oil type DODGE NEON 2000 Service Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2000, Model line: NEON, Model: DODGE NEON 2000Pages: 1285, PDF Size: 29.42 MB
Page 724 of 1285

ENGINE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
STANDARD SERVICE PROCEDURES........... 1
ENGINE DIAGNOSIS........................ 82.0L SOHC ENGINE....................... 15
STANDARD SERVICE PROCEDURES
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
GENERAL INFORMATION
FORM-IN-PLACE GASKETS & SEALERS........1
ENGINE GASKET SURFACE PREPARATION.....2
CRANKSHAFT DAMPER BOLT ACCESS PLUG . . . 2
ENGINE CORE PLUGS.....................2
ENGINE PERFORMANCE...................3HONING CYLINDER BORES.................3
MEASURING WITH PLASTIGAGE.............4
REPAIR OF DAMAGED OR WORN THREADS....5
HYDROSTATIC LOCKED ENGINE.............5
CHECKING ENGINE OIL LEVEL..............6
ENGINE OIL SERVICE......................7
GENERAL INFORMATION
FORM-IN-PLACE GASKETS & SEALERS
There are numerous places where form-in-place
gaskets are used on the engine. Care must be taken
when applying form-in-place gaskets to assure
obtaining the desired results.Do not use form-in-
place gasket material unless specified.Bead size,
continuity, and location are of great importance. Too
thin a bead can result in leakage while too much can
result in spill-over which can break off and obstruct
fluid feed lines. A continuous bead of the proper
width is essential to obtain a leak-free gasket.
There are numerous types of form-in-place gasket
materials that are used in the engine area. Mopart
Engine RTV GEN II, MopartATF-RTV, and Mopart
Gasket Maker gasket materials, each have different
properties and can not be used in place of the other.
MOPARtENGINE RTV GEN II
MopartEngine RTV GEN II is used to seal com-
ponents exposed to engine oil. This material is a spe-
cially designed black silicone rubber RTV that
retains adhesion and sealing properties when
exposed to engine oil. Moisture in the air causes the
material to cure. This material is available in three
ounce tubes and has a shelf life of one year. After one
year this material will not properly cure. Alwaysinspect the package for the expiration date before
use.
MOPARtATF RTV
MopartATF RTV is a specifically designed black
silicone rubber RTV that retains adhesion and seal-
ing properties to seal components exposed to auto-
matic transmission fluid, engine coolants, and
moisture. This material is available in three ounce
tubes and has a shelf life of one year. After one year
this material will not properly cure. Always inspect
the package for the expiration date before use.
MOPARtGASKET MAKER
MopartGasket Maker is an anaerobic type gasket
material. The material cures in the absence of air
when squeezed between two metallic surfaces. It will
not cure if left in the uncovered tube. The anaerobic
material is for use between two machined surfaces.
Do not use on flexible metal flanges.
MOPARtBED PLATE SEALANT
MopartBed Plate Sealant is a unique (green-in-
color) anaerobic type gasket material that is specially
made to seal the area between the bedplate and cyl-
inder block without disturbing the bearing clearance
or alignment of these components. The material
cures slowly in the absence of air when torqued
between two metallic surfaces, and will rapidly cure
when heat is applied.
PLENGINE 9 - 1
Page 730 of 1285

ENGINE OIL SERVICE
WARNING: NEW OR USED ENGINE OIL CAN BE
IRRITATING TO THE SKIN. AVOID PROLONGED OR
REPEATED SKIN CONTACT WITH ENGINE OIL.
CONTAMINANTS IN USED ENGINE OIL, CAUSED BY
INTERNAL COMBUSTION, CAN BE HAZARDOUS TO
YOUR HEALTH. THOROUGHLY WASH EXPOSED
SKIN WITH SOAP AND WATER. DO NOT WASH
SKIN WITH GASOLINE, DIESEL FUEL, THINNER, OR
SOLVENTS, HEALTH PROBLEMS CAN RESULT. DO
NOT POLLUTE, DISPOSE OF USED ENGINE OIL
PROPERLY. CONTACT YOUR DEALER OR GOVERN-
MENT AGENCY FOR LOCATION OF COLLECTION
CENTER IN YOUR AREA.
ENGINE OIL SPECIFICATION
CAUTION: Do not use non-detergent or straight
mineral oil when adding or changing crankcase
lubricant. Engine failure can result.
API SERVICE GRADE CERTIFIED
Use an engine oil that is API Service Grade Certi-
fied. MOPARtprovides engine oils that conforms to
this service grade.
SAE VISCOSITY
An SAE viscosity grade is used to specify the vis-
cosity of engine oil. Use only, engine oils with multi-
ple viscosities such as 5W-30 or 10W-30. These are
specified with a dual SAE viscosity grade which indi-
cates the cold-to-hot temperature viscosity range.
