vin DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.G Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1998, Model line: RAM 1500, Model: DODGE RAM 1500 1998 2.GPages: 2627
Page 662 of 2627

The passenger airbag on/off switch housing is con-
structed of molded plastic and has three integral
mounting tabs. These mounting tabs are used to
secure the switch to the back of the molded plastic
switch face plate with three small screws. The
molded plastic face plate also has three integral
mounting tabs that are used to secure the switch and
face plate unit to the instrument panel center bezel
with three additional screws. A molded plastic con-
nector receptacle on the back of the switch housing
connects the switch to the vehicle electrical system
through a dedicated take out and connector of the
instrument panel wire harness. The molded plastic
harness connector insulator is keyed and latched to
ensure proper and secure switch electrical connec-
tions. The passenger airbag on/off switch cannot be
adjusted or repaired and, if faulty or damaged, the
switch must be replaced.
OPERATION
The passenger airbag on/off switch allows the cus-
tomer to turn the passenger airbag function On or
Off to accommodate certain uses of the right front
seating position where airbag protection may not be
desired. See the owner's manual in the vehicle glove
box for specific recommendations on when to enable
or disable the passenger airbag. The Off indicator of
the switch will be illuminated whenever the switch is
turned to the Off position and the ignition switch is
in the On position.
The ignition key is the only key or object that
should ever be inserted into the key cylinder actuator
of the switch. The on/off switch requires only a par-
tial key insertion to fully depress a spring-loaded
locking plunger. The spring-loaded locking plunger
prevents the user from leaving the key in the switch.
The key will be automatically ejected when force is
not applied. To actuate the passenger airbag on/off
switch, insert the ignition key into the switch key
actuator far enough to fully depress the plunger, then
rotate the actuator to the desired switch position.
When the switch key actuator is rotated to its clock-
wise stop (the key actuator slot will be aligned with
the Off indicator), the Off indicator is illuminated
and the passenger airbag is disabled. When the
switch is rotated to its counterclockwise stop (the key
actuator slot will be in a vertical position), the Off
indicator will be extinguished and the passenger air-
bag is enabled.The passenger airbag on/off switch connects one of
two internal resistors in series between the passen-
ger airbag mux switch sense and passenger airbag
mux switch return circuits of the Airbag Control
Module (ACM). The ACM continually monitors the
resistance in these circuits to determine the switch
position that has been selected. When the switch is
in the Off position, the ACM provides a ground input
to the switch through the passenger airbag indicator
driver circuit, which energizes the Light-Emitting
Diode (LED) that illuminates the Off indicator of the
switch.
The ACM will also illuminate the Off indicator of
the switch for about seven seconds each time the
ignition switch is turned to the On position as a bulb
test. The ACM will store a Diagnostic Trouble Code
(DTC) for any fault it detects in the passenger airbag
on/off switch or Off indicator circuits, and will illumi-
nate the airbag indicator in the instrument cluster if
a fault is detected. For proper diagnosis of the pas-
senger airbag on/off switch or the ACM, a DRBIIIt
scan tool is required. Refer to the appropriate diag-
nostic information.
REMOVAL
WARNING: TO AVOID PERSONAL INJURY OR
DEATH, ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIRBAGS,
DISABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT SYS-
TEM BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING
WHEEL, STEERING COLUMN, AIRBAG, SEAT BELT
TENSIONER, IMPACT SENSOR, OR INSTRUMENT
PANEL COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE.
DISCONNECT AND ISOLATE THE BATTERY NEGA-
TIVE (GROUND) CABLE, THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES
FOR THE SYSTEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE
BEFORE PERFORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR
SERVICE. THIS IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DIS-
ABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT SYSTEM.
FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRECAUTIONS
COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOY-
MENT.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable. Wait two minutes for the system capacitor to
discharge before further service.
(2) Remove the center bezel from the instrument
panel. (Refer to 23 - BODY/INSTRUMENT PANEL/
INSTRUMENT PANEL CENTER BEZEL -
REMOVAL).
(3) From the back of the center bezel, remove the
three screws that secure the passenger airbag on/off
switch and face plate unit to the back of the bezel
(Fig. 40).
(4) Remove the passenger airbag on/off switch and
face plate from the center bezel as a unit.
DRRESTRAINTS 8O - 43
PASSENGER AIRBAG ON/OFF SWITCH (Continued)
Page 672 of 2627

retracted or extracted is a sure indication that the
seat belt tensioner has been deployed and requires
replacement. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/RE-
STRAINTS/FRONT OUTBOARD SEAT BELT &
RETRACTOR - REMOVAL).
OPERATION
The seat belt tensioners are deployed by a signal
generated by the Airbag Control Module (ACM)
through the driver and passenger seat belt tensioner
line 1 and line 2 (or squib) circuits. When the ACM
sends the proper electrical signal to the tensioners,
the electrical energy generates enough heat to ini-
tiate a small pyrotechnic gas generator. The gas gen-
erator is installed at the top of the tensioner housing
which contains a long metal tape that is routed
through two chambers within the housing. Each end
of the tape is wound around the outer sleeve of a
mechanical clutch mechanism secured to one end of
the torsion bar upon which the retractor spool is
secured. As the gas expands, it is directed against
the metal tape within the two chambers of the hous-
ing causing the tape to unwind from the clutch
sleeve. As the clutch rotates it engages the torsion
bar, which drives the seat belt retractor spool causing
the slack to be removed from the seat belt.
