air filter DODGE NEON 2000 Service User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2000, Model line: NEON, Model: DODGE NEON 2000Pages: 1285, PDF Size: 29.42 MB
Page 775 of 1285

CRANKSHAFT
REMOVAL
(1) Remove engine assembly. Refer to procedure in
this section.
(2) Remove structural collar from oil pan to tran-
saxle housing.
(3) Separate transaxle from engine.
(4) Remove drive plate/flywheel.
(5) Remove crankshaft rear oil seal. Refer to pro-
cedure in this section.
(6) Mount engine on a suitable repair stand.
(7) Remove crankshaft damper, timing belt, and
tensioner. Refer to procedures in this section.
(8) Remove camshaft sprocket and rear timing belt
cover. Refer to procedures in this section.
(9) Remove crankshaft sprocket. Refer to proce-
dure in this section.(10) Remove lower torque strut/air conditioning
compressor mounting bracket from engine (Fig. 95).
(11) Remove oil filter and adapter.
(12) Remove oil pan.
(13) Remove oil pump pick-up tube.
(14) Remove oil pump.
(15) Remove crankshaft position sensor.
(16) Using a permanent ink or paint marker, iden-
tify cylinder number on each connecting rod cap.
CAUTION: DO NOT use a number stamp or a punch
to mark connecting rods. Damage to connecting
rod could occur.
(17) Remove all connecting rod bolts and caps.
Care should be taken not to damage the fracture rod
and cap surfaces.
Fig. 94 Crankshaft and Components
1 ± OIL PASSAGE O-RING
2 ± SEAL
3 ± UPPER BEARING (GROOVED)
4 ± THRUST BEARINGS
5 ± BOLT
6 ± O-RING
7 ± NIPPLE8 ± OIL FILTER ADAPTER
9 ± CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR (CPS)
10 ± MAIN BEARING CAP/BED PLATE ASSEMBLY
11 ± CONNECTING ROD BEARINGS
12 ± PISTON AND CONNECTING ROD ASSEMBLY
13 ± SEAL
9 - 52 2.0L SOHC ENGINEPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 777 of 1285

INSTALLATION
(1) Install the main bearing shells with the lubri-
cation groove in the cylinder block. Install O-ring
into recess in the block (Fig. 98).
(2) Make certain oil holes in block line up with oil
hole in bearings and bearing tabs seat in the block
tab slots.
CAUTION: Do Not get oil on the bedplate mating
surface. It will affect the sealer ability to seal the
bedplate to cylinder block.
(3) Oil the bearings and journals and install
crankshaft in cylinder block.
CAUTION: Use only the specified anaerobic sealer
on the bedplate or damage may occur to the
engine.
(4) Apply 1.5±2.0 mm (0.059±0.078 in.) bead of
MopartBed Plate Sealant to cylinder block as shown
in (Fig. 99).
(5) Install lower main bearings into main bearing
cap/bedplate. Make certain the bearing tabs are
seated into the bedplate slots. Install the main bear-
ing/bedplate into engine block.
(6) Before installing the bolts oil threads with
clean engine oil, wipe off any excess oil.
(7) Install main bearing bedplate to engine block
bolts 11, 17 and 20 finger tight. Tighten these bolts
down together until the bedplate contacts the cylin-
der block (Fig. 100).(8) Install main bearing bedplate to engine block
bolts (1±10) and torque each bolt to 81 N´m (60 ft.
lbs.) in sequence shown in (Fig. 100).
(9) Install main bearing bedplate to engine block
bolts (11±20), with baffle studs in positions 12, 13
and 16 and torque each bolt to 34 N´m (25 ft. lbs.) in
sequence shown in (Fig. 100).
(10) After the main bearing bedplate is installed,
check the crankshaft turning torque. The turning
torque should not exceed 5.6 N´m (50 in. lbs.).
(11) If crankshaft end play is to be checked, refer
to service procedures in this section.
