fuse diagram DODGE NEON 2000 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2000, Model line: NEON, Model: DODGE NEON 2000Pages: 1285, PDF Size: 29.42 MB
Page 153 of 1285

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
SERVICE WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS
The ABS uses an electronic control module, the
CAB. This module is designed to withstand normal
current draws associated with vehicle operation.
Care must be taken to avoid overloading the CAB
circuits.
CAUTION: In testing for open or short circuits, do
not ground or apply voltage to any of the circuits
unless instructed to do so for a diagnostic proce-
dure.
CAUTION: These circuits should only be tested
using a high impedance multi-meter or the DRB
scan tool as described in this section. Power
should never be removed or applied to any control
module with the ignition in the ON position. Before
removing or connecting battery cables, fuses, or
connectors, always turn the ignition to the OFF
position.
CAUTION: Use only factory wiring harnesses. Do
not cut or splice wiring to the brake circuits. The
addition of after-market electrical equipment (car
phone, radar detector, citizen band radio, trailer
lighting, trailer brakes, etc.) on a vehicle equipped
with antilock brakes may affect the function of the
antilock brake system.
ABS GENERAL DIAGNOSTICS INFORMATION
This section contains information necessary to
diagnose the antilock brake system. Specifically, this
section should be used to help diagnose conditions
which result in any of the following:
(1) amber ABS warning lamp turned on.
(2) brakes lock-up on hard application.
Diagnosis of base brake conditions that are obvi-
ously mechanical in nature should be directed to
BASE BRAKE SYSTEM at the beginning of this
group.
Many ABS conditions judged to be a problem by
the driver may be normal operating conditions. See
ABS OPERATION in the DESCRIPTION AND
OPERATION section of this group to become famil-
iarized with the normal characteristics of this
antilock brake system.
ABS WIRING DIAGRAM INFORMATION
During the diagnosis and testing of the antilock
brake system it may become necessary to reference
the wiring diagrams covering the antilock brake sys-
tem and its components. For wiring diagrams refer to
GROUP 8W of this service manual. It will provide
you with the wiring diagrams and the circuit descrip-
tion and operation information covering the antilock
brake system.
ABS VEHICLE TEST DRIVE
Most ABS complaints will require a test drive to
properly duplicate and diagnose the condition.
WARNING: CONDITIONS THAT RESULT IN TURN-
ING ON THE RED BRAKE WARNING LAMP MAY
INDICATE REDUCED BRAKING ABILITY.
Before test driving a brake complaint vehicle, note
whether the red BRAKE warning lamp, amber ABS
warning lamp, or both are turned on. If it is the red
BRAKE warning lamp, there is a brake hydraulic
problem that must be corrected before driving the
vehicle. Refer to the BASE BRAKE SYSTEM for
diagnosis of the red BRAKE warning lamp. If the red
brake warning lamp is illuminated, there is also a
possibility that there is an ABS problem and the
amber ABS warning lamp is not able to illuminate,
so the MIC turns on the red Brake warning lamp by
default.
If the amber ABS warning lamp is on, test drive
the vehicle as described below. While the amber ABS
warning lamp is on, the ABS is not functional. The
ability to stop the car using the base brake system
should not be affected.
If a functional problem of the ABS is determined
while test driving the vehicle, refer to the Chassis
Diagnostic Procedures manual.
(1) Turn the key to the OFF position and then
back to the ON position. Note whether the amber
ABS warning lamp continues to stay on. If it does,
refer to the diagnostic manual.
(2) If the amber ABS warning lamp goes out, shift
into gear and drive the car to a speed of 20 kph (12
mph) to complete the ABS start-up and drive-off
cycles (see ABS ELECTRONIC DIAGNOSIS). If at
this time the amber ABS warning lamp comes on,
refer to the diagnostic manual.
(3) If the amber ABS warning lamp remains out,
drive the vehicle a short distance. Accelerate the
vehicle to a speed of at least 40 mph. Bring the vehi-
cle to a complete stop, braking hard enough to cause
the ABS to cycle. Again accelerate the vehicle past 25
mph. Refer to the diagnostic manual for further test-
ing of the antilock brake system.
5 - 74 BRAKESPL
Page 155 of 1285

junction block. A label on the underside of the PDC
cover identifies the locations of the ABS fuses.
(2) Inspect the 25-way electrical connector at the
CAB for damaged, spread, or backed-out wiring ter-
minals. Verify that the 25-way connector is fully
inserted in the socket of the CAB. Be sure that wires
are not stretched tight or pulled out of the connector.
(3) Verify that all the wheel speed sensor connec-
tions are secure.
(4) Look for poor mating of connector halves or ter-
minals not fully seated in the connector body.
(5)
Check for improperly formed or damaged termi-
nals. All connector terminals in a suspect circuit should
be carefully reformed to increase contact tension.
