ignition DODGE NEON 2000 Service User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2000, Model line: NEON, Model: DODGE NEON 2000Pages: 1285, PDF Size: 29.42 MB
Page 154 of 1285

ABS ELECTRONIC DIAGNOSIS
The following information is presented to give the
technician a general background on the diagnostic
capabilities of the ABS system. Complete electronic
diagnosis of the ABS system used on this vehicle is
covered in the Chassis Diagnostic Procedures manual.
Electronic diagnosis of the ABS system used on
this vehicle is performed using the DRBIIItscan
tool. The vehicle's scan tool diagnostic connector is
located under the steering column lower cover, to the
left side of the steering column (Fig. 10).
ABS SELF-DIAGNOSIS
The ABS system is equipped with a self-diagnosis
capability, which may be used to assist in the isola-
tion of ABS faults. The features are described below.
START-UP CYCLE
The self-diagnosis ABS start-up cycle begins when
the ignition switch is turned to the ON position.
Electrical checks are completed on ABS components,
including the CAB, solenoid continuity, and the relay
system operation. During this check the amber ABS
warning lamp is turned on for approximately 5 sec-
onds and the brake pedal may emit a popping sound,
moving slightly when the solenoid valves are
checked.
DRIVE-OFF CYCLE
The first time the vehicle is set in motion after an
ignition off/on cycle, the drive-off cycle occurs. This
cycle is performed when the vehicle reaches a speed
of approximately 20 kph (12 mph.).²The pump/motor is briefly activated to verify
function. When the pump/motor is briefly activated, a
whirling or buzzing sound may be heard by the
driver. This sound is normal, indicating the pump/
motor is running.
²The wheel speed sensor output correct operating
range is verified.
ONGOING TESTS
While the system is operating, these tests are per-
formed on a continuous basis:
²solenoid continuity
²wheel speed sensor continuity
²wheel speed sensor output
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (DTC's)
Diagnostic trouble codes (DTC's) are kept in the
controller's memory until either erased by the techni-
cian using the DRB, or erased automatically after
3500 miles or 255 ignition key cycles, whichever
occurs first. DTC's are retained by the controller
even if the ignition is turned off or the battery is dis-
connected. More than one DTC can be stored at a
time. When accessed, the number of occurrences
(ignition key cycles) and the DTC that is stored are
displayed. Most functions of the CAB and the ABS
system can be accessed by the technician for testing
and diagnostic purposes using the DRB.
LATCHING VERSUS NON-LATCHING DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE
CODES
Some DTC's detected by the CAB are ªlatchingº
codes. The DTC is latched and ABS braking is dis-
abled until the ignition switch is reset. Thus, ABS
braking is non-operational even if the original DTC
has disappeared. Other DTC's are non-latching. Any
warning lamps that are turned on are only turned on
as long as the DTC condition exists; as soon as the
condition goes away, the amber ABS warning lamp is
turned off, although, in most cases, a DTC is set.
INTERMITTENT DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
As with virtually any electronic system, intermit-
tent electrical problems in the ABS system may be
difficult to accurately diagnose. Most intermittent
electrical problems are caused by faulty electrical
connections or wiring. A visual inspection should be
done before trying to diagnose or service the antilock
brake system; this will eliminate unnecessary diag-
nosis and testing time. Perform a visual inspection
for loose, disconnected, damaged, or misrouted wires
or connectors; include the following components and
areas of the vehicle in the inspection.
(1) Inspect fuses in the power distribution center
(PDC) and the wiring junction block. Verify that all
fuses are fully inserted into the PDC and wiring
Fig. 10 ABS System Diagnostic Connector Location
1 ± DRIVER AIRBAG MODULE
2 ± PASSENGER AIRBAG MODULE
3 ± DATA LINK CONNECTOR
PLBRAKES 5 - 75
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 155 of 1285

junction block. A label on the underside of the PDC
cover identifies the locations of the ABS fuses.
(2) Inspect the 25-way electrical connector at the
CAB for damaged, spread, or backed-out wiring ter-
minals. Verify that the 25-way connector is fully
inserted in the socket of the CAB. Be sure that wires
are not stretched tight or pulled out of the connector.
(3) Verify that all the wheel speed sensor connec-
tions are secure.