(12) Install connecting rod bearings and caps.
Install new connecting rod bolts and tighten to 27
N´m (20 ft. lbs.) plus 1/4 turn.
(13) Install oil pump and crankshaft front oil seal.
(14) Install oil pick-up tube and oil pan. Refer to
procedure in the section.
(15) Install oil filter adapter and filter.
(16) Install lower torque strut/air conditioning
compressor mounting bracket to engine (Fig. 95).
Fig. 98 Installing Main Bearing Upper Shell
1 ± LUBRICATION GROOVES
2 ± O-RING
3 ± OIL HOLES
Fig. 99 Main Bearing Caps/Bedplate Sealing
Fig. 100 Main Bearing Caps/Bedplate Torque
Sequence
9 - 54 2.0L SOHC ENGINEPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 778 of 1285

(17) Install rear timing belt cover and camshaft
sprocket.
(18) Install crankshaft sprocket, timing belt ten-
sioner, timing belt, and cover.
(19) Install front engine mount bracket.
(20) Remove engine from repair stand and position
on Special Tools 6135 and 6710 Engine Dolly and
Cradle. Install safety straps around the engine to
cradle and tighten and lock them into position.
(21) Install crankshaft rear oil seal. Refer to proce-
dure in this section.
(22) Install drive plate/flywheel. Apply Mopart
Lock & Seal Adhesive to bolt threads and tighten to
95 N´m (70 ft. lbs.).
(23) Install transaxle to engine.
(24) Install structural collar. Refer to procedure in
this section.
(25) Install engine assembly. Refer to procedure in
this section.
(26) Perform camshaft and crankshaft timing
relearn procedure as follows:
²Connect the DRB scan tool to the data link
(diagnostic) connector. This connector is located in
the passenger compartment; at the lower edge of
instrument panel; near the steering column.
²Turn the ignition switch on and access the ªmis-
cellaneousº screen.
²Select ªre-learn cam/crankº option and follow
directions on DRB screen.
OIL FILTER ADAPTER
REMOVE AND INSTALL
Ensure O-ring is in the groove on adapter. Align
roll pin into engine block and tighten assembly to 80
N´m (60 ft. lbs.) (Fig. 101).
OIL FILTER
REMOVE AND INSTALL
CAUTION: When servicing the oil filter (Fig. 102),
avoid deforming the filter. Use an appropriate oil fil-
ter removing tool. Position filter wrench strap close
the seam at the base of the filter. The oil filter seam
that joins the can to the base, is reinforced by the
base plate.
(1) Turn filter counterclockwise to remove.
(2) Clean and check the filter mounting surface.
The surface must be smooth, flat and free of debris
or old pieces of rubber.
(3) To install, lubricate new filter gasket. Screw fil-
ter on until gasket contacts base. Tighten to 21 N´m
(15 ft. lbs.).
OIL PUMP
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove crankshaft damper, timing belt, and
tensioner. Refer to procedures in this section.
(3) Remove camshaft sprocket and rear timing belt
cover. Refer to procedures in this section.
(4) Remove oil pan. Refer to procedure in this sec-
tion.
(5) Remove crankshaft sprocket using Special Tool
6793 and insert C-4685-C2 (Fig. 103).
(6) Remove oil pick-up tube.
(7) Remove oil pump (Fig. 104) and front crank-
shaft seal.
Fig. 101 Engine Oil Filter Adapter to Engine Block
1 ± O-RING
2 ± LOCATING ROLL PIN
3 ± OIL FILTER ADAPTER
Fig. 102 Engine Oil Filter
1 ± OIL FILTER
2 ± DRAIN PLUG
PL2.0L SOHC ENGINE 9 - 55
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 824 of 1285

carbon monoxide emissions. The type and amount of
oxygenate used in the blend is important.