(6) Look for poor terminal-to-wire connections.
This requires removing the terminal from the connec-
tor body to inspect it.
(7) Verify pin presence in the connector assembly
(8) Check for proper ground connections. Check all
ground connections for signs of corrosion, loose fas-
teners, or other potential defects. Refer to the wiring
diagrams for ground locations.
(9) Look for problems with the main power sources
of the vehicle. Inspect the battery, generator, ignition
circuits and other related relays and fuses.
If a visual check does not find the cause of the
problem, operate the car in an attempt to duplicate
the condition and record any trouble codes.
Most failures of the ABS disable the ABS function
for the entire ignition cycle even if the fault clears
before key-off. There are some failure conditions,
however, that allow ABS operation to resume during
the ignition cycle in which the trouble occurred even
if the trouble conditions are no longer present.
The following trouble conditions may result in
intermittent illumination of the amber ABS warning
lamp.
²Low system voltage. If Low System Voltage is
detected by the CAB, the CAB will turn on the ABS
Warning Lamp until normal system voltage is
achieved. Once normal voltage is seen at the CAB,
normal operation resumes.
²High system voltage. If high system voltage is
detected by the CAB, the CAB will turn on the
Amber ABS Warning Lamp until normal system volt-
age is achieved. Once normal voltage is again
detected by the CAB, normal ABS operation resumes.
Additional possible causes that may result in the
illumination of the amber ABS warning lamp are as
follows:
²Any condition that interrupts electrical current
to the CAB may cause the amber ABS warning lamp
to turn on intermittently.
²If PCI communication between the body control-
ler and the CAB is interrupted, the body controller
can turn on the amber ABS warning lamp.
TONE WHEEL
Tone wheels can cause erratic wheel speed sensor
signals. Inspect tone wheels for the following possible
causes:
²missing, chipped, or broken teeth
²contact with the wheel speed sensor
²wheel speed sensor to tone wheel alignment
²wheel speed sensor to tone wheel clearance
²excessive tone wheel runout
²tone wheel loose on its mounting surface
If a front tone wheel is found to need replacement,
the drive shaft must be replaced. No attempt should
be made to replace just the tone wheel. Refer to the
DIFFERENTIAL AND DRIVELINE group in this
service manual for removal and installation.
If a rear tone wheel is found to need replacement,
the rear hub and bearing must be replaced. No
attempt should be made to replace just the tone
wheel. Refer to the SUSPENSION group in this ser-
vice manual for removal and installation.
If wheel speed sensor to tone wheel contact is evi-
dent, determine the cause and correct it before
replacing the wheel speed sensor or tone wheel.
Check the gap between the speed sensor head and
the tone wheel to ensure it is within specifications.
Refer to SPECIFICATIONS in this section of the ser-
vice manual for the minimum and maximum wheel
speed sensor to tone wheel clearance.
Excessive wheel speed sensor runout can cause
erratic wheel speed sensor signals. Refer to SPECI-
FICATIONS in this section of the service manual for
the maximum allowed tone wheel runout. If tone
wheel runout is excessive, determine if it is caused
by a defect in the driveshaft assembly or hub and
bearing. Replace as necessary.
Tone wheels are pressed onto their mounting sur-
faces and should not rotate independently from the
mounting surface. Replacement of the front drive-
shaft or rear hub and bearing is necessary.
BRAKE FLUID CONTAMINATION
Indications of fluid contamination are swollen or
deteriorated rubber parts. Swelling indicates the
presence of petroleum in the brake fluid.
To test for contamination, put a small amount of
drained brake fluid in clear glass jar. If the fluid sep-
arates into layers, there is mineral oil or other fluid
contamination of the brake fluid.
If the brake fluid is contaminated, drain and thor-
oughly flush the brake system. Replace all the rubber
parts or components containing rubber coming into
contact with the brake fluid including: the master
cylinder; proportioning valves; caliper seals; wheel
cylinder seals; ABS hydraulic control unit; and all
hydraulic fluid hoses.
5 - 76 BRAKESPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 214 of 1285

be checked. To determine if a high current draw con-
dition exists first check the vehicle with a test lamp.
(1) Verify that all electrical accessories are OFF.
²Remove key from ignition switch
²Turn off all lights
²Trunk lid is closed
²Engine compartment hood lamp is disconnected
or lamp removed
²Map lamp on rear view mirror
²Glove box door is closed
²Sun visor vanity lights are OFF
²All doors are closed
²Allow the ignition key lamp system to time out
in approximately 30 seconds, if equipped.
(2) Disconnect battery negative cable (Fig. 5).
(3) Connect a 12 Volt test lamp, with a cold resis-
tance of 5-7 ohms, between the battery negative cable
clamp and the negative post (Fig. 6). If test lamp
goes out system is OK. If test lamp lights and stays
ON, go to Test Lamp Stays ON procedure.
