fuel cap DODGE NEON 2000 Service User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2000, Model line: NEON, Model: DODGE NEON 2000Pages: 1285, PDF Size: 29.42 MB
Page 826 of 1285

OPERATION
The fuel pressure regulator is no longer mounted
to the fuel rail on any engine. It is now located on
the fuel tank mounted fuel pump module. Refer toFuel Filter/Fuel Pressure Regulator in the Fuel
Delivery System section of this group for information.
The fuel rail is not repairable.
FUEL INJECTORS
DESCRIPTION
The injectors are positioned in the intake manifold
with the nozzle ends directly above the intake valve
port (Fig. 4).
OPERATION
The fuel injectors are 12 ohm electrical solenoids
(Fig. 5). The injector contains a pintle that closes off
an orifice at the nozzle end. When electric current is
supplied to the injector, the armature and needle
move a short distance against a spring, allowing fuel
to flow out the orifice. Because the fuel is under high
pressure, a fine spray is developed in the shape of a
hollow cone. The spraying action atomizes the fuel,
adding it to the air entering the combustion chamber.
Fuel injectors are not interchangeable between
engines.
PRESSURE-VACUUM FILLER CAP
OPERATION
The loss of any fuel or vapor out of the filler neck
is prevented by the use of a safety filler cap. The cap
will release pressure only under significant pressure
of 10.9 to 13.45 kPa (1.58 to 1.95 psi). The vacuum
release for all gas caps is between 1.94 and 2.94 kPa
(0.28 and 0.43 psi). The cap must be replaced by a
similar unit if replacement is necessary.
Fig. 2 Side ViewÐFilter/Regulator
1 ± INTERNAL FUEL FILTER
2 ± FUEL FLOW TO FUEL INJECTORS
3 ± FUEL FILTER/FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR
4 ± O-RINGS
5 ± EXCESS FUEL BACK TO TANK
6 ± FUEL INLET
7 ± CALIBRATED SPRINGS
8 ± RUBBER GROMMET AT PUMP MODULE
9 ± LOCKING TAB
Fig. 3 Fuel Rail
Fig. 4 Fuel Injector LocationÐTypical
1 ± FUEL RAIL
2 ± INTAKE MANIFOLD
3 ± FUEL INJECTORS
PLFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 827 of 1285

WARNING: REMOVE FILLER CAP TO RELIEVE
TANK PRESSURE BEFORE REMOVING OR REPAIR-
ING FUEL SYSTEM COMPONENTS.
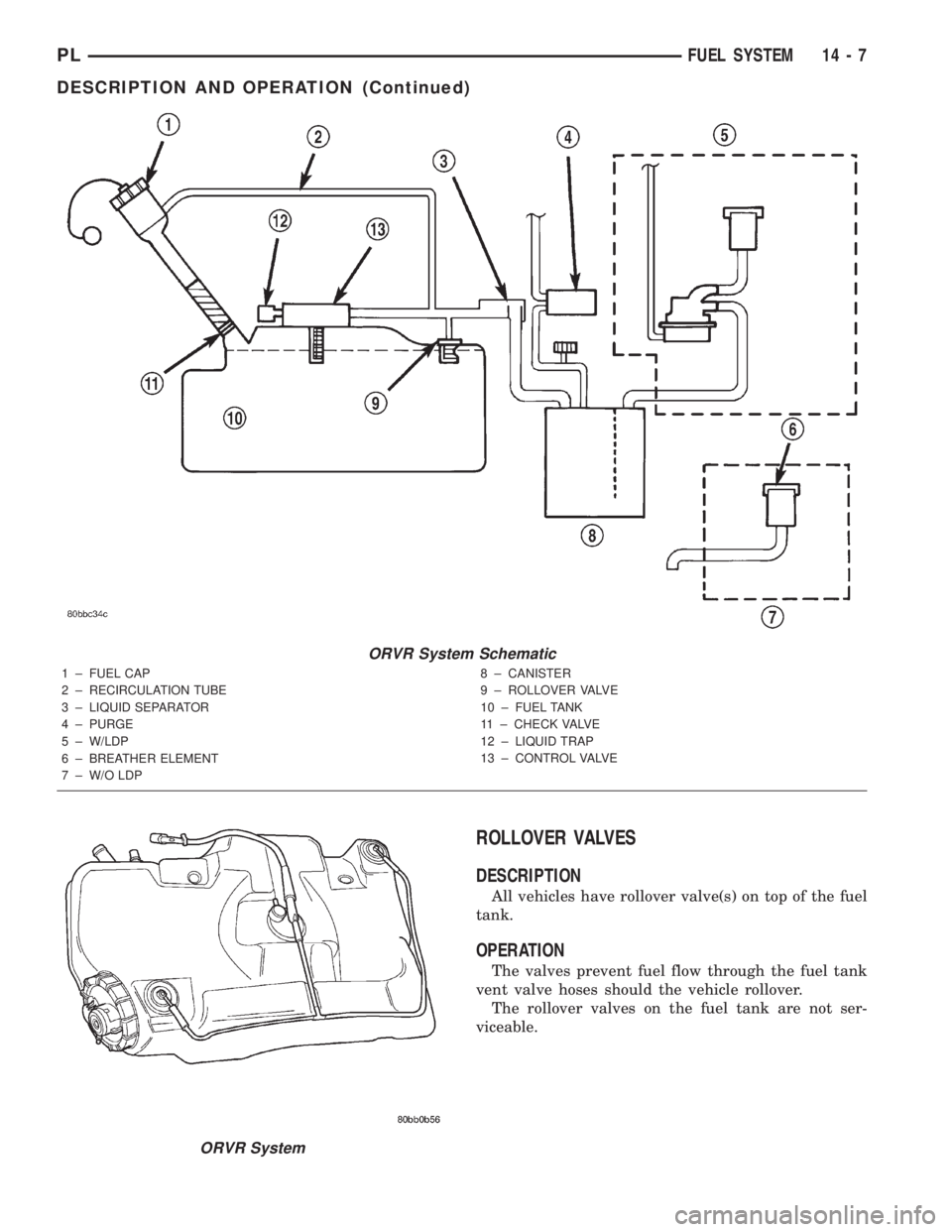
ONBOARD REFUELING VAPOR RECOVERY
OPERATION
The emission control principle used in the ORVR
system is that the fuel flowing into the filler tube
(appx. 1º I. D.) creates an aspiration effect which
draws air into the fill tube. During refueling, the fuel
tank is vented to the vapor canister to capture escap-
