load capacity DATSUN PICK-UP 1977 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DATSUN, Model Year: 1977, Model line: PICK-UP, Model: DATSUN PICK-UP 1977Pages: 537, PDF Size: 35.48 MB
Page 23 of 537

EE322
Fig
ET
15
Checking
diltribu
tor
point
gap
AIR
GAP
California
models
For
inspection
procedures
and
reference
data
refer
to
the
topic
Air
Gap
in
Section
EE
page
EE
29
DISTRIBUTOR
Check
centrifugal
advance
unit
for
loose
connection
or
improper
opera
tion
If
it
is
not
operating
properly
the
problem
may
be
due
to
a
sticky
spring
or
excessively
worn
parts
This
operation
needs
a
distributor
tester
For
inspection
procedures
and
ref
erence
data
refer
to
relative
topic
under
Distributor
in
Section
EE
If
vacuum
advance
mechanism
does
not
properly
operate
check
for
the
following
items
and
correct
the
prob
lem
as
required
1
Check
vacuum
inlet
for
signs
of
leakage
at
connection
If
necessary
retighten
or
replace
2
Check
vacuum
diaphragm
for
air
leak
If
necessary
replace
diaphragm
3
Inspect
breaker
plate
for
smooth
movement
If
plate
does
not
move
smoothly
this
condition
could
be
due
to
sticky
steel
balls
If
necessary
replace
break
er
plate
assembly
IGNITION
WIRING
Use
an
ohmmeter
to
check
resist
ance
of
secondary
cables
Disconnect
cables
from
spark
plugs
and
install
a
proper
adapter
between
cable
and
spark
plug
Remove
distributor
cap
and
secondary
cables
as
an
assembly
Do
not
remove
cables
from
cap
Check
resistance
of
one
cable
at
a
time
Connect
ohmmeter
between
spark
plug
adapter
and
corresponding
elec
trade
inside
cap
If
resistance
is
more
than
30
000
ohms
remove
cable
from
Engine
Tune
up
cap
and
check
cable
resistance
only
If
resistance
is
still
more
than
30
000
ohms
replace
cable
assembly
EF125
Checking
high
tension
cable
CHECKING
DISTRIBUTOR
CAP
ROTOR
AND
CONDENSER
Note
