Transmission fill DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1998, Model line: RAM 1500, Model: DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.GPages: 2627
Page 2210 of 2627

EXTENSION HOUSING SEAL
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support vehicle.
(2) Remove rear propeller shaft. (Refer to 3 - DIF-
FERENTIAL & DRIVELINE/PROPELLER SHAFT/
PROPELLER SHAFT - REMOVAL)
(3) Using a suitable pry tool or slide-hammer
mounted screw, remove the extension housing seal.
INSTALLATION
(1) Clean fluid residue from sealing surface and
inspect for defects.
(2) Using Installer D-163, install seal in extension
housing (Fig. 77).
(3) Install propeller shaft. (Refer to 3 - DIFFER-
ENTIAL & DRIVELINE/PROPELLER SHAFT/PRO-
PELLER SHAFT - INSTALLATION)
(4) Verify proper transfer case fluid level.
(5) Lower vehicle.
FLUID
STANDARD PROCEDURE - FLUID DRAIN AND
REFILL
The fill and drain plugs are both in the rear case
(Fig. 78).
(1) Raise vehicle.
(2) Position drain pan under transfer case.
(3) Remove drain and fill plugs and drain lubri-
cant completely.
(4) Install drain plug. Tighten plug to 20-34 N´m
(15-25 ft. lbs.).
(5) Remove drain pan.
(6)
Fill transfer case to bottom edge of fill plug open-
ing with MopartATF +4, Automatic Transmission fluid.
(7) Install and tighten fill plug to 20-34 N´m
(15-25 ft. lbs.).
(8) Lower vehicle.
FRONT OUTPUT SHAFT SEAL
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the front propeller shaft (Refer to 3 -
DIFFERENTIAL & DRIVELINE/PROPELLER
SHAFT/PROPELLER SHAFT - REMOVAL).
(2) Remove the front propeller shaft seal boot
retaining clamp (Fig. 79).
Fig. 79 Remove Boot Clamp
1 - SEAL BOOT
2 - BOOT CLAMP
Fig. 77 Install Rear Seal in Extension Housing
1 - SPECIAL TOOL C-4171
2 - SPECIAL TOOL D-163
Fig. 78 Fill/Drain Plug and I.D. Tag Location
1 - I.D. TAG
2 - FILL PLUG
3 - DRAIN PLUG
DRTRANSFER CASE - NV243 21 - 507
Page 2214 of 2627

²A flashing operating mode LED for the desired
gear indicates that a shift to that position has been
requested, but all of the driver controllable conditions
have not been met. This is in an attempt to notify the
driver that the transmission needs to be put into NEU-
TRAL, the vehicle speed is too great, or some other con-
dition outlined (other than a diagnostic failure that
would prevent this shift) elsewhere (Refer to 8 - ELEC-
TRICAL/ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODULES/TRANS-
FER CASE CONTROL MODULE - OPERATION) is not
met. Note that this flashing will continue indefinitely
until the conditions are eventually met, or the selector
switch position is changed, or if diagnostic routines no
longer allow the requested shift.
²If the driver attempts to make a shift into transfer
case NEUTRAL, and any of the driver controllable con-
ditions are not met, the request will be ignored until all
of the conditions are met or until the NEUTRAL select
button is released. Additionally the neutral lamp will
flash, or begin to flash while the button is depressed
and operator controllable conditions are not being met.
All of the LED's except the Neutral will flash if any of
the operator controllable conditions for shifting are not
met while the Neutral button is depressed. This9toggle9
type of feature is necessary because the TCCM would
interpret another request immediately after the shift
into transfer case NEUTRAL has completed.
²No LED's illuminated indicate a fault in the
transfer case control system.
SHIFT MOTOR
DESCRIPTION
The shift motor (Fig. 85) consists of a permanent
magnet D.C. motor with gear reduction to convert a
high speed-low torque device into a low speed-high
torque device. The output of the device is coupled to a
shaft which internally moves the mode and range forks
that change the transfer case operating ranges. The
motor is rated at 25 amps maximum at 72É F with 10
volts at the motor leads.
OPERATION
The transfer case shift motor responds to the Transfer
Case Control Module (TCCM) commands to move the
transfer case shift sector bi-directionally, as required, to
obtain the transfer case operating mode indicated by
the instrument panel mounted selector switch.