Once a seat belt tensioning sequence has been
completed, the forward momentum of the occupant
results in deformation of the torsion bar. As the tor-
sion bar deforms it allows the seat belt webbing to
unwind from the retractor spool, which causes the
metal tape to be wound back onto the clutch sleeve
until it is pulled tight against two cutter blades
within the housing, which immediately cut the metal
tape.
Removing excess slack from the seat belt not only
keeps the occupant properly positioned for an airbag
deployment following a frontal impact of the vehicle,
but also helps to reduce injuries that the occupant
might experience in these situations as a result of a
harmful contact with the steering wheel, steering col-
umn, instrument panel and/or windshield. The tor-
sion bar is designed to deform in order to control the
loading being applied to the occupant by the seat belt
during a frontal impact, further reducing the poten-
tial for occupant injuries.
The ACM monitors the condition of the seat belt
tensioners through circuit resistance. The ACM will
illuminate the airbag indicator in the ElectroMe-
chanical Instrument Cluster (EMIC) and store a
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) for any fault that is
detected. For proper diagnosis of the seat belt ten-
sioners, a DRBIIItscan tool is required. Refer to the
appropriate diagnostic information.
SEAT BELT TENSION
REDUCER
DESCRIPTION
A seat belt tension reducer is standard equipment
for the driver side front outboard seat belt on stan-
dard cab versions of this model (Fig. 49). The tension
reducer is integral to the driver side front outboard
seat belt and retractor unit, which is secured to the
inner B-pillar on the left side of the vehicle. The
retractor is concealed beneath the molded plastic
inner B-pillar trim. The seat belt tension reducer
consists primarily of a 12-volt Direct Current (DC)
solenoid and an integral connector receptacle that is
located on the forward facing end housing of the
retractor. The seat belt tension reducer is controlled
by a battery current output of the ignition switch and
a ground path provided by the seat belt switch, and
is connected to the vehicle electrical system through
a dedicated take out of the body wire harness by a
keyed and latching molded plastic connector insula-
tor to ensure a secure connection.
The seat belt tension reducer cannot be repaired
and, if faulty or damaged, the entire driver side front
outboard seat belt and retractor unit must be
replaced. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/RESTRAINTS/
FRONT OUTBOARD SEAT BELT & RETRACTOR -
REMOVAL).
Fig. 49 Seat Belt Tension Reducer
1 - TENSIONER HOUSING OR CHAMBER
2 - GAS GENERATOR
3 - TENSIONER PIGTAIL WIRE
4 - SPOOL
5 - TENSION REDUCER (DRIVER SIDE ON STANDARD CAB
ONLY)
6 - REDUCER CONNECTOR RECEPTACLE
DRRESTRAINTS 8O - 53
SEAT BELT TENSIONER (Continued)
Page 676 of 2627

pressed inert gas. When the ACM sends the proper
electrical signal to the airbag inflator, the electrical
energy creates enough heat to ignite chemical pellets
within the inflator. Once ignited, these chemicals
burn rapidly and produce the pressure necessary to
rupture a containment disk in the inert gas canister.
The inflator and inert gas canister are sealed and
connected to a tubular manifold so that all of the
released gas is directed into the folded side curtain
airbag cushion, causing the cushion to inflate.
As the airbag cushion inflates it will drop down
from the roof rail between the edge of the headliner
and the side glass/body pillars to form a curtain-like
cushion to protect the vehicle occupants during a side
impact collision. The front tether keeps the front por-
tion of the side curtain bag taut, thus ensuring that
the bag will deploy in the proper position. Following
the airbag deployment, the airbag cushion quickly
deflates by venting the inert gas through the loose
weave of the cushion fabric, and the deflated cushion
hangs down loosely from the roof rail.
REMOVAL
The following procedure is for replacement of a
faulty or damaged side curtain airbag. If the airbag
is faulty or damaged, but not deployed, review the
recommended procedures for handling non-deployed
supplemental restraints. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
RESTRAINTS - STANDARD PROCEDURE - HAN-
DLING NON-DEPLOYED SUPPLEMENTAL
RESTRAINTS). If the side curtain airbag has been
deployed, review the recommended procedures for
service after a supplemental restraint deployment
before removing the airbag from the vehicle. (Refer to
8 - ELECTRICAL/RESTRAINTS - STANDARD PRO-
CEDURE - SERVICE AFTER A SUPPLEMENTAL
RESTRAINT DEPLOYMENT).
WARNING: TO AVOID PERSONAL INJURY OR
DEATH, ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIRBAGS,
DISABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT SYS-
TEM BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING
WHEEL, STEERING COLUMN, AIRBAG, SEAT BELT
TENSIONER, IMPACT SENSOR, OR INSTRUMENT
PANEL COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE.