This
operation
is
to
be
per
formed
while
checking
distributor
points
Inspect
distributor
cap
for
cracks
and
flashover
External
surfaces
of
all
parts
of
secondary
system
must
be
cleaned
to
reduce
possibility
of
voltage
loss
All
wires
should
be
removed
from
distrib
utor
cap
and
coil
so
that
terminals
can
be
inspected
and
cleaned
Burned
or
corroded
terminals
indicate
that
wires
are
not
fully
seated
which
causes
arcing
between
end
of
wire
and
ter
minal
When
replacing
wires
in
ter
minai
be
sure
they
are
fully
seated
before
pushing
rubber
nipple
down
over
tower
Check
distributor
rotor
for
damage
and
distributor
cap
for
cracks
CONDENSER
I
Clean
outlet
of
condenser
lead
wire
and
check
for
loose
setscrew
Retighten
if
necessary
2
Check
condenser
with
a
con
denser
tester
Condenser
capacity
0
20
to
0
24
IF
Micro
Farad
Condenser
insulation
resistance
5Mn
Mega
ohms
ADJUSTING
CARBURETOR
IDLE
RPM
AND
MIXTURE
RATIO
Cautions
a
On
automatic
transmission
equip
T
11
ped
models
check
should
be
per
fonned
in
the
D
position
Be
sure
to
engage
parking
brake
and
to
lock
both
front
and
rear
wheels
with
wheel
chocks
b
Keep
your
foot
down
on
the
brake
pedal
while
depressing
the
accelera
tor
pedal
Otherwise
vehicle
surges
forward
dangerously
Notes
a
Do
not
attempt
to
screw
the
idle
adjusting
sc
ew
down
completely
Doing
so
could
cause
damage
to
tip
which
in
turn
will
tend
to
cause
malfunctions
b
If
idle
limiter
cap
obstructs
proper
adjustment
remove
it
To
install
idle
limiter
cap
refer
to
Idle
Limiter
Cap
c
After
idle
adjustment
has
been
made
shift
the
lever
to
the
N
or
P
position
for
automatic
trans
mission
d
When
measuring
CO
percentage
in
sert
probe
into
tail
pipe
more
than
40
em
15
7
in
CO
idle
adjustment
with
CD
meter
Idle
mixture
adjustment
requires
the
use
of
a
CO
meter
especially
for
California