REMOVAL
NOTE: New shift motor assemblies are shipped in the
2WD/AWD position. If a new shift motor assembly will
be installed, it will be necessary to shift the transfer
case to the 2WD/AWD position prior to motor removal.
(1) Raise the vehicle on a suitable hoist.
(2) Disengage the wiring connectors from the shift
motor and mode sensor.
(3) Remove the bolts holding the shift motor and
mode sensor assembly onto the transfer case.
(4) Separate the shift motor and mode sensor
assembly from the transfer case.
INSTALLATION
(1) Verify that the shift sector o-ring is clean and
properly positioned over the shift sector and against
the transfer case.
NOTE: Verify that the shift motor position and sec-
tor shaft orientation are aligned. It may be neces-
sary to manually shift the transfer case if the shift
motor and sector shaft are not aligned.
(2) Position the shift motor and mode sensor
assembly onto the transfer case.
(3) Install the bolts to hold the assembly onto the
transfer case. Tighten the bolts to 16-24 N´m (12-18
ft.lbs.).
CAUTION: If the original shift motor and mode sen-
sor assembly bolts are reused, be sure to use
MoparTLock & Seal or LoctiteŸ 242 to replenish
the lock patch material originally found on the bolts
(4) Engage the wiring connectors to the shift motor
and mode sensor.
(5) Refill the transfer case as necessary.
(6) Lower vehicle and verify transfer case opera-
tion.
Fig. 85 Shift Motor - Shown Inverted - Typical
1 - SHIFT MOTOR
DRTRANSFER CASE - NV243 21 - 511
SELECTOR SWITCH (Continued)
Page 2216 of 2627
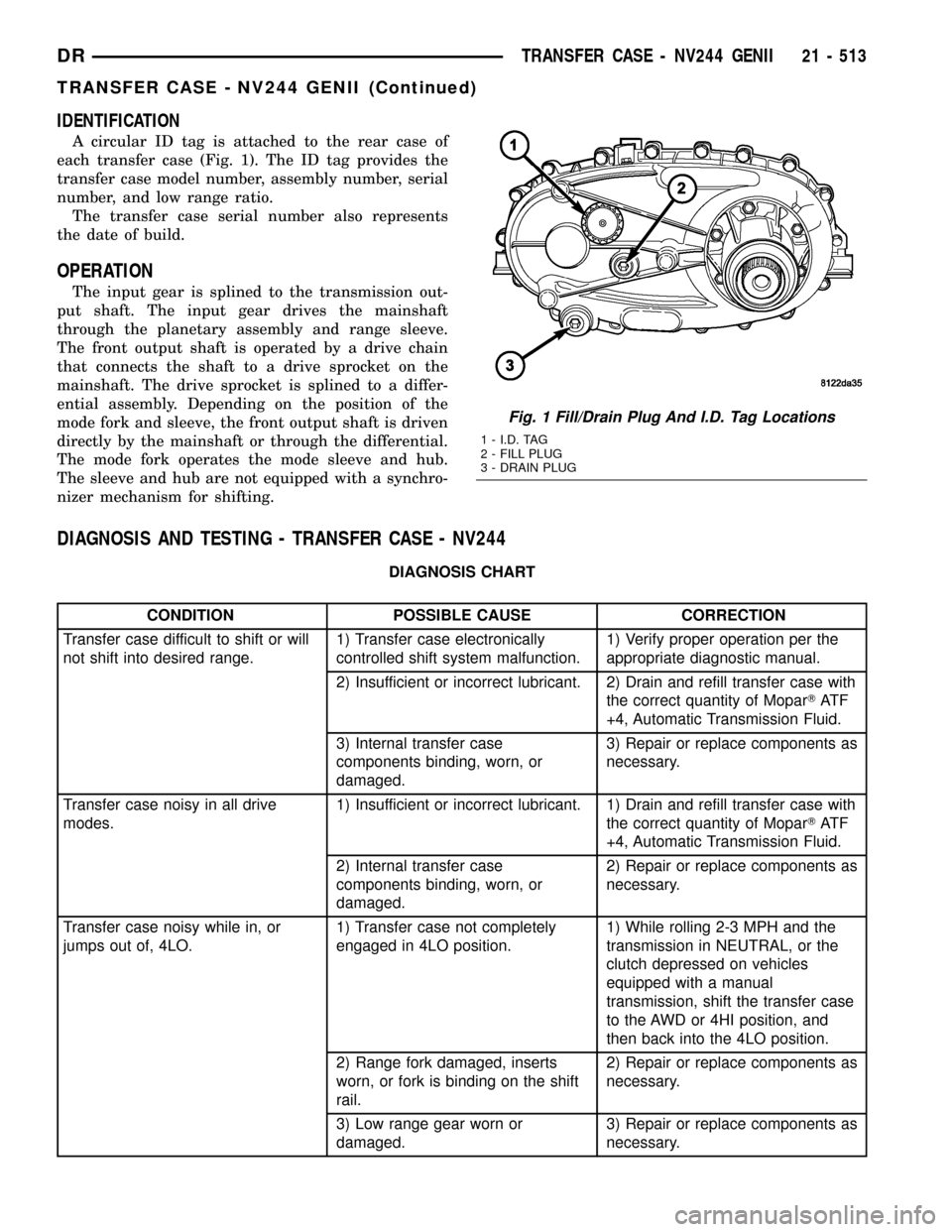
IDENTIFICATION
A circular ID tag is attached to the rear case of
each transfer case (Fig. 1). The ID tag provides the
transfer case model number, assembly number, serial
number, and low range ratio.
The transfer case serial number also represents
the date of build.
OPERATION
The input gear is splined to the transmission out-
put shaft. The input gear drives the mainshaft
through the planetary assembly and range sleeve.
The front output shaft is operated by a drive chain
that connects the shaft to a drive sprocket on the
mainshaft. The drive sprocket is splined to a differ-
ential assembly. Depending on the position of the
mode fork and sleeve, the front output shaft is driven
directly by the mainshaft or through the differential.
The mode fork operates the mode sleeve and hub.