DISCONNECT AND ISOLATE THE BATTERY NEGA-
TIVE (GROUND) CABLE, THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES
FOR THE SYSTEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE
BEFORE PERFORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR
SERVICE. THIS IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DIS-
ABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT SYSTEM.
FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRECAUTIONS
COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOY-
MENT.WARNING: TO AVOID PERSONAL INJURY OR
DEATH, WHEN REMOVING A DEPLOYED AIRBAG,
RUBBER GLOVES, EYE PROTECTION, AND A
LONG-SLEEVED SHIRT SHOULD BE WORN. THERE
MAY BE DEPOSITS ON THE AIRBAG UNIT AND
OTHER INTERIOR SURFACES. IN LARGE DOSES,
THESE DEPOSITS MAY CAUSE IRRITATION TO THE
SKIN AND EYES.
WARNING: TO AVOID PERSONAL INJURY OR
DEATH, USE EXTREME CARE TO PREVENT ANY
FOREIGN MATERIAL FROM ENTERING THE SIDE
CURTAIN AIRBAG, OR BECOMING ENTRAPPED
BETWEEN THE SIDE CURTAIN AIRBAG CUSHION
AND THE HEADLINER. FAILURE TO OBSERVE THIS
WARNING COULD RESULT IN OCCUPANT INJURIES
UPON AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT.
(1) Disconnect and isolate the battery negative
cable. Wait two minutes for the system capacitor to
discharge before further service.
(2) Remove the headliner from the vehicle. (Refer
to 23 - BODY/INTERIOR/HEADLINER -
REMOVAL).
(3) Remove the screw that secures the side curtain
airbag tether retainer to the base of the A-pillar near
the belt line (Fig. 53).
(4) Disengage the two side curtain airbag tether
plastic retainer clips from the A-pillar.
Fig. 53 Side Curtain Airbag Remove/Install - Typical
1 - ROOF SIDE RAIL
2 - SPRING NUT (4 - STD CAB/6 - QUAD CAB)
3 - SCREW (4 - STD CAB/6 - QUAD CAB)
4 - CLIP (2)
5 - RIVET NUT
6 - SCREW
7 - SIDE CURTAIN AIRBAG
8 - RETAINER (3 - STD CAB/5 - QUAD CAB)
9 - WIRE HARNESS CONNECTOR
DRRESTRAINTS 8O - 57
SIDE CURTAIN AIRBAG (Continued)
Page 677 of 2627

(5) Disconnect the body wire harness connector for
the side curtain airbag from the connector receptacle
at the back of the airbag inflator.
(6) Remove the four screws (standard cab) or six
screws (quad cab) that secure the side curtain airbag
inflator and manifold tube brackets to the nuts in the
roof rail.
(7) Grasp the extruded plastic side curtain airbag
channel firmly and pull it straight away from the
roof rail far enough to disengage all three (standard
cab) or five (quad cab) plastic push-in fasteners that
secure it.
(8) Remove the side curtain airbag from the vehi-
cle as a unit.
INSTALLATION
The following procedure is for replacement of a
faulty or damaged side curtain airbag. If the airbag
is faulty or damaged, but not deployed, review the
recommended procedures for handling non-deployed
supplemental restraints. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
RESTRAINTS - STANDARD PROCEDURE - HAN-
DLING NON-DEPLOYED SUPPLEMENTAL
RESTRAINTS). If the side curtain airbag has been
deployed, review the recommended procedures for
service after a supplemental restraint deployment
before removing the airbag from the vehicle. (Refer to
8 - ELECTRICAL/RESTRAINTS - STANDARD PRO-
CEDURE - SERVICE AFTER A SUPPLEMENTAL
RESTRAINT DEPLOYMENT).
WARNING: TO AVOID PERSONAL INJURY OR
DEATH, ON VEHICLES EQUIPPED WITH AIRBAGS,
DISABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT SYS-
TEM BEFORE ATTEMPTING ANY STEERING
WHEEL, STEERING COLUMN, AIRBAG, SEAT BELT
TENSIONER, IMPACT SENSOR, OR INSTRUMENT
PANEL COMPONENT DIAGNOSIS OR SERVICE.
DISCONNECT AND ISOLATE THE BATTERY NEGA-
TIVE (GROUND) CABLE, THEN WAIT TWO MINUTES
FOR THE SYSTEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE
BEFORE PERFORMING FURTHER DIAGNOSIS OR
SERVICE. THIS IS THE ONLY SURE WAY TO DIS-
ABLE THE SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT SYSTEM.
FAILURE TO TAKE THE PROPER PRECAUTIONS
COULD RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOY-
MENT.WARNING: TO AVOID PERSONAL INJURY OR
DEATH, WHEN REMOVING A DEPLOYED AIRBAG,
RUBBER GLOVES, EYE PROTECTION, AND A
LONG-SLEEVED SHIRT SHOULD BE WORN. THERE
MAY BE DEPOSITS ON THE AIRBAG UNIT AND
OTHER INTERIOR SURFACES. IN LARGE DOSES,
THESE DEPOSITS MAY CAUSE IRRITATION TO THE
SKIN AND EYES.