(4) Look for poor mating of connector halves or ter-
minals not fully seated in the connector body.
(5)
Check for improperly formed or damaged termi-
nals. All connector terminals in a suspect circuit should
be carefully reformed to increase contact tension.
(6) Look for poor terminal-to-wire connections.
This requires removing the terminal from the connec-
tor body to inspect it.
(7) Verify pin presence in the connector assembly
(8) Check for proper ground connections. Check all
ground connections for signs of corrosion, loose fas-
teners, or other potential defects. Refer to the wiring
diagrams for ground locations.
(9) Look for problems with the main power sources
of the vehicle. Inspect the battery, generator, ignition
circuits and other related relays and fuses.
If a visual check does not find the cause of the
problem, operate the car in an attempt to duplicate
the condition and record any trouble codes.
Most failures of the ABS disable the ABS function
for the entire ignition cycle even if the fault clears
before key-off. There are some failure conditions,
however, that allow ABS operation to resume during
the ignition cycle in which the trouble occurred even
if the trouble conditions are no longer present.
The following trouble conditions may result in
intermittent illumination of the amber ABS warning
lamp.
²Low system voltage. If Low System Voltage is
detected by the CAB, the CAB will turn on the ABS
Warning Lamp until normal system voltage is
achieved. Once normal voltage is seen at the CAB,
normal operation resumes.
²High system voltage. If high system voltage is
detected by the CAB, the CAB will turn on the
Amber ABS Warning Lamp until normal system volt-
age is achieved. Once normal voltage is again
detected by the CAB, normal ABS operation resumes.
Additional possible causes that may result in the
illumination of the amber ABS warning lamp are as
follows:
²Any condition that interrupts electrical current
to the CAB may cause the amber ABS warning lamp
to turn on intermittently.
²If PCI communication between the body control-
ler and the CAB is interrupted, the body controller
can turn on the amber ABS warning lamp.
TONE WHEEL
Tone wheels can cause erratic wheel speed sensor
signals. Inspect tone wheels for the following possible
causes:
²missing, chipped, or broken teeth
²contact with the wheel speed sensor
²wheel speed sensor to tone wheel alignment
²wheel speed sensor to tone wheel clearance
²excessive tone wheel runout
²tone wheel loose on its mounting surface
If a front tone wheel is found to need replacement,
the drive shaft must be replaced. No attempt should
be made to replace just the tone wheel. Refer to the
DIFFERENTIAL AND DRIVELINE group in this
service manual for removal and installation.
If a rear tone wheel is found to need replacement,
the rear hub and bearing must be replaced. No
attempt should be made to replace just the tone
wheel. Refer to the SUSPENSION group in this ser-
vice manual for removal and installation.
If wheel speed sensor to tone wheel contact is evi-
dent, determine the cause and correct it before
replacing the wheel speed sensor or tone wheel.
Check the gap between the speed sensor head and
the tone wheel to ensure it is within specifications.
Refer to SPECIFICATIONS in this section of the ser-
vice manual for the minimum and maximum wheel
speed sensor to tone wheel clearance.
Excessive wheel speed sensor runout can cause
erratic wheel speed sensor signals. Refer to SPECI-
FICATIONS in this section of the service manual for
the maximum allowed tone wheel runout. If tone
wheel runout is excessive, determine if it is caused
by a defect in the driveshaft assembly or hub and
bearing. Replace as necessary.
Tone wheels are pressed onto their mounting sur-
faces and should not rotate independently from the
mounting surface. Replacement of the front drive-
shaft or rear hub and bearing is necessary.
BRAKE FLUID CONTAMINATION
Indications of fluid contamination are swollen or
deteriorated rubber parts. Swelling indicates the
presence of petroleum in the brake fluid.
To test for contamination, put a small amount of
drained brake fluid in clear glass jar. If the fluid sep-
arates into layers, there is mineral oil or other fluid
contamination of the brake fluid.
If the brake fluid is contaminated, drain and thor-
oughly flush the brake system. Replace all the rubber
parts or components containing rubber coming into
contact with the brake fluid including: the master
cylinder; proportioning valves; caliper seals; wheel
cylinder seals; ABS hydraulic control unit; and all
hydraulic fluid hoses.