The sleeve and hub are not equipped with a synchro-
nizer mechanism for shifting.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TRANSFER CASE - NV244
DIAGNOSIS CHART
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
Transfer case difficult to shift or will
not shift into desired range.1) Transfer case electronically
controlled shift system malfunction.1) Verify proper operation per the
appropriate diagnostic manual.
2) Insufficient or incorrect lubricant. 2) Drain and refill transfer case with
the correct quantity of MoparTAT F
+4, Automatic Transmission Fluid.
3) Internal transfer case
components binding, worn, or
damaged.3) Repair or replace components as
necessary.
Transfer case noisy in all drive
modes.1) Insufficient or incorrect lubricant. 1) Drain and refill transfer case with
the correct quantity of MoparTAT F
+4, Automatic Transmission Fluid.
2) Internal transfer case
components binding, worn, or
damaged.2) Repair or replace components as
necessary.
Transfer case noisy while in, or
jumps out of, 4LO.1) Transfer case not completely
engaged in 4LO position.1) While rolling 2-3 MPH and the
transmission in NEUTRAL, or the
clutch depressed on vehicles
equipped with a manual
transmission, shift the transfer case
to the AWD or 4HI position, and
then back into the 4LO position.
2) Range fork damaged, inserts
worn, or fork is binding on the shift
rail.2) Repair or replace components as
necessary.
3) Low range gear worn or
damaged.3) Repair or replace components as
necessary.
Fig. 1 Fill/Drain Plug And I.D. Tag Locations
1 - I.D. TAG
2 - FILL PLUG
3 - DRAIN PLUG
DRTRANSFER CASE - NV244 GENII 21 - 513
TRANSFER CASE - NV244 GENII (Continued)
Page 2217 of 2627
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
Lubricant leaking from transfer case
seals or vent.1) Transfer case overfilled. 1) Drain lubricant to the correct
level.
2) Transfer case vent closed or
restricted.2) Clean or replace vent as
necessary.
3) Transfer case seals damaged or
installed incorrectly.3) Replace suspect seal.
Transfer case will not shift through
4HI (Part-time) range.1) Incomplete shift due to drivetrain
torque load.1) Drive in a straight line and
momentarily release the accelerator
pedal to complete the shift.
2) Incorrect tire pressure. 2) Correct tire pressure as
necessary.
3) Excessive tire wear. 3) Correct tire condition as
necessary.
