warning DATSUN B110 1973 Service User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DATSUN, Model Year: 1973, Model line: B110, Model: DATSUN B110 1973Pages: 513, PDF Size: 28.74 MB
Page 260 of 513
BODY
ELECTRICAL
Improper
cable
contact
Oil
pressure
and
ignition
warning
lamps
Condition
Oil
pressure
Want
ing
lamp
The
lamp
does
not
ligh
t
when
the
ignition
switch
is
set
to
ON
Probable
cause
Blown
off
fuse
or
faulty
contact
Broken
lamp
bulb
fIlarnent
or
faulty
cable
contact
Defective
oil
pressure
switch
The
lamp
does
not
Oil
pressure
is
too
low
go
out
while
the
engine
is
being
operated
Lack
of
engine
oil
Defective
oil
pressure
switch
Ignition
warning
lamp
The
lamp
does
not
light
when
the
ignition
switch
is
set
to
ON
Blown
off
fuse
or
faulty
contact
Burnt
out
light
bulb
filarnent
or
faulty
cable
contact
The
fuel
rneter
indicates
a
level
slightly
lower
than
the
actual
level
Method
of
inspection
Check
the
fuse
for
fusing
and
faulty
contact
The
warning
lamp
does
not
light
when
oil
pressure
switch
yellow
black
cable
is
grounded
The
warning
lamp
lights
through
the
above
inspection
Inspect
the
engine
oil
pressure
system
Check
oil
level
Continuity
exists
on
the
oil
pres
sure
switch
when
the
engine
is
being
operated
Check
the
fuse
for
fusing
and
faulty
contact
The
pilot
lamp
does
not
light
when
the
voltage
regulator
con
nector
is
disconnected
the
white
red
cable
is
grounded
