light DATSUN B110 1973 Service Manual PDF
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DATSUN, Model Year: 1973, Model line: B110, Model: DATSUN B110 1973Pages: 513, PDF Size: 28.74 MB
Page 418 of 513
FUEL
SYSTEM
Checking
fuel
tank
vacuum
relief
valve
operation
Remove
fuel
filler
cap
and
see
if
it
functions
properly
as
follows
Wipe
clean
valve
housing
and
have
it
in
your
mouth
2
Inhale
air
A
slight
resistance
accompanied
by
valve
indicates
that
valve
is
in
good
mechanical
condition
Note
also
that
by
further
inhaling
air
the
resistance
should
be
disappeared
with
valve
clicks
3
If
valve
seems
to
be
clogged
or
if
no
resistance
is
felt
replace
cap
as
an
assembled
unit
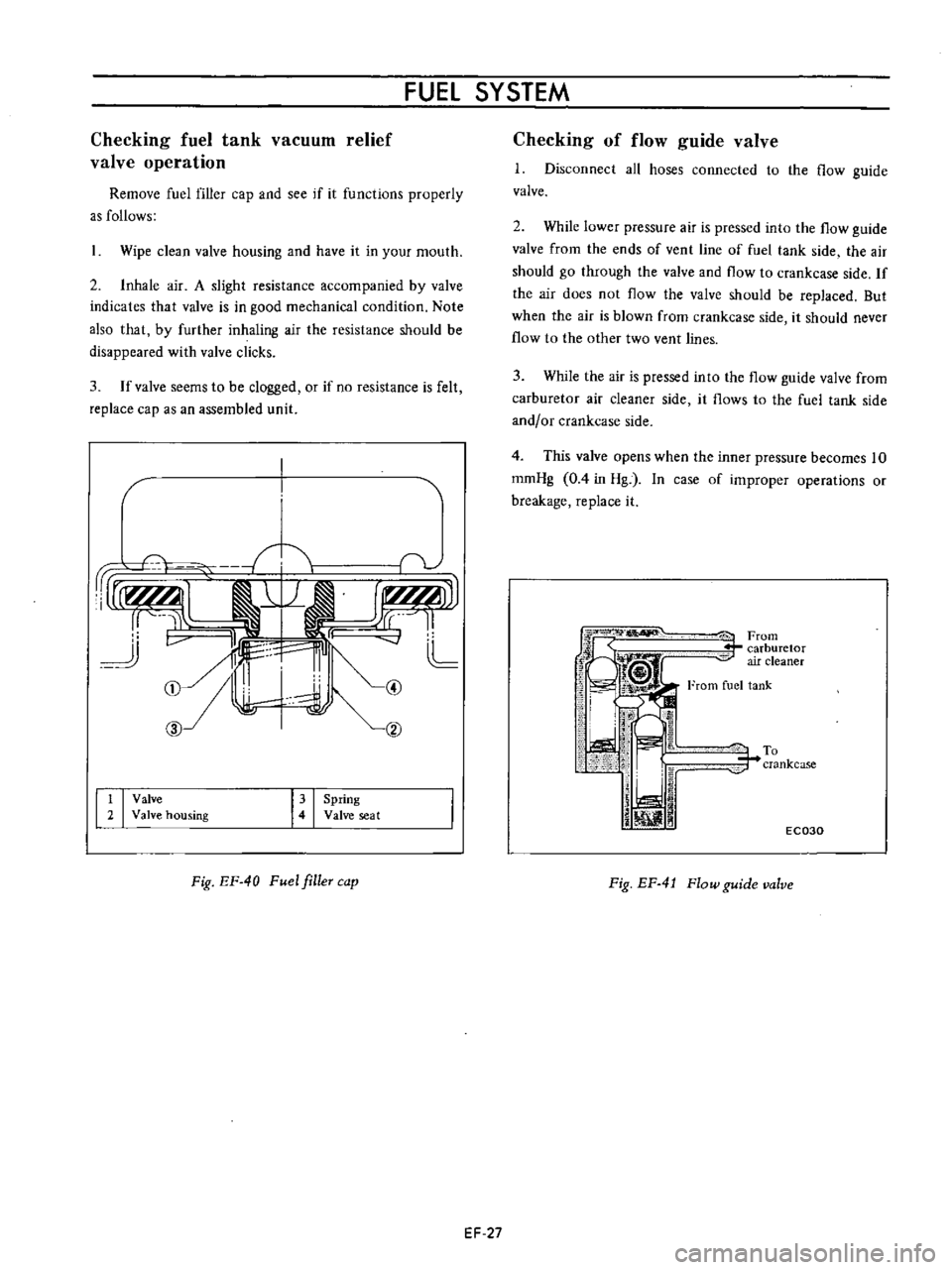
1
1
1I
L
CD
hl
cv
CID
t
I
Valve
2
Valve
housing
I
I
Spring
Valve
seat
Fig
EF
40
Fuel
filleT
cap
EF
27
Checking
of
flow
guide
valve
1
Disconnect
all
hoses
connected
to
the
flow
guide
valve
2
While
lower
pressure
air
is
pressed
into
the
flow
guide
valve
from
the
ends
of
vent
line
of
fuel
tank
side
the
air
should
go
through
the
valve
and
flow
to
crankcase
side
If
the
air
does
not
flow
the
valve
should
be
replaced
But
when
the
air
is
blown
from
crankcase
side
it
should
never
flow
to
the
other
two
vent
lines
3
While
the
air
is
pressed
into
the
flow
guide
valve
from
carburetor
air
cleaner
side
it
flows
to
the
fuel
tank
side
and
or
crankcase
side
4
This
valve
opens
when
the
inner
pressure
becomes
10
romHg
0
4
in
Hg
In
case
of
improper
operations
or
breakage
replace
it
iFrom
r
carburetor
air
cleaner
From
fuel
tank
To
r
crankcase
j
iJ
i
ill
1
1
EC030
Fig
EF
4
J
Flow
guide
valve
Page 425 of 513
ENGINE
ELECTRICAL
SYSTEM
2
Remove
two
bolts
llsed
to
secure
the
starting
motor
on
the
clutch
housing
Pull
the
starter
assembly
forward
and
remove
the
starting
motor
DISASSEMBLY
Remove
the
brush
cover
and
take
out
the
brush
6
Fig
EE
7
Removing
the
brush
cover
2
Loosen
the
nut
used
to
secure
the
connecting
plate
to
the
magnetic
switch