4) Excessive vehicle loading. 4) Correct as necessary.
REMOVAL
(1) Shift transfer case into AWD.
(2) Raise vehicle.
(3) Drain transfer case lubricant.
(4) Mark front and rear propeller shafts for align-
ment reference.
(5) Support transmission with jack stand.
(6)
Remove the transfer case skid plate, if equipped.
(7) Disconnect front and rear propeller shafts at
transfer case.
(8) Disconnect transfer case shift motor and mode
sensor wire connectors.
(9) Disconnect transfer case vent hose.
(10) Support transfer case with transmission jack.
(11) Secure transfer case to jack with chains.
(12) Remove nuts attaching transfer case to trans-
mission (Fig. 2).(13) Pull transfer case and jack rearward to disen-
gage transfer case.
(14) Remove transfer case from under vehicle.
DISASSEMBLY
Position transfer case in a shallow drain pan.
Remove drain plug and drain any remaining lubri-
cant remaining in case.
SHIFT MOTOR ASSEMBLY AND FRONT OUTPUT
SHAFT SEAL
(1) Remove the bolts (Fig. 3) which hold the shift
motor and mode sensor assembly to the transfer
case.
Fig. 2 Remove Transfer Case - Typical
1 - TRANSMISSION
2 - TRANSFER CASE
3 - MODE SENSOR CONNECTOR
Fig. 3 Remove the Shift Motor and Mode Sensor
Assembly Bolts - Typical
1 - TRANSFER CASE
2 - SHIFT MOTOR AND MODE SENSOR ASSEMBLY
3 - BOLT
21 - 514 TRANSFER CASE - NV244 GENIIDR
TRANSFER CASE - NV244 GENII (Continued)
Page 2237 of 2627

SEAL BOOT AND SHIFT MOTOR ASSEMBLY
(1) Install a new seal boot clamp onto the seal
boot.
(2) Install the seal boot (Fig. 76) and clamp onto
the slinger hub and tighten the clamp with Crimp
Tool C-4975-A.
(3) Position the shift motor and mode sensor
assembly onto the transfer case.
(4) Install the bolts (Fig. 77) to hold the shift
motor and mode sensor assembly to the transfer
case. Tighten the bolts to 16-25 N´m (12-18 ft. lbs.).
REAR EXTENSION
(1) Install new seal in rear extension housing seal
with Installer D-163 and Handle C-4171. Verify that
the weep hole in the rubber is oriented downward.
(2) Apply bead of MopartGasket Maker, or equiv-
alent, to mating surface of rear extension housing.
Keep sealer bead width to maximum of 3/16 inch. Do
not use excessive amount of sealer as excess could be
displaced into output bearing.
(3) Align and install rear extension on retainer
(Fig. 78).
(4) Apply MopartSilicone Sealer to threads of rear
extension housing bolts. Then install and tighten
bolts to 16-24 N´m (12-18 ft. lbs.) torque.
INSTALLATION
(1) Mount transfer case on a transmission jack.
(2) Secure transfer case to jack with chains.
(3) Position transfer case under vehicle.
(4) Align transfer case and transmission shafts
and install transfer case onto the transmission.
(5) Install and tighten transfer case attaching nuts
to 27-34 N´m (20-25 ft. lbs.) torque.
(6) Connect the vent hose.
(7) Connect the shift motor and mode sensor wir-
ing connectors. Secure wire harness to clips on trans-
fer case.
(8) Align and connect the propeller shafts.
(9) Fill transfer case with correct fluid. (Refer to
21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSFER CASE/FLUID -
STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(10) Install skid plate, if equipped.
(11) Remove transmission jack and support stand.
(12) Lower vehicle and verify transfer case shift
operation.