and
the
ignition
switch
is
set
to
ON
BE
25
Check
the
cable
from
the
fuel
meter
to
the
tank
unit
for
cable
being
about
to
break
poor
contact
and
faulty
grounding
and
repair
as
required
Corrective
action
Replace
after
corree
ting
the
fuse
the
cause
if
fused
Check
the
light
bulb
for
burnt
out
fIla
ment
and
replace
as
required
Replace
the
oil
pres
sure
switch
Add
oil
Replace
the
oil
pres
sure
switch
Repair
or
replace
as
required
Check
the
bulb
for
burnt
out
fIlament
and
replace
as
re
quired
Page 264 of 513
BODY
ELECTRICAL
Improper
stop
position
of
wiper
arm
Improperly
positioned
blade
and
arm
Correct
position
Damaged
or
worn
auto
stop
point
Replace
motor
Improper
wiping
Worn
rubber
blade
Replace
blade
Inadequate
pressing
force
of
wiper
arm
Replace
wiper
arm
IGNITION
SWITCH
AND
STEERING
LOCK
CONTENTS
IGNITION
SWITCH
Removal
IGNITION
SWITCH
WITH
STEER
ING
LOCK
BE
29
BE
29
BE
29
IGNITION
SWITCH
This
3
or
4
position
switch
is
installed
on
the
ignition
switch
bracket
which
is
installed
on
the
instrument
panel
with
two
screws
and
controls
the
engine
ignition
system
and
most
of
electrical
equipment
Removal
Remove
the
ignition
switch
connector
loosen
the
ring
nut
remove
the
ignition
switch
from
the
bracket
Description
Steering
lock
replacement
Warning
switch
and
warning
buzzer
BE
29
BE
30
BE
30
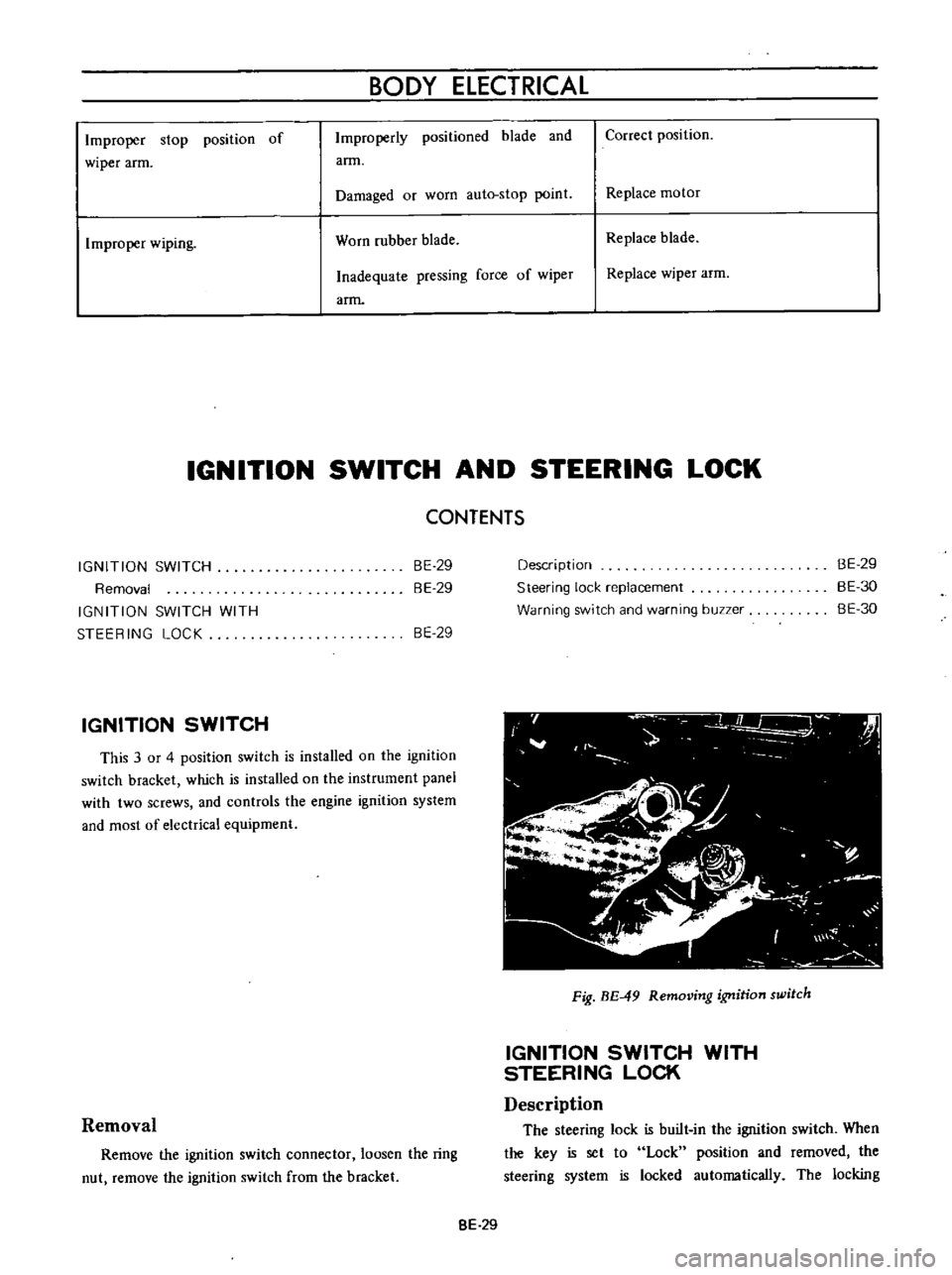
Fig
BE
49
Removing
ignition
switch
IGNITION