models
When
preparing
to
adjust
idle
mixture
it
is
essential
to
have
the
meter
thoroughly
warmed
up
and
calibrated
I
Check
carburetor
pipes
for
proper
connection
2
Warm
up
engine
until
water
tem
perature
indicator
points
to
the
middle
of
gauge
The
procedure
to
warm
up
engine
is
not
specifically
recom
mended
Either
driving
vehicle
or
oper
ating
engine
at
no
load
will
be
good
3
Make
sure
that
water
tempera
ture
indicator
points
to
the
middle
Further
keep
engine
running
at
about
2
000
rpm
for
about
5
minutes
with
out
applying
load
to
engine
in
order
to
stabilize
engine
condition
Engine
hood
should
be
open
4
Run
engine
for
about
10
minutes
at
idling
speed
During
this
10
minutes
proceeq
as
described
i
steps
5
to
9
below
5
Remove
air
hose
between
3
way
connector
5
way
connector
for
Cali
fornia
models
and
air
check
valve
as
shown
in
Figure
ET
17
Plug
the
dis
Page 105 of 537
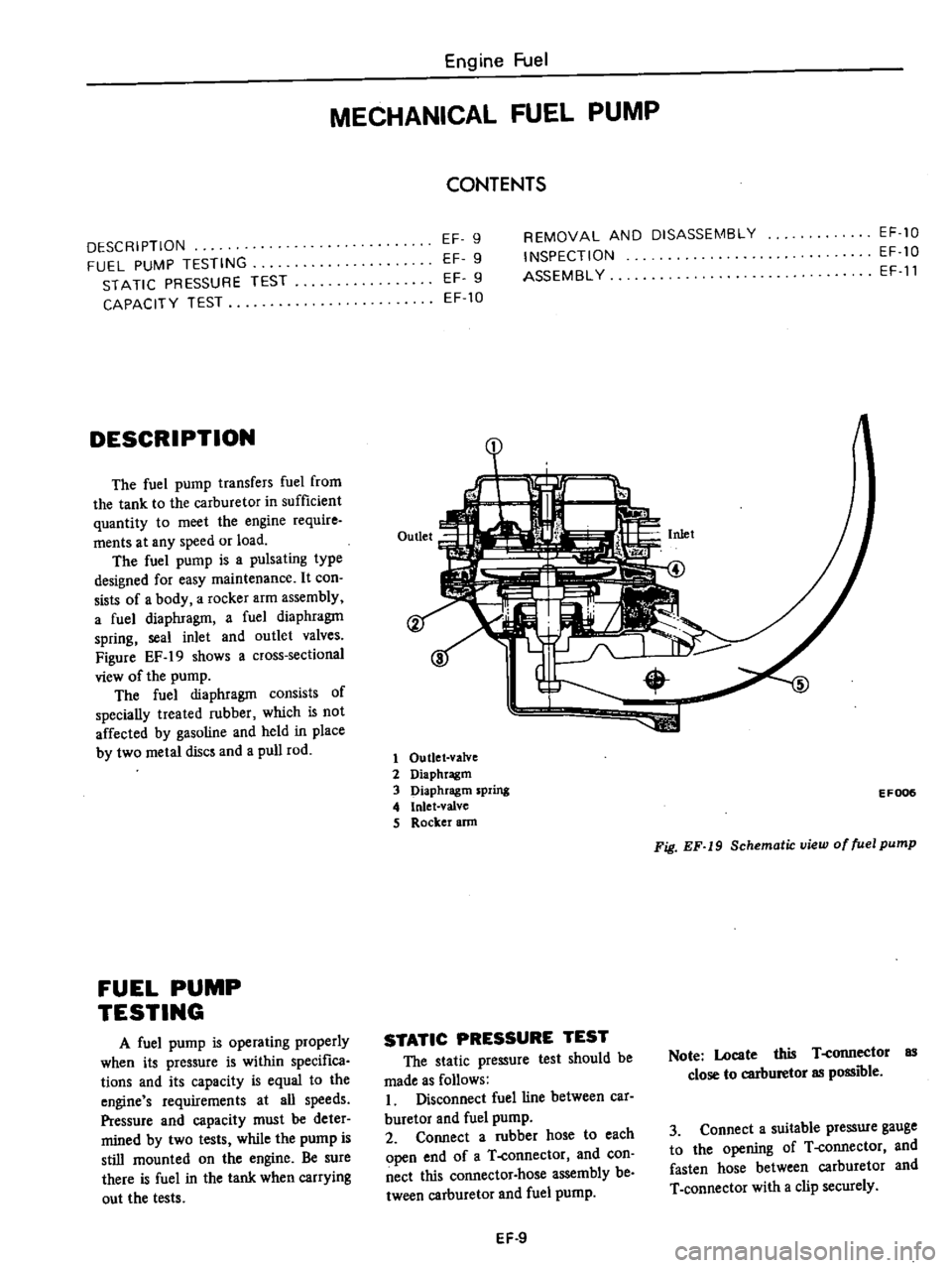
DESCRIPTION
FUEL
PUMP
TESTING
STATIC
PRESSURE
TEST
CAPACITY
TEST
DESCRIPTION
The
fuel
pump
transfers
fuel
from
the
tank
to
the
carburetor
in
sufficient
quantity
to
meet
the
engine
require
ments
at
any
speed
or
load
The
fuel
pump
is
a
pulsating
type
designed
for
easy
maintenance
It
con
sists
of
a
body
a
rocker
arm
assembly
a
fuel
diaphragm
a
fuel
diaphragm
spring
seal
inlet
and
outlet
valves
Figure
EF
19
shows
a
cross
sectional
view
of
the
pump
The
fuel
diaphragm
consists
of
specially
treated
rubber
which
is
not
affected
by
gasoline
and
held
in
place
by
two
metal
discs
and
a
pull
rod
FUEL
PUMP
TESTING
A
fuel
pump
is
operating
properly
when
its
pressure
is
within
specifica
tions
and
its
capacity
is
equal
to
the
engine
s
requirements
at
all
speeds
Pressure
and
capacity
must
be
deter
mined
by
two
tests
while
the
pump
is
still
mounted
on
the
engine
Be
sure
there
is
