fuel cap DAEWOO NUBIRA 2004 Service User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DAEWOO, Model Year: 2004, Model line: NUBIRA, Model: DAEWOO NUBIRA 2004Pages: 2643, PDF Size: 80.54 MB
Page 478 of 2643

1F – 232IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0444
EVAP PURGE CONTROL CIRCUIT NO SIGNAL
Circuit Description
The evaporative emission (EVAP) system includes the fol-
lowing components :
S Fuel tank.
S EVAP vent solenoid.
S Fuel tank pressure sensor.
S Fuel pipes and hoses.
S Fuel vapor lines.
S Fuel cap.
S EVAP canister.
S Purge lines.
S EVAP canister purge valve.
S EVAP service port.
The evaporative emission system is checked by applying
vacuum to the EVAP system and monitoring for a vacuum
decay. The engine control module(ECM) monitors the
vacuum level through the fuel tank pressure sensor signal.
At the appropriate time, the EVAP canister purge valve
and the EVAP vent solenoid are turned on, allowing the en-
gine to draw a small vacuum on the entire EVAP system.
After the desired vacuum level has been achieved, the
EVAP canister purge valve is turned OFF, sealing the sys-tem. If a sufficient vacuum level cannot be achieved, a
large leak is indicated. This can be caused by the following
conditions :
Missing or faulty fuel cap.
Disconnected or faulty fuel tank pressure sensor.
Disconnected, damaged, pinched, or blocked EVAP
purge line.
Disconnected or faulty EVAP canister purge valve.
Disconnected or faulty EVAP vent solenoid.
Open ignition feed circuit to the EVAP vent or purge sole-
noid.
Damaged EVAP canister.
Leaking fuel sensor assembly O–ring.
Leaking fuel tank or fuel filler beck.
Any of the above conditions can set DTC P0444.
The test is failed if the tank vacuum is less than 10 in H20
for 15 seconds and the manifold vacuum integral is greater
than 49512 (proportional to purge mass from the tank).
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S The canister purge solenoid circuit is an open con-
dition exist.
Page 479 of 2643
ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 233
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illuminate
after three consecutive trip with a fail.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fail. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
Although this DTC is considered a type. A diagnostic, it
acts like a type B diagnostic under certain conditions.
Whenever this diagnostic reports the system has passed,
or if the battery is disconnected, the diagnostic must fail
twice before setting a DTC. The initial failure is not re-ported to the diagnostic executive or displayed on a scan
tool. A passing system always reports to the diagnostic
executive immediately.
Check for the following conditions :
S Missing or damaged fuel cap.
S Missing or damaged O–rings at fuel vapor and
EVAP purge line canister fittings.
S Cracked or punctured EVAP canister.
S Damaged source vacuum line, EVAP purge line,
EVAP vent hose or fuel tank vapor line.
S Poor connection at the ECM. Inspect the harness
connectors for the following conditions.
S Backed–out terminals.
S Improper mating.
S Broken locks.
S Improperly formed.
S Damaged terminals.
S Poor terminal–to–wire connection.
S Damaged harness. Inspect the wiring harness to
the EVAP vent solenoid, EVAP canister purge
valve, and the fuel tank pressure sensor for an in-
termittent open or short circuit.
S Kinked, pinched or plugged vacuum source, EVAP
purge, or fuel tank vapor line. Verify that the lines
are not restricted.