Fig. 76 Install Seal Boot
1 - SEAL BOOT
2 - SEAL SLINGER
Fig. 77 Install the Shift Motor and Mode Sensor
Assembly Bolts - Typical
1 - TRANSFER CASE
2 - SHIFT MOTOR AND MODE SENSOR ASSEMBLY
3 - BOLT
Fig. 78 Install Rear Extension Bolts
1 - EXTENSION HOUSING
2 - TRANSFER CASE
21 - 534 TRANSFER CASE - NV244 GENIIDR
TRANSFER CASE - NV244 GENII (Continued)
Page 2246 of 2627
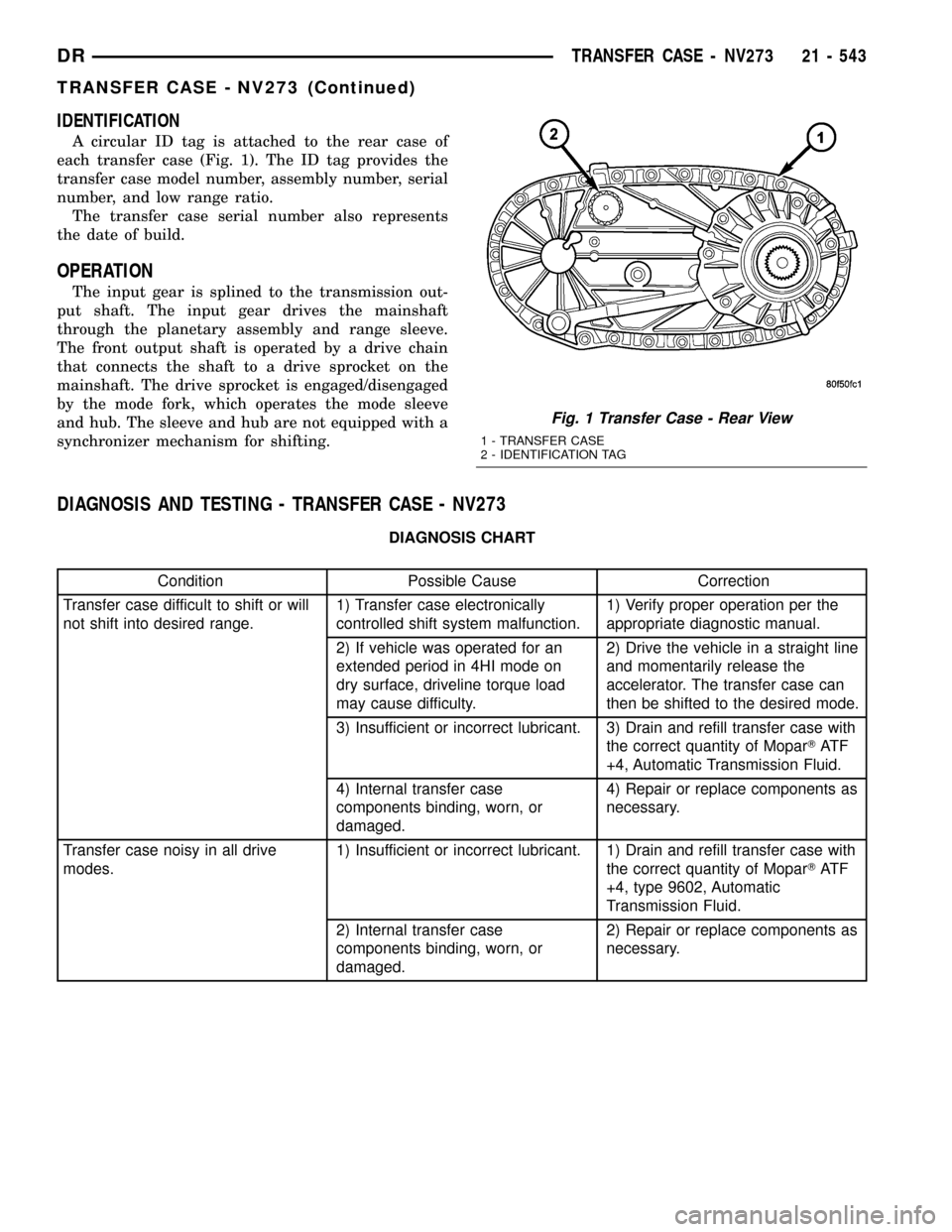
IDENTIFICATION
A circular ID tag is attached to the rear case of
each transfer case (Fig. 1). The ID tag provides the
transfer case model number, assembly number, serial
number, and low range ratio.
The transfer case serial number also represents
the date of build.
OPERATION
The input gear is splined to the transmission out-
put shaft. The input gear drives the mainshaft
through the planetary assembly and range sleeve.