WARNING: TO AVOID PERSONAL INJURY OR
DEATH, USE EXTREME CARE TO PREVENT ANY
FOREIGN MATERIAL FROM ENTERING THE SIDE
CURTAIN AIRBAG, OR BECOMING ENTRAPPED
BETWEEN THE SIDE CURTAIN AIRBAG CUSHION
AND THE HEADLINER. FAILURE TO OBSERVE THIS
WARNING COULD RESULT IN OCCUPANT INJURIES
UPON AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT.
(1) Position the side curtain airbag into the vehicle
as a unit.
(2) Align all three (standard cab) or five (quad cab)
plastic push-in fasteners that secure the extruded
plastic side curtain airbag channel with their holes
in the roof side rail and push them straight into the
roof rail until they are fully seated (Fig. 53).
(3) Working from the rear of the vehicle to the
front, install and tighten the four screws (standard
cab) or six screws (quad cab) that secure the side cur-
tain airbag inflator and manifold tube brackets to the
nuts in the roof rail. Tighten the screws to 5 N´m (40
in. lbs.).
(4) Reconnect the body wire harness connector for
the side curtain airbag to the connector receptacle at
the back of the airbag inflator. Be certain the connec-
tor is fully engaged and latched.
(5) Engage the two side curtain airbag tether plas-
tic retainer clips into the A-pillar.
(6) Install and tighten the screw that secures the
side curtain airbag tether retainer to the base of the
A-pillar near the belt line. Tighten the screw to 6
N´m (55 in. lbs.).
(7) Reinstall the headliner into the vehicle. (Refer
to 23 - BODY/INTERIOR/HEADLINER - INSTALLA-
TION).
(8) Do not reconnect the battery negative cable at
this time. The supplemental restraint system verifi-
cation test procedure should be performed following
service of any supplemental restraint system compo-
nent. (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/RESTRAINTS -
STANDARD PROCEDURE - VERIFICATION TEST).
8O - 58 RESTRAINTSDR
SIDE CURTAIN AIRBAG (Continued)
Page 682 of 2627
SPEED CONTROL
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
SPEED CONTROL
DESCRIPTION..........................1
OPERATION............................2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - VACUUM
SUPPLY TEST.........................2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - ROAD TEST....3
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE - SPEED CONTROL.............3
CABLE
DESCRIPTION..........................4
OPERATION............................4
REMOVAL.............................4
INSTALLATION..........................5
SERVO
DESCRIPTION..........................6OPERATION............................6
REMOVAL.............................6
INSTALLATION..........................6
SWITCH
DESCRIPTION..........................7
OPERATION............................7
REMOVAL.............................8
INSTALLATION..........................8
VACUUM RESERVOIR
DESCRIPTION..........................9
OPERATION............................9
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - VACUUM
RESERVOIR..........................9
REMOVAL.............................9
INSTALLATION.........................10
SPEED CONTROL
DESCRIPTION
All 3.7L/4.7LGas Engines and/or Diesel With
Automatic Trans.
The speed control system is operated by the use of
a cable and a vacuum controlled servo. On all
engines except diesels, electronic control of the speed
control system is integrated into the Powertrain Con-
trol Module (PCM). If equipped with a diesel engine,
electronic control of the speed control system is inte-
grated into the Engine Control Module (ECM). The
controls consist of two steering wheel mounted
switches. The switches are labeled: ON/OFF, RES/
ACCEL, SET, COAST, and CANCEL.
The system is designed to operate at speeds above
30 mph (50 km/h).
WARNING: THE USE OF SPEED CONTROL IS NOT
RECOMMENDED WHEN DRIVING CONDITIONS DO
NOT PERMIT MAINTAINING A CONSTANT SPEED,
SUCH AS IN HEAVY TRAFFIC OR ON ROADS THAT
ARE WINDING, ICY, SNOW COVERED, OR SLIP-
PERY.
5.7L Gas
The speed control system is fully electronically con-
trolled by the Powertrain Control Module (PCM).A
cable and a vacuum controlled servo are not
used. This is a servo-less system.The controls
consist of two steering wheel mounted switches. The
switches are labeled: ON/OFF, RES/ACCEL, SET,
COAST, and CANCEL.
The system is designed to operate at speeds above
30 mph (50 km/h).
WARNING: THE USE OF SPEED CONTROL IS NOT
RECOMMENDED WHEN DRIVING CONDITIONS DO
NOT PERMIT MAINTAINING A CONSTANT SPEED,
SUCH AS IN HEAVY TRAFFIC OR ON ROADS THAT
ARE WINDING, ICY, SNOW COVERED, OR SLIP-
PERY.
DRSPEED CONTROL 8P - 1
Page 683 of 2627

5.9L Diesel With Manual Trans.
The speed control system is fully electronically con-
trolled by the Engine Control Module (ECM).A
cable and a vacuum controlled servo are not
used if the vehicle is equipped with a manual
transmission and a diesel engine. This is a ser-
vo-less system.The controls consist of two steering
wheel mounted switches. The switches are labeled:
ON/OFF, RES/ACCEL, SET, COAST, and CANCEL.