M
terminal
Remove
two
screws
used
to
secure
the
magnetic
switch
Remove
the
cotter
pin
and
withdraw
the
shift
lever
pin
Now
remove
the
magnetic
switch
Fig
EE
8
Removing
the
magnetic
switch
assembly
3
Remove
two
through
bolts
and
rear
cover
assembly
Remove
the
yoke
assembly
by
lightly
tapping
with
a
wooden
mallet
Fig
EE
9
Removing
the
brush
cover
and
yoke
assembly
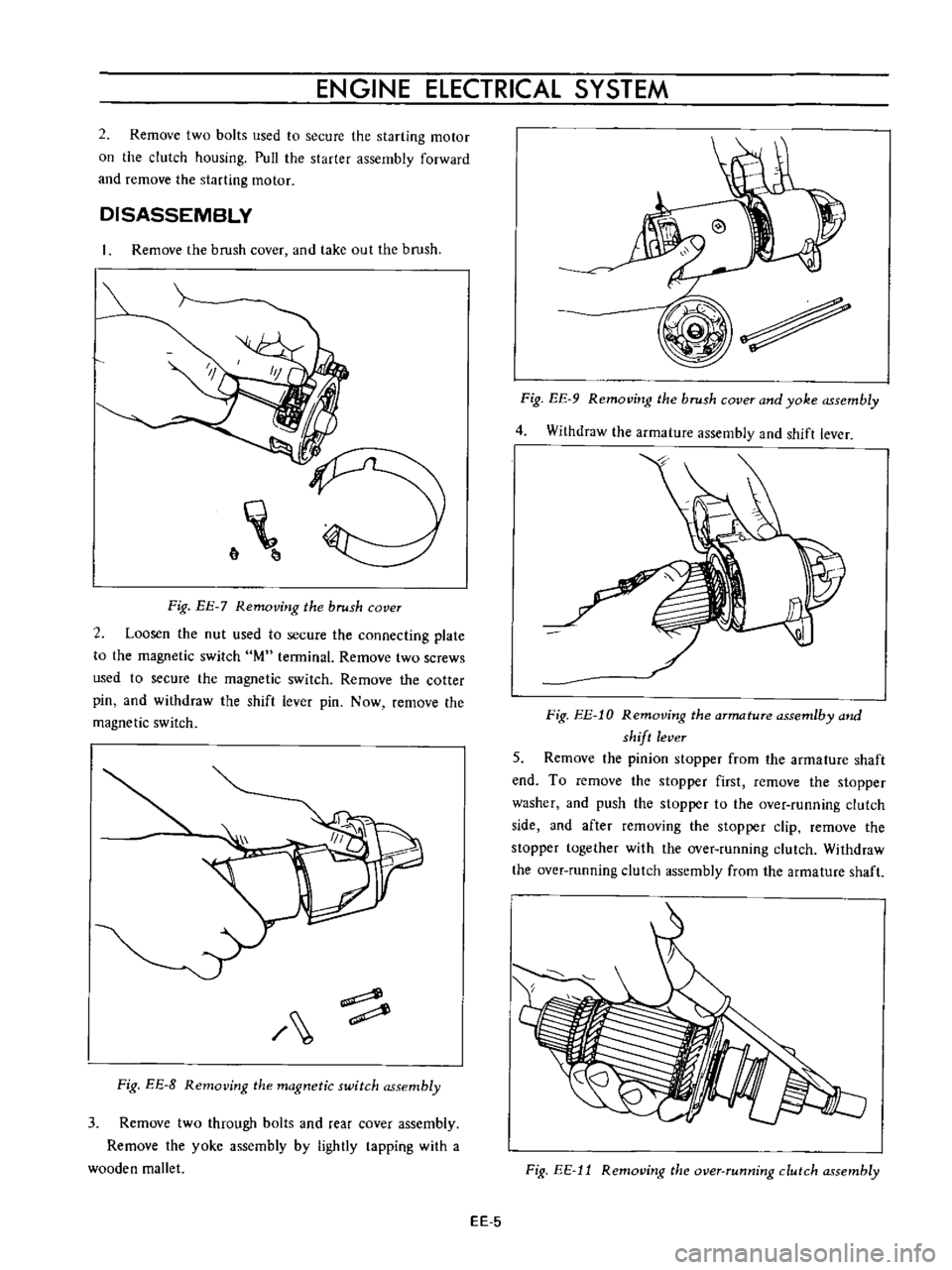
4
Withdraw
the
armature
assembly
and
shift
lever
Fig
EE
l0
Removing
the
armature
assemlby
and
shift
lever
5
Remove
the
pinion
stopper
from
the
armature
shaft
end
To
remove
the
stopper
first
remove
the
stopper
washer
and
push
the
stopper
to
the
over
running
clutch
side
and
after
removing
the
stopper
clip
remove
the
stopper
together
with
the
over
running
clutch
Withdraw
the
over
running
clutch
assembly
from
the
armature
shaft
Fig
EE
11
Removing
the
over
running
clutch
assembly
EE
5
Page 427 of 513
ENGINE
ElECTRICAL
SYSTEM
l
J
r
@
V
I
Fig
EE
14
Inspection
of
brush
spring
pressure
Armature
assembly
Check
external
appearance
of
the
armature
and
the
commutator
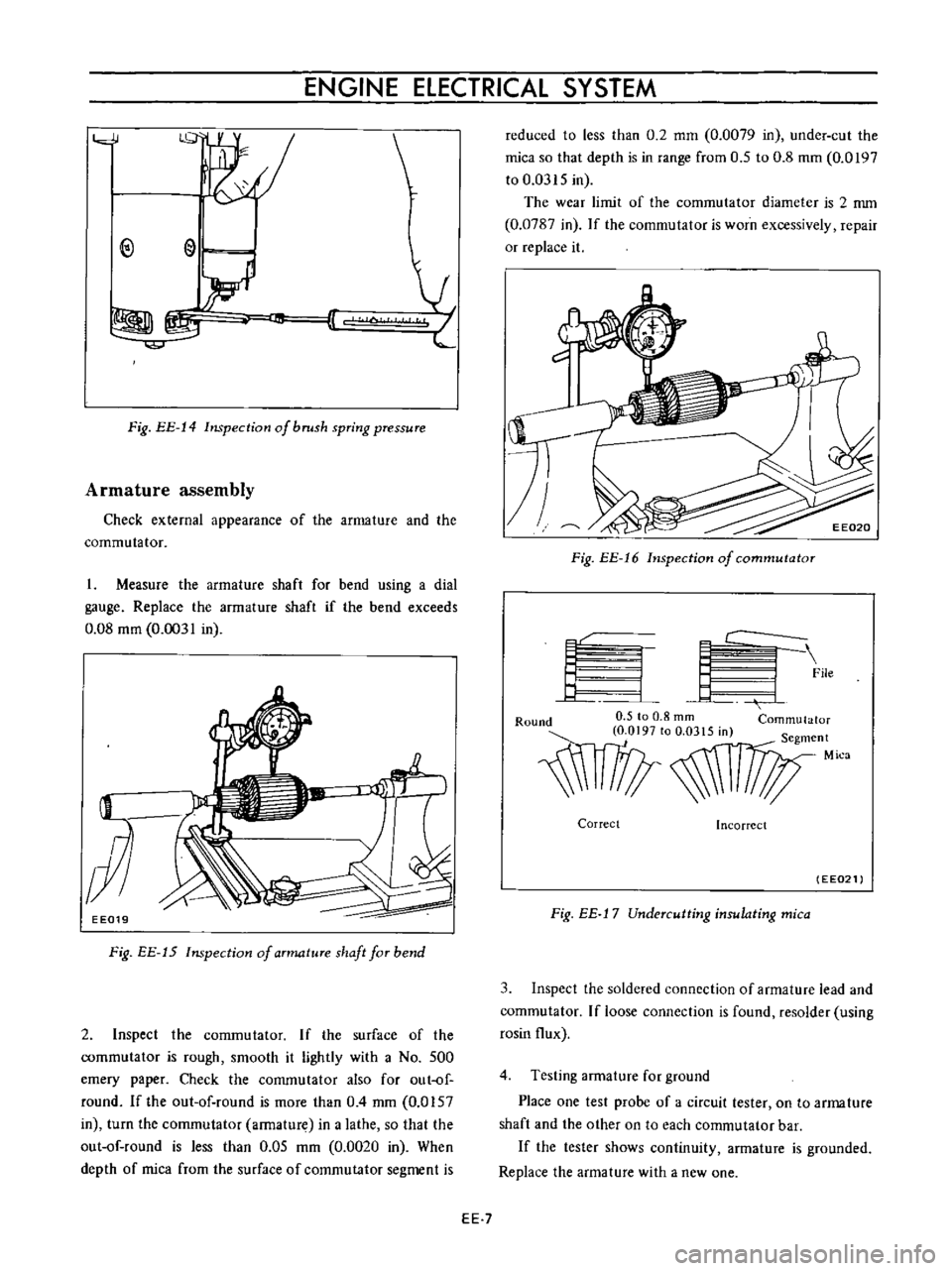
I
Measure
the
armature
shaft
for
bend
using
a
dial
gauge
Replace
the
armature
shaft
if
the
bend
exceeds
0
08
mm
0
0031
in
EE019
Fig
EE
15
Inspection
of
aTmatuTe
shaft
faT
bend
2
Inspect
the
commutator
If
the
surface
of
the
commutator
is
rough
smooth
it
lightly
with
a
No
500
emery
paper
Check
the
commutator
also
for
out
of
round
Ifthe
out
of
round
is
more
than
0
4
mm
0
0157
in
turn
the
commutator
armature
in
a
lathe
so
that
the
out
of
round
is
less
than
0
05
mm
0
0020
in
When
depth
of
mica
from
the
surface
of
commutator
segment
is
reduced
to
less
than
0
2
mm
0
0079
in
under
cut
the
mica
so
that
depth
is
in
range
from
0
5
to
0
8
mm
0
0197
to
0
0315
in
The
wear
limit
of
the
commutator
diameter
is
2
nun
0
0787
in
If
the
commutator
is
worn
excessively
repair
or
replace
it
Fig
EE
16
Inspection
of
commutator
f
L
I
C
9
File
4
J
Round
0