The following are generally used in gasoline
blends:
Ethanol- (Ethyl or Grain Alcohol) properly
blended, is used as a mixture of 10 percent ethanol
and 90 percent gasoline. Gasoline blended with etha-
nol may be used in your vehicle.
MTBE/ETBE- Gasoline and MTBE (Methyl Ter-
tiary Butyl Ether) blends are a mixture of unleaded
gasoline and up to 15 percent MTBE. Gasoline and
ETBE (Ethyl Tertiary Butyl Ether) are blends of gas-
oline and up to 17 percent ETBE. Gasoline blended
with MTBE or ETBE may be used in your vehicle.
Methanol- Methanol (Methyl or Wood Alcohol) is
used in a variety of concentrations blended with
unleaded gasoline. You may encounter fuels contain-
ing 3 percent or more methanol along with other
alcohols called cosolvents.
DO NOT USE GASOLINE CONTAINING
METHANOL.
Use of methanol/gasoline blends may result in
starting and driveability problems and damage criti-
cal fuel system components.
Problems that are the result of using methanol/
gasoline blends are not the responsibility of
DaimlerChrysler Corporation and may not be covered
by the vehicle warranty.
Reformulated Gasoline
Many areas of the country are requiring the use of
cleaner-burning fuel referred to asReformulated
Gasoline. Reformulated gasoline are specially
blended to reduce vehicle emissions and improve air
quality.
DaimlerChrysler Corporation strongly supports the
use of reformulated gasoline whenever available.
Although your vehicle was designed to provide opti-
mum performance and lowest emissions operating on
high quality unleaded gasoline, it will perform
equally well and produce even lower emissions when
operating on reformulated gasoline.
Materials Added to Fuel
Indiscriminate use of fuel system cleaning agents
should be avoided. Many of these materials intended
for gum and varnish removal may contain active sol-
vents of similar ingredients that can be harmful to
fuel system gasket and diaphragm materials.
FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM
OPERATION
The fuel delivery system consists of: the electric
fuel pump, fuel filter/fuel pressure regulator, fuel
tubes/lines/hoses, fuel rail, fuel injectors, fuel tank,
accelerator pedal and throttle cable.A fuel return system is used on all models (all
engines). Fuel is returned through the fuel pump
module and back into the fuel tank through the fuel
filter/fuel pressure regulator. A separate fuel return
line from the engine to the tank is no longer used
with any engine.
The fuel tank assembly consists of: the fuel tank,
filler tube, fuel gauge sending unit/electric fuel pump
module, a rollover valve(s) and a pressure-vacuum
filler cap.
Also to be considered part of the fuel system is the
evaporation control system or Onboard Refueling
Vapor recovery (ORVR). This is designed to reduce
the emission of fuel vapors into the atmosphere. The
description and function of the Evaporative Control
System is found in the Emission Control Systems
section.
FUEL PUMP MODULE
DESCRIPTION
The fuel pump module is installed in the fuel tank
(Fig. 1).
OPERATION
The fuel pump module contains the following:
²Electric fuel pump
²Fuel pump reservoir
²Inlet strainer
²Fuel filter/pressure regulator
²Fuel gauge sending unit
²Fuel supply line connection
Fig. 1 Fuel Pump Module
1 ± FUEL FILTER/PRESSURE REGULATOR
2 ± FUEL LEVEL SENSOR
3 ± FUEL RESERVOIR
4 ± INLET STRAINER
5 ± FLOAT
PLFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 3
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 826 of 1285

OPERATION
The fuel pressure regulator is no longer mounted
to the fuel rail on any engine. It is now located on
the fuel tank mounted fuel pump module. Refer toFuel Filter/Fuel Pressure Regulator in the Fuel
Delivery System section of this group for information.
The fuel rail is not repairable.
FUEL INJECTORS
DESCRIPTION
The injectors are positioned in the intake manifold
with the nozzle ends directly above the intake valve
port (Fig. 4).