5 - 76 BRAKESPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 157 of 1285

NOTE: It is not necessary to bleed the entire
hydraulic system after replacing just the master cyl-
inder unless the brake system has been open to air
for an excessive amount of time or air is present in
the lines. Only the master cylinder must be bled
and filled.
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
SERVICE WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS
Review this entire section prior to performing any
mechanical work on a vehicle equipped with ABS.
This section contains information on precautions per-
taining to potential component damage, vehicle dam-
age and personal injury which could result when
servicing an ABS equipped vehicle.
CAUTION: Only the recommended jacking or hoist-
ing positions for this vehicle are to be used when-
ever it is necessary to lift a vehicle. Failure to raise
a vehicle from the recommended locations could
result in lifting a vehicle by the hydraulic control
unit mounting bracket. Lifting a vehicle by the
hydraulic control unit mounting bracket will result
in damage to the mounting bracket and the hydrau-
lic control unit.
CAUTION: An attempt to remove or disconnect cer-
tain system components may result in improper
system operation. Only those components with
approved removal and installation procedures in
this manual should be serviced.CAUTION: Brake fluid will damage painted sur-
faces. If brake fluid is spilled on any painted sur-
faces, wash off with water immediately.
CAUTION: When performing any service procedure
on a vehicle equipped with ABS do not apply a
12-volt power source to the ground circuit of the
pump motor in the HCU. Doing this will damage the
pump motor and will require replacement of the
entire HCU.
CAUTION: If welding work is to be performed on
the vehicle, using an electric arc welder, the CAB
connector should be disconnected during the weld-
ing operation.
CAUTION: The CAB 25-way connector should never
be connected or disconnected with the ignition
switch in the ON position.
Many components of the ABS System are not ser-
viceable and must be replaced as an assembly. Do not
disassemble any component which is not designed to
be serviced.
MASTER CYLINDER
NOTE: Before proceeding with this procedure,
review SERVICE WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS at the
beginning of REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION in this
section.
REMOVAL
CAUTION: The vacuum in the power brake booster
must be pumped down before removing the master
cylinder to prevent the booster from sucking in any
contamination. This can be done by pumping the
brake pedal while the engine is not running until a
firm brake pedal is achieved.
(1) With the engine not running, pump the brake
pedal 4-5 strokes until the pedal feel is firm.
(2) Disconnect the negative (ground) cable from
the battery and isolate the cable.
(3) Disconnect the positive cable from the battery,
then remove the battery from the battery tray. There
is one nut securing the clamp on the backside of the
battery holding it in place.
(4) Disconnect the wiring harness connector from
the brake fluid level switch on the master cylinder
reservoir (Fig. 12).
Fig. 11 Bleeding Master Cylinder
1 ± WOODEN DOWEL
2 ± MASTER CYLINDER
5 - 78 BRAKESPL
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 168 of 1285

SERVICE DIAGNOSISÐCLUTCH GRAB/CHATTER
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
CLUTCH DISC
FACING COVERED
WITH OIL OR
GREASEOil leak at engine rear main or transaxle
input shaft sealCorrect leak and replace modular clutch
assembly
Too much grease applied to splines of disc
and input shaftApply lighter coating of grease to splines
NO FAULT FOUND
WITH CLUTCH
COMPONENTSProblem actually related to suspension or
driveline componentFurther diagnosis required. Check
engine/transmission mounts, suspension
attaching parts and other driveline
components as needed.
Engine related problems Check EFI and ignition systems
PARTIAL
ENGAGEMENT OF
CLUTCH DISCClutch cover, spring, or release fingers
bent, distorted (rough handling, improper
assembly)Replace modular clutch assembly
Clutch disc damaged or distorted Replace modular clutch assembly
Clutch misalignment Check alignment and runout of flywheel,
disc, or cover. Check clutch housing to
engine dowels and dowel holes for damage.
Correct as necessary.
SERVICE DIAGNOSISÐCLUTCH SLIPS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
DISC FACING
WORN OUTNormal wear. Replace modular clutch assembly.