TEST LAMP STAYS ON
There is either a short circuit or a fault in an elec-
tronic module. Two fuses in the Power Distribution
Center (PDC) feed the modules with ignition off
draw.
²Interior lamps fuse (10 Amp) (IOD) PDC
²Fuel pump fuse (20 Amp) in PDC.
(1) Remove interior lamp and fuel pump fuses. By
removing these fuses all ignition off draw from thevehicle electronics will be disconnected. The test
lamp should go out. If test lamp goes out go to Step
2. If test lamp does not go out there is a current
draw or short circuit. Refer to Group 8W, Wiring Dia-
grams.
(2) Install the fuel pump fuse. If test lamp lights,
there is a current draw or short circuit in the A14
wiring circuit feed.
(a) Disconnect Powertrain Control Module.
(b) If test lamp goes out, replace Powertrain
Control Module.
(c) If test lamp does not go out, there is a cur-
rent draw or short circuit in the A14 circuit feed.
Refer to Group 8W, Wiring Diagrams.
(3) Install the interior lamp fuse. If test lamp
lights, there is a current draw or short circuit in the
M01 circuit. Refer to Group 8W, Wiring Diagrams. If
test lamp stays out, go to Step 4.
(4) Use a multi-meter that has at least a range of
200 milliamperes. Install meter between the battery
negative cable and battery negative post (Fig. 7).
Carefully remove the test lamp without disconnecting
the meter. After all modules time-out the total vehi-
cle IOD should be less than 10 milliamperes. If igni-
tion off draw is more than 10 milliamperes go to Step
5.
(5) Remove both fuses from the Power Distribution
Center:
²Fuel pump fuse (20 Amp)
²Interior lamps fuse (10 Amp)
(6) If there is any reading with fuses removed
there is a current draw or short circuit in the wiring.
Fig. 5 Disconnect and Isolate Battery Negative
Cable
1 ± NEGATIVE CABLE
2 ± NEGATIVE BATTERY POST
Fig. 6 Ignition OFF (IOD) Test
1 ± NEGATIVE TERMINAL
2 ± 12 VOLT TEST LIGHT
3 ± PDC
4 ± AIR CLEANER HOUSING
5 ± NEGATIVE BATTERY POST
PLBATTERY 8A - 5
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 215 of 1285

Refer to Group 8W, Wiring Diagrams. If OK go to
Step 7.
(7) Install interior lamp fuse. After installing fuse,
the current can reach 250 milliamperes. After time-
out the reading should not exceed 8 milliamperes. If
NOT OK go to Step 8. If OK go to Step 9.
²Ignition key lamp system
²Radio
²Remote keyless entry module, if equipped
(8) Disconnect radio and ignition switch key lamp
one component at time, to see if any component is at
fault. If the high reading is not eliminated there is a
short circuit in the wiring. Refer to Group 8W, Wir-
ing Diagrams.
CAUTION: Always disconnect the meter before
opening a door.
(9) Remove interior lamps fuse and install the fuel
pump fuse. The reading should be between 1-3 milli-
amperes. If reading is higher than 3 milliamperes:
(a) Disconnect Powertrain Control Module.
(b) If reading drops to zero, replace Powertrain
Control Module.
(c) If reading remains the same there is a cur-
rent draw or short circuit in the A14 circuit. Refer
to Group 8W, Wiring Diagrams.
BATTERY LOAD TEST
A fully charged battery must have cranking capac-
ity, to provide the starter motor and ignition system
enough power to start the engine over a broad range
of ambient temperatures. A battery load test will ver-
ify the actual cranking capability of the battery.WARNING: IF BATTERY SHOWS SIGNS OF FREEZ-
ING, LEAKING, LOOSE POSTS, OR EXCESSIVELY
LOW ELECTROLYTE LEVEL, DO NOT TEST. ACID
BURNS OR AN EXPLOSIVE CONDITION MAY
RESULT.
(1) Remove both battery cables, negative cable
first. The battery top, cables and posts should be
clean. If green dot is not visible in indicator, charge
the battery. Refer to Battery Charging Procedures in
this group.
(2) Connect a Volt/Ammeter/Load tester to the bat-
tery posts (Fig. 8). Rotate the load control knob of the
Carbon pile rheostat to apply a 300 amp load. Apply
this load for 15 seconds to remove the surface charge
from the battery, and return the control knob to off
(Fig. 9).
(3) Allow the battery to stabilize for 2 minutes,
and then verify open circuit voltage.