OPERATION
The fuel injectors are 12 ohm electrical solenoids
(Fig. 5). The injector contains a pintle that closes off
an orifice at the nozzle end. When electric current is
supplied to the injector, the armature and needle
move a short distance against a spring, allowing fuel
to flow out the orifice. Because the fuel is under high
pressure, a fine spray is developed in the shape of a
hollow cone. The spraying action atomizes the fuel,
adding it to the air entering the combustion chamber.
Fuel injectors are not interchangeable between
engines.
PRESSURE-VACUUM FILLER CAP
OPERATION
The loss of any fuel or vapor out of the filler neck
is prevented by the use of a safety filler cap. The cap
will release pressure only under significant pressure
of 10.9 to 13.45 kPa (1.58 to 1.95 psi). The vacuum
release for all gas caps is between 1.94 and 2.94 kPa
(0.28 and 0.43 psi). The cap must be replaced by a
similar unit if replacement is necessary.
Fig. 2 Side ViewÐFilter/Regulator
1 ± INTERNAL FUEL FILTER
2 ± FUEL FLOW TO FUEL INJECTORS
3 ± FUEL FILTER/FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR
4 ± O-RINGS
5 ± EXCESS FUEL BACK TO TANK
6 ± FUEL INLET
7 ± CALIBRATED SPRINGS
8 ± RUBBER GROMMET AT PUMP MODULE
9 ± LOCKING TAB
Fig. 3 Fuel Rail
Fig. 4 Fuel Injector LocationÐTypical
1 ± FUEL RAIL
2 ± INTAKE MANIFOLD
3 ± FUEL INJECTORS
PLFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 833 of 1285
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
AUTOMATIC SHUTDOWN RELAY
The relay is located in the Power Distribution Cen-
ter (PDC) (Fig. 12). The PDC is located next to the
battery in the engine compartment. For the location
of the relay within the PDC, refer to the PDC cover
for location. Check electrical terminals for corrosion
and repair as necessary.
FUEL PUMP RELAY
The fuel pump relay is located in the PDC. The
inside top of the PDC cover has a label showing relay
and fuse location.
FUEL PUMP MODULE
REMOVAL
WARNING: RELEASE FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE
BEFORE SERVICING FUEL SYSTEM COMPONENTS.
SERVICE VEHICLES IN WELL VENTILATED AREAS
AND AVOID IGNITION SOURCES. NEVER SMOKE
WHILE SERVICING THE VEHICLE.
(1) Drain the fuel. Refer to Draining Fuel Tank in
the Fuel Tank section of this group.
WARNING: THE FUEL RESERVOIR OF THE FUEL
PUMP MODULE DOES NOT EMPTY OUT WHEN THE
TANK IS DRAINED. THE FUEL IN THE RESERVOIR
WILL SPILL OUT WHEN THE MODULE IS
REMOVED.
(2) Remove fuel tank, refer to the Fuel Tank
removal/installation section.
