wiring DATSUN PICK-UP 1977 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DATSUN, Model Year: 1977, Model line: PICK-UP, Model: DATSUN PICK-UP 1977Pages: 537, PDF Size: 35.48 MB
Page 179 of 537

Condition
Engine
Electrical
System
Probable
cause
Starting
motor
cranks
slowly
Dirty
or
worn
commutator
Armature
rubs
field
coil
Damaged
solenoid
switch
Starting
motor
operates
but
does
not
crank
engine
Worn
pinion
Locked
pinion
guide
Worn
ring
gear
Starting
motor
will
not
disengage
even
if
ignition
switch
is
turned
off
Damaged
solenoid
switch
Damaged
gear
teeth
The
charging
circuit
consists
of
the
battery
alternator
regulator
and
necessary
wiring
to
connect
these
parts
The
purpose
of
this
system
is
to
convert
mechanical
energy
from
the
engine
into
electrical
energy
which
is
used
to
operate
all
electrically
operat
ed
units
and
to
keep
the
battery
fully
charged
When
the
ignition
switch
is
set
to
ON
current
flows
from
the
battery
to
ground
through
the
ignition
switch
voltage
regulator
IG
terminal
primary
side
contact
point
PI
movable
contact
point
P2
voltage
regulator
IF
terminal
alternator
IF
terminal
rotor
field
coil
and
alternator
E
terminal
as
shown
in
Figure
EE
23
by
full
line
arrow
marks
Then
the
rotor
in
the
alternator
is
excited
On
the
other
hand
current
flows
from
the
battery
to
ground
through
the
ignition
switch
warning
lamp
voltage
regula
tor
L
terminal
lamp
side
contact
point
P4
movable
contact
point
P5
and
voltage
regulator
E
termi
nal
as
shown
by
dotted
line
arrow
CHARGING
CIRCUIT
marks
Then
the
warning
lamp
lights
When
the
alternator
begins
to
op
erate
three
phase
alternating
current
is
induced
in
the
stator
armature
coil
This
alternating
current
is
rectified
by
the
positive
and
negative
silicon
diodes
The
rectified
direct
current
output
reaches
the
alternator
A
and
E
terminals
On
the
other
hand
the
neutral
point
voltage
reaches
N
and
E
terminals
nearly
a
half
of
the
output
voltage
and
current
flows
from
voltage
regulator
N
terminal
to
E
terminal
or
ground
through
the
coil
VCI
as
shown
in
Figure
EE
24
by
the
dotted
line
arrow
marks
Then
the
coil
VCI
is
excited
and
the
movable
contact
point
IPS
comes
into
contact
with
voltage
winding
side
contact
point
P6
This
action
causes
to
turn
off
the
warning
lamp
and
complete
the
voltage
winding
circuit
as
shown
by
the
full
line
arrow
marks
When
the
alternator
speed
is
in
creased
or
the
voltage
starts
to
rise
excessively
the
movable
contact
point
EE
12
Corrective
action
Clean
and
repair
Replace
assembly
Repair
or
replace
Replace
Repair
Replace
Repair
or
replace
Replace
damaged
gear
P2
is
separated
from
the
primary
side
contact
PI
by
the
magnetic
force
of
coil
VC2
Therefore
registor
RI
is
applied
into
the
rotor
circuit
and
output
voltage
is
decreased
AJ
the
output
voltage
is
decreased
the
movable
contact
point
P2
and
primary
side
contact
Pin
comes
into
contact
once
again
and
the
alternator
voltage
increases
Thus
the
rapid
vibration
of
the
movable
contact
point
IPl
maintains
an
alternator
output
voltage
constant
When
the
alternator
speed
is
further
increased
or
the
voltage
starts
to
rise
excessively
the
movable
contact
point
P2
comes
into
contact
with
secondllJ
side
contact
point
P3
Then
the
rotor
current
is
shut
off
and
alternator