ing vapors. With air flowing into the filler tube, there
are no fuel vapors escaping to the atmosphere. Once
the refueling vapors are captured by the canister, the
vehicle's computer controlled purge system draws
vapor out of the canister for the engine to burn. The
vapors flow is metered by the purge solenoid so that
there is no or minimal impact on driveability or
tailpipe emissions.
As fuel starts to flow through the fill tube, it opens
the normally closed check valve and enters the fuel
tank. Vapor or air is expelled from the tank through
the control valve to the vapor canister. Vapor is
absorbed in the canister until vapor flow in the lines
stops, either following shut-off or by having the fuel
level in the tank rise high enough to close the control
valve. The control valve contains a float that rises to
seal the large diameter vent path to the canister. At
this point in the fueling of the vehicle, the tank pres-
sure increase, the check valve closes (preventing tank
fuel from spiting back at the operator), and fuel then
rises up the filler tube to shut-off the dispensing noz-
zle.If the engine is shut-off while the On-Board diag-
nostics test is running, low level tank pressure can
be trapped in the fuel tank and fuel can not be added
to the tank until the pressure is relieved. This is due
to the leak detection pump closing the vapor outlet
from the top of the tank and the one-way check valve
not allowing the tank to vent through the fill tube to
atmosphere. Therefore, when fuel is added, it will
back-up in the fill tube and shut off the dispensing
nozzle. The pressure can be eliminated in two ways:
1. Vehicle purge must be activated and for a long
enough period to eliminate the pressure. 2. Removing
the fuel cap and allowing enough time for the system
to vent thru the recirulation tube.
CONTROL VALVE/PRESSURE RELIEF
OPERATION
If the fuel tank should over-pressurize, the control
valve incorporates a pressure relief port that allows
pressure relief capability under extreme conditions.
Example, if the canister vent line was to get pinched
or obstructed, the relief valve would vent the pres-
sure.
QUICK-CONNECT FITTINGS
DESCRIPTION
Different types of quick-connect fittings are used to
attach various fuel system components. These are: a
single-tab type, a two-tab type or a plastic retainer
ring type. Some are equipped with safety latch clips.
Refer to the Removal/Installation section for more
information.