Driver frequently rides (slips) clutch, results
in rapid wear overheating.Replace modular clutch assembly
Insufficient clutch cover diaphragm spring
tensionReplace modular clutch assembly
CLUTCH DISC
FACING
CONTAMINATED
WITH OIL OR
GREASELeak at rear main oil seal or transaxle input
shaft sealReplace leaking seals. Replace modular
clutch assembly.
Excessive amount of grease applied to
input shaft splinesApply less grease to input shaft. Replace
modular clutch assembly
Road splash, water entering housing Seal housing. Inspect clutch assembly.
CLUTCH IS
RUNNING
PARTIALLY
DISENGAGEDRelease bearing sticking or binding, does
not return to normal running position.Verify that bearing is actually binding. Then,
replace bearing and transmission front
bearing retainer if sleeve surface is
damaged.
Cable self-adjuster mechanism sticking or
binding causing high preloadVerify that self-adjuster is free to move
PLCLUTCH 6 - 3
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 170 of 1285

DRIVE PLATE MISALIGNMENT
Common causes of misalignment are:
²Heat warping
²Mounting drive plate on a dirty crankshaft
flange
²Incorrect bolt tightening
²Improper seating on the crankshaft shoulder
²Loose crankshaft bolts
Clean the crankshaft flange before mounting the
drive plate. Dirt and grease on the flange surface
may misalign the flywheel, causing excessive runout.
Use new bolts when mounting drive plate to crank-
shaft. Tighten drive plate bolts to specified torque
only. Over-tightening can distort the drive plate hub
causing excessive runout.
CLUTCH CHATTER COMPLAINTS
For all clutch chatter complaints, do the following:
(1) Check for loose, misaligned, or broken engine
and transmission mounts. If present, they should be
corrected at this time. Test vehicle for chatter. If
chatter is gone, there is no need to go any further. If
chatter persists:
(2) Check to see if clutch cable routing is correct
and operates smoothly.
(3) Check for loose connections in drive train. Cor-
rect any problems and determine if clutch chatter
complaints have been satisfied. If not:
(4) Remove transaxle. See Group 21, Manual Tran-
saxle for procedure.
(5) Check to see if the release bearing is sticky or
binding. Replace bearing, if needed.
(6) Check linkage for excessive wear on the pivot
stud and fork fingers. Replace all worn parts.
(7) Check clutch assembly for contamination (dirt,
oil). Replace clutch assembly, if required.
(8) Check to see if the clutch disc hub splines are
damaged. Replace with new clutch assembly, if nec-
essary.
(9) Check input shaft splines for damage. Replace,
if necessary.
(10) Check for uneven wear on clutch fingers.
(11) Check for broken clutch cover diaphragm
spring fingers. Replace with new clutch assembly, if
necessary.
CLASH±INTO±REVERSE COMPLAINTS
Certain NV T350 (A-578) manual transaxles are
equipped with a reverse brake. It prevents clash
when shifting into reverse, but only if the vehicle is
not moving. See Group 21, Transaxle for further
diagnosis.
(1) Depress clutch pedal to floor and hold. After
three seconds, shift to reverse. If clash is present,
clutch has excessive spin time, and the reverse brake
may not be functioning.(2) Remove transaxle. See Group 21, Manual Tran-
saxle for procedure.
(3) Check the input shaft spline, clutch disc
splines, and release bearing for dry rust. If present,
clean rust off and apply a light coat of bearing grease
to the input shaft splines. Apply grease on the input
shaft splines only where the clutch disc slides. Verify
that the clutch disc slides freely along the input shaft
spline.
(4) Check to see if the clutch disc hub splines are
damaged, and replace with new clutch assembly if
required.
(5) Check the input shaft for damaged splines.
Replace as necessary.
(6) Check for broken clutch cover diaphragm
spring fingers.
(7) Install clutch assembly and transaxle.
CLUTCH INTERLOCK/UPSTOP SWITCH
The clutch interlock/upstop switch is an assembly
consisting of two switches: an engine starter inhibit
switch (clutch interlock) and a clutch pedal upstop
switch (Fig. 5). The switch assembly is located in the
clutch/brake pedal bracket assembly (Fig. 6), each
switch being fastened by four plastic wing tabs.