Fig. 7 Milliampere Meter Connection
1 ± NEGATIVE TERMINAL
2 ± MILLIAMPERE METER
3 ± PDC
4 ± AIR CLEANER HOUSING
5 ± NEGATIVE BATTERY POST
Fig. 8 Volt-Ammeter Load Tester Connections -
Typical
1 ± INDUCTION AMPMETER CLAMP
2 ± NEGATIVE CLAMP
3 ± POSITIVE CLAMP
Fig. 9 Remove Surface Charge From Battery
8A - 6 BATTERYPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 224 of 1285

STARTER RELAY PIN CALL-OUT
PIN CIRCUIT COLOR DESCRIPTION
1 (86) A041 YL IGNITION SWITCH OUTPUT (START)
2 (85) K090 TN PCM
3 (30) A001 RD FUSED B+
4 (87A) NOT USED
5 (87) T040 BR STARTER SOLENOID
RELAY CIRCUIT TEST
(1) The relay common feed terminal cavity (30) is
connected to battery voltage and should be hot at all
times. If OK, go to Step 2. If not OK, repair the open
circuit to the PDC fuse as required.
(2) The relay normally closed terminal (87A) is
connected to terminal 30 in the de-energized position,
but is not used for this application. Go to Step 3.
(3) The relay normally open terminal (87) is con-
nected to the common feed terminal (30) in the ener-
gized position. This terminal supplies battery voltage
to the starter solenoid field coils. There should be
continuity between the cavity for relay terminal 87
and the starter solenoid terminal at all times. If OK,
go to Step 4. If not OK, repair the open circuit to the
starter solenoid as required.
(4) The coil battery terminal (86) is connected to
the electromagnet in the relay. It is energized when
the ignition switch is held in the START position. On
vehicles with a manual transmission, the clutch
pedal must be fully depressed for this test. Check for
battery voltage at the cavity for relay terminal 86
with the ignition switch in the START position, and
no voltage when the ignition switch is released to the
ON position. If OK, go to Step 5. If not OK with an
automatic transmission, check for an open or short
circuit to the ignition switch and repair, if required.
If the circuit to the ignition switch is OK, see the
Ignition Switch Test procedure in this group. If not
OK with a manual transmission, check the circuit
between the relay and the clutch interlock/upstop
switch for an open or a short circuit. If the circuit is
OK, refer to the Clutch Interlock/Upstop Switch
Diagnosis and Testing in Group 6-Clutch.
(5) The coil ground terminal (85) is connected to
the electromagnet in the relay. It is grounded
through the PCM only when the gearshift selector
lever is in the Park or Neutral positions. On vehicles
with a manual transmission, it is grounded through
the PCM when the clutch pedal is depressed. Check
for continuity to ground at the cavity for relay termi-
nal 85. If not OK, check for an open or short circuit
to the park/neutral starting and back-up lamp
switch, or the clutch interlock/upstop switch. Repair,
as necessary. If the circuit is OK, refer to the Park/Neutral Starting and Back-Up Lamp Switch Removal
and Installation in Group 21-Transaxle. Testing is
located within the Removal and Installation proce-
dures.
SAFETY SWITCHES
For diagnosis of:
²Clutch Interlock/Upstop Switch, refer to Diagno-
sis and Testing in Group 6-Clutch.
²Park/Neutral Starting and Back-Up Lamp
Switch, refer to Removal and Installation in Group
21-Transaxle. Testing is located within the Removal
and Installation procedures.
IGNITION SWITCH
After testing starter solenoid and relay, test igni-
tion switch and wiring. Check all wiring for opens or
shorts, and all connectors for being loose or corroded.
Refer to Group 8D-Ignition Systems, or Group
8W-Wiring Diagrams.
BATTERY
Refer to Group 8A-Battery for Diagnosis and Test-
ing of the battery.
ALL RELATED WIRING AND CONNECTORS
Refer to Group 8W-Wiring Diagrams.
FEED CIRCUIT RESISTANCE
Before proceeding with this operation, review Diag-
nostic Preparation and Starter Feed Circuit Tests.
The following operation will require a voltmeter,
accurate to 1/10 of a volt.
CAUTION: Ignition system also must be disabled to
prevent engine start while performing the following
tests.
(1) To disable the ignition and fuel systems, dis-
connect the Automatic Shutdown (ASD) Relay. The
ASD relay is located in the Power Distribution Cen-
ter (PDC). Refer to the PDC cover for proper relay
location.
(2) With all wiring harnesses and components
properly connected, perform the following:
PLSTARTING SYSTEMS 8B - 3
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 238 of 1285

OPERATION
The Automatic Shutdown (ASD) relay supplies bat-
tery voltage to the fuel injectors, electronic ignition
coil and the heating elements in the oxygen sensors.
A buss bar in the Power Distribution Center (PDC)
supplies voltage to the solenoid side and contact side
of the relay. The fuse also protects the power circuit
for the fuel pump relay and pump. The fuse is
located in the PDC. Refer to the Wiring Diagrams for
circuit information.