SWITCH
WITH
STEERING
LOCK
Description
The
steering
lock
is
built
in
the
ignition
switch
When
the
key
is
set
to
Lock
position
and
rernoved
the
steering
system
is
locked
automatically
The
locking
8E
29
Page 265 of 513
mechanism
is
installed
on
the
steering
jacket
tube
When
the
key
is
set
to
Lock
position
and
removed
the
steering
lock
spindle
is
inserted
in
a
notch
in
the
collar
which
is
stationarity
set
on
the
steering
shaft
to
lock
the
steering
wheel
The
ignitiun
switch
is
installed
on
the
back
of
key
cylinder
with
a
attaching
screw
and
interchangeable
tf
iY
t
7
a
1
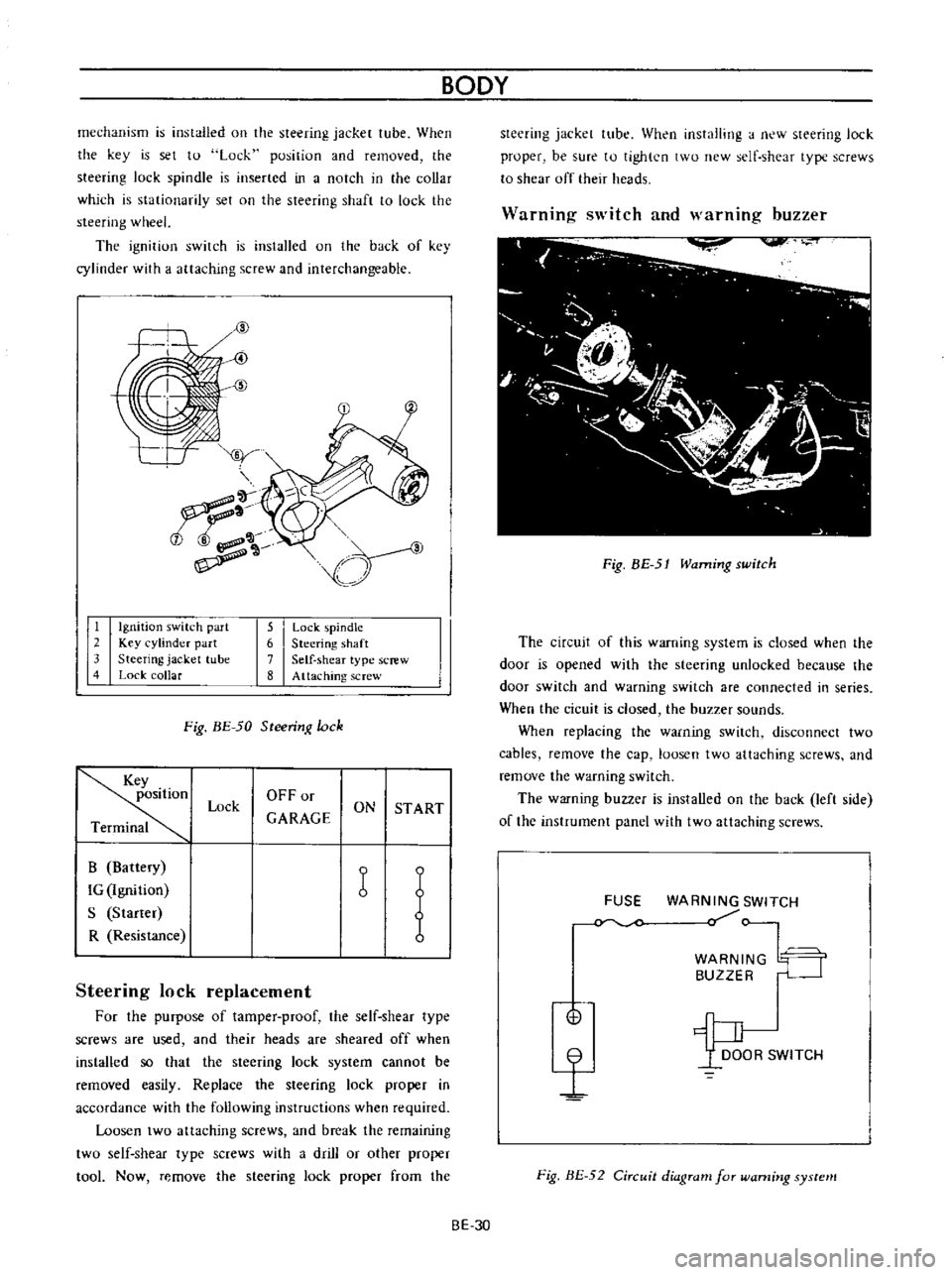
Ignition
switch
part
2
Key
cylinder
part
3
Steering
jacket
tube
4
Lock
collar
5
Lock
pindle
6
Steering
shaft
7
Self
shear
type
screw
8
Attaching
screw
Fig
BE
50
Steering
lock
Key
position
Terminal
OFFor
GARAGE
Lock
ON
ST
ART
B
Battery
IG
Ignition
S
Starter
R
Resistance
b
1
Steering
lock
replacement
For
the
purpuse
of
tamper
proof
the
self
shear
type
screws
are
used
and
their
heads
are
sheared
off
when
installed
so
that
the
steering
lock
system
cannot
be
removed
easily
Replace
the
steering
lock
proper
in
accordance
with
the
following
instructions
when
required
Loosen
two
attaching
screws
and
break
the
remaining
twu
self
shear
type
screws
with
a
drill
or
other
proper
tool
Now
remove
the
steering
lock
proper
from
the
BODY
BE
30
steering
jacket
tube
When
installing