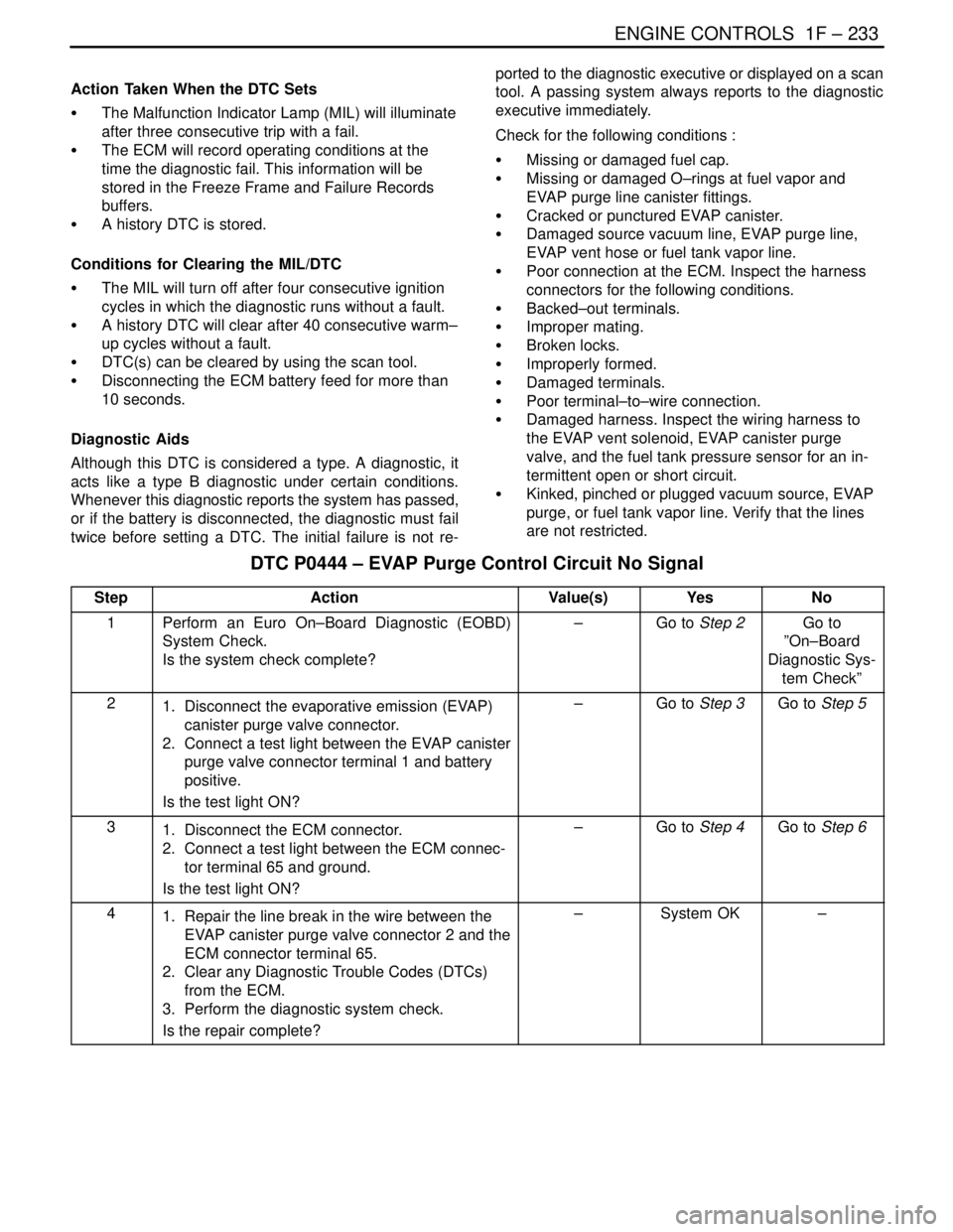
DTC P0444 – EVAP Purge Control Circuit No Signal
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an Euro On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD)
System Check.
Is the system check complete?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
21. Disconnect the evaporative emission (EVAP)
canister purge valve connector.
2. Connect a test light between the EVAP canister
purge valve connector terminal 1 and battery
positive.
Is the test light ON?–Go to Step 3Go to Step 5
31. Disconnect the ECM connector.
2. Connect a test light between the ECM connec-
tor terminal 65 and ground.
Is the test light ON?–Go to Step 4Go to Step 6
41. Repair the line break in the wire between the
EVAP canister purge valve connector 2 and the
ECM connector terminal 65.
2. Clear any Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
from the ECM.
