brake rotor DODGE NEON 2000 Service Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2000, Model line: NEON, Model: DODGE NEON 2000Pages: 1285, PDF Size: 29.42 MB
Page 136 of 1285
CALIPER PISTON AND SEALS
CALIPER PISTON REMOVAL
WARNING: UNDER NO CONDITION SHOULD HIGH
PRESSURE AIR EVER BE USED TO REMOVE A PIS-
TON FROM A CALIPER BORE. PERSONAL INJURY
COULD RESULT FROM SUCH A PRACTICE.
NOTE: The safest way to remove the piston from
the caliper bore is to use the hydraulic pressure of
the vehicle's brake system.
(1) Following the removal procedure in DISC
BRAKE SHOES found in this section, remove the
caliper from the brake rotor and hang the assembly
on a wire hook away from rotor and body of the vehi-
cle so brake fluid cannot get on these components.
Remove the brake shoes, and place a small piece of
wood between the piston and caliper fingers.
(2) Carefully depress the brake pedal to hydrauli-
cally push piston out of its bore. Once completed,
apply and hold down the brake pedal to any position
beyond the first inch of pedal travel using a brake
pedal holding tool. This will prevent the fluid in the
master cylinder reservoir from completely draining
out.(3) Disconnect the brake fluid flex hose from the
caliper assembly and remove it from the vehicle.
CALIPER SEAL REMOVAL
CAUTION: Do not use excessive force when clamp-
ing caliper in vise. Excessive vise pressure will
cause bore distortion.
(1) To disassemble the caliper, mount it in a vise
equipped with protective jaws.
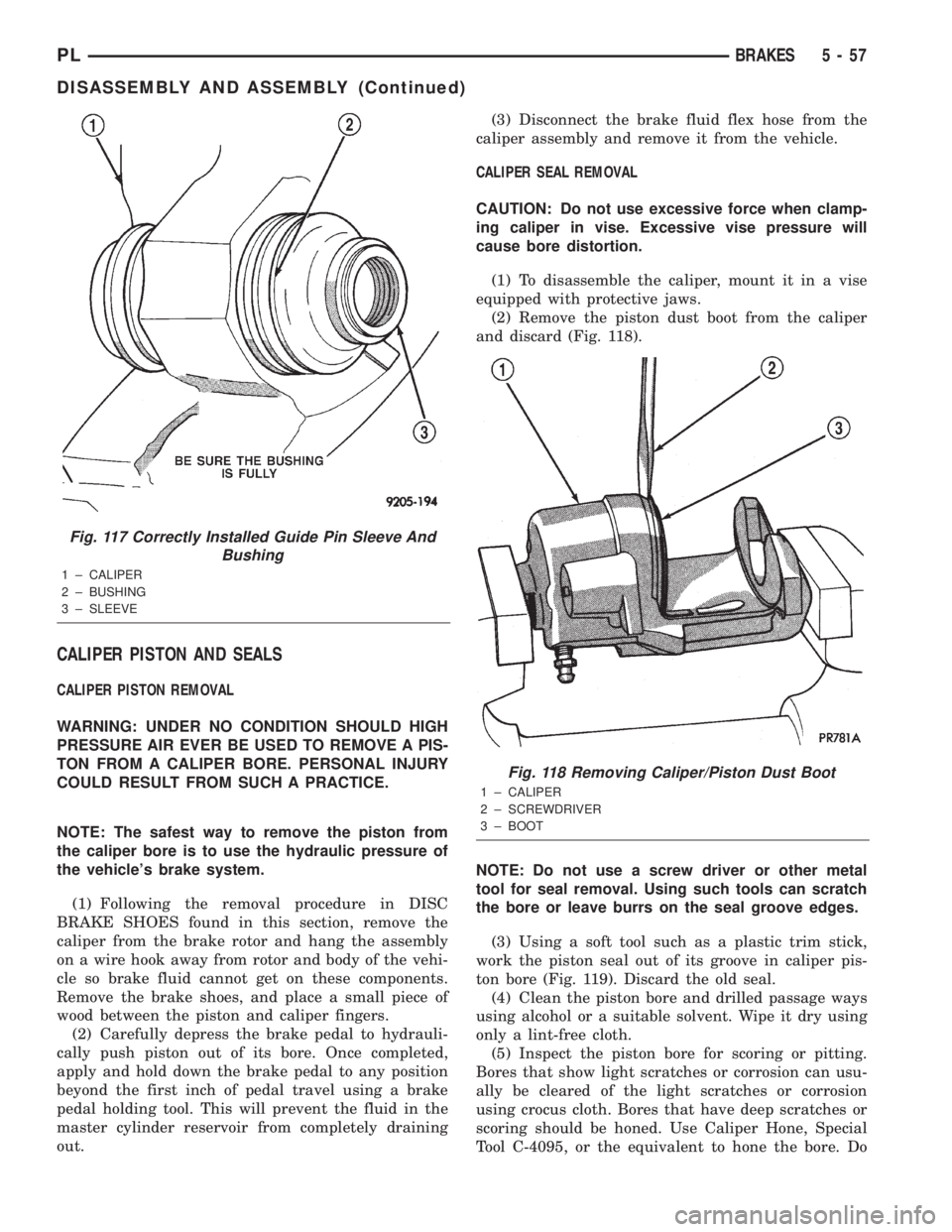
(2) Remove the piston dust boot from the caliper
and discard (Fig. 118).