The PCM controls the ASD relay by switching the
ground path for the solenoid side of the relay on and
off. The PCM turns the ground path off when the
ignition switch is in the Off position. When the igni-
tion switch is in On or Start, the PCM monitors the
crankshaft and camshaft position sensor signals to
determine engine speed and ignition timing (coil
dwell). If the PCM does not receive crankshaft and
camshaft position sensor signals when the ignition
switch is in the Run position, it will de-energize the
ASD relay.
CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSORÐPCM
INPUT
DESCRIPTION
The crankshaft position sensor mounts to the
engine block behind the generator, just above the oil
filter (Fig. 4).
The PCM uses the Crankshaft Position sensor to
calculate the following:
²Engine RPM²TDC number 1 and 4
²Ignition coil synchronization
²Injector synchronization
²Camshaft-to-crankshaft misalignment (Timing
belt skipped 1 tooth or more diagnostic trouble code).
OPERATION
The Crankshaft Position (CKP) sensor is a Hall-ef-
fect sensor. The second crankshaft counterweight has
two sets of four timing reference notches including a
60 degree signature notch (Fig. 5).
Fig. 5 Timing Reference Notches
1 ± MACHINED NOTCHES
2 ± CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
Fig. 4 Crankshaft Position Sensor
1 ± CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
2 ± OIL FILTER
3 ± GENERATOR
PLIGNITION SYSTEM 8D - 3
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 257 of 1285

INSTRUMENT PANEL CENTER BEZEL
REMOVAL
(1) Remove HVAC control knobs from control head.
(2) Remove both center A/C outlet louvers (Fig. 14)
by rolling downward and pulling out.
(3) Remove two screws retaining the top front of
the center bezel up inside the center A/C outlet duct.
(4) Using a trim stick (special tool #C-4755), gently
pry out on instrument panel center bezel.
(5) Remove bezel from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
For installation, reverse the above procedures.
INSTRUMENT PANEL END CAPS
REMOVAL
(1) Open the door, left or right, and pull on the
access handle to disengage the end cap clips. Fuse
diagram is located inside the left end cap. Fuse
Access is under the left end cap.
INSTALLATION
For installation, reverse the above procedure.
INSTRUMENT PANEL TOP COVER
REMOVAL
(1) Using a trim stick (special tool #C-4755), gently
pry out on both the left and right A-pillar trim panels
and remove.
(2) Use care not to scratch the panel. Lift up on
the bottom outer areas of the cluster bezel and along
the rearward edge of the top cover to disengage the
clips.
(3) Pull the top cover rearward until the forward
pins disengage from the instrument panel.
INSTALLATION
For installation, reverse the above procedures.
Position spring clips to instrument panel and push
firmly until seated.
LOWER INSTRUMENT PANEL COVER
REMOVAL
(1) Remove instrument cluster bezel, Refer to
Instrument Cluster Bezel Removal and Installation
in this section.
(2) Grasp left lower instrument panel cover from
the bottom and pull firmly rearward.
(3) Remove lower instrument panel cover from
vehicle.
INSTALLATION
For installation, reverse the above procedures.
LOWER STORAGE BIN
REMOVAL
(1) Using a trim stick (special tool #C-4755), gently
pry out on the side of the lower storage bin Refer to
(Fig. 7).
(2) Disconnect the center console flood lamp.
(3) Transfer the center console flood lamp housing
to new bin (if replacing).
INSTALLATION
For installation, reverse the above procedures.
Fig. 14 A/C Outlet Louvers
1 ± INSTRUMENT PANEL CENTER AIR DUCT
2 ± OUTSIDE AIR/RECIRC CONTROL KNOB
3 ± MODE CONTROL KNOB
4 ± BLOWER SPEED KNOB
5 ± TEMPERATURE CONTROL KNOB
8E - 10 INSTRUMENT PANEL SYSTEMSPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 270 of 1285

AUDIO SYSTEM
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
GENERAL INFORMATION
INTRODUCTION..........................1
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
INTERFERENCE ELIMINATION...............1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
AUDIO DIAGNOSTIC TEST PROCEDURES......1
TESTING................................1
BENCH TEST FOR ANTENNA MALFUNCTION...7REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
CD CHANGER............................7
FRONT DOOR SPEAKER....................8
INSTRUMENT PANEL SPEAKER(S)...........8
MAST and ANTENNA ASSEMBLY.............8
RADIO..................................9
REAR SHELF SPEAKER(S).................10
GENERAL INFORMATION
INTRODUCTION
Operating instructions for the factory installed
audio systems can be found in the Owner's Manual
provided with the vehicle.
The vehicles are equipped with an Interior (Igni-
tion Off Draw) fuse in the Power Distribution Center
located in the engine compartment. After the Interior
(IOD) fuse or battery has been disconnected the clock
will require resetting. The radio station presets have
a nonvolatile memory and will retain the preset sta-
tions after a battery disconnect.