output
voltage
is
decreased
immediately
This
action
causes
movable
contact
n
to
separate
from
secondary
contact
P3
Thus
the
rapid
vibration
of
the
movable
contact
point
P2
or
breaking
and
completing
the
rotor
circuit
maintains
an
alternator
output
voltage
constant
Page 193 of 537
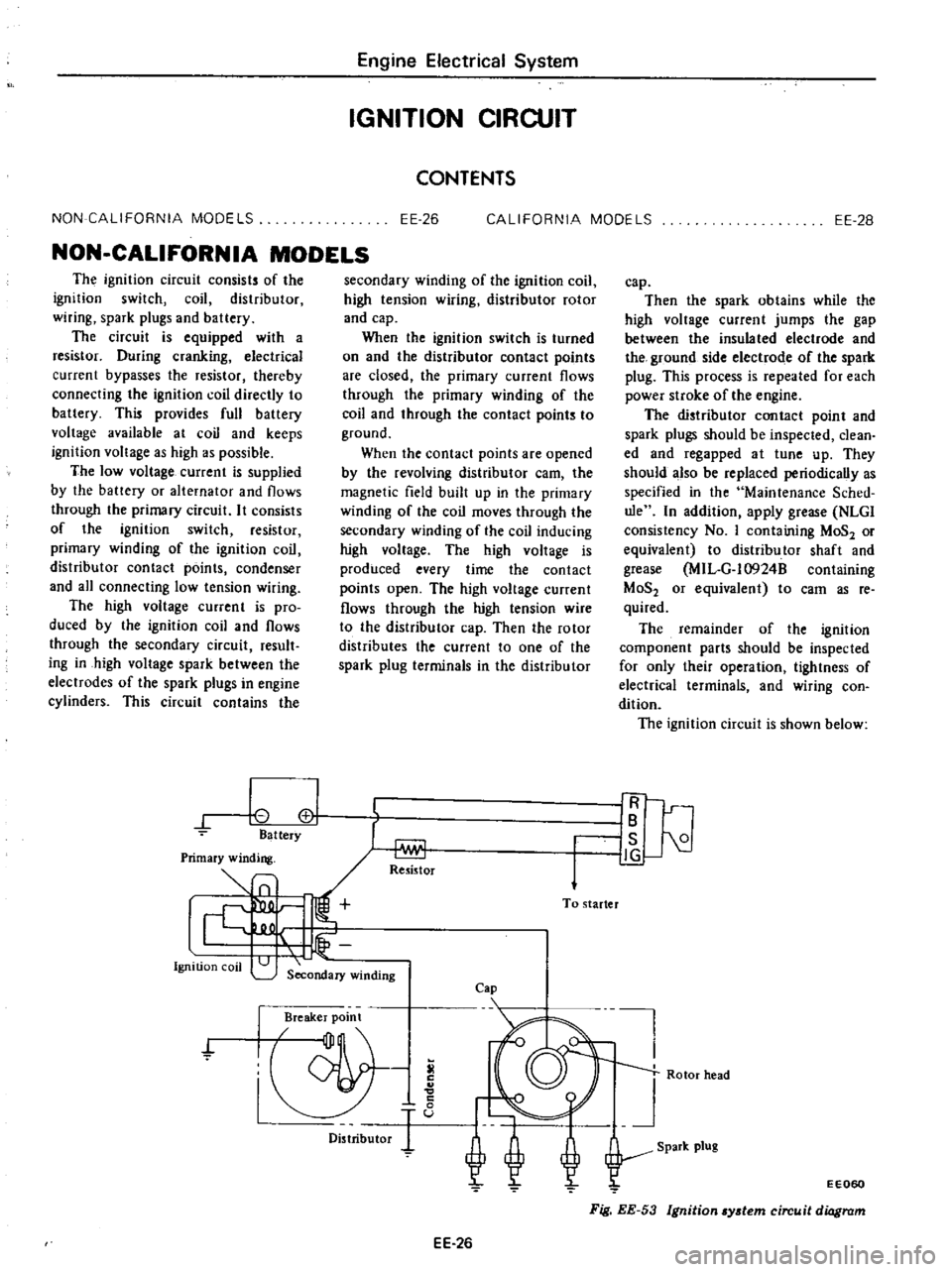
NON
CALIFORNIA
MODELS
Engine
Electrical
System
IGNITION
CIRCUIT
CONTENTS
EE
26
CALIFORNIA
MODELS
EE
2B
NON
CALIFORNIA
MODELS
The
ignition
circuit
consists
of
the
ignition
switch
coil
distributor
wiring
spark
plugs
and
battery
The
circuit
is
equipped
with
a
resistor
During
cranking
electrical
current
bypasses
the
resistor
thereby
connecting
the
ignition
coil
directly
to
battery
This
provides
full
battery
voltage
available
at
coil
and
keeps
ignition
voltage
as
high
as
possible
The
low
voltage
current
is
supplied
by
the
battery
or
alternator
and
flows
through
the
primary
circuit
It
consists
of
the
ignition
switch
resistor
primary
winding
of
the
ignition
coil
distributor
contact
points
condenser
and
all
connecting
low
tension
wiring
The
high
voltage
current
is
pro
duced
by
the
ignition
coil
and
flows
through
the
secondary
circuit
result
ing
in
high
voltage
spark
between
the
electrodes
of
the
spark
plugs
in
engine
cylinders
This
circuit
contains
the
0
cl
Battery
Ignition
coil
secondary
winding
of
the
ignition
coil
high
tension
wiring
distributor
rotor
and
cap
When
the
ignition
switch
is
turned
on
and
the
distributor
contact
points
are
closed
the
primary
current
flows
through
the
primary
winding
of
the
coil
and
through
the
contact
points
to
ground
When
the
contact
points
are
opened
by
the
revolving
distributor
earn
the
magnetic
field
built
up
in
the
primary
winding
of
the
coil
moves
through
the
secondary
winding
of
the
coil
inducing
high
voltage
The
high
voltage
is
produced
every
time
the
contact
points
open
The
high
voltage
current
flows
through
the
high
tension
wire
to
the
distributor
cap
Then
the
rotor
distributes
the
current
to
one
of
the
spark
plug
terminals
in
the
distributor
Re5istor
To
starter
Secondary
winding
Cap
Breaker
point
f
Distributor
EE
26
cap
Then
the
spark
obtains
while
the
high
voltage
current
jumps
the
gap
between
the
insulated
electrode
and
the
ground
side
electrode
of
the
spark
plug
This
process
is
repeated
for
each
power
stroke
of
the
engine
The
distributor
contact
point
and
spark
plugs
should
be
inspected
clean
ed
and
regapped
at
tune
up
They
should
also
be
replaced
periodically
as
specified
in
the
Maintenance
Sched
ule
In
addition
apply
grease
NLGl
consistency
No
I
containing
MoS2
or
equivalent
to
distributor
shaft
and
grease
MIL
G
l0924B
containing
MoS2
or
equivalent
to
cam
as
reo
quired
The
remainder
of
the
ignition
component
parts
should
be
inspected
for
only
their
operation
tightness
of
electrical
terminals
and
wiring
con
dition
The
ignition
circuit
is
shown
below
IR
IB
I
is
21
J
g
Rotor
head
EE060
Fig
EE
53
Ignition
ydem
circuit
diagram
Page 195 of 537
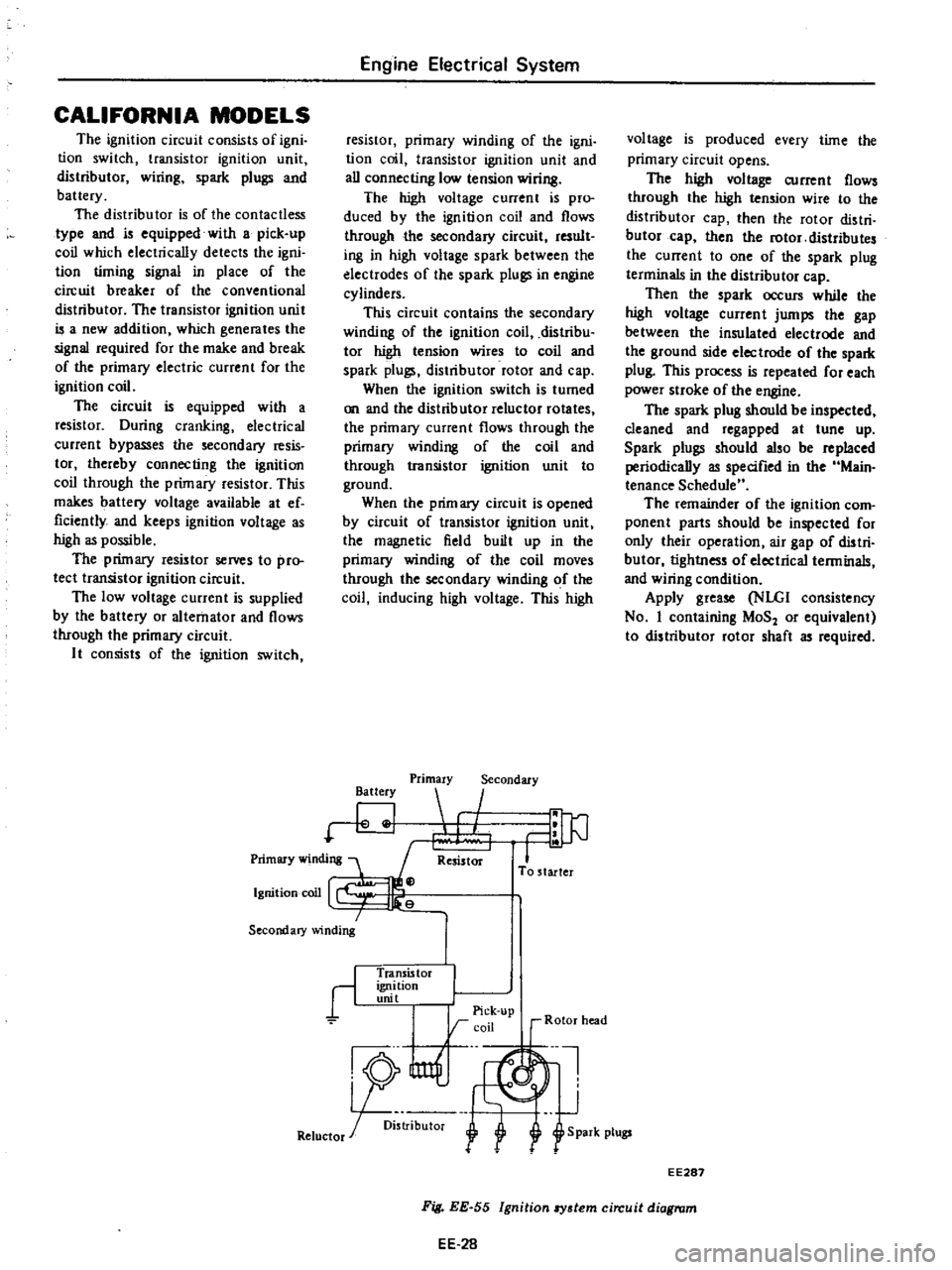
Primary
winding
1
Ignition
coo
I
Secondary
winding
CALIFORNIA
MODELS
The
ignition
circuit
consists
of
igni
tion
switch
transistor
ignition
unit
distributor
wiring
spark
plugs
and
battery
The
distributor
is
of
the
contactless
type
and
is
equipped