5
to
0
8
rom
Commutator
O
OI97tOO
0315m
S
t
egmen
1l1
Mica
Correct
Incorrect
EE021
Fig
EE
j
7
Undercutting
insulating
mica
3
Inspect
the
soldered
connection
of
armature
lead
and
commutator
If
loose
connection
is
found
resolder
using
rosin
flux
4
Testing
armature
for
ground
Place
one
test
probe
of
a
circuit
tester
on
to
arma
ture
shaft
and
the
other
on
to
each
commutator
bar
If
the
tester
shows
continuity
armature
is
grounded
Replace
the
armature
with
a
new
one
EE
7
Page 429 of 513
ENGINE
ElECTRICAL
SYSTEM
shunt
coil
is
satisfactory
if
the
plunger
is
attracted
continuously
s
SERIES
COIL
S
SHUNT
COIL
Fig
EE
21
Inspecting
series
and
shunt
coils
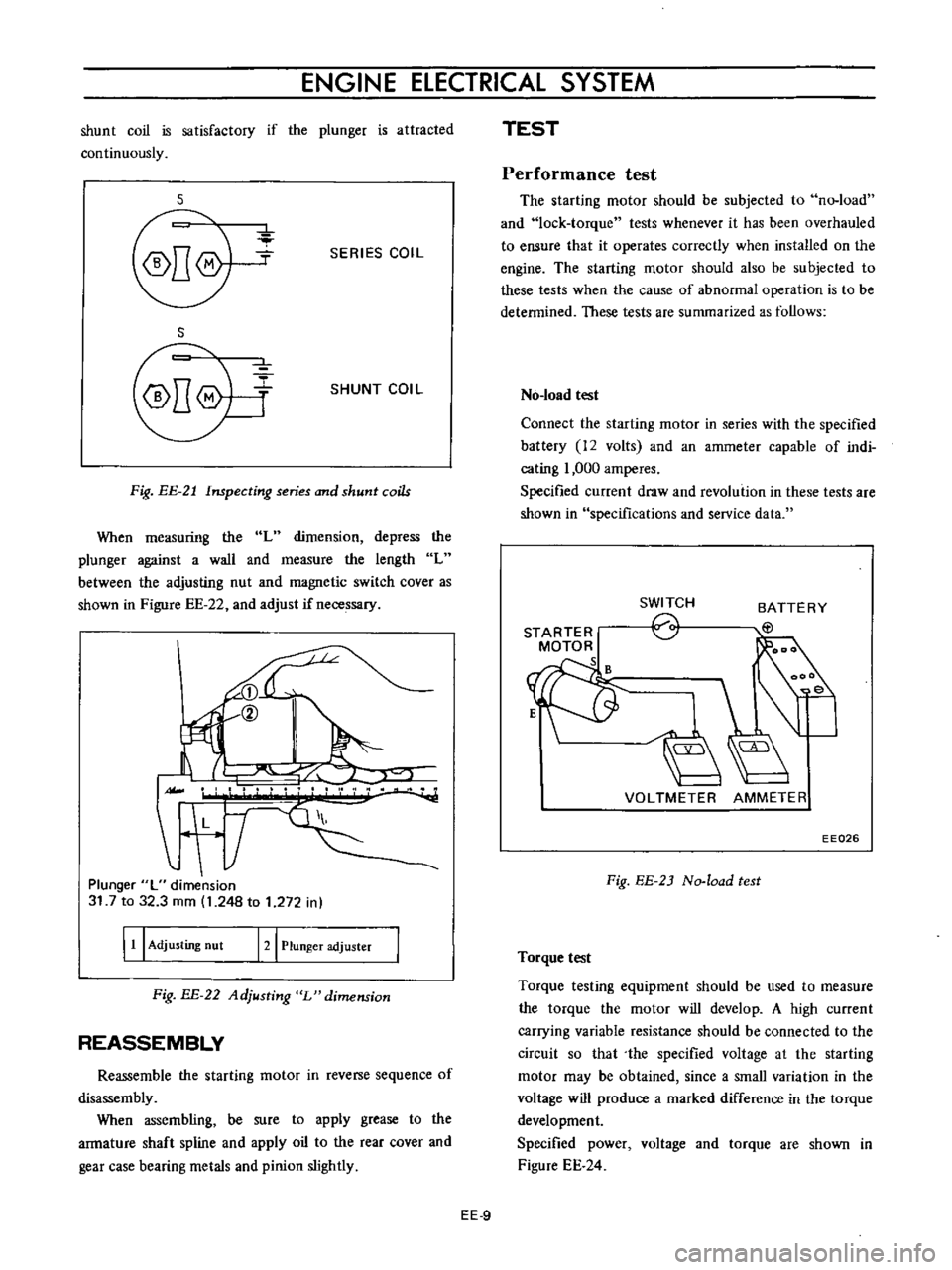
When
measuring
the
L
dimension
depress
the
plunger
against
a
wall
and
measure
the
length
L
between
the
adjusting
nut
and
magnetic
switch
cover
as
shown
in
Figure
EE
22
and
adjust
if
necessary
II
L
T
Plunger
L
dimension
31
7
to
32
3
mm
1
248
to
1
272
in
I
11
I
Adjusting
nut
121
Plunger
adjuster
Fig
BE
22
Adjusting
L
dimension
REASSEMBLY
Reassemble
the
starting
motor
in
reverse
sequence
of
disassembly
When
assembling
be
sure
to
apply
grease
to
the
armature
shaft
spline
and
apply
oil
to
the
rear
cover
and
gear
case
bearing
metals
and
pinion
slightly
TEST
Performance
test
The
starting
motor
should
be
subjected
to
no
load
and
lock
torque
tests
whenever
it
has
been
overhauled
to
ensure
that
it
operates
correctly
when
installed
on
the
engine
The
starting
motor
should
also
be
subjected
to
these
tests
when
the
cause
of
abnormal
operation
is
to
be
determined
These
tests
are
summarized
as
follows
No
load
test
Connect
the
starting
motor
in
series
with
the
specified
battery
12
volts
and
an
ammeter
capable
of
indi
cating
1
000
amperes
Specified
current
draw
and
revolution
in
these
tests
are
shown
in
specifications
and
service
data
STARTER
MOTOR
s
SWITCH
o
BATTERY
EtJ
VOLTMETER
AMMETER
EE026
Fig
EE
2J
No
load
test
Torque
test
Torque
testing
equipment
should