The system is designed to operate at speeds above
30 mph (50 km/h).
WARNING: THE USE OF SPEED CONTROL IS NOT
RECOMMENDED WHEN DRIVING CONDITIONS DO
NOT PERMIT MAINTAINING A CONSTANT SPEED,
SUCH AS IN HEAVY TRAFFIC OR ON ROADS THAT
ARE WINDING, ICY, SNOW COVERED, OR SLIP-
PERY.
OPERATION
When speed control is selected by depressing the
ON switch, the PCM (the ECM with a diesel engine)
allows a set speed to be stored in its RAM for speed
control. To store a set speed, depress the SET switch
while the vehicle is moving at a speed between 35
and 85 mph. In order for the speed control to engage,
the brakes cannot be applied, nor can the gear selec-
tor be indicating the transmission is in Park or Neu-
tral.
The speed control can be disengaged manually by:
²Stepping on the brake pedal
²Depressing the OFF switch
²Depressing the CANCEL switch.
²Depressing the clutch pedal (if equipped).
NOTE: Depressing the OFF switch or turning off the
ignition switch will erase the set speed stored in
the PCM (the ECM with a diesel engine).
For added safety, the speed control system is pro-
grammed to disengage for any of the following condi-
tions:
²An indication of Park or Neutral
²A rapid increase rpm (indicates that the clutch
has been disengaged)
²Excessive engine rpm (indicates that the trans-
mission may be in a low gear)
²The speed signal increases at a rate of 10 mph
per second (indicates that the coefficient of friction
between the road surface and tires is extremely low)
²The speed signal decreases at a rate of 10 mph
per second (indicates that the vehicle may have
decelerated at an extremely high rate)Once the speed control has been disengaged,
depressing the RES/ACCEL switch (when speed is
greater than 30 mph) restores the vehicle to the tar-
get speed that was stored in the PCM (the ECM with
a diesel engine).
While the speed control is engaged, the driver can
increase the vehicle speed by depressing the RES/AC-
CEL switch. The new target speed is stored in the
PCM (the ECM with a diesel engine) when the RES/
ACCEL is released. The PCM (the ECM with a diesel
engine) also has a9tap-up9feature in which vehicle
speed increases at a rate of approximately 2 mph for
each momentary switch activation of the RES/AC-
CEL switch.
A ªtap downº feature is used to decelerate without
disengaging the speed control system. To decelerate
from an existing recorded target speed, momentarily
depress the COAST switch. For each switch activa-
tion, speed will be lowered approximately 1 mph.DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - VACUUM SUPPLY
TEST
3.7L / 4.7L Gas Powered Engines
3.7L/4.7L gas powered engines: actual engine vac-
uum, a vacuum reservoir, a one-way check valve and
vacuum lines are used to supply vacuum to the speed
control servo.
(1) Disconnect vacuum hose at speed control servo
and install a vacuum gauge into the disconnected
hose.
(2) Start engine and observe gauge at idle. Vac-
uum gauge should read at least ten inches of mer-
cury.
(3) If vacuum is less than ten inches of mercury,
determine source of leak. Check vacuum line to
engine for leaks. Also check actual engine intake
manifold vacuum. If manifold vacuum does not meet
this requirement, check for poor engine performance
and repair as necessary.
(4) If vacuum line to engine is not leaking, check
for leak at vacuum reservoir. To locate and gain
access to reservoir, refer to Vacuum Reservoir Remov-
al/Installation in this group. Disconnect vacuum line
at reservoir and connect a hand-operated vacuum
pump to reservoir fitting. Apply vacuum. Reservoir
vacuum should not bleed off. If vacuum is being lost,
replace reservoir.
8P - 2 SPEED CONTROLDR
SPEED CONTROL (Continued)
Page 687 of 2627

(5) Before starting engine, operate accelerator
pedal to check for any binding.
(6) Install cable/lever cover.
SERVO
DESCRIPTION
A speed control servo is not used with any
5.7L V-8 engine, or with the 5.9L diesel engine
when equipped with a manual transmission.
The speed control servo is attached to the bottom
of the battery tray.
The servo unit consists of a solenoid valve body,
and a vacuum chamber. The solenoid valve body con-
tains three solenoids:
²Vacuum
²Vent
²Dump
The vacuum chamber contains a diaphragm with a
cable attached to control the throttle linkage.
OPERATION
A speed control servo is not used with any
5.7L V-8 engine, or with the 5.9L diesel engine
when equipped with a manual transmission.
The following information applies only to
vehicles equipped with a mechanical servo.
When/if a servo is used on gasoline powered vehi-
cles, the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) controls
the solenoid valve body. When/if a servo is used on
certain diesel powered vehicles, the Engine Control
Module (ECM) controls the solenoid valve body. The
solenoid valve body controls the application and
release of vacuum to the diaphragm of the vacuum
servo. The servo unit cannot be repaired and is ser-
viced only as a complete assembly.
Power is supplied to the servo's by the PCM/ECM
through the brake switch. The PCM/ECM controls
the ground path for the vacuum and vent solenoids.