with
a
pick
up
coil
which
electrically
detects
the
igni
tion
timing
signal
in
place
of
the
circuit
breaker
of
the
conventional
distributor
The
transistor
ignition
unit
is
a
new
addition
which
generates
the
signal
required
for
the
make
and
break
of
the
primary
electric
current
for
the
ignition
coil
The
circuit
is
equipped
with
a
resistor
During
cranking
electrical
current
bypasses
the
secondary
resis
tor
thereby
connecting
the
ignition
coil
through
the
primary
resistor
This
makes
battery
voltage
available
at
ef
ficiently
and
keeps
ignition
voltage
as
high
as
possible
The
primary
resistor
selVeS
to
pro
tect
transistor
ignition
circuit
The
low
voltage
current
is
supplied
by
the
battery
or
alternator
and
flows
through
the
primary
circuit
It
consists
of
the
ignition
switch
Engine
Electrical
System
resistor
primary
winding
of
the
igni
tion
coil
transistor
ignition
unit
and
all
connecting
low
tension
wiring
The
high
voltage
current
is
pro
duced
by
the
ignition
coil
and
flows
through
the
secondary
circuit
result
ing
in
high
voltage
spark
between
the
electrodes
of
the
spark
plugs
in
engine
cylinders
This
circuit
contains
the
secondary
winding
of
the
ignition
coil
distribu
tor
high
tension
wires
to
coil
and
spark
plugs
distributor
rotor
and
cap
When
the
ignition
switch
is
turned
on
and
the
distributor
reluctor
rotates
the
primary
current
flows
through
the
primary
winding
of
the
coil
and
through
transistor
ignition
unit
to
ground
When
the
prim
ary
circuit
is
opened
by
circuit
of
transistor
ignition
unit
the
magnetic
field
built
up
in
the
primary
winding
of
the
coil
moves
through
the
secondary
winding
of
the
coil
inducing
high
voltage
This
high
Battery
Primary
Secondary
I
Resistor
To
starter
r
Transis
tor
ignition
unit
I
I
Pick
up
rcoil
r
Rotor
head
nl
J
R5
U1f
1
Retuctor
r
oi
l
f
S
park
plugs
voltage
is
produced
every
time
the
primary
circuit
opens
The
high
voltage
current
flows
through
the
high
tension
wire
to
the
distributor
cap
then
the
rotor
distri
butor
cap
then
the
rotor
distributes
the
current
to
one
of
the
spark
plug
terminals
in
the
distributor
cap
Then
the
spark
occurs
while
the
high
voltage
current
jumps
the
gap
between
the
insulated
electrode
and
the
ground
side
electrode
of
the
spark
plug
This
process
is
repeated
for
each
power
stroke
of
the
engine
The
spark
plug
should
be
inspected
cleaned
and
regapped
at
tune
up
Spark
plugs
should
also
be
replaced
periodically
as
specified
in
the
Main
tenance
Schedule
The
remainder
of
the
ignition
com
ponent
parts
should
be
inspected
for
only
their
operation
air
gap
of
distri
butor
tightness
of
electrical
terminals
and
wiring
condition
Apply
grease
NLGI
consistency
No
I
containing
MoS
or
equivalent
to
distributor
rotor
shaft
as
required
EE287
EE
28
Fig
EE
55
Ignition
8Y3tem
circuit
diagram
Page 204 of 537
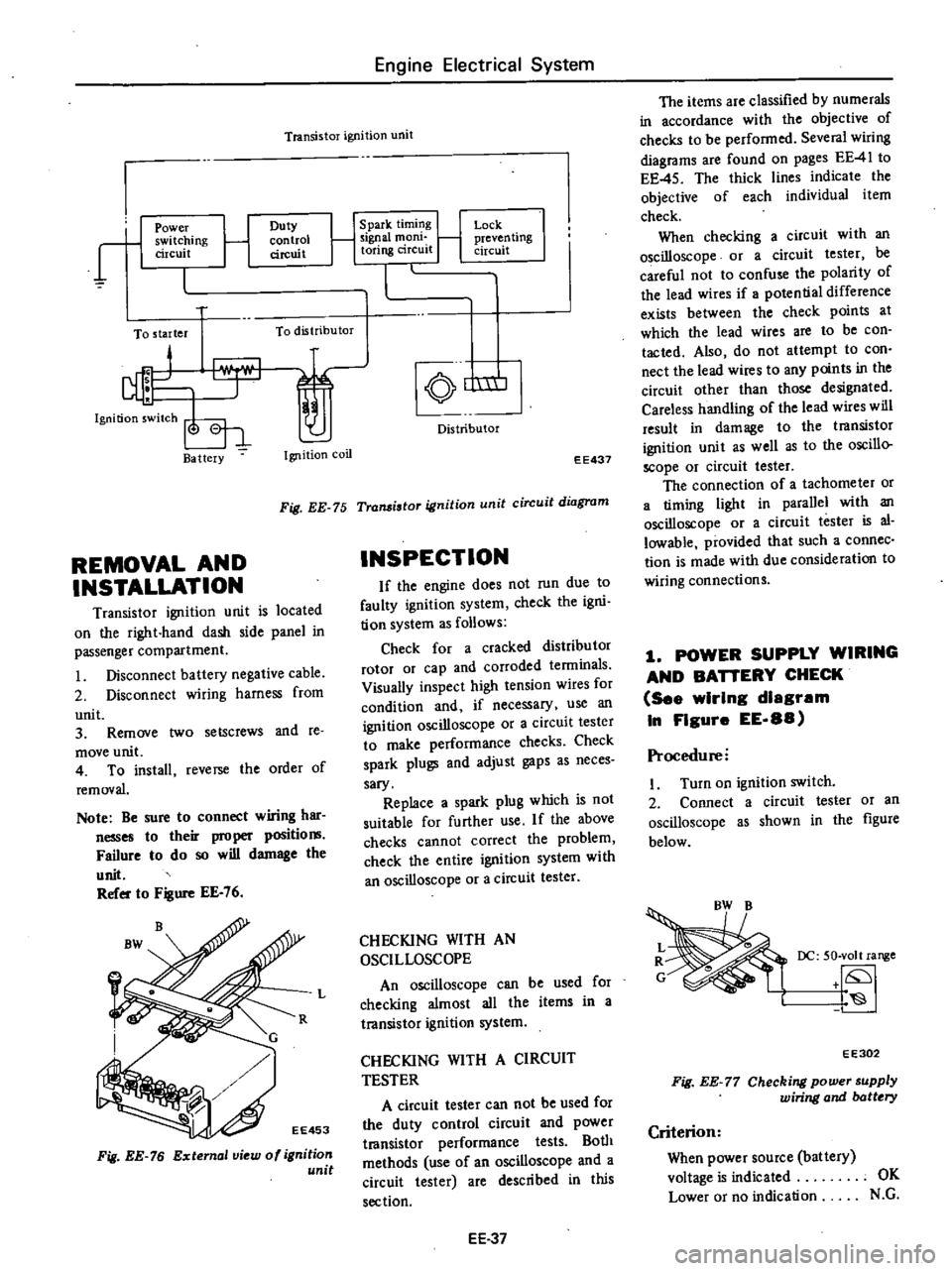
Engine
Electrical
System
Transistor
ignition
unit
r
1
Power
switching
circuit
Duty
control
circuit
To
starter
To
distributor
Ba
ttery
Ignition
coil
1
Spark
timing
1
Signal
mom
toring
circuit
Lock
j
preven
ling
circuit
nm
Distributor
EE437
Fig
EE
75
Transistor
ignition
unit
circuit
diagram
REMOVAL
AND
INSTALLATION
Transistor
ignition
unit
is
located
on
the
right
hand
dash
side
panel
in
passenger