NOTE: Do not use a screw driver or other metal
tool for seal removal. Using such tools can scratch
the bore or leave burrs on the seal groove edges.
(3) Using a soft tool such as a plastic trim stick,
work the piston seal out of its groove in caliper pis-
ton bore (Fig. 119). Discard the old seal.
(4) Clean the piston bore and drilled passage ways
using alcohol or a suitable solvent. Wipe it dry using
only a lint-free cloth.
(5) Inspect the piston bore for scoring or pitting.
Bores that show light scratches or corrosion can usu-
ally be cleared of the light scratches or corrosion
using crocus cloth. Bores that have deep scratches or
scoring should be honed. Use Caliper Hone, Special
Tool C-4095, or the equivalent to hone the bore. Do
Fig. 117 Correctly Installed Guide Pin Sleeve And
Bushing
1 ± CALIPER
2 ± BUSHING
3 ± SLEEVE
Fig. 118 Removing Caliper/Piston Dust Boot
1 ± CALIPER
2 ± SCREWDRIVER
3 ± BOOT
PLBRAKES 5 - 57
DISASSEMBLY AND ASSEMBLY (Continued)
Page 860 of 1285

PROPORTIONAL PURGE SOLENOIDÐPCM
OUTPUT
DESCRIPTION
OPERATION
All vehicles use a proportional purge solenoid. The
solenoid regulates the rate of vapor flow from the
EVAP canister to the throttle body. The PCM oper-
ates the solenoid.
During the cold start warm-up period and the hot
start time delay, the PCM does not energize the sole-
noid. When de-energized, no vapors are purged.
The proportional purge solenoid operates at a fre-
quency of 200 hz and is controlled by an engine con-
troller circuit that senses the current being applied
to the proportional purge solenoid (Fig. 23) and then
adjusts that current to achieve the desired purge
flow. The proportional purge solenoid controls the
purge rate of fuel vapors from the vapor canister and
fuel tank to the engine intake manifold.
GENERATOR FIELDÐPCM OUTPUT
OPERATION
Refer to the Battery section for information and
refer to the Charging section for information. The
PCM regulates the charging system voltage within a
range of 12.9 to 15.0 volts. The charging system is
turned ON and OFF with the Ignition Switch. When
the Ignition Switch is turned to the ON position, bat-
tery voltage is applied to the generator rotor through
one of the two field terminals to produce a magnetic
field. The amount of DC current produced by the
generator is controlled by the Electronic Voltage Reg-
ulator (EVR) in the PCM. This circuitry is connectedin series with the second rotor field terminal and
ground.
The voltage determined by the PCM as the final
goal for the charging system is called ªtarget charg-
ing voltage.º The PCM monitors battery voltage. If
the sensed voltage is 0.5 volts or lower than the tar-
get voltage, the PCM grounds the field winding until
sensed battery voltage is 0.5 volts above target volt-
age.
IDLE AIR CONTROL MOTORÐPCM OUTPUT
DESCRIPTION
The Idle Air Control (IAC) motor is mounted on the
throttle body. The PCM operates the idle air control
motor (Fig. 24).
OPERATION
The PCM adjusts engine idle speed through the
idle air control motor to compensate for engine load,
coolant temperature or barometric pressure changes.
The throttle body has an air bypass passage that
provides air for the engine during closed throttle idle.
The idle air control motor pintle protrudes into the
air bypass passage and regulates air flow through it.
The PCM adjusts engine idle speed by moving the
IAC motor pintle in and out of the bypass passage.
The adjustments are based on inputs the PCM
receives. The inputs are from the throttle position
sensor, crankshaft position sensor, coolant tempera-
ture sensor, MAP sensor, vehicle speed sensor and
various switch operations (brake, park/neutral, air
conditioning).
When engine rpm is above idle speed, the IAC is
used for the following functions:
²Off-idle dashpot
²Deceleration air flow control
²A/C compressor load control (also opens the pas-
sage slightly before the compressor is engaged so
that the engine rpm does not dip down when the
compressor engages)
Target Idle
Target idle is determined by the following inputs:
²Gear position
²ECT Sensor
²Battery voltage
²Ambient/Battery Temperature Sensor
²VSS
²TPS
²MAP Sensor
Fig. 23 Proportional Purge Solenoid
PLFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 39
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)