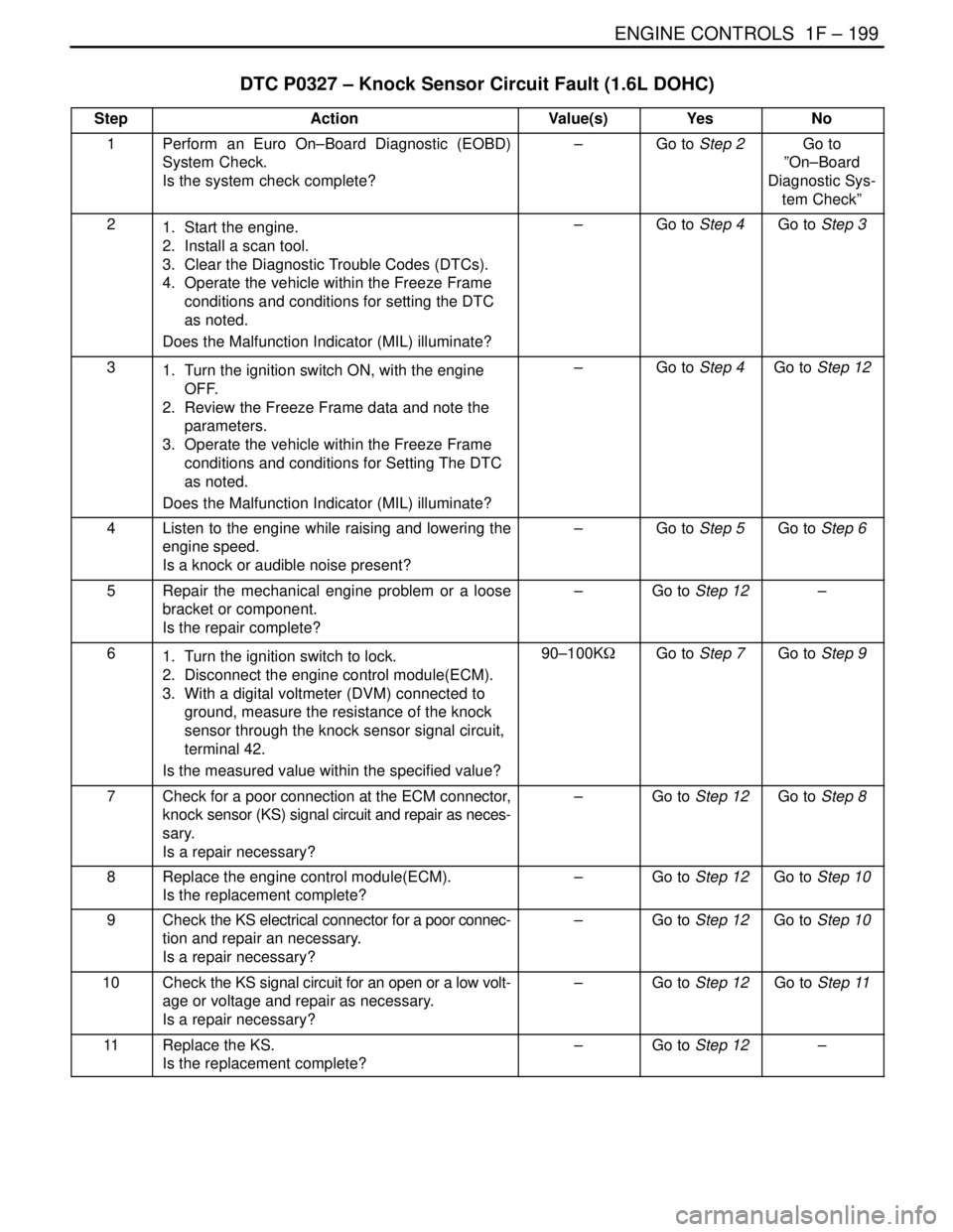
ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 199
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DTC P0327 – Knock Sensor Circuit Fault (1.6L DOHC)
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an Euro On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD)
System Check.
Is the system check complete?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
21. Start the engine.
2. Install a scan tool.
3. Clear the Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs).
4. Operate the vehicle within the Freeze Frame
conditions and conditions for setting the DTC
as noted.
Does the Malfunction Indicator (MIL) illuminate?–Go to Step 4Go to Step 3
31. Turn the ignition switch ON, with the engine
OFF.
2. Review the Freeze Frame data and note the
parameters.
3. Operate the vehicle within the Freeze Frame
conditions and conditions for Setting The DTC
as noted.
Does the Malfunction Indicator (MIL) illuminate?–Go to Step 4Go to Step 12
4Listen to the engine while raising and lowering the
engine speed.
Is a knock or audible noise present?–Go to Step 5Go to Step 6
5Repair the mechanical engine problem or a loose
bracket or component.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 12–
61. Turn the ignition switch to lock.
2. Disconnect the engine control module(ECM).
3. With a digital voltmeter (DVM) connected to
ground, measure the resistance of the knock
sensor through the knock sensor signal circuit,
terminal 42.
Is the measured value within the specified value?90–100KWGo to Step 7Go to Step 9
7Check for a poor connection at the ECM connector,
knock sensor (KS) signal circuit and repair as neces-
sary.
Is a repair necessary?–Go to Step 12Go to Step 8
8Replace the engine control module(ECM).
Is the replacement complete?–Go to Step 12Go to Step 10
9Check the KS electrical connector for a poor connec-
tion and repair an necessary.
Is a repair necessary?–Go to Step 12Go to Step 10
10Check the KS signal circuit for an open or a low volt-
age or voltage and repair as necessary.
Is a repair necessary?–Go to Step 12Go to Step 11
11Replace the KS.
Is the replacement complete?–Go to Step 12–