compartment
Disconnect
battery
negative
cable
2
Disconnect
wiring
harness
from
unit
3
Remove
two
setscrews
and
te
move
unit
4
To
install
reverse
the
order
of
removal
Note
Be
sure
to
connect
wiring
har
nesses
to
their
proper
positio
Failure
to
do
so
will
damage
the
unit
Refer
to
Figure
EE
76
Fig
EE
76
External
view
of
ignition
unit
INSPECTION
If
the
engine
does
not
run
due
to
faulty
ignition
system
check
the
igni
tion
system
as
follows
Check
for
a
cracked
distributor
rotor
or
cap
and
corroded
tenninals
Visually
inspect
high
tension
wires
for
condition
and
if
necessary
use
an
ignition
oscilloscope
or
a
circuit
tester
to
make
performance
checks
Check
spark
plugs
and
adjust
gaps
as
neces
sary
Replace
a
spark
plug
which
is
not
suitable
for
further
use
If
the
above
checks
cannot
correct
the
problem
check
the
entire
ignition
system
with
an
oscilloscope
or
a
circuit
tester
L
CHECKING
WITH
AN
OSCILLOSCOPE
An
oscilloscope
can
be
used
for
checking
almost
all
the
items
in
a
transistor
ignition
system
CHECKING
WITH
A
CIRCUIT
TESTER
A
circuit
tester
can
not
be
used
for
the
duty
control
circuit
and
power
t18nsistor
performance
tests
Both
methods
use
of
an
oscilloscope
and
a
circuit
tester
are
described
in
this
section
EE
37
The
items
are
classified
by
numerals
in
accordance
with
the
objective
of
checks
to
be
performed
Several
wiring
diagrams
are
found
on
pages
EE
41
to
EE
45
The
thick
lines
indicate
the
objective
of
each
individual
item
check
When
checking
a
circuit
with
an
oscilloscope
or
a
circuit
tester
be
careful
not
to
confuse
the
polarity
of
the
lead
wires
if
potential
difference
exists
between
the
check
points
at
which
the
lead
wires
are
to
be
con
tacted
Also
do
not
attempt
to
con
nect
the
lead
wires
to
any
points
in
the
circuit
other
than
those
designated
Careless
handling
of
the
lead
wires
will
result
in
damage
to
the
transistor
ignition
unit
as
well
as
to
the
oscillo
scope
or
circuit
tester
The
connection
of
a
tachometer
or
a
timing
light
in
parallel
with
an
oscilloscope
or
a
circuit
tester
is
al
lowable
provided
that
such
a
connec
tion
is
made
with
due
consideration
to
wiring
connections
1
POWER
SUPPLY
WIRING
AND
BAnERY
CHECK
See
wIrIng
diagram
In
FIgure
EE
88
Procedure
I
Turn
on
ignition
switch
2
Connect
a
circuit
tester
or
an
oscilloscope
as
shown
in
the
figure
below
DC
50
volt
range
EE302
Fig
EE
77
Checking
power
supply
wiring
and
batt
ry
Criterion
When
power
source
battery
voltage
is
indicated
OK
Lower
or
no
indication
N
G
Page 205 of 537
If
the
result
is
N
C
Take
the
following
measures
I
Check
BW
and
B
color
wire
harness
respectively
for
proper
con
ductance
2
Check
battery
terminals
for
proper
connection
3
Check
charge
condition
of
bat
tery
if
an
excessively
low
voltage
is
indicated
2
CONTINUITY
CHECK
OF
PRIMARY
CIRCUIT
2
1
CheckIng
prImary
circuit
See
wiring
diagram
In
Fig
EE
89
Proced
ure
I
Disconnect
L
color
wire
from
ignition
unit
2
Turn
on
ignition
switch
3
C
ooneet
a
cireui
t
tester
or
an
oscilloscope
as
shown
in
Figure
EE
78
DC
50
volt
range
tf
S
EE303
Fig
EE
78
Checking
primary
circuit
Criterion
When
Donnal
power
Source
battery
voltage
is
indicated
OK
Lower
or
no
indication
N
G
If
the
result
is
N
C
Take
the
following
measures
1
Check
BW
and
L
color
wire
Engine