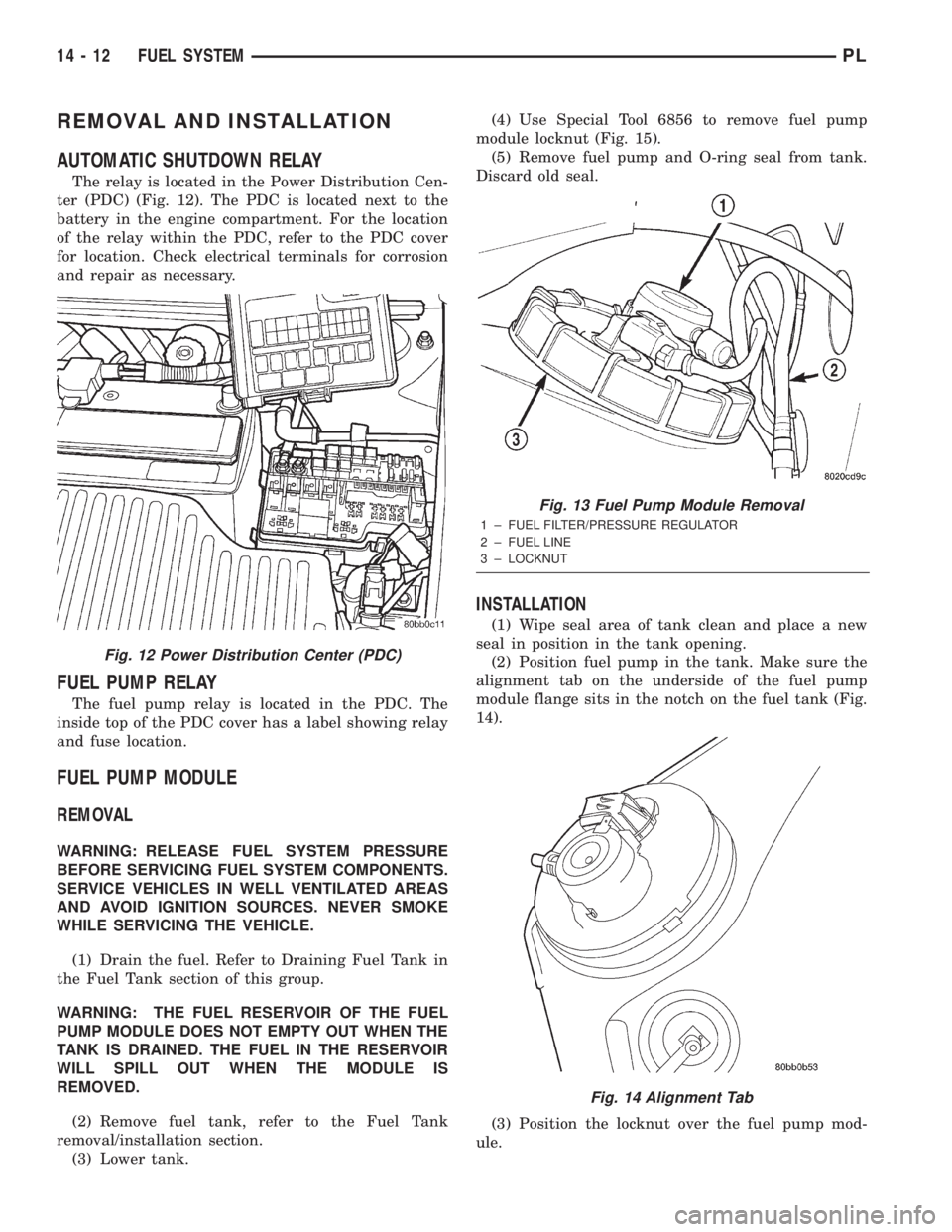
(3) Lower tank.(4) Use Special Tool 6856 to remove fuel pump
module locknut (Fig. 15).
(5) Remove fuel pump and O-ring seal from tank.
Discard old seal.
INSTALLATION
(1) Wipe seal area of tank clean and place a new
seal in position in the tank opening.
(2) Position fuel pump in the tank. Make sure the
alignment tab on the underside of the fuel pump
module flange sits in the notch on the fuel tank (Fig.
14).
(3) Position the locknut over the fuel pump mod-
ule.