be
used
to
measure
the
torque
the
motor
will
develop
A
high
current
carrying
variable
resistance
should
be
connected
to
the
circuit
so
that
the
specified
voltage
at
the
starting
motor
may
be
obtained
since
a
small
variation
in
the
voltage
will
produce
a
marked
difference
in
the
torque
development
Specified
power
voltage
and
torque
are
shown
in
Figure
EE
24
EE
9
Page 436 of 513
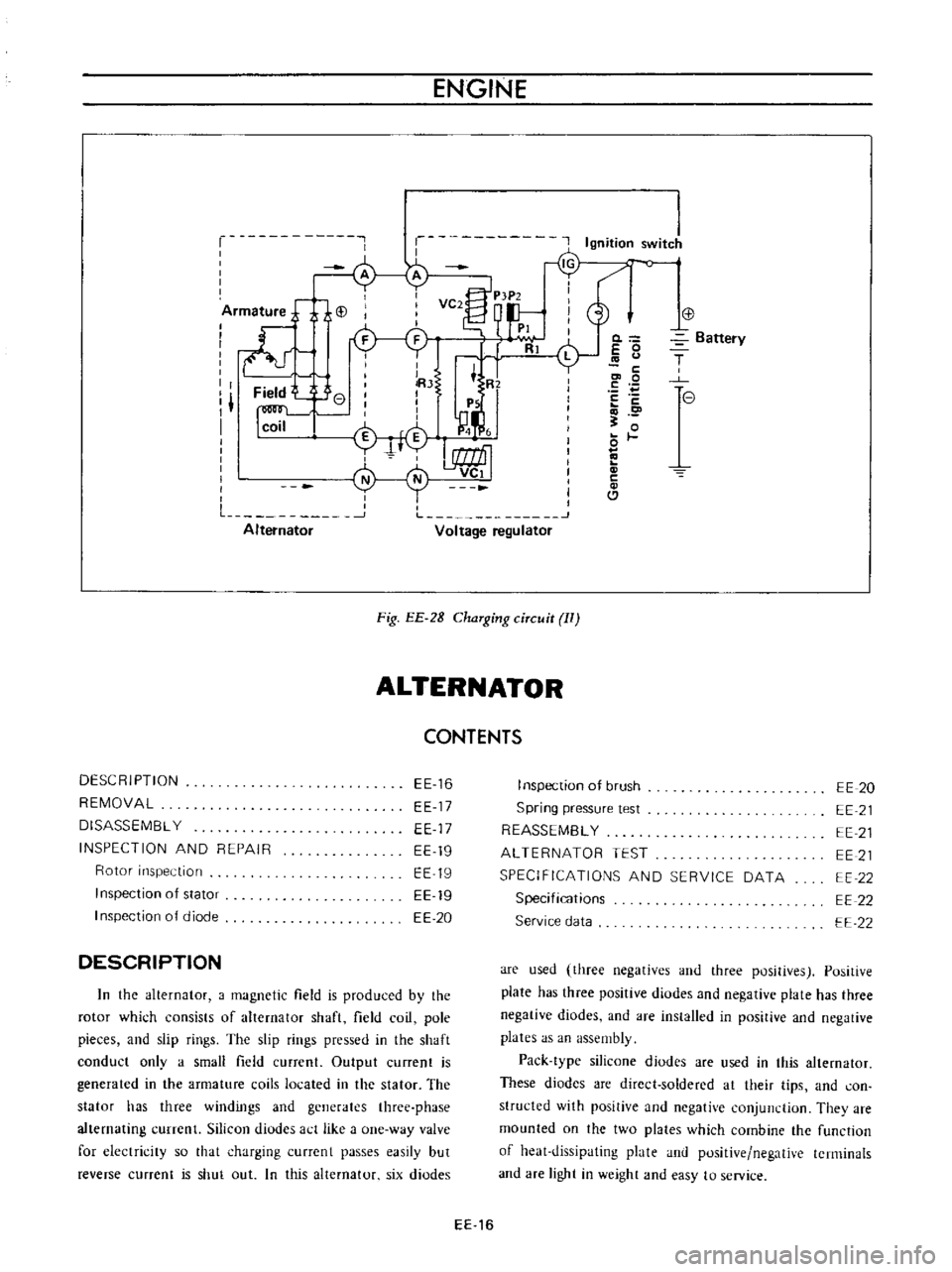
ENGINE
r
Ignition
switJ
c
o
iArm
ture
j
i
i
VC2
P
tP2
d
I
I
I
PI
I
ll
Rl
L
I
I
lRJ
t
R
I
Field
e
I
I
I
I
Ps
I
1
I
I
n
I
coil
M
4
i
f
I
L
1
J
Alternator
Voltage
regulator
Fig
EE
2B
ChaTging
ciTcuit
II
ALTERNATOR
CONTENTS
DESCRIPTION
REMOVAL
DISASSEMBL
Y
INSPECTION
AND
REPAIR
Rotor
inspection
Inspection
of
stator
I
nspection
of
diode
EE
16
EE
17
EE
17
EE
19
EE
19
EE
19
EE
20
DESCRIPTION
In
the
alternator
a
magnetic
field
is
produced
by
the
rotor
which
consists
of
alternator
shaft
field
coil
pole
pieces
and
slip
rings
The
slip
rings
pressed
in
the
shaft
conduct
only
a
small
field
current
Output
current
is
generated
in
the
armature
coils
located
in
the
stator
The
stator
has
three
windings
and
generates
three
phase
alternating
currenl
Silicon
diudes
act
like
a
one
way
valve
for
electricity
so
that
charging
currcnt
passes
easily
but
reverse
current
is
shut
out
In
this
alternator
six
diodes
0
E
0
c
co
0
E
c
o
0
c
Cl
Battery
T
e
I
nspection
of
brush
Spring
pressure
test
REASSEMBL
Y
ALTERNATOR
TEST
SPECIFICATIONS
AND
SERVICE
DATA
Specifications
Service
data
EE
20
EE
21
EE
21
EE
21
EE
22
EE
22
EE
22
are
used
three
negatives
and
three
positives
Positive
plate
has
three
positive
diodes
and
negative
plate
has
three
negative
diodes
and
are
installed
in
positive
and
negative
plates
as
an
assembly
Pack
type
silicone
diodes
are
used
in
this
alternator
These
diodes
are
direct
soldered
at
their
tips
and
con
structed
with
positive
and
negative
conjunction
They
are
mounted
on
the
two
plates
which
combine
the
function
of
heat