CLUTCH INTERLOCK SWITCH
Mechanical Test
(1) With the park brake set and the transaxleIN
NEUTRAL,turn the ignition key to the start posi-
tion. The engine starter should not crank with the
clutch pedal at rest (not depressed). If the starter
cranks, proceed to the electrical test to determine
whether the switch is defective or the circuit is
shorted. If the vehicle does not crank, proceed to the
next step.
(2) With the park brake set and the transaxleIN
NEUTRAL,fully depress the clutch pedal and turn
Fig. 5 Clutch Interlock/Upstop Switch
1 ± UPSTOP SWITCH
2 ± INTERLOCK SWITCH
3 ± CONNECTOR
PLCLUTCH 6 - 5
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 171 of 1285

the ignition key to the start position. The engine
starter should crank. If the starter does not crank,
visually inspect the clutch pedal for obstructions
(floor mat, etc.). Also make sure the clutch pedal
blade contacts and fully
Electrical Test
(1) Move ignition key to the ªOFF/LOCKº position
and remove key.
(2) Set park brake.
(3) Disconnect the clutch interlock/upstop switch
connector.
(4) Using an ohmmeter, check for continuity
between terminals2&3with the interlock switchnot depressed (clutch pedal at rest). There should be
no continuity between the terminals (open circuit).
(5) Fully depress the clutch pedal to close the
switch at least 1.25 mm (0.050 in.). The ohmmeter
should show continuity (0 ohms).
(6) If ohmmeter readings do not fall within these
ranges, the switch assembly is defective and should
be replaced. If the switch tests ok, wiring is defective.
Refer to Group 8W, Wiring Diagrams and repair
defective wiring.
UPSTOP SWITCH
Mechanical Test
(1) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(2) Start engine and operate speed control to main-
tain speed.
(3) Depress clutch pedal at least 33 mm (1.30 in.).
Speed control operation should terminate. If speed
control does not terminate, the upstop switch is
defective or the related wiring is shorted. Proceed to
the upstop switch electrical test.
Electrical Test
(1) Move ignition key to the ªOFF/LOCKº position
and remove key.
(2) Set park brake.
(3) Disconnect the clutch interlock/upstop switch
connector.
(4) Using an ohmmeter, check for continuity
between terminals1&2with the upstop switch
depressed (clutch pedal at rest). The ohmmeter
should show continuity (0 ohms).
(5) Depress the clutch pedal at least 33 mm (1.30
in.) check for continuity between terminals1&2.
There should be no continuity between the terminals
(open circuit).
(6) If ohmmeter readings do not fall within these
ranges, the switch assembly is defective and should
be replaced. If the switch tests ok, wiring is defective.
Refer to Group 8W, Wiring Diagrams and repair
defective wiring.
Fig. 6 Clutch/Brake Pedal Bracket Assembly
1 ± UPSTOP SWITCH
2 ± CLUTCH PEDAL
3 ± INTERLOCK SWITCH
4 ± CONNECTOR
6 - 6 CLUTCHPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 187 of 1285

CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
TEMPERATURE GAUGE READS
HIGH OR ENGINE COOLANT
WARNING LAMP ILLUMINATES.
COOLANT MAY OR MAY NOT BE
LOST FROM SYSTEM. (CONT.)6. Poor seals at radiator cap. 6. (a) Check condition of cap and
cap seals. Refer to Radiator cap
Inspection. Replace cap if
necessary.
(b) Check condition of filler neck. If
neck is bent or damaged, replace
neck.
7. Coolant level low in radiator, but
not in coolant recovery/reserve
container. This indicates the
radiator is not drawing coolant from
the coolant recovery/reserve
container as the engine cools. As
the engine cools, a vacuum is
formed inside the cooling system. If
the radiator cap seals are defective,
or the cooling system has a leak, a
vacuum cannot be formed.7. (a) Check condition of radiator
cap and cap seals. Replace cap if
necessary.
(b) Check condition of filler neck.
Replace if damaged.
(c) Check condition of hose from
filler neck to coolant container. It
should be tight at both ends without
any kinks or tears. Replace hose as
necessary.
(d) Check coolant recovery/reserve
container and hose for blockage.
Repair as necessary.
8. Freeze point of coolant not
correct. Mixture ratio may be too
rich.8. Check coolant concentration.
Refer to Coolant Concentration
Testing in this section. Adjust
glycol-to-water ration as required.