CAUTION: The interior components (o-rings, spac-
ers) of quick-connect fitting are not serviced sepa-
rately. Do not attempt to repair damaged fittings or
fuel lines/tubes. If repair is necessary, replace the
complete fuel tube assembly.
Fuel tubes connect fuel system components with
plastic quick-connect fuel fittings. The fitting con-
tains non-serviceable O-ring seals (Fig. 6).
CAUTION: Quick-connect fittings are not serviced
separately. Do not attempt to repair damaged quick-
connect fittings or fuel tubes. Replace the complete
fuel tube/quick-connect fitting assembly.
The quick-connect fitting consists of the O-rings,
retainer and casing (Fig. 6). When the fuel tube
enters the fitting, the retainer locks the shoulder of
the nipple in place and the O-rings seal the tube.
Fig. 5 Fuel Injector
1 ± FUEL INJECTOR
2 ± NOZZLE
3 ± TOP (FUEL ENTRY)
14 - 6 FUEL SYSTEMPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 828 of 1285
ROLLOVER VALVES
DESCRIPTION
All vehicles have rollover valve(s) on top of the fuel
tank.
OPERATION
The valves prevent fuel flow through the fuel tank
vent valve hoses should the vehicle rollover.
The rollover valves on the fuel tank are not ser-
viceable.
ORVR System Schematic
1 ± FUEL CAP
2 ± RECIRCULATION TUBE
3 ± LIQUID SEPARATOR
4 ± PURGE
5 ± W/LDP
6 ± BREATHER ELEMENT
7 ± W/O LDP8 ± CANISTER
9 ± ROLLOVER VALVE
10 ± FUEL TANK
11 ± CHECK VALVE
12 ± LIQUID TRAP
13 ± CONTROL VALVE
ORVR System
PLFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 7
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 830 of 1285

INSTALLATION
(1) Connect electrical connectors at all fuel injec-
tors. To install connector, refer to (Fig. 8). Push con-
nector onto injector (1) and then push and lock red
colored slider (2). Verify connector is locked to injec-
tor by lightly tugging on connector.
DRAINING FUEL TANK
WARNING: RELEASE FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE
BEFORE SERVICING FUEL SYSTEM COMPONENTS.
SERVICE VEHICLES IN WELL VENTILATED AREAS
AND AVOID IGNITION SOURCES. NEVER SMOKE
WHILE SERVICING THE VEHICLE.
(1) Remove fuel filler cap.
(2) Perform the Fuel System Pressure Release pro-
cedure.
(3) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(4) Raise vehicle and support.
(5) Remove quick connect cap from drain port.
(6) Drain fuel tank into holding tank or a properly
labeledGasolinesafety container.
(7) Replace quick connect cap.
HOSES AND CLAMPS
Inspect all hose connections (clamps and quick con-
nect fittings) for completeness and leaks. Replace
cracked, scuffed, or swelled hoses. Replace hoses that
rub against other vehicle components or show sign of
wear.
Fuel injected vehicles use specially constructed
hoses. When replacing hoses, only use hoses marked
EFM/EFI.
When installing hoses, ensure that they are routed
away from contact with other vehicle components
that could rub against them and cause failure. Avoid
contact with clamps or other components that cause
abrasions or scuffing. Ensure that rubber hoses are
properly routed and avoid heat sources.
The hose clamps have rolled edges to prevent the
clamp from cutting into the hose. Only use clamps
that are original equipment or equivalent. Other
types of clamps may cut into the hoses and cause
high pressure fuel leaks. Tighten hose clamps to 1
N´m (10 in. lbs.) torque.
QUICK-CONNECT FITTINGS
REMOVAL
When disconnecting a quick-connect fitting, the
retainer will remain on the fuel tube nipple.
WARNING: RELEASE FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE
BEFORE DISCONNECTING A QUICK-CONNECT FIT-
TINGS. REFER TO THE FUEL PRESSURE RELEASE
PROCEDURE.
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery or aux-
iliary jumper terminal.
(2) Perform Fuel Pressure Release Procedure.
Refer to the Fuel Pressure Release Procedure in this
section.