SAE 5W-30 engine oil is preferred. Select an engine
oil that is best suited to your particular temperature
range and variation (Fig. 9).
ENERGY CONSERVING OIL
An Energy Conserving type oil is recommended for
gasoline engines. The designation of ENERGY CON-
SERVING is located on the label of the engine oil
container.
CONTAINER IDENTIFICATION
Standard engine oil identification notations have
been adopted to aid in the proper selection of engine
oil. The identifying notations are located on the label
of engine oil plastic bottles and the top of engine oil
cans (Fig. 10).
ENGINE OIL CHANGE
Change engine oil at mileage and time intervals
described in the Group 0, Lubrication and Mainte-
nance.TO CHANGE ENGINE OIL
Run engine until achieving normal operating tem-
perature.
(1) Position the vehicle on a level surface and turn
engine off.
(2) Hoist and support vehicle on safety stands.
Refer to Group 0, Lubrication and Maintenance for
Hoisting and Jacking Recommendations.
(3) Remove oil fill cap.
(4) Place a suitable drain pan under crankcase
drain.
(5) Remove drain plug from crankcase and allow
oil to drain into pan. Inspect drain plug threads for
stretching or other damage. Replace drain plug and
gasket if damaged.
(6) Install drain plug in crankcase.
(7) Lower vehicle and fill crankcase with specified
type and amount of engine oil described in this sec-
tion.
(8) Install oil fill cap.
(9) Start engine and inspect for leaks.
(10) Stop engine and inspect oil level.
Fig. 9 Temperature/Engine Oil Viscosity
Fig. 10 Engine Oil Container Standard Notations
PLENGINE 9 - 7
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 740 of 1285
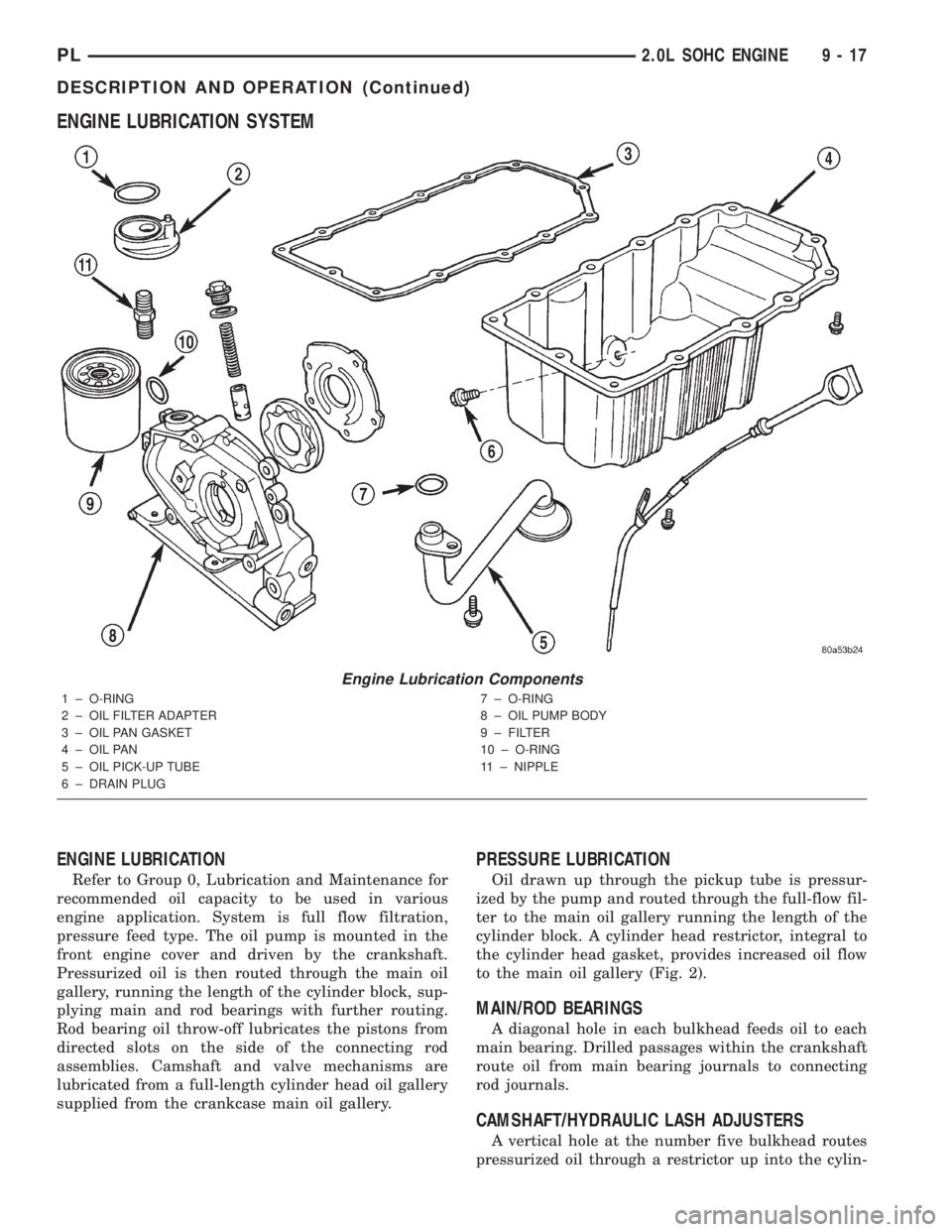
ENGINE LUBRICATION SYSTEM
ENGINE LUBRICATION
Refer to Group 0, Lubrication and Maintenance for
recommended oil capacity to be used in various
engine application. System is full flow filtration,
pressure feed type. The oil pump is mounted in the
front engine cover and driven by the crankshaft.