9. Coolant not flowing through
system.9. Check for coolant flow at filler
neck with some coolant removed,
engine warm, and thermostat open.
Coolant should be observed flowing
through filler neck. If flow is not
observed, determine reason for lack
of flow and repair as necessary.
10. Radiator or A/C condenser fins
are dirty or clogged.10. Clean obstruction from fins.
11. Radiator core is plugged or
corroded.11. Replace or re-core radiator.
12. Fuel or ignition system
problems.12. Refer to Fuel and Ignition
System groups for diagnosis. Also
refer to the appropriate Powertrain
Diagnostic Procedure manual.
13. Dragging Brakes. 13. Inspect brake system and repair
as necessary. Refer to Group 5,
Brakes for diagnosis.
14 Bug screen or other aftermarket
accessory is being used causing
reduced air flow.14. Remove bug screen or
accessory.
15. Thermostat partially or
completely closed. This is more
prevalent on high mileage vehicles.15. Check thermostat operation and
replace as necessary. Refer to
thermostat in this section for
procedure.
7 - 8 COOLING SYSTEMPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 189 of 1285
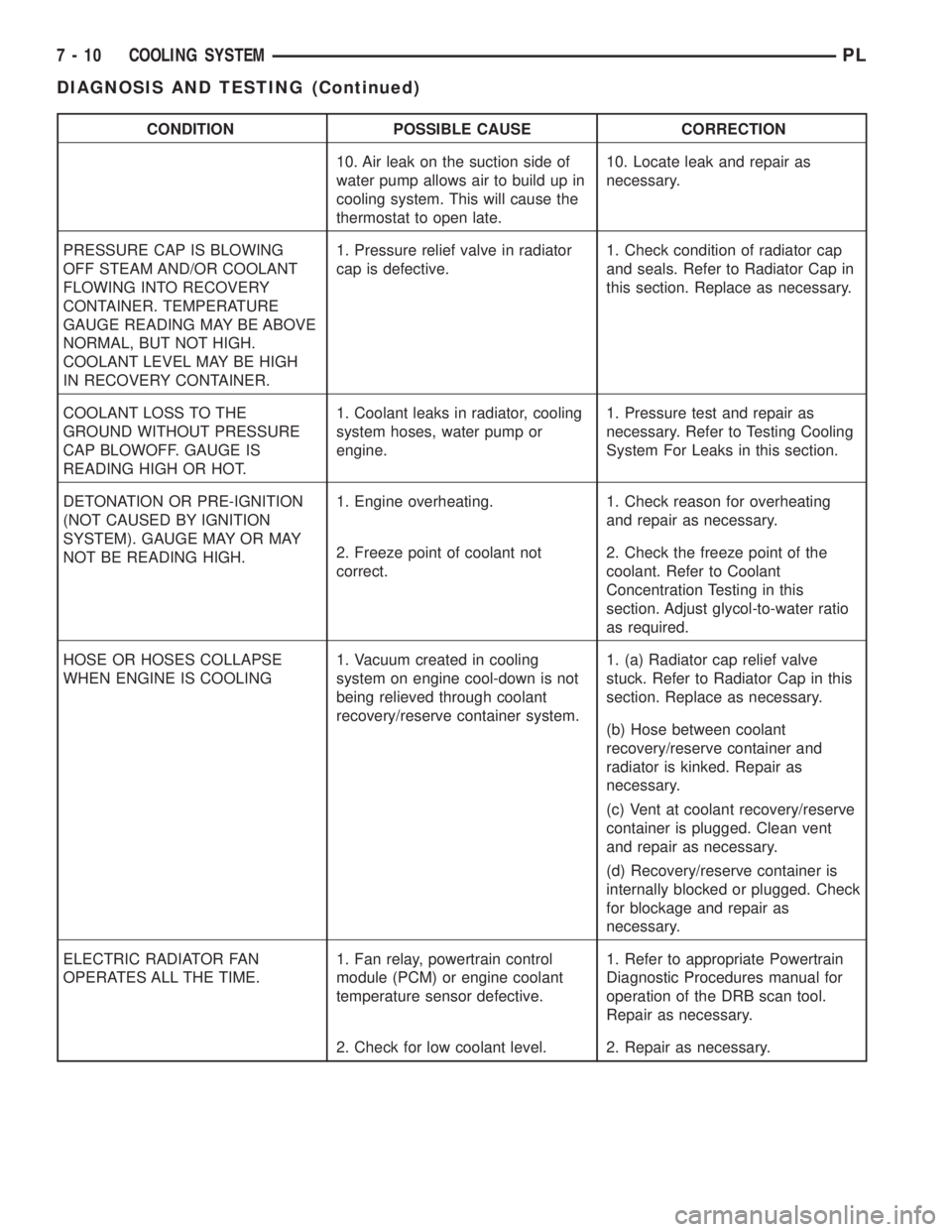
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
10. Air leak on the suction side of
water pump allows air to build up in
cooling system. This will cause the
thermostat to open late.10. Locate leak and repair as
necessary.