3. Perform the diagnostic system check.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
Page 481 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 235
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0445
EVAP PURGE CONTROL CIRCUIT FAULT
Circuit Description
The evaporative emission (EVAP) system includes the fol-
lowing components :
S Fuel tank.
S EVAP vent solenoid.
S Fuel tank pressure sensor.
S Fuel pipes and hoses.
S Fuel vapor lines.
S Fuel cap.
S EVAP canister.
S Purge lines.
S EVAP canister purge valve.
S EVAP service port.
The evaporative emission system is checked by applying
vacuum to the EVAP system and monitoring for a vacuum
decay. The engine control module(ECM) monitors the
vacuum level through the fuel tank pressure sensor signal.
At the appropriate time, the EVAP canister purge valve
and the EVAP vent solenoid are turned on, allowing the en-
gine to draw a small vacuum on the entire EVAP system.
After the desired vacuum level has been achieved, the
EVAP canister purge valve is turned OFF, sealing the sys-tem. If a sufficient vacuum level cannot be achieved, a
large leak is indicated. This can be caused by the following
conditions :
Missing or faulty fuel cap.
Disconnected or faulty fuel tank pressure sensor.
Disconnected, damaged, pinched, or blocked EVAP
purge line.
Disconnected or faulty EVAP canister purge valve.
Disconnected or faulty EVAP vent solenoid.
Open ignition feed circuit to the EVAP vent or purge sole-
noid.
Damaged EVAP canister.
Leaking fuel sensor assembly O–ring.
Leaking fuel tank or fuel filler beck.
Any of the above conditions can set DTC P0445.
The test is failed if the tank vacuum is less than 10 in H20
for 15 seconds and the manifold vacuum integral is greater
than 49512 (proportional to purge mass from the tank).
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S The canister purge solenoid valve circuit is a short
to battery or short to ground condition exist.
Page 482 of 2643
1F – 236IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illuminate
after three consecutive trip with a fail.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fail. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
Although this DTC is considered a type. A diagnostic, it
acts like a type B diagnostic under certain conditions.
Whenever this diagnostic reports the system has passed,
or if the battery is disconnected, the diagnostic must fail
twice before setting a DTC. The initial failure is not re-ported to the diagnostic executive or displayed on a scan
tool. A passing system always reports to the diagnostic
executive immediately.
Check for the following conditions :
S Missing or damaged fuel cap.
S Missing or damaged O–rings at fuel vapor and
EVAP purge line canister fittings.
S Cracked or punctured EVAP canister.
S Damaged source vacuum line, EVAP purge line,
EVAP vent hose or fuel tank vapor line.
S Poor connection at the ECM. Inspect the harness
connectors for the following conditions.
S Backed–out terminals.
S Improper mating.
S Broken locks.
S Improperly formed.
S Damaged terminals.
S Poor terminal–to–wire connection.
S Damaged harness. Inspect the wiring harness to
the EVAP vent solenoid, EVAP canister purge
valve, and the fuel tank pressure sensor for an in-
termittent open or short circuit.
S Kinked, pinched or plugged vacuum source, EVAP
purge, or fuel tank vapor line. Verify that the lines
are not restricted.