Pressurized oil is then routed through the main oil
gallery, running the length of the cylinder block, sup-
plying main and rod bearings with further routing.
Rod bearing oil throw-off lubricates the pistons from
directed slots on the side of the connecting rod
assemblies. Camshaft and valve mechanisms are
lubricated from a full-length cylinder head oil gallery
supplied from the crankcase main oil gallery.
PRESSURE LUBRICATION
Oil drawn up through the pickup tube is pressur-
ized by the pump and routed through the full-flow fil-
ter to the main oil gallery running the length of the
cylinder block. A cylinder head restrictor, integral to
the cylinder head gasket, provides increased oil flow
to the main oil gallery (Fig. 2).
MAIN/ROD BEARINGS
A diagonal hole in each bulkhead feeds oil to each
main bearing. Drilled passages within the crankshaft
route oil from main bearing journals to connecting
rod journals.
CAMSHAFT/HYDRAULIC LASH ADJUSTERS
A vertical hole at the number five bulkhead routes
pressurized oil through a restrictor up into the cylin-
Engine Lubrication Components
1 ± O-RING
2 ± OIL FILTER ADAPTER
3 ± OIL PAN GASKET
4 ± OIL PAN
5 ± OIL PICK-UP TUBE
6 ± DRAIN PLUG7 ± O-RING
8 ± OIL PUMP BODY
9 ± FILTER
10 ± O-RING
11 ± NIPPLE
PL2.0L SOHC ENGINE 9 - 17
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 741 of 1285

der head. The rocker shafts route oil to the rocker
arms/hydraulic lash adjuster assemblies.
SPLASH LUBRICATION
Oil returning to the pan from pressurized compo-
nents supplies lubrication to the valve stems. Cylin-
der bores and wrist pins are splash lubricated from
directed slots on the connecting rod thrust collars.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
CHECKING ENGINE OIL PRESSURE
(1) Remove oil pressure switch and install gauge
assembly C-3292 with adaptor.
(2) Run engine until thermostat opens.
CAUTION: If oil pressure is 0 at idle, Do Not per-
form the 3000 RPM test in the next step.
(3) Oil Pressure:Curb Idle25 kPa (4 psi) mini-
mum3000 RPM170-550 kPa (25-80 psi).
(4) If oil pressure is 0 at idle. Shut off engine,
check for pressure relief valve stuck open, a clogged
oil pick-up screen or a damaged oil pick-up tube
O-ring.
SERVICE PROCEDURES
CYLINDER BORE AND PISTON SIZING
The cylinder walls should be checked for out-of-
round and taper with recommended tool C-119 or
equivalent (Fig. 3). The cylinder bore out-of-roundand cylinder bore taper must within service limits.
Refer to Engine Specifications in this section. If the
cylinder walls are badly scuffed or scored, the cylin-
der block should be rebored and honed, and new pis-
tons and rings fitted. Whatever type of boring
equipment is used, boring and honing operations
should be closely coordinated with the fitting of pis-
tons and rings in order to maintain specified clear-
ances.Refer to Honing Cylinder Bores in the
Standard Service Procedures for procedures.
Measure the cylinder bore at three levels in direc-
tions A and B (Fig. 3). Top measurement should be
10 mm (3/8 inch) down and bottom measurement
should be 10 mm (3/8 inch.) up from bottom of bore.
Refer to Engine Specifications in this section for cyl-
inder block specifications.
SIZING PISTONS
Piston and cylinder wall must be clean and dry.