PRESSURE CAP IS BLOWING
OFF STEAM AND/OR COOLANT
FLOWING INTO RECOVERY
CONTAINER. TEMPERATURE
GAUGE READING MAY BE ABOVE
NORMAL, BUT NOT HIGH.
COOLANT LEVEL MAY BE HIGH
IN RECOVERY CONTAINER.1. Pressure relief valve in radiator
cap is defective.1. Check condition of radiator cap
and seals. Refer to Radiator Cap in
this section. Replace as necessary.
COOLANT LOSS TO THE
GROUND WITHOUT PRESSURE
CAP BLOWOFF. GAUGE IS
READING HIGH OR HOT.1. Coolant leaks in radiator, cooling
system hoses, water pump or
engine.1. Pressure test and repair as
necessary. Refer to Testing Cooling
System For Leaks in this section.
DETONATION OR PRE-IGNITION
(NOT CAUSED BY IGNITION
SYSTEM). GAUGE MAY OR MAY
NOT BE READING HIGH.1. Engine overheating. 1. Check reason for overheating
and repair as necessary.
2. Freeze point of coolant not
correct.2. Check the freeze point of the
coolant. Refer to Coolant
Concentration Testing in this
section. Adjust glycol-to-water ratio
as required.
HOSE OR HOSES COLLAPSE
WHEN ENGINE IS COOLING1. Vacuum created in cooling
system on engine cool-down is not
being relieved through coolant
recovery/reserve container system.1. (a) Radiator cap relief valve
stuck. Refer to Radiator Cap in this
section. Replace as necessary.
(b) Hose between coolant
recovery/reserve container and
radiator is kinked. Repair as
necessary.
(c) Vent at coolant recovery/reserve
container is plugged. Clean vent
and repair as necessary.
(d) Recovery/reserve container is
internally blocked or plugged. Check
for blockage and repair as
necessary.
ELECTRIC RADIATOR FAN
OPERATES ALL THE TIME.1. Fan relay, powertrain control
module (PCM) or engine coolant
temperature sensor defective.1. Refer to appropriate Powertrain
Diagnostic Procedures manual for
operation of the DRB scan tool.
Repair as necessary.
2. Check for low coolant level. 2. Repair as necessary.
7 - 10 COOLING SYSTEMPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 199 of 1285

(4) Rotate pump by hand to check for freedom of
movement.
(5) Install rear timing belt cover and camshaft
sprocket.
(6) Install timing belt tensioner and timing belt.
Refer to Group 9, Engine for procedure.
(7) Install right engine mount bracket. Refer to
Group 9, Engine for procedure.
(8) Install upper and lower torque isolator struts.
Refer to Group 9, Engine for procedure.
(9) Fill cooling system. Refer to procedures in this
section.
(10) Install accessory drive belts. Refer to proce-
dure in this section.
(11) Perform camshaft and crankshaft timing
relearn procedure as follows:
²Connect the DRB scan tool to the data link
(diagnostic) connector. This connector is located in
the passenger compartment; at the lower edge of
instrument panel; near the steering column.
²Turn the ignition switch on and access the ªmis-
cellaneousº screen.
²Select ªre-learn cam/crankº option and follow
directions on DRB screen.
WATER PUMP INLET TUBE
The inlet tube connects the water pump to the
radiator and heater core. This tube is sealed by an
O-ring and held in place by fasteners to the block.