The front output shaft is operated by a drive chain
that connects the shaft to a drive sprocket on the
mainshaft. The drive sprocket is engaged/disengaged
by the mode fork, which operates the mode sleeve
and hub. The sleeve and hub are not equipped with a
synchronizer mechanism for shifting.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - TRANSFER CASE - NV273
DIAGNOSIS CHART
Condition Possible Cause Correction
Transfer case difficult to shift or will
not shift into desired range.1) Transfer case electronically
controlled shift system malfunction.1) Verify proper operation per the
appropriate diagnostic manual.
2) If vehicle was operated for an
extended period in 4HI mode on
dry surface, driveline torque load
may cause difficulty.2) Drive the vehicle in a straight line
and momentarily release the
accelerator. The transfer case can
then be shifted to the desired mode.
3) Insufficient or incorrect lubricant. 3) Drain and refill transfer case with
the correct quantity of MoparTAT F
+4, Automatic Transmission Fluid.
4) Internal transfer case
components binding, worn, or
damaged.4) Repair or replace components as
necessary.
Transfer case noisy in all drive
modes.1) Insufficient or incorrect lubricant. 1) Drain and refill transfer case with
the correct quantity of MoparTAT F
+4, type 9602, Automatic
Transmission Fluid.
2) Internal transfer case
components binding, worn, or
damaged.2) Repair or replace components as
necessary.
Fig. 1 Transfer Case - Rear View
1 - TRANSFER CASE
2 - IDENTIFICATION TAG
DRTRANSFER CASE - NV273 21 - 543
TRANSFER CASE - NV273 (Continued)
Page 2247 of 2627
Condition Possible Cause Correction
Transfer case noisy while in, or
jumps out of, 4LO mode.1) Transfer case not completely
engaged in 4LO position.1) While rolling 2-3 MPH and the
transmission in NEUTRAL, or clutch
depressed on vehicles equipped
with a manual transmission, shift
transfer case to the 2WD or 4HI
position, and then back into the 4LO
position.
2) Range fork damaged, inserts
worn, or fork is binding on the shift
rail.2) Repair or replace components as
necessary.
3) Low range gear worn or
damaged.3) Repair or replace components as
necessary.
Lubricant leaking from transfer case
seals or vent.1) Transfer case overfilled. 1) Drain lubricant to the correct
level.
2) Transfer case vent closed or
restricted.2) Clean or replace vent as
necessary.
3) Transfer case seals damaged or
installed incorrectly.3) Replace suspect seal.
Abnormal tire wear. 1) Extended operation in 4HI mode
on dry surfaces,1) Operate vehicle in 2WD mode on
dry surfaces.
REMOVAL
(1) Shift transfer case into 2WD.
(2) Raise vehicle.
(3) Drain transfer case lubricant.
(4) Mark front and rear propeller shafts for align-
ment reference.
(5) Support transmission with jack stand.
(6) Remove the transfer case skid plate, if
equipped.
(7) Disconnect front and rear propeller shafts at
transfer case.
(8) Disconnect transfer case shift motor and mode
sensor wire connectors.
(9) Disconnect transfer case vent hose.
(10) Support transfer case with transmission jack.
(11) Secure transfer case to jack with chains.
(12) Remove nuts attaching transfer case to trans-
mission (Fig. 2).
(13) Pull transfer case and jack rearward to disen-
gage transfer case.
(14) Remove transfer case from under vehicle.
DISASSEMBLY
Position transfer case in a shallow drain pan.
Remove drain plug and drain any remaining lubri-
cant remaining in case.
Fig. 2 Remove Transfer Case - Typical
1 - TRANSMISSION
2 - TRANSFER CASE
3 - MODE SENSOR CONNECTOR
21 - 544 TRANSFER CASE - NV273DR
TRANSFER CASE - NV273 (Continued)
Page 2271 of 2627

(7) Install the front companion flange onto the
front output shaft.
(8) Install two bolts 180É apart into the front out-
put shaft companion flange.
(9) Place holder over the bolts and against the
companion flange (Fig. 88).
(10) Install a new front companion flange nut.
Tighten the companion flange nut to 176-271 N´m
(130-200 ft.lbs.).
INSTALLATION
(1) Mount transfer case on a transmission jack.
(2) Secure transfer case to jack with chains.
(3) Position transfer case under vehicle.