Piston diameter should be measured 90 degrees to
piston pin about 17.5 mm (11/16 inch) from the bot-
tom of the skirt as shown in (Fig. 4). Cylinder bores
should be measured halfway down the cylinder bore
and transverse to the engine crankshaft center line
shown in (Fig. 3). Correct piston to bore clearance
must be established in order to assure quiet and eco-
nomical operation. Refer to Engine Specifications in
this section for cylinder block and piston specifica-
tions.
DaimlerChrysler engines use pistons designed spe-
cifically for each engine model. Clearance and sizing
locations vary with respect to engine model.
Fig. 2 Engine Lubrication SystemÐ SOHC
Fig. 3 Checking Cylinder Bore Size
9 - 18 2.0L SOHC ENGINEPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 791 of 1285

SPECIFICATIONS
2.0L SOHC ENGINE
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
General Specification
Type In-Line OHV, SOHC
Number of Cylinders 4
Displacement 2.0 Liters
(122 cu. in.)
Bore 87.5 mm
(3.445 in.)
Stroke 83.0 mm
(3.268 in.)
Compression Ratio 9.8:1
Firing Order 1-3-4-2
Compression Pressure 1172±1551 kPa
(170±225 psi)
Max. Variation Between
Cylinders25%
Cylinder Block
Cylinder Bore Diameter 87.4924±87.5076 mm
(3.4446±3.4452 in.)
Out-of-Round (Max.) 0.051 mm
(0.002 in.)
Taper (Max.) 0.051 mm
(0.002 in.)
Pistons (Federal Emission)
Piston Diameter 87.463±87.481 mm
(3.4434±3.4441 in.)
Clearance 17.5 mm
(11/16 in.) from bottom of
skirt0.012±0.044 mm
(0.0004±0.0017 in.)
Weight 325±335 grams
(11.47±11.82 oz.)
Land Clearance
(Diametrical)0.734±0.797 mm
(0.029±0.031 in.)
Piston Length 64 mm
(2.520 in.)
Piston Ring Groove
Depth No. 13.989±4.188 mm
(0.157±0.165 in.)
Piston Ring Groove
Depth No. 24.462±4.661 mm
(0.176±0.184 in.)
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Piston Ring Groove
Depth No. 33.847±4.131 mm
(0.151±0.163 in.)
Pistons (Low Emission VehicleÐLEV/ULEV)
Piston Diameter 87.456±87.474 mm
(3.4432±3.4439 in.)
Clearance 10.42 mm
(0.42 in.) from bottom of
skirt0.018±0.50 mm
(0.0008±0.0020 in.)
Weight 320±329 grams
(11.29±11.60 oz.)
Land Clearance
(Diametrical)0.758±0.790 mm
(0.0299±0.0312 in.)
Piston Length 55.8 mm
(2.197 in.)
Piston Ring Groove
Depth No. 13.989±4.188 mm
(0.157±0.165 in.)
Piston Ring Groove
Depth No. 24.462±4.661 mm
(0.176±0.184 in.)
Piston Ring Groove
Depth No. 33.847±4.131 mm
(0.151±0.163 in.)
Piston Pins
Clearance in Piston 0.008±0.015 mm
(0.0003±0.0006 in.)
Clearance in Connecting
RodInterference
Diameter 21.000±21.003 mm
(0.8268±0.8269 in.)
End Play None
Length 74.75±75.25 mm
(2.943±2.963 in.)
Piston Rings
Ring GapÐTop
Compression Ring0.23±0.52 mm
(0.009±0.020 in.)
Wear Limit 0.8 mm
(0.031 in.)
Ring GapÐ2nd
Compression Ring0.49±0.78 mm
(0.019±0.031 in.)
Wear Limit 1.0 mm
(0.039 in.)
Ring GapÐOil Control
Steel Rails0.23±0.66 mm
(0.009±0.026 in.)