The dump solenoid is energized anytime it receives
power. If power to the dump solenoid is interrupted,
the solenoid dumps vacuum in the servo. This pro-
vides a safety backup to the vent and vacuum sole-
noids.
The vacuum and vent solenoids must be grounded
at the PCM/ECM to operate. When the PCM/ECM
grounds the vacuum servo solenoid, the solenoid
allows vacuum to enter the servo and pull open the
throttle plate using the cable. When the PCM/ECM
breaks the ground, the solenoid closes and no more
vacuum is allowed to enter the servo. The PCM/ECM
also operates the vent solenoid via ground. The vent
solenoid opens and closes a passage to bleed or hold
vacuum in the servo as required.The PCM/ECM duty cycles the vacuum and vent
solenoids to maintain the set speed, or to accelerate
and decelerate the vehicle. To increase throttle open-
ing, the PCM/ECM grounds the vacuum and vent
solenoids. To decrease throttle opening, the PCM/
ECM removes the grounds from the vacuum and
vent solenoids. When the brake is released, if vehicle
speed exceeds 30 mph to resume, 35 mph to set, and
the RES/ACCEL switch has been depressed, ground
for the vent and vacuum circuits is restored.
REMOVAL
The speed control servo assembly is attached to the
bottom of the battery tray (Fig. 6).
(1) Disconnect negative battery cable at battery
(both cables at both batteries if diesel).
(2) To gain access to servo, remove plastic wheel-
house splash shield over left-front wheel.
(3) Disconnect vacuum line at servo (Fig. 6).
(4) Disconnect electrical connector at servo (Fig. 6).
(5) Remove 3 servo mounting screws (Fig. 6).
Depending on engine application, different sets of
mounting lugs (Fig. 6) are used to support servo to
battery tray. While removing, note proper lugs.
(6) Disconnect servo cable at throttle body. Refer to
Servo Cable Removal/Installation.
(7) Remove 2 mounting nuts holding servo cable
sleeve to bracket (Fig. 7).
(8) Pull speed control cable sleeve and servo away
from servo mounting bracket to expose cable retain-
ing clip (Fig. 7) and remove clip. Note: The servo
mounting bracket displayed in (Fig. 7) is a typical
bracket and may/may not be applicable to this model
vehicle.
(9) Remove servo from mounting bracket. While
removing, note orientation of servo to bracket.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position servo to mounting bracket (Fig. 7).
(2) Align hole in cable connector with hole in servo
pin. Install cable-to-servo retaining clip (Fig. 7).
(3) Insert servo mounting studs through holes in
servo mounting bracket.
(4) Install 2 servo-to-mounting bracket nuts and
tighten. Refer to torque specifications.
(5) Position servo assembly to correct mounting
lugs on battery tray (Fig. 6) and install 3 screws.
Tighten 3 screws. Refer to torque specifications.
(6) Connect vacuum line at servo.
(7) Connect electrical connector at servo.
(8) Connect servo cable to throttle body. Refer to
servo Cable Removal/Installation.
(9) Install left-front wheel-well liner.
(10) Connect negative battery cable to battery
(connect both cables if diesel).
8P - 6 SPEED CONTROLDR
CABLE (Continued)
Page 688 of 2627

(11) Before starting engine, operate accelerator
pedal to check for any binding.
SWITCH
DESCRIPTION
Two separate switch pods operate the speed control
system. The steering-wheel-mounted switches use
multiplexed circuits to provide inputs to the PCM (to
the ECM for diesel) for ON, OFF, RESUME, ACCEL-
ERATE, SET, DECEL and CANCEL modes. Refer to
the owner's manual for more information on speed
control switch functions and setting procedures.
The individual switches cannot be repaired. If one
switch fails, the entire switch module must be
replaced.
Depending on engine control computer (JTEC
having a 3± plug connector or NGC having a 4±
plug connector), 2 types of switches are used.
Both types of switches are internally and exter-
nally different. The switch used with the NGC
system has an attached pigtail lead. The switch
used with the JTEC system does not have an
attached pigtail lead.
OPERATION
When speed control is selected by depressing the
ON, OFF switch, the PCM(ECM for diesel)allows
a set speed to be stored in its RAM for speed control.
To store a set speed, depress the SET switch while
the vehicle is moving at a speed between approxi-
mately 35 and 85 mph. In order for the speed control
to engage, the brakes cannot be applied, nor can the
gear selector be indicating the transmission is in
Park or Neutral.
The speed control can be disengaged manually by:
²Stepping on the brake pedal
²Depressing the OFF switch
²Depressing the CANCEL switch.
The speed control can be disengaged also by any of
the following conditions:
²An indication of Park or Neutral (auto. trans.)
²The VSS signal increases at a rate of 10 mph
per second (indicates that the co-efficient of friction
between the road surface and tires is extremely low)
²Depressing the clutch pedal (manual trans.).
²Excessive engine rpm (indicates that the trans-
mission may be in a low gear)
²The VSS signal decreases at a rate of 10 mph
per second (indicates that the vehicle may have
decelerated at an extremely high rate)
²If the actual speed is not within 20 mph of the
set speed
Fig. 6 SPEED CONTROL SERVO LOCATION
1 - BATTERY TRAY
2 - MOUNTING LUGS
3 - SERVO
4 - ELEC. CONNEC.