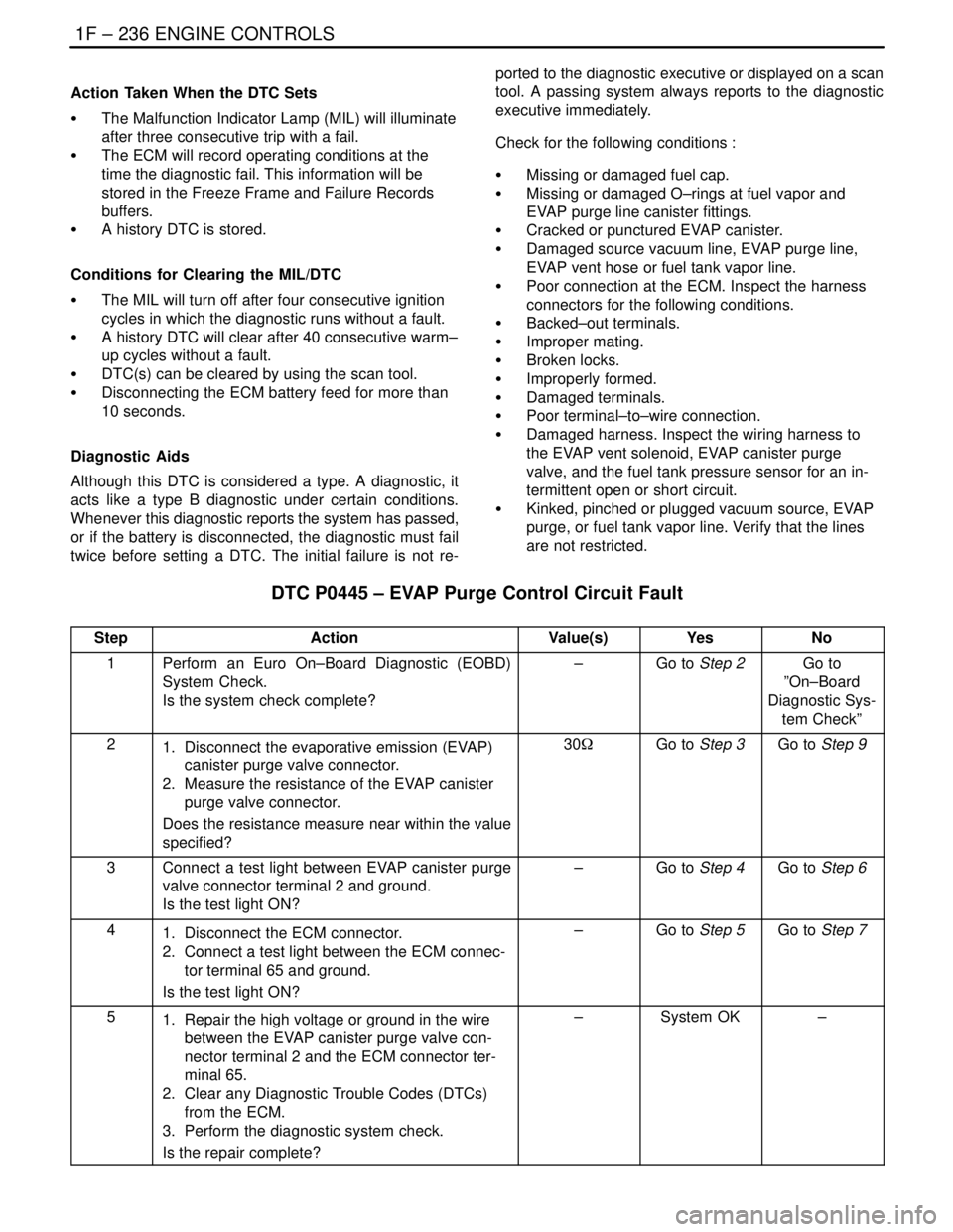
DTC P0445 – EVAP Purge Control Circuit Fault
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an Euro On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD)
System Check.
Is the system check complete?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
21. Disconnect the evaporative emission (EVAP)
canister purge valve connector.
2. Measure the resistance of the EVAP canister
purge valve connector.
Does the resistance measure near within the value
specified?30WGo to Step 3Go to Step 9
3Connect a test light between EVAP canister purge
valve connector terminal 2 and ground.
Is the test light ON?–Go to Step 4Go to Step 6
41. Disconnect the ECM connector.
2. Connect a test light between the ECM connec-
tor terminal 65 and ground.
Is the test light ON?–Go to Step 5Go to Step 7
51. Repair the high voltage or ground in the wire
between the EVAP canister purge valve con-
nector terminal 2 and the ECM connector ter-
minal 65.
2. Clear any Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs)
from the ECM.