The available radio options are:
²AM/FM Stereo Cassette w/Clock
²AM/FM/CD
²AM/FM Cassette w/CD Changer Controls and
Display
²CD/4 Disc Changer - In-Dash (used w/Radio CD
Changer Controls)
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
INTERFERENCE ELIMINATION
The radio utilizes a ground wire plugged on to a
blade terminal and is bolted to the radio chassis.
Both connector and terminal should be securely
attached. The engine has two separate ground straps
to suppress ignition noise which may interfere with
radio reception.
²Left engine mount clip on strap
²Engine to shock tower reinforcement
Inductive type spark plug cables in the high ten-
sion circuit of the ignition system complete the inter-
ference suppression. Faulty or deteriorated spark
plug wires should be replaced.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
AUDIO DIAGNOSTIC TEST PROCEDURES
CAUTION: The CD player will only operate between
approximate temperatures of -23ÉC and +65ÉC (-10ÉF
and +145ÉF).
Whenever a radio malfunction occurs;
(1) First check FUSES:
(a) Power Distribution Center (PDC), Interior
lamp fuse, M1 - Radio Memory Feed
(b) Fuse Block:
(I) Fuse 12, Illumination in the fuse block
(II) Fuse 16, Ignition feed in the fuse block
NOTE: The vehicles are shipped with the INTERIOR
LAMP fuse disconnected.
(2) Verify, the radio wire harness are properly con-
nected before starting normal diagnosis and repair
procedures. Refer to Audio Diagnostic Charts and/or
Group 8W, Wiring Diagrams, Radio Section.
TESTING
The antenna has a short cable which connects into
the instrument panel harness. The connection is
made on the right side of the instrument panel.
Antenna performance may be tested by substitut-
ing a known good antenna. It is also possible to
check short or open circuits with an ohmmeter or
continuity light once the antenna cable is discon-
nected from the radio as follows:
(1) Continuity should be present between the
antenna mast and radio end pin of antenna cable
plug (Fig. 1).
(2) No continuity should be observed or a very
high resistance of several megohms between the
ground shell of the connector and radio end pin.
PLAUDIO SYSTEM 8F - 1
Page 280 of 1285
HORNS
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
INTRODUCTION..........................1
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