Fig. 7 Fuel Injectors
Fig. 8 Remove/Install Injector Connector
PLFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 9
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 837 of 1285
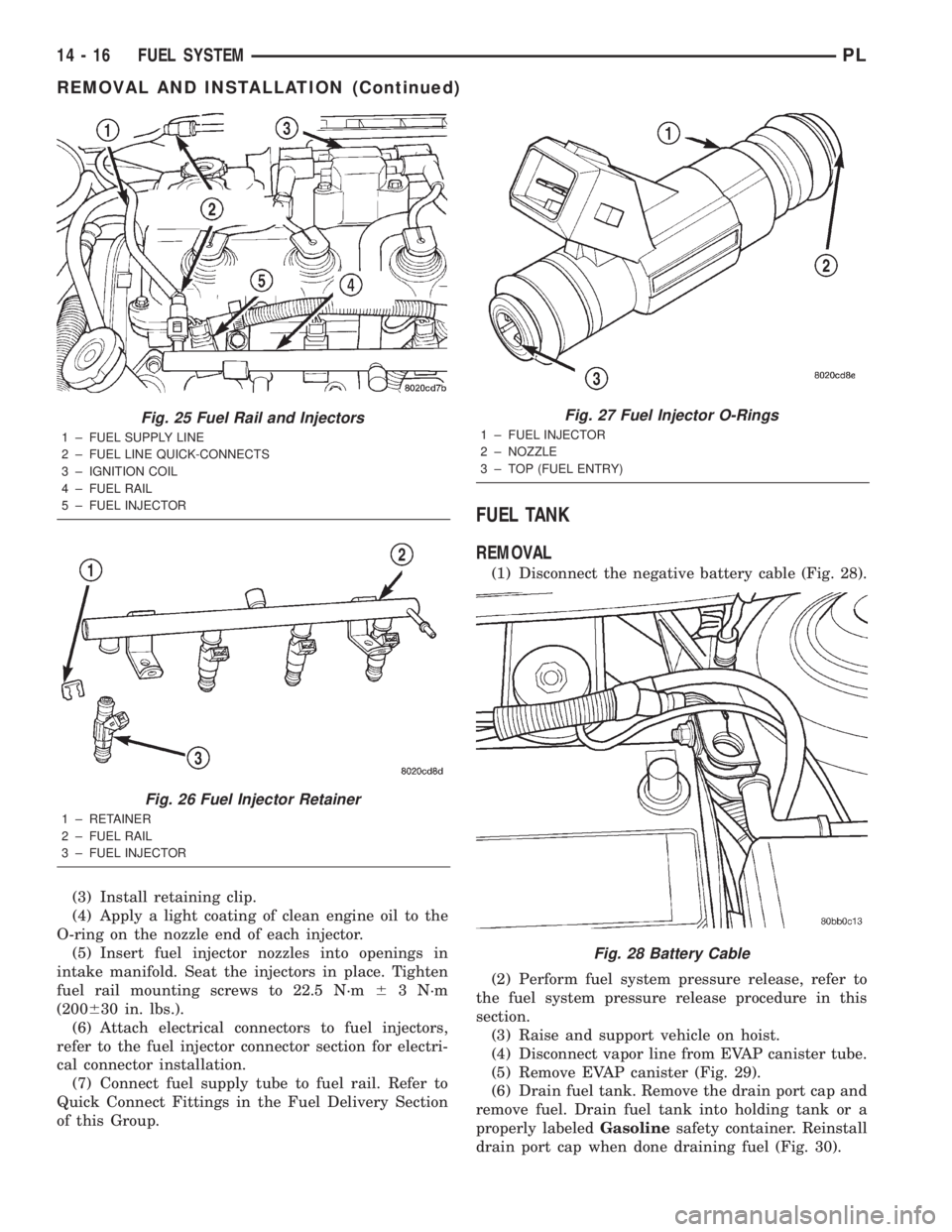
(3) Install retaining clip.
(4) Apply a light coating of clean engine oil to the
O-ring on the nozzle end of each injector.
(5) Insert fuel injector nozzles into openings in
intake manifold. Seat the injectors in place. Tighten
fuel rail mounting screws to 22.5 N´m63 N´m
(200630 in. lbs.).
(6) Attach electrical connectors to fuel injectors,
refer to the fuel injector connector section for electri-
cal connector installation.
(7) Connect fuel supply tube to fuel rail. Refer to
Quick Connect Fittings in the Fuel Delivery Section
of this Group.
FUEL TANK
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect the negative battery cable (Fig. 28).
(2) Perform fuel system pressure release, refer to
the fuel system pressure release procedure in this
section.