Fig. 12 Power Distribution Center (PDC)
Fig. 13 Fuel Pump Module Removal
1 ± FUEL FILTER/PRESSURE REGULATOR
2 ± FUEL LINE
3 ± LOCKNUT
Fig. 14 Alignment Tab
14 - 12 FUEL SYSTEMPL
Page 967 of 1285

31TH AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
GENERAL INFORMATION
IN VEHICLE SERVICE.....................55
FLUID REQUIREMENTS...................55
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
31TH GENERAL INFORMATION..............55
FLUID LEVEL AND CONDITION..............56
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH.............56
HYDRAULIC CONTROL SYSTEM.............56
PRESSURE SUPPLY SYSTEM...............56
PRESSURE REGULATING VALVES...........56
FLOW CONTROL VALVES..................56
CLUTCHES, BAND SERVOS, AND
ACCUMULATOR........................57
BRAKE TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK
SYSTEM..............................57
GEARSHIFT AND PARKING LOCK CONTROLS . . 57
COOLER BYPASS VALVE..................57
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH SOLENOID
WIRING CONNECTOR...................58
GOVERNOR.............................58
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
TRANSAXLE PRELIMINARY DIAGNOSIS.......58
ROAD TEST.............................65
HYDRAULIC PRESSURE TESTS.............66
CLUTCH AND SERVO AIR PRESSURE TESTS . . 68
FLUID LEAKAGE-TRANSAXLE TORQUE
CONVERTER HOUSING AREA.............70
BRAKE TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK....70
SERVICE PROCEDURES
TRANSAXLE FLUID AND FILTER SERVICE.....70
ALUMINUM THREAD REPAIR...............71
FLUSHING COOLERS AND TUBES...........72
OIL PUMP VOLUME CHECK................72
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
GEARSHIFT CABLE.......................73
GEARSHIFT MECHANISM..................76
THROTTLE VALVE (KICKDOWN) CABLE.......77
BRAKE TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK
CABLE...............................79
INTERLOCK MECHANISM..................82
VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR PINION GEAR......83
PARK/NEUTRAL STARTING AND BACK-UP
LAMP SWITCH.........................84TRANSAXLE AND TORQUE CONVERTER......84
PUMP OIL SEAL.........................88
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
TRANSAXLE............................89
VALVE BODY............................91
OIL PUMP.............................104
FRONT CLUTCH........................105
REAR CLUTCH ASSEMBLY................108
FRONT PLANETARY AND ANNULUS
GEAR-RECONDITION...................110
LOW/REVERSE (REAR) SERVO-
RECONDITION........................112
ACCUMULATOR-RECONDITION............113
KICKDOWN SERVO (CONTROLLED LOAD)-
RECONDITION........................113
TRANSFER SHAFT REPAIR................114
PARKING PAWL.........................121
OUTPUT SHAFT REPAIR..................121
DIFFERENTIAL REPAIR...................129
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
VALVE BODY...........................135
ADJUSTMENTS
GEARSHIFT CABLE......................135
THROTTLE VALVE CABLE ADJUSTMENT
PROCEDURE.........................136
BRAKE TRANSMISSION SHIFT INTERLOCK
SYSTEM.............................137
BAND ADJUSTMENT.....................138
HYDRAULIC CONTROL PRESSURE
ADJUSTMENTS.......................138
BEARING ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURES......138
OUTPUT SHAFT BEARING................139
DIFFERENTIAL BEARING.................139
TRANSFER SHAFT BEARING..............140
SCHEMATICS AND DIAGRAMS
31TH TRANSAXLE HYDRAULIC SCHEMATIC . . 142
SPECIFICATIONS
31TH AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE.............150
31TH TRANSAXLE TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS . 150
SPECIAL TOOLS
31TH AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE.............151
21 - 54 TRANSAXLEPL
Page 968 of 1285

GENERAL INFORMATION
IN VEHICLE SERVICE
The following components are serviceable in the
vehicle without transaxle removal:
²Valve Body Assembly
²Converter Clutch Solenoid
²Governor
²Vehicle Speed Sensor & Pinion
²Park/Neutral & Back-up Lamp Switch
²Transfer Gears and Transfer Shaft
²Low/Reverse Servo
²Kickdown Servo
²Accumulator
FLUID REQUIREMENTS
NOTE: The transmission and differential have a
common oil sump with an opening between the
two.
TRANSMISSION/DIFFERENTIAL
MopartATF+4 (Automatic Transmission Fluid
Type 9602) is required in this transaxle. Substitute
fluids must meet fluid specification MS-9602.