a
new
steering
lock
proper
be
sure
tu
tighten
two
new
self
shear
type
screws
to
shear
off
their
heads
Warning
switch
and
warnmg
buzzer
Fig
BE
51
Warning
switch
The
circuit
of
this
warning
system
is
closed
when
the
door
is
opened
with
the
steering
unlocked
because
the
door
switch
and
warning
switch
are
connected
in
series
When
the
cicuit
is
closed
the
buzzer
sounds
When
replacing
the
warning
switch
disconnect
two
cables
remove
the
cap
loosen
two
attaching
screws
and
remove
the
warning
switch
The
warning
buzzer
is
installed
on
the
back
left
side
of
the
instrument
panel
with
two
attaching
screws
FUSE
WARNING
SWITCH
WARN
BUZZ
G
n
WITCH
t
Fig
BE
52
Circuit
diagram
for
warning
system
Page 435 of 513
ENGINE
ElECTRICAL
SYSTEM
CHARGING
CIRCUIT
IGNITION
1
i
n
ITCH
r
B
i
i
vel
oU
ARMATURE
lip
J
l
t
lJ
FIEL
Df
e
I
I
3
2
I
u
P
5
0
IL
U
p
P
f
H
i
I
I
L
J
L
J
ALTERNATOR
VOL
TAGE
REGULATOR
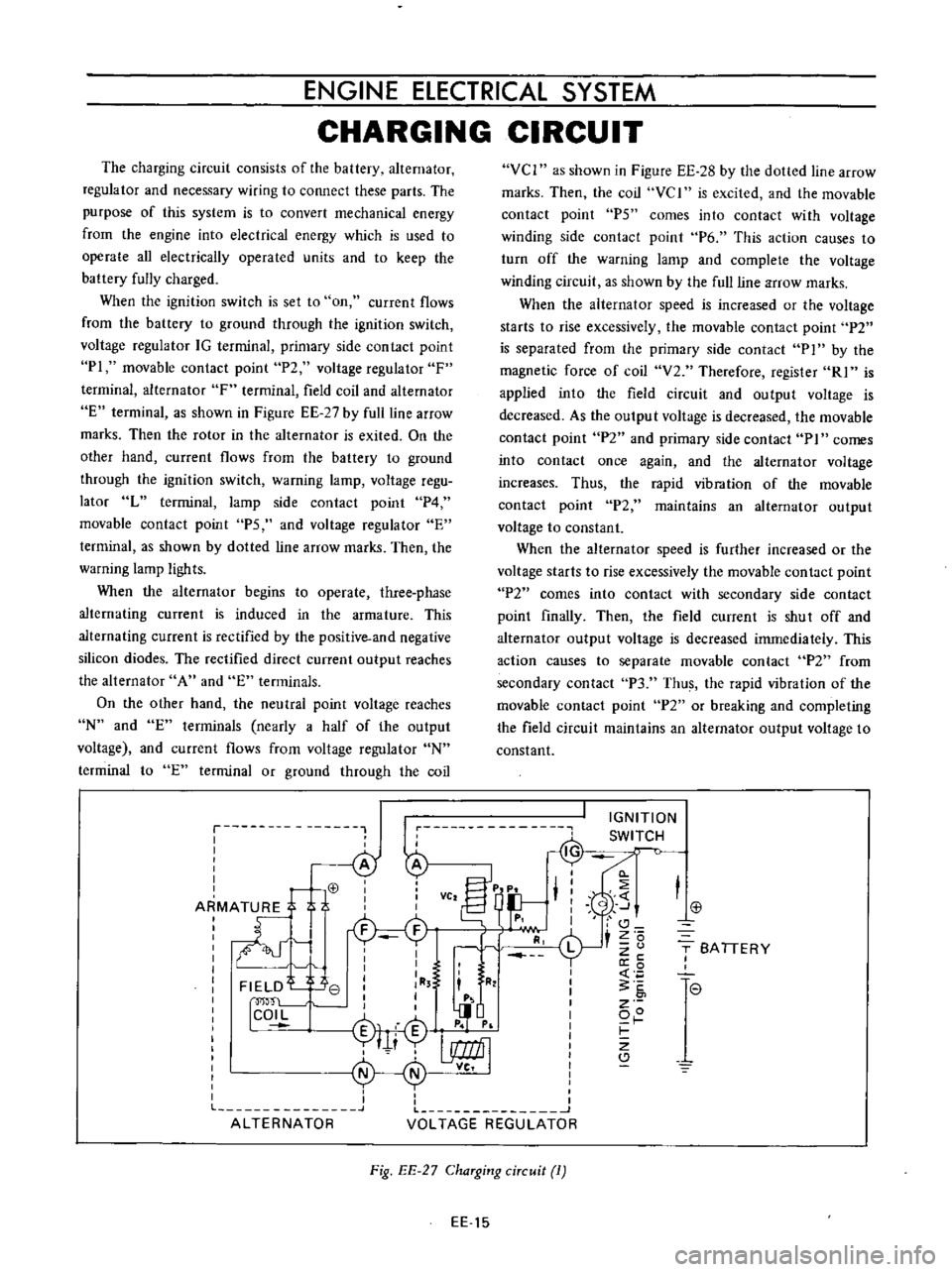
The
charging
circuit
consists
of
the
battery
alternator
regulator
and
necessary
wiring
to
connect
these
parts
The
purpose
of
this
system
is
to
convert
mechanical
energy
from
the
engine
into
electrical
energy
which
is
used
to
operate
all
electrically
operated
units
and
to
keep
the
battery
fully
charged
When
the
ignition
switch
is
set
to
on
current
flows
from
the
battery
to
ground
through
the
ignition
switch
voltage
regulator
IG
terminal
primary
side
contact