9 - 68 2.0L SOHC ENGINEPL
Page 831 of 1285
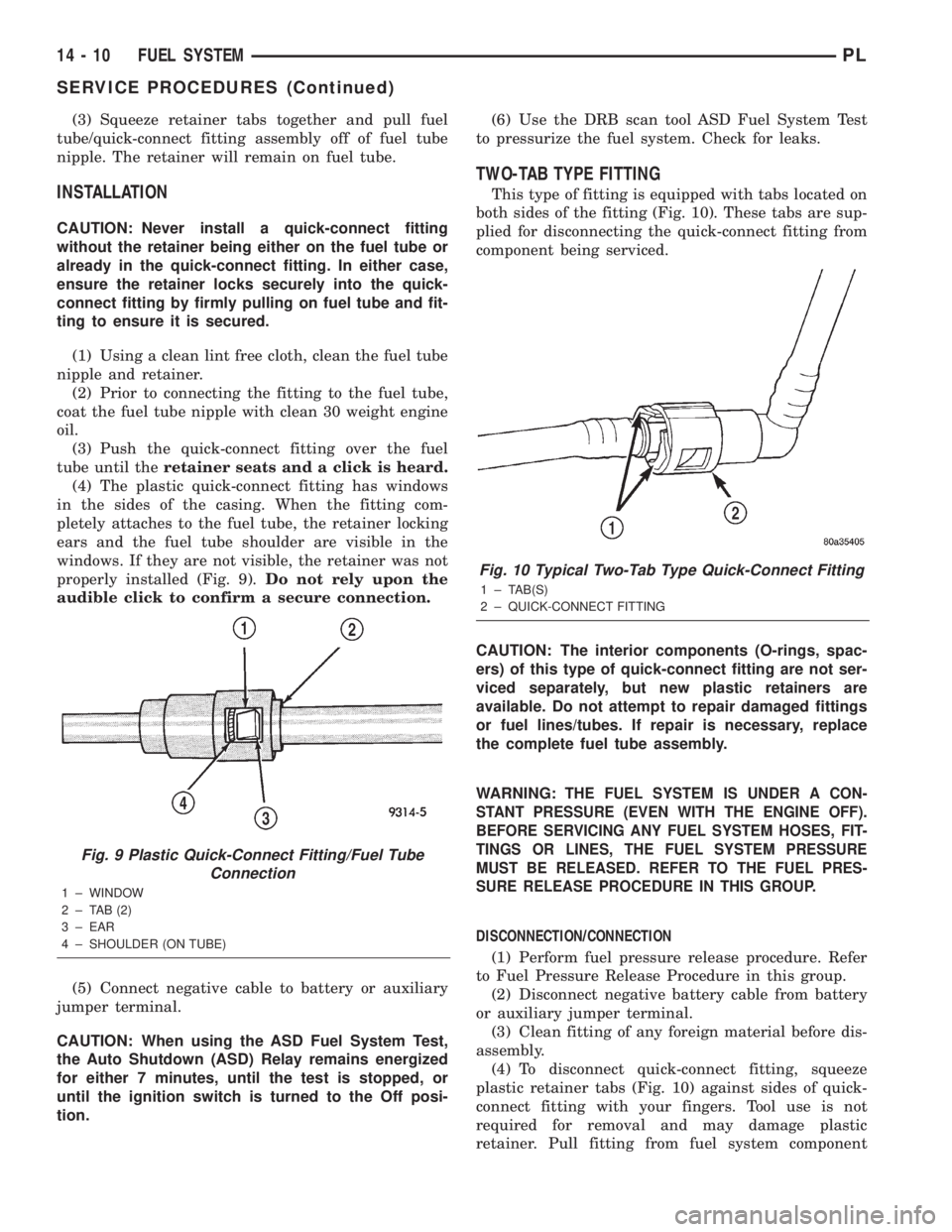
(3) Squeeze retainer tabs together and pull fuel
tube/quick-connect fitting assembly off of fuel tube
nipple. The retainer will remain on fuel tube.
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: Never install a quick-connect fitting
without the retainer being either on the fuel tube or
already in the quick-connect fitting. In either case,
ensure the retainer locks securely into the quick-
connect fitting by firmly pulling on fuel tube and fit-
ting to ensure it is secured.
(1) Using a clean lint free cloth, clean the fuel tube
nipple and retainer.
(2) Prior to connecting the fitting to the fuel tube,
coat the fuel tube nipple with clean 30 weight engine
oil.
(3) Push the quick-connect fitting over the fuel
tube until theretainer seats and a click is heard.
(4) The plastic quick-connect fitting has windows
in the sides of the casing. When the fitting com-
pletely attaches to the fuel tube, the retainer locking
ears and the fuel tube shoulder are visible in the
windows. If they are not visible, the retainer was not
properly installed (Fig. 9).Do not rely upon the
audible click to confirm a secure connection.
(5) Connect negative cable to battery or auxiliary
jumper terminal.
CAUTION: When using the ASD Fuel System Test,
the Auto Shutdown (ASD) Relay remains energized
for either 7 minutes, until the test is stopped, or
until the ignition switch is turned to the Off posi-
tion.(6) Use the DRB scan tool ASD Fuel System Test
to pressurize the fuel system. Check for leaks.
TWO-TAB TYPE FITTING
This type of fitting is equipped with tabs located on
both sides of the fitting (Fig. 10). These tabs are sup-
plied for disconnecting the quick-connect fitting from
component being serviced.
CAUTION: The interior components (O-rings, spac-
ers) of this type of quick-connect fitting are not ser-
viced separately, but new plastic retainers are
available. Do not attempt to repair damaged fittings
or fuel lines/tubes. If repair is necessary, replace
the complete fuel tube assembly.