FLUID ADDITIVES
Chrysler Corporation strongly recommends against
the addition of any fluids to the transmission, other
than those automatic transmission fluids listed
above. Exceptions to this policy are the use of special
dyes to aid in detecting fluid leaks.
Various ªspecialº additives and supplements exist
that claim to improve shift feel/quality and converter
clutch operation, inhibit overheating, oxidation, var-
nish and sludge. These claims have not been sup-
ported to Chrysler's satisfaction and these additives
must not be used. The use of transmission ªsealersº
should also be avoided, since they may adversely
affect the integrity of tranmission seals.
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
31TH GENERAL INFORMATION
NOTE: Safety goggles should be worn at all times
when working on these transaxles.
This transaxle combines torque converter, three
speed transmission, final drive gearing, and differen-
tial into a front wheel drive system.
NOTE: Transaxle operation requirements are differ-
ent for each vehicle and engine combination. Some
internal parts will be different to provide for this.Therefore, when replacing parts, refer to the seven
digit part number stamped on rear of the transaxle
oil pan flange.
Within this transaxle, there are three primary
areas:
(1) Main center line plus valve body.
(2) Transfer shaft center line (includes governor
and parking sprag).
(3) Differential center line.
Center distances between the main rotating parts
in these three areas are held precise to maintain a
low noise level.
The torque converter, transaxle area, and differen-
tial are housed in an integral aluminum die casting.
The differential oil sump is common with the
transaxle sump. Separate filling of the differen-
tial is NOT necessary.
The torque converter is attached to the crankshaft
through a flexible driving plate. Cooling of the con-
verter is accomplished by circulating the transaxle
fluid through a remote cooler. There are two types of
coolers used. An oil-to-water type cooler located in
the radiator side tank and/or an oil-to-air heat
exchanger. The torque converter assembly is a sealed
unit that cannot be disassembled.
The transaxle fluid is filtered by an internal filter
attached to the lower side of the valve body assembly.
Engine torque is transmitted to the torque con-
verter and then through the input shaft to multiple-
disc clutches in the transaxle. The power flow
depends on the application of the clutches and bands.
Refer to Elements in Use Chart in Diagnosis and
Tests section.
The transaxle consists of:
²Two multiple-disc clutches
²An overrunning clutch
²Two servos
²A hydraulic accumulator
²Two bands
²Two planetary gear sets
This provides three forward ratios and a reverse
ratio. The common sun gear of the planetary gear
sets is connected to the front clutch by a driving
shell. The driving shell is splined to the sun gear and
front clutch retainer. The hydraulic system consists
of an oil pump and a single valve body which con-
tains all of the valves except the governor valves.
The transaxle sump and differential sump are both
vented through the dipstick. Output torque from the
main center line is delivered through helical gears to
the transfer shaft. This gear set is a factor in the
transaxle final drive (axle) ratio. The shaft also car-
ries the governor and parking sprag. An integral heli-
cal gear on the transfer shaft drives the differential
ring gear.
PLTRANSAXLE 21 - 55
Page 972 of 1285

Hydraulic pressure tests should be performed
when a transaxle internal failure is suspected. The
hydraulic flow charts, in the Schematics and Dia-
grams section of this group, outline fluid flow and
hydraulic circuitry. Circuit operation is provided for
all gear ranges. Normal working pressures are also
supplied for each of the gear ranges.
TRANSAXLE DIAGNOSIS CHARTS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
HARSH ENGAGEMENT
(FROM NEUTRAL TO
DRIVE OR REVERSE)1. Fluid Level Low 1. Add Fluid
2. Throttle Linkage Misadjusted 2. Adjust linkage - setting may be too long.
3. Excessive Pinion Backlash 3. Check per Service Manual. Correct as
needed.
4. Hydraulic Pressure Incorrect 4. Check pressure. Remove, overhaul or
adjust valve body as needed.