point
PI
movable
contact
point
P2
voltage
regulator
F
terminal
alternator
F
terminal
field
coil
and
alternator
E
terminal
as
shown
in
Figure
EE
27
by
full
line
arrow
marks
Then
the
rotor
in
the
alternator
is
exited
On
the
other
hand
current
flows
from
the
battery
to
ground
through
the
ignition
switch
warning
lamp
voltage
regu
lator
L
terminal
lamp
side
contact
point
P4
movable
contact
point
PS
and
voltage
regulator
E
terminal
as
shown
by
dotted
line
arrow
marks
Then
the
warning
lamp
ligh
ts
When
the
alternator
begins
to
operate
three
phase
alternating
current
is
induced
in
the
armature
This
alternating
current
is
rectified
by
the
positive
and
negative
silicon
diodes
The
rectified
direct
current
output
reaches
the
alternator
A
and
E
terminals
On
the
other
hand
the
neutral
point
voltage
reaches
N
and
E
terminals
nearly
a
half
of
the
output
voltage
and
current
flows
from
voltage
regulator
N
terminal
to
E
terminal
or
ground
through
the
coil
VCI
as
shown
in
Figure
EE
28
by
the
dolled
line
arrow
marks
Then
the
coil
vc
I
is
excited
and
the
movable
contact
point
P5
comes
into
contact
with
voltage
winding
side
contact
point
P6
This
action
causes
to
turn
off
the
warning
lamp
and
complete
the
voltage
winding
circuit
as
shown
by
the
ullline
arrow
marks
When
the
alternator
speed
is
increased
or
the
voltage
starts
to
rise
excessively
the
movable
contact
point
P2
is
separated