3. Perform the diagnostic system check.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
Page 634 of 2643

1F – 388IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0137
REAR HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR (HO2S2) LOW
VOLTAGE
Circuit Description
In order to control emissions, a catalytic converter is used
to convert harmful emissions into harmless water vapor
and carbon dioxide.
The Engine Control Module (ECM) has the ability to moni-
tor this process by using a Rear Heated Oxygen Sensor
(HO2S2). The HO2S2, located in the exhaust stream past
the catalytic converter, produces an output signal which in-
dicates the storage capacity of the catalyst. This in turn in-
dicates the catalyst’s ability to convert exhaust emissions
effectively. If the catalyst is functioning properly, the
HO2S2 signal will be far less active than the signal pro-
duced by the Front Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S1).
If the HO2S2 pigtail wiring, connector, or terminal is dam-
aged, the entire HO2S2 assembly must be replaced. Do
not attempt to repair the wiring, connector, or terminals. In
order for the sensor to function properly, it must have a
clean air reference provided to it. This clean air reference
is obtained by way of the HO2S2 wire(s). Any attempt to
repair the wires, connector, or terminals could result in the
obstruction of the air reference and degrade the HO2S2
performance.Conditions for Setting the DTC
S HO2S2 voltage is less than 0.05 volt in Closed
Loop control or less than 0.35 volt in Power Enrich-
ment (PE) mode.
S Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) is greater than
60°C (140°F).
S System voltage is greater than 10 volts.
S Closed Loop test: 3 seconds delay after in Closed
Loop and air flow is greater than 9 g/sec.
S Power Enrichment test: Air/Fuel ration is less than
or equal to 13.5 and 3 seconds delay after in Power
Enrichment mode.
S DTCs P0106, P0107, P0108, P0117, P0118,
P0122, P0123, P0171, P0172, P0201, P0202,
P0203, P0204, P0300, P0336, P0337, P0351,
P0352, P0141, P0402, P0404, P0405, P0406,
P0506, P0507, P1404, and P0443 are not set.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illuminate
after three consecutive ignition cycle with a fail.
Page 637 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 391
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0138
REAR HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR (HO2S2) HIGH
VOLTAGE
Circuit Description
In order to control emissions, a catalytic converter is used
to convert harmful emissions into harmless water vapor
and carbon dioxide.
The Engine Control Module (ECM) has the ability to moni-
tor this process by using a Rear Heated Oxygen Sensor
(HO2S2). The HO2S2, located in the exhaust stream past
the catalytic converter, produces an output signal which in-
dicates the storage capacity of the catalyst. This in turn in-
dicates the catalyst¡¯s ability to convert exhaust emissions
effectively. If the catalyst is functioning properly, the
HO2S2 signal will be far less active than the signal pro-
duced by the Front Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S1).
If the HO2S2 pigtail wiring, connector, or terminal is dam-
aged, the entire HO2S2 assembly must be replaced. Do
not attempt to repair the wiring, connector, or terminals. In
order for the sensor to function properly, it must have a
clean air reference provided to it. This clean air reference
is obtained by way of the HO2S2 wire(s). Any attempt to
repair the wires, connector, or terminals could result in the
obstruction of the air reference and degrade the HO2S2
performance.Conditions for Setting the DTC
S HO2S2 voltage is greater than 0.952 volt in Closed
Loop control or greater than 0.55 volt in Decel Fuel
Cutoff (DFCO) mode.
S Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) is greater than
60°C (140°F).
S System voltage is greater than 10 volts.
S Closed Loop test: 3 seconds delay after in Closed
Loop and airflow is greater than 9 g/sec.
S DFCO test: 2 seconds delay after in DFCO.
S DTCs P0106, P0107, P0108, P0117, P0118,
P0122, P0123, P0171, P0172, P0201, P0202,
P0203, P0204, P0300, P0336, P0337, P0351,
P0352, P0141, P0402, P0404, P0405, P0406,
P0506, P0507, P1404, and P0443 are not set.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illuminate
after three consecutive ignition cycle with a fail.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
Page 640 of 2643

1F – 394IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0140
REAR HEATED OXYGEN SENSOR (HO2S2) NO ACTIVITY
OR OPEN
Circuit Description
In order to control emissions, a catalytic converter is used
to convert harmful emissions into harmless water vapor
and carbon dioxide.