5. Band Misadjusted. 5. Adjust rear band.
6. Valve Body Check Balls Missing. 6. Inspect valve body for proper check ball
installation.
7. Clutch, band or planetary
component Damaged.7. Remove, disassemble and repair
transmission as necessary.
8. Converter Clutch (if equipped)
Faulty.8. Replace converter and flush cooler and
line before installing new converter.
DELAYED ENGAGEMENT
(FROM NEUTRAL TO
DRIVE OR REVERSE)1. Fluid Level Low. 1. Correct level and check for leaks.
2. Filter Clogged. 2. Change filter.
3. Gearshift Linkage Misadjusted. 3. Adjust linkage and repair linkage if worn
or damaged.
4. Rear Band Misadjusted. 4. Adjust band.
5. Valve Body Filter Plugged. 5. Replace fluid and filter. If oil pan and old
fluid were full of clutch disc material and/or
metal particles, overhaul will be necessary.
6. Oil Pump Gears Worn/Damaged. 6. Remove transmission and replace oil
pump.
7. Hydraulic Pressure Incorrect. 7. Perform pressure test, remove
transmission and repair as needed.
8. Reaction Shaft Seal Rings
Worn/Broken.8. Remove transmission, remove oil pump
and replace seal rings.
9. Rear Clutch/Input Shaft, Rear
Clutch Seal Rings Damaged.9. Remove and disassemble transmission
and repair as necessary.
10. Governor Valve Stuck. 10. Remove and inspect governor
components. Replace worn or damaged
parts.
11. Regulator Valve Stuck. 11. Clean.
PLTRANSAXLE 21 - 59
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 973 of 1285

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
NO DRIVE RANGE
(REVERSE OK)1. Fluid Level Low. 1. Add fluid and check for leaks if drive is
restored.
2. Gearshift Linkage/Cable
Loose/Misadjusted.2. Repair or replace linkage components.
3. Rear Clutch Burnt. 3. Remove and disassemble transmission
and rear clutch and seals. Repair/replace
worn or damaged parts as needed.
4. Valve Body Malfunction. 4. Remove and disassemble valve body.
Replace assembly if any valves or bores
are damaged.
5. Transmission Overrunning Clutch
Broken.5. Remove and disassemble transmission.
Replace overrunning clutch.
6. Input Shaft Seal Rings Worn/
Damaged.6. Remove and disassemble transmission.
Replace seal rings and any other worn or
damaged parts.
7. Front Planetary Failed Broken. 7. Remove and repair.
NO DRIVE OR REVERSE
(VEHICLE WILL NOT
MOVE)1. Fluid Level Low. 1. Add fluid and check for leaks if drive is
restored.
2. Gearshift Linkage/Cable
Loose/Misadjusted.2. Inspect, adjust and reassemble linkage
as needed. Replace worn/damaged parts.
3. Filter Plugged. 3. Remove and disassemble transmission.
Repair or replace failed components as
needed. Replace filter. If filter and fluid
contained clutch material or metal particles,
an overhaul may be necessary. Perform
lube flow test. Flush oil. Replace cooler as
necessary.
4. Oil Pump Damaged. 4. Perform pressure test to confirm low
pressure. Replace pump body assembly if
necessary.
5. Valve Body Malfunctioned. 5. Check press and inspect valve body.
Replace valve body (as assembly) if any
valve or bore is damaged. Clean and
reassemble correctly if all parts are in good
condition.
6. Transmission Internal Component
Damaged.6. Remove and disassemble transmission.
Repair or replace failed components as
needed. Remove and disassemble
transmission. Repair or replace failed
components as needed.
7. Park Sprag not Releasing - Check
Stall Speed, Worn/Damaged/Stuck.7. Remove, disassemble, repair.
8. Torque Converter Damage. 8. Inspect and replace as required.
21 - 60 TRANSAXLEPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)