fuel
in
the
tank
when
carrying
out
the
tests
Engine
Fuel
MECHANICAL
FUEL
PUMP
CONTENTS
EF
9
EF
9
EF
9
EF
10
REMOVAL
AND
DISASSEMBLY
INSPECTION
ASSEMBL
Y
EF
10
EF
10
EF
11
1
1
Outlet
valve
2
Diaphragm
3
Diaphragm
spring
4
Inlet
valve
S
Rocker
ann
EF006
Fig
EF
19
Schematic
view
of
fuel
pump
STATIC
PRESSURE
TEST
The
static
pressure
test
should
be
made
as
follows
I
Disconnect
fuel
line
between
car
buretor
and
fuel
pump
2
Connect
a
rubber
hose
to
each
open
end
of
a
T
connector
and
con
nect
this
connector
hose
assembly
be
tween
carburetor
and
fuel
pump
Note
Locate
this
T
connector
as
close
to
carburetor
as
possible
3
Connect
a
suitable
pressure
gauge
to
the
opening
of
T
connector
and
fasten
hose
between
carburetor
and
T
connector
with
a
clip
securely
EF
9
Page 265 of 537
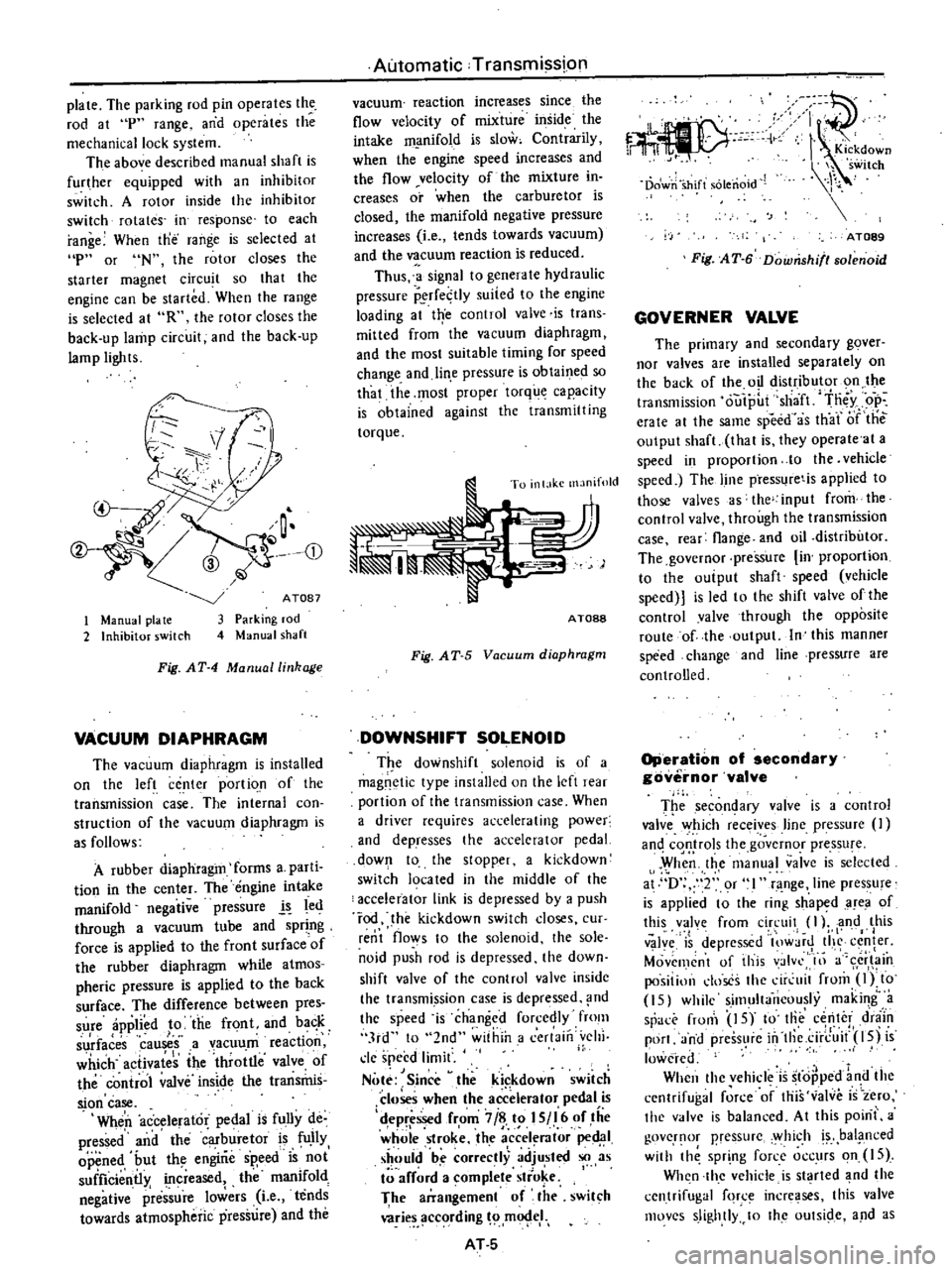
plate
The
parking
rod
pin
operates
the
rod
at
p
range
and
operates
the
mechanical
lock
system
The
above
described
manual
shaft
is
further
equipped
with
an
inhibitor
switch
A
rotor
inside
the
inhibitor
switch
rotates
in
response
to
each
range
When
tne
range
is
selected
at
p
or
N
the
rotor
closes
the
starter
magnet
circuit
so
that
the
engine
can
be
started
When
the
range
is
selected
at
R
the
rolor
closes
the
back
up
lamp
circuit
and
the
back
up
lamp
lights
CD
1
Manual
pia
te
2
Inhibitor
switch
ATOB7
Parking
rod
Manual
shaft
Fig
AT
4
Manual
linkage
VACUUM
DIAPHRAGM
The
vacuum
diaphragm
is
installed
on
the
left
center
portio
n
of
the
transmission
case
The
internal
con
struction
of
the
vacuum
diaphragm
is
as
follows
A
rubber
diaphragm
forms
a
parti
tion
in
the
center
The
engine
intake
manifold
negative
pressure
l
led
through
a
vacuum
tube
and
spring
force
is
applied
to
the
front
surfaceof
the
rubber
diaphragm
while
atmos
pheric
pressure
is
applied
to
the
back
surface
The