HORN..................................2
HORN RELAY............................2
HORN SWITCH...........................2HORN SYSTEM TEST......................2
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
HORN..................................4
HORN RELAY............................4
HORN SWITCH...........................5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
INTRODUCTION
WARNING: ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIR-
BAG, SEE GROUP 8M, PASSIVE RESTRAINT SYS-
TEMS FOR STEERING WHEEL REMOVAL.
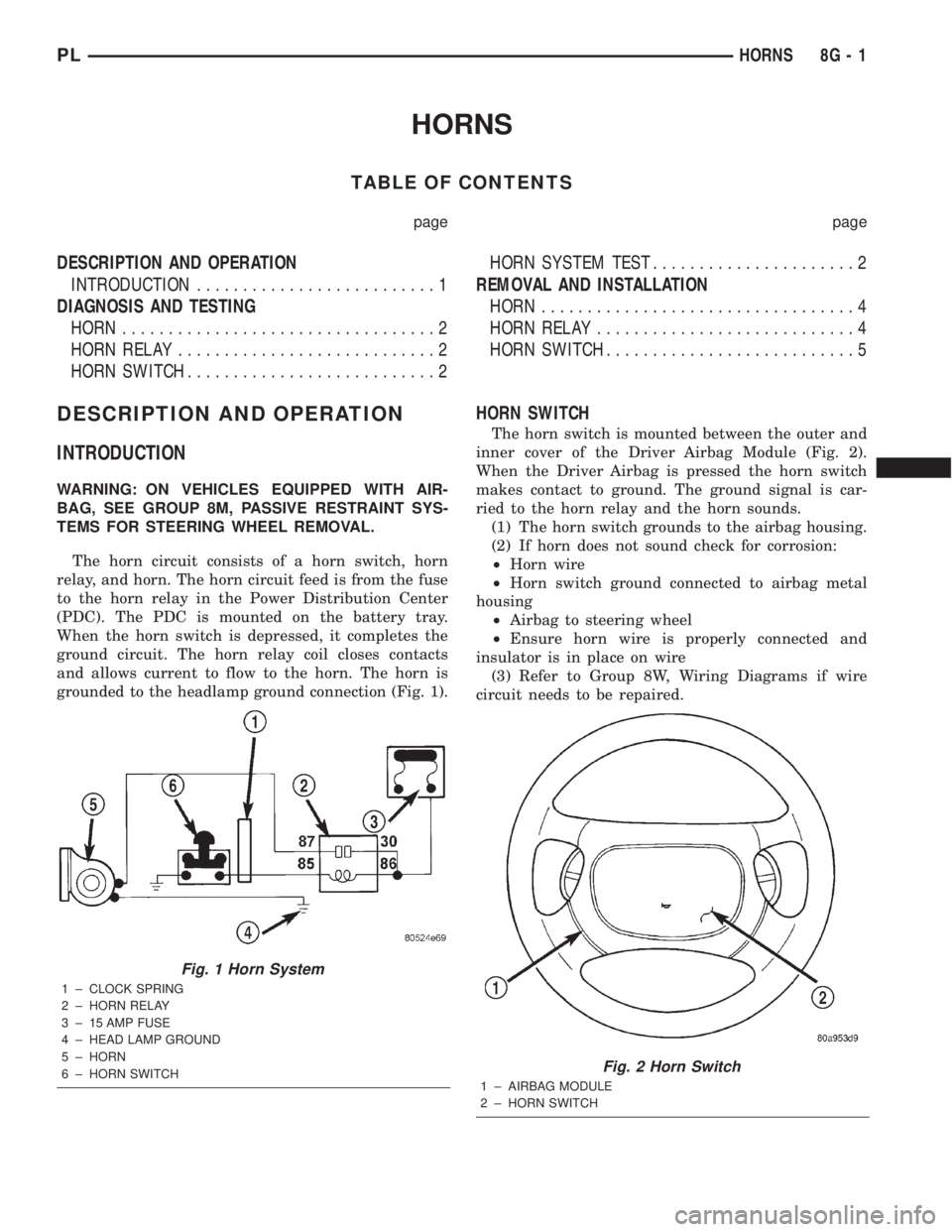
The horn circuit consists of a horn switch, horn
relay, and horn. The horn circuit feed is from the fuse
to the horn relay in the Power Distribution Center
(PDC). The PDC is mounted on the battery tray.
When the horn switch is depressed, it completes the
ground circuit. The horn relay coil closes contacts
and allows current to flow to the horn. The horn is
grounded to the headlamp ground connection (Fig. 1).
HORN SWITCH
The horn switch is mounted between the outer and
inner cover of the Driver Airbag Module (Fig. 2).
When the Driver Airbag is pressed the horn switch
makes contact to ground. The ground signal is car-
ried to the horn relay and the horn sounds.
(1) The horn switch grounds to the airbag housing.
(2) If horn does not sound check for corrosion:
²Horn wire
²Horn switch ground connected to airbag metal
housing
²Airbag to steering wheel
²Ensure horn wire is properly connected and
insulator is in place on wire
(3) Refer to Group 8W, Wiring Diagrams if wire
circuit needs to be repaired.
Fig. 1 Horn System
1 ± CLOCK SPRING
2 ± HORN RELAY
3 ± 15 AMP FUSE
4 ± HEAD LAMP GROUND
5 ± HORN
6 ± HORN SWITCH
Fig. 2 Horn Switch
1 ± AIRBAG MODULE
2 ± HORN SWITCH
PLHORNS 8G - 1
Page 281 of 1285
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
HORN
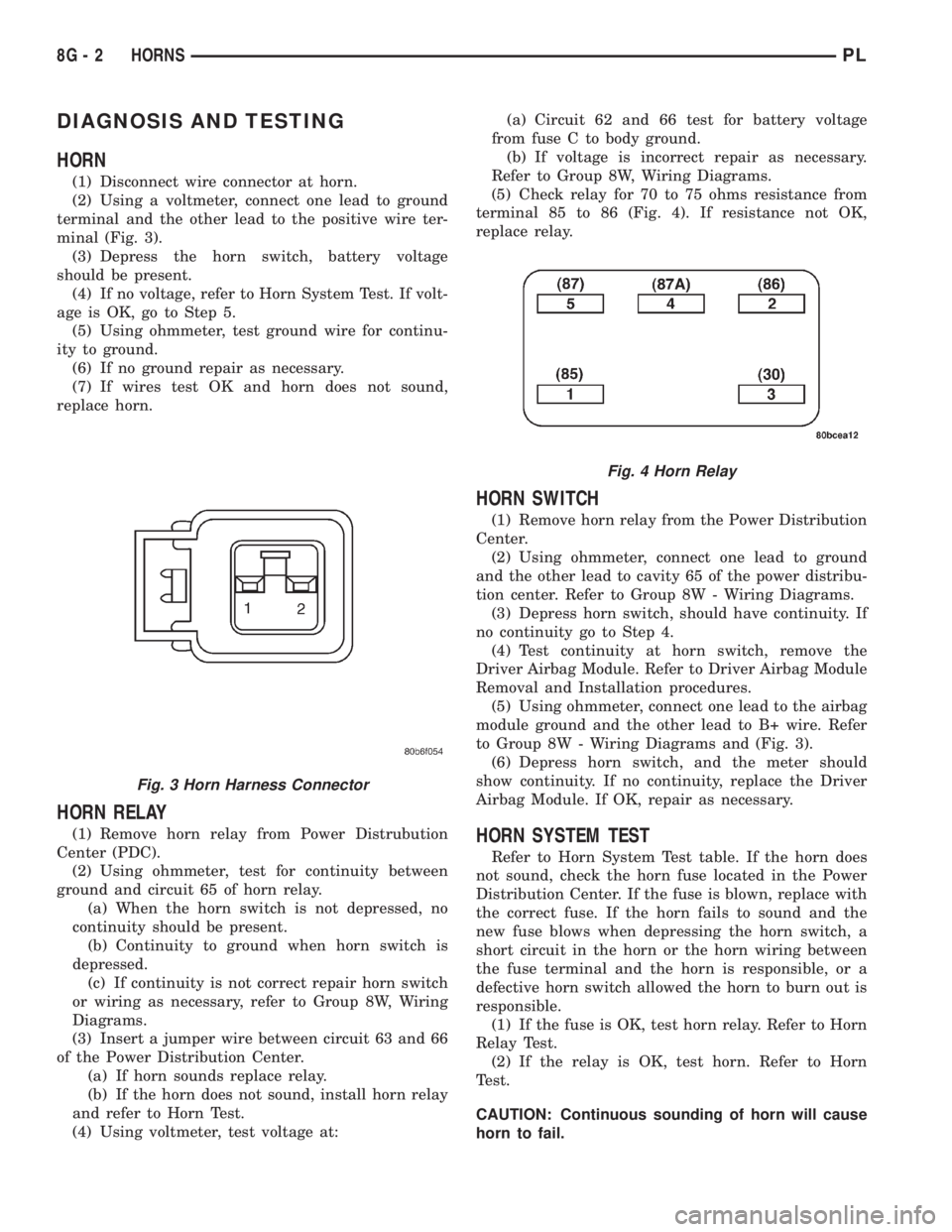
(1) Disconnect wire connector at horn.
(2) Using a voltmeter, connect one lead to ground
terminal and the other lead to the positive wire ter-
minal (Fig. 3).
(3) Depress the horn switch, battery voltage
should be present.
(4) If no voltage, refer to Horn System Test. If volt-
age is OK, go to Step 5.
(5) Using ohmmeter, test ground wire for continu-
ity to ground.
(6) If no ground repair as necessary.
(7) If wires test OK and horn does not sound,