(4) Align transfer case and transmission shafts
and install transfer case onto the transmission.
(5) Install and tighten transfer case attaching nuts
to 27-34 N´m (20-25 ft. lbs.) torque.
(6) Connect the vent hose.
(7) Connect the shift motor and mode sensor wir-
ing connectors. Secure wire harness to clips on trans-
fer case.
(8) Align and connect the propeller shafts.
(9) Fill transfer case with correct fluid. (Refer to
21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSFER CASE/FLUID -
STANDARD PROCEDURE)
(10) Install skid plate, if equipped.(11) Remove transmission jack and support stand.
(12) Lower vehicle and verify transfer case shift
operation.
SPECIFICATIONS
TRANSFER CASE - NV273
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
DESCRIPTION N-m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Plug, Detent 16-24 12-18 -
Plug, Drain/Fill 20-34 15-25 -
Bolt, Extension Housing 27-34 20-25 -
Bolt, Case Half 27-34 20-25 -
Support, Sector 27-34 20-25 -
Nuts, Mounting 30-41 20-30 -
Bolts, Shift Motor and
Mode Sensor Assembly16-25 12-18 -
Nut, Companion Flange 176-271 130-200 -
Fig. 88 Install Companion Flange Nut
1 - HOLDER 6719
2 - BOLTS
21 - 568 TRANSFER CASE - NV273DR
TRANSFER CASE - NV273 (Continued)
Page 2278 of 2627

have not been met. This is in an attempt to notify
the driver that the transmission needs to be put into
NEUTRAL, the vehicle speed is too great, or some
other condition outlined (other than a diagnostic fail-
ure that would prevent this shift) elsewhere (Refer to
8 - ELECTRICAL/ELECTRONIC CONTROL MOD-
ULES/TRANSFER CASE CONTROL MODULE -
OPERATION) is not met. Note that this flashing will
continue indefinitely until the conditions are eventu-
ally met, or the selector switch position is changed,
or if diagnostic routines no longer allow the
requested shift.
²
If the driver attempts to make a shift into transfer
case NEUTRAL, and any of the driver controllable con-
ditions are not met, the request will be ignored until all
of the conditions are met or until the NEUTRAL select
button is released. Additionally the neutral lamp will
flash, or begin to flash while the button is depressed
and operator controllable conditions are not being met.
All of the LED's except the Neutral will flash if any of
the operator controllable conditions for shifting are not
met while the Neutral button is depressed. This9toggle9
type of feature is necessary because the TCCM would
interpret another request immediately after the shift
into transfer case NEUTRAL has completed.
²No LED's illuminated indicate a fault in the
transfer case control system.
SHIFT MOTOR
DESCRIPTION
The shift motor (Fig. 96) consists of a permanent
magnet D.C. motor with gear reduction to convert a
high speed-low torque device into a low speed-high
torque device. The output of the device is coupled to
a shaft which internally moves the mode and range
forks that change the transfer case operating ranges.
The motor is rated at 25 amps maximum at 72É F
with 10 volts at the motor leads.
OPERATION
The transfer case shift motor responds to the
Transfer Case Control Module (TCCM) commands to
move the transfer case shift sector bi-directionally, as
required, to obtain the transfer case operating mode
indicated by the instrument panel mounted selector
switch.
REMOVAL
NOTE: New shift motor assemblies are shipped in
the 2WD/AWD position. If a new shift motor assem-
bly will be installed, it will be necessary to shift the
transfer case to the 2WD/AWD position prior to
motor removal.(1) Raise the vehicle on a suitable hoist.
(2) Disengage the wiring connectors from the shift
motor and mode sensor.
(3) Remove the bolts holding the shift motor and
mode sensor assembly onto the transfer case.
(4) Separate the shift motor and mode sensor
assembly from the transfer case.
INSTALLATION
(1) Verify that the shift sector o-ring is clean and
properly positioned over the shift sector and against
the transfer case.
NOTE: Verify that the shift motor position and sec-
tor shaft orientation are aligned. It may be neces-
sary to manually shift the transfer case if the shift
motor and sector shaft are not aligned.
(2) Position the shift motor and mode sensor
assembly onto the transfer case.
(3) Install the bolts to hold the assembly onto the
transfer case. Tighten the bolts to 16-24 N´m (12-18
ft.lbs.).