REMOVAL
CAUTION: Do not use any sharp tools to remove
hoses from inlet tube. This may cause the tube to
leak.
(1) Drain cooling system. Refer to procedure in
this section.
(2) Remove upper radiator hose to access the hose
connections at the inlet tube.(3) Remove intake manifold. Refer to Group 9,
Engine for procedure.
(4) Remove lower radiator hose and heater hose
from the inlet tube.
(5) Remove lower intake manifold support bracket.
(6) Remove the inlet tube to the block fasteners.
(7) Rotate tube while removing the tube from the
engine block (Fig. 21).
INSTALLATION
(1) Inspect the O-ring for damage before installing
the tube into the cylinder block (Fig. 21). Replace
O-ring as necessary.
(2) Lubricate O-ring with MopartDielectric
Grease and install inlet tube into the cylinder block
opening.
(3) Install inlet tube fasteners and tighten fasten-
ers to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs.).
(4) Install intake manifold lower support bracket
fasteners and tighten to 12 N´m (105 in. lbs.).
(5) Connect lower radiator hose and heater hose to
inlet tube.
(6) Install intake manifold. Refer to Group 9,
Engine for procedure.
(7) Install upper radiator hose.
(8) Fill cooling system. Refer to procedure in this
section.
(9) Pressure system to 104 kPa (15 psi) to check
for leaks.
ENGINE THERMOSTAT
REMOVAL
(1) Drain cooling system to the thermostat level or
below.
(2) Remove coolant recovery/reserve system hose
and upper radiator hose.
Fig. 20 Water Pump Body
1 ± IMPELLER
2 ± PUMP BODY
3 ± O-RING
Fig. 21 Water Pump Inlet Tube
1 ± O-RING
2 ± WATER PUMP INLET TUBE
FRONT
7 - 20 COOLING SYSTEMPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 210 of 1285

BATTERY
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
GENERAL INFORMATION
INTRODUCTION..........................1
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
BATTERY IGNITION OFF DRAW (IOD).........2
CHARGING TIME REQUIRED................2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
BATTERY BUILT-IN TEST INDICATOR.........3
BATTERY IGNITION OFF DRAW (IOD).........4
BATTERY LOAD TEST......................6
BATTERY OPEN CIRCUIT VOLTAGE...........7
SERVICE PROCEDURES
BATTERY CHARGING......................7CHARGING COMPLETELY DISCHARGED
BATTERY..............................8
VISUAL INSPECTION......................9
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
BATTERY...............................10
BATTERY THERMOWRAP..................10
BATTERY TRAY..........................11
SPECIFICATIONS
BATTERY SPECIFICATIONS................11
TORQUE...............................11
GENERAL INFORMATION
INTRODUCTION
The battery (Fig. 1) stores, stabilizes, and delivers
electrical current to operate various electrical sys-
tems in the vehicle. The determination of whether a
battery is good or bad is made by its ability to accept
a charge. It also must supply high-amperage current
for a long enough period to be able to start the vehi-
cle. The capability of the battery to store electrical
current comes from a chemical reaction. This reac-
tion takes place between the sulfuric acid solution
(electrolyte) and the lead +/- plates in each cell of the
battery. As the battery discharges, the plates react
with the acid from the electrolyte. When the charging
system charges the battery, the water is converted to
sulfuric acid in the battery. The concentration of acid
in the electrolyte is measured as specific gravity
using a hydrometer. The original equipment (OE)
battery is equipped with a hydrometer (test indica-
tor) built into the battery cover. The specific gravity
indicates the battery's state-of-charge. The OE bat-
tery is sealed and water cannot be added.
The battery is vented to release gases that are cre-
ated when the battery is being charged and discharged.
The battery top, posts, and terminals should be cleaned
when other under hood maintenance is performed.
When the electrolyte level is below the top of the
plates, Yellow/Clear in the test Indicator, the battery
must be replaced. The battery must be completely
charged, and the battery top, posts, and cable clamps
must be cleaned before diagnostic procedures are per-
formed.
Fig. 1 Battery Location
1 ± BATTERY
2 ± LEFT STRUT TOWER
3 ± PDC
4 ± THROTTLE BODY
5 ± AIR CLEANER HOUSING
PLBATTERY 8A - 1