Electrical
System
harness
respectively
for
proper
con
ductance
2
Check
resistor
and
ignition
coil
terminals
for
loose
contact
3
Check
resistor
and
ignition
coil
for
discontinuity
4
Check
WB
color
wire
harness
of
ignition
coil
assembly
for
proper
continuity
2
2
Chacklng
IgnitIon
coil
auembly
See
wiring
diagram
In
Fig
EE
90
Procedure
I
Disconnect
ignition
coil
and
dis
tributor
harness
from
ignition
coil
external
resistor
2
Connect
a
circuit
tester
as
shown
in
the
figure
below
Resistance
1
range
Q
o
fD
ro
EE336
Fig
EE
79
Checking
ignition
coil
assembly
Criterion
When
approximately
1
6
to
2
0
ohm
is
indicated
OK
More
than
2
0
ohm
N
C
If
the
result
is
N
C
Replace
ignition
coil
assembly
3
PICK
UP
COIL
CONTINUITY
CHECK
See
wirIng
dIagram
In
Figure
EE
91
Procedure
Disconnect
R
and
G
color
wires
from
ignition
unit
2
Connect
a
circuit
tester
as
shown
in
the
figure
below
EE
3B
Resistance
10
range
fp
EE305
Fig
EE
BO
Checking
pick
up
coil
Criterion
When
approximately
720
ohm
is
indicated
OK
Far
less
than
or
more
than
720
ohm
N
C
If
the
result
is
N
C
Replace
pick
up
coil
assembly
4
PICK
UP
COIL
POWER
SIGNAL
PULSE
CHECK
Procedure
I
Disconnect
anti
dieseling
solenoid
valve
connector
2
Connect
a
circuit
tester
as
shown
in
the
figure
below
3
Rotate
starter
motor
4
Read
the
tester
indication
AC
2
S
volt
range
EE306
Fig
EE
81
Checking
pick
up
coil
power
aignal
pulse
Criterion
When
pointer
deflects
slightly
OK
When
pointer
does
not
deflect
at
all
N
C
If
the
result
is
N
C
Replace
pick
up
coil
assembly
Page 206 of 537
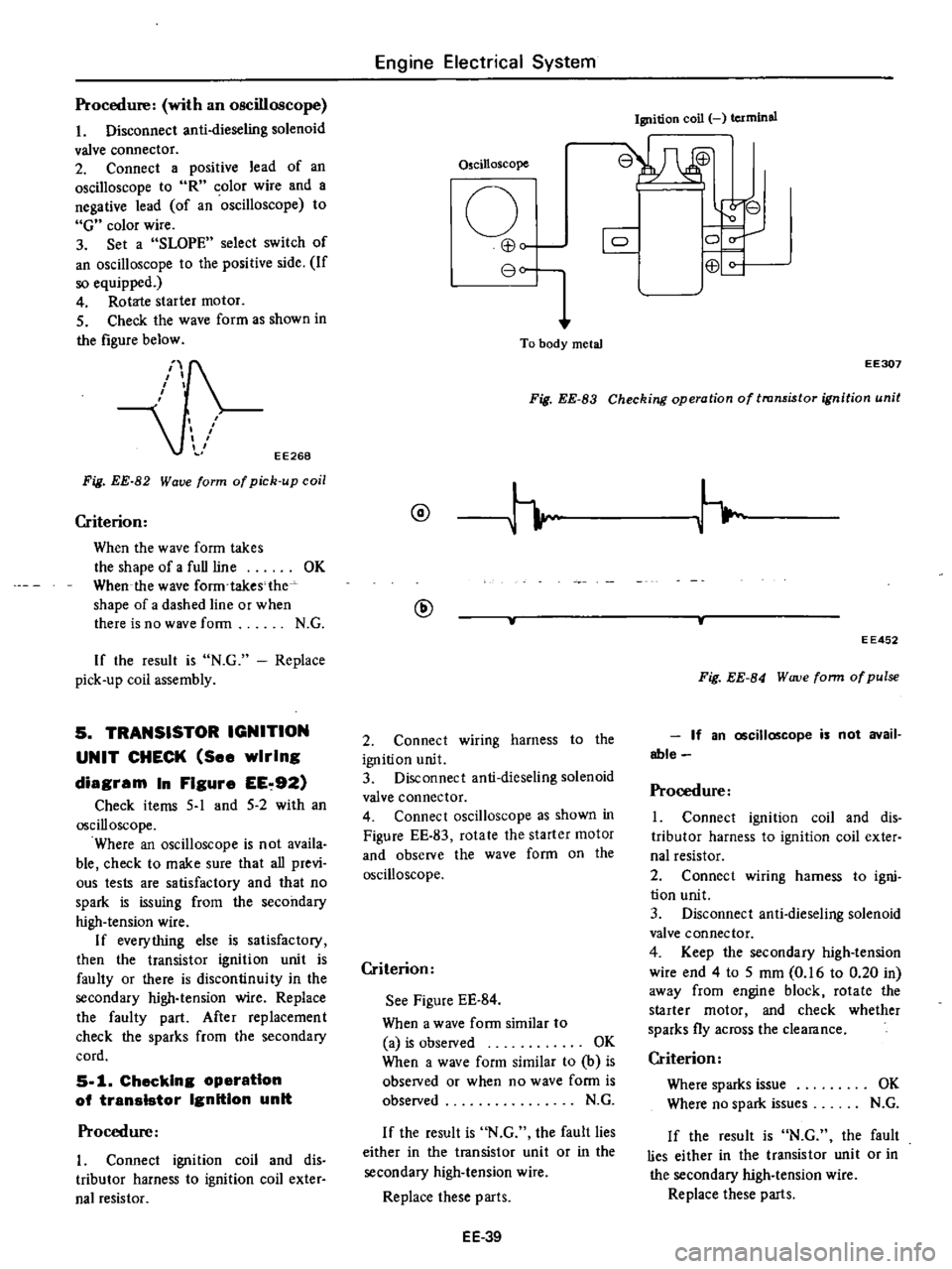
Procedure
with
an
oscilloscope
1
Disconnect
anti
dieseling
solenoid
valve
connector
2
Connect
a
positive
lead
of
an
oscilloscope
to
R
olor
wire
and
a
negative
lead
of
an
oscilloscope
to
G
color
wire
3
Set
a
SLOPE
select
switch
of
an
oscilloscope
to
the
positive
side
If
so
equipped
4
Rotate
starter
motor
5
Check
the
wave
form
as
shown
in
the
figure
below
EE268
Fig
EE
82
Wave
form
of
pick
up
coil
Criterion
When
the
wave
form
takes
the
shape
of
a
full
line
OK
When
the
wave
form
takes
the
shape
of
a
dashed
line
or
when
there
is
no
wave
form
N
G
If
the
result
is
N
G
Replace
pick
up
coil
assembly
5
TRANSISTOR
IGNITION
UNIT
CHECK
See
wiring
diagram
In
Figure
EE
92
Check
items
5
1
and
5
2
with
an
oscilloscope
Where
an
oscilloscope
is
not
availa
ble
check
to
make
sure
that
all
previ
ous
tests
are
satisfactory
and
that
no
spark
is
issuing
from
the
secondary
high
tension
wire
If
everything
else
is
satisfactory
then
the
transistor
ignition
unit
is
faulty
or
there
is
discontinuity
in
the
secondary
high
tension
wire
Replace
the
faulty
part
After
replacement
check
the
sparks
from
the
secondary
cord
5
1
Checking
operatIon
of
transIstor
Ignition
unit
Procedure
I
Connect
ignition
coil
and
dis
tributor
harness
to
ignition
coil
exter
nal
resistor
Engine
Electrical
System
Oscilloscope
o
EB
80
To
body
metal
Ignition
coil
terminal
8W
r
8
0
C
0
EB
Fig
EE
83
Checking
operation
of
transistor
ignition
unit
EE307
@
@
2
Connect
wiring
harness
to
the
ignition
unit
3
Disconnect
anti
dieseling
solenoid
valve
connector
4
Connect
oscilloscope
as
shown
in
Figure
EE
83
rotate
the
starter
motor
and
observe
the
wave
form
on
the
oscilloscope
Criterion
See
Figure
EE
84
When
a
wave
form