CAUTION: If the original shift motor and mode sen-
sor assembly bolts are reused, be sure to use
MoparTLock & Seal or LoctiteŸ 242 to replenish
the lock patch material originally found on the bolts
(4) Engage the wiring connectors to the shift motor
and mode sensor.
(5) Refill the transfer case as necessary.
(6) Lower vehicle and verify transfer case
operation.
Fig. 96 Shift Motor - Shown Inverted - Typical
1 - SHIFT MOTOR
DRTRANSFER CASE - NV273 21 - 575
SELECTOR SWITCH (Continued)
Page 2531 of 2627

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - REFRIGERANT
SYSTEM LEAKS
WARNING: R-134a SERVICE EQUIPMENT OR VEHI-
CLE A/C SYSTEM SHOULD NOT BE PRESSURE
TESTED OR LEAK TESTED WITH COMPRESSED
AIR. MIXTURE OF AIR and R-134a CAN BE COM-
BUSTIBLE AT ELEVATED PRESSURES. THESE MIX-
TURES ARE POTENTIALLY DANGEROUS AND MAY
RESULT IN FIRE OR EXPLOSION CAUSING INJURY
OR PROPERTY DAMAGE.
AVOID BREATHING A/C REFRIGERANT AND LUBRI-
CANT VAPOR OR MIST. EXPOSURE MAY IRRITATE
EYES, NOSE AND THROAT. USE ONLY APPROVED
SERVICE EQUIPMENT MEETING SAE REQUIRE-
MENTS TO DISCHARGE R-134a SYSTEM. IF ACCI-
DENTAL SYSTEM DISCHARGE OCCURS,
VENTILATE WORK AREA BEFORE RESUMING SER-
VICE.
NOTE: The refrigerant system does come from the
factory with a yellow tracer dye already installed to
aid in detection of leaks.
If the A/C system is not cooling properly, determine
if the refrigerant system is fully charged with
R-134a. This is accomplished by performing a system
Charge Level-Check or Fill. If while performing this
test A/C liquid line pressure is less than 345 kPa (50
psi) proceed to System Empty procedure. If liquid
line pressure is greater than 345 kPa (50 psi) proceed
to System Low procedure. If the refrigerant system is
empty or low in refrigerant charge, a leak at any line
fitting or component seal is likely. A review of the fit-
tings, lines and components for oily residue is an
indication of the leak location. To detect a leak in the
refrigerant system, perform one of the following pro-
cedures as indicated by the symptoms.
SYSTEM EMPTY
(1) Evacuate the refrigerant system to the lowest
degree of vacuum possible (approx. 28 in Hg.). Deter-
mine if the system holds a vacuum for 15 minutes. If
vacuum is held, a leak is probably not present. If sys-
tem will not maintain vacuum level, proceed with
this procedure.(2) Prepare a 0.284 Kg. (10 oz.) refrigerant charge
to be injected into the system.
(3) Connect and dispense 0.284 Kg. (10 oz.) of
refrigerant into the evacuated refrigerant system.
(4) Proceed to Step 2 of System Low procedure.
SYSTEM LOW
(1) Determine if there is any (R-134a) refrigerant
in the system.
(2) Position the vehicle in a wind free work area.
This will aid in detecting small leaks.
(3) Bring the refrigerant system up to operating
temperature and pressure. This is done by allowing
the engine to run for five minutes with the system
set to the following:
²Transmission in Park or Neutral with parking
brake set
²Engine idling at 700 rpm
²A/C controls set in 100 percent outside air
²Blower switch in the high A/C position
²A/C in the ON position
²Open all windows
CAUTION: A leak detector designed for R-12 refrig-
erant (only) will not detect leaks in a R-134a refrig-
erant system.
(4) Shut off the vehicle and wait 2 to 7 minutes.
Then use an Electronic Leak Detector that is
designed to detect R-134a type refrigerant and search
for leaks. Fittings, lines, or components that appear
to be oily usually indicates a refrigerant leak. To
inspect the evaporator core for leaks, insert the leak
detector probe into the drain tube opening or a heat
duct. A R-134a dye is available to aid in leak detec-
tion, use only DaimlerChrysler approved refrigerant
dye.
24 - 44 PLUMBINGDR
PLUMBING (Continued)