5 - MOUNTING SCREWS (3)
6 - MOUNTING BRACKET
7 - VACUUM LINE
Fig. 7 SERVO CABLE CLIP REMOVE/INSTALL Ð
TYPICAL
1 - SERVO MOUNTING NUTS (2)
2 - SERVO
3 - CABLE RETAINING CLIP
4 - SERVO CABLE AND SLEEVE
DRSPEED CONTROL 8P - 7
SERVO (Continued)
Page 689 of 2627

The previous disengagement conditions are pro-
grammed for added safety.
Once the speed control has been disengaged,
depressing the ACCEL switch restores the vehicle to
the target speed that was stored in the PCM's RAM
(ECM for diesel).
NOTE: Depressing the OFF switch will erase the set
speed stored in the PCM's/ECM's RAM.
If, while the speed control is engaged, the driver
wishes to increase vehicle speed, the PCM(ECM for
diesel)is programmed for an acceleration feature.
With the ACCEL switch held closed, the vehicle
accelerates slowly to the desired speed. The new tar-
get speed is stored in the PCM's/ECM's RAM when
the ACCEL switch is released. The PCM/ECM also
has a9tap-up9feature in which vehicle speed
increases at a rate of approximately 2 mph for each
momentary switch activation of the ACCEL switch.
The PCM/ECM also provides a means to decelerate
without disengaging speed control. To decelerate from
an existing recorded target speed, depress and hold
the COAST switch until the desired speed is reached.
Then release the switch. The ON, OFF switch oper-
ates two components: the PCM's/ECM's ON, OFF
input, and the battery voltage to the brake switch.
REMOVAL
Depending on engine control computer (JTEC
having a 3±plug connector or 5.7L V-8 NGC hav-
ing a 4±plug connector), 2 types of switches are
used. Both types of switches are internally and
externally different. The switches used with the
NGC system have attached pigtail leads (Fig. 9).
The switch used with the JTEC system does not
have an attached pigtail lead.
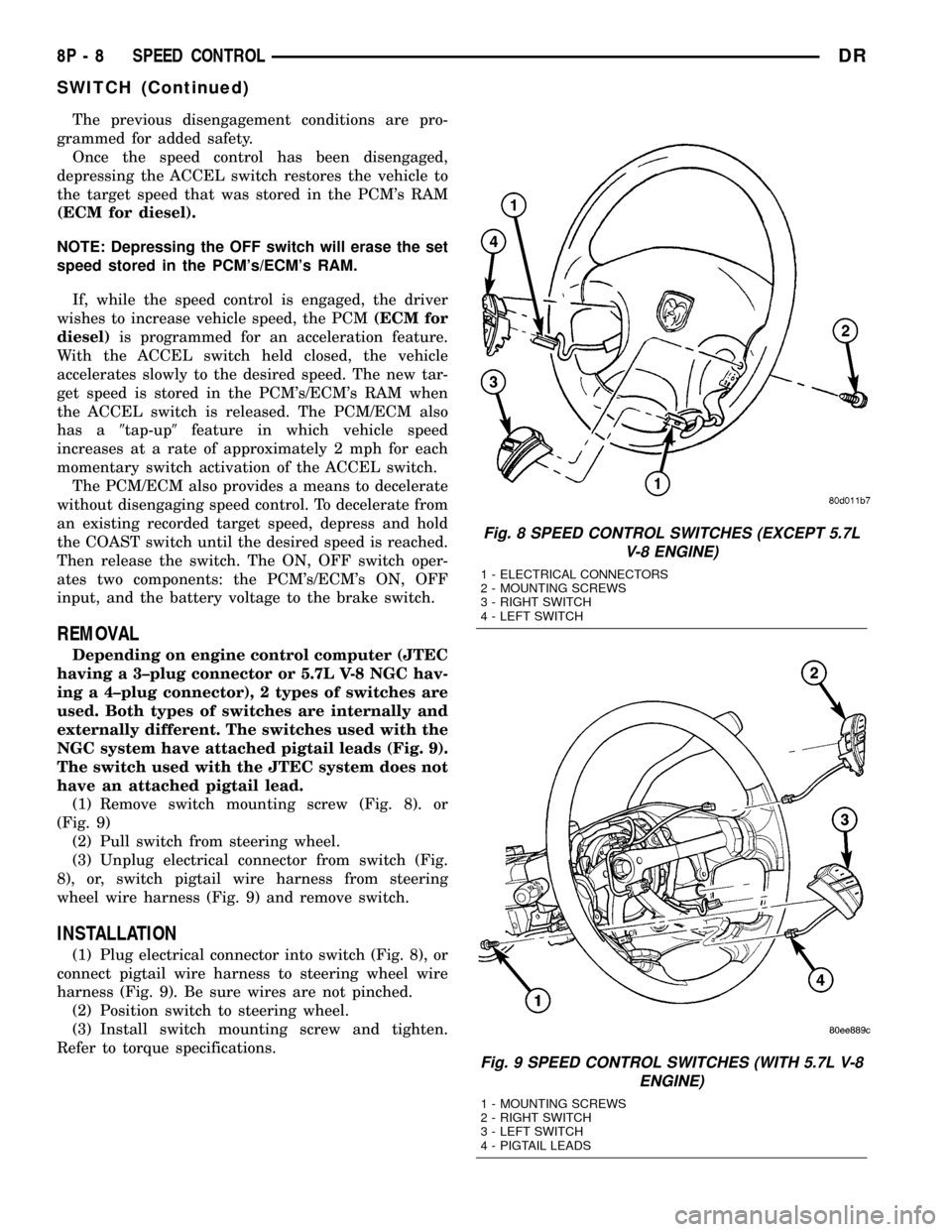
(1) Remove switch mounting screw (Fig. 8). or
(Fig. 9)
(2) Pull switch from steering wheel.