(3) Raise and support vehicle on hoist.
(4) Disconnect vapor line from EVAP canister tube.
(5) Remove EVAP canister (Fig. 29).
(6) Drain fuel tank. Remove the drain port cap and
remove fuel. Drain fuel tank into holding tank or a
properly labeledGasolinesafety container. Reinstall
drain port cap when done draining fuel (Fig. 30).
Fig. 25 Fuel Rail and Injectors
1 ± FUEL SUPPLY LINE
2 ± FUEL LINE QUICK-CONNECTS
3 ± IGNITION COIL
4 ± FUEL RAIL
5 ± FUEL INJECTOR
Fig. 26 Fuel Injector Retainer
1 ± RETAINER
2 ± FUEL RAIL
3 ± FUEL INJECTOR
Fig. 27 Fuel Injector O-Rings
1 ± FUEL INJECTOR
2 ± NOZZLE
3 ± TOP (FUEL ENTRY)
Fig. 28 Battery Cable
14 - 16 FUEL SYSTEMPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 838 of 1285

(7) Disconnect fuel pump module electrical connec-
tor and ground wire (Fig. 31).
(8) Disconnect the fuel tube from Fuel Filter/Reg-
ulator. Refer to Quick Connect Fittings in the Fuel
Delivery section of this group.
(9) Disconnect fuel filler tube and filler vent tube
from filler hose at fuel tank.
(10) Support tank with transmission jack. Loosen
tank mounting straps and lower tank slightly.
(11) Remove tank mounting straps and lower tank.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position fuel tank on transmission jack.
(2) Raise tank into position.
(3) Tighten fuel tank strap nuts to 22.5 N´m (200
in. lbs.) torque. Remove transmission jack. Ensure
straps are not twisted or bent.(4) Connect fuel filler tube tank inlet nipple.
Tighten clamp.
(5) Connect EVAP vent hose.
(6) Attach fuel tubes to pump module and chassis
fuel tube. Refer to Quick Connect Fittings in the Fuel
Delivery section of this Group.
(7) Attach electrical connector and ground wire to
fuel pump module.
(8) Install vapor lines to EVAP canister.
(9) Install EVAP canister.
(10) Lower vehicle.
(11) Fill fuel tank, install filler cap, and connect
battery cable.
CAUTION: When using the ASD Fuel System Test,
the Auto Shutdown (ASD) Relay remains energized
for either 7 minutes, until the test is stopped, or
until the ignition switch is turned to the Off posi-
tion.
(12) Use the DRB scan tool ASD Fuel System Test
to pressurize the fuel system. Check for leaks.
FUEL FILLER NECK
REMOVAL
(1) Loosen fuel filler tube cap.
(2) Remove fuel filler neck screws (Fig. 32).