dissipating
plate
and
positive
negative
terminals
and
are
light
in
weight
and
easy
to
service
EE
16
Page 438 of 513
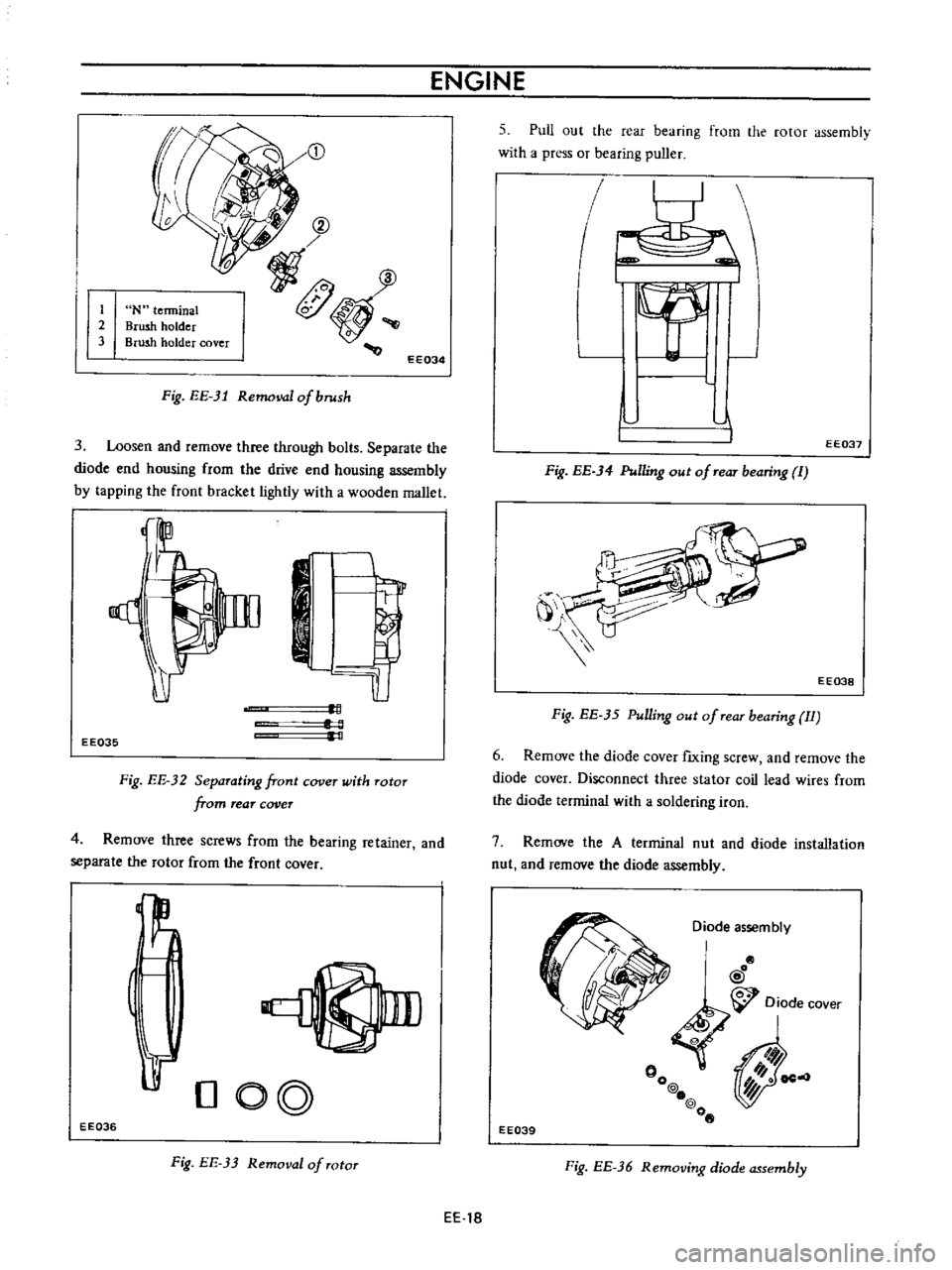
ENGINE
G
2
3
N
terminal
Brush
holder
Brush
holder
cover
@
f
fI
0
EE034
Fig
EE
31
Removal
of
brush
3
Loosen
and
remove
three
through
bolts
Separate
the
diode
end
housing
from
the
drive
end
housing
assembly
by
tapping
the
front
bracket
lightly
with
a
wooden
mallet
1
L
c
EE035
Fig
EE
32
Separating
front
cover
with
Totor
from
rear
cover
4
Remove
three
screws
from
the
bearing
retainer
and
separate
the
rotor
from
the
front
cover
L1
1
t
DO
L
EE036
Fig
EE
33
Removal
of
TOtOT
5
Pull
out
the
rear
bearing
from
the
rotor
assembly
with
a
press
or
bearing
puller
I
I
l
I
EE037
Fig
EE
34
Pulling
out
of
TeaT
bearing
I
j
EE038
Fig
EE
35
Pulling
out
of
Tear
bearing
II
6
Remove
the
diode
cover
fIxing
screw
and
remove
the
diode
cover
Disconnect
three
stator
coil
lead
wires
from
the
diode
terminal
with
a
soldering
iron
7
Remove
the
A
terminal
nut
and
diode
installation
nut
and
remove
the
diode
assembly
Diode
assembly
I
o
@
Diode
cover
rJ
0
00
@
Y
o@
o
EE039
Fig
EE
36
Removing
diode
assembly
EE
18
Page 442 of 513
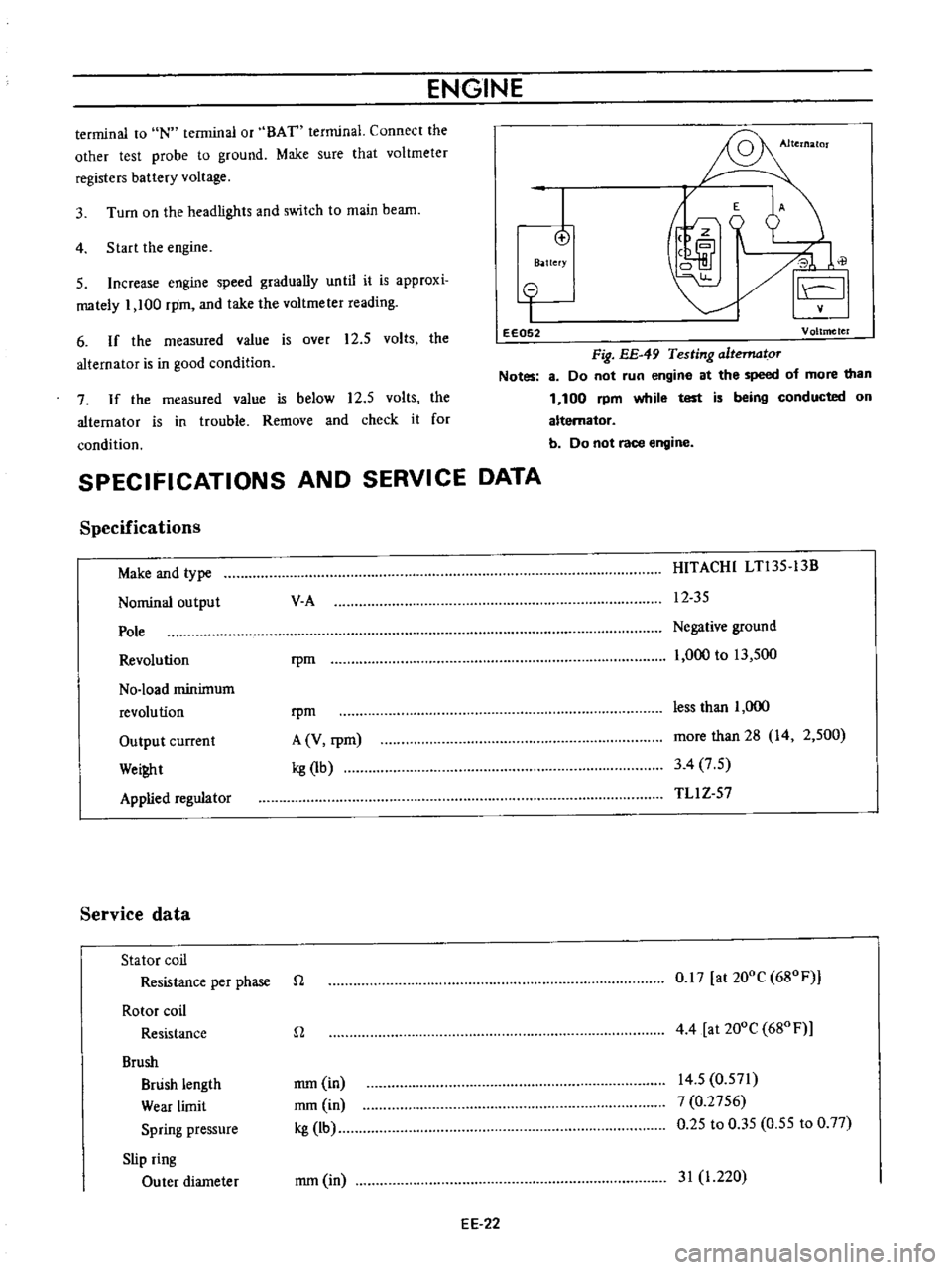
ENGINE
terminal
to
IN
terminal
or
BAT
terminal
Connect
the
other
test
probe
to
ground
Make
sure
that
voltmeter
registers
battery
voltage
4
Start
the
engine
3
Turn
on
the
headlights
and
switch
to
main
beam
I
o
B
ttefY
E
A
J
0
il
I
5
Increase
engine
speed
gradually
until
it
is
approxi
mately
1
100
rpm
and
take
the
voltmeter
reading
6
If
the
measured
value
is
over
12
5
volts
the
alternator
is
in
good
condition
o
I
eE052
Voltmeter
Fig
EE
49
Testing
altematoT
Notes
8
Do
not
run
engine
at
the
speed
of
more
than
1
100
rpm
while
test
is
being
conducted
on
alternator
b
Do
not
race
engine
7
If
the
measured
value
is
below
12
5
volts
the
alternator
is
in
trouble
Remove
and
check
it
for
condition
SPECIFICATIONS
AND
SERVICE
DATA
Specifications
Make
and