similar
to
a
is
observed
OK
When
a
wave
form
similar
to
b
is
obseIVed
or
when
no
wave
form
is
observed
N
G
If
the
result
is
N
G
the
fault
lies
either
in
the
transistor
unit
or
in
the
secondary
high
tension
wire
Replace
these
parts
EE
39
EE452
Fig
EE
84
W
uve
form
of
pulse
If
an
oscilloscope
is
not
avail
able
Procedure
1
Connect
ignition
coil
and
dis
tributor
harness
to
ignition
coil
exter
nal
resistor
2
Connect
wiring
harness
to
igni
tion
unit
3
Disconnect
anti
dieseling
solenoid
valve
connector
4
Keep
the
secondary
high
tension
wire
end
4
to
5
mm
0
16
to
0
20
in
away
from
engine
block
rotate
the
starter
motor
and
check
whether
sparks
fly
across
the
clearance
Criterion
Where
sparks
issue
OK
Where
no
spark
issues
N
G
If
the
result
is
N
G
the
fault
lies
either
in
the
transistor
unit
or
in
the
secondary
high
tension
wire
Replace
these
paris
Page 208 of 537

It
nitionS
l
tC
1
1
1
1
BR
o
IgnitiOn
coil
auemblY
i
stn
Utot
r
Terminal
b
oC
II
o
llW
Power
switching
dtCuit
L
R
G
sparlt
timing
sign
1
l
lonltoriOi
circui
t
Duty
control
circuit
rn
5
l1
l1
n
Harne
s
c
am
P
oClt
preventing
cllcuit
1
A
l1
3
19nition
unit
E
E438
1
r
and
batte
c
c
Fill
EE
88
Wiring
di
l8
ram
for
item
l
PO
er
uPP
y
I
Page 313 of 537

In
these
cases
the
transmission
must
be
repaired
Notes
a
In
checking
oil
level
use
special
paper
cloth
to
handle
the
level
gauge
and
be
careful
not
to
let
the
scraps
of
paper
and
cloth
stick
to
the
gauge
b
Insert
the
gauge
fully
and
take
it
out
quickly
before
splashing
oil
adheres
to
the
gauge
Then
observe
the
level
c
Use
automatic
transmission
fluid
having
DEXRON
identifications
only
in
the
3N71B
automatic
trans
mission
d
Pay
attention
because
the
oil
to
be
used
differs
from
that
used
in
the
Nissan
Full
Automatic
TranSJTIis
sion
3N71A
Never
mix
the
oils
INSPECTION
AND
REPAIR
OF
OIL
LEAKAGE
When
oil
leakage
takes
place
the
portion
near
the
leakage
is
covered
with
oil
presenting
difficulty
in
detecting
the
spot
Therefore
the
places
where
oil
seals
and
gaskets
are
equipped
are
enumerated
below
11
Converter
housing
Rubber
ring
of
oil
pump
housing
Oil
seal
of
oil
pump
housing
Oil
seal
of
engine
crankshaft
Bolts
of
converter
housing
to
case
2
Trarismission
and
rear
extension
Junction
of
transm
ss
ion
and
rear
extension
J
Oil
cooler
tube
connectors
Oil
pan
Oil
pressure
inspection
holes
Refer
to
Figure
AT
il2
Mounting
portion
of
vacuum
dia
phragm
and
downshift
solenoid
Breather
and
oil
charging
pipe
Speedometer
pinion
sleeve
Oil
se
l
of
rear
extension
To
exactly
locate
the
place
of
oil
leaka
le
proceed
as
follows
Place
the
vehicle
in
a
pit
and
by
sampling
the
leaked
oil
determine
if
it
is
the
torque
converter
oil
The
torque
converter
oil
has
a
color
like
r
d
wine
So
it
is
easily
distinguished
from
engine
oil
or
gear
oil
Automatic
rransmission
Wipe
off
the
leaking
oil
and
dust
and
deiecl
the
spol
of
oil
eakage
l
se
nonflammable
organic
solve
t
s
ch
as
carbon
tetrachloride
for
wiping
Raise
the
oil
tcmperalure
by
op
erating
the
engine
and
shift
the
lever
to
D
to
increase
the
oil
pressure
The
spot
of
oil
lcakage
will
then
be
found
more
easily
Note
As
oil
leakage
from
the
breaih
er
does
not
take
place
except
when
running
at
high
speed
it
is
impos
sible
to
locate
this
leakage
with
vehicle
stationary