The Engine Control Module (ECM) has the ability to moni-
tor this process by using a Rear Heated Oxygen Sensor
(HO2S2). The HO2S2, located in the exhaust stream past
the catalytic converter, produces an output signal which in-
dicates the storage capacity of the catalyst. This in turn in-
dicates the catalyst is ability to convert exhaust emissions
effectively. If the catalyst is functioning properly, the
HO2S2 signal will be far less active than the signal pro-
duced by the Front Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S1).
If the HO2S2 pigtail wiring, connector, or terminal is dam-
aged, the entire HO2S2 assembly must be replaced. Do
not attempt to repair the wiring, connector, or terminals. In
order for the sensor to function properly, it must have a
clean air reference provided to it. This clean air reference
is obtained by way of the HO2S2 wire(s). Any attempt to
repair the wires, connector, or terminals could result in the
obstruction of the air reference and degrade the HO2S2
performance.Conditions for Setting the DTC
S HO2S2 voltage is between 0.422 and 0.478 volts.
S Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) is greater than
60°C (140°F).
S Engine rum time is greater than 60 seconds.
S System voltage is greater than 10 volts.
S Closed Loop stoichiometry.
S 3 second delay after exiting Decel Fuel Cutoff
(DFCO) mode.
S DTCs P0106, P0107, P0108, P0117, P0118,
P0122, P0123, P0171, P0172, P0201, P0202,
P0203, P0204, P0300, P0336, P0337, P0351,
P0352, P0141, P0402, P0404, P0405, P0406,
P0506, P0507, P1404, and P0443 are not set.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illuminate
after three consecutive ignition cycle with a fail.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
Page 667 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 421
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0300
MULTIPLE CYLINDER MISFIRE DETECTED
System Description
The Engine Control Module (ECM) monitors the crank-
shaft and camshaft positions to detect if the engine is mis-
firing. The ECM looks for a quick drop in crankshaft speed.
This test is executed in blocks of 100 engine revolution
tests. It may take between one to several tests to store a
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) and illuminate the Mal-
function Indicator Lamp (MIL). Under light misfire condi-
tions, it may also take more than one trip to set a DTC. Se-
vere misfire will flash the MIL, indicating that catalyst
damage is possible.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S Emission threshold is 3%.
S 20 engine cycles have occurred since cranking has
started.
S A/C compressor clutch has not just engaged or dis-
engaged.
S Engine load and engine speed is in a detectable
region and is at or above zero torque.
S Camshaft Position (CMP) sensor is in synchroniza-
tion.
S Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) flow diagnostic is
not in progress.
S Fuel level is greater than 12% of rated tank capac-
ity.
S Decel Fuel Cutoff (DFCO) not active.
S Throttle position change is less than 3% per 125
ms.
S Vehicle has not encountered an abusive engine
speed of 7000 rpm.
S Crankshaft speed patters are normal.
S Throttle position is less than 3% when vehicle
speed is greater than 10 km/h (6 mph).
S Vehicle voltage is between 11 and 16 volts.
S Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) is between
–7°C (19°F) and 120°C (248°F).
S There is the correct ratio between Crankshaft Posi-
tion (CKP) sensor pulses and CMP sensor pulses.
S DTCs P0106, P0107, P0108, P0117, P0118,
P0122, P0123, P0336, P0337, P0341, P0342 and
P0502 are not set.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The MIL will illuminate after two consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs with the fault
active.
Or
S The MIL will illuminate immediately and flash if mis-
fire is present.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault
within the freeze frame conditions that the DTC
failed.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S The DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent can also be the result of a defective reluctor
wheel. Remove the CKP sensor and inspect the reluctor
wheel through the sensor mount hole. Check for porosity
and the condition of wheel. If the DTC is intermittent refer
to ”Symptoms Diagnosis” in this section.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diag-
nostic Table.