(3) Raise and support vehicle.
(4) Remove splash shield from wheel well.
(5) Disconnect fuel fill vapor tube.
(6) Disconnect fuel filler tube from fuel tank.
(7) Remove groundstrap from body.
(8) Remove filler neck (Fig. 33).
Fig. 29 EVAP Canister
Fig. 30 Fuel Tank
Fig. 31 Pump Module Electrical Connector
1 ± ELECTRICAL CONNECTOR
2 ± FUEL LINE
PLFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 17
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 839 of 1285
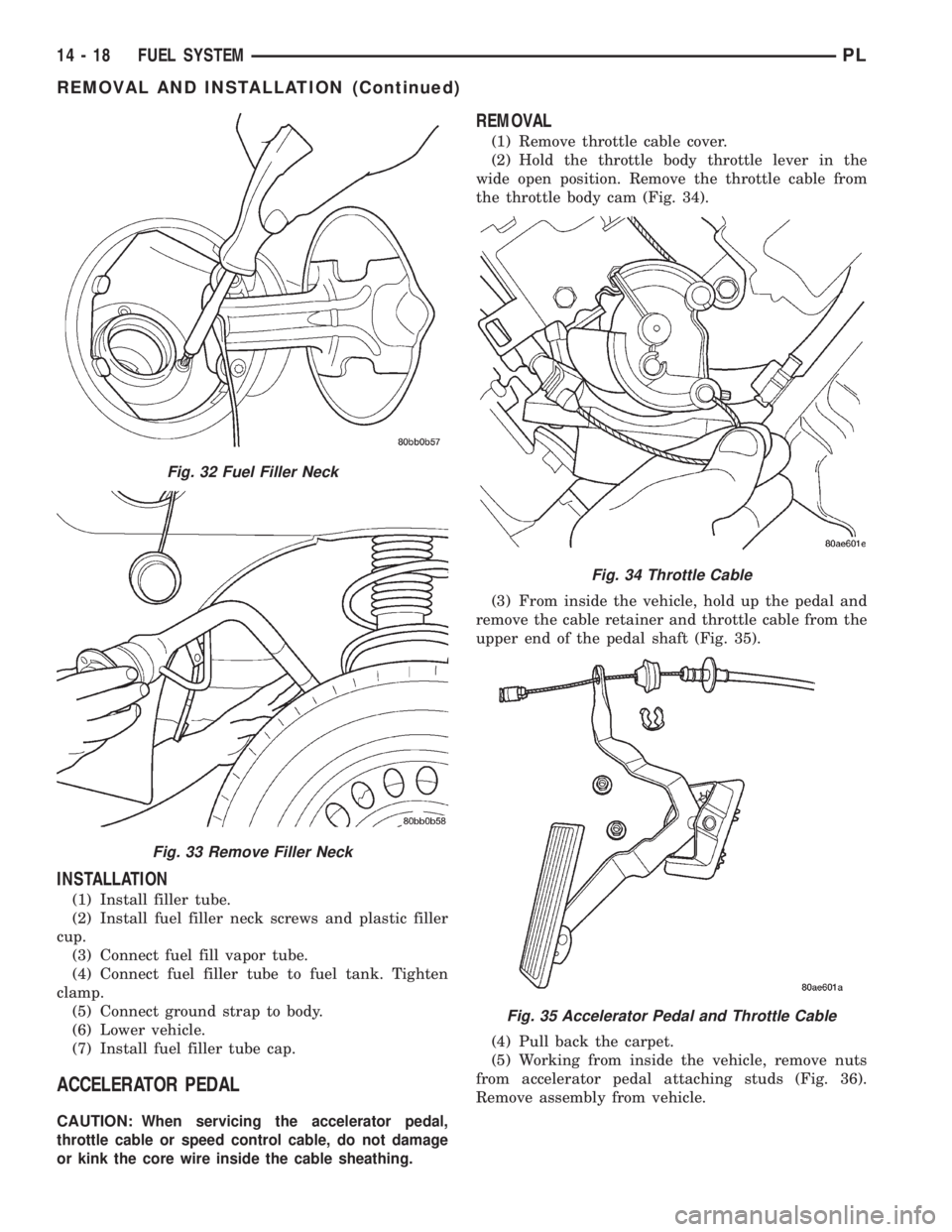
INSTALLATION
(1) Install filler tube.
(2) Install fuel filler neck screws and plastic filler
cup.
(3) Connect fuel fill vapor tube.
(4) Connect fuel filler tube to fuel tank. Tighten
clamp.
(5) Connect ground strap to body.
(6) Lower vehicle.
(7) Install fuel filler tube cap.
ACCELERATOR PEDAL
CAUTION:When servicing the accelerator pedal,
throttle cable or speed control cable, do not damage
or kink the core wire inside the cable sheathing.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove throttle cable cover.
(2) Hold the throttle body throttle lever in the
wide open position. Remove the throttle cable from
the throttle body cam (Fig. 34).
(3) From inside the vehicle, hold up the pedal and
remove the cable retainer and throttle cable from the
upper end of the pedal shaft (Fig. 35).
(4) Pull back the carpet.
(5) Working from inside the vehicle, remove nuts
from accelerator pedal attaching studs (Fig. 36).
Remove assembly from vehicle.
Fig. 32 Fuel Filler Neck
Fig. 33 Remove Filler Neck
Fig. 34 Throttle Cable
Fig. 35 Accelerator Pedal and Throttle Cable
14 - 18 FUEL SYSTEMPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 852 of 1285

OPERATION
The combination coolant temperature sensor has
two elements. One element supplies coolant temper-
ature signal to the PCM. The other element supplies
coolant temperature signal to the instrument panel
gauge cluster. The PCM determines engine coolant
temperature from the coolant temperature sensor.
As coolant temperature varies the coolant temper-
ature sensors resistance changes resulting in a differ-
ent input voltage to the PCM and the instrument
panel gauge cluster.When the engine is cold, the PCM will provide
slightly richer air- fuel mixtures and higher idle
speeds until normal operating temperatures are
reached.