from
the
primary
side
contact
P
1
by
the
magnetic
force
of
coil
V2
Therefore
register
RI
is
applied
into
the
field
circuit
and
output
voltage
is
decreased
As
the
outpu
t
voltage
is
decreased
the
movable
contact
point
P2
and
primary
side
contact
PI
comes
into
contact
once
again
and
the
alternator
voltage
increases
Thus
the
rapid
vibration
of
the
movable
contact
point
P2
maintains
an
alternator
output
voltage
to
constant
When
the
alternator
speed
is
further
increased
or
the
voltage
starts
to
rise
excessively
the
movable
contact
point
P2
comes
into
contact
with
secondary
side
contact
point
finally
Then
the
field
current
is
shut
off
and
alternator
output
voltage
is
decreased
immediately
This
action
causes
to
separate
movable
contact
P2
from
secondary
contact
P3
Thus
the
rapid
vibration
of
the
movable
contact
point
P2
or
breaking
and
completing
the
field
circuit
maintains
an
alternator
output
voltage
to
constant
j
T
SA
TIERY
I
l
e
7
Fig
EE
27
ChaTging
ciTcuit
1
EE
15
Page 443 of 513
Charge
relay
SPECIFICATIONS
AND
SERVICE
DATA
TROUBLE
DIAGNOSES
AND
CORRECTIONS
ENGINE
ElECTRICAL
SYSTEM
Reduction
limit
Repair
limit
Repair
accuracy
mm
in
mm
in
mm
in
REGULATOR
CONTENTS
DESCRIPTiON
MEASUREMENT
OF
REGULATING
VOLTAGE
ADJUSTMENT
Voltage
regu
lator
EE
23
EE
24
EE
25
EE
25
DESCRIPTION
I
0
0394
0
3
0
0118
0
05
0
0197
EE
26
EE
26
EE
27
1
I
T
r
@
V
The
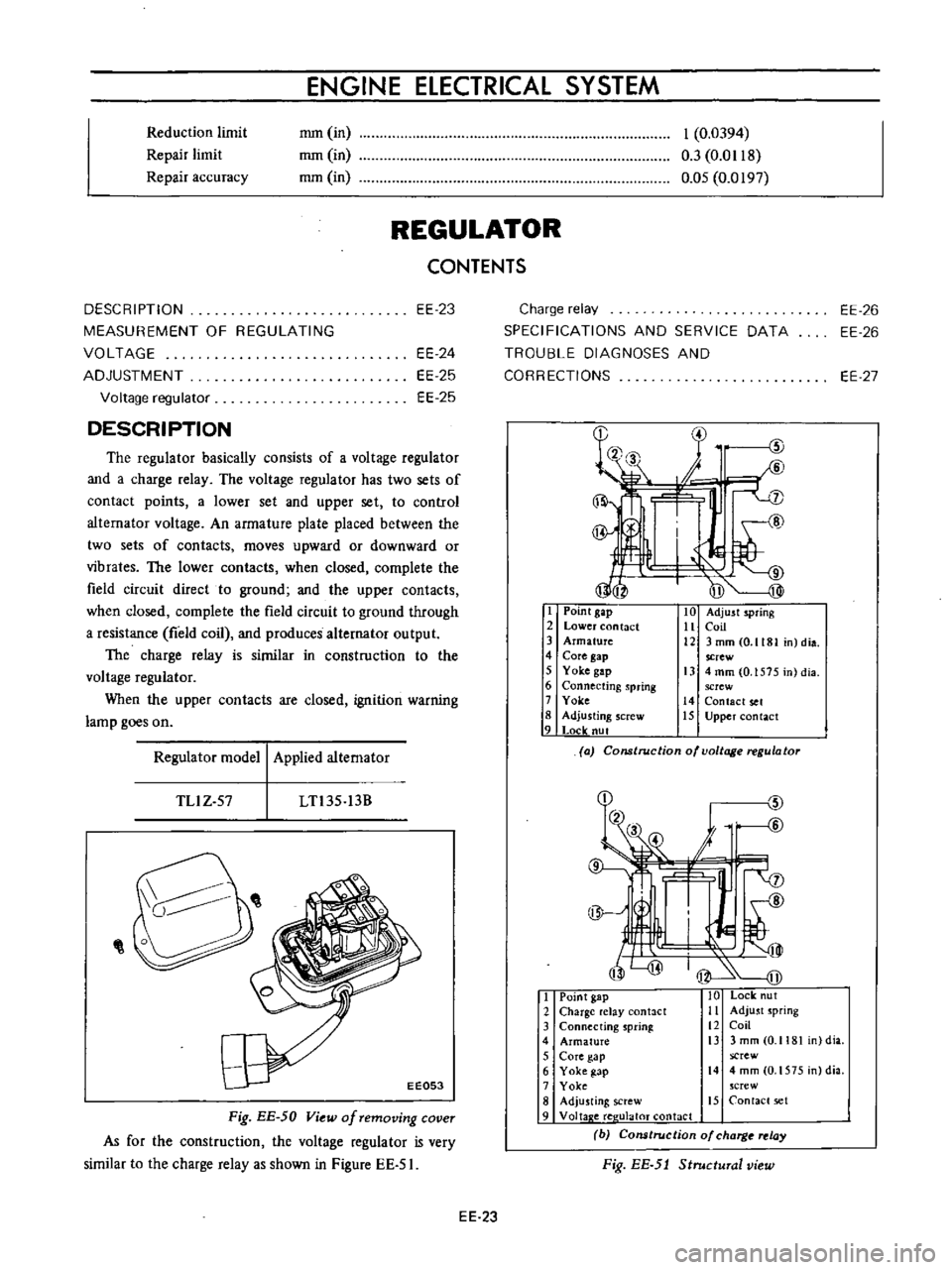