difference
between
pres
sure
applied
to
the
front
and
ba
K
I
surfaces
causes
a
vacuum
reactIOn
which
activates
the
throttle
valve
of
the
control
valve
inside
the
transrhis
sion
case
Wheri
accelerator
pedal
is
fully
de
pressed
and
the
buretor
is
fU
IIy
opened
but
th
engirie
sp
eed
is
not
suificientl
increased
the
manifold
negative
plre
sure
lowers
Le
tends
towards
atmospheric
pressure
and
the
Automatic
Transmission
vacuum
reaction
increases
since
the
flow
velocity
of
mixture
inside
the
intake
m
mifold
is
slow
Contrarily
when
the
engine
speed
increases
and
the
flow
velocity
of
the
mixture
in
creases
or
when
the
carburetor
is
closed
the
manifold
negative
pressure
increases
Le
tends
towards
vacuum
and
the
vacuum
reaction
is
reduced
Thus
a
signal
to
genera
Ie
hydraulic
pressure
P
rfe
tly
suited
to
the
engine
loading
at
trye
control
valve
is
trans
mitted
from
the
vacuum
diaphragm
and
the
most
suitable
timing
for
speed
change
and
lin
e
pressure
is
obtaine
so
that
the
most
proper
torque
capacity
is
obtained
against
the
transmitting
torque
To
inl
lkc
manifold
AT088
Fig
AT
5
Vacuum
diaphragm
DOWNSHIFT
SOLENOID
T
e
downshift
solenoid
is
of
a
magnetic
type
installed
on
the
left
re
r
portion
of
the
transmission
case
When
a
driver
requires
accelerating
power
and
dePresses
the
accelerator
pedal
down
to
the
stopper
a
kickdown
switch
19ca
ted
in
the
middle
of
the
accelerator
link
is
depressed
by
a
push
rod
he
kickdown
switch
doses
cur
rent
flows
to
the
solenoid
the
sole
noid
push
rod
is
depressed
the
down
shift
valve
of
the
control
valvc
insidc
the
transmi
ssion
case
is
depressed
nd
the
speed
is
changed
forcedly
fmm
3rd
to
2nd
within
a
cerlaill
vehi
cle
speed
limit
Note
Since
theki
kdown
switch
closes
when
the
accelerator
pedal
is
d
epr
ssed
from
7
i
t
I
S
I
6
of
tiie
whole
stroke
the
a