1. The On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System Check
prompts the technician to complete some basic
checks and store the freeze frame and failure re-
cords data on the scan tool if applicable. This
creates an electronic copy of the data taken when
the malfunction occurred. The information is then
stored on the scan tool for later reference.
3. A visual/physical inspection should include check-
ing the following components:
S The wiring for proper connections, pinches or
cuts.
S The ECM grounds for being clean and tight.
S The vacuum hoses for splits, kinks, and proper
connections as shown on the Vehicle Emission
Information label. Check thoroughly for any type
of leak or restriction.
S For air leaks at the throttle body mounting area
and intake manifold sealing surfaces.
5. When all the accumulators are relatively equal, then
the misfire is being caused by something that af-
fects the entire engine. When they are not then the
misfire is being caused by something that is specif-
ic to two or more cylinders.
6. Whenever the misfire is not present operating the
vehicle may be necessary to duplicate the condi-
tions in the Freeze Frame Data in order to detect
misfire. Depending on the engine load, the condi-
tions may have to be maintained for up to 20 sec-
onds. Whenever the misfire accumulators start to
increment, then misfire is present. A history misfire
counter will store the number of misfires that have
occurred until the DTC is cleared.
Page 672 of 2643

1F – 426IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0301
CYLINDER 1 MISFURE
System Description
The Engine Control Module (ECM) monitors the crank-
shaft and camshaft positions to detect if the engine is mis-
firing. The ECM looks for a quick drop in crankshaft speed.
This test is executed in blocks of 100 engine revolution
tests. It may take between one to several tests to store a
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) and illuminate the Mal-
function Indicator Lamp (MIL). Under light misfire condi-
tions, it may also take more than one trip to set a DTC. Se-
vere misfire will flash the MIL, indicating that catalyst
damage is possible.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S Emission threshold is 3%.
S 20 engine cycles have occurred since cranking has
started.
S A/C compressor clutch has not just engaged or dis-
engaged.
S Engine load and engine speed is in a detectable
region and is at or above zero torque.
S Camshaft Position (CMP) sensor is in synchroniza-
tion.
S Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) flow diagnostic is
not in progress.
S Fuel level is greater than 12% of rated tank capac-
ity.
S Decel Fuel Cutoff (DFCO) not active.
S Throttle position change is less than 3% per 125
ms.
S Vehicle has not encountered an abusive engine
speed of 7000 rpm.
S Crankshaft speed patters are normal.
S Throttle position is less than 3% when vehicle
speed is greater than 10 km/h (6 mph).
S Vehicle voltage is between 11 and 16 volts.
S Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) is between
–7°C (19°F) and 120°C (248°F).
S There is the correct ratio between Crankshaft Posi-
tion (CKP) sensor pulses and CMP sensor pulses.
S DTCs P0106, P0107, P0108, P0117, P0118,
P0122, P0123, P0336, P0337, P0341, P0342 and
P0502 are not set.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The MIL will illuminate after two consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs with the fault
active.
Or
S The MIL will illuminate immediately and flash if mis-
fire is present.S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault
within the freeze frame conditions that the DTC
failed.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S The DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent can also be the result of a defective reluctor
wheel. Remove the CKP sensor and inspect the reluctor
wheel through the sensor mount hole. Check for porosity
and the condition of wheel. If the DTC is intermittent refer
to ”Symptoms Diagnosis” in this section.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diag-
nostic Table.
1. The On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System Check
prompts the technician to complete some basic
checks and store the freeze frame and failure re-
cords data on the scan tool if applicable. This
creates an electronic copy of the data taken when
the malfunction occurred. The information is then
stored on the scan tool for later reference.
3. A visual/physical inspection should include check-
ing the following components:
S The wiring for proper connections, pinches or
cuts.
S The ECM grounds for being clean and tight.