CHECKING
ENGINE
IDLING
REVOLUTION
The
engine
idling
revolution
should
be
properly
adjusted
If
the
engine
revolution
is
too
low
the
engine
does
not
operate
smoothly
and
if
too
high
a
strong
shock
or
creep
develops
when
changing
over
from
N
to
D
or
R
CHECKING
AND
ADJUSTING
KICK
DOWN
SWITCH
AND
DOWNSHIFT
SOLENOID
When
the
kickdown
operation
is
not
made
properly
or
the
speed
chang
ing
point
s
too
high
check
the
kick
down
switch
downshift
solenoid
and
wiring
between
them
When
the
igni
li
n
key
is
pqsitioned
a
t
the
I
st
stage
nd
the
accelerator
pedal
is
depressed
deeply
the
switch
contact
should
be
closed
and
the
solenoid
should
click
If
it
does
not
click
it
indicates
a
defect
Then
check
each
part
with
the
testing
instruments
See
Figure
ATl09
d
I
t
AT10S
Fig
AT
109
Downshift
solenoid
Note
Watch
for
oil
leakage
from
transmission
case
AT
4Q
INSPECTION
AND
ADJUSTMENT
OF
MANUAL
LINKAGE
The
adjustmcnt
of
manual
linkage
is
equaUy
important
as
Inspection
of
Oil
Level
for
the
automatic
transmis
sion
Thereforc
great
care
should
be
exercised
because
incorrect
adjustment
will
rcsult
in
the
brcakdown
of
the
transmission
Inspection
Pull
the
selector
lever
toward
you
and
turn
it
as
far
as
P
to
I
range
wherc
clicks
will
be
felt
by
the
hand
This
is
the
detcnt
of
manual
valve
in
the
valve
body
and
indicates
th
correct
position
of
the
lever
Inspect
whether
the
pointer
of
selector
dial
corresponds
to
this
point
and
also
whether
the
lever
comes
in
alignment
with
the
stepping
of
posi
tion
plate
when
it
is
released
Adjustment
This
procedure
can
be
accomplish
ed
by
refcrring
to
page
AT
35
for
Removal
and
Installa
tion
CHECKING
AND
ADJUSTING
INHIBITOR
SWITCH
The
inhibitor
switch
lights
the
re
verse
lamp
in
the
range
R
of
the
transmission
operatio
l
and
also
rotates
the
starter
motor
in
the
ranges
N
and
P
CD
@
b
ell
If
L
t
7
4l
@
1l
j7
@
@
@
dl
AT109
6
Washer
7
Nut
8
Inhibitor
switch
9
Range
select
lever
t
Inhibitor
switch
2
Manual
shaft
3
Washer
4
Nut
5
Manual
plate
Fig
AT
110
Construction
of
inhibitor
switch
Page 317 of 537
Automatic
Transmission
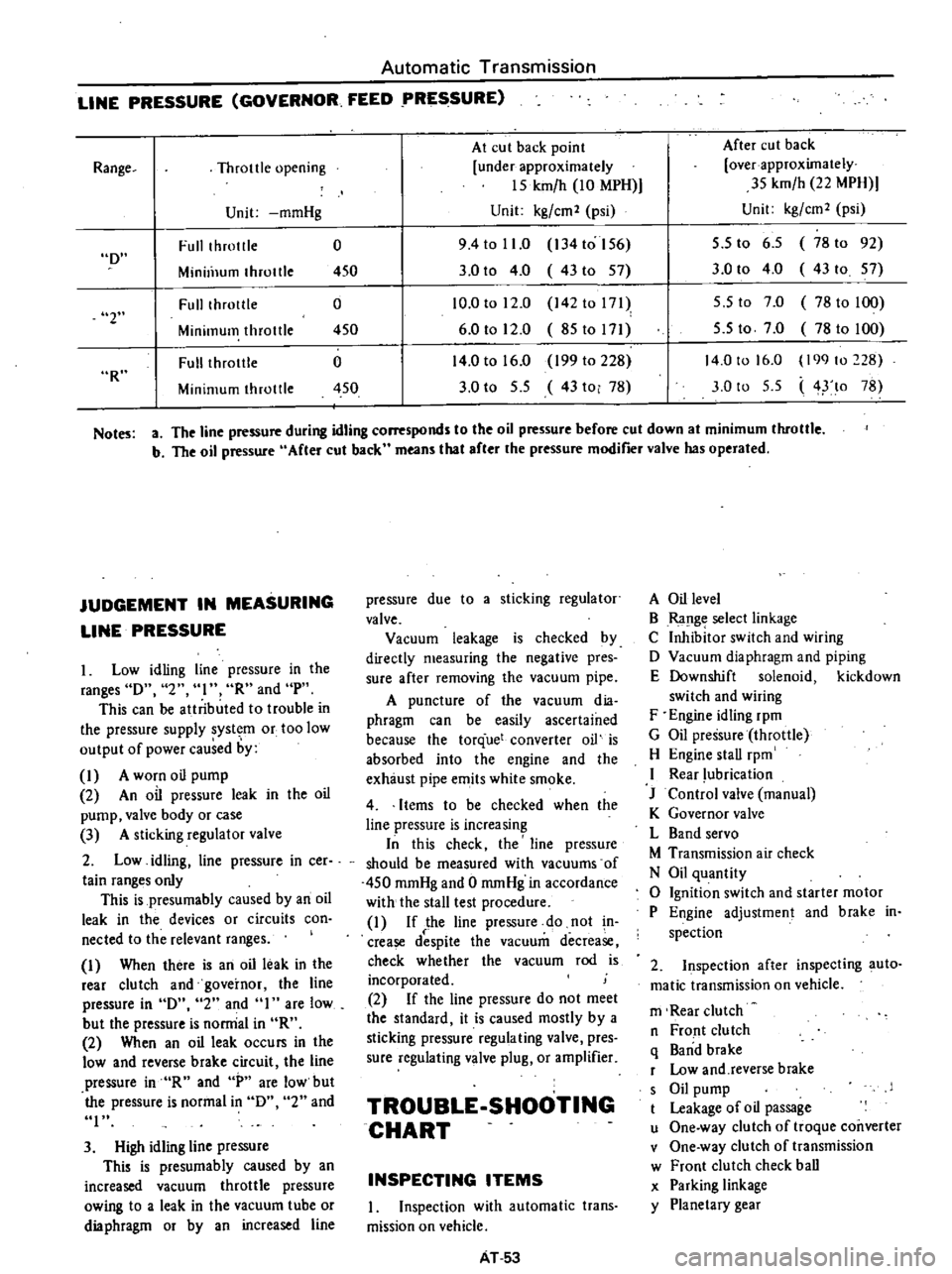
LINE
PRESSURE
GOVERNOR
FEED
PRESSURE
At
cut
back
point
After
cut
back
Throttle
opening
under
approximately
over
approximately
15
kmfh
10
MPH
35
kmfh
22
MPH
Unit
mmHg
Unit
kgfcm2
psi
Unit
kgfcm2
psi
Full
throtlle
0
9
4
to
11
0
134
to
156
5
5
to
6
5
78
to
92
Minill1um
throttle
450
3
0
to
4
0
43to
57
3
0
to
4
0
43
to
57
Fulllhrotlle
0
10
0
to
12
0
142
to
171
5
5
to
7
0
78
to
100
Minimum
throttle
450
6
0
to
12
0
85to171
5
5
to
7
0
78
to
100
Full
throtlle
0
14
0
to
16
0
199
to
228
14
0
to
16
0
199
to
228
Minimum
throttle
450
3
0
to
5
5
43
to
78
3
0
to
5
5
4
lo
78
Range
D
2
R
Notes
a
The
line
pressure
during
idling
corresponds
to
the
oil
pressure
before
cut
down
at
minimum
throttle
b
The
oil
pressure
After
cut
back
means
that
after
the
pressure
modifier
valve
has
operated
JUDGEMENT
IN
MEASURING
LINE
PRESSURE
Low
idling
line
pressure
in
the
ranges
D
2
I
R
and
pH
This
can
be
atlributed
to
trouble
in
the
pressure
supply
system
or
too
low
output
of
power
caused
by
I
A
worn
oil
pump
2
An
oil
pressure
leak
in
the
oil
pump
valve
body
or
case
3
A
sticking
regulator
valve
2
Low
idling
line
pressure
in
cer
tain
ranges
only
This
is