type
Nominal
output
Pole
Revolution
No
load
minimum
revolution
Output
current
Wei
t
Applied
regulator
Service
data
Stator
coil
Resistance
per
phase
Rotor
coil
Resistance
Brush
Brush
length
Wear
limit
Spring
pressure
Slip
ring
Outer
diameter
V
A
HITACHI
LTl35
13B
12
35
rpm
Negative
ground
1
000
to
13
500
rpm
A
V
rpm
kg
1b
less
than
1
000
more
than
28
14
2
500
3
4
7
5
TLl
Z
57
n
0
17
at
200C
680F
n
4
4
at
200e
680
F
mm
in
mm
in
kg
lb
14
5
0
571
7
0
2756
0
25
to
0
35
0
55
to
0
77
mm
in
31
1
220
EE
22
Page 445 of 513
ENGINE
ElECTRICAL
SYSTEM
Ambient
temperature
Rated
regulating
voltage
roC
OF
V
10
14
14
6
to
15
6
0
32
14
45
to
15
45
10
50
14
3
to
15
3
20
68
14
15
to
15
15
30
86
14
0
to
15
0
40
104
13
85
to
14
85
Note
8
Do
not
measure
voltage
immediately
after
driv
ing
Do
this
while
regulator
is
cold
b
To
measure
voltage
raise
engine
speed
gradual
ly
from
idling
to
rated
speed
c
Voltage
may
be
approximately
O
3V
higher
than
the
rated
for
two
to
three
minutes
after
engine
is
started
or
more
specifically
when
regulator
becomes
self
heated
Measurements
should
then
be
made
within
one
minute
after
starting
engine
or
when
regulator
is
cold
d
The
regulator
is
of
a
temperature
compensating
type
Before
measuring
voltage
be
sure
to
meas
ure
surrounding
temperature
and
correct
measure
ments
according
to
the
table
in
the
left
hand
side
ADJUSTMENT
Voltage
regulator
As
the
result
of
above
measurement
when
the
regu
lating
voltage
is
deviated
from
the
rated
value
adjust
the
regulator
in
accordance
with
the
following
instructions
I
Inspect
contact
surface
and
if
rough
lightly
polish
the
surface
with
fine
emery
paper
500
or
600
2
Measure
each
gap
and
adjust
if
necessary
Adjust
the
core
gap
and
point
gap
in
that
order
No
adjustment
is
required
for
the
yoke
gap
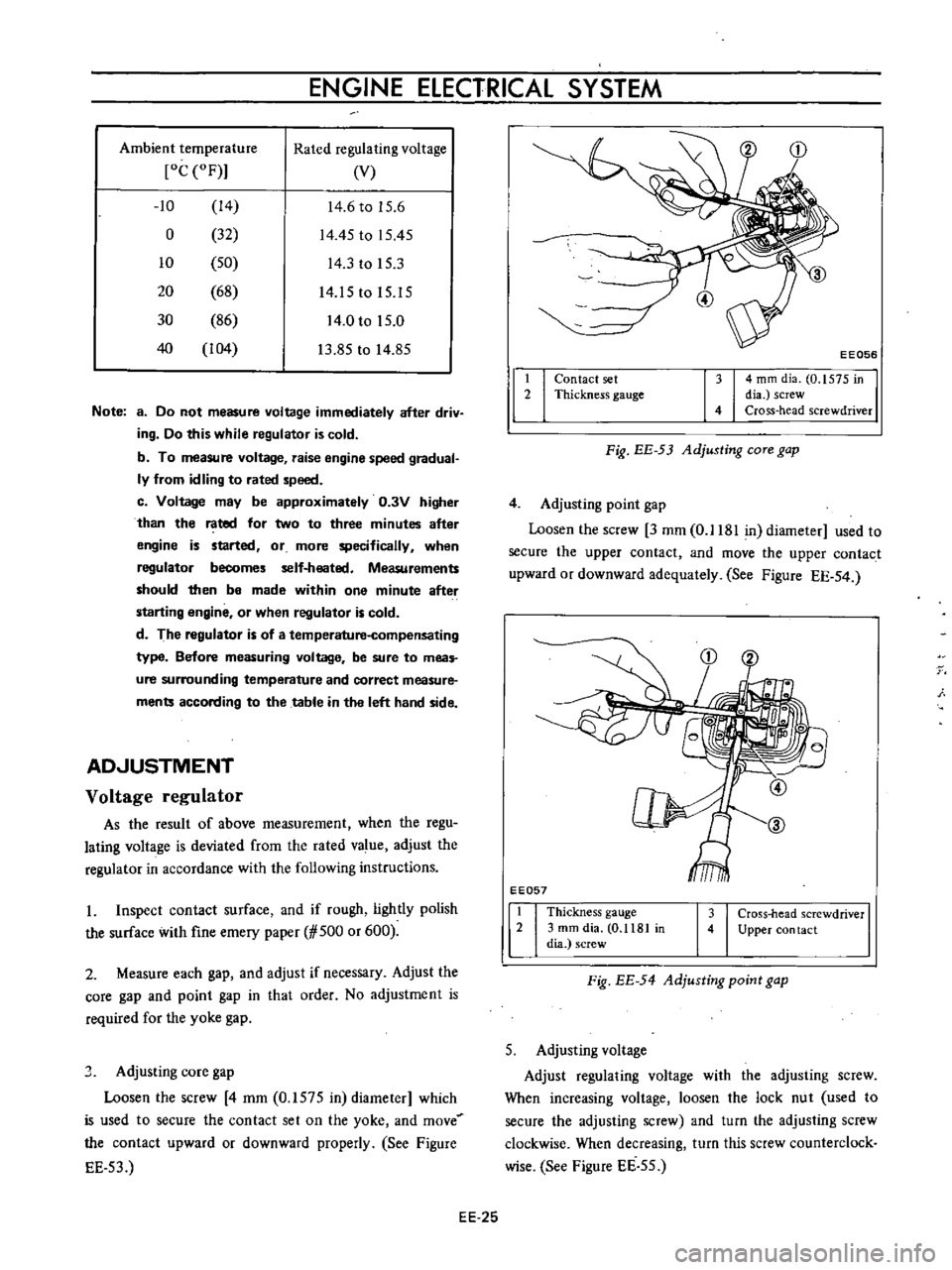
J
Adjusting
core
gap
Loosen
the
screw
4
mm
0
1575
in
diameter
which
is
used
to
secure
the
contact
set
on
the
yoke
and
move
the
contact
upward
or