S The vacuum hoses for splits, kinks, and proper
connections as shown on the Vehicle Emission
Information label.
S Check thoroughly for any type of leak or restric-
tion.
S For air leaks at the throttle body mounting area
and intake manifold sealing surfaces.
5. When all the accumulators are relatively equal, then
the misfire is being caused by something that af-
fects the entire engine. When they are not then the
misfire is being caused by something that is specif-
ic to two or more cylinders.
6. Whenever the misfire is not present operating the
vehicle may be necessary to duplicate the condi-
tions in the Freeze Frame Data in order to detect
Page 677 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 431
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0302
CYLINDER 2 MISFIRE
System Description
The Engine Control Module (ECM) monitors the crank-
shaft and camshaft positions to detect if the engine is mis-
firing. The ECM looks for a quick drop in crankshaft speed.
This test is executed in blocks of 100 engine revolution
tests. It may take between one to several tests to store a
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) and illuminate the Mal-
function Indicator Lamp (MIL). Under light misfire condi-
tions, it may also take more than one trip to set a DTC. Se-
vere misfire will flash the MIL, indicating that catalyst
damage is possible.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S Emission threshold is 3%.
S 20 engine cycles have occurred since cranking has
started.
S A/C compressor clutch has not just engaged or dis-
engaged.
S Engine load and engine speed is in a detectable
region and is at or above zero torque.
S Camshaft Position (CMP) sensor is in synchroniza-
tion.
S Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) flow diagnostic is
not in progress.
S Fuel level is greater than 12% of rated tank capac-
ity.
S Decel Fuel Cutoff (DFCO) not active.
S Throttle position change is less than 3% per 125
ms.
S Vehicle has not encountered an abusive engine
speed of 7000 rpm.
S Crankshaft speed patters are normal.
S Throttle position is less than 3% when vehicle
speed is greater than 10 km/h (6 mph).
S Vehicle voltage is between 11 and 16 volts.
S Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) is between
–7°C (19°F) and 120°C (248°F).
S There is the correct ratio between Crankshaft Posi-
tion (CKP) sensor pulses and CMP sensor pulses.
S DTCs P0106, P0107, P0108, P0117, P0118,
P0122, P0123, P0336, P0337, P0341, P0342 and
P0502 are not set.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The MIL will illuminate after two consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs with the fault
active.
Or
S The MIL will illuminate immediately and flash if mis-
fire is present.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault
within the freeze frame conditions that the DTC
failed.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S The DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent can also be the result of a defective reluctor
wheel. Remove the CKP sensor and inspect the reluctor
wheel through the sensor mount hole. Check for porosity
and the condition of wheel. If the DTC is intermittent refer
to”Symptoms Diagnosis” in this section.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the Diag-
nostic Table.
1. The On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System Check
prompts the technician to complete some basic
checks and store the freeze frame and failure re-
cords data on the scan tool if applicable. This
creates an electronic copy of the data taken when
the malfunction occurred. The information is then
stored on the scan tool for later reference.
3. A visual/physical inspection should include check-
ing the following components:
S The wiring for proper connections, pinches or
cuts.
S The ECM grounds for being clean and tight.
S The vacuum hoses for splits, kinks, and proper
connections as shown on the Vehicle Emission
Information label. Check thoroughly for any type
of leak or restriction.
S For air leaks at the throttle body mounting area
and intake manifold sealing surfaces.
5. When all the accumulators are relatively equal, then
the misfire is being caused by something that af-
fects the entire engine. When they are not then the
misfire is being caused by something that is specif-
ic to two or more cylinders.
6. Whenever the misfire is not present operating the
vehicle may be necessary to duplicate the condi-
tions in the Freeze Frame Data in order to detect
misfire. Depending on the engine load, the condi-
tions may have to be maintained for up to 20 sec-
onds. Whenever the misfire accumulators start to
increment, then misfire is present. A history misfire
counter will store the number of misfires that have
occurred until the DTC is cleared.