The PCM has a dual temperature range program
for better sensor accuracy at cold temperatures. At
key-ON the PCM sends a regulated five volt signal
through a 10,000 ohm resistor to the sensor. When
the sensed voltage reaches approximately 1.25 volts
the PCM turns on the transistor. The transistor con-
nects a 1,000 ohm resistor in parallel with the 10,000
ohm resistor. With this drop in resistance the PCM
recognizes an increase in voltage on the input circuit.
FUEL LEVEL SENSORÐPCM INPUT
DESCRIPTION
The fuel gauge level sending unit is attached to the
fuel pump module.
OPERATION
The fuel level sensor (fuel gauge sending unit)
sends a signal to the PCM to indicate fuel level. The
purpose of this feature is to prevent a false setting of
misfire and fuel system monitor trouble codes if the
fuel level is less than approximately 15 percent of its
rated capacity. It is also used to send a signal for fuel
gauge operation via the PCI bus circuits.
Fig. 9 Timing Reference Notches
1 ± MACHINED NOTCHES
2 ± CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
Fig. 10 Engine Coolant Temperature SensorÐSOHC
1 ± ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR
2 ± CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
PLFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 31
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1075 of 1285
SERVICE PROCEDURES
PRESSURE GAUGES
A quality air pressure gauge is recommended to
check tire pressure. After checking the air pressure,
replace valve cap finger tight.
TIRE INFLATION PRESSURES
Under inflation causes rapid shoulder wear, tire
flexing, and can result in tire failure (Fig. 5).
Over inflation causes rapid center wear and loss of
the tire's ability to cushion shocks (Fig. 6).
Improper inflation can cause:
²Uneven wear patterns
²Reduced tread life
²Reduced fuel economy
²Unsatisfactory ride²The vehicle to drift.
For proper tire pressure specification refer to the
Tire Inflation Pressure Chart Placard provided with
the vehicle.
Tire pressures have been chosen to provide safe
operation, vehicle stability, and a smooth ride. Tire
pressure should be checked cold once per month.
Check tire pressure more frequently when the
weather temperature varies widely. Tire pressure will
decrease when the outdoor temperature drops.
Inflation pressures specified on the placard are
always the cold inflation pressure of the tire. Cold
inflation pressure is obtained after the vehicle has
not been operated for at least 3 hours, or the vehicle
is driven less than one mile after being inoperative
for 3 hours. Tire inflation pressures may increase
from 2 to 6 pounds per square inch (psi) during oper-
ation. Do not reduce this normal pressure build-up.
WARNING: OVER OR UNDER INFLATED TIRES
CAN AFFECT VEHICLE HANDLING. THE TIRE CAN
FAIL SUDDENLY, RESULTING IN LOSS OF VEHICLE
CONTROL.
TIRE PRESSURE FOR HIGH SPEED
OPERATION
DaimlerChrysler Corporation advocates driving at
safe speeds within posted speed limits. Where speed
limits allow the vehicle to be driven at high speeds,
correct tire inflation pressure is very important. For
speeds up to and including 120 km/h (75 mph), tires
must be inflated to the pressures shown on the tire
placard. For continuous speeds in excess of 120 km/h
(75 mph), tires must be inflated to the maximum
pressure specified on the tire sidewall.
Vehicles loaded to the maximum capacity should
not be driven at continuous speeds above 75 mph
(120 km/h).
For emergency vehicles that are driven at speeds
over 90 mph (144 km/h), special high speed tires
must be used. Consult tire manufacturer for correct
inflation pressure recommendations.
TIRE AND WHEEL ROTATION
NON-DIRECTIONAL TREAD PATTERN TIRES
Tires on the front and rear axles operate at differ-
ent loads and perform different functions. For these
reasons, they wear at unequal rates, and tend to
develop irregular wear patterns. These effects can be
reduced by timely rotation of tires. The benefits of
rotation are especially worthwhile. Rotation will
increase tread life, help to maintain mud, snow, and
wet traction levels, and contribute to a smooth, quiet
ride.