regulator
basically
consists
of
a
voltage
regulator
and
a
charge
relay
The
voltage
regulator
has
two
sets
of
contact
points
a
lower
set
and
upper
set
to
control
altemator
voltage
An
armature
plate
placed
between
the
two
sets
of
contacts
moves
upward
or
downward
or
vibrates
The
lower
contacts
when
closed
complete
the
field
circuit
direct
to
ground
and
the
upper
contacts
when
closed
complete
the
field
circuit
to
ground
through
a
resistance
field
coil
and
produces
alternator
output
The
charge
relay
is
similar
in
construction
to
the
voltage
regulator
When
the
upper
contacts
are
closed
ignition
warning
lamp
goes
on
I
Point
gap
2
Lower
contact
3
Armature
4
Core
gap
5
Yoke
gap
6
Connecting
spring
7
Yoke
8
Adjusting
screw
9
Locle
nut
10
Adjust
spring
11
Coil
12
3mmCO
1181
n
dia
screw
13
4
mm
0
1575
in
dia
screw
14
Contact
set
15
Upper
contact
Regulator
model
Applied
alternator
a
Construction
of
voltage
regulator
TLlZ
57
LTl35
13B
I
Point
gap
10
Lock
ut
2
Charge
elay
antact
Ii
Adjust
spring
3
Connecting
sprinl
12
Coil
4
Armature
i3
3
mm
0
1181
dia
5
Core
gap
screw
6
Yoke
gap
14
4mm
O
1575
n
dia
7
Yoke
crew
8
Adju
ting
screw
15
Contact
set
9
Voltap
e
ree
ulaloT
contact
b
Cons
rue
ion
of
charg
relay
Fig
EE
5J
Structural
view
Fig
EE
50
View
of
removing
cover
As
for
the
construction
the
voltage
regulator
is
very
similar
to
the
charge
relay
as
shown
in
Figure
EE
51
EE
23