ccel
rator
ped
1
should
be
correctly
adjusted
so
as
arf
rd
a
omplete
stro
e
I
The
arrangement
of
the
swit
h
wries
ccording
m
eI
AT
S
c
C
r
11
I
Kickdown
h
switch
Dowri
shift
solenoid
AT089
Fig
AT
6
Downshifl80lenoid
GOVERNER
VALVE
The
primary
and
secondary
gover
nor
valves
are
installed
separately
on
the
back
of
the
oil
distributor
on
the
transmission
outp
t
sha
ft
tn
y
op
erate
al
the
same
speed
as
th
ar
iJf
tile
output
shaft
thai
is
they
operate
at
a
speed
in
proportion
10
the
vehicle
speed
The
line
press
retis
applied
to
those
valves
s
the
input
from
the
control
valve
through
the
transmission
case
rear
flange
and
oil
distributor
The
governor
pressure
in
proportion
to
the
ouiput
shaft
speed
vehicle
speed
is
led
to
the
shift
valve
ofthe
control
valve
through
the
opposite
route
of
the
output
In
this
manner
speed
change
and
line
pressure
are
controlled
Operation
of
secondary
governor
valve
T
e
secon
ary
valve
is
a
contro
valve
Y
hich
receives
line
pressure
an
cqQ
rols
the
governor
pressu
e
When
the
manual
valve
is
selected
at
D
2
or
l
range
line
pressure
is
applied
t
the
ri
g
sh
aped
area
of
this
valve
from
circuit
I
l
and
this
I
v
Jy
is
depressed
lOW
jr
tI
c
fer
Movemcnt
of
this
valvl
III
a
cr
in
positillll
doses
the
dr
uit
from
Olto
15
while
simultaneously
making
a
sr
rronl
IS
to
Iii
center
d
niin
port
and
press
re
in
tllc
ci
rJ
it
l5j
is
lowered
When
thc
vehicle
is
stopped
1
d
the
cenlrifugal
force
of
this
valve
is
zero
the
v
lve
is
balanced
At
this
poini
a
govcr
lOr
pressurc
y
hich
bal
i1
nced
with
th
spr
ng
force
occurs
on
IS
Wh
n
thc
vehicle
is
st
rted
nd
the
centrifugal
fqr
incre
ses
this
valve
movcs
slightly
10
Ihc
oUlSide
and
as
Page 341 of 537
P
ROPELLER
SHAFT
DIFFERENTIAL
CARRIER
c
Flank
oontact
Adjust
in
the
same
manner
as
in
b
cV
t
PD195
Fig
PD
25
Flank