WARNING:
THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER A CON-
STANT PRESSURE (EVEN WITH THE ENGINE OFF).
BEFORE SERVICING ANY FUEL SYSTEM HOSES, FIT-
TINGS OR LINES, THE FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE
MUST BE RELEASED. REFER TO THE FUEL PRES-
SURE RELEASE PROCEDURE IN THIS GROUP.
DISCONNECTION/CONNECTION
(1) Perform fuel pressure release procedure. Refer
to Fuel Pressure Release Procedure in this group.
(2) Disconnect negative battery cable from battery
or auxiliary jumper terminal.
(3) Clean fitting of any foreign material before dis-
assembly.
(4) To disconnect quick-connect fitting, squeeze
plastic retainer tabs (Fig. 10) against sides of quick-
connect fitting with your fingers. Tool use is not
required for removal and may damage plastic
retainer. Pull fitting from fuel system component
Fig. 9 Plastic Quick-Connect Fitting/Fuel Tube
Connection
1 ± WINDOW
2 ± TAB (2)
3 ± EAR
4 ± SHOULDER (ON TUBE)
Fig. 10 Typical Two-Tab Type Quick-Connect Fitting
1 ± TAB(S)
2 ± QUICK-CONNECT FITTING
14 - 10 FUEL SYSTEMPL
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 832 of 1285

being serviced. The plastic retainer will remain on
component being serviced after fitting is discon-
nected. The O-rings and spacer will remain in quick-
connect fitting connector body.
(5) Inspect quick-connect fitting body and compo-
nent for damage. Replace as necessary.
CAUTION:
When the quick-connect fitting was dis-
connected, the plastic retainer will remain on the com-
ponent being serviced. If this retainer must be
removed, very carefully release the retainer from the
component with two small screwdrivers. After removal,
inspect the retainer for cracks or any damage.
(6) Prior to connecting quick-connect fitting to
component being serviced, check condition of fitting
and component. Clean parts with a lint-free cloth.
Lubricate with clean engine oil.
(7) Insert quick-connect fitting to component being
serviced and into plastic retainer. When a connection
is made, a click will be heard.
(8) Verify a locked condition by firmly pulling on
fuel tube and fitting (15-30 lbs.).
(9) Connect negative cable to battery or auxiliary
jumper terminal.
(10) Start engine and check for leaks.
PLASTIC RETAINER RING TYPE FITTING
This type of fitting can be identified by the use of a
full-round plastic retainer ring (Fig. 11) usually black
in color.
CAUTION: The interior components (O-rings, spac-
ers, retainers) of this type of quick-connect fitting
are not serviced separately. Do not attempt to repair
damaged fittings or fuel lines/tubes. If repair is nec-
essary, replace the complete fuel tube assembly.
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER A CON-
STANT PRESSURE (EVEN WITH THE ENGINE OFF).
BEFORE SERVICING ANY FUEL SYSTEM HOSES,
FITTINGS OR LINES, THE FUEL SYSTEM PRES-
SURE MUST BE RELEASED. REFER TO THE FUEL
SYSTEM PRESSURE RELEASE PROCEDURE IN
THIS GROUP.
DISCONNECTION/CONNECTION
(1) Perform fuel pressure release procedure. Refer
to Fuel Pressure Release Procedure in this section.
(2) Disconnect negative battery cable from battery
or auxiliary jumper terminal.
(3) Clean fitting of any foreign material before dis-
assembly.
(4) To release fuel system component from quick-
connect fitting, firmly push fitting towards compo-nent being serviced while firmly pushing plastic
retainer ring into fitting (Fig. 11). With plastic ring
depressed, pull fitting from component.The plastic
retainer ring must be pressed squarely into fit-
ting body. If this retainer is cocked during
removal, it may be difficult to disconnect fit-
ting. Use an open-end wrench on shoulder of
plastic retainer ring to aid in disconnection.
(5) After disconnection, plastic retainer ring will
remain with quick-connect fitting connector body.
(6) Inspect fitting connector body, plastic retainer
ring and fuel system component for damage. Replace
as necessary.
(7) Prior to connecting quick-connect fitting to
component being serviced, check condition of fitting
and component. Clean parts with a lint-free cloth.
Lubricate with clean engine oil.
(8) Insert quick-connect fitting into component
being serviced until a click is felt.
(9) Verify a locked condition by firmly pulling on
fuel tube and fitting (15-30 lbs.).
(10) Connect negative battery cable to battery or
auxiliary jumper terminal.
(11) Start engine and check for leaks.