downward
properly
See
Figure
EE
53
t
2
I
I
EE056
4
mm
dia
0
1575
in
dia
screw
Cross
head
screwdriver
Contact
set
Thickness
gauge
Fig
EE
53
Adjusting
COTe
gap
4
Adjusting
point
gap
Loosen
the
screw
3
mm
0
1181
in
diameter
used
to
secure
the
upper
contact
and
move
the
upper
contact
upward
or
downward
adequately
See
Figure
EE
54
EE057
1
Thickness
gauge
2
3
mm
dia
0
1181
in
dia
screw
3
Cross
head
screwdriver
4
Upper
con
tact
Fig
EE
54
Adjusting
point
gap
5
Adjusting
voltage
Adjust
regulating
voltage
with
the
adjusting
screw
When
increasing
voltage
loosen
the
lock
nut
used
to
secure
the
adjusting
screw
and
turn
the
adjusting
screw
clockwise
When
decreasing
turn
this
screw
counterclock
wise
See
Figure
EE
55
EE
25
Page 446 of 513
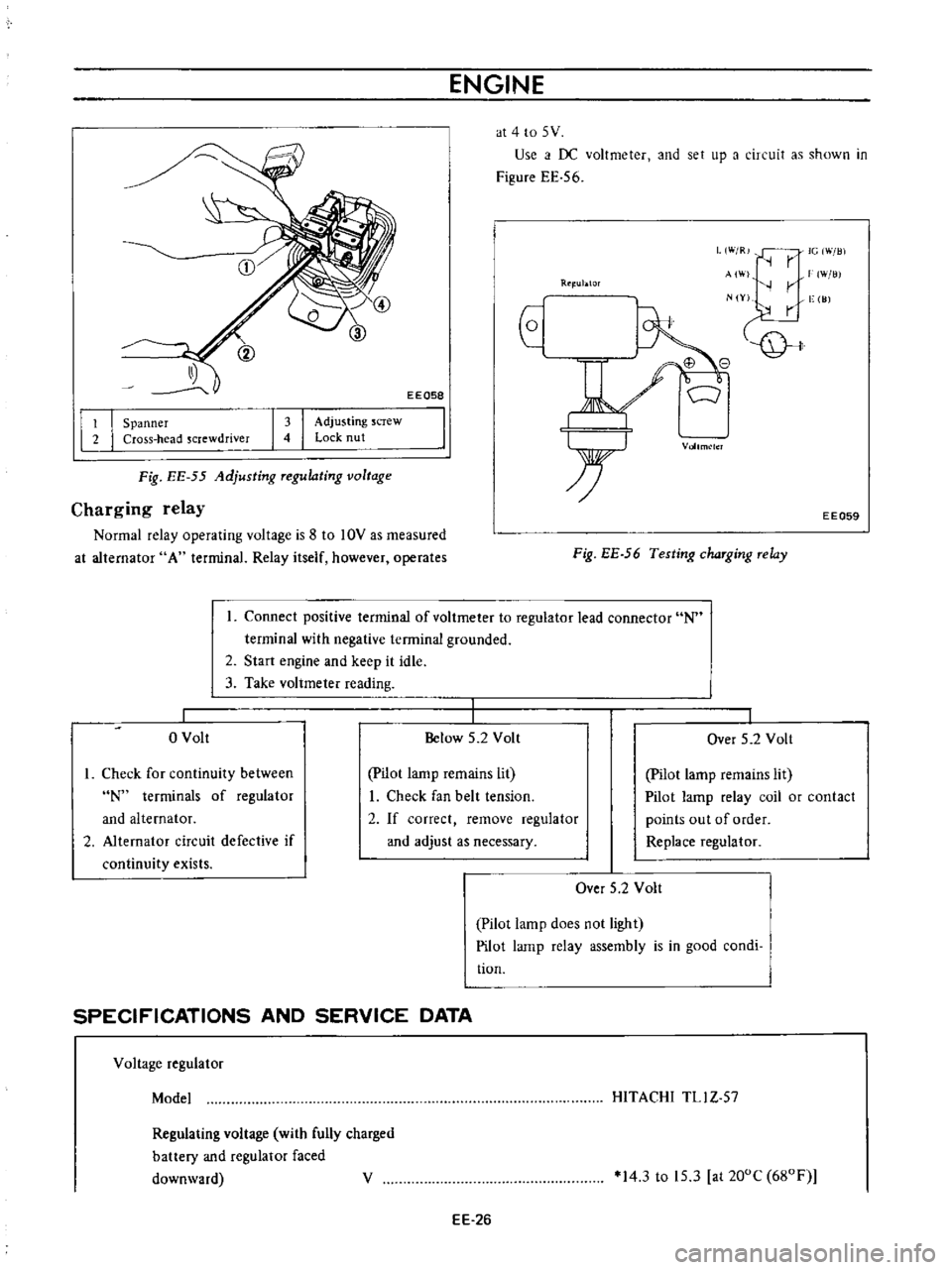
ENGINE
at
4
to
5
V
Use
i
f
DC
voltmeter
and
set
up
a
circuit
as
shown
in
Figure
EE
56
EEQ58
L
W
R
IG
Will
r
AI
W
lli
r
N
Y
vge
I
JJ
Rtl
ublOr
I
I
Spanner
Cross
head
screwdriver
I
I
Adjusting
screw
Lock
nut
Vollm
lcl
Fig
EE
55
Adjusting
Tegulating
voltage
Charging
relay
Normal
relay
operating
voltage
is
8
to
10V
as
measured
at
alternator
A
terminal
Relay
itself
however
operates
EE059
Fig
EE
56
Testing
chaTging
Telay
Connect
positive
terminal
of
voltmeter
to
regulator
lead
connector
N
terminal
with
negative
terminal
grounded
2
Start
engine
and
keep
it
idle
3
Take
voltmeter
reading
o
Volt
Below
5
2
Volt
I
Over
5
2
Volt
I
Check
for
continuity
between
N
terminals
of
regulator
and
alternator
2
Alternator
circuit
defective
if
continuity
exists
pilot
lamp
remains
lit
I
Check
fan
belt
tension
2
If
correct
remove
regulator
and
adjust
as
necessary
Pilot
lamp
remains
lit
Pilot
lamp
relay
coil
or
contact
points
out
of
order
Replace
regulator
Over
5
2
Volt
Pilot
lamp
does
not
light
Pilot
lamp
relay
assembly
is
in
good
condi
tion
SPECIFICATIONS
AND
SERVICE
DATA
Voltage
regulator
Model
HITACHI
TLl
Z
57
Regulating
voltage
with
fully
charged
battery
and
regulator
faced
downward