contact
d
Face
contact
Adjust
in
the
same
manner
as
in
a
P0196
t
Fig
PD
26
Face
contact
e
Correct
tooth
contact
Fig
PD
27
Correct
contact
Note
Change
in
thickness
of
adjWll
ing
washer
is
accompanied
by
change
in
backlash
Oled
it
when
instaIIi
gear
INSTALLATION
Installing
can
be
done
in
the
reverse
order
of
removal
Tightening
torque
Gear
carrier
to
rear
axle
case
1
7
to
2
5
kg
m
12
to
18
ft
lb
Drain
and
filler
plug
6
0
to
10
0
kg
m
43
to
72
ft
lb
Gear
oil
capacity
1
0
liter
2
US
pt
I
Y
Imp
pt
REPLACEMENT
OF
FRONT
OIL
SEAL
Replacement
of
front
oil
seal
with
d
ifferential
carrier
assembly
installed
on
the
vehicle
When
replacing
front
oil
seal
do
as
follows
1
Drain
gear
oil
2
Raise
the
rear
end
of
vehicle
and
support
it
with
safety
stands
3
Detach
propeller
shaft
from
com
panion
flange
of
carrier
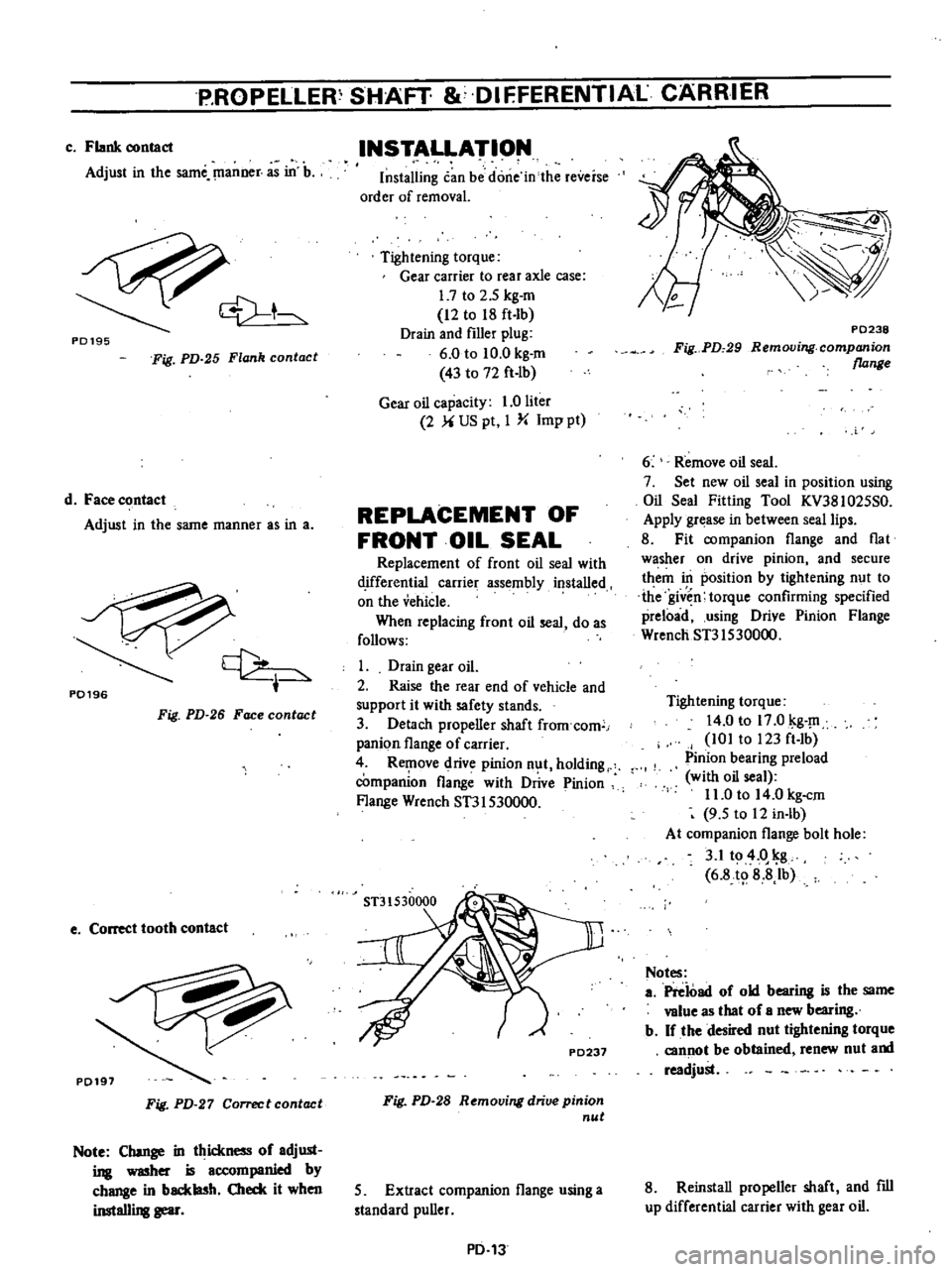
4
R
1
ove
drive
pinion
n
t
holding
companion
flange
with
Drive
Pinion
Flange
Wrench
ST31S30000
P0238
Fig
PD
29
Removing
companion
flange
6
Remove
oil
seal
7
Set
new
oil
seal
in
position
using
Oil
Seal
Fitting
Tool
KV38102SS0
Apply
grease
in
between
seal
lips
8
Fit
companion
flange
and
flat
w
sher
on
drive
pinion
and
secure
them
in
position
by
tightening
nut
to
the
given
torque
confirming
specified
preload
using
Drive
Pinion
Flange
WrencliST31530000
Tightening
torque
14
0
to
17
0
kg
101
to
123
ft
Ib
Pinion
bearing
preload
with
oil
seal
11
0
to
14
0
kg
cm
9
5
to
12
in
lb
At
companion
flange
bolt
hole
3
1
to
4
o
g
6
8
8
8Ib
Notes
a
Preioad
of
old
bearing
is
the
same
value
as
that
of
a
new
bearing
b
If
the
desired
nut
tightening
torque
P0237
can
ot
be
obtained
renew
nut
and
readjust
Fig
PD
28
R
moving
drive
pinion
nut
S
Extract
companion
flange
using
a
standard
puller
PD
13
8
Reinstall
propeller
shaft
and
fill
up
differential
carrier
with
gear
oil