Fig. 11 Plastic Retainer Ring Type Fitting
1 ± FUEL TUBE
2 ± QUICK CONNECT FITTING
3 ± PUSH
4 ± PLASTIC RETAINER
5 ± PUSH
6 ± PUSH
7 ± PUSH
8 ± PUSH
PLFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 11
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 873 of 1285

POWER STEERING FLUID HOSES
The power steering fluid hoses connect the compo-
nents of the power steering system. They transfer
fluid from one component to the next.
The power steering fluid pressure hose is a high
pressure hose that connects the power steering pump
to the gear. At both ends of the flexible hose portion
are steel fittings that are pressure crimped to the
flexible hose. A standard tube nut fitting with an
O-ring is used at each end to connect it to either the
power steering pump or the gear.
The power steering fluid return hose is a special
rubber hose that connects the power steering gear or
the power steering fluid cooler on some models, back
to the fluid reservoir mounted on the power steering
pump. The power steering gear has a steel fitting
attached to its outlet port that the return hose is
pushed onto. On vehicles equipped with a power
steering fluid cooler, the return hose attaches to the
cooler outlet tube instead of the steering gear steel
fitting. The hose is secured to either component using
a standard adjustable clamp. The other end of the
power steering fluid return hose attaches to the
power steering fluid reservoir on the power steering
pump using a standard adjustable clamp.
POWER STEERING FLUID COOLER
Some models of this vehicle are equipped with a
cooler for the power steering system fluid (Fig. 1).
The purpose of the cooler is to keep the temperature
of the power steering system fluid from rising to a
level that would affect the performance of the power
steering system.
The power steering fluid cooler is located at the
front of the front suspension crossmember. It is
mounted to the crossmember top surface using 2 fas-
teners.The cooler is placed in series with the power steer-
ing fluid return hose, between the steering gear fluid
outlet port and the fluid return hose leading to the
power steering fluid reservoir. The power steering
gear has a steel fitting attached to its outlet port
that a short hose leading to the cooler is pushed onto.
This hose is secured to both the steering gear outlet
fitting and the cooler using standard adjustable
clamps. The cooler is secured to the power steering
fluid return hose using a standard adjustable clamp.
The cooler used on this vehicle is referred to as a
fluid-to-air type cooler. This means that the air flow
across the tubes of the cooler is used to extract the
heat from the cooler which it has absorbed from the
power steering fluid flowing through it. Utilizing a
small air dam mounted to its base to redirect air
across its coils, the cooler lowers the temperature of
the power steering fluid prior to it entering the
power steering fluid reservoir where it is resupplied
to the power steering pump.
Fig. 1 Power Steering Fluid Cooler
1 ± POWER STEERING FLUID COOLER
2 ± TRANSAXLE
3 ± CLAMP
4 ± AIR DAM
5 ± CROSSMEMBER
19 - 2 STEERINGPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 887 of 1285

POWER STEERING PUMP
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
POWER STEERING PUMP.................16
POWER STEERING FLUID RESERVOIR.......17
SERVICE PROCEDURES
POWER STEERING PUMP INITIAL
OPERATION...........................17
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
SERVICE WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS........17
POWER STEERING PUMP.................17DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY
POWER STEERING PUMP (PULLEY).........19
SPECIFICATIONS
POWER STEERING PUMP FLOW
SPECIFICATIONS.......................20
POWER STEERING FASTENER TORQUE
SPECIFICATIONS.......................20
SPECIAL TOOLS
POWER STEERING PUMP.................20
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
POWER STEERING PUMP
The hydraulic pressure for operation of the power
steering gear is provided by a belt driven power
steering pump (Fig. 1) manufactured by TTA. The
TTA power steering pump is a constant flow rate and
displacement vane-type pump.
In the event of a power steering pump drive belt
failure, manual steering control of the vehicle can
still be maintained. However, under these conditions,
steering effort will be significantly increased.No repair procedures are to be done on the internal
components of the power steering pump. The only
serviceable components of the power steering pump
are the power steering pump pulley and the pump
itself. The power steering fluid reservoir is serviced
with the pump.
Because of unique shaft bearings, flow control lev-
els or pump displacements, power steering pumps
may be used only on specific vehicle applications. Be
sure that all power steering pumps are only replaced
with a pump that is the correct replacement for that
specific application.
Hydraulic pressure is provided for operation of the
power steering gear by the belt driven power steering
pump (Fig. 1). It is a constant displacement, vane
type pump. The power steering pump is connected to
the steering gear by a power steering fluid pressure
hose and return hose.
Rectangular pumping vanes in the shaft driven
rotor move power steering fluid from the intake to
the cam ring pressure cavities of the power steering
pump. As the rotor begins to turn, centrifugal force
throws the vanes against the inside surface of the
cam ring to pickup residual oil. This oil is then forced
into the high pressure area. As more oil is picked up
by the vanes, the additional oil is forced into the cav-
ities of the thrust plate through two crossover holes
in the cam ring and pressure plate. The crossover
holes empty into the high pressure area between the
pressure plate and the housing end cover.