replace horn.
HORN RELAY
(1) Remove horn relay from Power Distrubution
Center (PDC).
(2) Using ohmmeter, test for continuity between
ground and circuit 65 of horn relay.
(a) When the horn switch is not depressed, no
continuity should be present.
(b) Continuity to ground when horn switch is
depressed.
(c) If continuity is not correct repair horn switch
or wiring as necessary, refer to Group 8W, Wiring
Diagrams.
(3) Insert a jumper wire between circuit 63 and 66
of the Power Distribution Center.
(a) If horn sounds replace relay.
(b) If the horn does not sound, install horn relay
and refer to Horn Test.
(4) Using voltmeter, test voltage at:(a) Circuit 62 and 66 test for battery voltage
from fuse C to body ground.
(b) If voltage is incorrect repair as necessary.
Refer to Group 8W, Wiring Diagrams.
(5) Check relay for 70 to 75 ohms resistance from
terminal 85 to 86 (Fig. 4). If resistance not OK,
replace relay.
HORN SWITCH
(1) Remove horn relay from the Power Distribution
Center.
(2) Using ohmmeter, connect one lead to ground
and the other lead to cavity 65 of the power distribu-
tion center. Refer to Group 8W - Wiring Diagrams.
(3) Depress horn switch, should have continuity. If
no continuity go to Step 4.
(4) Test continuity at horn switch, remove the
Driver Airbag Module. Refer to Driver Airbag Module
Removal and Installation procedures.
(5) Using ohmmeter, connect one lead to the airbag
module ground and the other lead to B+ wire. Refer
to Group 8W - Wiring Diagrams and (Fig. 3).
(6) Depress horn switch, and the meter should
show continuity. If no continuity, replace the Driver
Airbag Module. If OK, repair as necessary.
HORN SYSTEM TEST
Refer to Horn System Test table. If the horn does
not sound, check the horn fuse located in the Power
Distribution Center. If the fuse is blown, replace with
the correct fuse. If the horn fails to sound and the
new fuse blows when depressing the horn switch, a
short circuit in the horn or the horn wiring between
the fuse terminal and the horn is responsible, or a
defective horn switch allowed the horn to burn out is
responsible.
(1) If the fuse is OK, test horn relay. Refer to Horn
Relay Test.
(2) If the relay is OK, test horn. Refer to Horn
Test.
CAUTION: Continuous sounding of horn will cause
horn to fail.
Fig. 3 Horn Harness Connector
Fig. 4 Horn Relay
8G - 2 HORNSPL