V
14
3
to
15
3
at
200C
680F
EE
26
Page 457 of 513
ENGINE
ElECTRICAL
SYSTEM
SPECIFICATIONS
Make
and
type
Primary
voltage
v
Spark
gap
mm
in
Primary
resistance
at
200C
680
F
n
Secondary
resistance
at
200C
680F
Kn
External
resistor
at
200C
680
F
n
Applied
resistor
HANSHIN
HITACHI
H5
15
2
C6R
601
12
12
more
than
7
more
than
7
0
28
0
28
1
17
to
I
43
l
l
7
to
I
43
11
2
to
16
8
11
2
to
16
8
l
3tol7
l
3tol7
RC
15
5560R
151O
SPARK
PLUG
CONTENTS
DESCRIPTION
INSPECTION
CLEANING
AND
REGAP
EE
37
EE
37
EE
38
DESCRIPTION
The
spark
plugs
are
of
the
resister
type
having
14
mm
0
551
in
threads
and
0
8
to
0
9
mm
0
031
to
0
Q35
in
gap
Note
All
spark
plugs
installed
on
an
engine
must
be
of
the
same
brand
and
number
of
heat
range
INSPECTION
1
Remove
spark
plug
wire
by
pulling
on
boot
not
on
wire
itself
2
Remove
spark
plugs
3
Check
electrodes
and
inner
and
outer
porcelains
of
plugs
noting
the
type
of
deposits
and
the
degree
of
electrode
erosion
Refer
to
Figure
EE
74
Normal
Brown
to
grayish
tan
deposits
and
slight
elec
trode
wear
indicate
correct
spark
plug
heat
range
SPECIFICATIONS
AND
SERVICE
DATA
TROUBLE
DIAGNOSES
AND
CORRECTIONS
EE
38
EE
39
Carbon
fouled
Dry
fluffy
carbon
deposits
on
the
insula
tor
and
electrode
were
mostly
caused
by
slow
speed
driving
in
city
weak
ignition
too
rich
fuel
mixture
dirty
air
cleaner
etc
H
is
advisable
to
replace
with
plugs
having
hotter
heat
range
Oil
fouled
Wet
black
deposits
show
excessive
oil
en
trance
into
combustion
chamber
through
worn
rings
and
pistons
or
excessive
clearance
between
valve
guides
and
stems
If
the
same
condition
remains
after
repair
use
a
hotter
plug
Overheating
White
or
light
gray
insulator
with
black
or
gray
brown
spots
and
bluish
burnt
electrodes
indicate
engine
overheating
Moreover
the
appearance
results
from
incorrect
ignition
timing
loose
spark
plugs
low
fuel
pump
pressure
wrong
selection
of
fuel
a
hotter
plug
etc
H
is
advisable
to
replace
with
plugs
having
colder
heat
range
EE
37