Fig. 5 Under Inflation Wear
1 ± THIN TIRE TREAD AREAS
Fig. 6 Over Inflation Wear
1 ± THIN TIRE TREAD AREA
22 - 6 TIRES AND WHEELSPL
Page 1104 of 1285

The PCM is programmed to maintain the optimum
air/fuel ratio of 14.7 to 1. This is done by making
short term corrections in the fuel injector pulse width
based on the O2S output. The programmed memory
acts as a self calibration tool that the engine control-
ler uses to compensate for variations in engine spec-
ifications, sensor tolerances and engine fatigue over
the life span of the engine. By monitoring the actual
air-fuel ratio with the O2S (short term) and multiply-
ing that with the program long-term (adaptive) mem-
ory and comparing that to the limit, it can be
determined whether it will pass an emissions test. If
a malfunction occurs such that the PCM cannot
maintain the optimum A/F ratio, then the MIL will
be illuminated.
Monitor OperationÐFuel systems monitors do
not have a pre-test because they are continuously
running monitors. Therefore, the PCM constantly
monitors Short Term Compensation and Long Term
Adaptive memory.
Lean: If at anytime during a lean engine operation,
short term compensation multiplied by long term
adaptive exceeds a certain percentage for an
extended period, the PCM sets a Fuel System Lean
Fault for that trip and a Freeze Frame is entered.
Rich: If at anytime during a rich operation, Short
Term Compensation multiplied by Long Term Adap-
tive is less than a predetermined value, the PCM
checks the Purge Free Cells.
Purge Free Cells are values placed in Adaptive
Memory cells when the EVAP Purge Solenoid is OFF.
Two, three or four Purge Free cells are used. One cor-
responds to an Adaptive Memory cell at idle, the
other to a cell that is off-idle. For example, if a Purge
Free cell is labeled PFC1, it would hold the value for
Adaptive Memory cell C1 under non-purge condi-
tions.
If all Purge Free Cells are less than a certain per-
centage, and the Adaptive Memory factor is less than
a certain percentage, the PCM sets a Fuel System
Rich fault for that trip and a Freeze Frame is
entered.
The Fuel Monitor is a two trip monitor. The PCM
records engine data in Freeze Frame upon setting of
the first fault, or maturing code. When the fuel mon-
itor fails on a second consecutive trip, the code is
matured and the MIL is illuminated. The stored
Freeze Frame data is still from the first fault.
In order for the PCM to extinguish the MIL, the
Fuel Monitor must pass in a Similar Condition Win-
dow. The similar conditions relate to RPM and load.
The engine must be within a predetermined percent-
age of both RPM and load when the monitor runs to
count a good trip. As with all DTCs, three good tripsare required to extinguish the MIL and 40 warm up
cycles are required to erase the DTC. If the engine
does not run in a Similar Conditions Window, the
Task Manager extinguishes the MIL after 80 good
trips.
Enabling ConditionsÐThe following conditions
must be met to operate the fuel control monitor:
²PCM not in fuel crank mode (engine running)
²PCM in Closed Loop fuel control
²Fuel system updating Long Term Adaptive
²Fuel level above 15% of capacity
²Fuel level below 85% of capacity
Pending ConditionsÐThe Fuel Control Monitor
does not operate if the MIL is illuminated for any of
the following:
²Misfire Monitor
²Upstream O2S
²EVAP Purge Solenoid Electrical PCM Self Test
Fault
²Camshaft or Crankshaft Position Sensor
²Fuel Injectors
²Ignition Coil Primary
²Throttle Position (TPS) Sensor
²Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
²Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
²Idle Air Control (IAC)
²5V Output Too Low
²EGR Monitor
²EGR Solenoid Circuit
²Vehicle Speed Sensor
²Oxygen Sensor Monitor
²Oxygen Sensor Heater Monitor
²Oxygen Sensor Electrical
²Idle Speed Rationality
²Intake Air Temperature
SuspendÐThe Task Manager will suspend
maturing a Fuel System fault if any of the following
are present:
²Oxygen Sensor Response, Priority 1
²O2 Heater, Priority 1
²Misfire Monitor, Priority 2
EVAPORATIVE EMISSIONS MONITOR
LEAK DETECTION PUMP MONITORÐThe
leak detection assembly incorporates two primary
functions: it must detect a leak in the evaporative
system and seal the evaporative system so the leak
detection test can be run.
The primary components within the assembly are:
A three port solenoid that activates both of the func-
tions listed above; a pump which contains a switch,
two check valves and a spring/diaphragm, a canister
vent valve (CVV) seal which contains a spring loaded
vent seal valve.
PLEMISSION CONTROL SYSTEMS 25 - 17
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)