As the high pressure area is filled, oil flows under
the vanes in the rotor slots, forcing the vanes to fol-
low the inside surface of the cam ring. As the vanes
reach the restricted area of the cam ring, oil is forced
out from between the vanes. When excess oil flow is
generated during high-speed operation, a regulated
amount of oil returns to the pump intake side
through a flow control valve. The flow control valve
Fig. 1 Power Steering Pump
1 ± POWER STEERING FLUID RESERVOIR
2 ± POWER STEERING PUMP
3 ± PULLEY
4 ± PUMP PRESSURE FITTING
19 - 16 STEERINGPL
Page 888 of 1285

reduces the power required to drive the pump and
holds down temperature build-up.
When steering conditions exceed maximum pres-
sure requirements, such as when the wheels are
turned against the stops, the pressure built up in the
steering gear exerts pressure on the spring end of the
flow control valve. The high pressure lifts the relief
valve ball from its seat and allows oil to flow through
a trigger orifice located in the outlet fitting. This
reduces pressure on the spring end of the flow con-
trol valve which then opens and allows the oil to
return to the intake side of the pump. This action
limits maximum pressure output of the pump to a
safe level.
Under normal power steering pump operating con-
ditions, pressure requirements of the pump are below
maximum, causing the pressure relief valve to
remain closed.
POWER STEERING FLUID RESERVOIR
The power steering fluid reservoir is mounted on
the power steering pump using 3 bolts (Fig. 1). It
stores fluid for the power steering system.
The power steering fluid reservoir is considered an
integral part of the power steering pump and is not
serviced separately.
SERVICE PROCEDURES
POWER STEERING PUMP INITIAL OPERATION
CAUTION: The fluid level should be checked with
engine off to prevent injury from moving compo-
nents. Use only MoparTPower Steering Fluid. Do
not use automatic transmission fluid. Do not over-
fill.
Wipe the filler cap clean, then check the fluid level.
The dipstick should indicateCOLDwhen the fluid is
at normal temperature, approximately 21ÉC to 27ÉC
(70ÉF to 80ÉF).
(1) Fill the power steering fluid reservoir to the
proper level and let the fluid settle for at least two
minutes.
(2) Start the engine and let run for a few seconds,
then turn the engine off.
(3) Add fluid if necessary. Repeat the above proce-
dure until the fluid level remains constant after run-
ning the engine.
(4) Raise the front wheels off the ground.
(5) Start the engine. Slowly turn the steering
wheel right and left, lightly contacting the wheel
stops.
(6) Add power steering fluid if necessary.
(7) Lower the vehicle and turn the steering wheel
slowly from lock to lock.(8) Stop the engine. Check the fluid level and refill
as required.
(9) If the fluid is extremely foamy, allow the vehi-
cle to stand a few minutes and repeat the above pro-
cedure.
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
SERVICE WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS
WARNING: POWER STEERING FLUID, ENGINE
PARTS AND EXHAUST SYSTEM MAY BE
EXTREMELY HOT IF ENGINE HAS BEEN RUNNING.
DO NOT START ENGINE WITH ANY LOOSE OR DIS-
CONNECTED HOSES. DO NOT ALLOW HOSES TO
TOUCH HOT EXHAUST MANIFOLD OR CATALYST.
WARNING: FLUID LEVEL SHOULD BE CHECKED
WITH THE ENGINE OFF TO PREVENT PERSONAL
INJURY FROM MOVING PARTS.
CAUTION: When the system is open, cap all open
ends of the hoses, power steering pump fittings or
power steering gear ports to prevent entry of for-
eign material into the components.
NOTE: Do not use any type of automatic transmis-
sion fluid in the power steering system.
POWER STEERING PUMP
NOTE: Before proceeding with this removal and
installation procedure, review SERVICE WARNINGS
AND CAUTIONS at the beginning of REMOVAL AND
INSTALLATION in this section.
REMOVAL
(1) Remove battery cable from the negative post on
the battery.
(2) Siphon as much fluid as possible from the
power steering fluid reservoir.
(3) Remove the power steering pump drive belt
from the power steering pump pulley. Refer to
ACCESSORY DRIVE BELTS in the COOLING SYS-
TEM service manual group for the required removal
and installation procedure.
(4) Remove the hose clamp securing the return
hose to the power steering fluid reservoir. Slide the
hose off the end of the reservoir fitting. (Fig. 2).
(5) Back out the tube nut securing the power
steering fluid pressure hose to the power steering
pump and remove the hose from the pump (Fig. 2).
PLSTEERING 19 - 17
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)