presumably
caused
by
an
oil
leak
in
the
devices
or
circuits
con
nected
to
the
relevant
ranges
I
When
there
is
an
oil
leak
in
the
rear
clutch
and
governor
the
line
pressure
in
D
2
and
I
are
low
but
the
pressure
is
norrrial
in
R
2
When
an
oil
leak
occurs
in
the
low
and
reverse
brake
circuit
the
line
pressure
in
R
and
P
are
low
but
the
pressure
is
normal
in
D
2
and
I
3
High
idling
line
pressure
This
is
presumably
caused
by
an
increased
vacuum
throttle
pressure
owing
to
a
leak
in
the
vacuum
tube
or
dia
phragm
or
by
an
increased
line
pressure
due
to
a
sticking
regulator
valve
Vacuum
leakage
is
checked
by
directly
measuring
the
negative
pres
sure
after
removing
the
vacuum
pipe
A
puncture
of
the
vacuum
dia
phragm
can
be
easily
ascertained
because
the
torque
converter
oil
is
absorbed
into
the
engine
and
the
exhaust
pipe
emits
white
smoke
4
Items
to
be
checked
when
the
line
pressure
is
increasing
In
this
check
the
line
pressure
should
be
measured
with
vacuums
of
450
mmHg
and
0
mmHg
in
accordance
with
the
stall
test
procedure
I
If
the
line
pressure
do
not
n
crease
despite
the
vacuum
decrease
check
whether
the
vacuum
rod
is
incorporated
2
If
the
line
pressure
do
not
meet
the
standard
it
is
caused
mostly
by
a
sticking
pressure
regulating
valve
pres
sure
regulating
valve
plug
or
amplifier
TROUBLE
SHOOTING
CHART
INSPECTING
ITEMS
1
Inspection
with
automatic
trans
mission
on
vehicle
AT
53
A
Oil
level
B
Ra
lge
select
linkage
C
Inhibitor
switch
and
wiring
D
Vacuum
diaphragm
and
piping
E
Downshift
solenoid
kickdown
switch
and
wiring
F
Engine
idling
rpm
G
Oil
pressure
throttle
H
Engine
stall
rpm
I
Rear
lubrication
J
Control
valve
manual
K
Governor
valve
L
Band
servo
M
Transmission
air
check
N
Oil
quantity
o
Ignition
switch
and
starter
motor
P
Engine
adjustment
and
brake
in
spection
2
Inspection
after
inspecting
auto
matic
transmission
on
vehicle
m
Rear
clutch
n
Front
clutch
q
Band
brake
r
Low
and
reverse
brake
s
Oil
pump
t
Leakage
of
oil
passage
u
One
way
clutch
of
troque
coilVerter
v
One
way
clutch
of
transmission
w
Front
clutch
check
ball
x
Parking
linkage
y
Planetary
gear
Page 429 of 537
Body
Frame
30
For
installation
reverse
above
steps
However
observe
the
following
instructions
i
If
the
cab
body
is
to
be
replaced
note
position
and
location
of
insula
tors
and
washers
used
See
Figure
BF
4
2
Adjust
hand
brake
stroke
pro
perly
3
Air
bleed
brake
and
clutch
system
thorougWy
Cab
body
to
frame
mounting
bolt
torque
1
6
to
2
2
kg
m
12
to
16
ft
Ib
o
i
k
q
1Q
j
b
crru
V
J
8F630
rr
1
4
n
Fig
BF
5
Lifting
up
cab
body
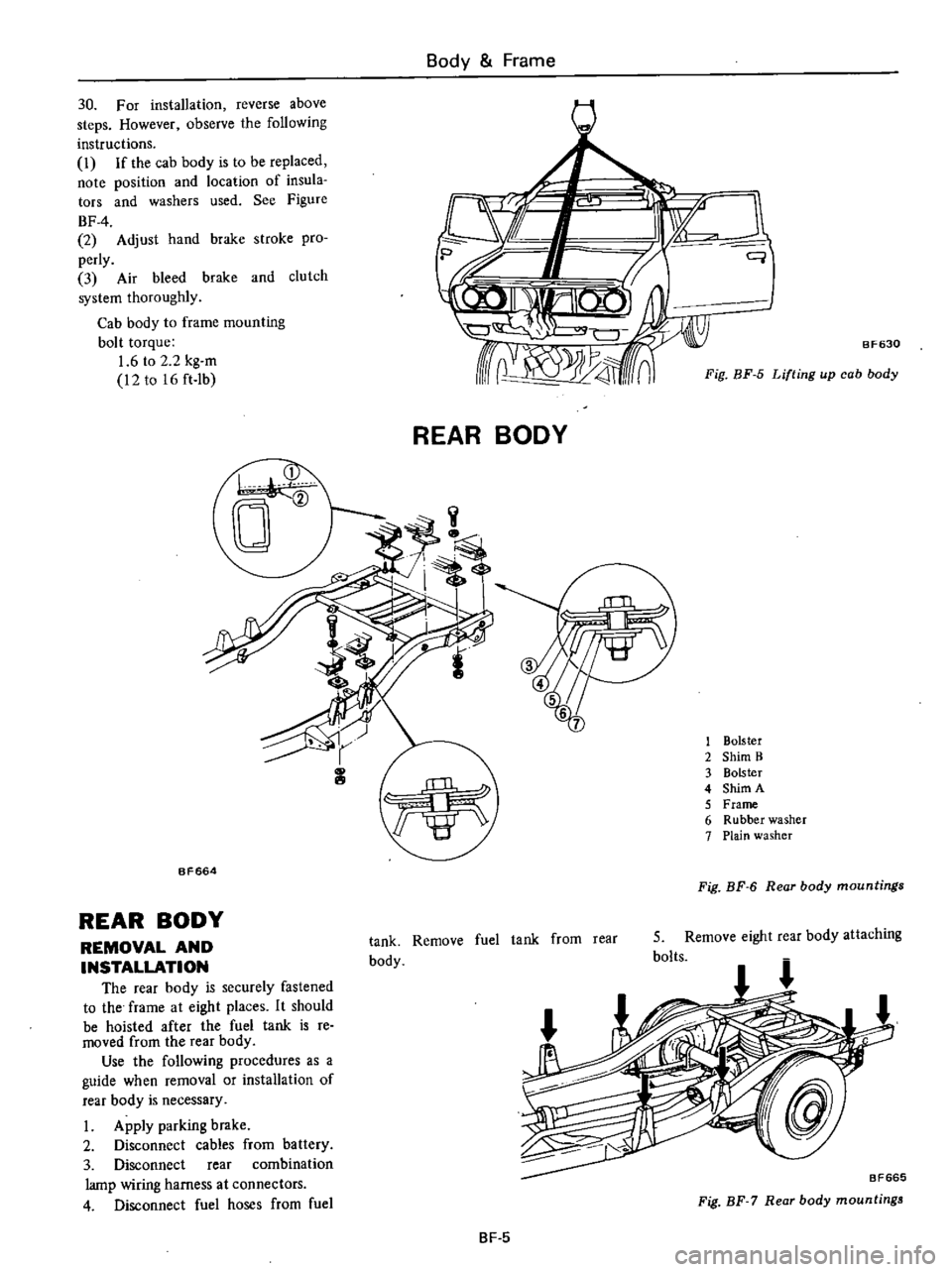
REAR
BODY
1
Bolster
2
Shim
B
3
Bolster
4
Shim
A
5
Frame
6
Rubber
washer
7
Plain
washer
BF664
Fig
BF
6
Rear
body
mountings
REAR
BODY
REMOVAL
AND
INSTALLATION
The
rear
body
is
securely
fastened
to
the
frame
at
eight
places
It
should
be
hoisted
after
the
fuel
tank
is
re
moved
from
the
rear
body
Use
the
following
procedures
as
a
guide
when
removal
or
installation
of
rear
body
is
necessary
I
Apply
parking
brake
2
Disconnect
cables
from
battery
3
Disconnect
rear
combination
lamp
wiring
harness
at
connectors
4
Disconnect
fuel
hoses
from
fuel
tank
Remove
fuel
tank
from
rear
body
5
Remove
eight
rear
body
attaching
bolts
BF665
Fig
BF
7
Rear
body
mountings
BF
5