(3) Unplug electrical connector from switch (Fig.
8), or, switch pigtail wire harness from steering
wheel wire harness (Fig. 9) and remove switch.
INSTALLATION
(1) Plug electrical connector into switch (Fig. 8), or
connect pigtail wire harness to steering wheel wire
harness (Fig. 9). Be sure wires are not pinched.
(2) Position switch to steering wheel.
(3) Install switch mounting screw and tighten.
Refer to torque specifications.
Fig. 8 SPEED CONTROL SWITCHES (EXCEPT 5.7L
V-8 ENGINE)
1 - ELECTRICAL CONNECTORS
2 - MOUNTING SCREWS
3 - RIGHT SWITCH
4 - LEFT SWITCH
Fig. 9 SPEED CONTROL SWITCHES (WITH 5.7L V-8
ENGINE)
1 - MOUNTING SCREWS
2 - RIGHT SWITCH
3 - LEFT SWITCH
4 - PIGTAIL LEADS
8P - 8 SPEED CONTROLDR
SWITCH (Continued)
Page 690 of 2627

VACUUM RESERVOIR
DESCRIPTION
The vacuum reservoir is a plastic storage tank con-
nected to an engine vacuum source by vacuum lines.
A vacuum reservoir is not used with diesel engines or
the 5.7L gas powered engine.
OPERATION
The vacuum reservoir is used to supply the vac-
uum needed to maintain proper speed control opera-
tion when engine vacuum drops, such as in climbing
a grade while driving. A one-way check valve is used
in the vacuum line between the reservoir and the
vacuum source. This check valve is used to trap
engine vacuum in the reservoir. On certain vehicle
applications, this reservoir is shared with the heat-
ing/air-conditioning system. The vacuum reservoir
cannot be repaired and must be replaced if faulty.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - VACUUM
RESERVOIR
(1) Disconnect vacuum hose at speed control servo
and install a vacuum gauge into the disconnected
hose.
(2) Start engine and observe gauge at idle. Vac-
uum gauge should read at least ten inches of mer-
cury.
(3) If vacuum is less than ten inches of mercury,
determine source of leak. Check vacuum line to
engine for leaks. Also check actual engine intake
manifold vacuum. If manifold vacuum does not meet
this requirement, check for poor engine performance
and repair as necessary.
(4) If vacuum line to engine is not leaking, check
for leak at vacuum reservoir. To locate and gain
access to reservoir, refer to Vacuum Reservoir Remov-
al/Installation in this group. Disconnect vacuum line
at reservoir and connect a hand-operated vacuum
pump to reservoir fitting. Apply vacuum. Reservoir
vacuum should not bleed off. If vacuum is being lost,
replace reservoir.
(5) Verify operation of one-way check valve and
check it for leaks.Certain models may be
equipped with 2 check-valves.
(a) Locate one-way check valve. The valve is
located in vacuum line between vacuum reservoir
and engine vacuum source. Disconnect vacuum
hoses (lines) at each end of valve.(b) Connect a hand-operated vacuum pump to
reservoir end of check valve. Apply vacuum. Vac-
uum should not bleed off. If vacuum is being lost,
replace one-way check valve.
(c) Connect a hand-operated vacuum pump to
vacuum source end of check valve. Apply vacuum.
Vacuum should flow through valve. If vacuum is
not flowing, replace one-way check valve. Seal the
fitting at opposite end of valve with a finger and
apply vacuum. If vacuum will not hold, diaphragm
within check valve has ruptured. Replace valve.
REMOVAL
The vacuum reservoir is located in the engine com-
partment under the fresh air cowl grill panel (Fig.
10).
(1) Remove wiper blades and arms. Refer to Wiper
Arm Removal / Installation in the Wipers / Washers
section.
(2) Remove fresh air cowl grill. Refer to Cowl Grill
Removal / Installation.
(3) Disconnect vacuum line at reservoir (Fig. 11).
(4) Remove 2 reservoir mounting nuts (Fig. 11).
(5) Remove reservoir from cowl.
Fig. 10 VACUUM RESERVOIR LOCATION
1 - COWL GRILL
2 - WIPER ARMS / BLADES
3 - VACUUM RESERVOIR
DRSPEED CONTROL 8P - 9